-
摘要:
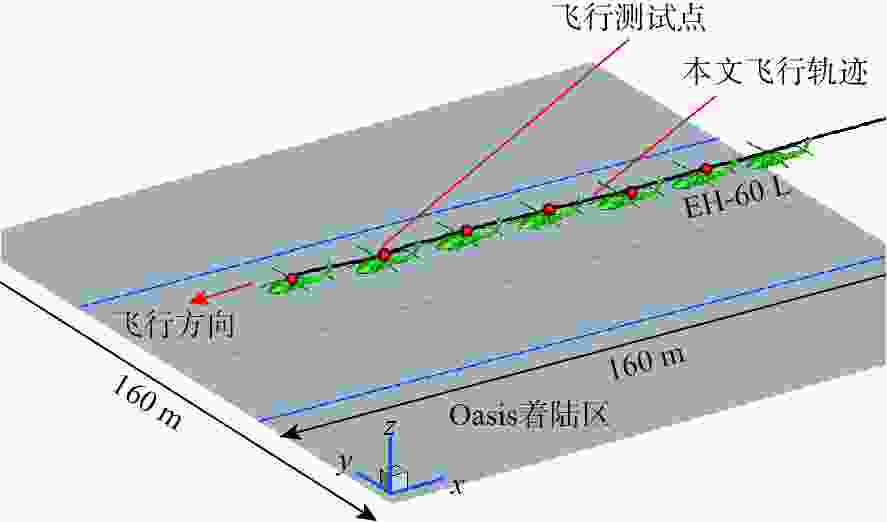
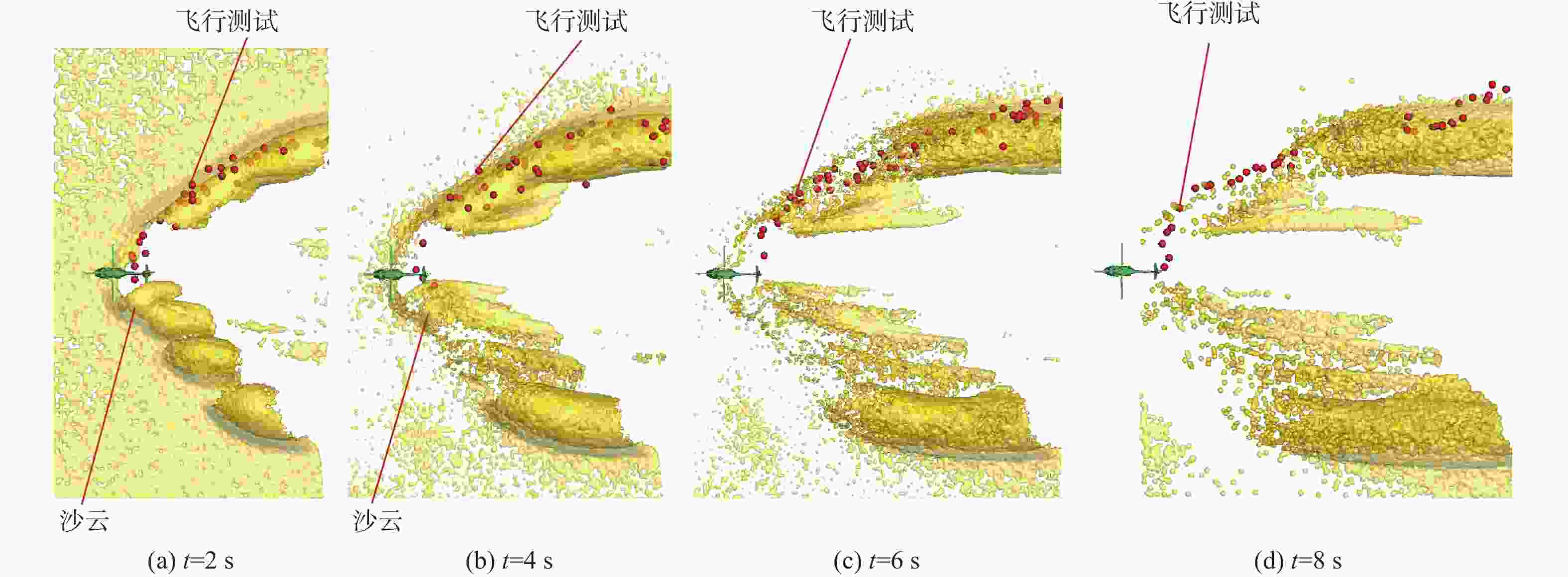
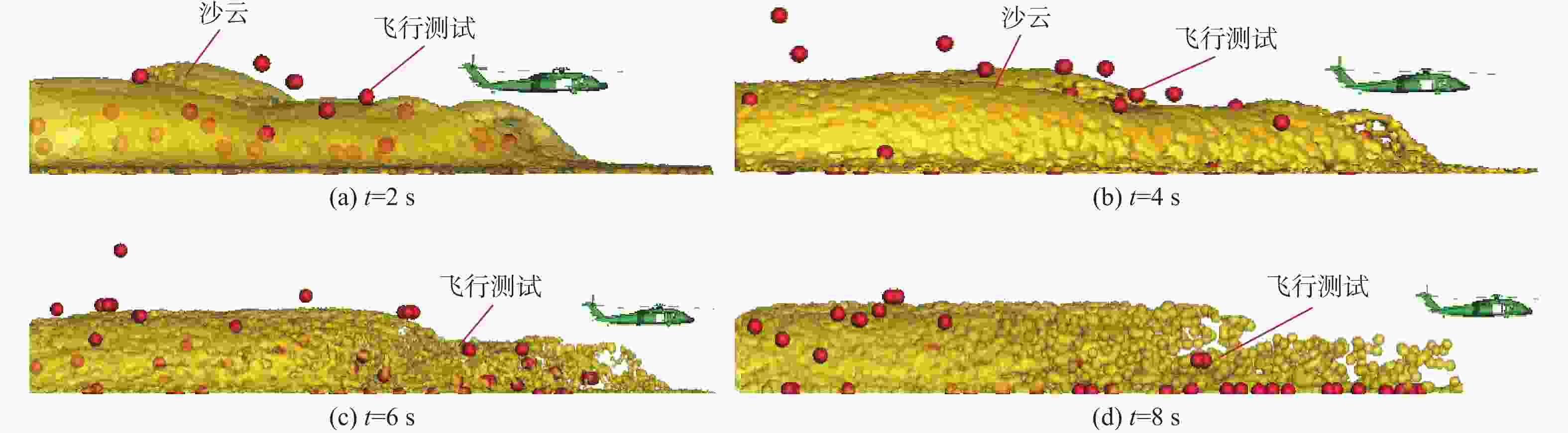
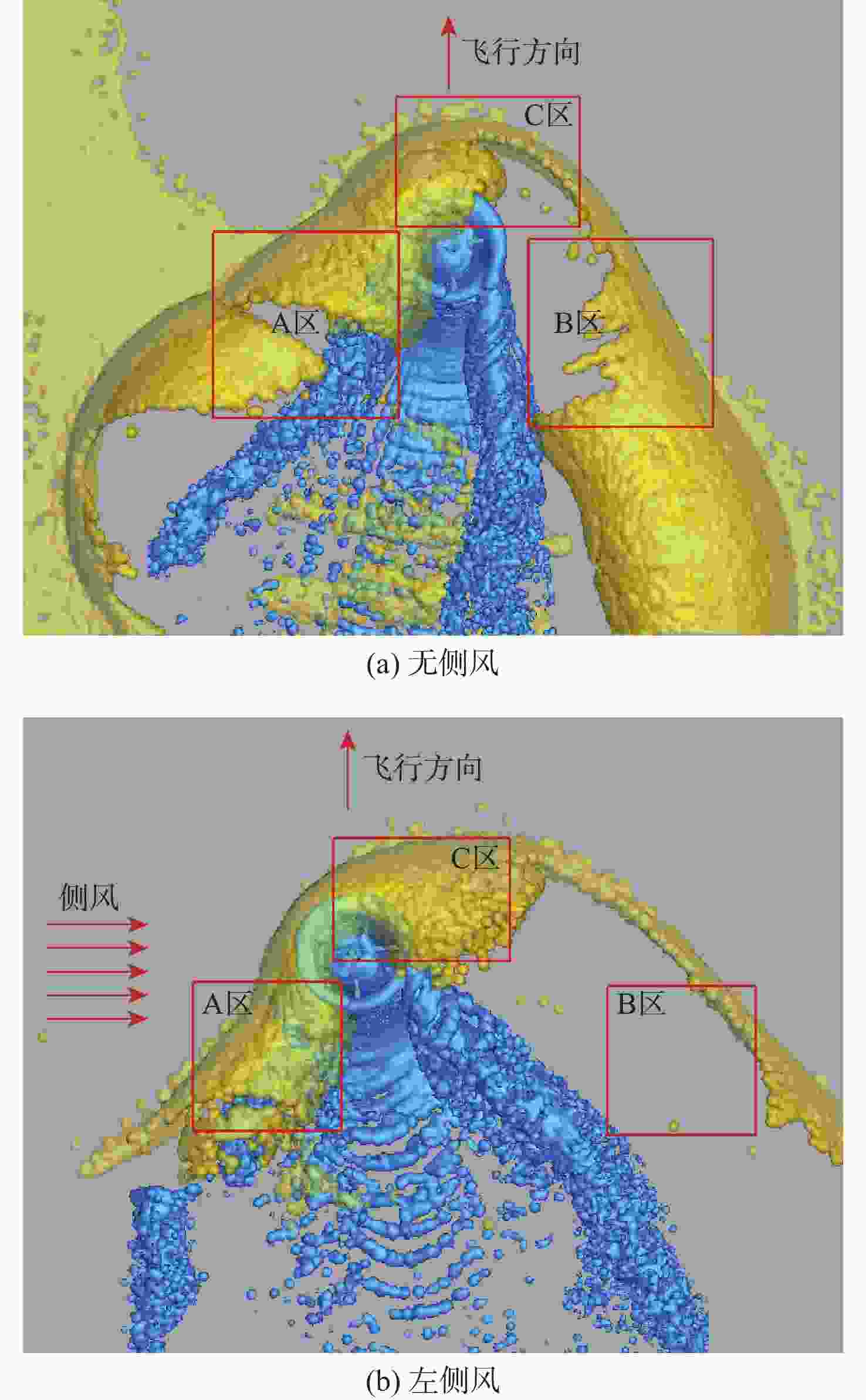
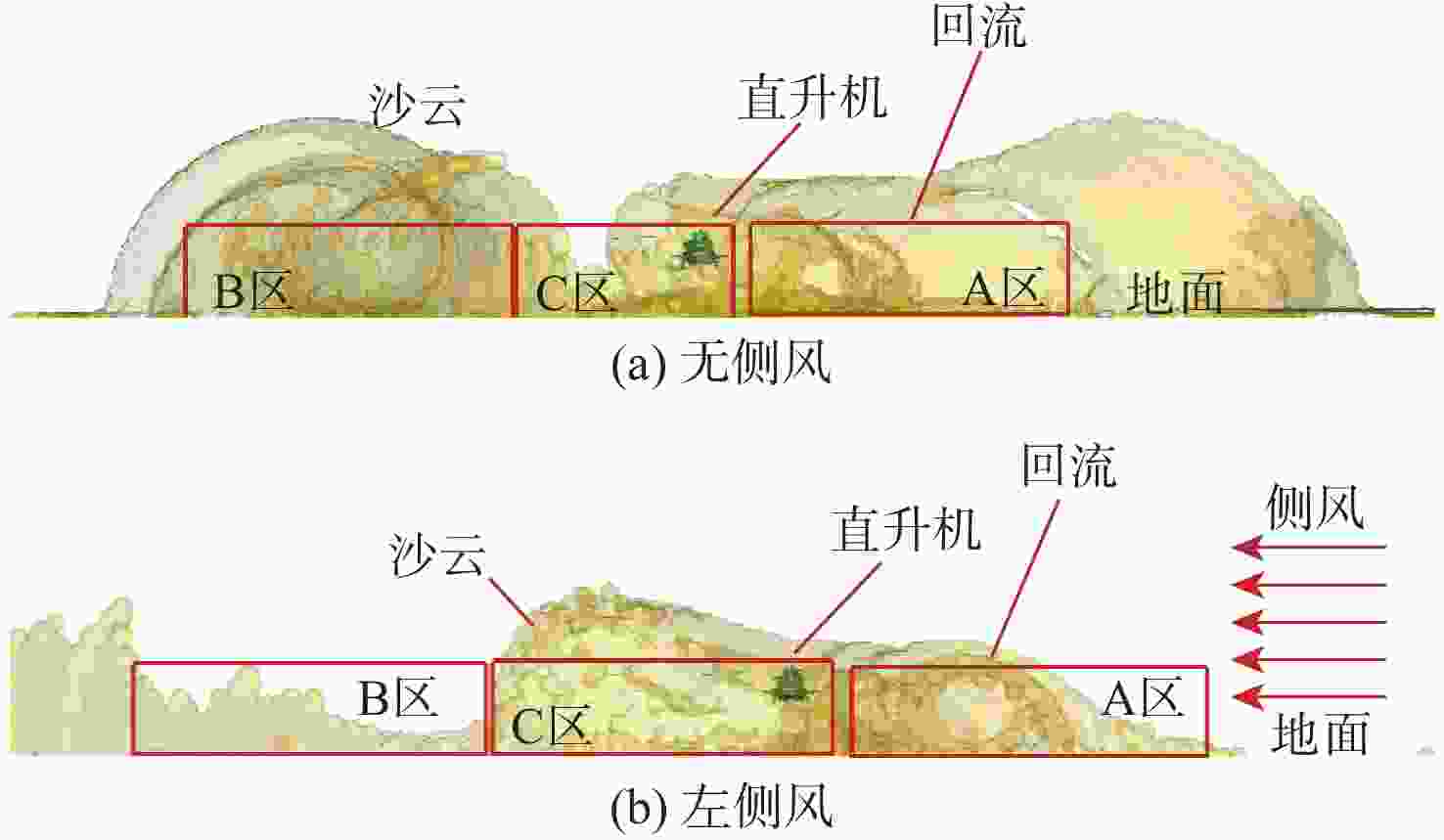
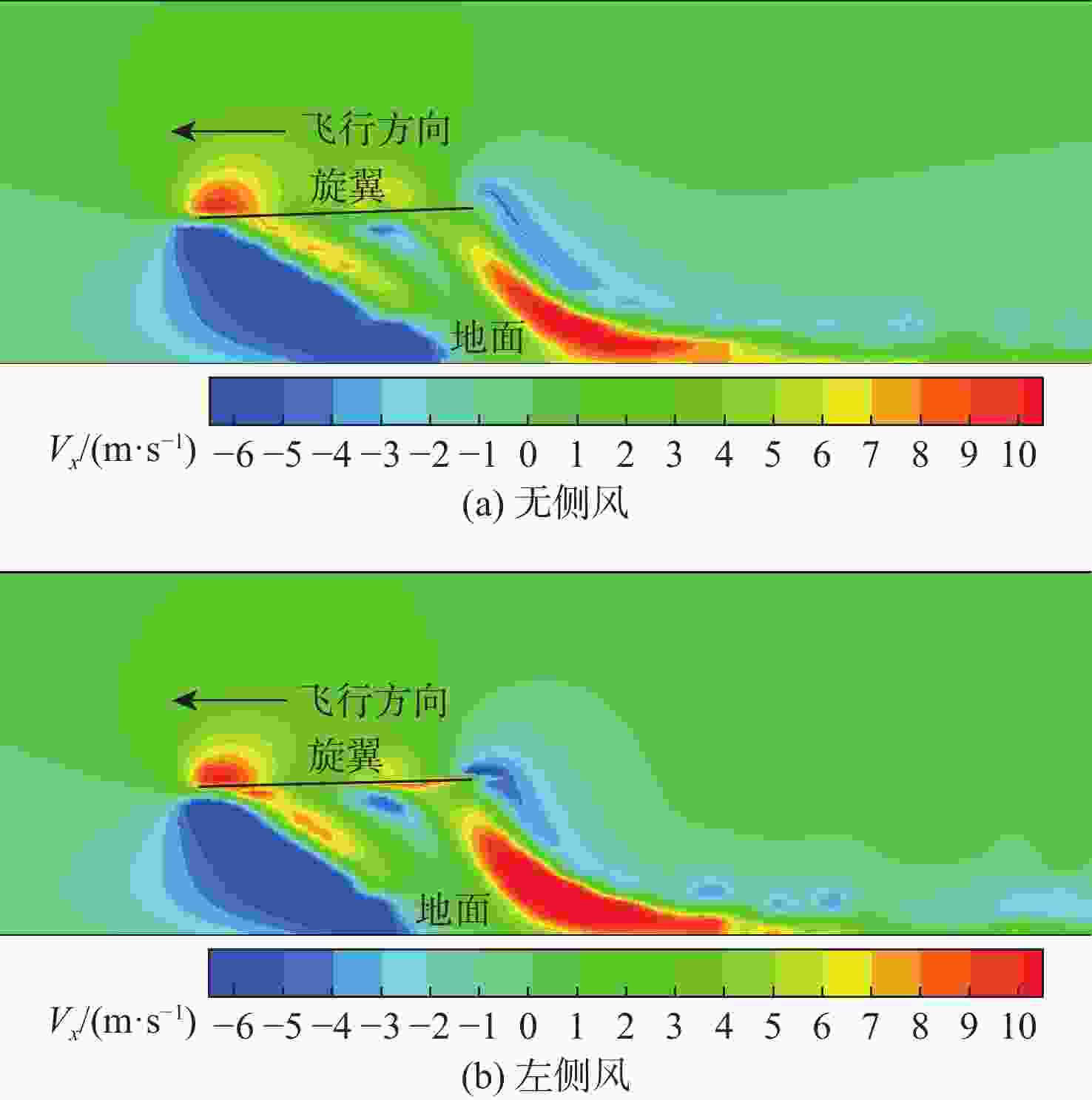
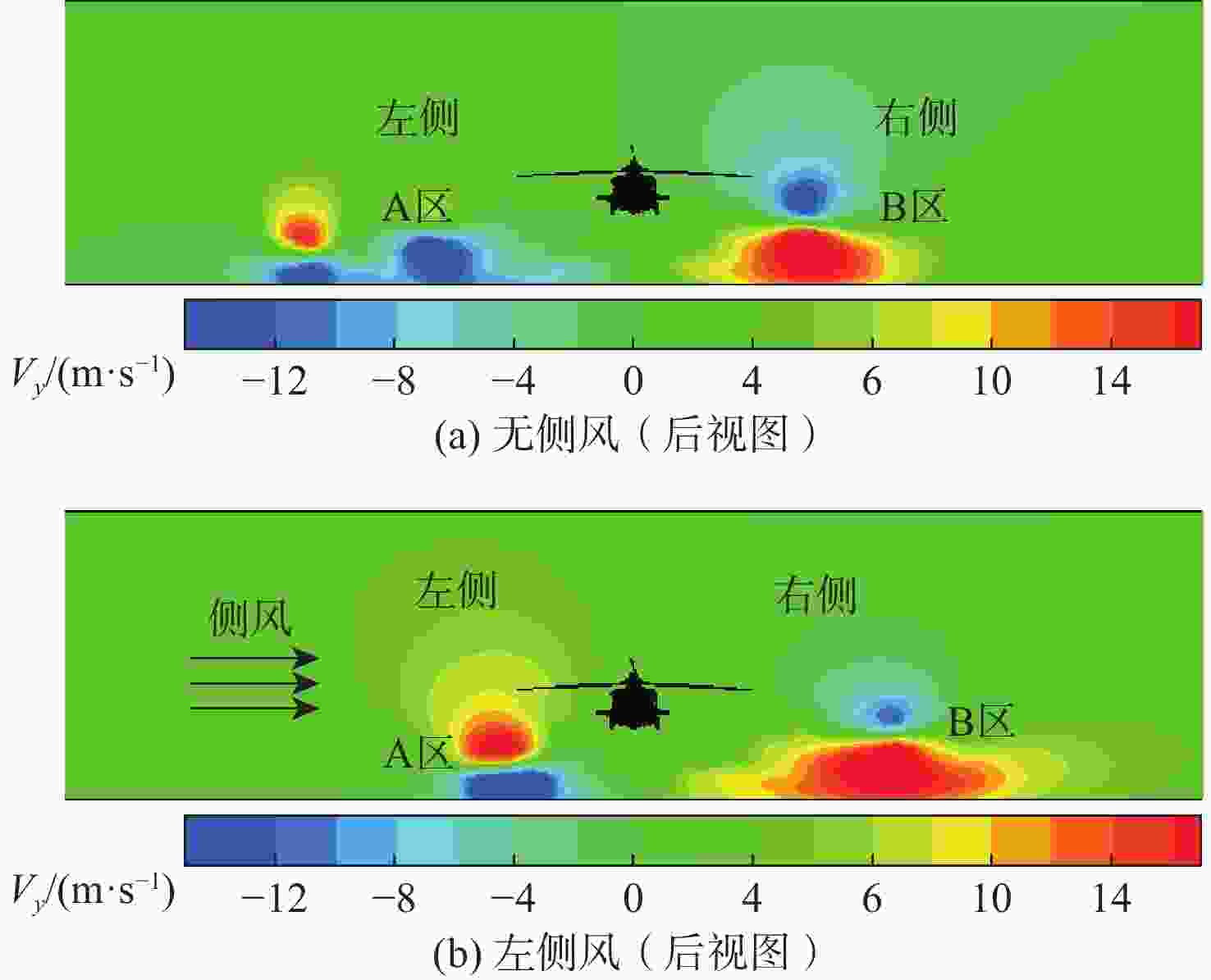
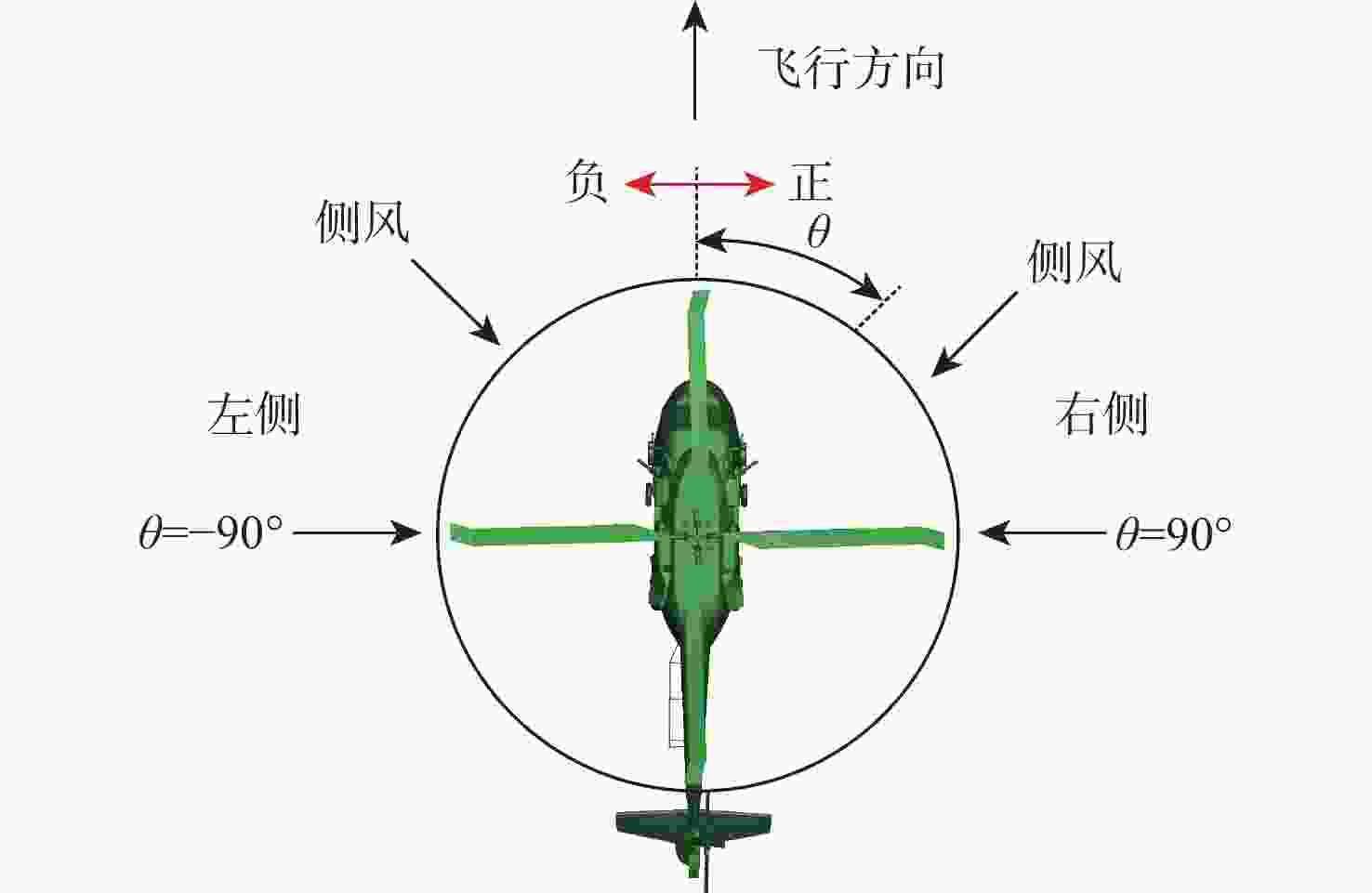
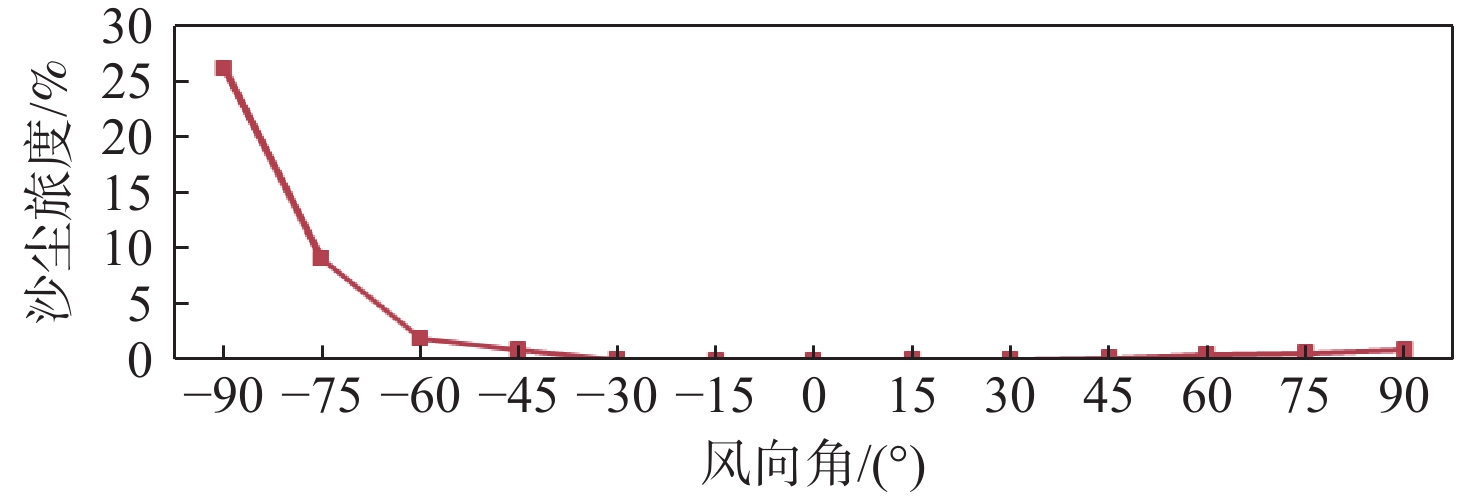
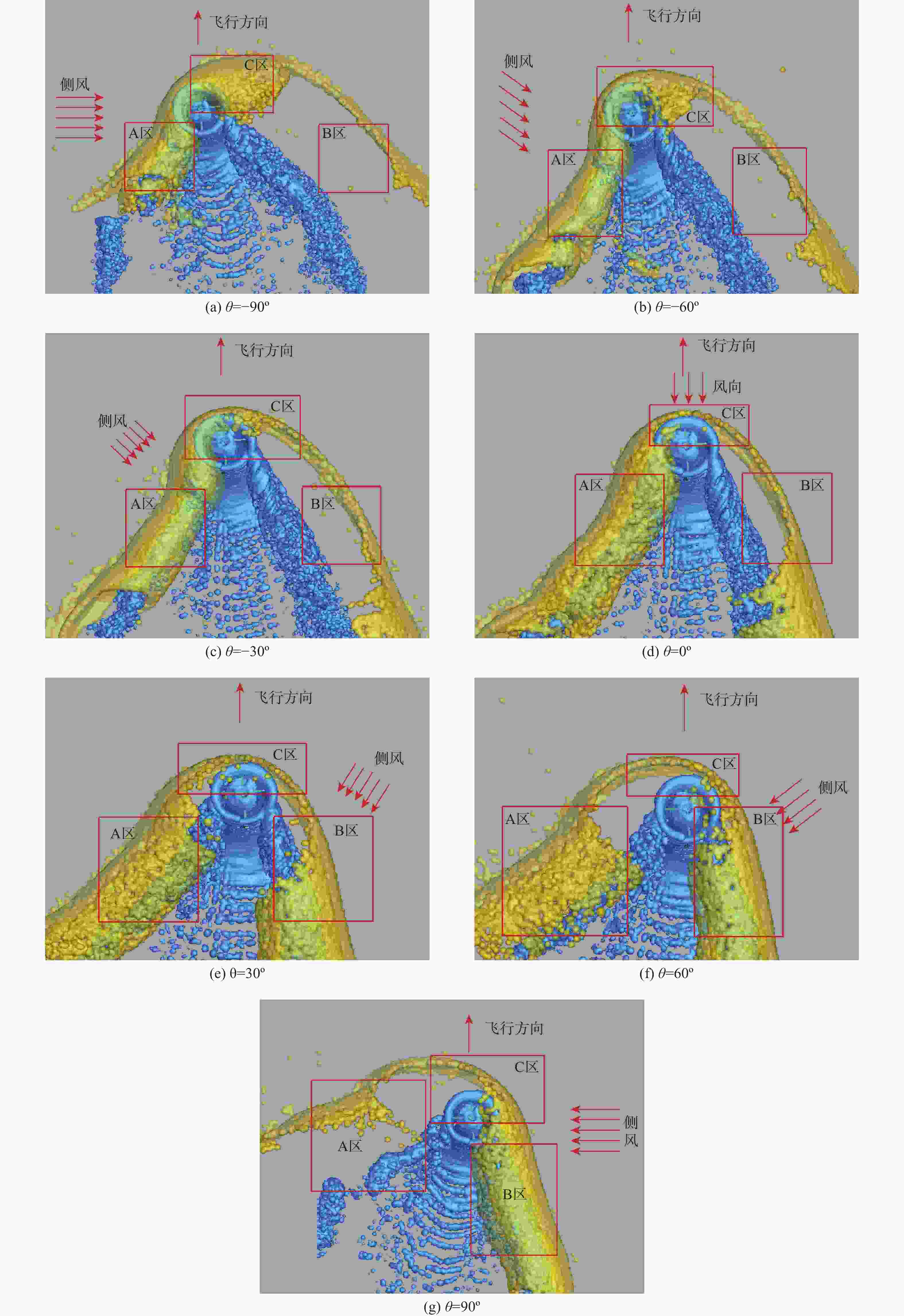
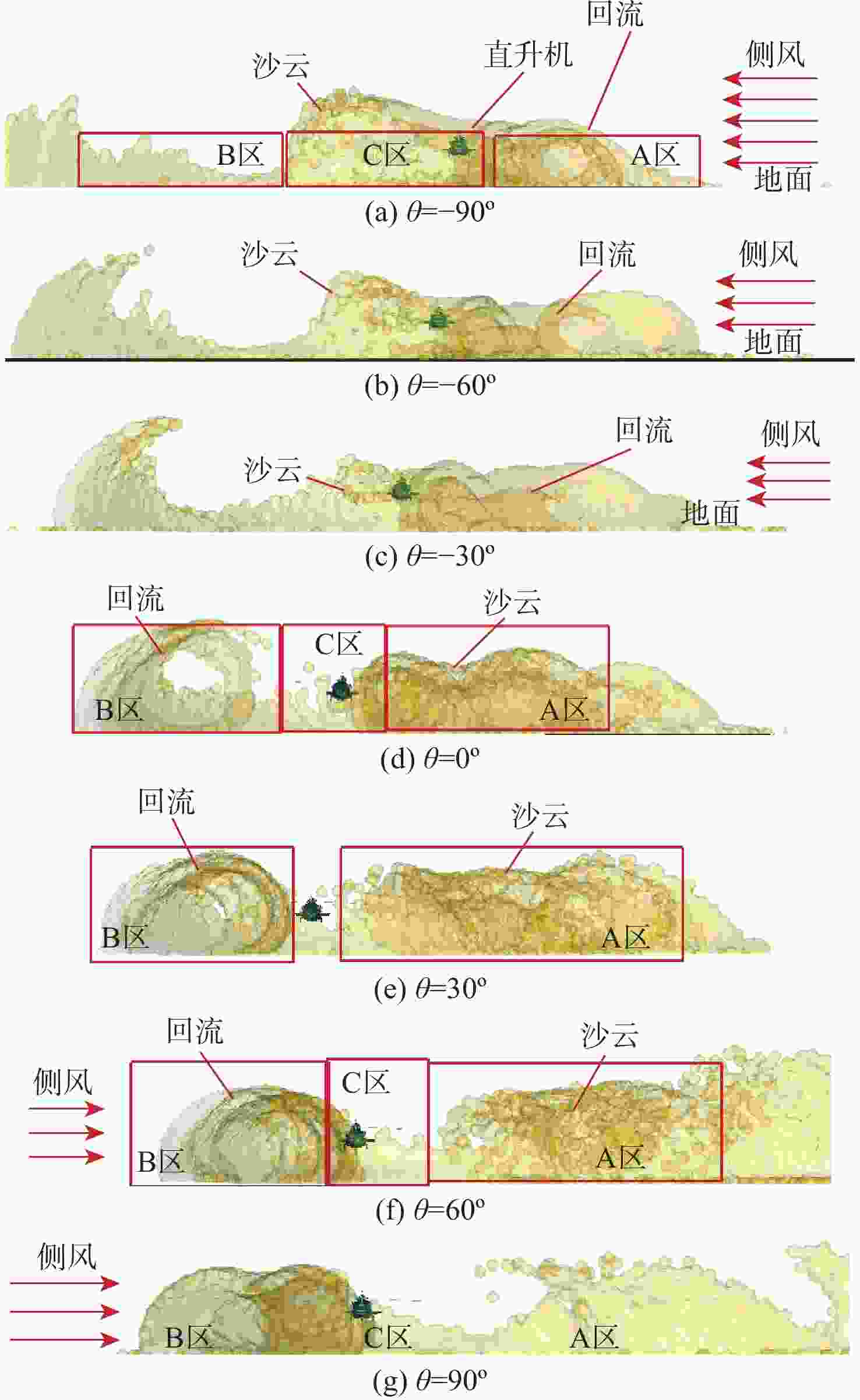
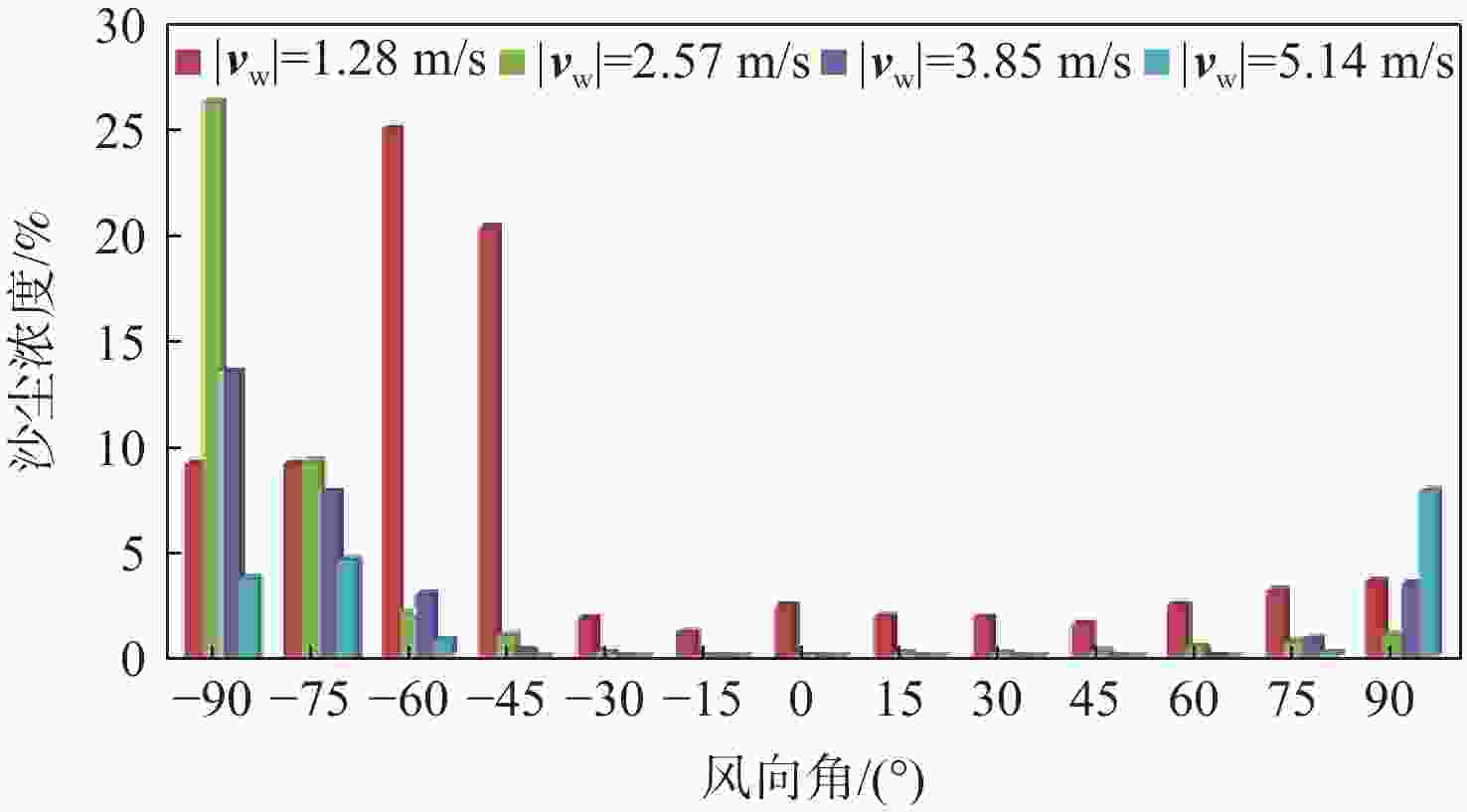
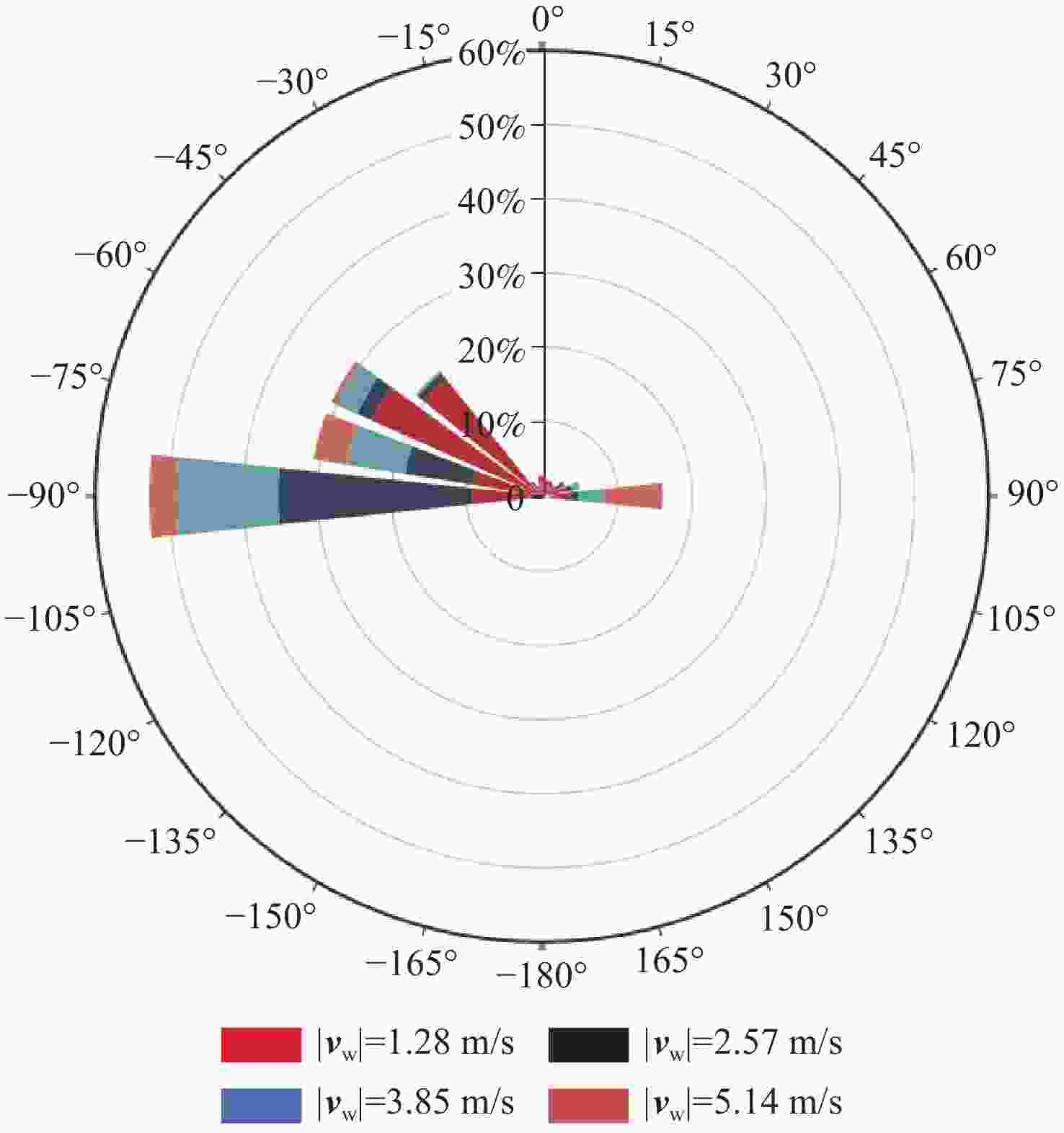
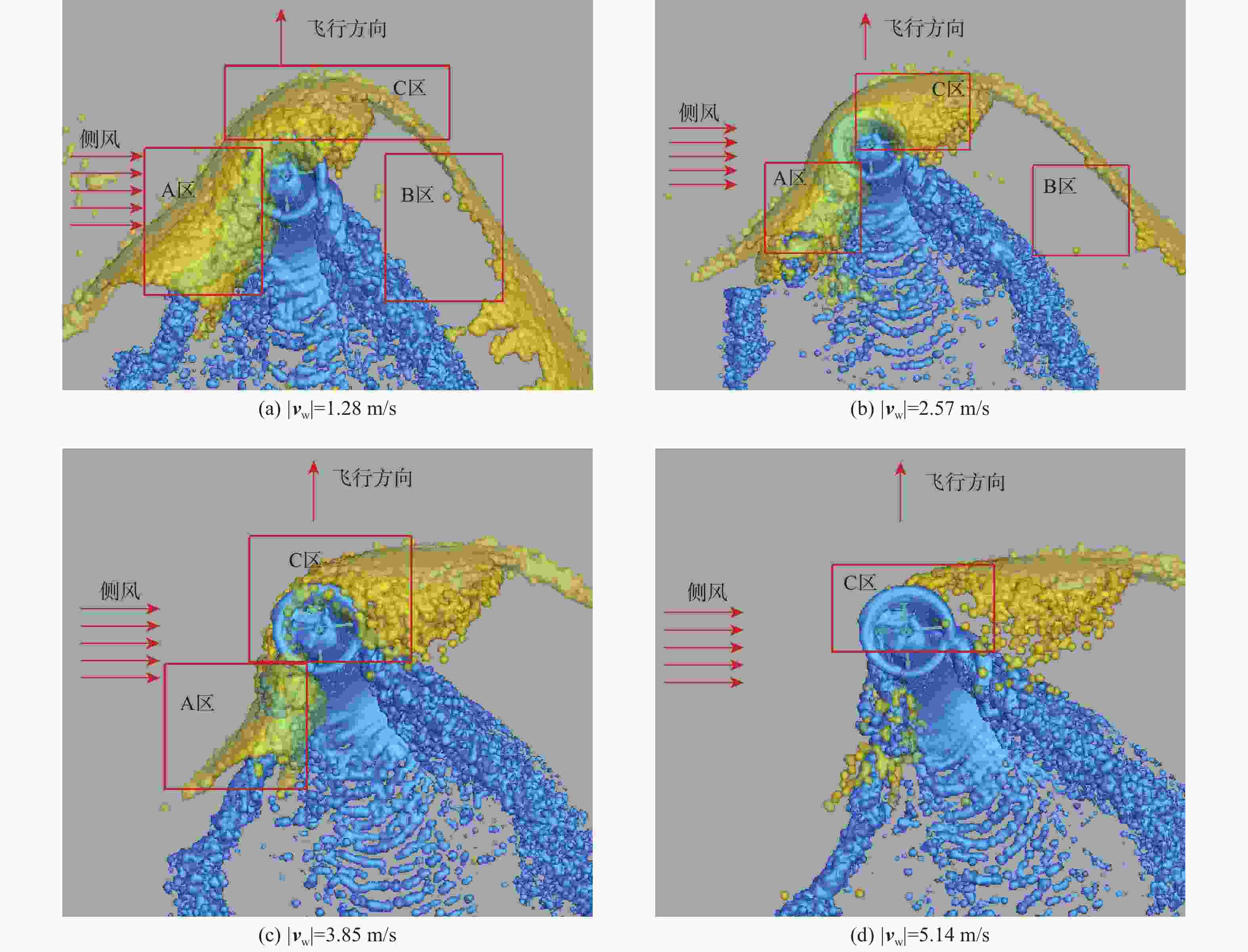
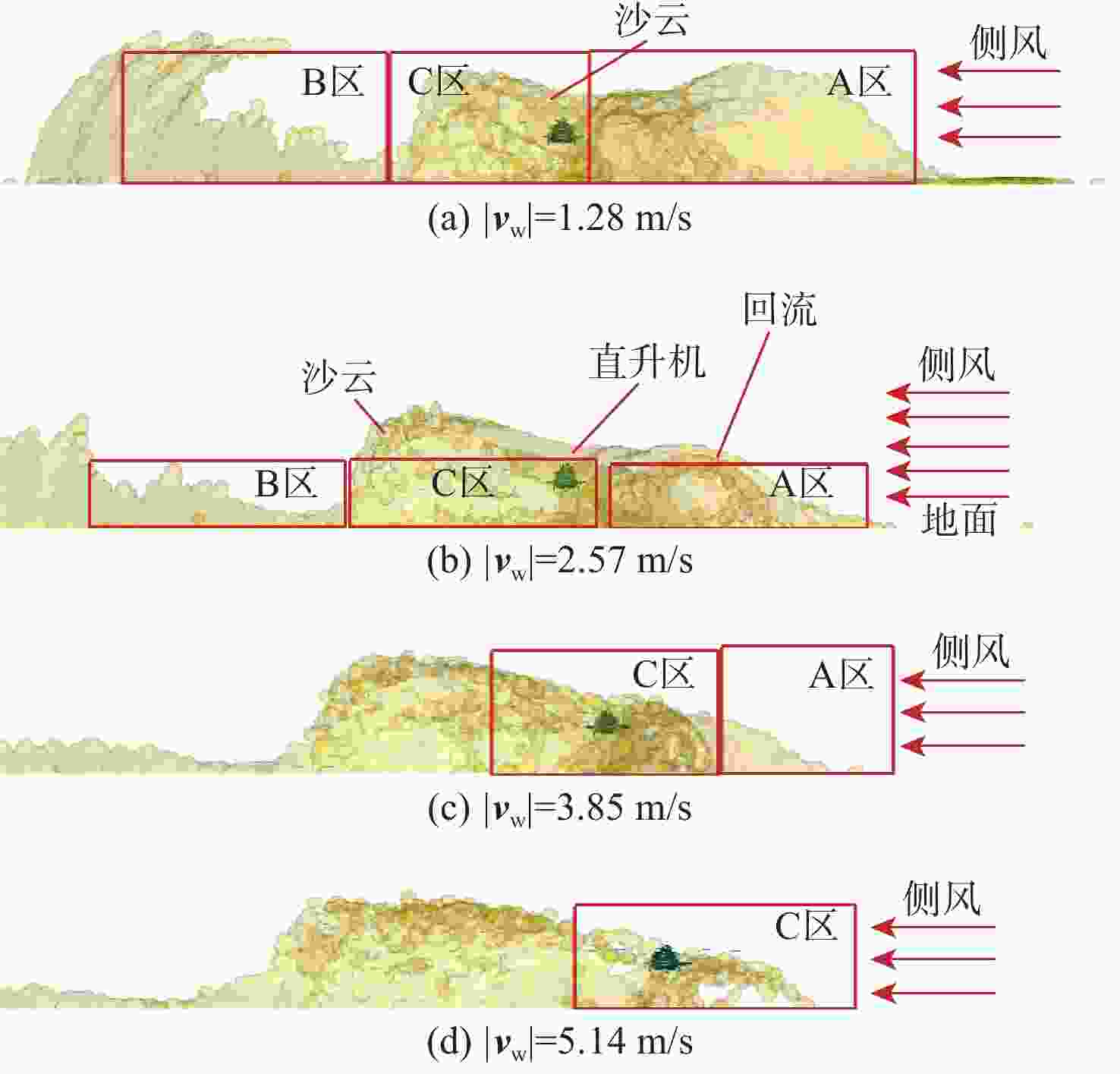
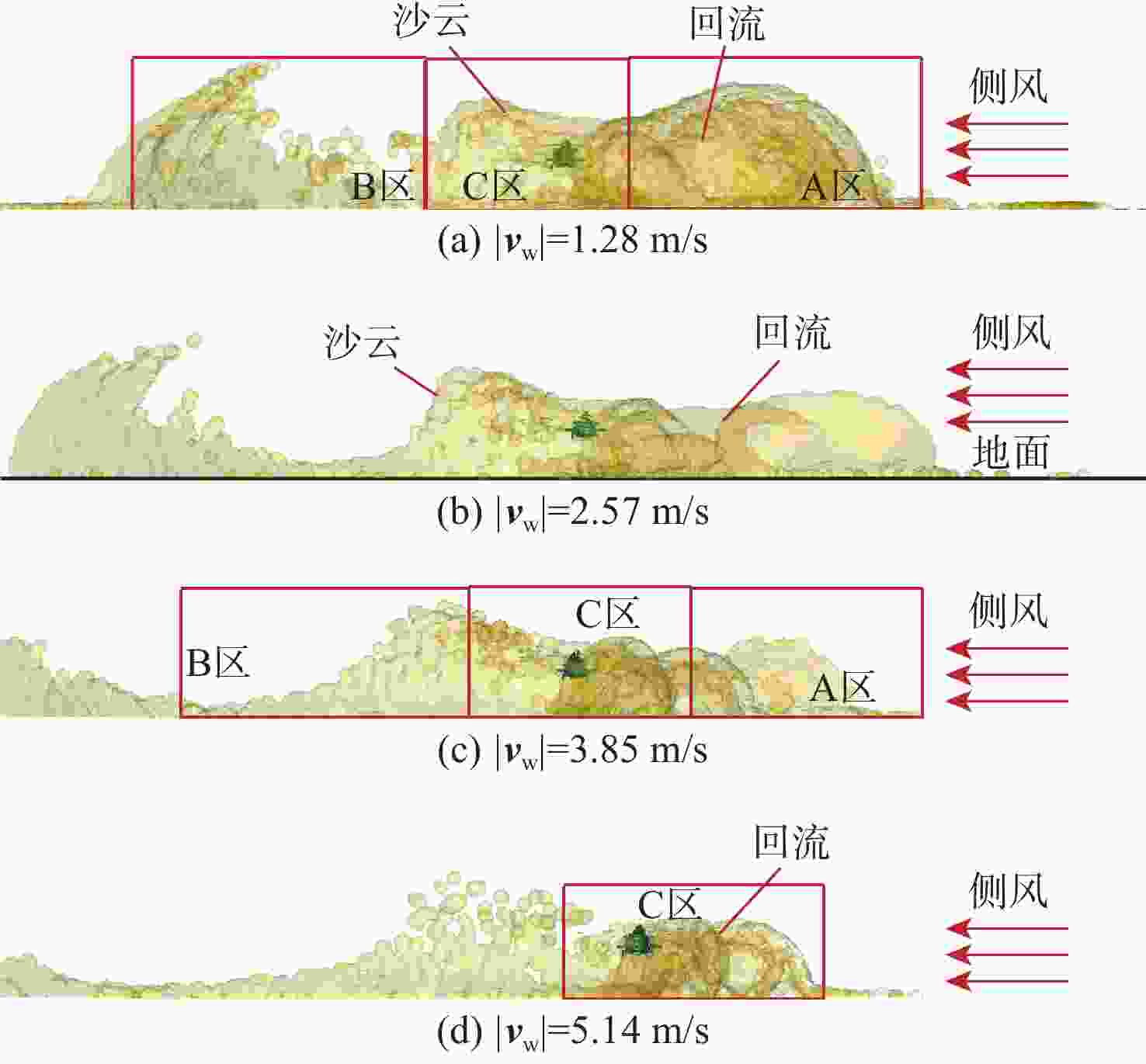
直升机旋翼与地面复杂干扰流场诱导沙床沙粒运动,形成沙盲现象,然而侧风改变旋翼与地面干扰流场,改变沙云形态和沙盲现象。因此,将侧风作用项嵌入基于黏性涡粒子的旋翼/地面气动干扰模型,体现侧风对旋翼与地面干扰流场的作用,并基于离散单元法的沙粒动力学模型,增加侧风引起的气动力,体现侧风对沙粒运动的作用。研究侧风对直升机前飞沙盲特性的影响,并分析侧风速度、风向对直升机沙盲特性的影响规律。结果表明:侧风对直升机沙盲沙云形态影响显著,且左侧风显著增强沙尘浓度,而迎风状态减小沙尘浓度;随着侧风速度的增加,左侧风状态下的沙尘浓度先增加后减小。
Abstract:The complex interaction flow between the helicopter rotor and ground induced the movement of sand particles in the sand bed and then yielded helicopter brownout. However, a crosswind will change the rotor-ground interaction flow field, and influence the brownout. Therefore, a crosswind is coupled into the helicopter rotor-ground aerodynamic model based on viscous vortex particles to consider the influence of the crosswind on the rotor-ground interaction flow field. In order to take into account how the crosswind affects sand movement, the air force caused by the crosswind is also incorporated to the sand particle dynamic model based on DEM. Then, the effect of the crosswind on the process of helicopter brownout at forward flight is analyzed, and the influences of velocity, and direction of the crosswind on the brownout are also investigated. Results show that the crosswind has a significant influence on the helicopter brownout, the density of dust cloud obviously increases with the crosswind at the port side, and it is restrained at forward flight. The density of the dust cloud firstly increases and then decreases with increasing the velocity of crosswind at the port side.
-
Key words:
- crosswind /
- brownout /
- rotor-ground aerodynamic interaction /
- discrete element method /
- helicopter
-
-
[1] SZOBOSZLAY Z, DAVIS B, FUJIZAWA B T, et al. Degraded visual environment mitigation (DVE-M) program, Yuma 2016 flight trials in brownout[C]//Proceedings of the AHS International 73rd Annual Forum&Technology Display. Alexandria: AHS, 2017: 1-20. [2] MILLER J, GODFROY-COOPER M, SZOBOSZLAY Z. Degraded visual environment mitigation (DVE-M) program, bumper RADAR obstacle cueing flight trials 2020[C]//Proceedings of the Vertical Flight Society’s 77th Annual Forum& Technology Display. Alexandria: AHS, 2021: 16747. [3] WACHSPRESS D A, WHITEHOUSE G R, KELLER J D, et al. A high fidelity brownout model for real-time flight simulations and trainers[C]//Proceedings of the American Helicopter Society 65th Annual Forum. Alexandria: AHS, 2009: 1281-1304. [4] WHITEHOUSE G R, WACHSPRESS D A, QUACKENBUSH T R, et al. Exploring aerodynamic methods for mitigating brownout[C]//Proceedings of the American Helicopter Society 65th Annual Forum. Alexandria: AHS, 2009: 349-364. [5] JOHNSON B, LEISHMAN J G, SYDNEY A. Investigation of sediment entrainment using dual-phase, high-speed particle image velocimetry[J]. Journal of the American Helicopter Society, 2010, 55(4): 1-16. [6] SYDNEY A, LEISHMAN J G. Measurements of rotor/airframe interactions in ground effect over a sediment bed[J]. Annual Forum Proceedings - AHS International, 2013, 3: 1812-1836. [7] WONG O D, TANNER P E. Photogrammetric measurements of an EH-60L brownout cloud[J]. Journal of the American Helicopter Society, 2016, 61(1): 1-10. [8] RYERSON C, HAEHNEL R, KOENIG G, et al. Visibility enhancement in rotorwash clouds[C]//Proceedings of the 43rd AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit. Reston: AIAA, 2005: 263. [9] HAEHNEL R B, MOULTON M A, WENREN W, et al. A model to simulate rotorcraft-induced brownout[C]//Proceedings of the 64th Annual Forum of the American Helicopter Society. Alexandria: AHS, 2008: 589-601. [10] THOMAS S, LAKSHMINARAYAN V K, KALRA T S, et al. Eulerian-Lagrangian analysis of cloud evolution using CFD coupled with a sediment tracking algorithm[J]. Annual Forum Proceedings - AHS International, 2011, 1: 298-315. [11] THOMAS S, AMIRAUS M, BAEDER J. GPU-accelerated FVM-RANS hybrid solver for simulating two-phase flow beneath a hovering rotor[C]//Proceedings of the 69th Annual Forum of the American Helicopter Society. Alexandria: AHS, 2013: 2462-2484. [12] KUTZ B M, GUNTHER T, RUMPF A, et al. Numerical examination of a model rotor in brownout conditions[C]//Proceedings of the 70th Annual Forum of the American Helicopter Society. Montreal: Engineering, 2014: 2450-2461. [13] 胡健平, 徐国华, 史勇杰, 等. 基于CFD-DEM耦合数值模拟的全尺寸直升机沙盲形成机理[J]. 航空学报, 2020, 41(3): 123363.HU J P, XU G H, SHI Y J, et al. Formation mechanism of brownout in full-scale helicopter based on CFD-DEM couplings numerical simulation[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2020, 41(3): 123363 (in Chinese). [14] GOVINDARAJAN B M, LEISHMAN J G. Predictions of rotor and rotor/airframe configurational effects on brownout dust clouds[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 2016, 53(2): 545-560. doi: 10.2514/1.C033447 [15] 谭剑锋, 何龙, 于领军, 等. 基于黏性涡粒子/沙粒DEM的直升机沙盲建模[J]. 航空学报, 2022, 43(8): 125536. doi: 10.7527/j.issn.1000-6893.2022.8.hkxb202208025TAN J F, HE L, YU L J, et al. Helicopter brownout modeling based on viscous vortex particle and sand particle DEM[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2022, 43(8): 125536 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7527/j.issn.1000-6893.2022.8.hkxb202208025 [16] 谭剑锋, 韩水, 王畅, 等. 基于DEM的直升机沙盲加速计算方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2023, 49(6): 1352-1361.TAN J F, HAN S, WANG C, et al. Accelerated computational method of helicopter brownout based on DEM[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2023, 49(6): 1352-1361 (in Chinese). [17] TAN J, GAO J W, BARAKOS G, et al. Novel approach to helicopter brownout based on vortex and discrete element methods[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2021, 116: 106839. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2021.106839 [18] TAN J F, YON T, HE L, et al. Accelerated method of helicopter brownout with particle-particle collisions[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2022, 124: 107511. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2022.107511 [19] 谭剑锋, 周天熠, 王畅, 等. 旋翼地面效应的气动建模与特性[J]. 航空学报, 2019, 40(6): 122602.TAN J F, ZHOU T Y, WANG C, et al. Aerodynamic model and characteristics of rotor in ground effect[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2019, 40(6): 122602 (in Chinese). -






 下载:
下载: