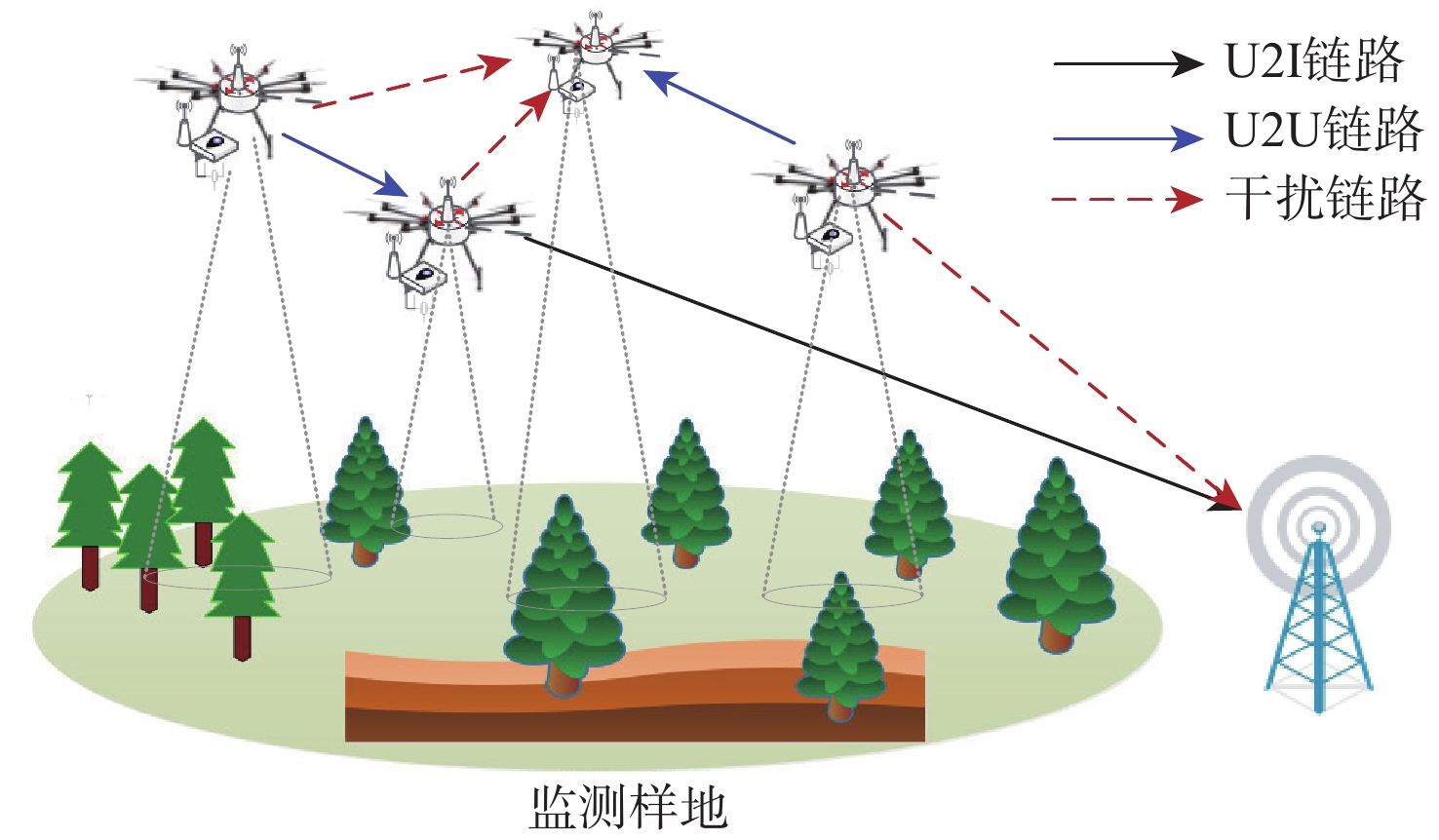
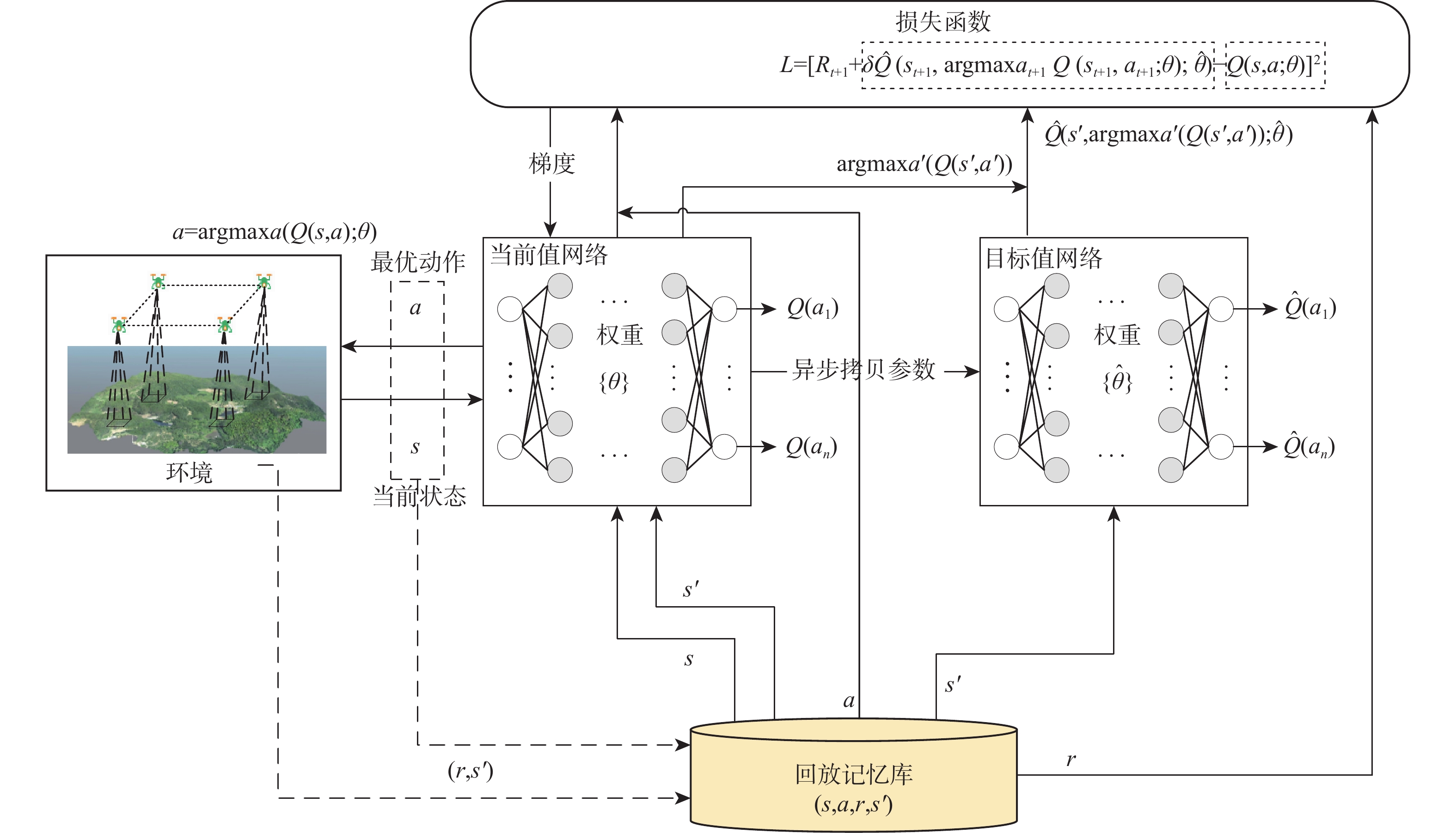
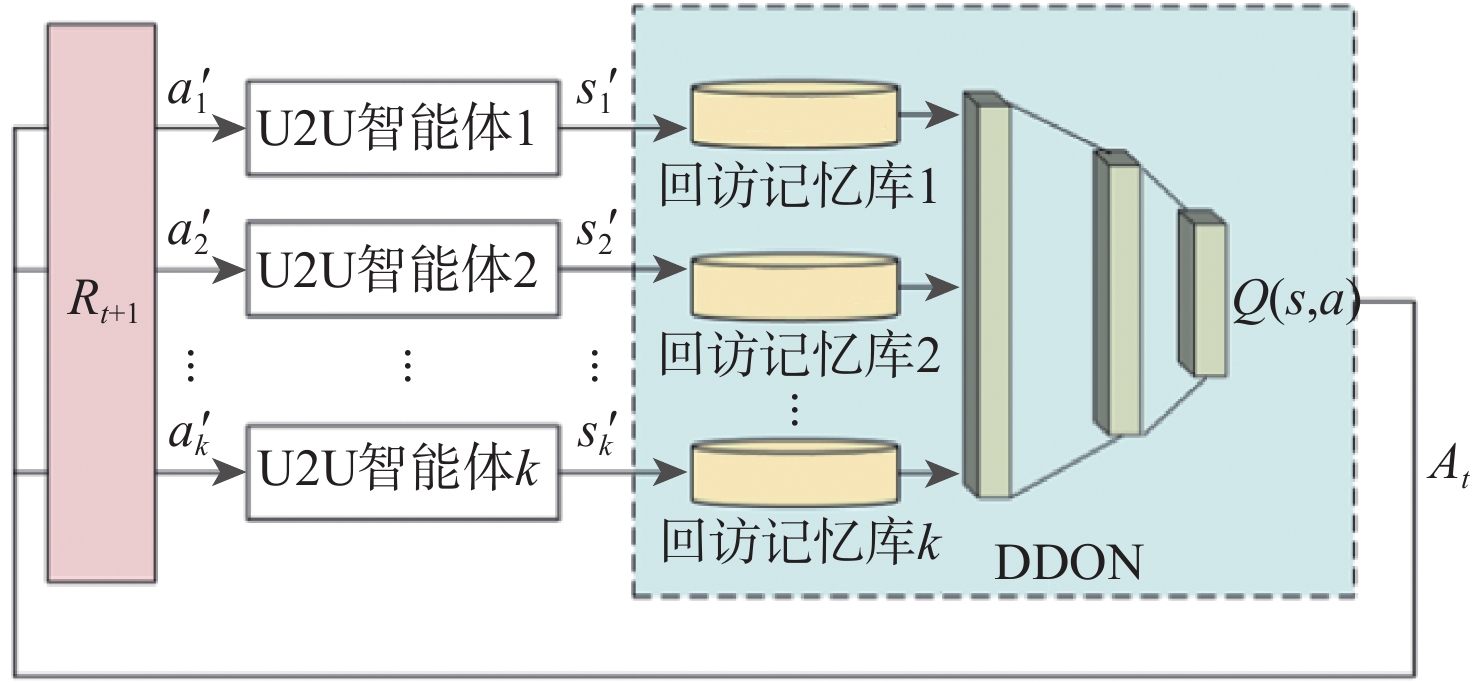
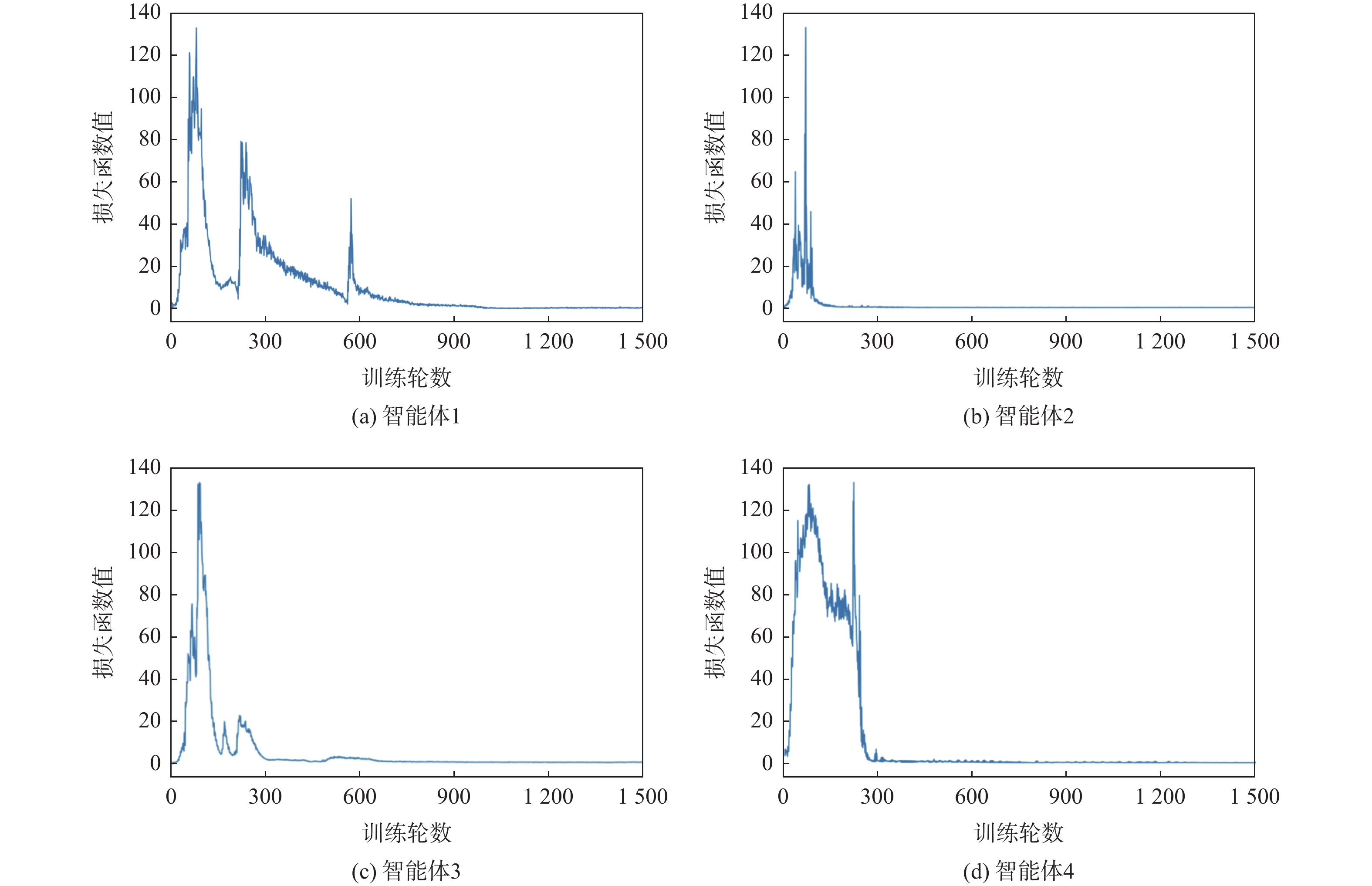
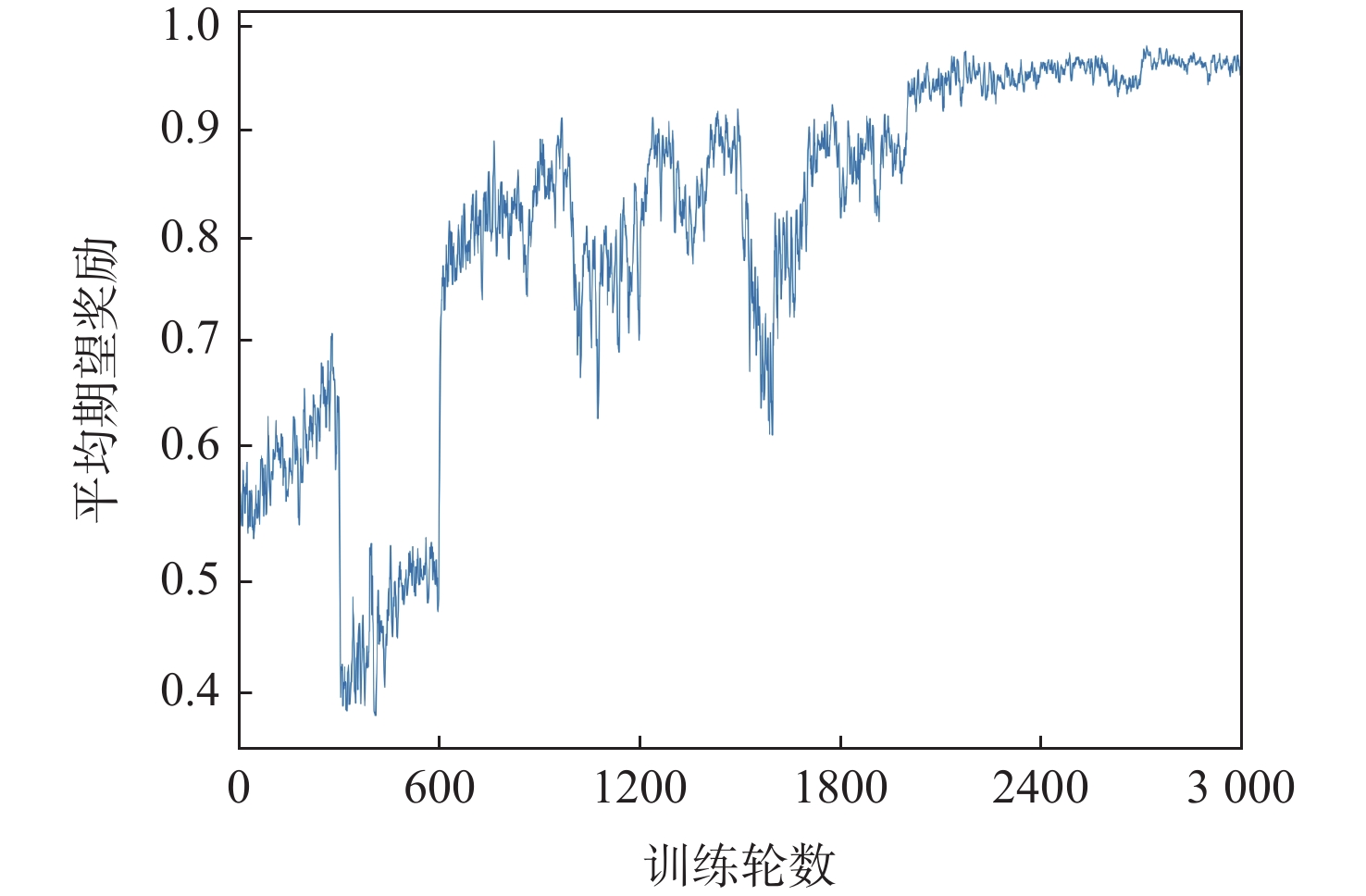
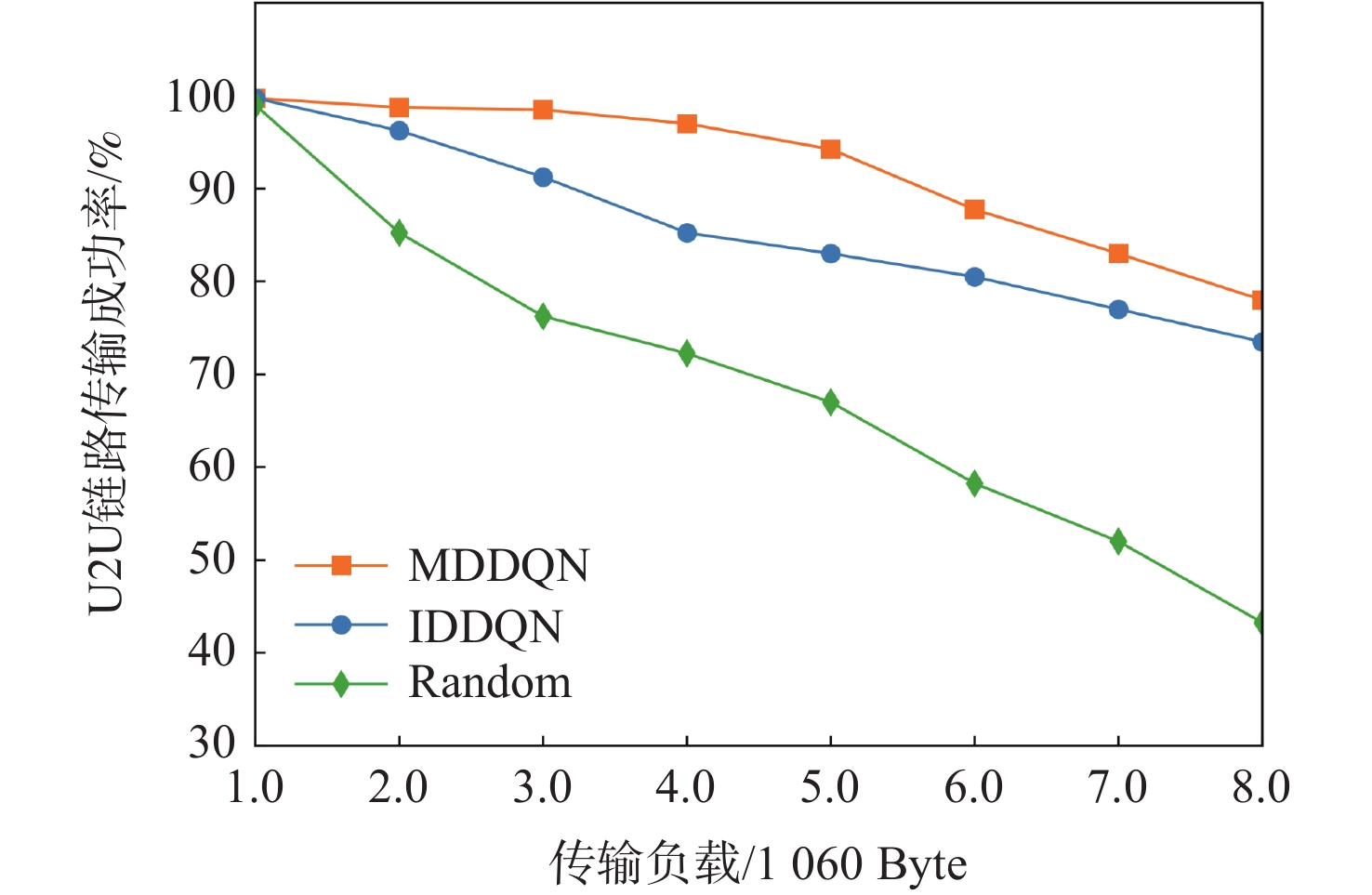
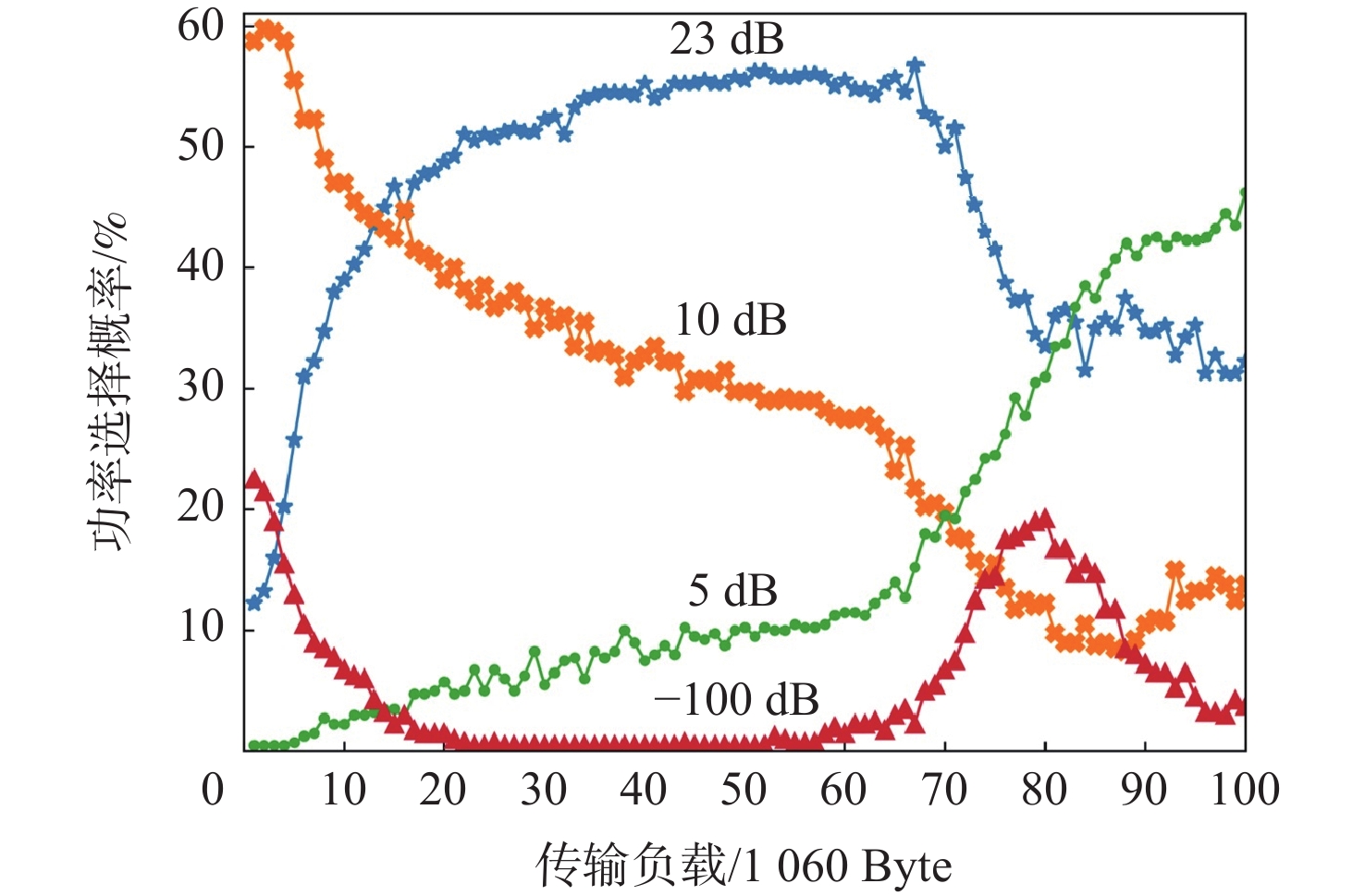
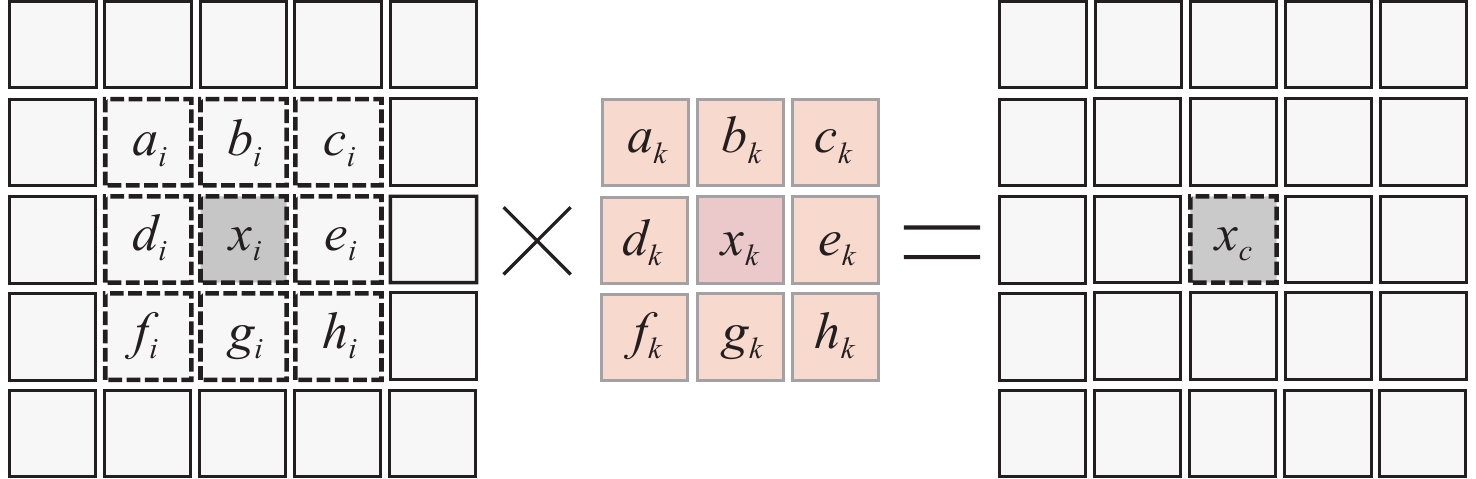-
摘要:
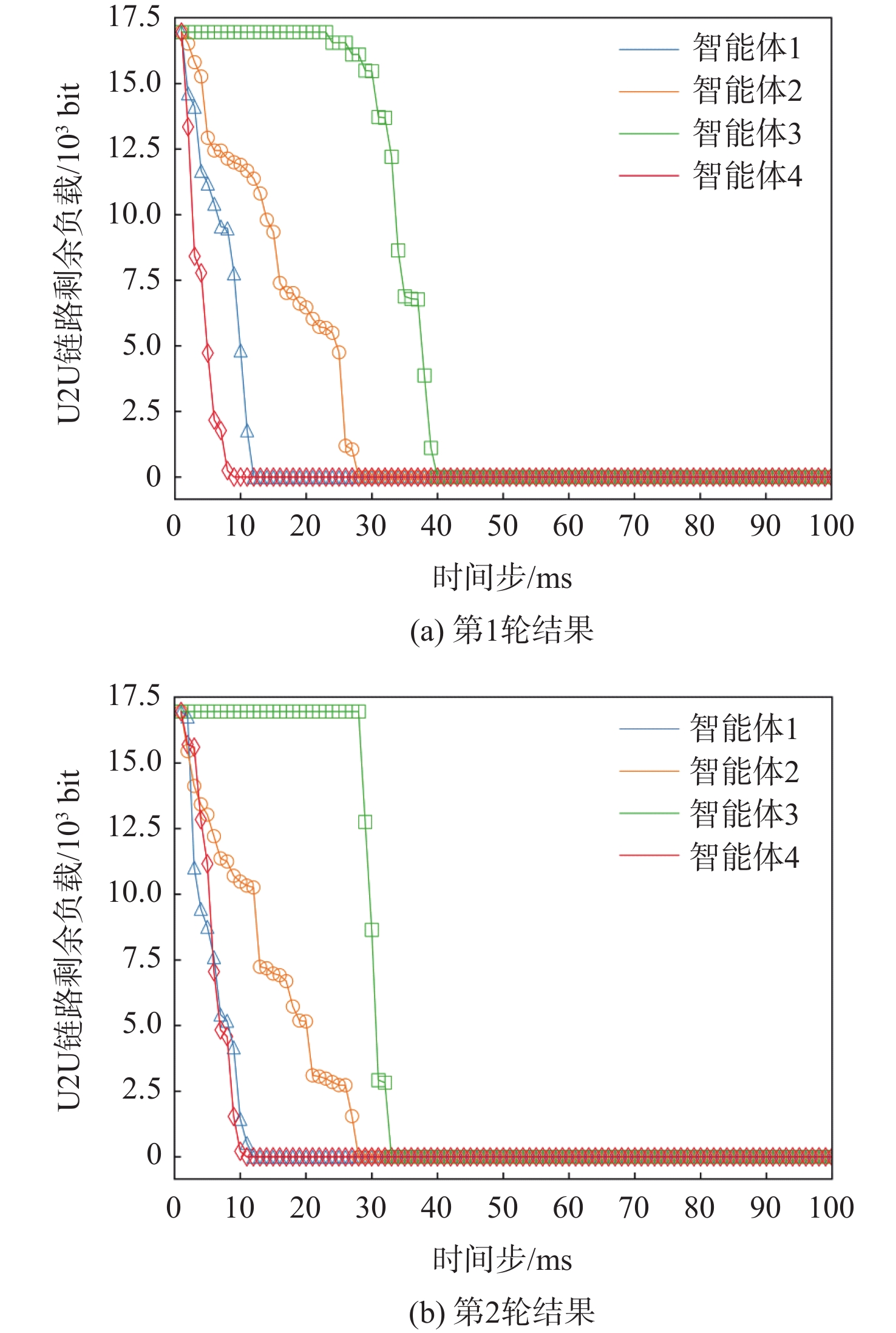
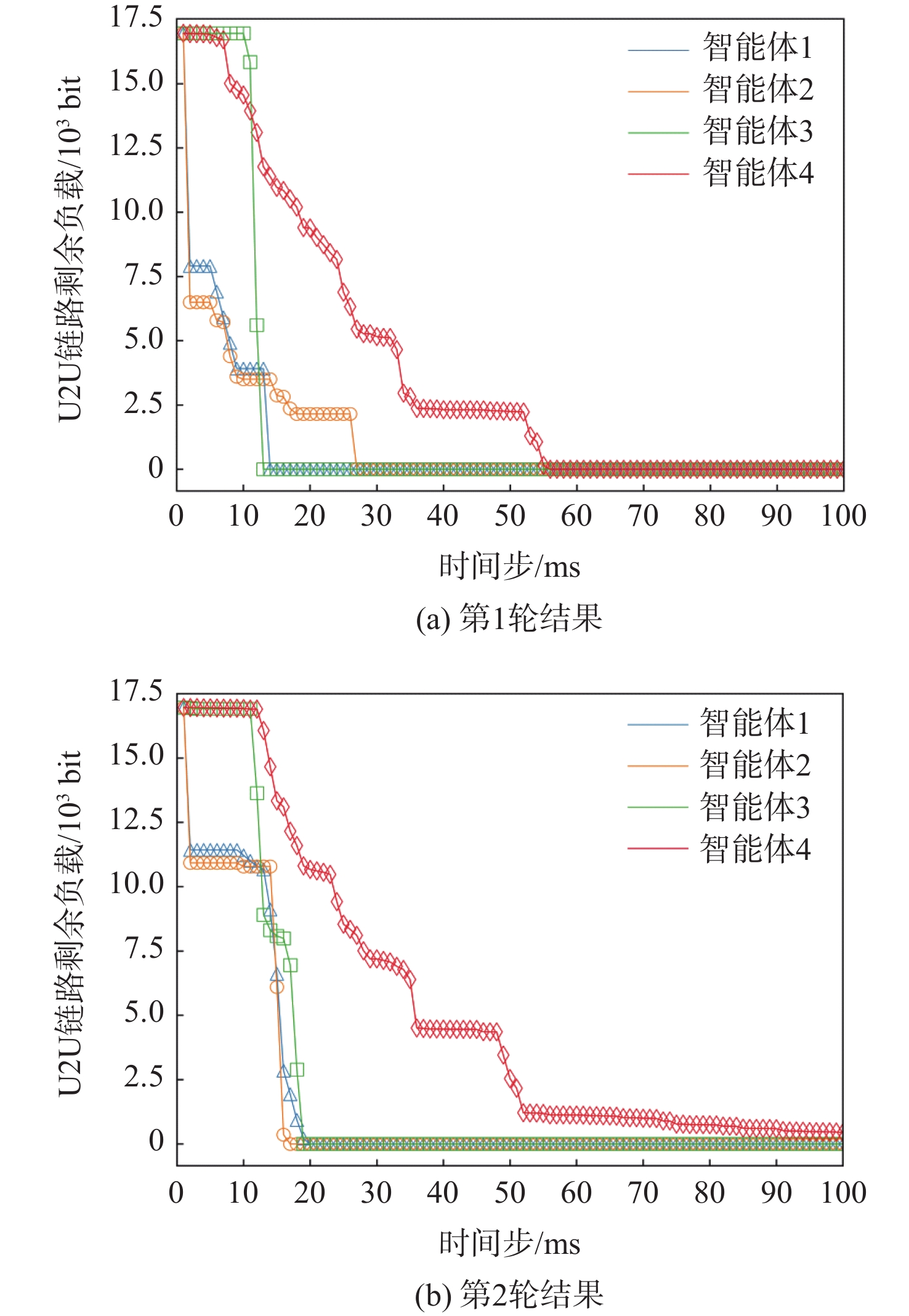
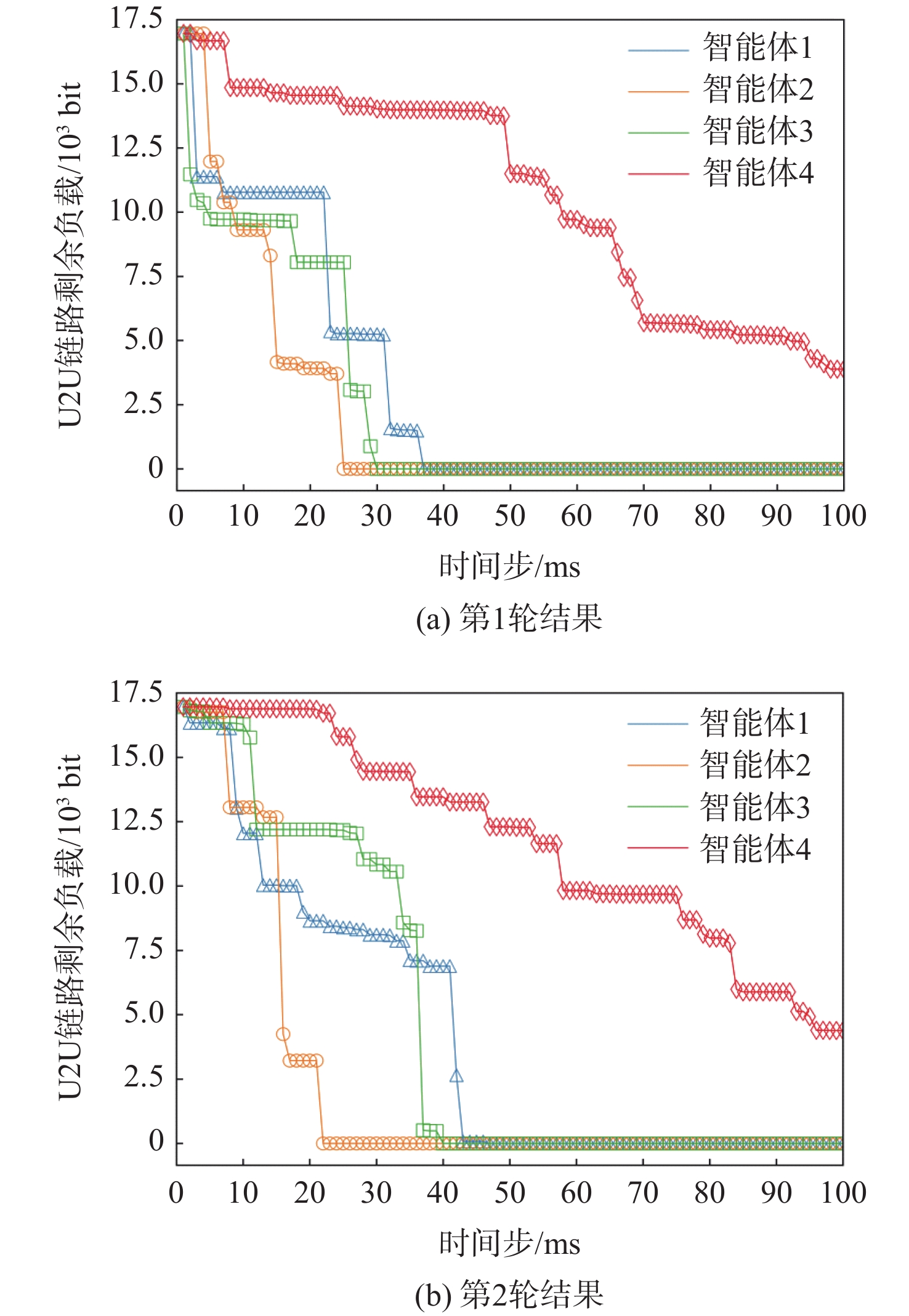
针对多无人机区域覆盖任务中的机间通信资源分配问题,提出了一种基于强化学习的多智能体动态通信资源分配模型。利用多智能体生成树覆盖方法生成任务区域内各个无人机的覆盖航线,对无人机与地面基站及无人机之间的通信链路进行建模。由于飞行环境的不确定性,将长期的资源分配问题建模为随机博弈模型,将无人机间的空-空链路视作一个智能体,每个智能体采取的动作包含选择工作频段和发送端的传输功率。在此基础上,基于双深度Q网络(DDQN)设计多智能体强化学习(MARL)模型,使得每个智能体通过奖励函数的反馈学习到最优通信资源分配策略。仿真结果表明:MARL模型能够在动态航迹下自适应选择最佳通信资源分配策略,提高时延约束下的负载交付成功率,同时降低空-空链路对空地下行链路的干扰并增大信道总容量。
Abstract:This study presents a reinforcement learning-based multi-agent dynamic communication resource allocation model that addresses the issue of communication resource allocation in multi-UAV area coverage tasks. We first generate the coverage route of each UAV in the mission area by the multi-agent spanning tree coverage (MSTC) method, and model the communication link between the UAV and ground base station as well as UAV pairs. The uncertainty inherent in the flight environment motivates the modeling of the long-term resource allocation problem as a random game. T Considered an agent, the air-to-air connection between UAVs entails receiver, subchannel, and transmission power selection, among other modifications. We then design a multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) model based on the double deep Q-network (DDQN), where each agent learns the optimal communication resource allocation strategy through the feedback of the reward function. As shown by simulation results, the proposed MARL method can increase the overall channel capacity, decrease interference from air-to-ground uplink, and optimize communication resource allocation strategies under dynamic trajectories and delay constraints, while also improving the success rate of load delivery.
-
当前,卷积神经网络(convolutional neural network, CNN)广泛应用于图像分类、人脸识别等领域。作为CNN计算的前序步骤,图像预处理在扩充训练数据集、降低CNN推理或训练误差等方面均有重要意义。Pal等[1]调研了归一化、标准化和零分量分析(zero component analysis, ZCA)对3种不同结构的CNN识别准确率的影响,结果表明,经过预处理的数据识别准确率相比原始数据提升约10%。Şaban和Akdemir[2]研究了归一化、中值滤波和维纳滤波等图像预处理算法对病理学图像识别的影响,结果显示,预处理使CNN训练收敛速度更快,并使推理准确率提升约1.7%。多项研究表明,高效的图像预处理算法可有效改善CNN的性能[3-4]。
CNN常用的图像预处理算法从应用角度可以分为3类:①统一图像或数据格式,以满足CNN的输入要求,如标准化、归一化、图像缩放、通道转换等;②扩充CNN训练数据集,在许多应用场景中,供CNN训练的数据集往往是不充分的,预处理能够有效增加CNN训练的样本量,从而提高CNN的泛化能力,常见的扩充数据集的图像预处理算法有旋转、镜像、平移、裁剪、亮度调整、对比度调整、添加随机噪声等;③图像增强,目的是提高推理速度和准确率,常见的方法包括灰度化、二值化、各类滤波算法、图像分割、边缘检测、锐化(边缘增强)等。
在嵌入式应用环境中, CPU+CNN加速器的异构组合是常见的深度学习计算平台。在该异构平台中,CPU负责图像的预处理和加速器的控制,加速器负责CNN的计算。在先前的研究中,大量的工作集中在CNN推理或训练部分的优化[5-6]。然而,在嵌入式平台中,由于CPU并行度低,性能不佳,图像预处理也会成为瓶颈。在多项研究[7-9]中,图像预处理占据了60%以上的计算时间。因此,加速图像预处理成为了进一步提升性能的关键。
为解决这一问题,NVIDIA发布了图像预处理计算库NVIDIA Data Loading Library (DALI)[10],该计算库能够高效地进行CNN计算中的图像解码和预处理等操作,其加速原理是将在CPU上进行的图像预处理工作部署到图形处理单元(graphics processing unit, GPU)上,但是,DALI仅能被应用在CPU+GPU的深度学习平台,不适用于CPU+CNN加速器的嵌入式深度学习环境。Ma[11]通过高层次综合(high level synthesis, HLS)的方法将灰度化、图像缩放和显著性分析算法固化成IP核,相比ARM CPU实现了约20倍的加速效果。
RISC-V是一种开源的CPU指令集架构(instruction set architecture, ISA)。除了标准的整数指令集外,RISC-V还针对不同的应用需求定义了扩展指令集,如嵌入式扩展(embedded extension)、位操作扩展(bit manipulation extension)、向量扩展(vector extension)、加密扩展(cryptographic extension)等。此外,RISC-V还支持用户自定义指令集。RISC-V指令集扩展在算法加速、硬件安全等领域表现出优秀的性能和良好的灵活性。Kuo等[12]扩展了一组迦瓦罗域的RISC-V计算指令,对非二进制纠错码和后量子密码算法进行加速,实现了约5倍的加速效果,同时硬件逻辑资源消耗仅增加1.27%;Razilov等[13]使用高性能RISC-V向量处理器Ara[14]和RISC-V向量扩展(RISC-V vector extension, RVV)指令来加速广义频分复用(generalized frequency division multiplexing, GFDM)算法,实现了约60倍的加速效果;刘强和李一可[15]基于RISC-V指令扩展提出了一种可配置的故障注入检测方法,支持时间冗余和信息冗余2种检测模式,相比单一的信息冗余检测方法,故障检测率提高了13.34%,仅引入4.4%的资源开销。
RVV是一种单指令多数据流(single instruction multiple data, SIMD)的技术。RVV1.0[16]是RVV的技术规范,在2021年被批准。支持RVV的RISC-V处理器有用于实时和嵌入式计算的向量处理器Vicuna[17]、64位高性能向量处理器Ara[14]等。
由于不同网络结构和应用场景所需的图像预处理算法不同,图像预处理难以被设计成专用集成电路(application specific integrated circuit, ASIC)进行加速。同时,图像预处理算法对并行度要求高,通用的嵌入式CPU往往并行计算能力较差。RVV能够增强RISC-V CPU的并行计算能力,还可以通过自定义向量指令实现对特定应用的定制化加速。因此,本文采用RVV方案对图像预处理进行加速。
使用RISC-V向量处理器加速图像预处理算法面临以下2个问题:①图像预处理算法种类多,难以设计通用加速方案;②现有标准RISC-V指令集不能完全满足图像预处理加速的需求。
为解决上述问题,本文面向常用的CNN图像预处理算法提出了一种基于RVV的加速方案。
1) 针对标准化、缩放、旋转、镜像、平移、亮度调整、灰度化、二值化、高斯滤波、拉普拉斯滤波、索贝尔边缘检测11种常用的CNN图像预处理算法,按照计算模式分为4类,对每类算法设计了加速方案。
2) 在标准向量扩展的基础上新增了6条自定义向量指令,用于进一步加速图像预处理算法中的操作。为实现这些指令,对编译器进行修改,并设计了相应的译码和计算模块。
3) 使用现场可编程门阵列(field programmable gate array, FPGA)对本文方法和硬件架构进行验证和评估,实验结果显示,与标量处理器相比,本文设计的加速方法能够实现3.13~9.97倍的加速。
1. 硬件架构
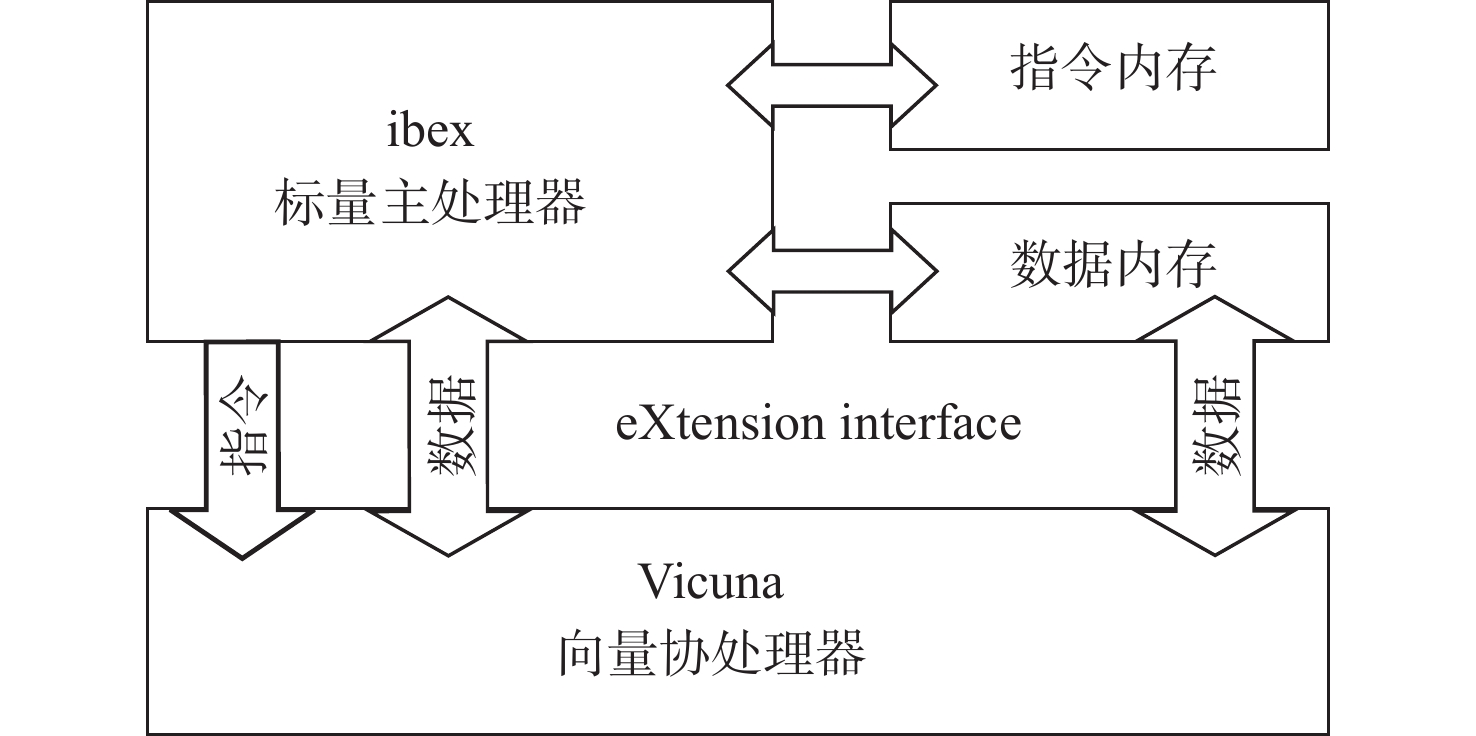
在嵌入式深度学习应用中,硬件资源和功耗往往是受限的。因此,本文采用轻量级处理器ibex[18]+ 向量协处理器Vicuna[17]的组合来开展研究,如图1所示。其中,ibex是32位的标量主处理器,设有2级流水线,支持RV32IEMCB指令集,该处理器核的优点是可配置且轻量化,适合嵌入式控制应用。Vicuna是32位整数向量协处理器,支持8、16、32位的向量元素宽度,其遵循RVV1.0规范,实现了Zve32x指令集(向量扩展的一个子集)。
ibex和Vicuna通过eXtension interface[19]相互连接。当取到标量指令时,由主处理器ibex执行;当取到向量指令时,ibex会将该指令通过eXtension interface发送至Vicuna执行。Vicuna在执行向量指令时,能够直接从数据内存中读取数据到向量寄存器文件(vector register file, VRF)中,并在计算完成后将结果写回数据内存。在此期间,如果存在数据依赖,则ibex会停滞流水线直到Vicuna完成写回,如果不存在数据依赖,则ibex可以和Vicuna同时运行。
2. 图像预处理算法加速方案设计
由于卷积运算的独特性,本文按照是否涉及卷积运算,将11种图像预处理算法分为非卷积类和卷积类。卷积类算法包括高斯滤波、拉普拉斯滤波和索贝尔边缘检测。非卷积类算法按照特点又可以分为3类,分别为像素位置变化类、像素数值变化类及求全局平均值类。其中,像素位置变化类包括旋转、镜像、平移和缩放,像素数值变化类包括灰度化、二值化和亮度调整,求全局平均值类包括标准化。
2.1 非卷积类算法
2.1.1 像素位置变化类算法
涉及像素位置变化的算法包括旋转、镜像、平移和缩放。其中,旋转和缩放采用最近邻插值法,其他插值方法(如线性插值法)由于需要单独计算每个像素点数值的变化,不适合进行向量化。
这类算法的特点是:输出图像与输入图像之间,仅像素值的存储地址发生了变化,像素值本身并未发生变化。本文方法使用RVV中的索引加载(indexload)指令对这类算法实现定制化加速。
RVV中的加载指令用于实现从数据内存中读取数据并加载到向量处理器的向量寄存器文件中。按照加载方式的不同,加载指令可以分为以下3类:①unit-strideload,该指令能够从内存中加载一组相邻的数据元素到向量寄存器中,是最常用的加载指令;②stridedload,该指令能按照一定的步长(stride)间隔加载一组固定间隔的数据到向量寄存器中;③indexload,即索引加载指令,该指令能够按照索引矩阵中描述的顺序加载一组数据元素到向量寄存器中。
索引加载指令能够按照既定的顺序加载数据。而涉及像素位置变化的图像预处理算法本质上是数据存储位置的变化。当使用索引加载指令实现这些算法时,原有的图像数据被按照索引矩阵描述的顺序读取到向量寄存器中重新排列,再写回数据内存,以此完成像素数据位置的变化。
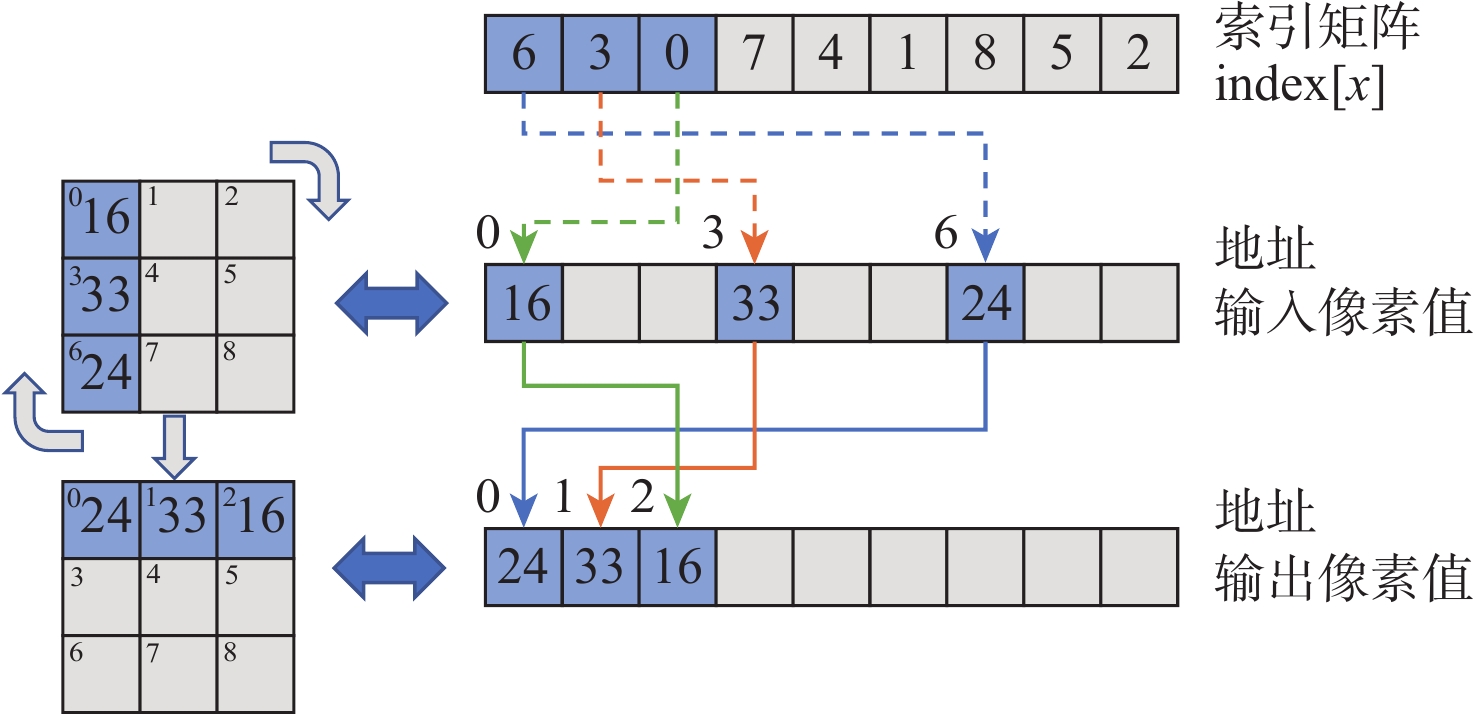
如图2所示,以一张3×3大小的图像顺时针旋转90°为例,说明索引加载指令如何实现像素位置的变化。
图2最上方是索引矩阵,左侧是旋转前后的图像,右侧是旋转前后的图像像素值在一维数组中存储的变化。在索引加载指令操作过程中,输入像素值按照式(1)进行重排序:
output[x]=input[index[x]] (1) 例如,索引矩阵中第一个元素为6,则向量处理器会加载输入数组地址为6的元素到向量寄存器地址0的位置,后续元素同理。加载完毕后,将向量寄存器中的数据写回数据内存,以此来实现像素位置的变化。标量处理器完成同样的操作需要对每个数据进行单独读写,这需要大量的指令开销,而一条索引加载指令能够完成一批数据的位置变化,显著提高效率。
另外,索引矩阵决定了算法中像素位置变化的规则,如果多张图像都采用同一种变换方式,则索引矩阵可以被提前计算好并作为常量存储,以减少计算量。
2.1.2 像素数值变化类算法
涉及像素数值变化的算法包括灰度化、二值化和亮度调整。这类算法的特点是:输出图像和输入图像之间仅像素值发生变化,像素位置并未发生变化。在实现过程中,可以使用常规的unit-strideload加载指令加载数据,按照算法原理使用对应的向量算数运算指令进行计算,将计算结果写回数据内存。
本节以灰度化为例说明加速这类算法的方法。灰度化有多种实现方法,如分量法、最大值法、均值法和加权平均法。本文采用图像处理库OpenCV中的加权平均来保证通用性。
Gray[x]=0.072B[x]+0.715G[x]+0.213R[x] (2) 式中:Gray[x]表示像素x的灰度值;B、G、R分别表示蓝、绿、红3个颜色通道。
计算灰度值的加权平均公式有浮点乘法,需要消耗大量的计算资源。因此,本文将式(2)中等号右侧所有系数都乘以256再右移8位,如式(3)所示。这种方式使用8位的整数乘法和移位来代替浮点乘法,易于硬件实现。经过评估,由此带来的精度损失不超过1%。
Gray[x]=(18B[x]+183G[x]+55R[x])≫8 (3) 使用RVV指令对算法进行实现,伪代码如算法1所示。其中,输入为B、G、R这3个通道的像素值,输出结果RES为灰度值;循环次数n取决于需要处理的数据量和向量寄存器的长度;src表示该变量存储在数据内存中,vec表示该变量存储在向量处理器的寄存器中。
使用向量指令实现的灰度化算法可以分为以下4步:①将数据从内存加载到向量寄存器中(算法1的第2~4行)。②在3个通道上分别进行乘累加操作(第5~7行),其中,括号内的第1个参数代表需要累加的数据,后2个参数代表指令中的操作数1和操作数2。在该算法使用的乘累加指令中,操作数1的数据类型是整形,操作数2的数据类型是向量寄存器的地址。在实际运算中,会根据地址调取该向量寄存器中的所有元素进行计算,实现SIMD的效果。③将乘累加后的结果右移8位(第8行)。④将结果从向量寄存器写回数据内存(第9行)。
算法1 灰度化算法的向量实现。
输入:src_B, src_G, src_R。
输出:src_RES。
1. for i = 1 to n do
2. vec_Bi = VLOAD(src_Bi);
3. vec_Gi = VLOAD(src_Gi);
4. vec_Ri = VLOAD(src_Ri);
5. vec_RESi = VMAC(vec_RESi,18,vec_Bi);
6. vec_RESi = VMAC(vec_RESi,183,vec_Gi);
7. vec_RESi = VMAC(vec_RESi,55,vec_Ri);
8. vec_RESi = VSHIFT(vec_RESi,8);
9. src_RESi = VSTORE(vec_RESi);
10. end for
2.1.3 求全局平均值类算法
许多CNN算法在图像数据输入卷积层前需要进行数据标准化的操作。标准化涉及求图像全局的平均值。求平均值要先求全局像素值的和,本文使用规约求和指令实现该类算法的加速。
规约指令是RVV指令中的一类特殊指令,能够对指定向量寄存器中的元素两两运算,将其规约为一个标量值。RVV中的规约指令有规约求和、规约求最大值、规约求与等。
首先,使用规约求和指令求得所有像素的和;然后,使用移位代替除法求得图像的全局平均值;最后,在当前像素值的基础上调用向量减法指令减去全局平均值,即可实现数据标准化。
2.2 卷积类算法
高斯滤波、拉普拉斯滤波和索贝尔边缘检测等算法的共同特点是需要对比或计算像素点与其周围像素点的关系,类似卷积运算。因此,本文设计了一种基于RVV的卷积加速方案。
2.2.1 卷积加速方案
使用RVV指令实现卷积操作的难点在于向量指令易于实现地址连续的操作,但是卷积运算处理的二维数据的地址是不连续的。如图3所示,左侧为原始图像,中间为卷积核,右侧为计算结果。在原始图像中,像素点ai、bi、ci的存储地址是连续的,而像素点ci和像素点di由于处在不同行,其地址不是连续的,这不利于向量指令进行算法实现。
在卷积运算过程中,卷积核按照一定的步长遍历整个图像。以图3为例,当卷积的步长为1时,卷积核会均匀地滑过图像中的所有像素点。图像中的每个元素都要与卷积核中每个权重相乘。
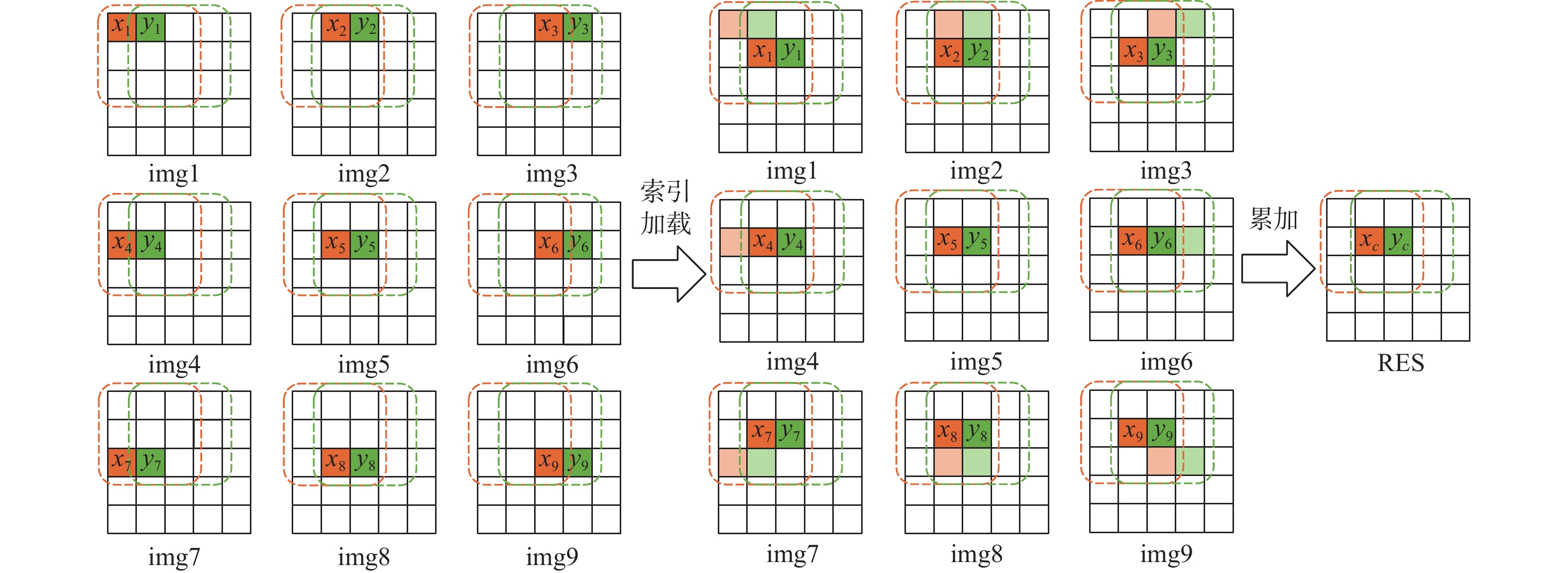
基于以上分析,本文方案第1步为计算该图像和卷积核中所有元素的乘积。这一步操作是地址连续的向量与标量的相乘,易于向量实现。以图3中的卷积核为例,ak与图像所有像素点相乘得到第1张图像,bk与图像所有像素点相乘得到第2张图像,后续同理,一共产生9张图像img1~img9,如图4左侧所示。这9张图像称为临时卷积图像。
卷积运算的过程实际上是乘累加的过程,第1步相当于完成了“乘累加”中的乘法操作,下一步需要从9张临时卷积图像中找到需要的值并累加。
图4的最右侧是计算结果RES,其中,xc对应的9个临时乘积分别位于临时卷积图像img1~img9中x1~x9的位置。因此,xc = x1 + x2 + ··· + x9。假设xc在数组中的位置为m,在计算xc时,需采用以下公式:
xc=RES[m]=img1[m−r−1]+img2[m−r]+img3[m−r+1]+img4[m−1]+img5[m]+img6[m+1]+img7[m+r−1]+img8[m+r]+img9[m+r+1] (4) 式中:r为临时卷积图像一行的元素数量。然而,由于x1~x9在数组中的位置不统一,这种计算方式也难以进行向量实现。
2.1.1节中提到的索引加载指令能够改变像素的存储位置。为使操作易于向量化,本文方法使用索引加载指令索引img1~img9,以此统一x1~x9在数组中的位置。索引矩阵决定了像素位置变换的规则,如img1对应的索引矩阵负责将所有像素往右下移动一格,img2对应的索引矩阵负责将所有像素往下移动一格,其余索引矩阵同理,共9个。索引加载过程如图4所示。
索引加载完成后,计算xc采用的公式为
xc=RES[m]=img1[m]+img2[m]+img3[m]+img4[m]+img5[m]+img6[m]+img7[m]+img8[m]+img9[m] (5) 这种计算方式易于进行向量实现。此外,不仅计算xc需要的x1~x9位置进行了统一,图像中的其他点,如计算yc需要的y1~y9位置也得到了统一。调用向量指令将索引后的9张临时卷积图像累加,便得到了整张图像的卷积计算结果。至此,完成了“乘累加”中的累加。
本文提出的卷积加速方法可以概括为以下4步:①将图像与卷积核中的每个权重相乘,得到9张临时卷积图像;②计算9个索引矩阵;③用索引矩阵索引9张临时卷积图像;④累加,得到实际卷积结果。值得注意的是,如果需要处理大量图像的卷积,9个索引矩阵实际上只需要被计算一次。
2.2.2 卷积加速方案实例——高斯滤波
高斯滤波算法通过计算像素值的加权和来平滑图像并减少噪声,提高CNN推理的准确率。其算法原理是:取图像中每个像素点相邻的矩形窗口,按照权重矩阵计算窗口内所有像素点的加权和。计算式如式(6)所示。高斯滤波的计算过程本质上是一种卷积。权重矩阵的权重值遵循二元正态分布,越接近矩阵中心,权重值越大。
C(x,y)=y+n∑j=y−nx+n∑i=x−nW(i,j)∗P(i,j) (6) 式中:C为计算结果;W和P分别为权重和该点周围的像素。
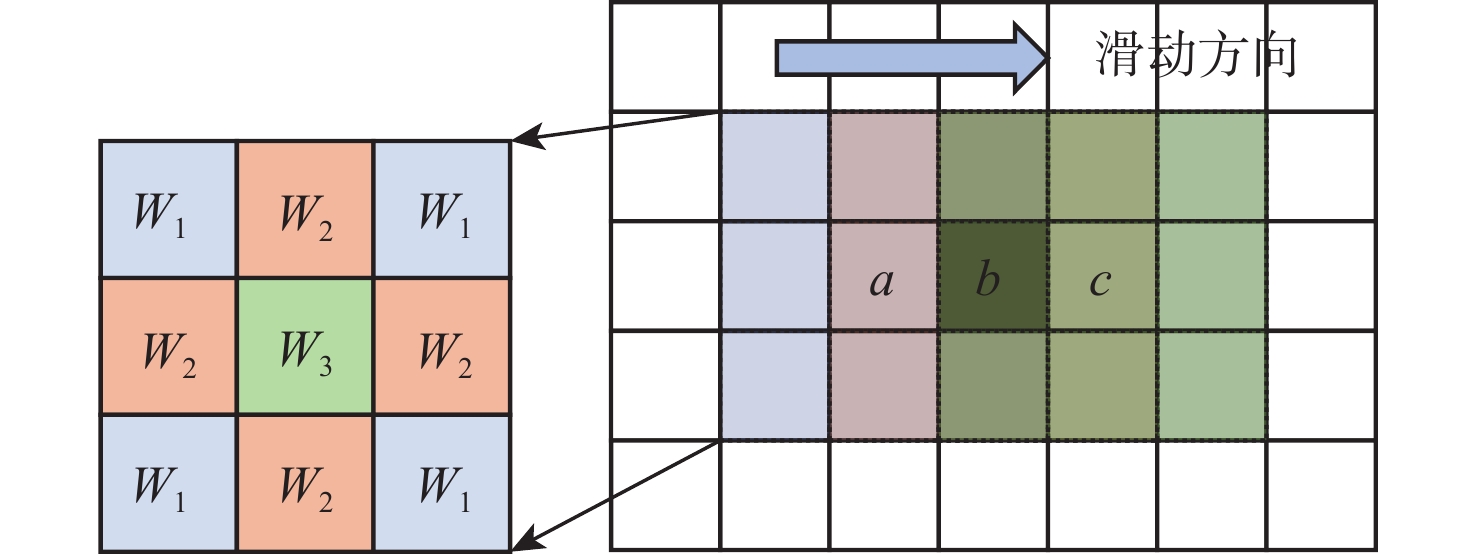
本文提出的卷积加速方法还有一个常规卷积计算方法不具备的优势,即当卷积核中有重复的权值时,可以避免重复计算。图5展示了图像中像素点a、b、c的高斯滤波计算过程。高斯滤波权重矩阵中,距离卷积核中心距离相等的点权值相同。根据2.2.1节的分析,图像中每个像素点在卷积计算的过程中会与权重矩阵中的所有元素相乘,即乘4次W1,4次W2,1次W3。重复的计算会导致资源和功耗的浪费,实际上,每个点只需要分别与W1、W2、W3相乘1次。因此,本文提出的卷积加速方法能够规避卷积核中有重复权值产生的额外乘法计算。高斯滤波算法向量实现伪代码如算法2所示。
将输入图像从数据内存加载到向量寄存器(算法2的第2行)后,先计算图像的所有像素点与W1、W2、W3这3个权重的乘积,由于权重均为浮点数据,采取2.1.2节中用到的方法,用整数乘法和移位来代替浮点乘法,得到3张临时卷积图像(第4~6行)。计算完毕后,利用索引加载指令,索引在上一步中计算完毕的临时卷积图像。直到9张临时卷积图像都被索引并累加完毕(第9~11行)。最后,将计算结果写回数据内存(第13行)。
算法2 高斯滤波算法的向量实现。
输入:src_input, W1, W2, W3, src_index1~src_index9。
输出:src_RES。
1. for i = 1 to n do
2. vec_inputi = VLOAD(src_inputi);
3. for j = 1 to 3 do
4. vec_Wj = VMUL(vec_inputi, Wj);
5. vec_Wj = VSHIFT(vec_Wi, 8);
6. src_Wj = VSTORE(vec_Wj);
7. end for
8. for k = 1 to 9 do
9. vec_indexk = VLOAD(src_indexk);
10. vec_RESk = VINDEX(src_W, vec_indexk);
11. vec_RESk = VADD(vec_RESk, vec_RESk);
12. end for
13. src_RES = VSTORE(vec_RES);
14. end for
3. 自定义向量指令
在使用RVV指令对图像预处理算法进行加速时,标准的RVV并不能完全满足算法向量化的要求。例如,索贝尔边缘检测中需要进行阈值判断并置位,这在标准RVV中不被支持。
因此,为实现标准RVV中不支持的功能和进一步对算法进行加速,本文新增了6条自定义向量指令,并通过修改编译器、设计硬件电路的译码和执行模块实现了这6条指令。
3.1 指令定义与结构
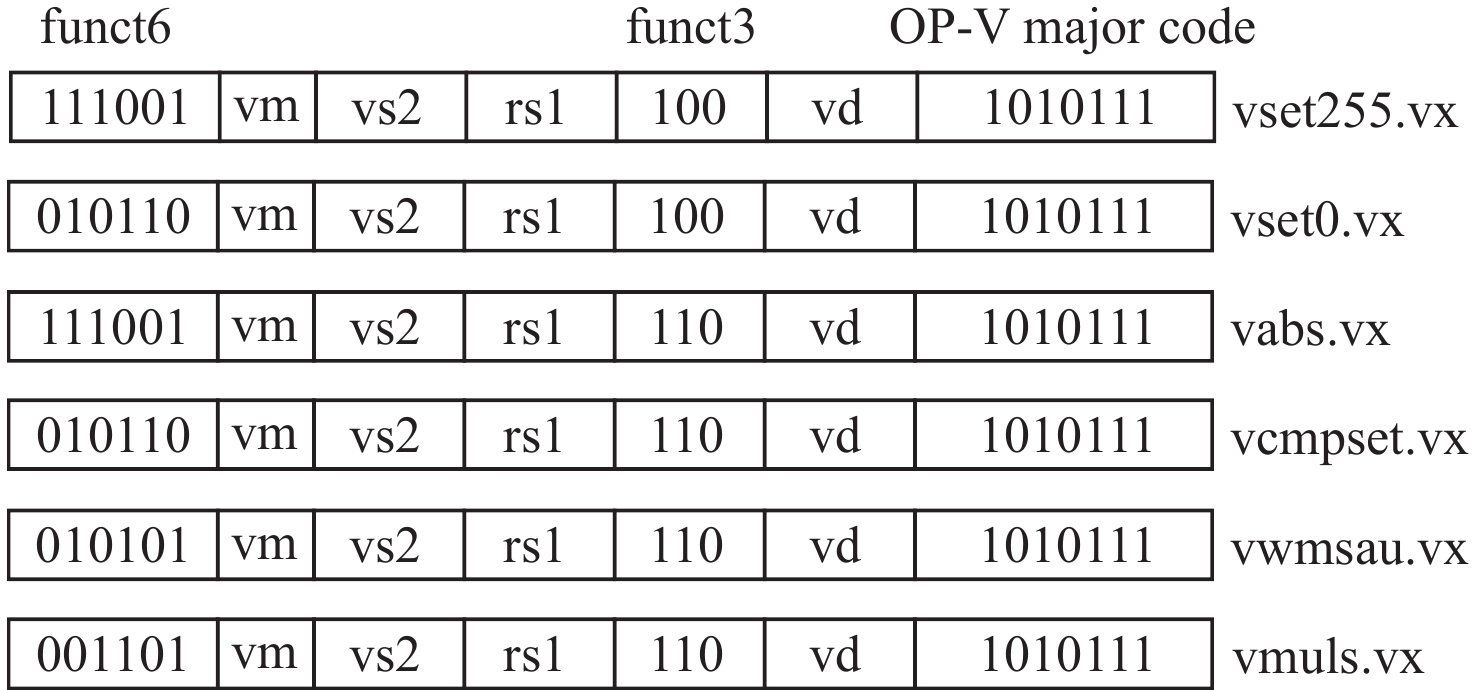
新增的6条自定义向量指令如图6所示。指令的长度为32位,其中,不同的编码段代表的意义不同。OP-V major code表示该指令属于RVV指令;funct6用于和该指令集内的其他指令进行区分。因此,在自定义向量指令时,该编码段不能与已有的标准向量指令重复。考虑到自定义向量指令的需求,RVV1.0预留了一些没有被使用的编码空间。每条指令都有2个操作数,使用funct3来区分2个操作数的类型,其中,funct3 = 110和100分别表示该指令的2个操作数分别为向量和标量;vs2和rs1分别表示向量源寄存器和标量源寄存器的地址,vd表示目的寄存器的地址;vm表示掩码位。
在本文实现的图像预处理算法中,需要扩展指令的操作有:在拉普拉斯滤波和亮度调整算法中,需要判断像素值改变后是否越界(0~255);在索贝尔边缘检测和二值化算法中,需要判断像素值是否大于阈值并进行置位;在索贝尔边缘检测算法中,需要计算数据的绝对值。
针对上述操作,本文新增了4条自定义指令,其逻辑功能如表1所示。vset255和vset0这2条指令能够将越界的数据调整为上限或下限数据;vabs指令判断输入操作数的正负,如果操作数为负则取反,否则返回原值;vcmpset指令先判断2个操作数的大小,如果操作数1大于操作数2,则返回一个置位值,否则返回另一个置位值。
表 1 自定义向量指令功能Table 1. Function of customized vector instructions指令 功能 vset255 vd = vs1 >rs2 ? 255: vs1 vset0 vd = vs1 >rs2 ?vs1:0 vabs vd = vs1 > rs2 ? vs1: −vs1 vcmpset vd = vs1 > rs2 ?255: 0 vwmsau vd = vd + (vs1·rs2 >> 8) vmuls vd = vs1·rs2 >>8 此外,本文使用乘法和移位代替浮点运算,为进一步减少指令调度,提高加速效果,本文将这2步操作进行合并,新增了无符号加宽型向量乘移位累加vwmsau和向量乘移位vmuls,其逻辑功能如表1所示,2条指令的主要区别在于是否累加。
3.2 自定义向量指令的实现
自定义指令的实现分为2部分:对编译器的修改和对处理器本身的修改。
以GNU编译套件(GNU compiler collection, GCC)为例,在修改编译器前,按照RVV指令规范定义向量编码。将自定义的指令变量添加到GCC的二进制工具(RISC-V binutils)中并重新编译,使GCC能够成功识别自定义向量指令并生成对应的机器码。
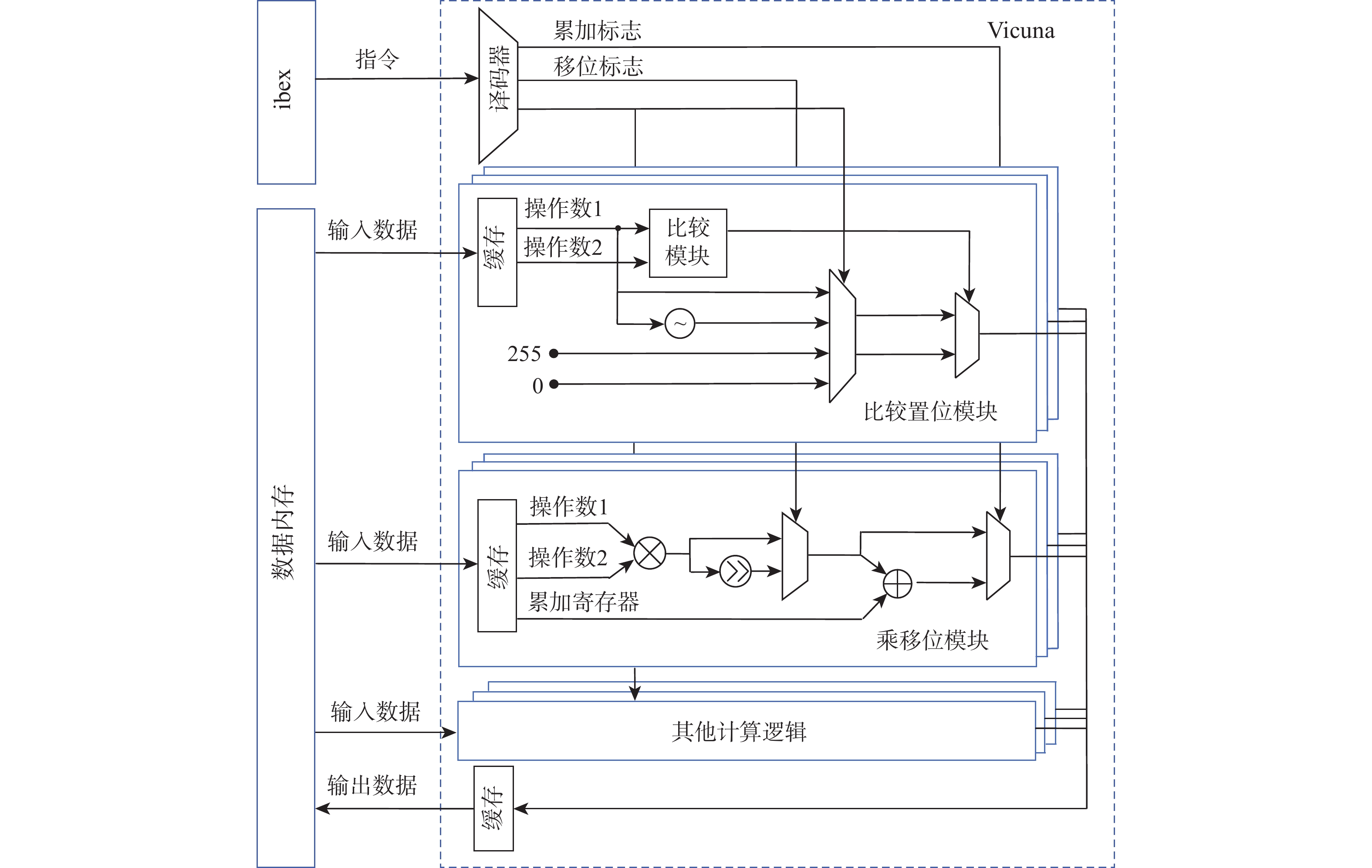
自定义向量指令的硬件实现如图7所示。左侧是标量处理器ibex和数据内存,右侧是向量处理器Vicuna。Vicuna中的比较置位模块实现了vset255、vset0、vabs和vcmpset指令,乘移位模块实现了vwmsau和vmuls指令。
实现自定义向量指令需要先对指令译码器进行修改,译码器根据指令的funct6和funct3编码段来辨别自定义向量指令,按照指令的操作类型生成控制信号及操作数据,并发送到对应的执行模块。
为实现vset255、vset0、vabs和vcmpset指令,本文设计了比较置位模块。数据进入该模块时,会先进入比较置位模块进行大小比较。在该模块中,根据指令的功能定义设置了4种不同的置位值:vs1(操作数1)、−vs1、255和0,根据译码阶段的控制信号及比较置位模块的输出信号,通过两级多路复用器(multiplexer, MUX)选择置位值输出。这4条指令复用了比较置位模块。
为实现vwmsau和vmuls指令,本文设计了乘移位模块。该模块复用了Vicuna原有的乘法模块逻辑,仅增加移位标志、移位器和MUX,以减少资源开销。如果译码模块遇到这2条指令,移位标志就会被置为1。由于没有影响原乘法器的功能,乘移位模块根据不同指令能够实现4种操作,分别为乘法、乘累加、乘移位和乘移位累加。
4. 实验结果与分析
4.1 仿真及实验环境
本文选择riscv32-unknown-elf-gcc v12.0.1作为编译工具,选择Verilator v4.210作为仿真工具来测试自定义模块的功能正确性和图像预处理算法的加速效果。使用Vivado v2019.2进行硬件电路的综合和实现,并部署到Xilinx Artix-7 FPGA 开发板上进行性能验证,评估面积和功耗,工作频率为50 MHz。用于测试的图像数据来自数据集CIFAR-10[20],图像大小为32×32×3。
4.2 不同处理器配置下的性能与资源消耗
本文以周期数为指标评价性能。由于时间=周期数/频率,经评估,本文设计并未影响处理器的关键路径,其依然能按照原有的最大频率工作。因此,周期数的变化能准确反映计算时间的变化。
不同的处理器配置会对性能和面积产生影响。本节就2种参数的配置对图像预处理加速实验结果的影响展开讨论,分别为向量寄存器长度VLEN和向量处理单元位宽PIPE_W。
4.2.1 向量寄存器长度
RISC-V向量处理器设有32个向量寄存器v0~v31,每个向量寄存器的长度为VLEN,单位为bit。RVV中,向量寄存器长度不是固定的,Vicuna的向量寄存器长度可配置的范围为64~
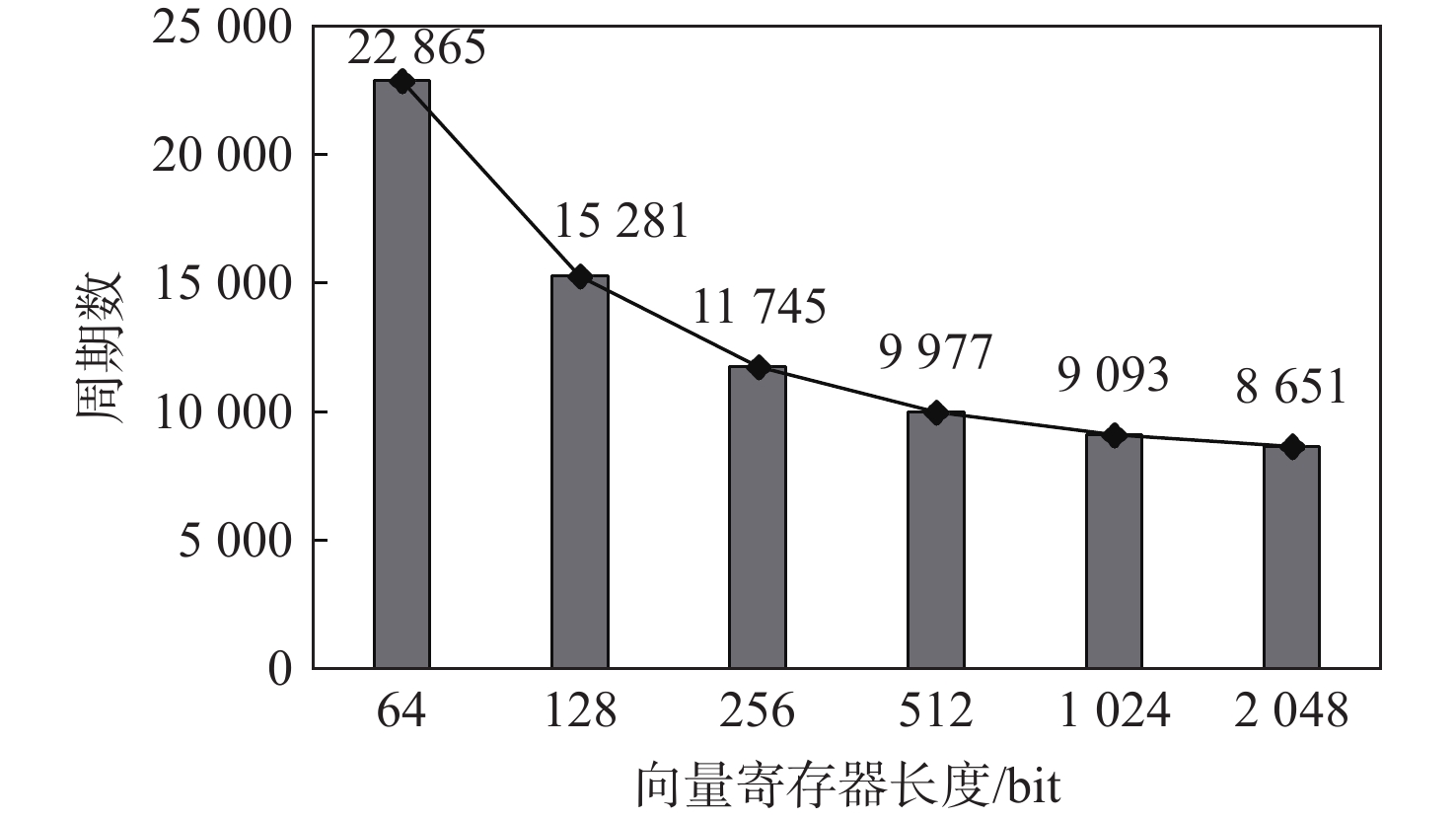
2048 bit。向量寄存器长度可配置是指在硬件电路中,向量寄存器有不同长度的实现,而不是软件层面的配置。图8展示了随向量寄存器长度的变化,单张图像灰度化算法向量实现周期数的变化(向量处理单元位宽固定为32 bit)。可以发现,随着向量寄存器长度增长,算法需要的周期数显著减少,向量寄存器长度从64 bit增加到
1024 bit,周期数减少了60.2%。当向量寄存器长度增大时,单条向量指令(如加载指令、运算指令和存储指令)处理的数据量得到提升。不同向量寄存器长度配置下,FPGA查找表(look up table, LUT)、触发器(flip flop, FF)、块随机存取存储器(block random access memory, BRAM)和数字信号处理单元(digital signal processor, DSP)的消耗量如表2所示。向量寄存器长度的变化不会影响BRAM和DSP的用量,但LUT和FF的消耗会增加。向量寄存器长度的变化对性能和资源消耗均有明显影响,因此,应针对不同的应用环境要求选择合适的向量寄存器长度配置。
表 2 不同向量寄存器长度配置下资源消耗及功耗Table 2. Resource and power consumption under different vector register length configurations向量寄存器长度/bit LUT FF BRAM DSP 功耗/W 64 9880 5976 64 7 0.336 128 10373 6964 64 7 0.346 256 11312 8716 64 7 0.353 512 13262 12168 64 7 0.373 1024 17374 19079 64 7 0.424 2048 41836 33068 64 7 0.533 4.2.2 向量处理单元位宽
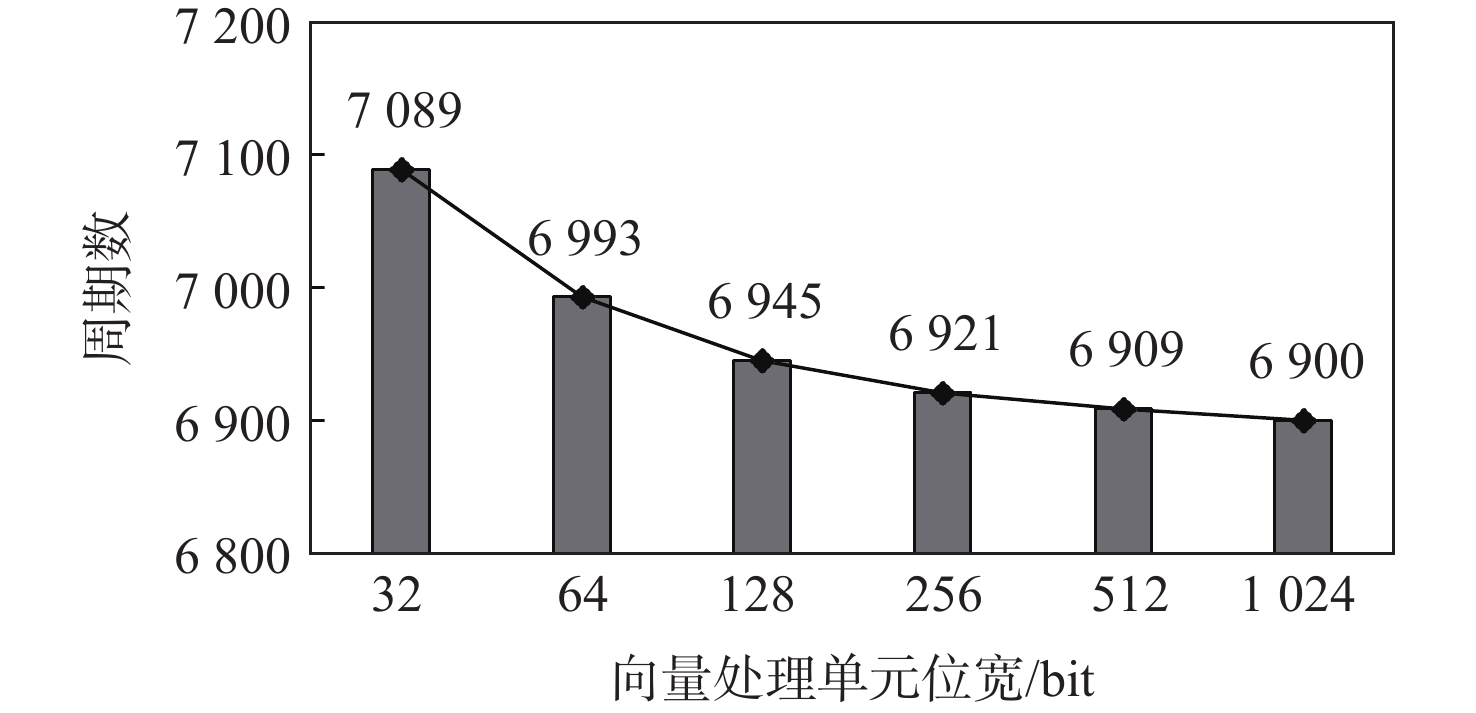
向量处理单元位宽是向量处理单元的位宽,即算术逻辑单元(arithmetic logical unit, ALU)、乘法单元等运算模块能同时处理的数据量,代表了向量处理单元的计算性能。不同向量处理单元位宽对灰度化算法周期数的影响如图9所示。资源消耗如表3所示(向量寄存器长度固定为
2048 bit)。向量处理单元位宽取值范围为32~VLEN/2,单位为bit。表 3 不同向量处理单元位宽配置下资源消耗及功耗Table 3. Resource and power consumption under different vector processing pipe width configurations向量处理单元位宽/bit LUT FF BRAM DSP 功耗/W 32 41386 33068 64 7 0.533 64 42693 33642 64 11 0.539 128 44133 34772 64 19 0.545 256 47470 37058 64 35 0.577 512 52061 41584 64 67 0.607 1024 81279 48705 64 131 0.738 向量处理单元位宽影响了LUT、FF和DSP资源的使用量,但其增加对周期数的影响并不明显。向量处理单元位宽从32 bit提升到512 bit,周期数仅减少了2.5%。由于图像预处理算法是数据密集型的应用,限制算法效率的往往不是向量处理单元的计算性能,而是可用的内存带宽。Vicuna的内存读取端口宽度为32 bit,限制了算法的效率,因此,向量处理单元位宽的变化并不会显著影响性能。此外,只涉及像素位置变化的算法,如旋转、镜像、平移等,不会用到逻辑运算单元,向量处理单元位宽的增加对这些算法的效率没有影响。因此,在图像预处理类应用中,本文选择尽量小的向量处理单元位宽来减少资源消耗。
4.3 加速效果及分析
结合4.2节中对向量处理器关键参数配置的分析,本节的实验结果均基于向量寄存器长度为
2048 bit、向量处理单元位宽为32 bit的处理器配置。以标量处理器ibex的执行周期数为基准,列举了文中方法对各类图像预处理算法的加速效果。使用索引加载指令对像素位置变化类算法进行加速,效果如表4所示。实验结果显示,本文方法对像素位置变化类算法相比标量处理器实现了6.93~9.75倍的加速效果。索引加载指令能够对这类算法实现高效的加速。
表 4 像素位置变化类算法加速效果Table 4. Acceleration results of pixel location change algorithms算法 标量基准周期数 RVV周期数 加速倍数 旋转/镜像 46728 4791 9.75 平移 47439 5679 8.35 缩放 40681 5868 6.93 对像素数值变化类算法进行加速,效果如表5所示。实验结果显示,本文方法对3种像素数值变化类算法相比标量处理器实现了6.69~9.97倍的加速。标准向量扩展仅对灰度化算法有较好的加速效果,对二值化和亮度调整算法没有明显的加速效果。其中,二值化算法无法使用标准向量扩展指令加速,因此,其周期数与标量基准一致;由于标准向量指令集不支持亮度调整算法中的比较置位运算,这部分运算需要在标量处理器上执行,额外的标量处理器读写和运算操作导致加速效果被严重稀释。
表 5 像素数值变化类算法加速效果Table 5. Acceleration results of pixel value change algorithms算法 标量基准
周期数标准RVV
周期数标准RVV
加速倍数自定义RVV
周期数自定义RVV
加速倍数灰度化 60488 10786 5.61 8651 6.99 二值化 42576 42576 1.00 4272 9.97 亮度调整 116627 80730 1.44 17422 6.69 高效的自定义RVV指令实现了标准RVV指令集不支持的功能,解决了加速效果被标量处理器稀释的问题,使得二值化和亮度调整算法的效率大幅提升。合并乘法与移位的扩展指令也使得灰度化算法得到进一步的加速。
求全局平均值类算法为标准化算法。本文使用规约求和指令对这类算法进行加速,效果如表6所示。实验结果显示,本文方法对求全局平均值类算法实现了7.52倍的加速效果。
表 6 求全局平均值类算法加速效果Table 6. Acceleration results of global average computation algorithms算法 标量基准周期数 RVV周期数 加速倍数 标准化 65620 8724 7.52 卷积类算法包括高斯滤波、拉普拉斯滤波和索贝尔边缘检测,应用本文提出的卷积加速方案对这类算法进行加速,结果如表7所示。实验结果显示,本文方法对3种卷积类算法相比标量处理器实现了3.13~4.26倍的加速。应用本文提出的卷积加速方案,在使用标准RVV指令时,能取得一定的加速效果,但仍存在加速效果被稀释的现象。而结合卷积加速方案和自定义RVV指令能够解决这一问题,运算效率得到进一步提升。
表 7 卷积类算法加速效果Table 7. Acceleration results of convolution algorithms算法 标量基准
周期数标准RVV
周期数标准RVV
加速倍数自定义RVV
周期数自定义RVV
加速倍数高斯滤波 268604 66178 4.06 63037 4.26 拉普拉斯滤波 214456 105235 2.04 57650 3.72 索贝尔边缘检测 214783 197202 1.09 68542 3.13 4.4 CNN应用中的资源消耗与功耗
以文献[21]中的MobileNet加速器为例,预估本文硬件平台在实际CNN加速应用中的资源消耗,如表8所示。Vicuna的配置为:向量寄存器长度为
2048 bit,向量处理单元位宽为32 bit。应用于CPU+CNN加速器的深度学习平台中,向量处理器导致的资源消耗增长仅约10%,自定义指令导致的额外硬件资源开销小于0.1%。表 8 资源消耗及功耗Table 8. Resource and power consumption硬件架构 LUT FF BRAM DSP 功耗/W ibex+CNN 310840 279836 957 2161 11.65 ibex+Vicuna+CNN 349618 311699 1005 2168 11.88 ibex+自定义Vicuna+CNN 349835 311964 1005 2168 11.88 4.5 在CNN中的应用实例
本节选取嵌入式图像分类应用[9]和车牌识别应用为例,预估本文方法在深度学习应用场景中的效果。
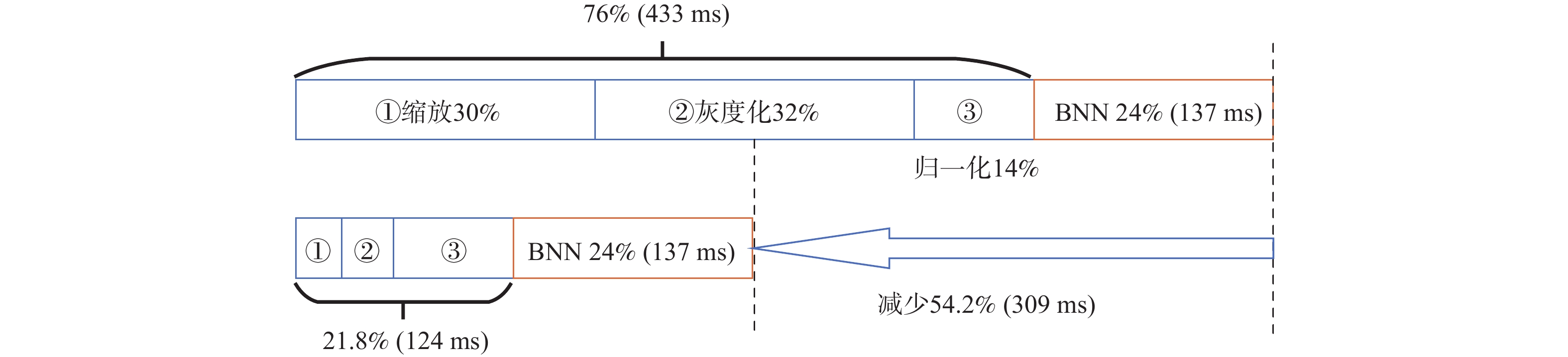
如图10所示,在图像分类应用中,CPU预处理阶段先进行图像的缩放、灰度化和归一化,再由二值神经网络(binary neural network, BNN)加速器进行推理分类。整个计算过程中,加速器占用时间为24%(137 ms),CPU图像预处理占用时间为76%(433 ms),其中,缩放占用30%(171 ms),灰度化占用32%(182 ms),归一化占用14%(80 ms)。应用本文方法,CPU图像预处理的占用时间大幅缩短,整体计算时间相比原来减少54.2%(309 ms)。
如图11所示,在车牌识别应用中,预处理阶段进行灰度化、高斯滤波和索贝尔边缘检测,再由3层的反向传播神经网络(back propagation neural network, BPN)进行识别。BPN占用时间为28%(70 ms),CPU图像预处理占用时间为72%(181 ms),其中,灰度化占用8%(20 ms),高斯滤波占用36%(91 ms),索贝尔边缘检测占用28%(70 ms),应用本文方法,整体计算时间相比原来减少53.4%(134 ms),有效解决了CPU图像预处理在CNN计算中的性能瓶颈问题。
5. 结 论
1) 针对11种常见的图像预处理算法,按照算法特点分为4类,并针对每种分类设计了基于RISC-V向量扩展的加速方案。
2) 为解决标准向量扩展不能满足图像预处理加速需求的问题,自定义了4条向量指令;为进一步提高算法运算效率,自定义了2条向量指令以合并乘法与移位运算。通过设计RISC-V处理器微架构实现了这6条指令。
3) 实验结果表明,本文提出的方案与标量处理器相比实现了3.13~9.97倍的加速效果。在2种实际应用中,预估能减少50%左右的整体计算时间,可有效解决CPU图像预处理在CNN整体计算中的性能瓶颈问题。
-
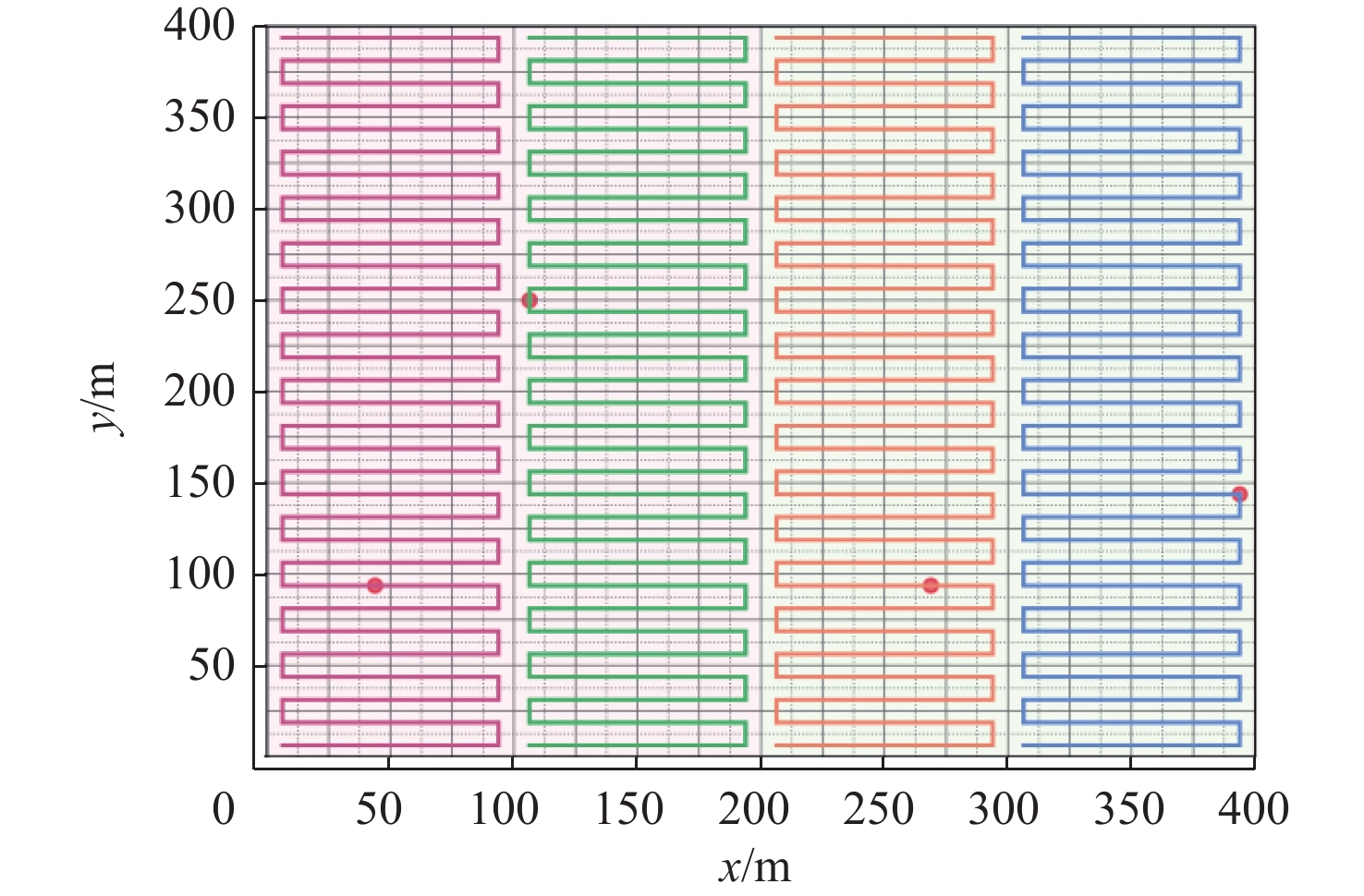
表 1 环境参数
Table 1. 1Environmental parameters
参数 数值 U2U智能体数目k/个 4 带宽W/MHz 4 载频fc/GHz 2 基站天线高度/m 25 无人机高度/m 100 无人机速度/(m·s−1) [16,20] 传输时延T/ms 100 传输负载L/Byte 2×1 060 U2U传输功率等级/dBm [23,10,5,−100] U2I传输功率/dBm 23 覆盖区域大小/(m×m) 400×400 表 2 DDQN网络参数
Table 2. 2Parameters of the DDQN network
参数 数值 全连接层数/层 3 每层神经元个数/个 [500,250,120] 最小贪婪系数ε 0.02 折扣率δ 1.0 训练轮数emax/轮 3 000 每轮训练步数N/步 100 记忆库容量/条 200 000 采样大小B/条 100 更新目标值网络步数c/步 400 -
[1] HANSCOM A F B, BEDFORD M A. Unmanned aircraft system (UAS) service demand 2015-2035: Literature review & projections of future usage[R]. Washington: Department of Transportation, 2013. [2] 李艳庆. 基于遗传算法和深度强化学习的多无人机协同区域监视的航路规划[D]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学, 2018.LI Y Q. Cooperative path planning for region surveillance of multi-UAV based on genetic algorithm and deep reinforcement learning[D]. Xi’an: Xidian University, 2018(in Chinese). [3] 赵林, 张宇飞, 姚明旿, 等. 无人机集群协同技术发展与展望[J]. 无线电工程, 2021, 51(8): 823-828. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3106.2021.08.023ZHAO L, ZHANG Y F, YAO M W, et al. Development and trend of UAV swarm cooperative techniques[J]. Radio Engineering, 2021, 51(8): 823-828(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3106.2021.08.023 [4] 刘立辉, 赵彦杰, 赵小虎, 等. 一种无人集群系统仿真平台设计[J]. 中国电子科学研究院学报, 2017, 12(5): 506-512. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5692.2017.05.013LIU L H, ZHAO Y J, ZHAO X H, et al. Design of a simulation platform of unmanned swarm system[J]. Journal of China Academy of Electronics and Information Technology, 2017, 12(5): 506-512(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5692.2017.05.013 [5] BUCAILLE I, HÉTHUIN S, MUNARI A, et al. Rapidly deployable network for tactical applications: aerial base station with opportunistic links for unattended and temporary events ABSOLUTE example[C]//2013 IEEE Military Communications Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2013: 1116-1120. [6] XIAO Z Y, XIA P F, XIA X G. Enabling UAV cellular with millimeter-wave communication: potentials and approaches[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2016, 54(5): 66-73. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2016.7470937 [7] JIANG B, YANG J C, XU H F, et al. Multimedia data throughput maximization in internet-of-things system based on optimization of cache-enabled UAV[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(2): 3525-3532. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2886964 [8] MARDANI A, CHIABERGE M, GIACCONE P. Communication-aware UAV path planning[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 52609-52621. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2911018 [9] ZHAN C, HU H, SUI X F, et al. Joint resource allocation and 3D aerial trajectory design for video streaming in UAV communication systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2021, 31(8): 3227-3241. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2020.3035618 [10] 胡欣颖. 面向信息采集场景的无人机轨迹规划与通信资源分配研究[D]. 北京: 北京邮电大学, 2021: 8-19.HU X Y. Trajectory design and resource allocation of uav for data collection in WSNs[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2021: 8-19(in Chinese). [11] MANZOOR A, KIM D H, HONG C S. Energy efficient resource allocation in UAV-based heterogeneous networks[C]// 2019 20th Asia-Pacific Network Operations and Management Symposium. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 1-4. [12] ZENG F Z, HU Z Z, XIAO Z, et al. Resource allocation and trajectory optimization for QoE provisioning in energy-efficient UAV-enabled wireless networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(7): 7634-7647. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.2986776 [13] LU W D, SI P Y, HUANG G X, et al. Interference reducing and resource allocation in UAV-powered wireless communication system[C]// 2020 International Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 220-224. [14] 陶丽佳, 赵宜升, 徐新雅. 无人机协助边缘计算的能量收集MEC系统资源分配策略[J]. 南京邮电大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 42(1): 37-44.TAO L J, ZHAO Y S, XU X Y. Resource allocation strategy for UAV-assisted edge computing in energy harvesting MEC system[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 42(1): 37-44(in Chinese). [15] QIN X T, SONG Z Y, HAO Y Y, et al. Joint resource allocation and trajectory optimization for multi-UAV-assisted multi-access mobile edge computing[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2021, 10(7): 1400-1404. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2021.3068793 [16] 龚广伟, 谢添, 赵海涛, 等. 基于图着色的大规模无人机群三维网络资源分配算法[J]. 信号处理, 2022, 38(8): 1693-1702.GONG G W, XIE T, ZHAO H T, et al. A three-dimension resources allocation algorithm for large-scale UAV network based on graph coloring[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2022, 38(8): 1693-1702(in Chinese). [17] 吴启晖, 陈佳馨, 吴盛君, 等. 一种基于动态航迹的无人机群频谱资源分配方法: CN108632831A[P]. 2021-08-10.WU Q H, CHEN J X, WU S J, et al. A dynamic trajectory-based spectrum resource allocation method for UAV swarms: CN108632831A[P]. 2021-08-10(in Chinese). [18] CHEN M Z, SAAD W, YIN C C. Liquid state machine learning for resource allocation in a network of cache-enabled LTE-U UAVs[C]//2017 IEEE Global Communications Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1-6. [19] CHEN J X, WU Q H, XU Y H, et al. Distributed demand-aware channel-slot selection for multi-UAV networks: a game-theoretic learning approach[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 14799-14811. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2811372 [20] ZHANG X C, ZHAO H T, XIONG J, et al. Scalable power control/beamforming in heterogeneous wireless networks with graph neural networks[C]// 2021 IEEE Global Communications Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 1-6. [21] 贺颖. 基于深度强化学习的无线网络多维资源分配技术研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2018.HE Y. Research on multi-dimensional resource allocation of wireless networks based on deep reinforcement learning[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2018(in Chinese). [22] ZHANG Q Q, MOZAFFARI M, SAAD W, et al. Machine learning for predictive on-demand deployment of uavs for wireless communications[C]// 2018 IEEE Global Communications Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 1-6. [23] SUN N, WU J X. Minimum error transmissions with imperfect channel information in high mobility systems[C]//2013 IEEE Military Communications Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2013: 922-927. [24] CHUA M Y K, YU F R, LI J, et al. Medium access control for unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) ad-hoc networks with full-duplex radios and multipacket reception capability[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2013, 62(1): 390-394. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2012.2211905 [25] 任博, 刘圣宇, 崔连柱, 等. 多无人机侦察航路规划[C]// 2014(第五届)中国无人机大会论文集. 北京: 航空工业出版社, 2014: 793-797.REN B, LIU S Y, CUI L Z, et al. Multi-UAV reconnaissance route planning[C]//Proceedings of China Drone Conference. Beijing: Aviation Industry Press, 2014: 793-797(in Chinese). [26] ACEVEDO J J, ARRUE B C, MAZA I, et al. Distributed cooperation of multiple UAVs for area monitoring missions[M]//CARBONE G, GOMEZ-BRAVO F. Motion and Operation Planning of Robotic Systems. Cham: Springer, 2015: 471-494. [27] 张睿文, 宋笔锋, 裴扬, 等. 复杂任务场景无人机集群自组织侦察建模与仿真[J]. 航空工程进展, 2020, 11(3): 316-325,343.ZHANG R W, SONG B F, PEI Y, et al. Modelling and simulation of UAV swarm self-organized surveillance in complex mission scenarios[J]. Advances in Aeronautical Science and Engineering, 2020, 11(3): 316-325,343(in Chinese). [28] HAZON N, KAMINKA G A. On redundancy, efficiency, and robustness in coverage for multiple robots[J]. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2008, 56(12): 1102-1114. doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2008.01.006 [29] GABRIELY Y, RIMON E. Spanning-tree based coverage of continuous areas by a mobile robot[C]// Proceedings 2001 ICRA. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2001: 1927-1933. [30] 3GPP. Study on enhanced LTE support for aerial vehicles: TR 36.777[S]. Nice, France: ETSI, 2017. [31] 3GPP. 5G; Study on channel model for frequencies from 0.5 to 100 GHz: TR 38.901[S]. Nice, France: ETSI, 2020. [32] 3GPP. 5G; Unmanned aerial system (UAS) support in 3GPP: TS 22.125[S]. Nice, France: ETSI, 2020. [33] RICE M, DYE R, WELLING K. Narrowband channel model for aeronautical telemetry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2000, 36(4): 1371-1376. doi: 10.1109/7.892684 [34] GODDEMEIER N, WIETFELD C. Investigation of air-to-air channel characteristics and a UAV specific extension to the rice model[C]// 2015 IEEE Globecom Workshops. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 1-5. [35] AHMED N, KANHERE S S, JHA S. On the importance of link characterization for aerial wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2016, 54(5): 52-57. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2016.7470935 [36] ABUALHAOL I Y, MATALGAH M M. Performance analysis of multi-carrier relay-based UAV network over fading channels[C]// 2010 IEEE Globecom Workshops. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2010: 1811-1815. [37] GODDEMEIER N, ROHDE S, WIETFELD C. Experimental validation of RSS driven UAV mobility behaviors in IEEE 802.11s networks[C]// 2012 IEEE Globecom Workshops. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2012: 1550-1555. [38] NOWÉ A, VRANCX P, DE HAUWERE Y M. Game theory and multi-agent reinforcement learning[M]// WIERING M, VAN OTTERLO M. Reinforcement Learning. Berlin: Springer, 2012: 441-470. [39] NEYMAN A. From Markov chains to stochastic games[M]// Stochastic Games and Applications. Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands, 2003: 9-25. [40] SUTTON R S, BARTO A G. Reinforcement learning: an introduction[M]. Cambridge: MIT Press, 1998. [41] TAMPUU A, MATIISEN T, KODELJA D, et al. Multiagent cooperation and competition with deep reinforcement learning[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(4): e0172395. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172395 -








 下载:
下载:










 下载:
下载: