LEO satellite positioning method and simulation verification aided by airborne navigation equipment
-
摘要:
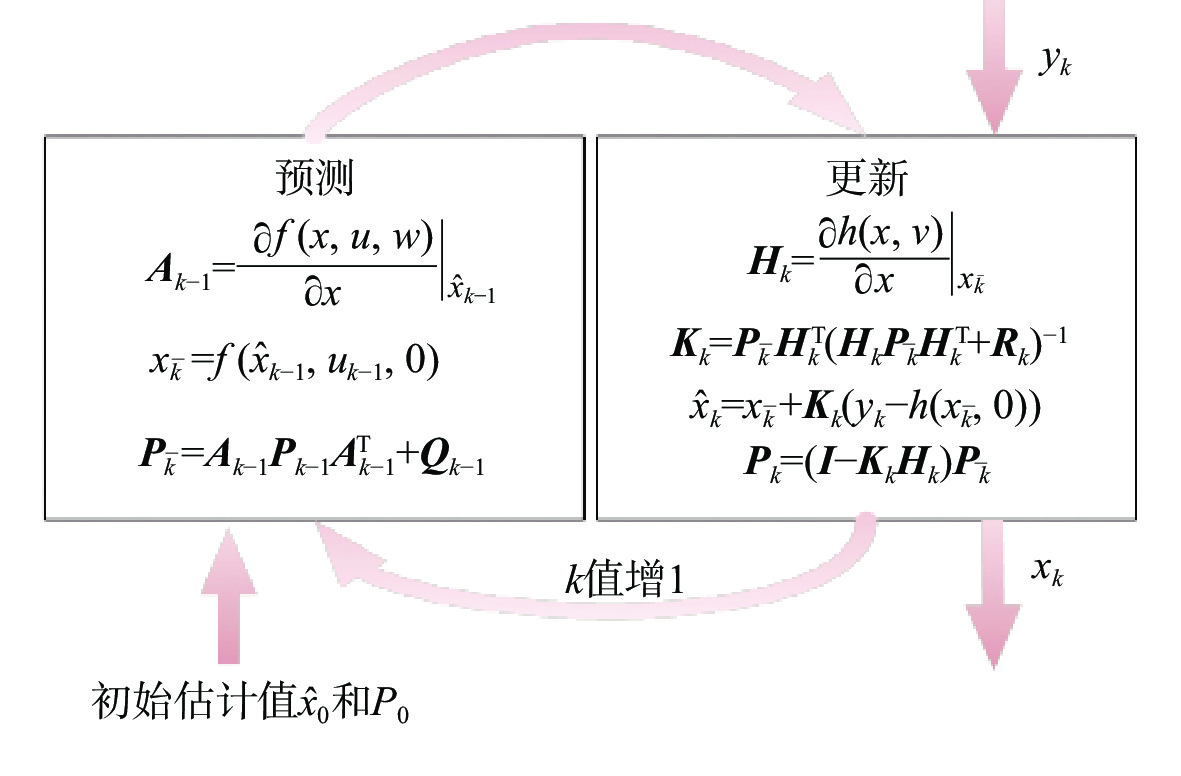
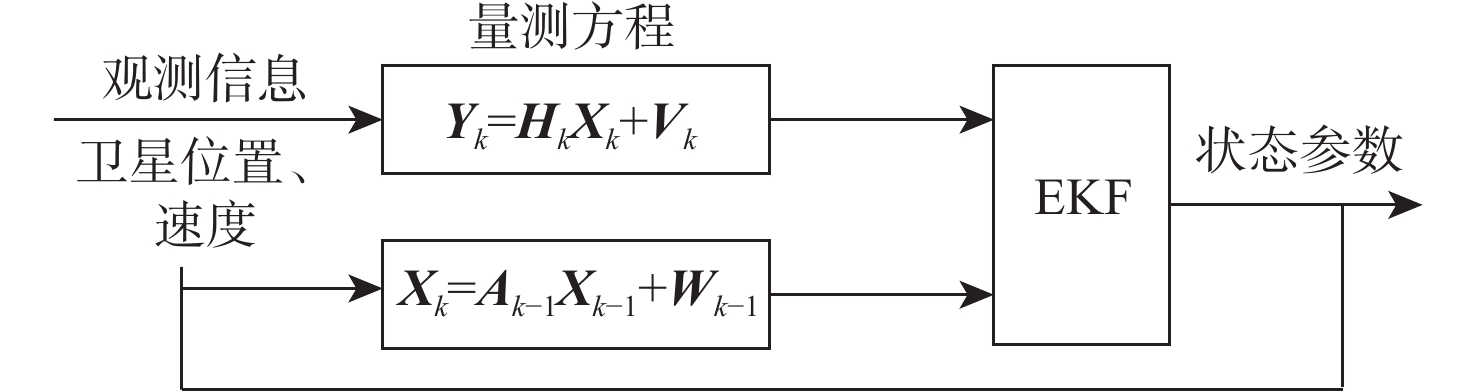
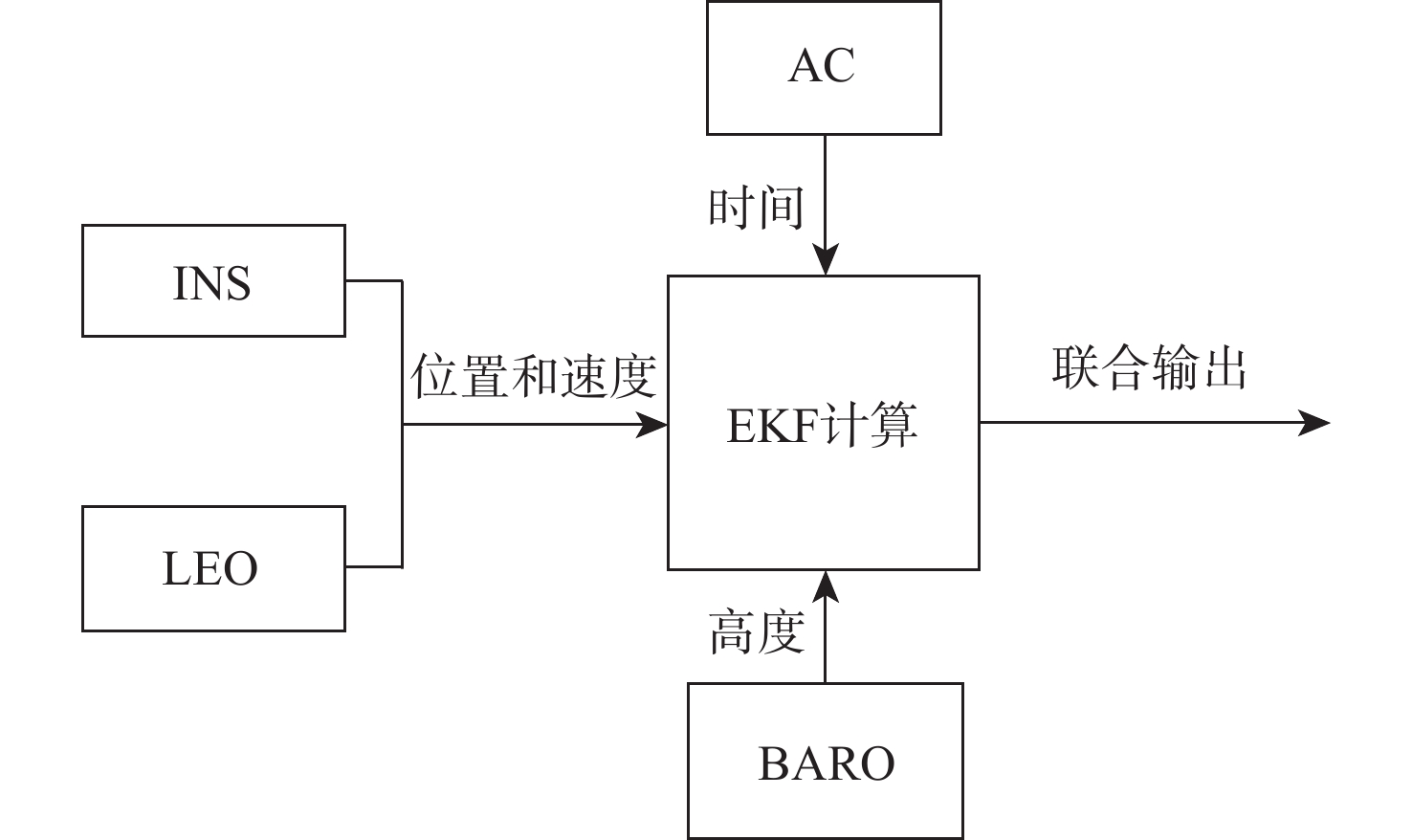
复杂电磁环境下全球导航卫星系统(GNSS)容易被欺骗和干扰导致不可使用,而近地轨道(LEO)通导一体化卫星系统具有落地功率高和星座几何形状变化快的优势,是一种很好的应急备份导航源。但大多数LEO卫星系统在中低纬度地区可见卫星的数量仅有1~2颗,无法实现实时动态定位。因此,提出一种基于机载惯性导航系统(INS)、气压计辅助的组合定位算法,将INS、气压计当作伪卫星使用,通过配置原子钟联合来解决可观性不足的问题。所提算法利用LEO卫星观测数据修正INS的误差,同时针对可观性不能定量分析的问题提出一种衡量滤波器稳定的可估计性指标。仿真验证表明:所提算法利用LEO观测数据在9 min内将INS误差降低了60%左右,定位误差达到50 m以下,能够实现实时、稳定定位,提出的可估计性指标也能够衡量系统的稳定性。
Abstract:Global navigation satellite system (GNSS) is easy to be deceived and jammed in a complex electromagnetic environment, while the low earth orbit (LEO) integrated communication and navigation satellite system has the advantages of high landing power and rapid constellation geometry changes, and it is a good emergency backup navigation source. However, most of the LEO satellite systems only have 1–2 satellites visible in the middle and low latitudes, which fail to realize real-time dynamic positioning. Therefore, a combined positioning algorithm based on airborne inertial navigation system (INS) and barometer assistance was proposed. The INS and barometer were used as pseudolites, and the problem of insufficient observability was solved by configuring atomic clocks. The algorithm used the LEO satellite observation data to correct the error of the INS. At the same time, an estimability index was proposed to measure the stability of the filter for solving the problem that the observability cannot be quantitatively analyzed. The simulation verification shows that the algorithm uses the LEO observation data to reduce the INS error by about 60% within nine minutes, and the positioning error can reach up to 50 meters, realizing real-time stable positioning. The proposed estimability index can measure the stability of the system.
-
表 1 陀螺仪、加速度计精度
Table 1. Accuracy of gyroscope and accelerometer
激光陀螺NV-G300/((°)·s−1) 加速度计/(m·s−2) 3.0×10 −6 9.8×10 −6 表 2 INS初始对准误差
Table 2. Initial alignment error of INS
经度
误差/(′)纬度
误差/(′)高度
误差/m东向速度
误差/(m·s−1)北向速度
误差/(m·s−1)天向速度
误差/(m·s−1)0.1 0.1 10 0.1 0.1 0.1 表 3 滤波器过程噪声方差
Table 3. Noise variance of filter process m2
σ2x σ2y σ2z σ2δt 10−4 10−4 10−4 10−9 表 4 滤波器观测噪声方差
Table 4. Observed noise variance of filter
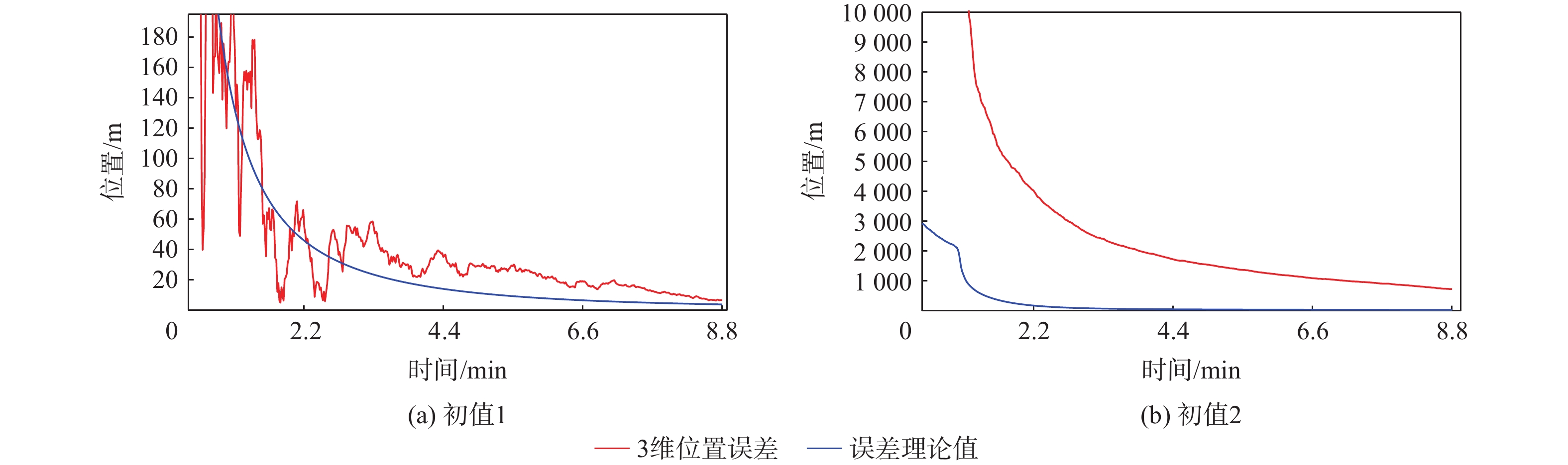
σ2ρ/ m2 σ2f/Hz2 16 0.04 表 5 不同初值LEO卫星定位误差统计
Table 5. Statistics of positioning errors of LEO satellites with different initial values
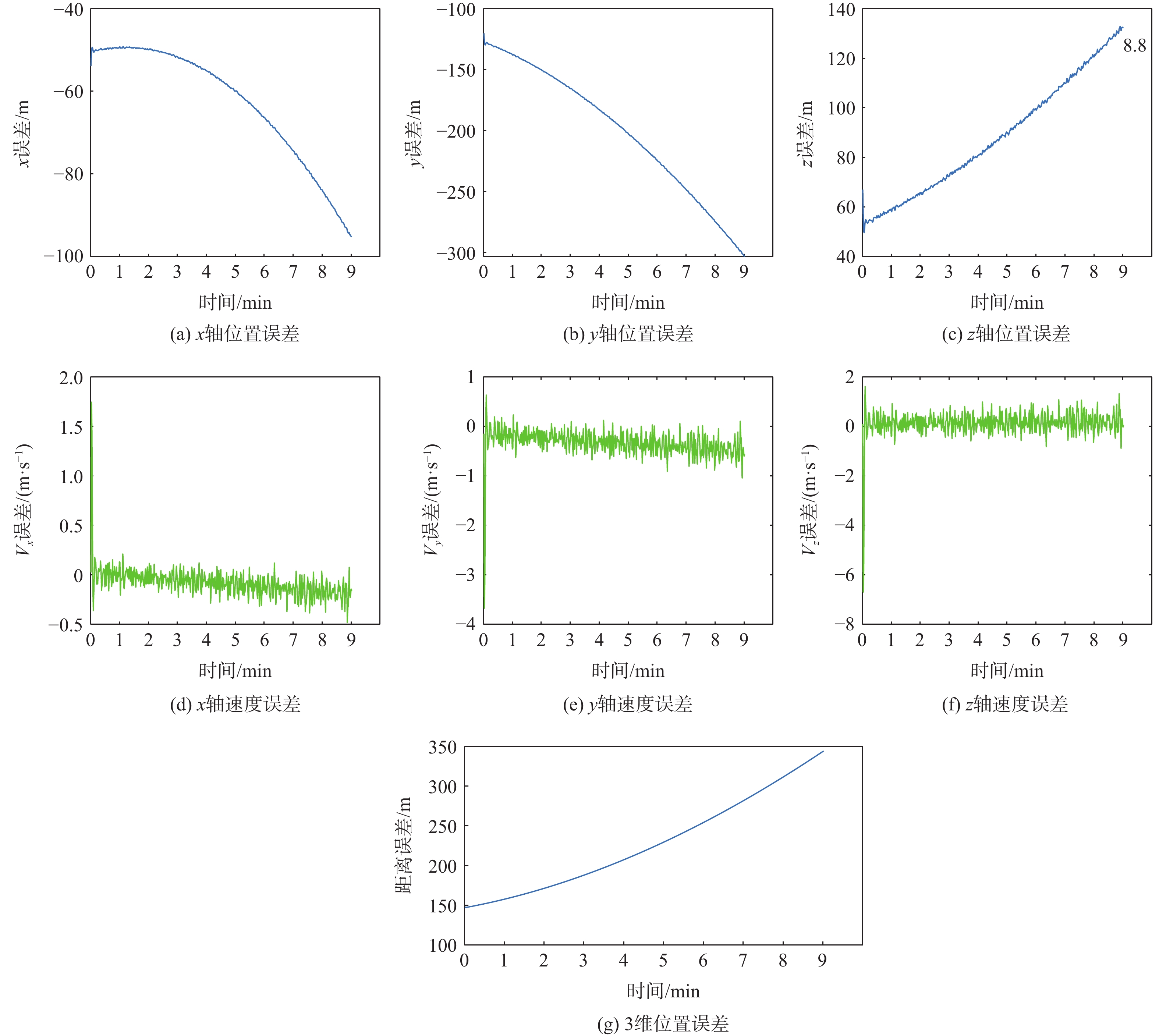
m 初值 95%水平的RMS 95%垂直的RMS 95%距离的RMS 初值1 10.4137 9.3430 13.9906 初值2 658.6316 848.4234 103 表 6 INS、气压计辅助LEO卫星定位误差统计
Table 6. Error statistics of INS and barometer-assisted LEO satellite positioning
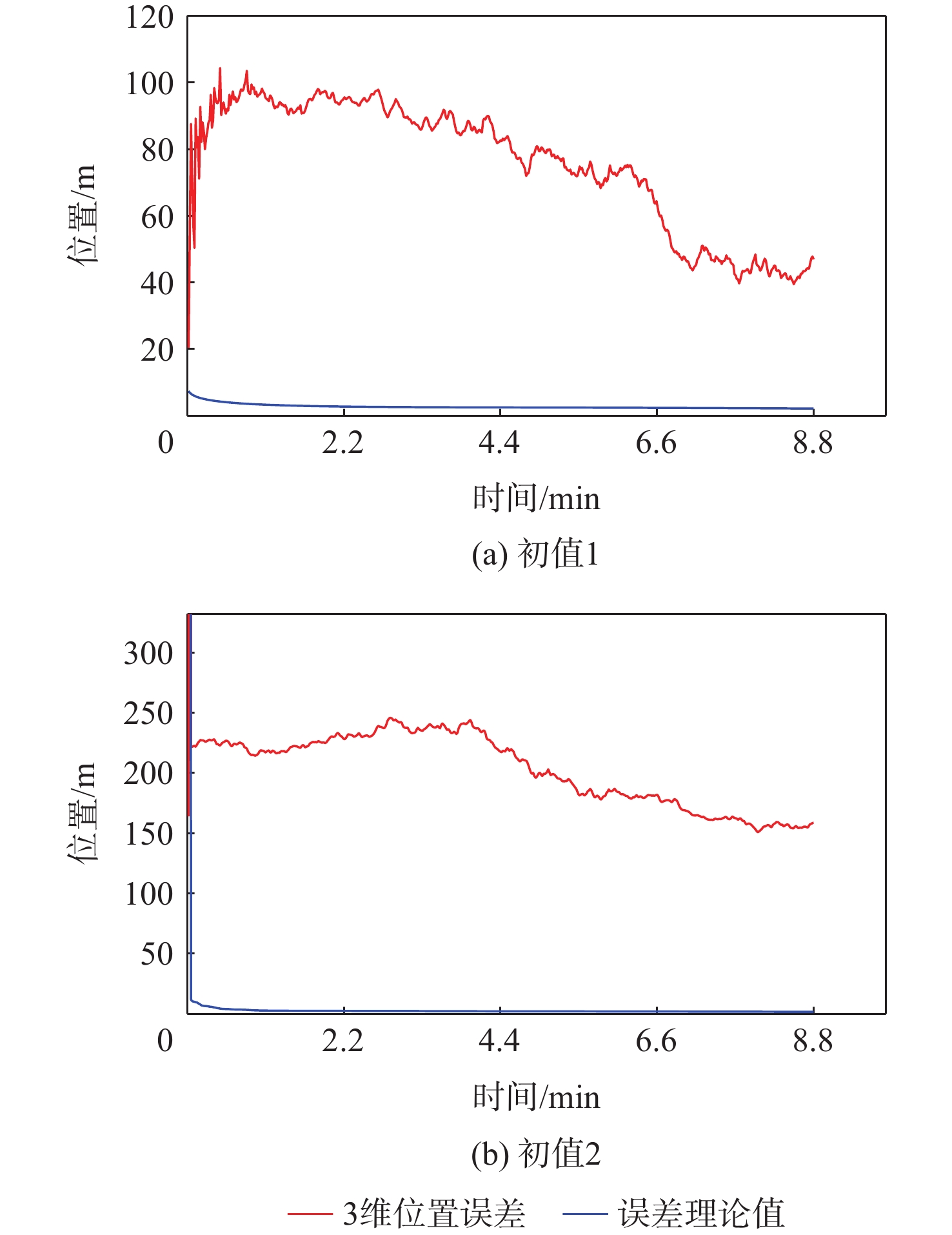
m 初值 95%水平的RMS 95%垂直的RMS 95%距离的RMS 初值1 22.5107 46.4294 48.8029 初值2 148.2198 52.4217 156.2592 表 7 INS、气压计、原子钟辅助LEO卫星定位误差统计
Table 7. Error statistics of INS, barometer, and atomic clock- assisted LEO satellite positioning
m 初值 95%水平的RMS 95%垂直的RMS 95%距离的RMS 初值1 32.0051 31.0504 44.3448 初值2 34.0362 37.5253 50.6617 -
[1] SU Y T, LIU Y Q, ZHOU Y Q, et al. Broadband LEO satellite communications: Architectures and key technologies[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2019, 26(2): 55-61. doi: 10.1109/MWC.2019.1800299 [2] TAN Y K , SCOTT C A , DEMPSTER A G . Detecting object movement through the use of two GNSS satellites[C]//Ignss Symp, JejuL Tan Y K, 2009: 103-114. [3] YE L , YANG Y , JING X , et al. Single-satellite integrated navigation algorithm based on broadband leo constellation communication links[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(7): 703. [4] DANCHIK R J. An overview of transit development[J]. Johns Hopkins Apl Technical Digest, 1998, 19(3): 18-26. [5] STANSELL Jr, Thomas A. Transit, the navy navigation satellite system[J]. Navigation, 1971, 18(1): 93-109. doi: 10.1002/j.2161-4296.1971.tb00077.x [6] LEVANON N. Instant active positioning with one LEO satellite[J]. Navigation, 1999, 46(2): 87-95. doi: 10.1002/j.2161-4296.1999.tb02397.x [7] LEVANON N. Quick position determination using 1 or 2 LEO satellites[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1998, 34(3): 736-754. doi: 10.1109/7.705883 [8] TAN Y K. Positioning techniques with two GNSS satellites over time[C]//Proceedings of International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation. Porfland: Oregon lonvention Center, 2010: 207-216. [9] ALSHAMAA D, MOURAD-CHEHADE F, HONEINE P. Tracking of mobile sensors using belief functions in indoor wireless networks[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018, 18(1): 310-319. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2017.2766630 [10] RABINOWITZ M, SPILKER J J. A new positioning system using television synchronization signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Broadcasting, 2005, 51(1): 51-61. doi: 10.1109/TBC.2004.837876 [11] BORENOVIC M, NESKOVIC A, NESKOVIC N. Vehicle positioning using GSM and cascade-connected ANN structures[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2013, 14(1): 34-46. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2012.2207116 [12] WEBB T A, GROVES P D, CROSS P A, et al. A new differential positioning method using modulation correlation of signals of opportunity[C]// IEEE/ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2010: 972-981. [13] 黄高明, 景桐, 田威. 机会信号导航综述[J]. 控制与决策, 2019, 34(6): 1121-1131.HUANG G M, JING T, TIAN W. Survey on navigation via signal of opportunity[J]. Control and Decision, 2019, 34(6): 1121-1131 (in Chinese). [14] MORALES J J, KHALIFE J J, KASSAS Z M. Information fusion strategies for collaborative inertial radio SLAM[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(8): 12935-12952. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2021.3118678 [15] 孙国良, 沈士团, 丁子明, 等. 一种无源双星与多普勒导航系统组合的实现方法[J]. 航空学报, 2006, 27(4): 682-686.SUN G L, SHEN S T, DING Z M, et al. An integration method for passive RDSS and DNS[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2006, 27(4): 682-686 (in Chinese). [16] YE L Y, YANG Y K, JING X L, et al. Single-satellite integrated navigation algorithm based on broadband LEO constellation communication links[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(4): 703. doi: 10.3390/rs13040703 [17] KATARZYNA S, WIELGOSZ P, PAZIEWSKI J. Accuracy analysis of the Klobuchar ionosphere model transmitted by the GPS system[C]//Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Environmental Engineering. Vilnius: J Paziewski, 2014: 246-252. [18] Leandro, Rodrigo , M. Santos , and R. B. Langley . UNB neutral atmosphere models: Development and performance[C]//Proceedings of the National Technical Meeting of the Institute of Navigation Ntm. Florida: IOW, 2006: 215-226. [19] Hargrave P J. A tutorial introduction to Kalman filtering[C]//IEE Colloquium on Kalman Filters: Introduction, Applications and Future Developments. Pissataway: IEEE Press, 1989: 1-6. [20] Li X R , Jilkov V P . Survey of maneuvering target tracking: decision-based methods[C]//International Symposium on Optical Science & Technology. International Society for Optics and Photonics. Paris: SPIE, 2000: 368-383. [21] FAWCETT J A. Effect of course maneuvers on bearings-only range estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1988, 36(8): 1193-1199. doi: 10.1109/29.1648 [22] LE CADRE J E, JAUFFRET C. Discrete-time observability and estimability analysis for bearings-only target motion analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1997, 33(1): 178-201. doi: 10.1109/7.570737 [23] 滕云龙, 师奕兵, 郑植. 恶劣环境下GPS接收机定位算法研究[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2011, 32(8): 1879-1884.TENG Y L, SHI Y B, ZHENG Z. Research on GPS receiver positioning algorithm under bad conditions[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2011, 32(8): 1879-1884 (in Chinese). [24] 李博, 徐超, 李孝辉, 等. 遮挡环境下原子钟和气压测高仪辅助北斗定位方法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(9): 2212-2218.LI B, XU X, LI X H, et al. BeiDou navigation satellite system in challenge environment using an atomic clock and barometric altimeter[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2018, 40(9): 2212-2218. -







 下载:
下载: