-
摘要:
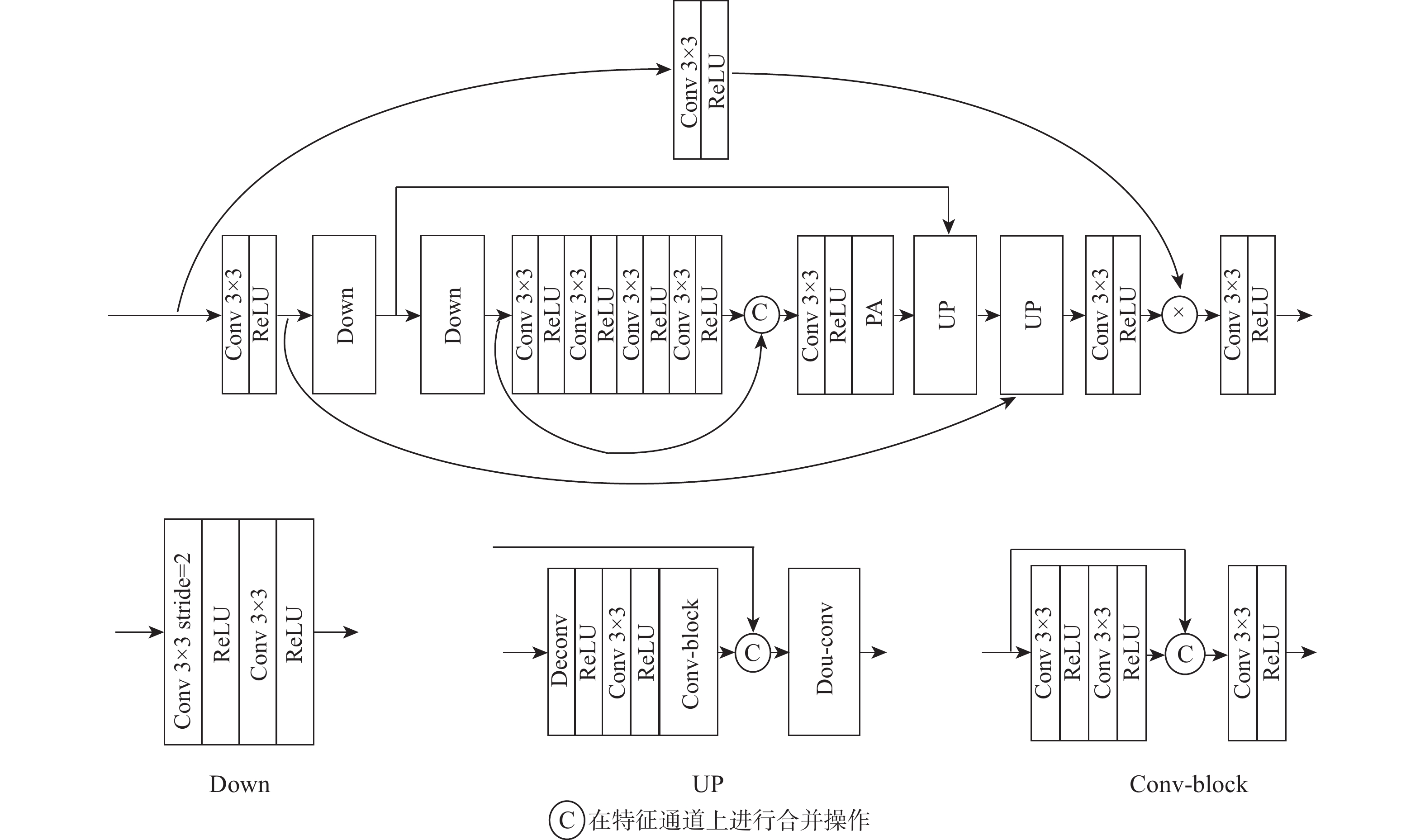
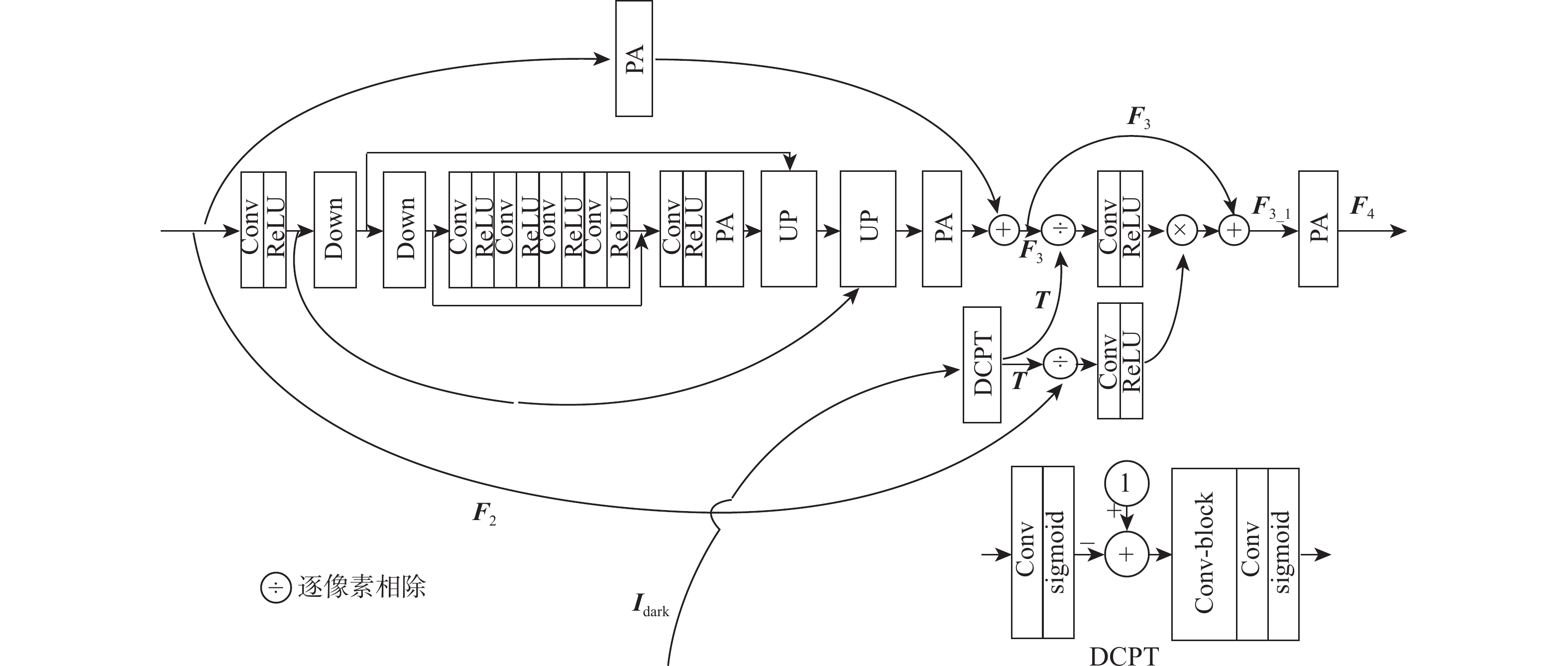
基于深度学习的去雾方法多数直接学习有雾图像和无雾图像之间的映射关系,未结合有雾图像自身特点,存在雾信息检测不精确、去雾不彻底的问题。针对该问题,提出一种基于暗通道先验引导的图像去雾网络(DCPDNet)。通过卷积层提取有雾图像的浅层特征;构建2个特征增强模块(FEB)来增强图像的空间特征,该模块在2个尺度上对图像特征进行增强,即利用深层特征图实现语义特征的增强,浅层特征图对实现图像细节特征的增强;为使提取的特征更关注雾的区域,基于有雾图像中雾的成像特点设计基于引导图的特征校正模块(FCB),利用暗通道先验理论构建引导图将网络学习的注意力引导到有雾区域,对提取的深层特征图做进一步的细化和校正;利用残差结构的跳转连接,将增强的浅层特征补充网络丢失的细节特征,并经过卷积操作重建去雾后图像。实验结果证明:DCPDNet可以在保持模型轻量型及运行速度较快的情况下实现良好的去雾效果。与近年先进的去雾方法进行比较,DCPDNet不仅在效率上占有优势,其去雾效果在主观视觉感受和客观评价结果上都获得了更好的效果。
Abstract:Currently, the majority of dehazing techniques that utilize deep learning focus on directly acquiring the mapping relationship between a foggy image and a non-fog image.Because of the lack of combination with the characteristics of fog images, there are problems such as inaccurate detection of fog information and incomplete dehazing. In order to address the aforementioned issues, this study introduces a novel approach called the dark channel prior-guided image dehazing network (DCPDNet), which operates in an end-to-end manner. First, the shallow features of the input foggy image are extracted by several convolution layers. Secondly, two feature enhancement blocks (FEB) are constructed to enhance the spatial features of the image, which can enhance the image features on two scales, that is, the deep feature map is used to enhance the semantic features, and the shallow feature map is used to enhance the image details. Thirdly, in order to make the extracted features pay more attention to the fog area, a feature correction block (FCB) based on the guidance map is designed by considering the imaging characteristics of fog in the fog image. The FCB uses the dark channel theory to build a guidance map to guide the attention of network learning to the fog area, and further refine and correct the extracted deep feature map. Finally, by using the skip connection of the residual structure, the enhanced shallow features are used to supplement the details lost in the network, and the image after dehazing is reconstructed through several convolution operations. Multiple trials have demonstrated that DCPDNet is capable of achieving a satisfactory dehazing effect while maintaining a lightweight model and quick execution. Compared with some advanced dehazing methods proposed in recent years, DCPDNet has better performance in terms of efficiency, subjective visual perception and objective evaluation results.
-
Key words:
- image dehazing /
- dark channel prior /
- guidance map /
- residual learning /
- feature enhancement
-
表 1 SOTS室外数据集测试结果
Table 1. Test results of SOTS outdoor dataset
表 2 HSTS数据集测试结果
Table 2. Test results of HSTS dataset
表 3 SOTS室内数据集测试结果
Table 3. Test results of SOTS indoor dataset
表 4 平均运行时间对比
Table 4. Average runtime comparison
表 5 模型大小对比
Table 5. Comparison of model size
表 6 消融实验
Table 6. Ablation experiments
Baseline FEB FCB SSIM PSNR √ × × 0.9579 27.17 √ √ × 0.9673 29.24 √ × √ 0.9731 29.63 √ √ √ 0.9749 31.06 -
[1] SALAZAR-COLORES S, CABAL-YEPEZ E, RAMOS-ARREGUIN J M, et al. A fast image dehazing algorithm using morphological reconstruction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(5): 2357-2366. [2] HE K M, SUN J, TANG X O. Single image haze removal using dark channel prior[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2011, 33(12): 2341-2353. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2010.168 [3] GAO Y Y, HU H M, LI B, et al. Detail preserved single image dehazing algorithm based on airlight refinement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2019, 21(2): 351-362. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2018.2856095 [4] WANG W C, YUAN X H, WU X J, et al. Fast image dehazing method based on linear transformation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2017, 19(6): 1142-1155. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2017.2652069 [5] ZHU M Z, HE B W, WU Q. Single image dehazing based on dark channel prior and energy minimization[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2018, 25(2): 174-178. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2017.2780886 [6] LIU Q, GAO X B, HE L H, et al. Single image dehazing with depth-aware non-local total variation regularization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(10): 5178-5191. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2849928 [7] YANG Y, WANG Z W. Haze removal: Push DCP at the edge[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2020, 27: 1405-1409. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2020.3013741 [8] YEH C H, HUANG C H, KANG L W. Multi-scale deep residual learning-based single image haze removal via image decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 3153-3167. [9] CHEN W T, DING J J, KUO S Y. PMS-Net: Robust haze removal based on patch map for single images[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 11681-11689. [10] LI B Y, PENG X L, WANG Z Y, et al. AOD-Net: All-in-one dehazing network[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 4770-4778. [11] MEI K F, JIANG A W, LI J C, et al. Progressive feature fusion network for realistic image dehazing[C]//Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 203-215. [12] WANG A N, WANG W H, LIU J L, et al. AIPNet: Image-to-image single image dehazing with atmospheric illumination prior[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 28(1): 381-393. [13] SONG Y F, LI J, WANG X G, et al. Single image dehazing using ranking convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2018, 20(6): 1548-1560. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2017.2771472 [14] ZHENG Z R, REN W Q, CAO X C, et al. Ultra-high-definition image dehazing via multi-guided bilateral learning[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 16180-16189. [15] CHEN T Y, FU J H, JIANG W T, et al. SRKTDN: Applying super resolution method to dehazing task[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2021: 487-496. [16] LI Y N, LIU Y H, YAN Q X, et al. Deep dehazing network with latent ensembling architecture and adversarial learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 1354-1368. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.3044208 [17] KIM G, PARK S W, KWON J. Pixel-wise Wasserstein autoencoder for highly generative dehazing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 5452-5462. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3084743 [18] QIN X, WANG Z L, BAI Y C, et al. FFA-Net: Feature fusion attention network for single image dehazing[C]//Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Palo Alto: AAAI, 2020, 34(7): 11908-11915. [19] LU Z W, LONG B Y, YANG S Q. Saturation based iterative approach for single image dehazing[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2020, 27: 665-669. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2020.2985570 [20] JOHNSON J, ALAHI A, LIF F. Perceptual losses for real-time style transfer and super-resolution[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 694-711. [21] LI B Y, REN W Q, FU D P, et al. Benchmarking single-image dehazing and beyond[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 28(1): 492-505. [22] MENG G F, WANG Y, DUAN J Y, et al. Efficient image dehazing with boundary constraint and contextual regularization[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2013: 617-624. [23] BERMAN D, TREIBITZ T, AVIDAN S. Non-local image dehazing[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 1674-1682. [24] QU Y Y, CHEN Y Z, HUANG J Y, et al. Enhanced pix2pix dehazing network[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 8160-8168. [25] ULLAH H, MUHAMMAD K, IRFAN M, et al. Light-DehazeNet: Anovel lightweight CNN architecture for single image dehazing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 8968-8982. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3116790 [26] ZHAO S Y, ZHANG L, SHEN Y, et al. RefineDNet: A weakly supervised refinement framework for single image dehazing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 3391-3404. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3060873 -







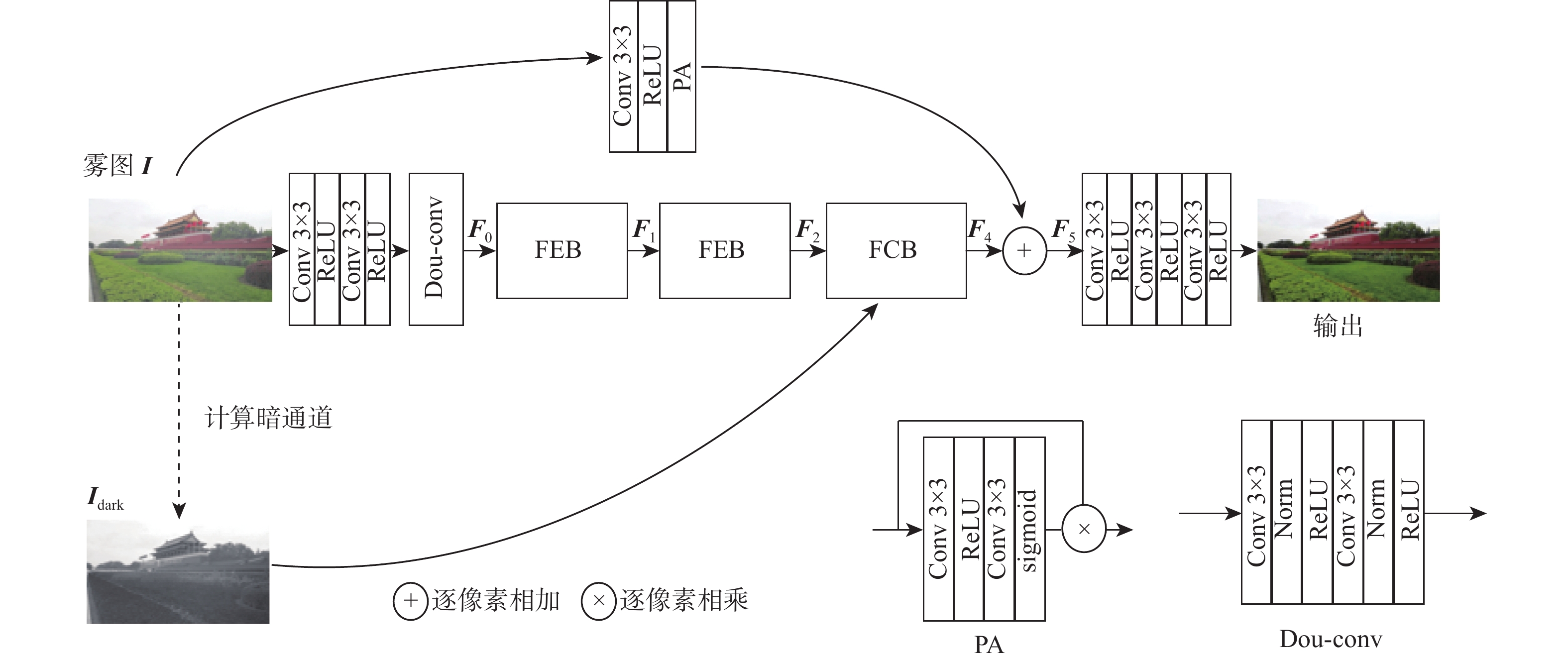
 下载:
下载: