-
摘要:
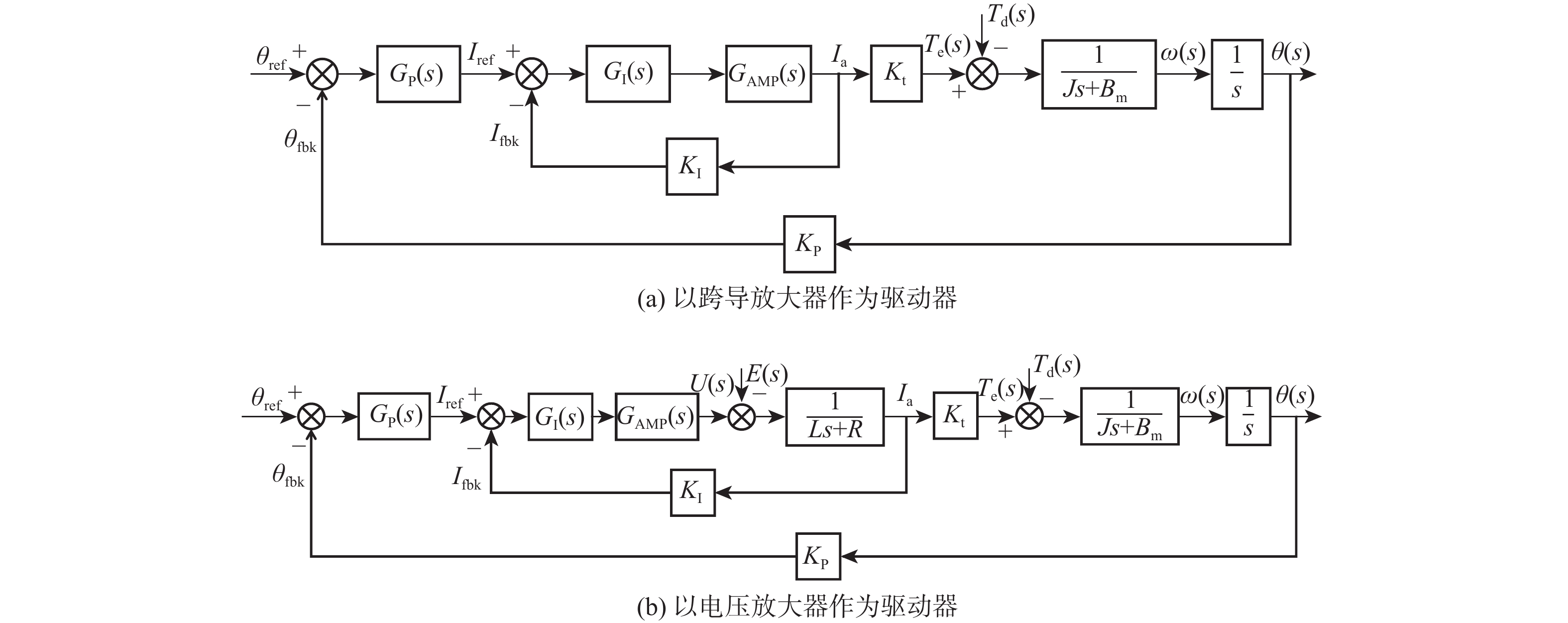
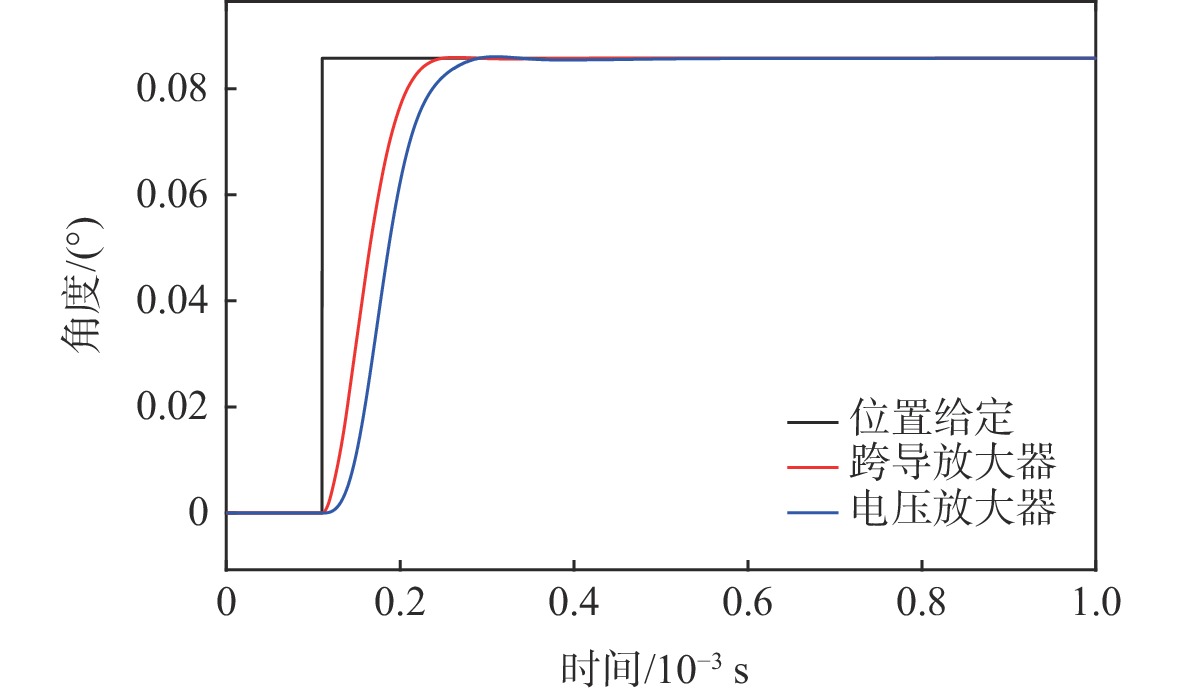
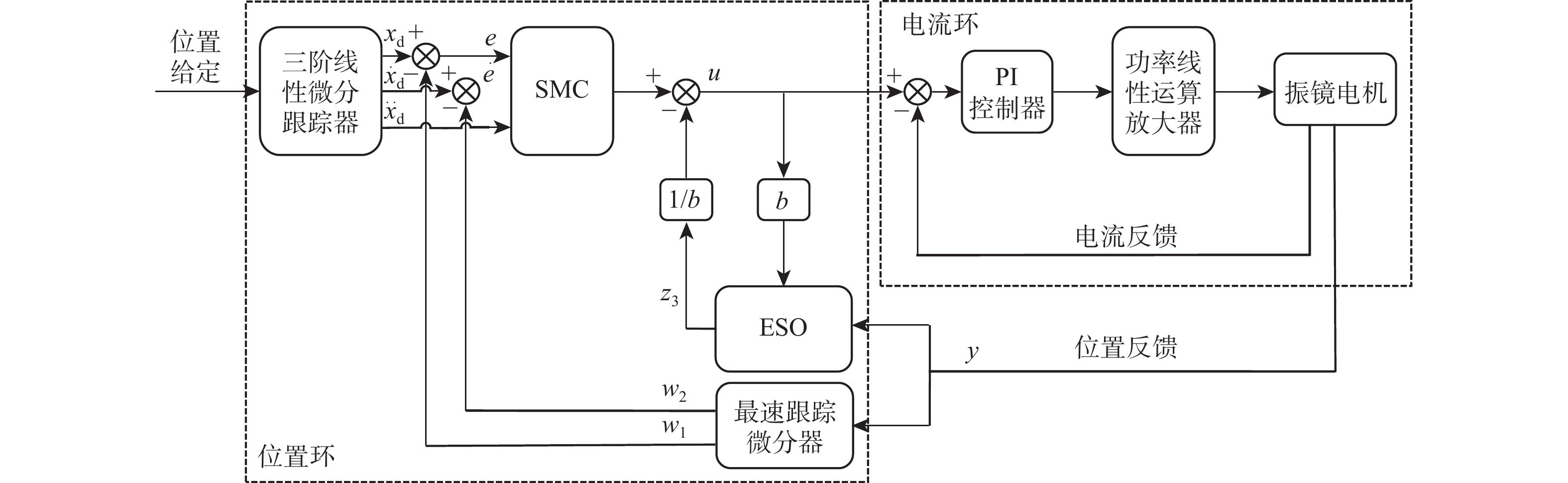
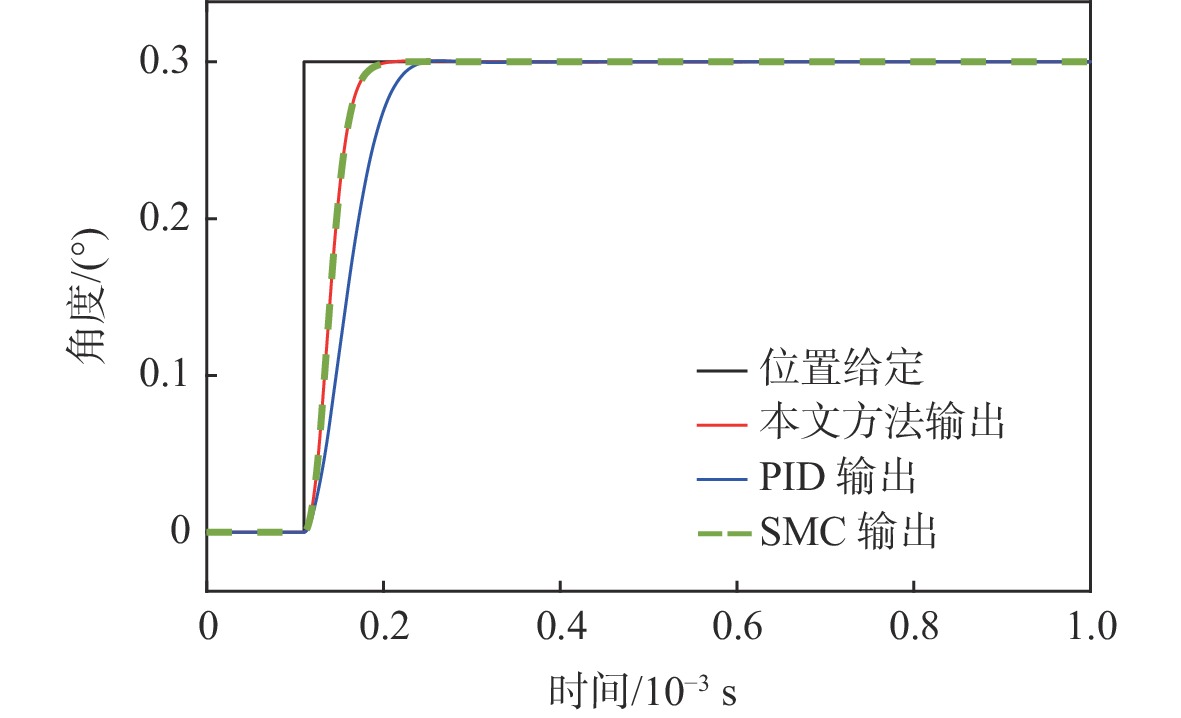
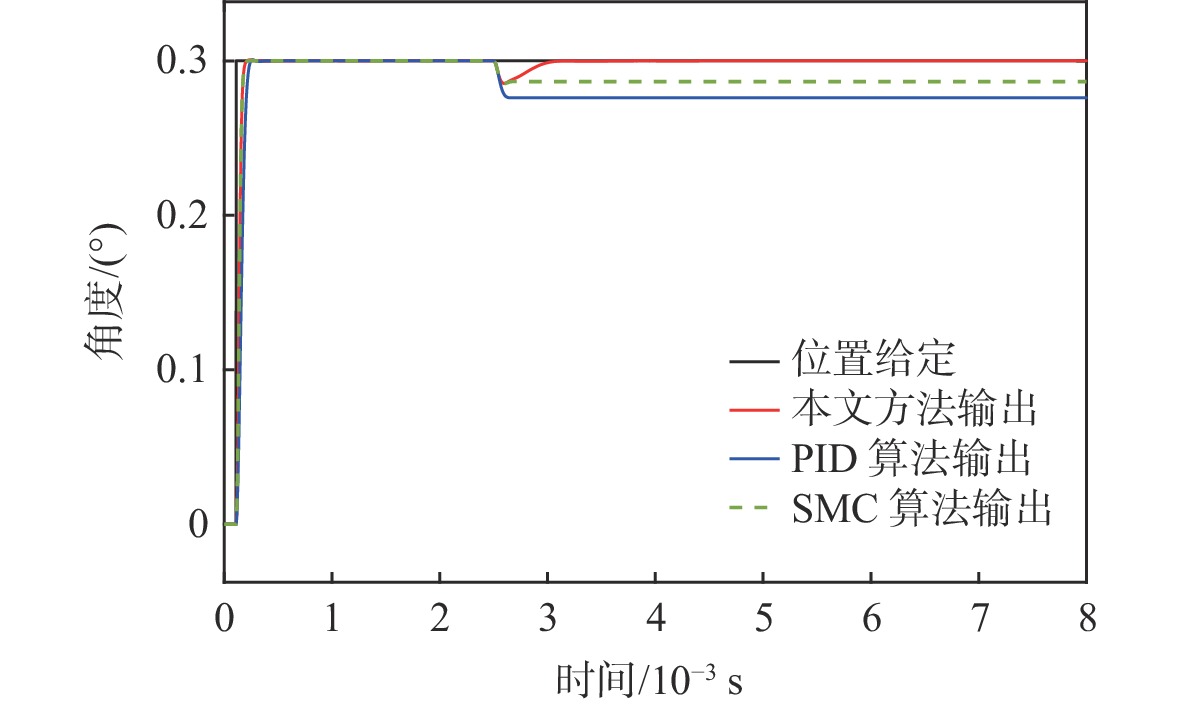
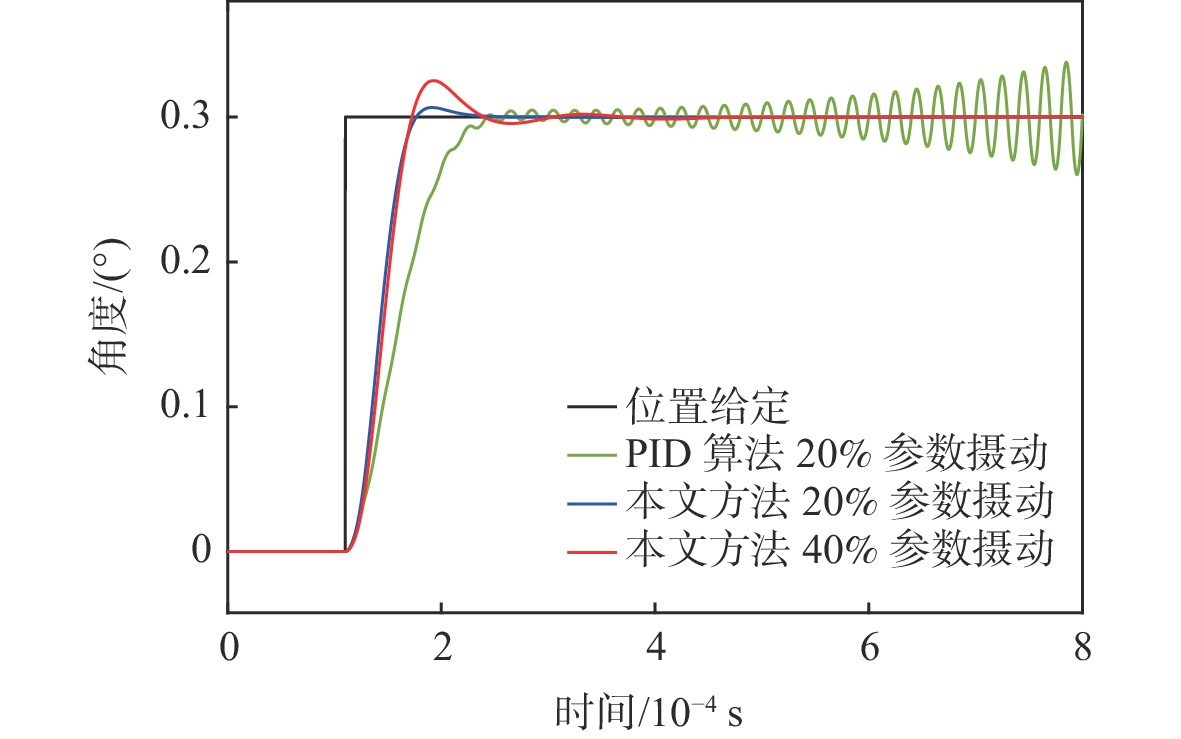
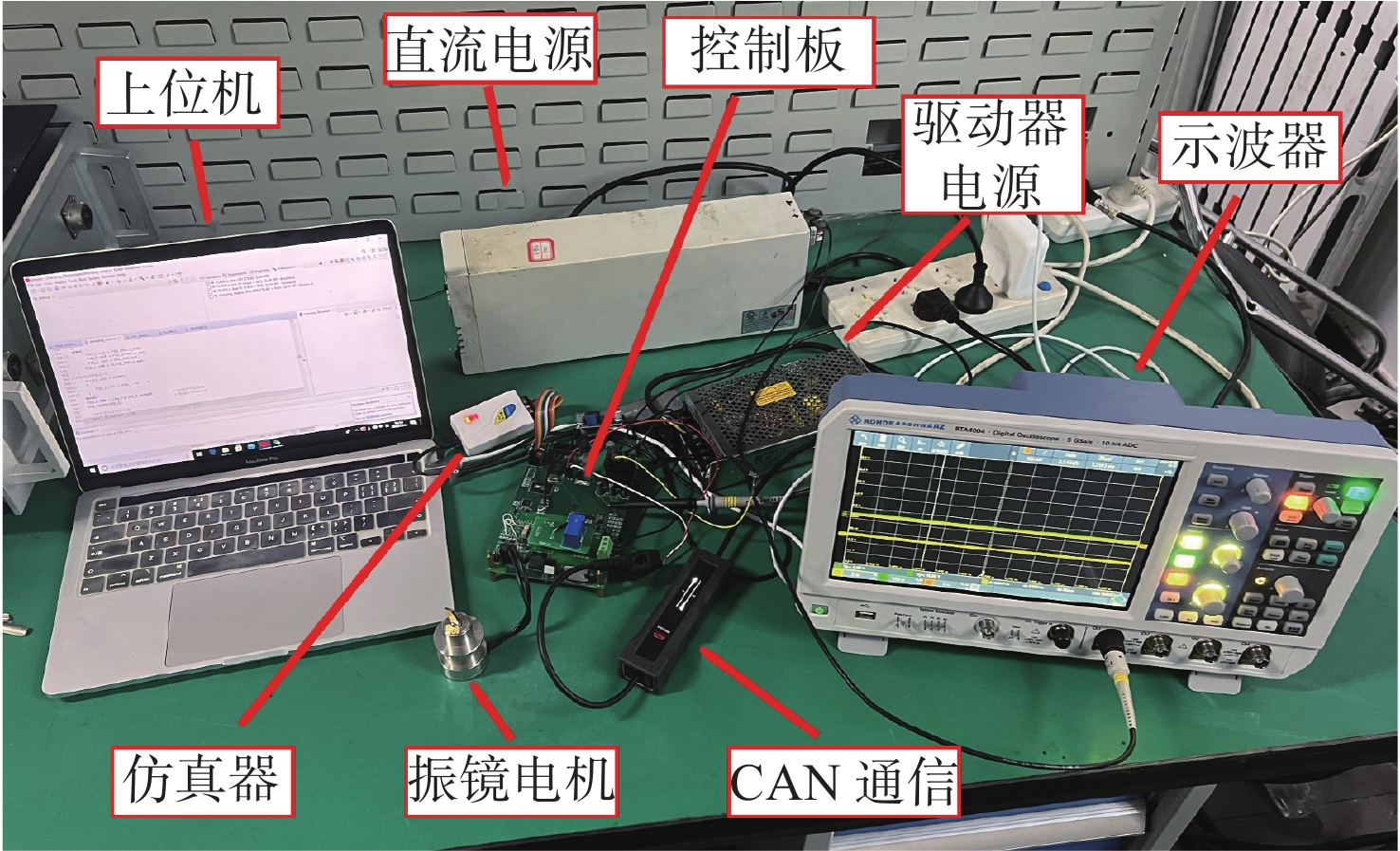
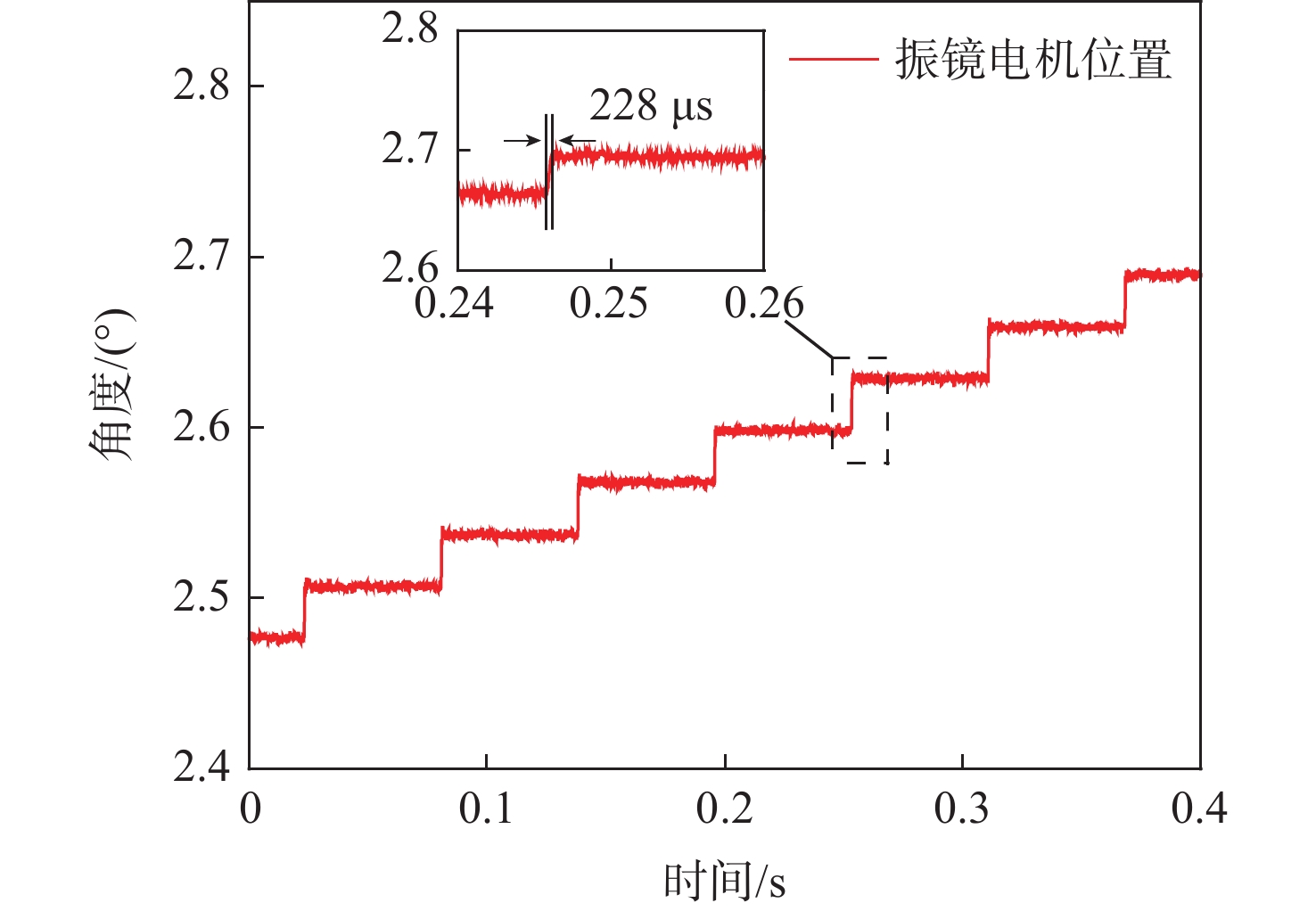
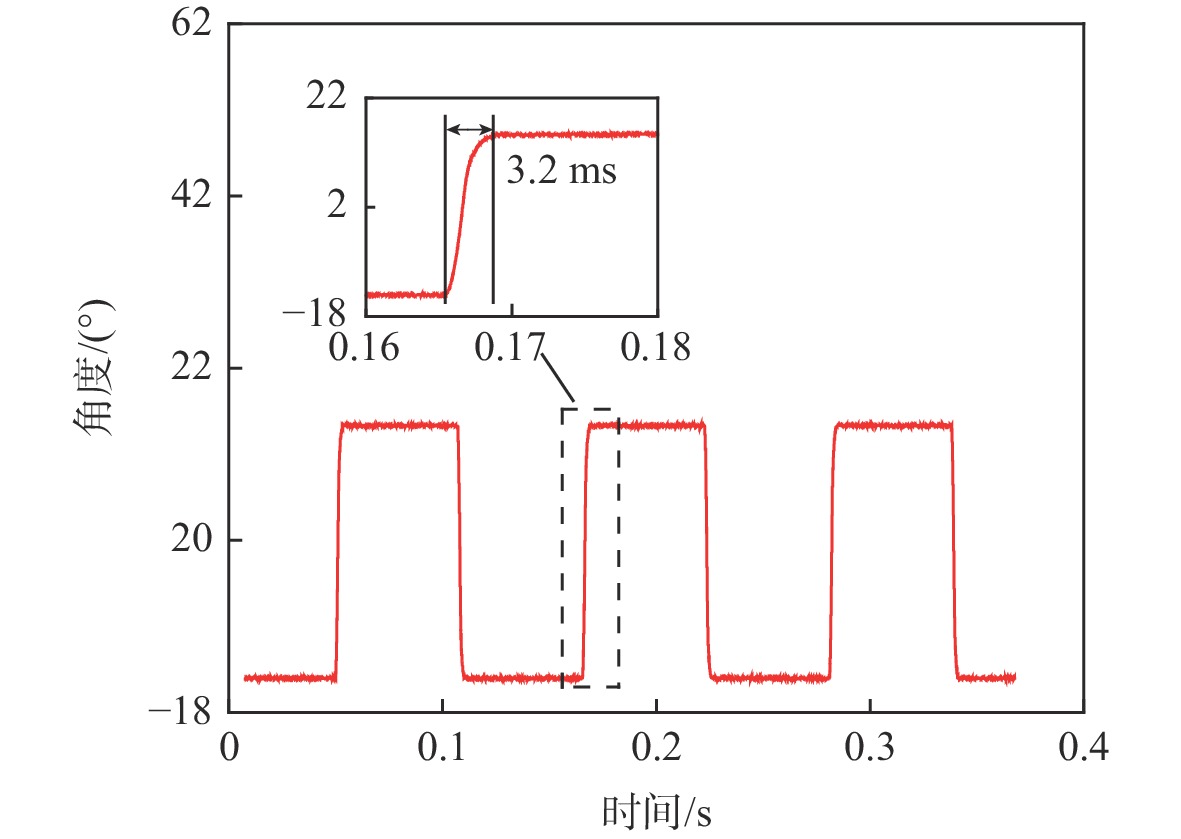
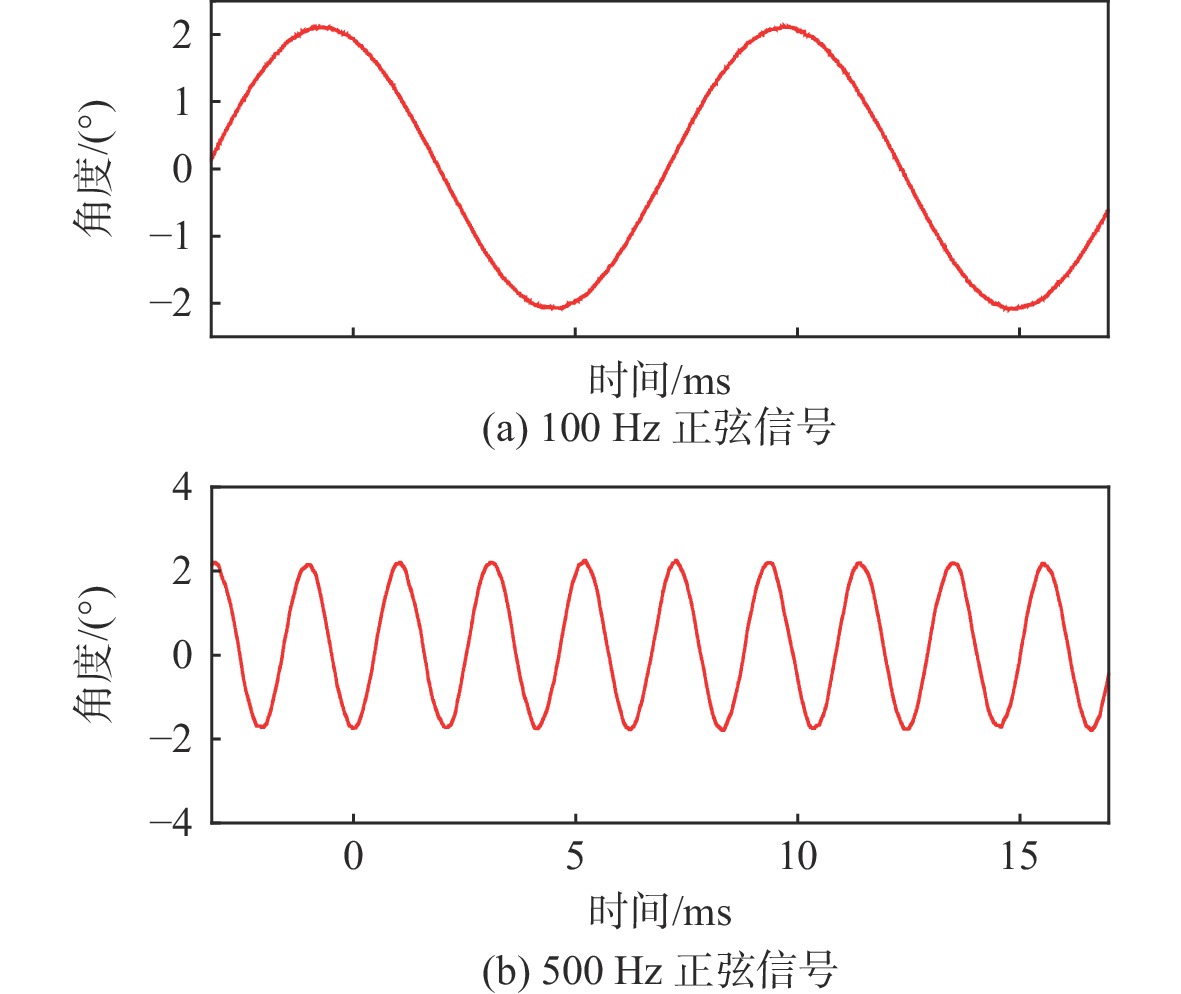
为满足振镜电机系统高精度和高动态性能的控制需求,提出数模混合架构和扩张状态观测器(ESO)-滑模控制(SMC)复合的高性能驱动控制方法。采用基于数字式控制器和模拟式驱动器的数模混合架构设计,一方面便于实现高性能的非线性控制算法,另一方面能够消除数字式驱动器中脉冲宽度调制(PWM)技术导致的高频电流纹波。基于ESO和SMC复合的振镜电机位置环控制方法,通过ESO估计系统的各种扰动,利用SMC实时消除扰动影响,显著地提升了振镜电机系统的动态性能和鲁棒性。仿真和实验结果表明:相较于比例-积分-微分(PID)控制器,所提方法能够有效地提升系统的鲁棒性和动态响应性能,其中动态响应性能提升了29.4%。
Abstract:To improve the control performance, the digital-analog hybrid control with the extended state observer (ESO) and sliding mode control (SMC) is proposed for the galvanometer laser scanner in this paper. The digital-analog hybrid control scheme is first proposed, which adopts the digital controller and analog driver for the high-performance control algorithm implementation and eliminates the ripple current due to the pulse width modulation (PWM) chopping. Then the ESO and SMC based nonlinear control is proposed to enhance the control accuracy and dynamic performance of the galvanometer laser scanner regardless of various disturbances. According to the mathematical model of the galvanometer laser scanner, the stability of the system is verified by the Lyapunov stability criterion. The findings of the simulation and testing demonstrate that the suggested control can enhance the step response time of the 1% range by roughly 29.4% when compared to the proportion-integral-derivative (PID) controller, hence improving the system's dynamic performance. At the same time, the anti-interference ability and robustness can also be improved.
-
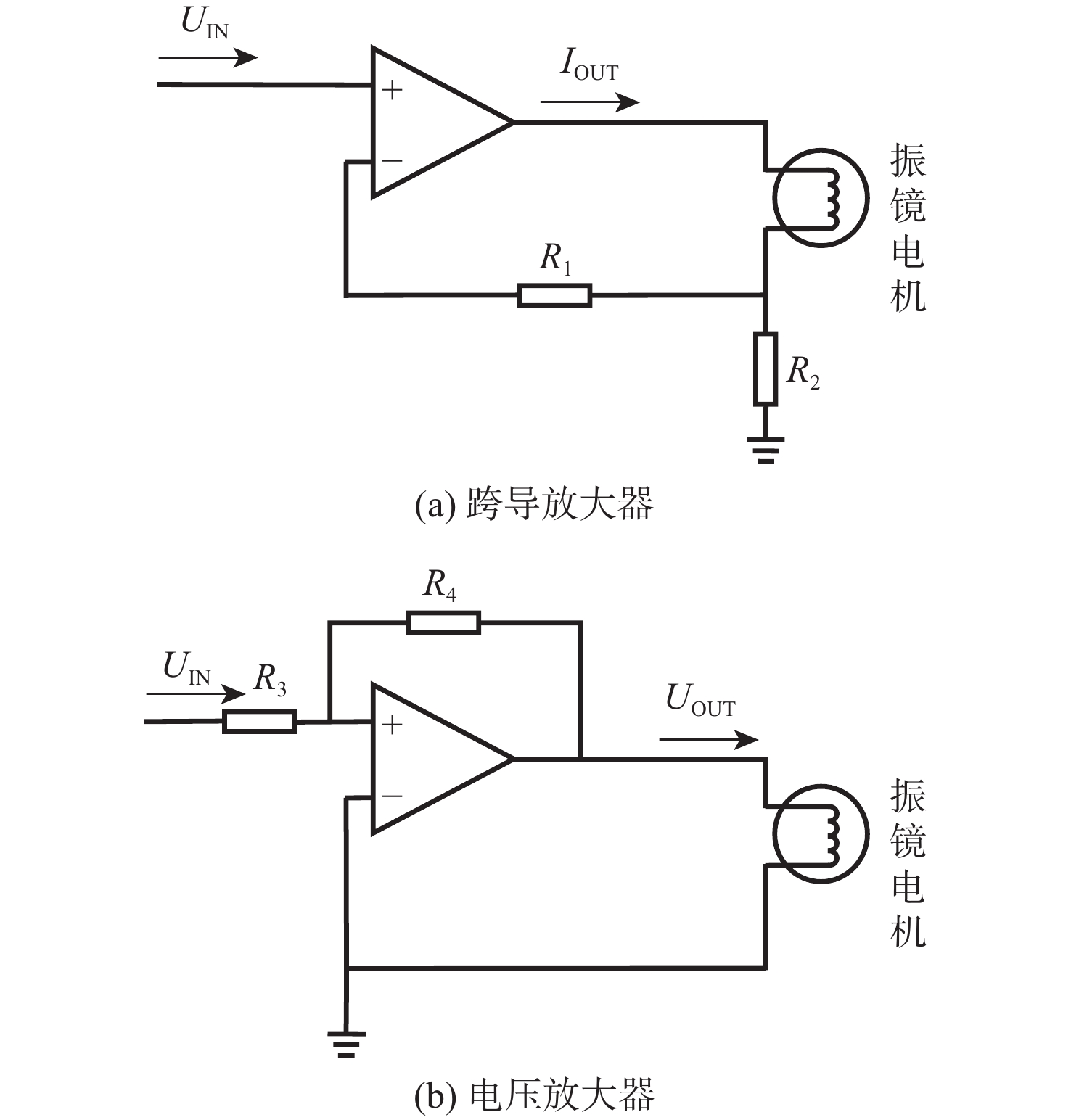
表 1 运算放大器的4种组态
Table 1. Four forms of operational amplifier
组态 输入信号 输出信号 放大公式 电压串联式 Ui Uo Kv=Uo/Ui 电压并联式 Ui Io Ks=Io/Ui 电流串联式 Ii Uo KΩ=Uo/Ii 电流并联式 Ii Io Ki=Io/Ii 表 2 振镜电机基本参数
Table 2. Basic Parameters of Galvo Motor
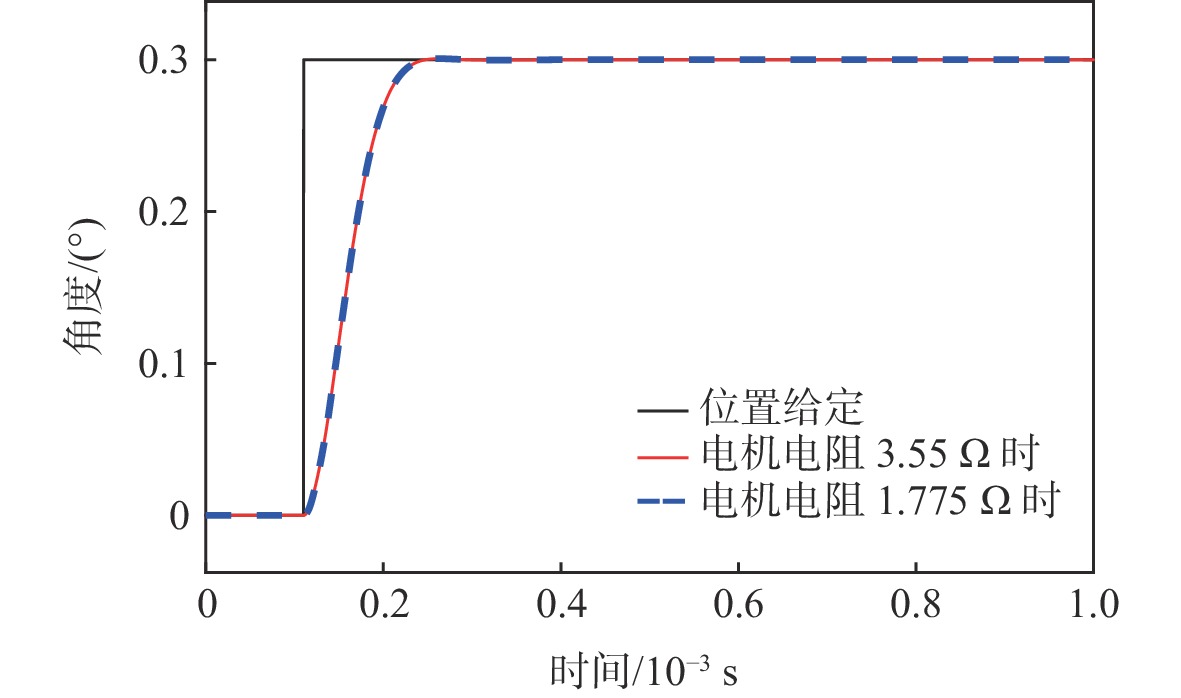
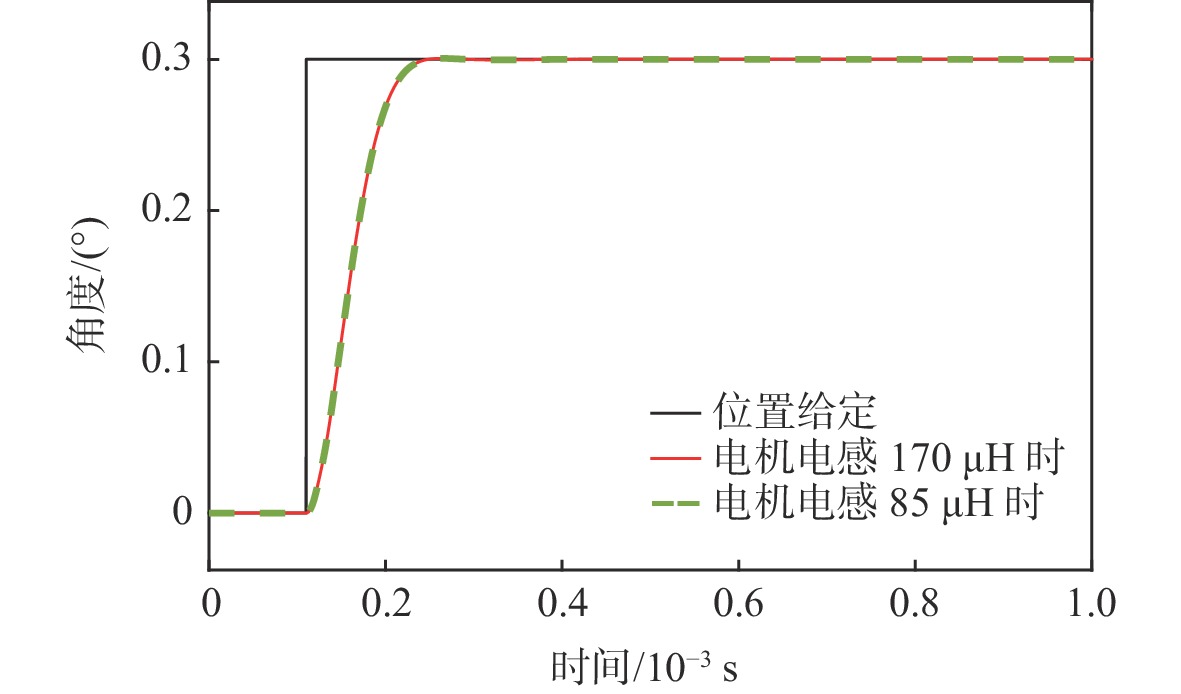
参数 数值 电机电阻/Ω 3.55 电机电感/μH 170 额定电压/V 30 额定电流/A 3 最大电流/A 6 力矩系数/(Nm·A−1) 0.017 反电势常数/(V·(rad·s−1)−1) 8.3×10−3 转动惯量/(kg·m3) 1.25×10−8 最大摆角/(°) 30 -
[1] 陈波, 孟正, 马程远, 等. 扫描振镜激光TC4钛合金焊接性能及熔池流动行为[J]. 航空学报, 2022, 43(4): 525223.CHEN B, MENG Z, MA C Y, et al. Welding properties and molten pool flow behavior of TC4 titanium alloy by oscillating galvanometer laser[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2022, 43(4): 525223 (in Chinese). [2] 李昊岳, 刘永江, 赵振兴, 等. 航空传感元件振镜激光钎焊界面组织及连接机理[J]. 航空学报, 2022, 43(2): 625020.LI H Y, LIU Y J, ZHAO Z X, et al. Interface microstructure and formation mechanism of oscillating laser brazed joints for aerial sensing elements[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2022, 43(2): 625020 (in Chinese). [3] 朱小伟. 面向航空复合材料构件维修的激光分层雕刻工艺软件设计[D]. 温州: 温州大学, 2021: 9-12.ZHU X W. The design of a laser layered engraving software for CFRP aviation component maintenance[D]. Wenzhou: Wenzhou University, 2021: 9-12(in Chinese). [4] 乔明蕊. 基于可变论域模糊PID的振镜控制技术研究[D]. 西安: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院西安光学精密机械研究所), 2016: 1-11.QIAO M R. Research on galvanometer control technology base on variable universe fuzzy-PID[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2016: 1-11(in Chinese). [5] 李乐. 针对低慢小目标的激光武器粗瞄控制系统研究与设计[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2018: 1-4.LI L. Research and design of aiming control system of laser weapon for low slow small target[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2018: 1-4(in Chinese). [6] 黄勇, 邓建辉. 高能激光武器的跟瞄精度要求分析[J]. 电光与控制, 2006, 13(6): 86-88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2006.06.023HUANG Y, DENG J H. On tracking & pointing accuracy requirement of high energy laser weapon[J]. Electronics Optics & Control, 2006, 13(6): 86-88(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2006.06.023 [7] 刘小强, 杨修林, 陆培国, 等. 激光武器控制系统研究[J]. 激光与红外, 2022, 52(8): 1238-1245. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2022.08.021LIU X Q, YANG X L, LU P G, et al. Analysis of control system for high energy laser system[J]. Laser & Infrared, 2022, 52(8): 1238-1245 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2022.08.021 [8] 叶乔. 高速振镜理论研究及实践[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2004: 48-52.YE Q. A study of high speed galvanometer and practise[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2004: 48-52 (in Chinese). [9] 井峰. 数字式振镜控制系统的研究[D]. 西安: 中国科学院研究生院(西安光学精密机械研究所), 2012: 60-62.JING F. Research on digital galvanometer control system[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2012: 60-62 (in Chinese). [10] 权晓. 激光扫描振镜控制系统研究[D]. 太原: 中北大学, 2021: 53-60.QUAN X. Research on control system of laser scanning galvanometer[D]. Taiyuan: North University of China, 2021: 53-60(in Chinese). [11] YUE Z Y, YAN P. Fractional-order robust controller for high precision galvanometer scanner[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Manipulation, Manufacturing and Measurement on the Nanoscale. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 118-123. [12] QIN W Y, GUO H, XU J Q, et al. High precision position control based on active disturbance rejection control for galvanometer scanner system[C]//Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 1-4. [13] MNERIE C A, PREITL S, DUMA V F. Performance enhancement of galvanometer scanners using extended control structures[C]//Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Applied Computational Intelligence and Informatics. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2013: 127-130. [14] JEAN M. Moving magnet galvanometers having a varied density winding distribution coil for a desired performance characteristic: US5225770[P]. 1993-07-06. [15] JEAN M . Torque motor or moving-magnet galvanometer - useful for optical scanner e. g. for guiding laser beam: DE4205725B4[P]. 1992-04-20. [16] 王丰尧. 滑模变结构控制[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 1995: 244-270.WANG F Y. Sliding mode variable structure control[M]. Beijing: China Machine Press, 1995: 244-270(in Chinese). [17] 魏科鹏, 胡健, 姚建勇, 等. 航空机电作动器神经网络快速终端滑模控制[J]. 航空学报, 2021, 42(6): 624540.WEI K P, HU J, YAO J Y, et al. Fast terminal sliding mode control of neural networks for aeromechanical actuators[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2021, 42(6): 624540(in Chinese). [18] 汪文涛, 刘正江, 李新民. 用于离心式作动器的变滑模面滑模控制[J]. 航空学报, 2019, 40(12): 323210. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2019.23210WANG W T, LIU Z J, LI X M. Variable sliding mode sliding mode controller for centrifugal harmonic force generator[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2019, 40(12): 323210(in Chinese). doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2019.23210 [19] 高为炳, 程勉. 变结构控制系统的品质控制[J]. 控制与决策, 1989, 4(4): 1-6. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-0920.1989.04.002GAO W B, CHENG M. Quality control of variable structure control systems[J]. Control and Decision, 1989, 4(4): 1-6(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-0920.1989.04.002 [20] 韩京清. 自抗扰控制技术: 估计补偿不确定因素的控制技术[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2008: 183-207.HAN J Q. Active disturbance rejection control technique[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2008: 183-207(in Chinese). [21] 张科, 姜海旭, 王靖宇. 基于滑动最速跟踪微分器的遥测数据滤波方法[J]. 西北工业大学学报, 2020, 38(3): 515-522. doi: 10.1051/jnwpu/20203830515ZHANG K, JIANG H X, WANG J Y. A sliding window optimal tracking differentiator filtering method for satellite telemetry data[J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2020, 38(3): 515-522(in Chinese). doi: 10.1051/jnwpu/20203830515 [22] 李海涛, 房建成. 基于扩张状态观测器的DGMSCMG框架伺服系统振动抑制方法[J]. 航空学报, 2010, 31(6): 1213-1219.LI H T, FANG J C. Study on system vibration suppression method based on ESO used in gimbal servo system of DGMSCMG[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2010, 31(6): 1213-1219 (in Chinese). [23] 路遥. 基于跟踪微分器的高超声速飞行器Backstepping控制[J]. 航空学报, 2021, 42(11): 524737.LU Y. Backstepping control for hypersonic flight vehicles based on tracking differentiator[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2021, 42(11): 524737(in Chinese). 期刊类型引用(1)
1. 黄磊,杜思勋,林晓刚,解伟. 基于DSP的振镜电机数模混合驱动电路设计. 电力电子技术. 2025(01): 13-16 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(0)
-








 下载:
下载:

 百度学术
百度学术

