Dual-frequency continuous wave pseudo-signal interference effect in swept-frequency radar
-
摘要:
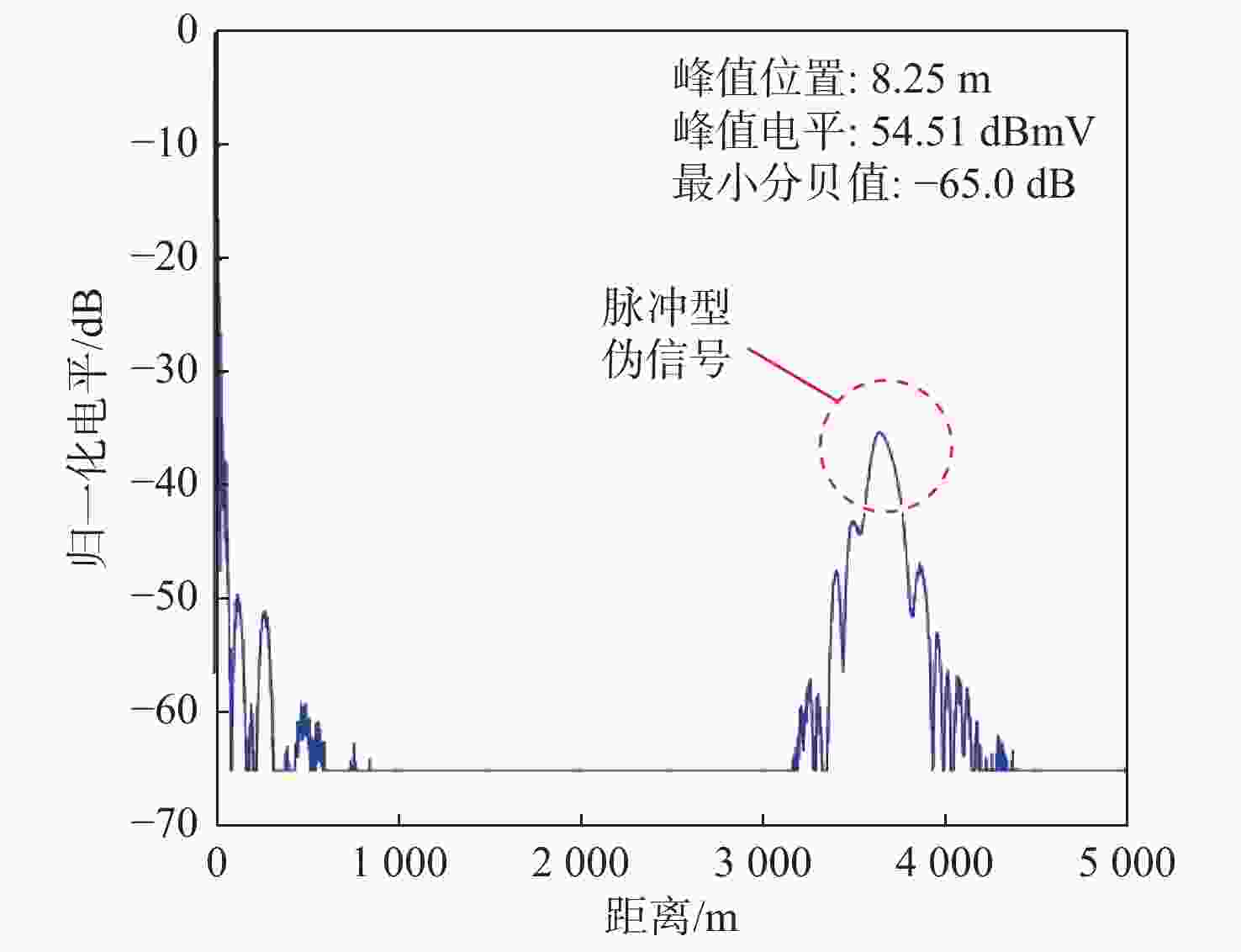
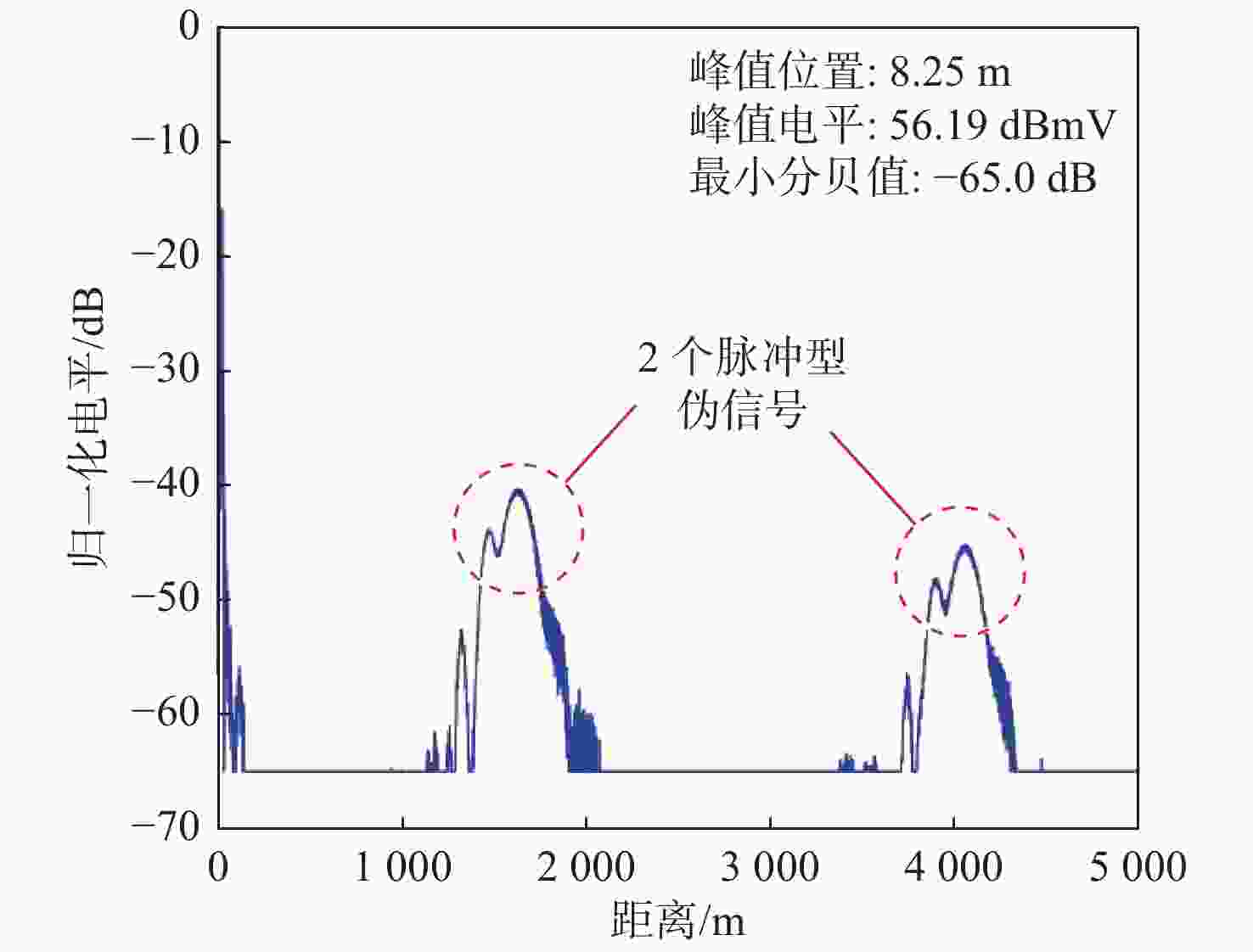
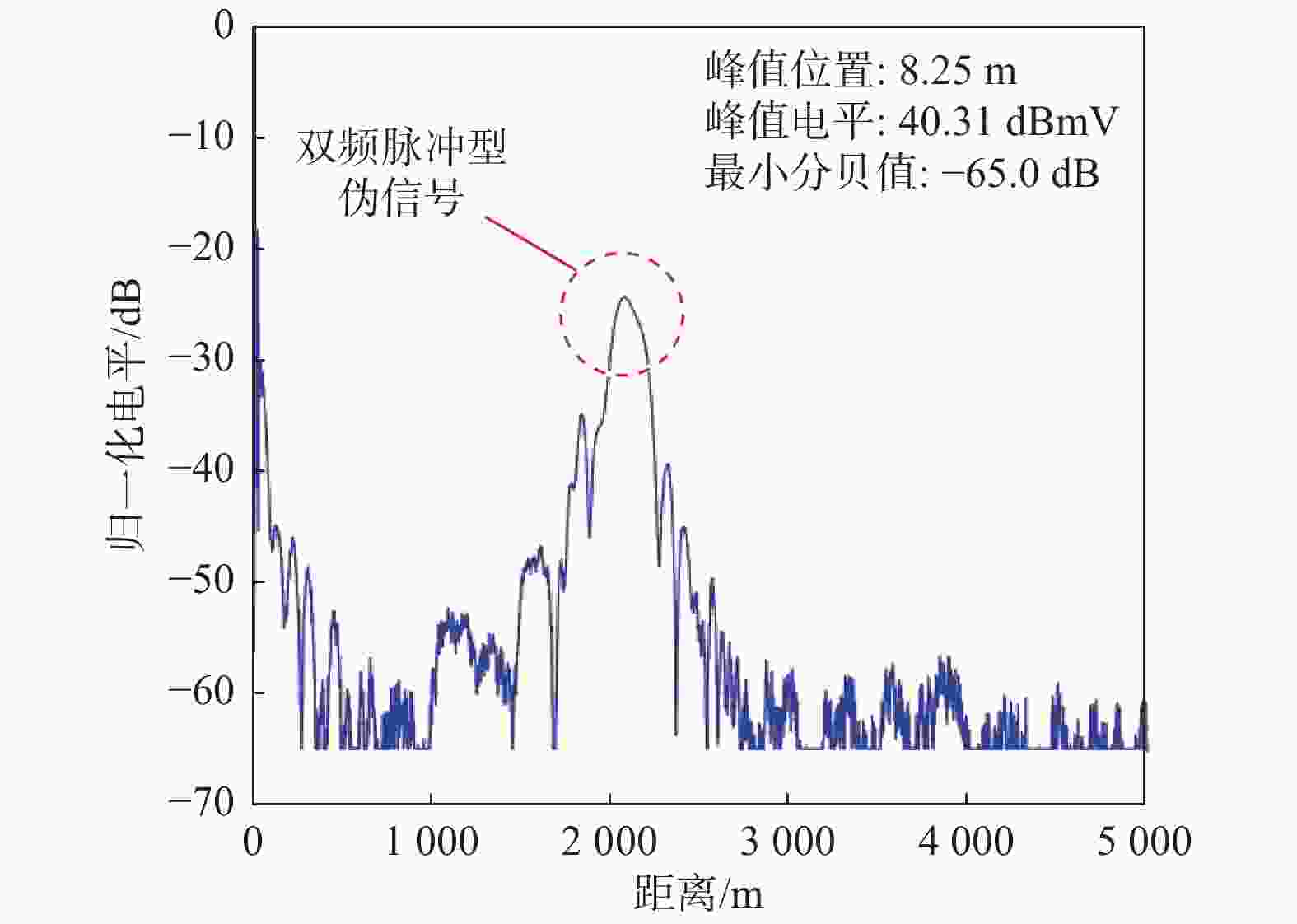
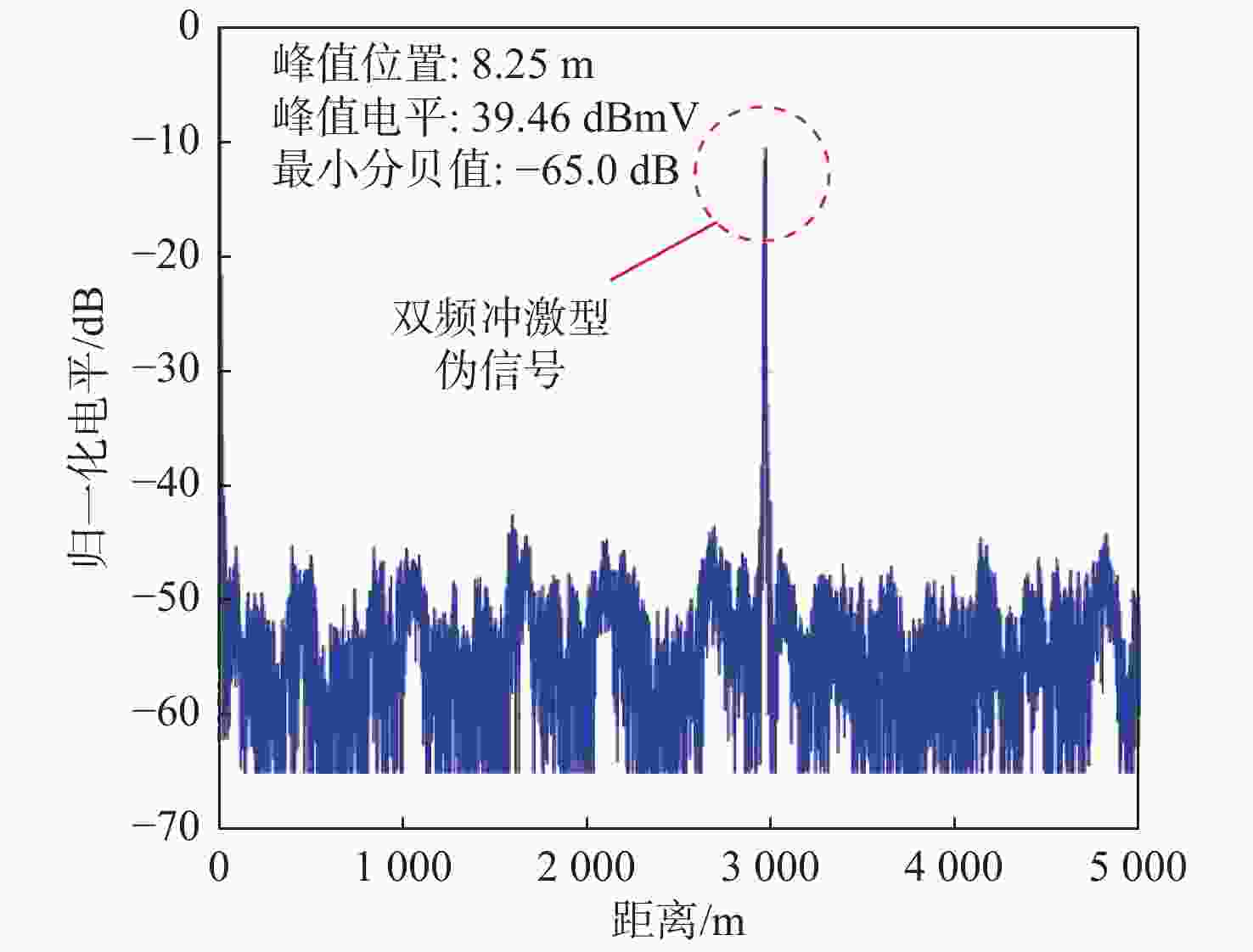
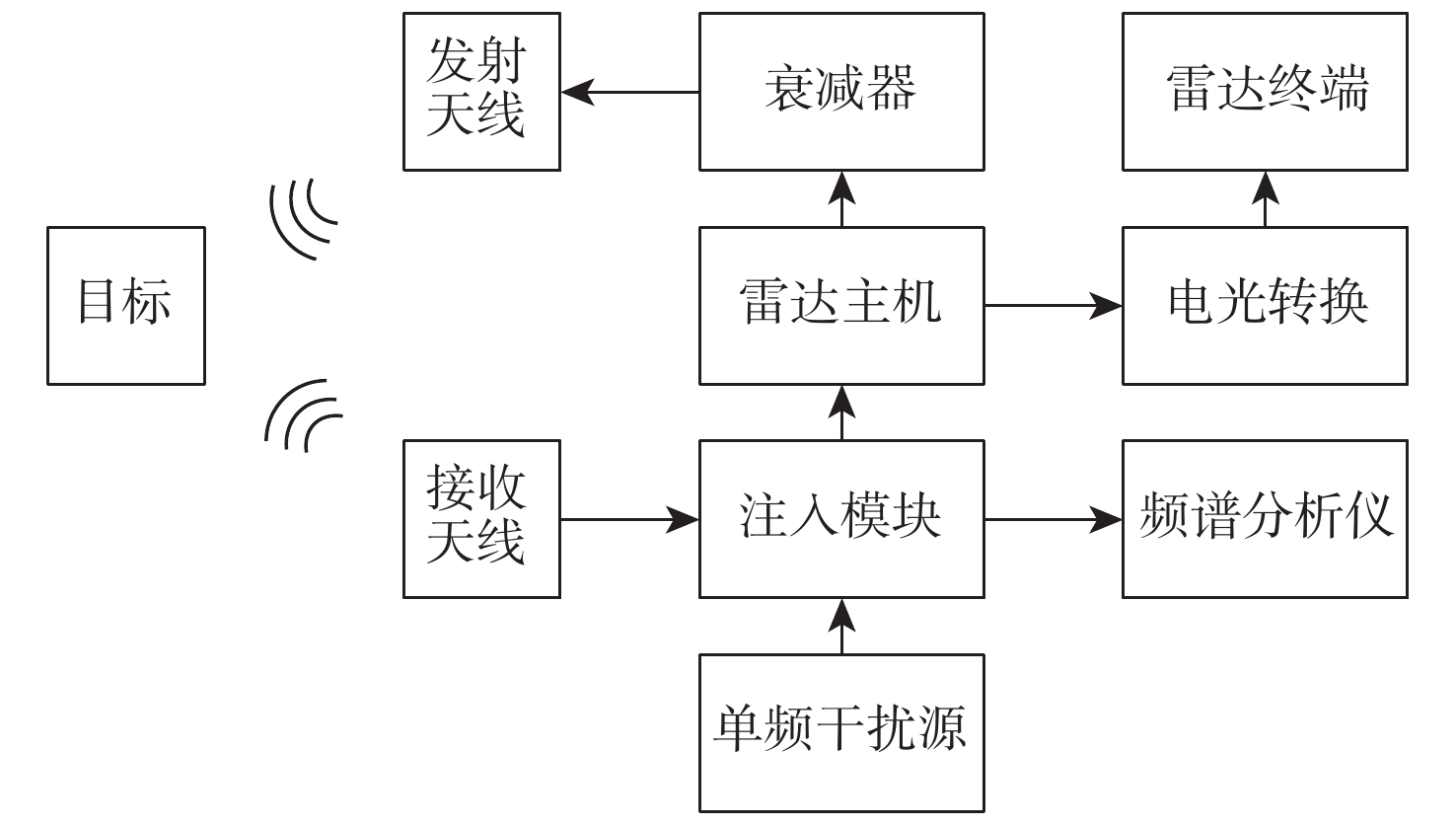
为掌握典型雷达双频电磁辐射伪信号干扰的效应规律,揭示双频伪信号干扰效应机理,以某型Ku波段扫频测距雷达为试验对象,开展双频连续波伪信号干扰效应试验,分别揭示了二阶互调射频干扰、二阶互调低频干扰和三阶交互调低频干扰效应机理,并确定了伪信号电平随干扰场强的变化规律,解释明了伪信号的形态特征和产生位置。试验结果表明:当干扰频差为540~660 MHz时,带外双频二阶互调信号会造成脉冲型伪信号干扰,伪信号产生的位置随机;当干扰频差小于5 MHz时,双频二阶互调信号和三阶交互调信号均会造成冲激型伪信号干扰,伪信号产生的位置固定。
Abstract:To fully understand the impact of dual-frequency electromagnetic radiation pseudo-signal interference on radar and uncover the underlying mechanism behind this interference effect. Taking a Ku-band swept-frequency ranging radar as the test object, a dual-frequency continuous wave pseudo-signal interference effect test was carried out, and the effect mechanism of second-order intermodulation RF interference, second-order intermodulation low-frequency interference and third-order intermodulation low-frequency interference was revealed respectively. The variation rule of the pseudo-signal level with the interference field intensity was determined, and the morphological characteristics and generation position of the pseudo-signal were explained. The test results indicate that when the difference in interference frequency is approximately between 540 MHz and 660 MHz, the out-of-band dual-frequency second-order intermodulation signal will generate pseudo-signal interference of the wide-pulse type, with a random location for the pseudo-signal. On the other hand, when the difference in interference frequency is less than 5 MHz, both the dual-frequency second-order intermodulation signal and the third-order intermodulation signal will produce pseudo-signal interference of the impulse type, with a fixed location for the pseudo-signal.
-
表 1 双频干扰信号进入扫频雷达各结构后输出分量频率
Table 1. Output component frequencies of dual-frequency interfering signals entering each structure of the swept-frequency radar
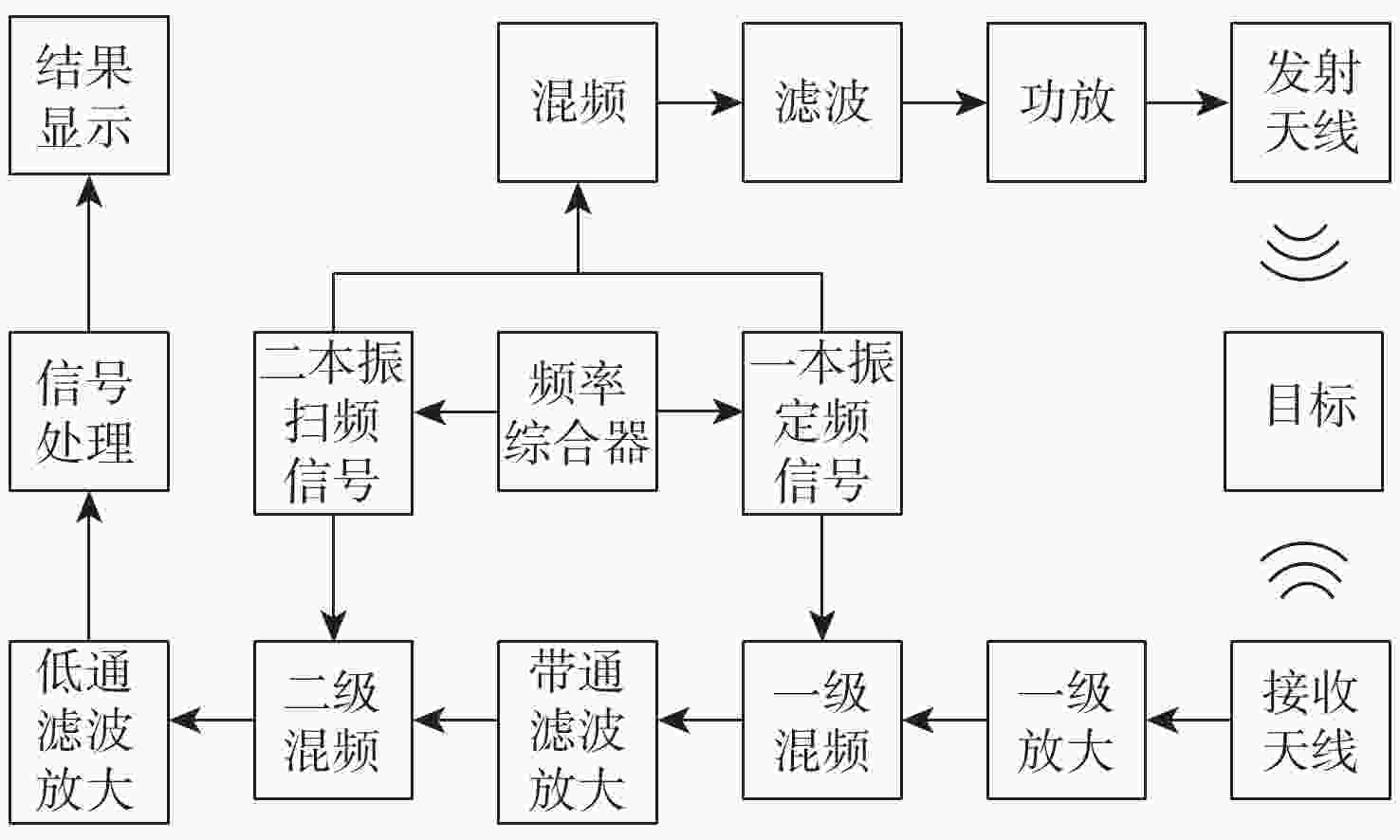
结构 带外双频脉冲型 带内双频冲激型 天线接收 $ {F_0} $,$ {f_1} $,$ {f_2} $ $ {F_0} $,$ {f_3} $,$ {f_4} $ 一级放大 $ {F_0} $,$ {f_1} $,$ {f_2} $,$ {F_0} \pm {f_1} $,$ {F_0} \pm {f_2} $,$ {f_2} \pm {f_1} $,$ {F_0} \pm \left( {{f_2} - {f_1}} \right) $ $ {F_0} $,$ {f_3} $,$ {f_4} $,$ {F_0} \pm {f_3} $,$ {F_0} \pm {f_4} $,$ {f_4} \pm {f_3} $,$ {F_0} \pm \left( {{f_4} - {f_3}} \right) $ 一级混频($ {f_{\text{a}}} $) $ {F_0} $,$ {f_1} $,$ {f_2} $,$ {F_0} \pm {f_1} $,$ {F_0} \pm {f_2} $,$ {f_2} \pm {f_1} $,$ {F_0} \pm \left( {{f_2} - {f_1}} \right) $,
$ {F_0} \pm {f_{\text{a}}} $,$ {f_1} \pm {f_{\text{a}}} $,$ {f_2} \pm {f_{\text{a}}} $,$ {F_0} \pm {f_1} \pm {f_{\text{a}}} $,$ {F_0} \pm {f_2} \pm {f_{\text{a}}} $,
$ {f_2} \pm {f_1} \pm {f_{\text{a}}} $,$ {F_0} \pm \left( {{f_2} - {f_1}} \right) \pm {f_{\text{a}}} $$ {F_0} $,$ {f_3} $,$ {f_4} $,$ {F_0} \pm {f_3} $,$ {F_0} \pm {f_4} $,$ {f_4} \pm {f_3} $,$ {F_0} \pm \left( {{f_4} - {f_3}} \right) $,
$ {F_0} \pm {f_{\text{a}}} $,$ {f_3} \pm {f_{\text{a}}} $,$ {f_4} \pm {f_{\text{a}}} $,$ {F_0} \pm {f_3} \pm {f_{\text{a}}} $,$ {F_0} \pm {f_4} \pm {f_{\text{a}}} $,
$ {f_4} \pm {f_3} \pm {f_{\text{a}}} $,$ {F_0} \pm \left( {{f_4} - {f_3}} \right) \pm {f_{\text{a}}} $带通滤波($ {f_{\text{b}}} \pm {f_{\text{H}}} $) $ {F_0} - {f_{\text{a}}} $,$ {f_2} - {f_1} $ $ {F_0} - {f_{\text{a}}} $,$ {f_3} - {f_{\text{a}}} $,$ {f_4} - {f_{\text{a}}} $,$ {F_0} \pm \left( {{f_4} - {f_3}} \right) - {f_{\text{a}}} $ 二级混频 ($ {F_{\text{b}}} $) $ {F_0} - {f_{\text{a}}} $,$ {f_2} - {f_1} $,$ {F_0} - {f_{\text{a}}} \pm {F_{\text{b}}} $,
$ {f_2} - {f_1} \pm {F_{\text{b}}} $,$ {F_0} - {f_{\text{a}}} \pm \left( {{f_2} - {f_1}} \right) $$ {F_0} - {f_{\text{a}}} $,$ {f_3} - {f_{\text{a}}} $,$ {f_4} - {f_{\text{a}}} $,$ {F_0} \pm \left( {{f_4} - {f_3}} \right) - {f_{\text{a}}} $,
$ {F_0} - {f_{\text{a}}} \pm {F_{\text{b}}} $,$ {f_3} - {f_{\text{a}}} \pm {F_{\text{b}}} $,$ {f_4} - {f_{\text{a}}} \pm {F_{\text{b}}} $,
$ {F_0} \pm \left( {{f_4} - {f_3}} \right) - {f_{\text{a}}} \pm {F_{\text{b}}} $,$ {f_4} \pm {f_3} $,$ {F_0} \pm {f_3} $,$ {F_0} \pm {f_4} $
低通(窄带)滤波
$ {F_0} - {f_{\text{a}}} - {F_{\text{b}}} $(真实目标回波信号)
$ {f_2} - {f_1} - {F_{\text{b}}} $(二阶互调脉冲型伪信号)$ {F_0} - {f_{\text{a}}} - {F_{\text{b}}} $(真实目标回波信号)
$ {F_0} \pm \left( {{f_4} - {f_3}} \right) - {f_{\text{a}}} - {F_{\text{b}}} $(三阶交互调冲激型伪信号)
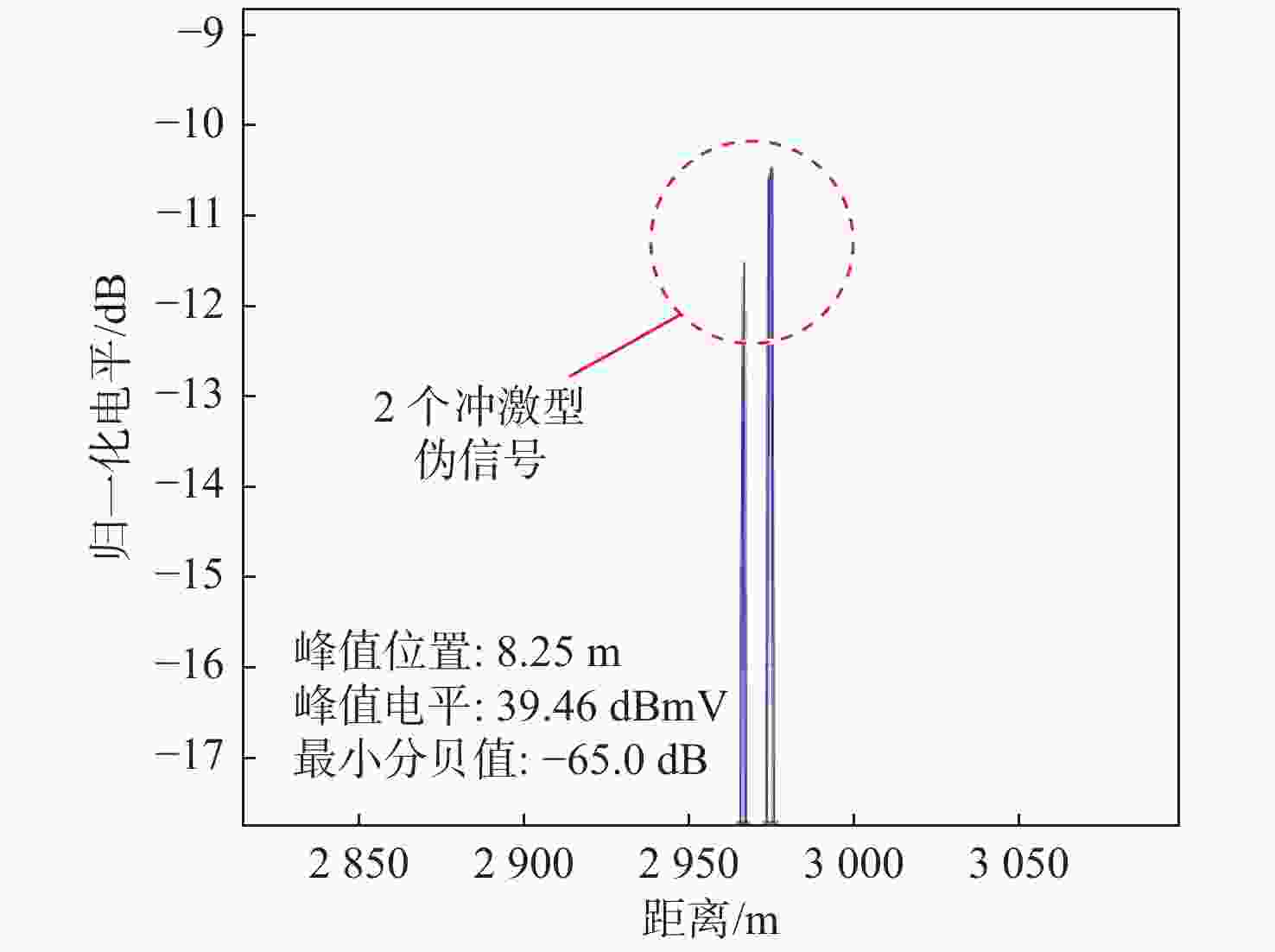
$ {f_4} - {f_3} $(二阶互调冲激型伪信号)
$ {f_3} - {f_{\text{a}}} - {F_{\text{b}}} $(一阶脉冲型伪信号)
$ {f_4} - {f_{\text{a}}} - {F_{\text{b}}} $(一阶脉冲型伪信号)表 2 带外双频二阶互调脉冲型伪信号试验结果
Table 2. Test results of out-of-band dual-frequency second-order intermodulation pulse pseudo-signals
发射信号
衰减程度/dB干扰场强1/
(dBV·m−1)干扰场强2/
(dBV·m−1)伪信号
电平/dBmV伪信号中心
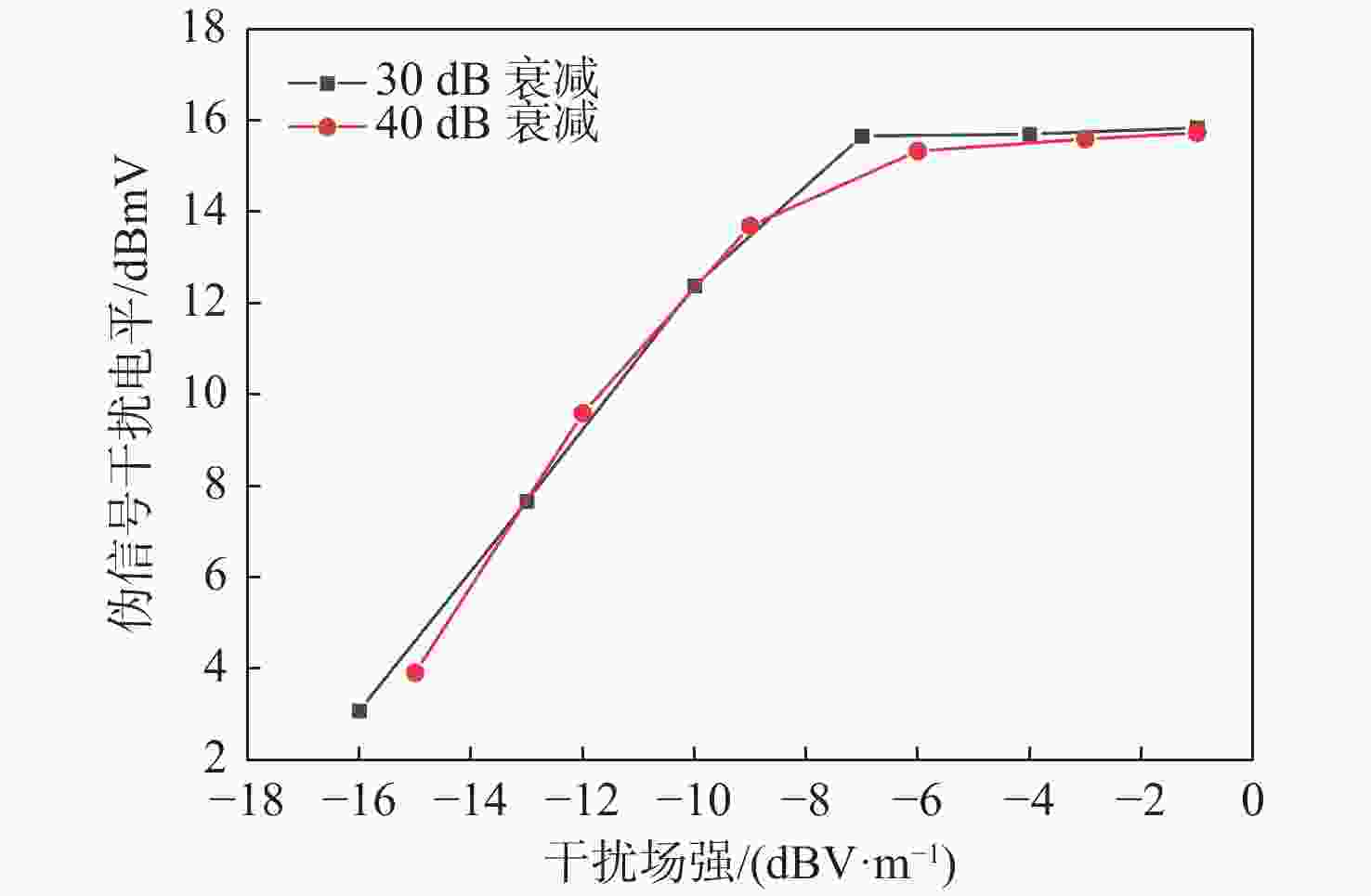
距离/m30 −16 −16 3.08 2893 −13 −13 7.66 4011 −10 −10 12.38 329.4 −7 −7 15.66 1892 −4 −4 15.70 2939 −1 −1 15.84 224.5 40 −15 −15 3.91 3741 −12 −12 9.59 3462 −9 −9 13.69 660.4 −6 −6 15.33 1548 −3 −3 15.59 1254 −1 −1 15.73 2143 表 3 双频二阶互调与三阶交互调冲激型伪信号试验结果
Table 3. Test results of two-frequency second-order intermodulation and third-order intermodulation impulse pseudo-signal
发射信号
衰减程度/dB干扰场强1/
(dBV·m−1)干扰场强2/
(dBV·m−1)二阶互调伪信号
电平/dBmV三阶交互调伪信号
电平/dBmV二阶互调伪信号
距离/m三阶交互调伪信号
距离/m距离差/m 30 −60 −60 2.91 13.27 755.9 764.1 8.3 −55 −55 7.26 19.99 759.7 767.8 8.2 −50 −50 13.23 26.69 758.9 767.1 8.3 −45 −45 17.5 31.24 758.2 766.3 8.2 −40 −40 21.77 33.74 762.7 770.8 8.2 −35 −35 25.92 32.97 762.7 770.8 8.2 −30 −30 28.45 29.99 746.9 755.1 8.3 −25 −25 28.78 27.52 749.2 757.3 8.2 −20 −20 27.43 24.25 746.2 754.4 8.3 −15 −15 27.54 20.98 745.4 753.6 8.3 −10 −10 28.18 17.81 748.4 756.6 8.3 −5 −5 28.22 14.39 752.2 760.3 8.2 40 −60 −60 2.21 4.77 749.5 757.6 8.2 −55 −55 8.53 10.83 746.5 754.7 8.3 −50 −50 13.25 16.52 751 759.1 8.2 −45 −45 16.58 20.3 751 759.1 8.2 −40 −40 21.13 21.92 753.2 761.4 8.3 −35 −35 25.05 19.99 753.2 761.4 8.3 −30 −30 27.51 18.03 748 756.1 8.2 −25 −25 28.74 15.14 748.7 756.9 8.3 −20 −20 27.35 12.67 751.7 759.8 8.3 −15 −15 27.55 10.74 749.5 757.6 8.2 −10 −10 27.32 8.13 750.2 758.4 8.3 −5 −5 28.31 5.91 751 759.1 8.2 -
[1] 许彤, 陈亚洲, 王玉明, 等. 无人机数据链带内连续波电磁干扰效应研究[J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2021, 41(10): 1084-1094.XU T, CHEN Y Z, WANG Y M, et al. Research on in-band continuous wave electromagnetic interference effect of unmanned aerial vehicle data link[J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2021, 41(10): 1084-1094(in Chinese). [2] 刘尚合, 武占成, 张希军. 电磁环境效应及其发展趋势[J]. 国防科技, 2008, 29(1): 1-6.LIU S H, WU Z C, ZHANG X J. Electromagnetic enviroment effect and its development trends[J]. National Defense Science & Technology, 2008, 29(1): 1-6(in Chinese). [3] 孙国至, 刘尚合, 陈京平, 等. 战场电磁环境效应对信息化战争的影响[J]. 军事运筹与系统工程, 2006, 20(3): 43-47.SUN G Z, LIU S H, CHEN J P, et al. The influence on information-based war of battle field electromagnetic environment effects[J]. Military Operations Research and Systems Engineering, 2006, 20(3): 43-47(in Chinese). [4] 毛二可, 龙腾, 韩月秋. 频率步进雷达数字信号处理[J]. 航空学报, 2001, 22(S1): 16-25.MAO E K, LONG T, HAN Y Q. Digital signal processing of stepped frequency radar[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2001, 22(S1): 16-25(in Chinese). [5] TIKOLAM M, SAMCOVIC A, NIKOLIC D, et al. An algorithm for detection of electromagnetic interference in high frequency radar range-Doppler images caused by LEDs[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 84413-84419. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2924532 [6] 郭栋, 王世军, 魏冬峰. 高功率微波武器对雷达的威胁及其防护[J]. 指挥信息系统与技术, 2011, 2(5): 74-77.GUO D, WANG S J, WEI D F. Threat of high power microwave weapon on radars and its countermeasures[J]. Command Information System and Technology, 2011, 2(5): 74-77(in Chinese). [7] SEIFI Z, GHORBANI A, ABDIPOUR A. Analysis and experimental study of radiative microwave pulses effects on the nonlinear performance of a low-noise amplifier[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2021, 49(3): 1105-1114. doi: 10.1109/TPS.2021.3057613 [8] 张冬晓, 陈亚洲, 程二威, 等. 无人机信息链路电磁干扰效应规律研究[J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2019, 39(7): 756-762.ZHANG D X, CHEN Y Z, CHENG E W, et al. Effects of electromagnetic interference (EMI) on information link of UAV[J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2019, 39(7): 756-762(in Chinese). [9] 赵宏泽, 魏光辉, 杜雪, 等. 卫星导航接收机三阶互调阻塞效应分析[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2022, 44(4): 1336-1342.ZHAO H Z, WEI G H, DU X, et al. Analysis of third-order intermodulation blocking effect for satellite navigation receiver[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(4): 1336-1342(in Chinese). [10] OLIVIER K, CILLIERS J, DU PLESSIS M. Design and performance of wideband DRFM for radar test and evaluation[J]. Electronics Letters, 2011, 47(14): 824-825. doi: 10.1049/el.2011.0362 [11] LI Y, CHEN D, ZHANG X L. Research on EMI radiation source model based on battlefield EMC prediction analysis[J]. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2019, 569(3): 032075. doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/569/3/032075 [12] 丁国胜. 舰船大功率雷达电磁辐射场强分析和改善技术研究[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2012.DING G S. Study on analysis of electromagnetic radiation field strength from ship-borne high power radar and improvement technology[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2012(in Chinese). [13] ZHAO B, ZHOU F, BAO Z. Deception jamming for squint SAR based on multiple receivers[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2015, 8(8): 3988-3998. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2014.2322612 [14] ZHAO B, HUANG L, ZHANG J H. Single channel SAR deception jamming suppression via dynamic aperture processing[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2017, 17(13): 4225-4230. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2017.2695001 [15] ZHAO H Z, WEI G H, PAN X D, et al. Pseudo-signal interference regularity of single-frequency electromagnetic radiation to stepped-frequency radar[J]. Electronics, 2022, 11(17): 2768. doi: 10.3390/electronics11172768 [16] DU X, WEI G, ZHAO H Z, et al. Research on continuous wave electromagnetic effect in swept frequency radar[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2021, 2021: 4862451. [17] 李文臣, 黄烽, 杨会民, 等. 雷达噪声干扰和多假目标干扰效能分析[J]. 中国电子科学研究院学报, 2013, 8(4): 403-406.LI W C, HUANG F, YANG H M, et al. Efficiency analysis of radar noise jamming and multiple false target jamming[J]. Journal of China Academy of Electronics and Information Technology, 2013, 8(4): 403-406(in Chinese). [18] 徐飞虎. 系统非线性对高频雷达目标探测的影响[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2010.XU F H. The impact on target detection of high frequency radar as system’s nonlinearity[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2010(in Chinese). [19] BIONDI A, VALLOZZI L, ROGIER H, et al. Electromagnetic compatibility aware design and testing of intermodulation distortion under multiple co-located sources illumination[J]. IET Science, Measurement & Technology, 2012, 6(2): 105-112. [20] 杜文越. Ku 波段导航雷达系统设计与实现[D]. 北京: 北京理工大学, 2019.DU W Y. Design and implementation of Ku band navigation radar system[D]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology, 2019(in Chinese). [21] 中央军委装备发展部. 系统电磁环境效应试验方法: GJB 8848—2016[S]. 北京: 中央军委装备发展部, 2016: 51-53.Equipment Development Department of the Central Military Commission. Electromagnetic environmental effects test methods for systems: GJB 8848—2016[S]. Beijing: Equipment Development Department of the Central Military Commission, 2016: 51-53(in Chinese). -






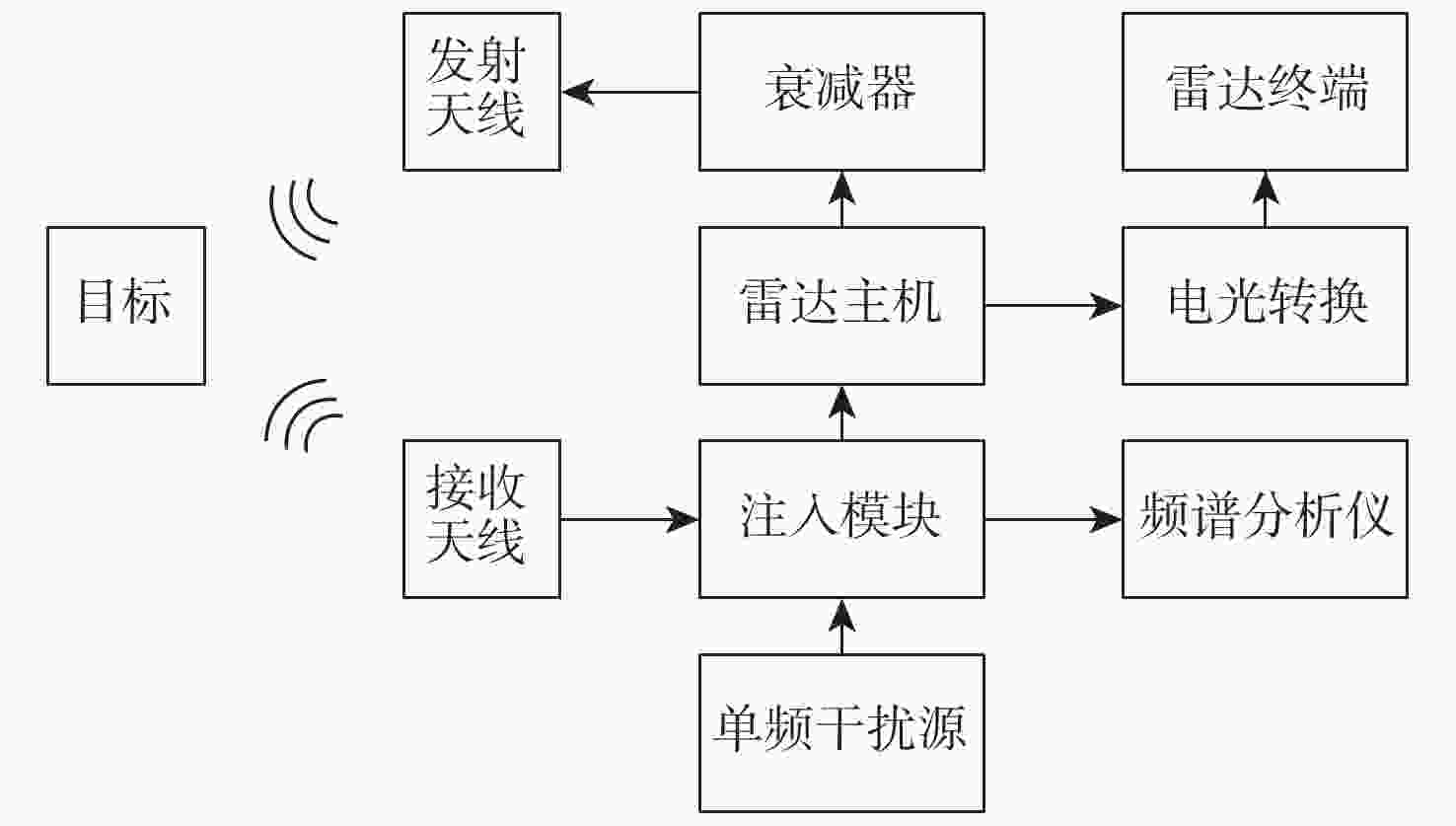
 下载:
下载: