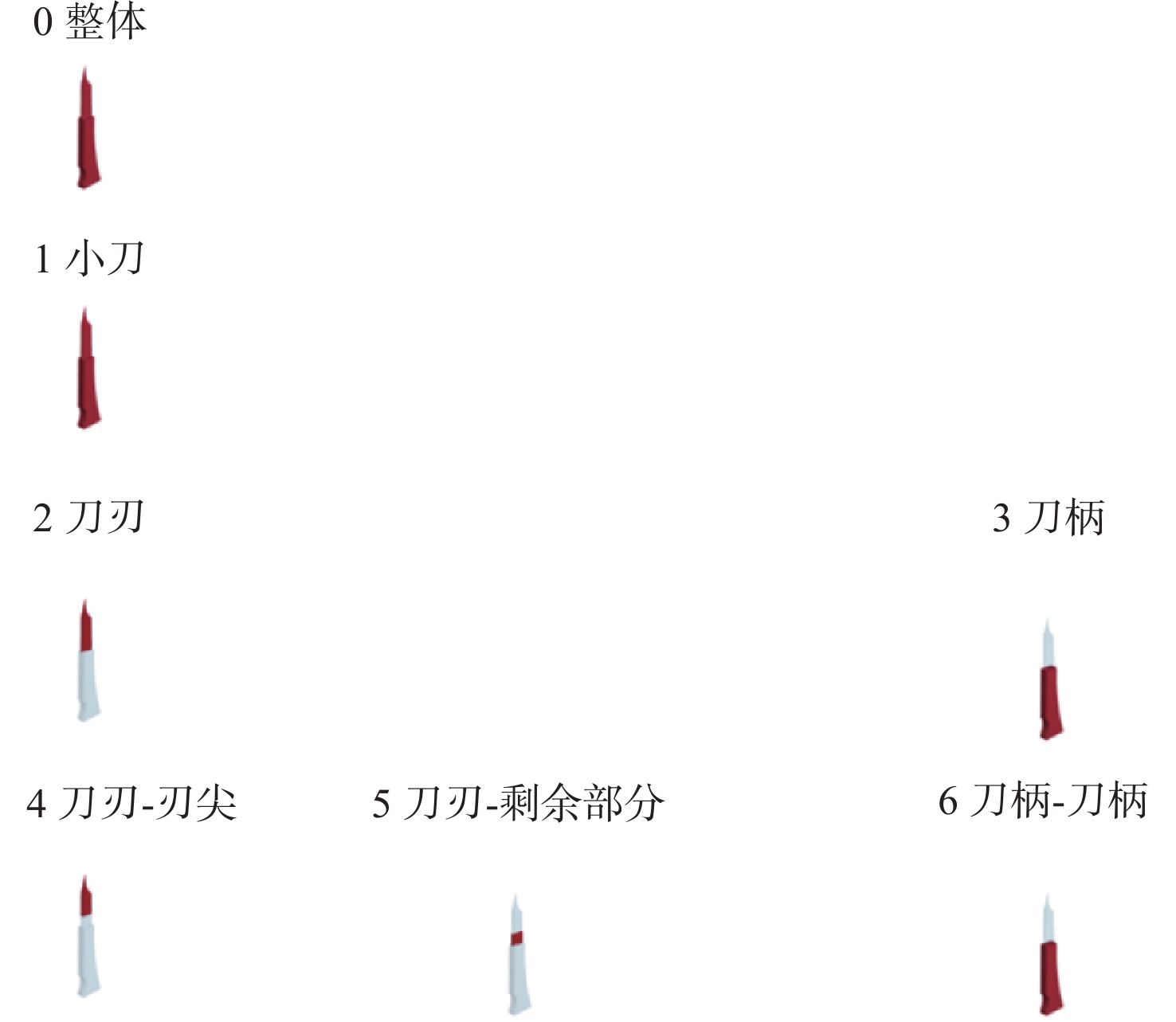
Semantic part based single-view implicit field for 3D shape reconstruction technology
-
摘要:
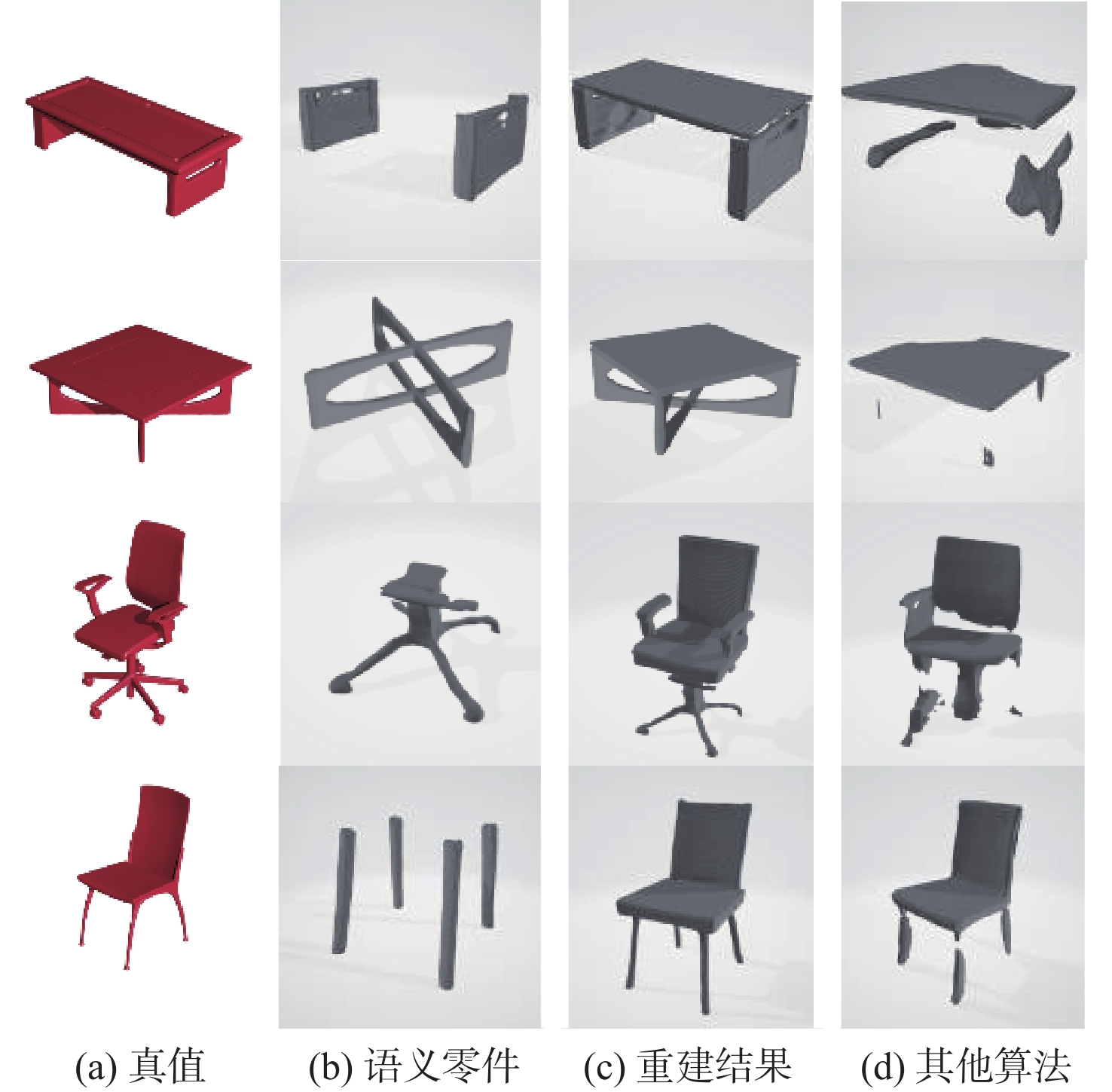
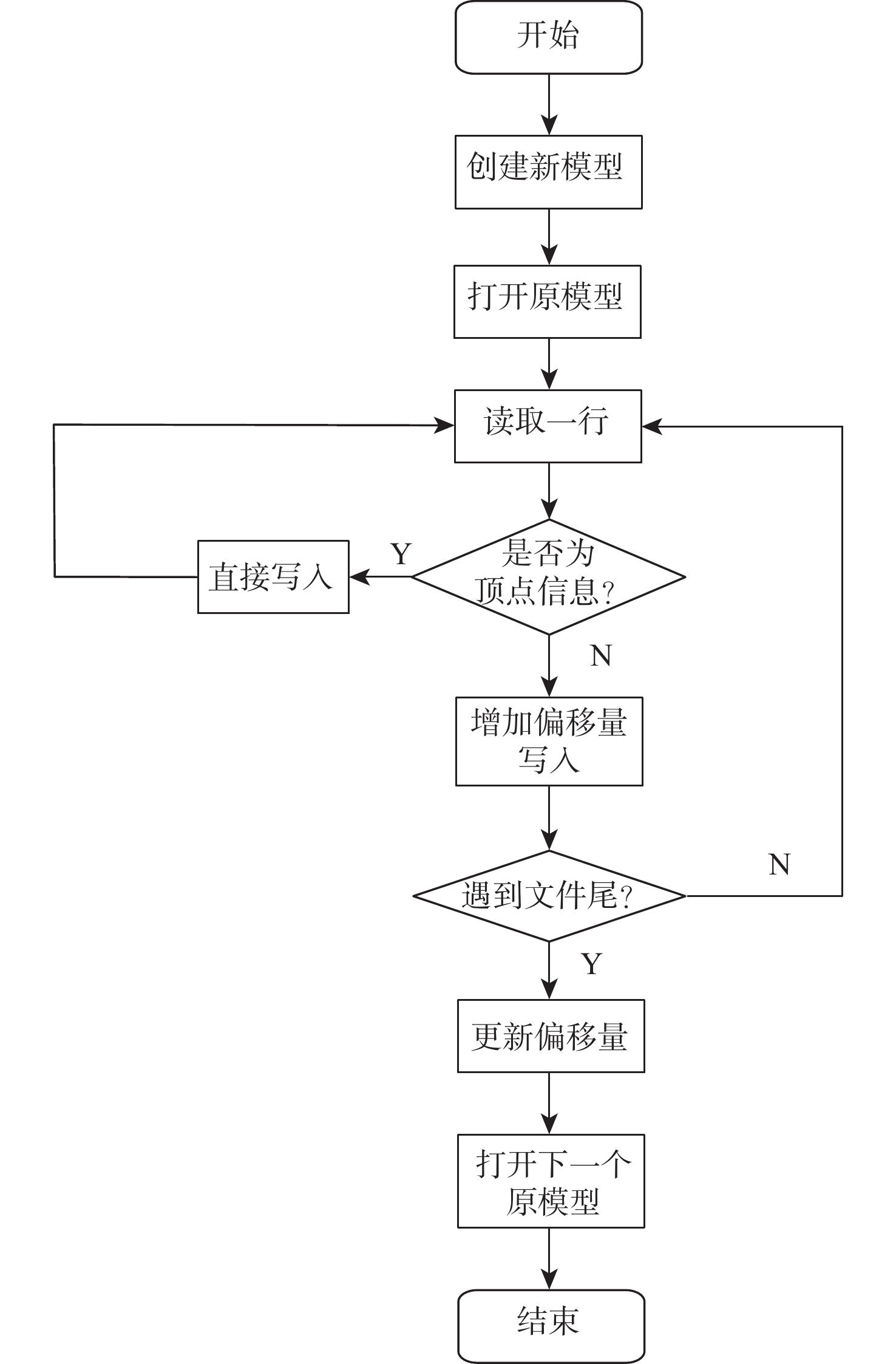
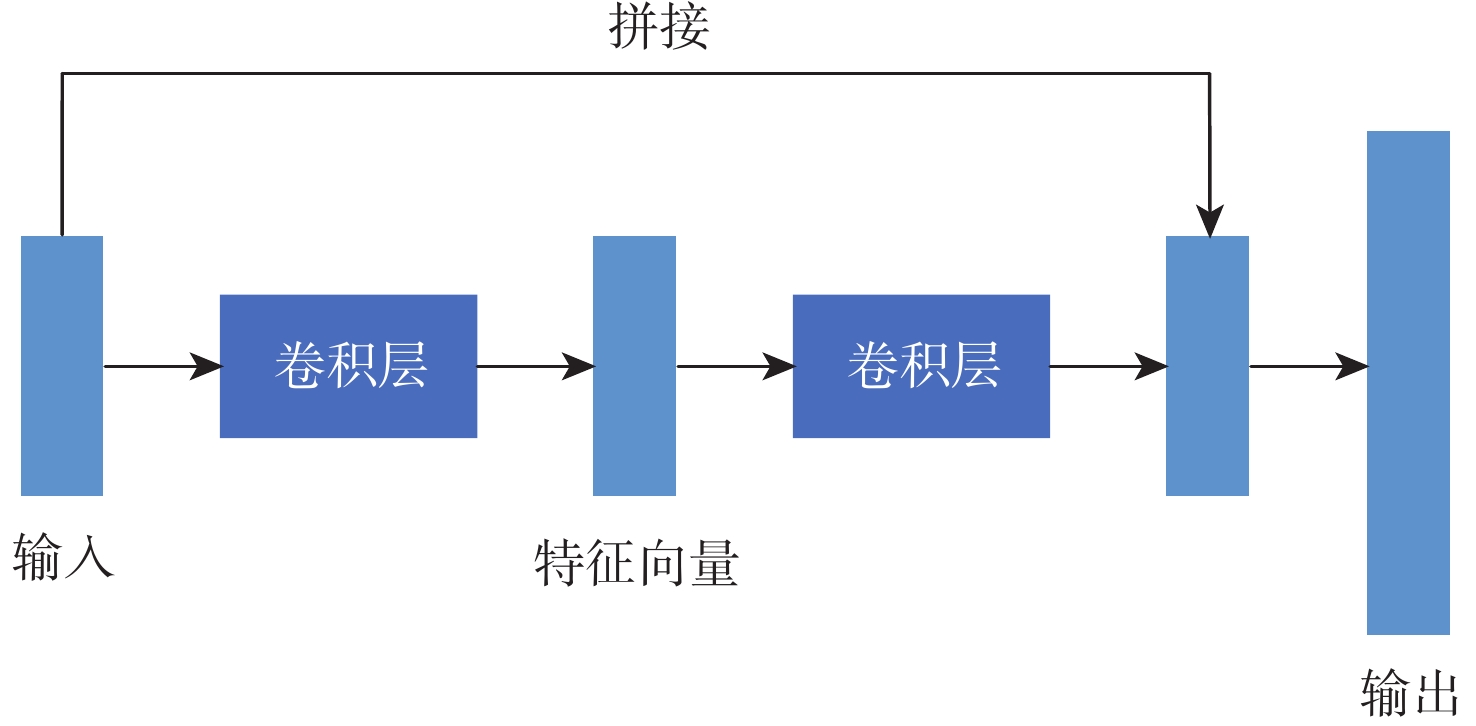
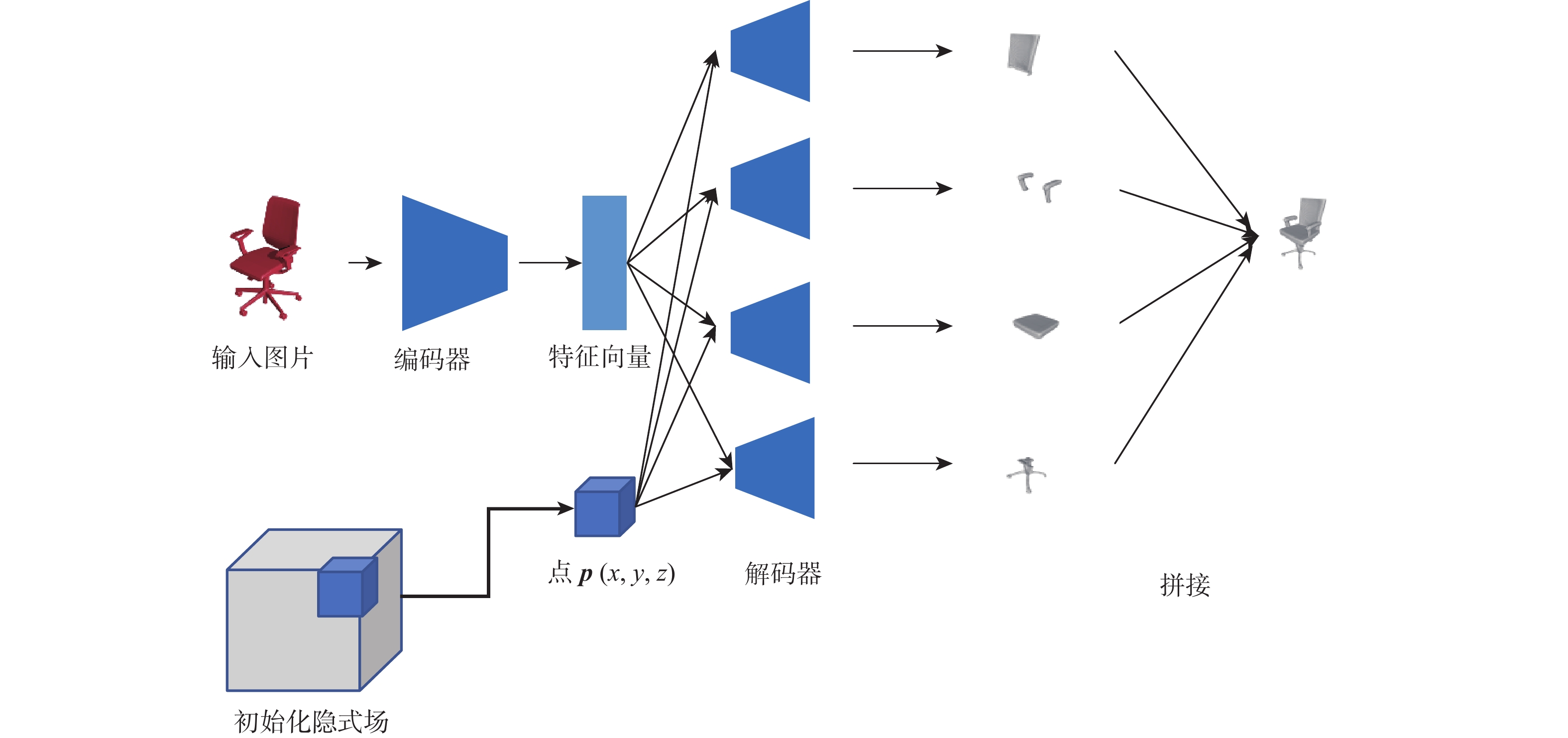
随着对深度学习的深入研究,基于隐式场的三维重建技术成为三维领域的研究热点,隐式场重建相比于显式重建得到了更好的重建结果,但仍存在缺少语义信息、重建结果缺失局部特征等缺点。针对现有的隐式场重建中存在的语义信息缺失问题,对隐式场重建算法提出改进,相比于直接由隐式解码器恢复出整体模型,改进方法选择先重建模型的各个语义零件,再将各个零件进行拼接得到整体模型,进而提高隐式场三维重建的完整度。基于改进方法,提出基于语义关系的多分支隐式重建网络,并在多个国际通用三维模型数据集中与现有隐式场重建算法在5个类别的模型上利用多项评价指标进行定量测试,取得了优于当前隐式场重建算法的重建结果。
Abstract:With the development of deep learning techniques, learning implicit field for 3D shape reconstruction has become a heated topic, because implicit field can help networks learn a reasonable and sophisticated reconstruction model than explicit methods. However, there are still some challenges to be solved including lacking semantic information, local detail incompletions and so on. Thus, rather than recreating the entire model from a decoder directly, we first reconstruct the semantic components of a single model using an implicit filed structure based on semantic sections in our paper. Then we aggregate the reconstructed semantic parts together to get the final model. Finally, we test those results on the public 3D shape dataset PartNet and compare them to other cutting-edge single-view reconstruction approaches. It’s obvious that using a semantic part-based implicit field can learn more reasonable shape representations for reconstruction.
-
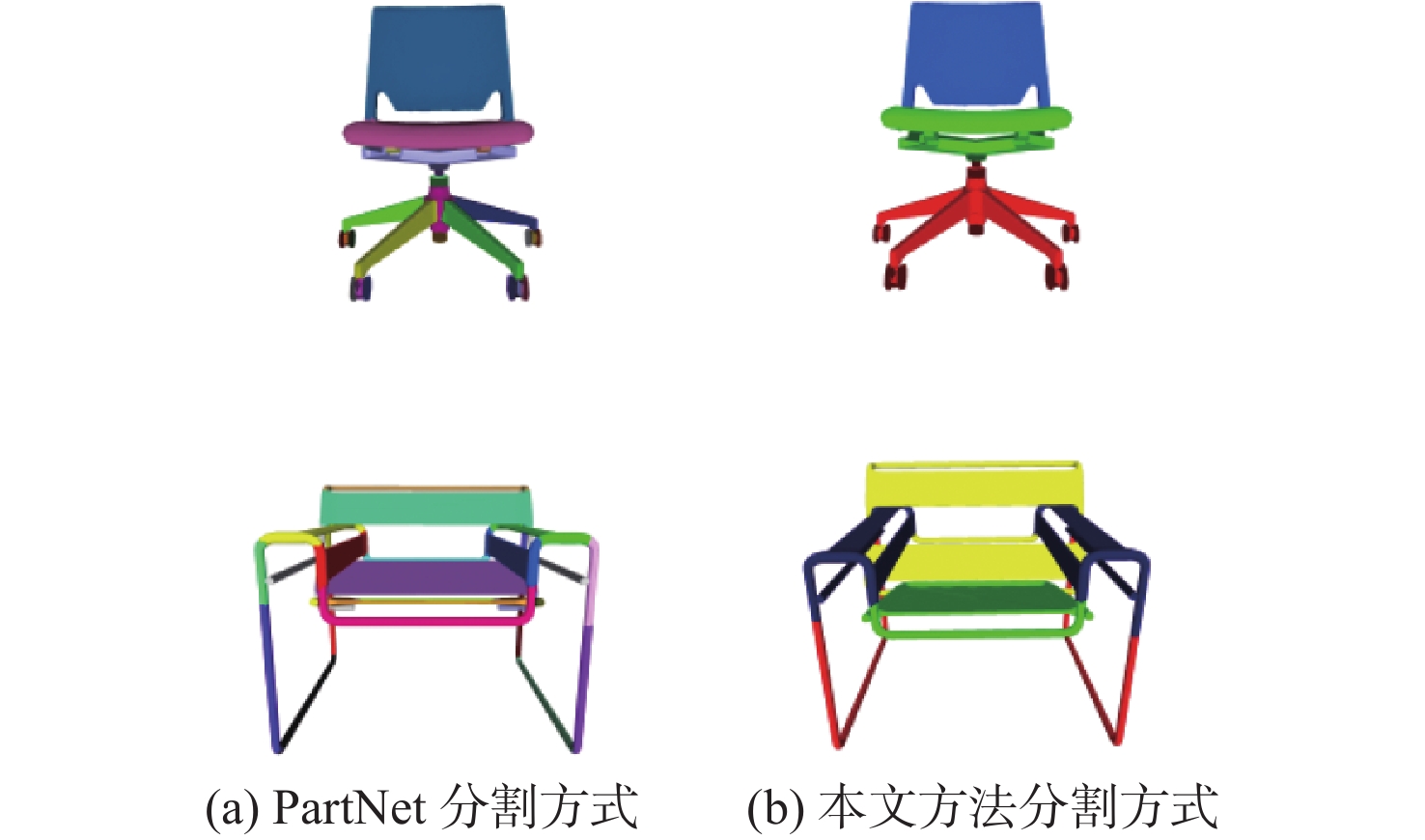
表 1 语义分割后模型平均零件数量
Table 1. Average number of parts in the model after segmentation
模型类别 PartNet 本文方法 椅子 18.33 3.36 桌子 5.24 2 台灯 11.35 2 水槽 13.02 2.66 储物柜 9.51 2 表 2 重建交并比结果
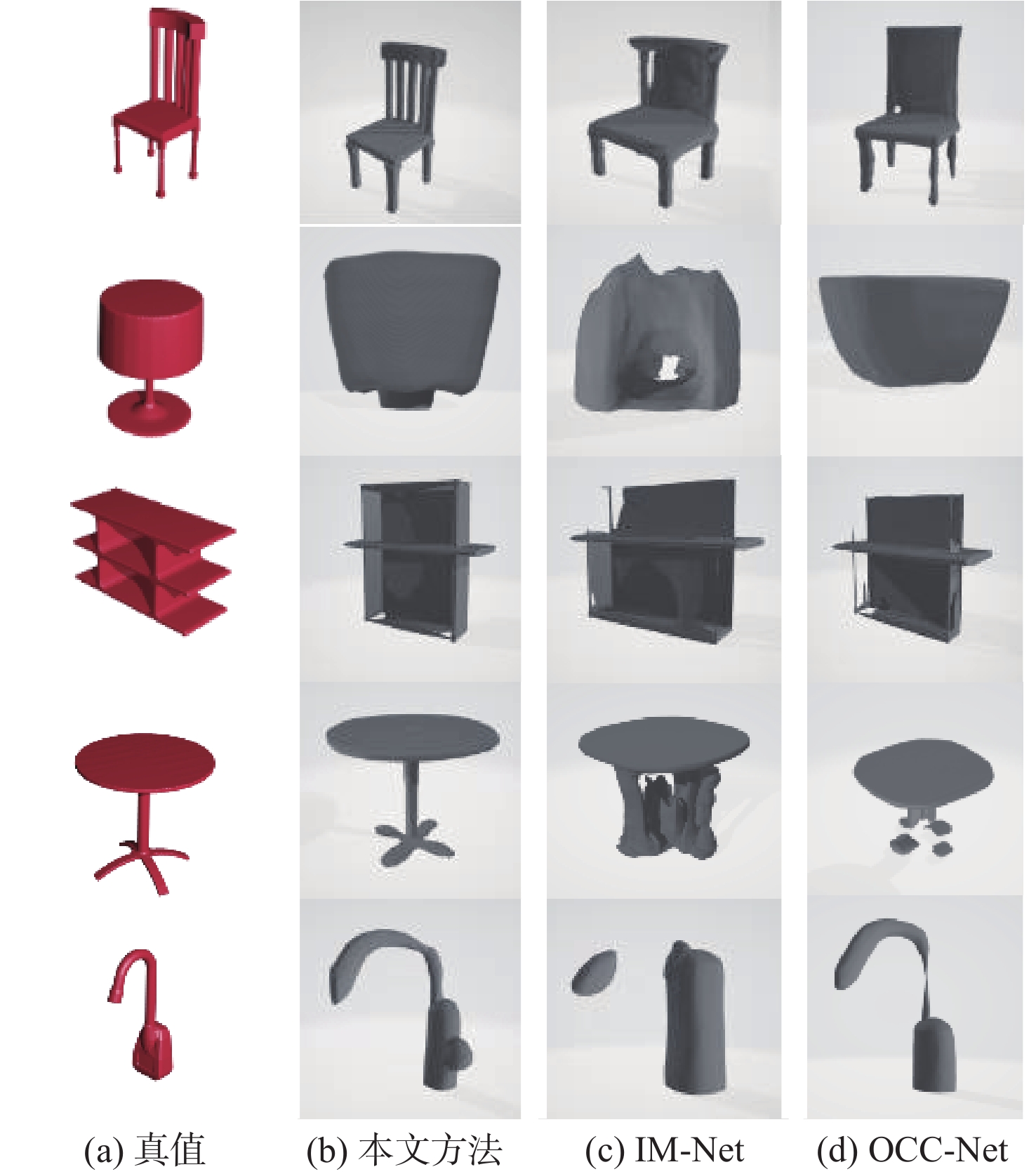
Table 2. Result of IoU
模型类别 IM-Net 本文方法 OCC-Net 椅子 41.57 46.56 42.05 桌子 58.71 62.37 59.15 台灯 38.33 39.12 39.10 水槽 37.17 39.15 34.98 储物柜 46.16 48.23 45.88 表 3 重建钱伯距离结果
Table 3. Result of rebuilding CD
模型类别 IM-Net 本文方法 OCC-Net 椅子 0.973 0.968 0.981 桌子 0.835 0.788 0.812 台灯 1.150 1.095 1.152 水槽 1.205 1.135 1.213 储物柜 1.011 0.983 1.001 表 4 重建时间及显存消耗
Table 4. Rebuild time and memory comparison
算法名称 重建时间/s 显存开销/GB 本文方法 10.3 2.9 IM-Net 5.6 3.2 OCC-Net 6.2 3.5 -
[1] LI M Y, ZHANG H. D2IM-Net: Learning detail disentangled implicit fields from single images[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 10241-10250. [2] PARK J J, FLORENCE P, STRAUB J, et al. DeepSDF: learning continuous signed distance functions for shape representation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 165-174. [3] HORN B K P. Shape from shading: a method for obtaining the shape of a smooth opaque object from one view[M]. America: Project on Mathematics and Computation, 1970: 4-5. [4] 包晓敏, 白晨. 单目三维重建技术综述[J]. 智能计算机与应用, 2020, 10(7): 49-52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2163.2020.07.011BAO X M, BAI C. Overview of monocular 3D reconstruction techniques[J]. Intelligent Computer and Applications, 2020, 10(7): 49-52(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2163.2020.07.011 [5] GENG J. Structured-light 3D surface imaging: a tutorial[J]. Advances in Optics and Photonics, 2011, 3(2): 128-160. doi: 10.1364/AOP.3.000128 [6] 陈荣, 许宏丽, 杨东学, 等. 一种基于空间编码结构光的稠密三维重建算法[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报, 2021, 48(6): 123-130.CHEN R, XU H L, YANG D X, et al. A dense 3D reconstruction algorithm based on spatially encoded structured light[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 2021, 48(6): 123-130(in Chinese). [7] SNAVELY N, SEITZ S M, SZELISKI R. Photo tourism: exploring photo collections in 3D[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2006, 25(3): 835-846. doi: 10.1145/1141911.1141964 [8] LOWE D G. Object recognition from local scale-invariant features[C]//Proceedings of the Seventh IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2002: 1150-1157. [9] CHOY C B, XU D F, GWAK J, et al. 3D-R2N2: a unified approach for single and multi-view 3D object reconstruction[M]//Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Berlin: Springer International Publishing, 2016: 628-644. [10] SIMONYAN K, ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[EB/OL]. (2015-04-10)[2023-01-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.1556. [11] WU J, ZHANG C, XUE T, et al. Learning a probabilistic latent space of object shapes via 3d generative-adversarial modeling[C]//Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New York: MIT Press, 2016: 82-90. [12] XIE H Z, YAO H X, SUN X S, et al. Pix2Vox: context-aware 3D reconstruction from single and multi-view images[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 2690-2698. [13] WU J, WANG Y, XUE T, et al. Marrnet: 3D shape reconstruction via 2.5 d sketches[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New York: MIT Press, 2017: 171-190. [14] WANG H Q, YANG J L, LIANG W, et al. Deep single-view 3D object reconstruction with visual hull embedding[J]. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2019, 33(1): 8941-8948. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v33i01.33018941 [15] PONTES J K, KONG C, SRIDHARAN S, et al. Image2Mesh: a learning framework for single image 3D reconstruction[M]//Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Berlin: Springer International Publishing, 2019: 365-381. [16] JACK D, PONTES J K, SRIDHARAN S, et al. Learning free-form deformations for 3D object reconstruction[M]//Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Berlin: Springer International Publishing, 2019: 317-333. [17] LI K J, PHAM T, ZHAN H Y, et al. Efficient dense point cloud object reconstruction using deformation vector fields[M]//Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Berlin: Springer International Publishing, 2018: 508-524. [18] KONG C, LIN C H, LUCEY S. Using locally corresponding CAD models for dense 3D reconstructions from a single image[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 5603-5611. [19] GROUEIX T, FISHER M, KIM V G, et al. A papier-Mache approach to learning 3D surface generation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 216-224. [20] CHEN Z Q, ZHANG H. Learning implicit fields for generative shape modeling[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 5932-5941. [21] MESCHEDER L, OECHSLE M, NIEMEYER M, et al. Occupancy networks: learning 3D reconstruction in function space[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 4455-4465. [22] WANG T C, LIU M Y, ZHU J Y, et al. High-resolution image synthesis and semantic manipulation with conditional GANs[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 8798-8807. [23] BECHTOLD J, TATARCHENKO M, FISCHER V, et al. Fostering generalization in single-view 3D reconstruction by learning a hierarchy of local and global shape priors[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 15875-15884. [24] MO K C, ZHU S L, CHANG A X, et al. PartNet: a large-scale benchmark for fine-grained and hierarchical part-level 3D object understanding[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 909-918. -







 下载:
下载: