Extensible evaluation model of aircraft tire hydroplaning risk based on connection cloud
-
摘要:
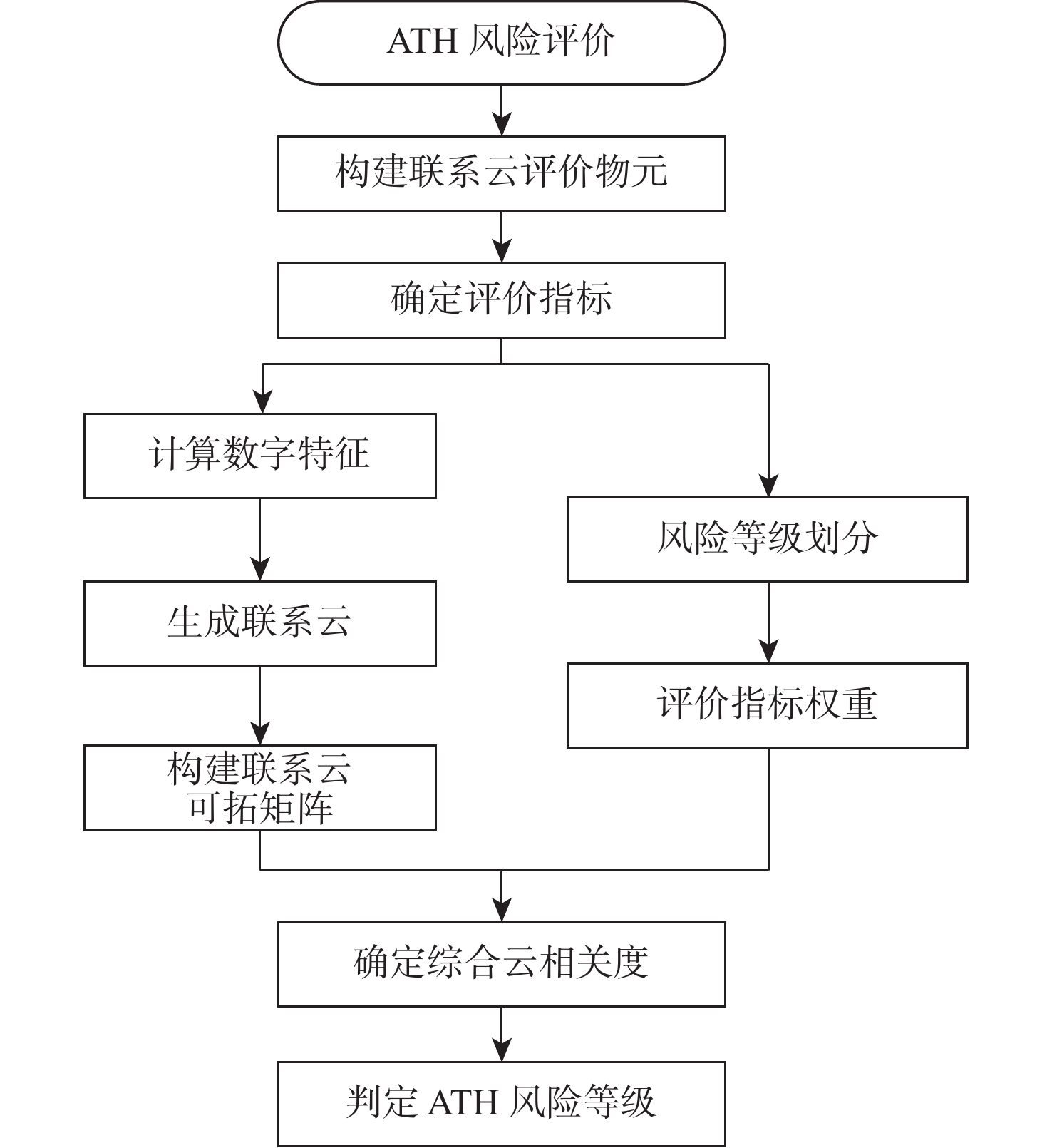
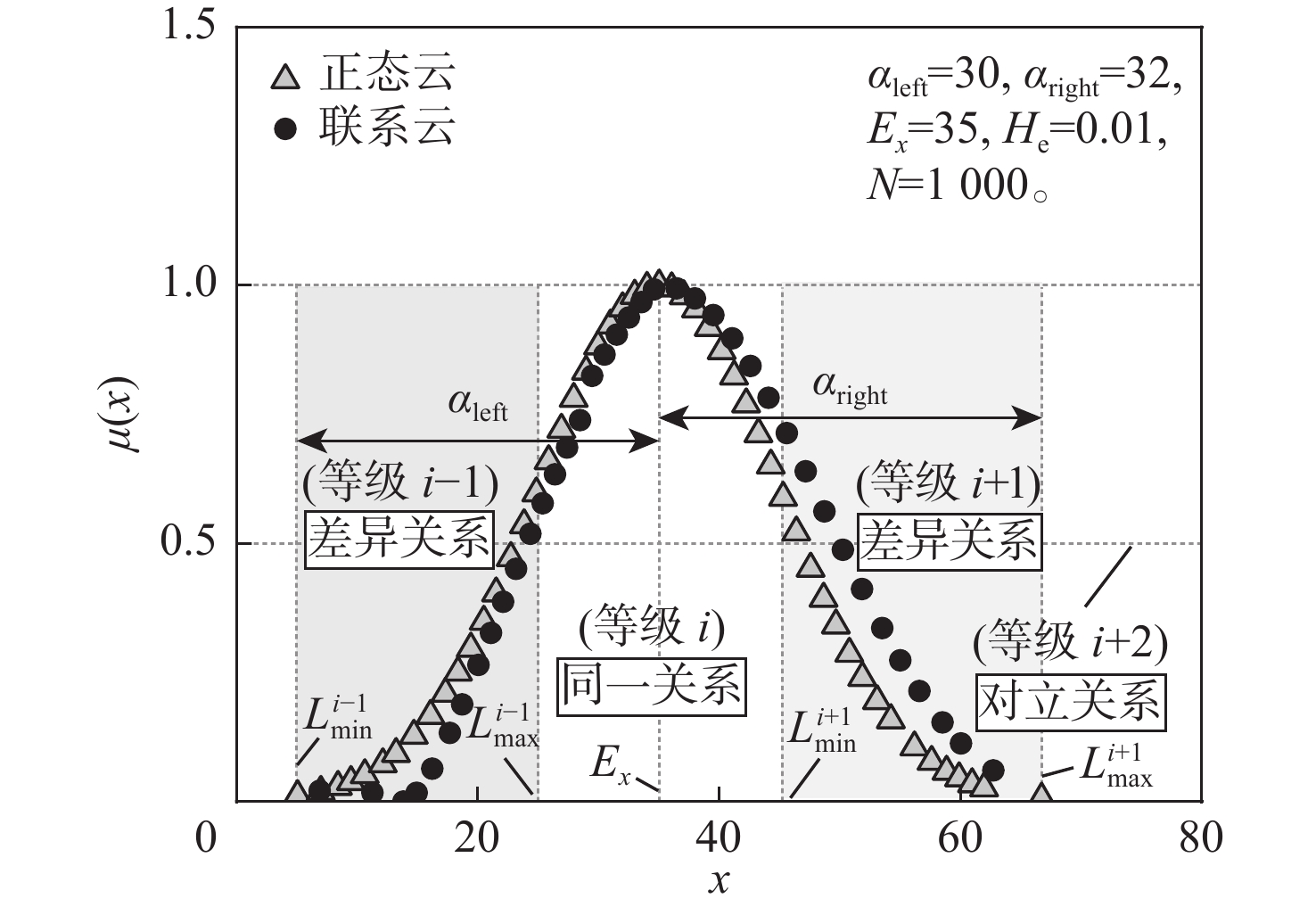
针对飞机轮胎滑水问题影响因素多、评价指标具备随机模糊与离散性特征问题,基于联系云可拓理论建立滑水风险评价模型,定量描述滑水评价指标在不同分类等级之间的转换态势。根据评价指标分级标准确定联系云数字特征,生成有限区间内联系云,由云相关度构建联系云可拓矩阵,结合变权权重综合评定最终风险等级,表征待评价物元与风险等级之间的动态联系;依托飞机轮胎滑水流固耦合仿真获得案例分析数据,弥补经典滑水试验工况变量条件少的不足。分析结果表明:传统正态云模型与可拓联系云模型对滑水事件样本1和样本3评价结论一致;对于样本2,由所提方法计算滑水风险等级为Ⅲ级,同等参数条件下风险控制标准更严格,上述样本风险评价置信因子均小于0.01,评价可信程度较高;所提分析模型为多重不相容指标的随机模糊及不确定性分析提供了可能,克服了正态云模型无法有效模拟指标在有限区间内分布的缺陷。
Abstract:Since aircraft tire hydroplaning can be influenced by several factors, and the characteristic of evaluation indexes can be described as fuzzy, random, and discrete, a hydroplaning risk evaluation model based on extension theory and connection cloud was established, so as to quantify the transformation of hydroplaning evaluation indexes among different classification levels. The numerical characteristics of the connection cloud were calculated according to the leveling criteria of evaluation indexes, and the connection cloud within a limited range was generated. The extensible matrix of the connection cloud was built by using certainty degrees. In this way, the final risk level could be obtained on the basis of variable weights, which demonstrated the dynamic connection between elements to be evaluated and risk level. The case analysis data was obtained by the fluid-solid coupling simulation of aircraft tire hydroplaning to make up for the lack of variable conditions in the classic hydroplaning test. The analysis results show that the evaluation conclusions of sample 1 and sample 3 are consistent based on the traditional normal cloud model and extensible connection cloud model. The hydroplaning risk level of sample 2 is given as Ⅲ by using the proposed model in this paper. Therefore, the risk control is considered more restrict under the same parameter condition. The confidence factor of the above sample risk assessment is less than 0.01, and the credibility of the evaluation results is high. The proposed model in this paper provides an alternative method for random-fuzzy and uncertainty analysis involving multiple incompatibility indexes. Hence, the defect of the normal cloud model in simulating the distribution of evaluation indexes within a limited range can be overcome.
-
Key words:
- tire hydroplaning /
- connection cloud /
- extension theory /
- fluid-solid coupling /
- risk evaluation
-
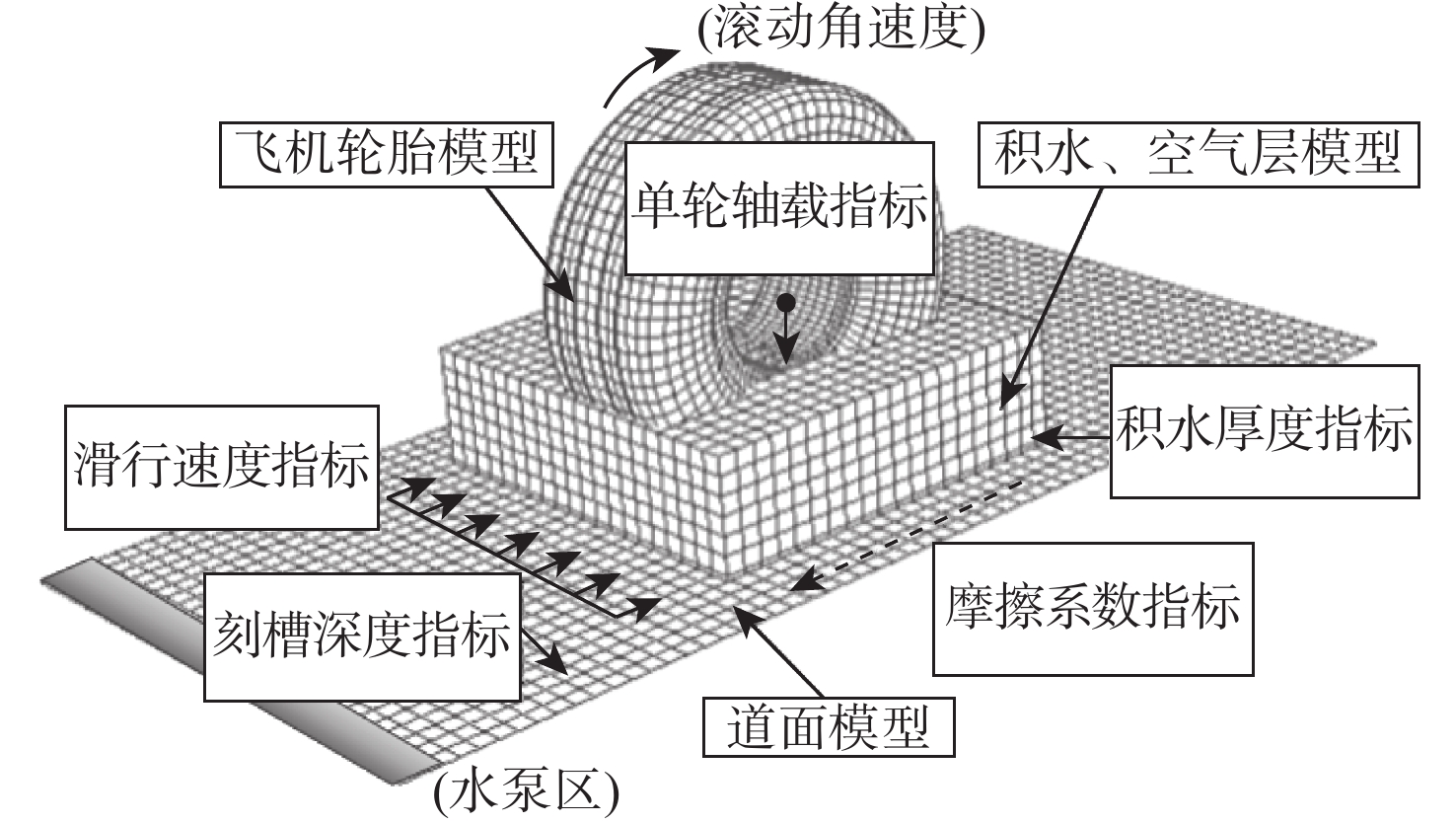
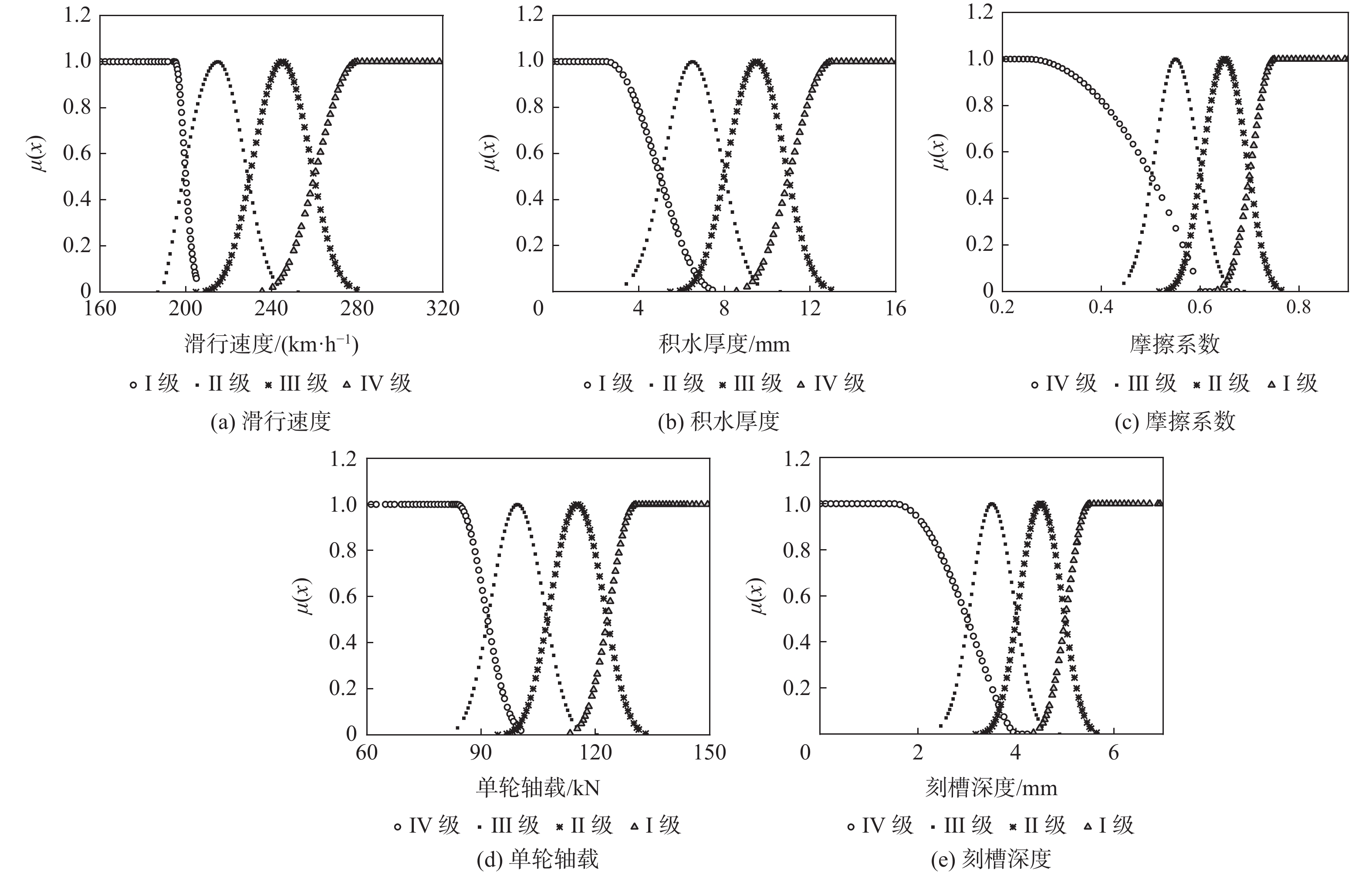
表 1 ATH风险等级评价指标分类标准
Table 1. Classification standards of evaluation indexes for ATH risk grades
风险
等级滑行速度/
(km∙h−1)积水厚度/
mm摩擦
系数单轮轴载/
kN刻槽深度/
mmⅠ ≤200 ≤5 >0.7 >123.1 >5 Ⅱ ≤230 ≤8 ≤0.7 ≤123.1 ≤5 Ⅲ ≤260 ≤11 ≤0.6 ≤107.3 ≤4 Ⅳ >260 >11 ≤0.6 ≤91.7 ≤3 表 2 滑水事故征候跑道运行参数组合
Table 2. Parameter combination of operating runway of hydroplaning symptoms
样本 滑行速度/
(km∙h−1)积水厚度/
mm单轮轴载/
kN刻槽深度/
mm摩擦
系数1 220 3 138.8 6 0.76 2 250 5 100.4 5 0.66 3 280 8 76.5 2 0.60 表 3 ATH风险安全性评价结果及对比
Table 3. Safety evaluation results of ATH risks and comparison
样本 综合云相关度 置信因子 稳定性等级与起降条件 Ⅰ Ⅱ Ⅲ Ⅳ 本文方法 正态云法 规范判定 1 0.9229 0.0687 0.0082 0 0.0039 Ⅰ Ⅰ 允许起降 2 0.2127 0.4418 0.3903 0.0376 0.0012 Ⅱ Ⅲ 允许起降 3 0.0007 0.1713 0.2885 0.5462 0.0083 Ⅳ Ⅳ 允许起降 -
[1] 赵安家, 孙丽莹, 孟哲理. 飞机轮胎滑水与预防控制措施研究综述[J]. 飞机设计, 2015, 35(5): 46-51.ZHAO A J, SUN L Y, MENG Z L. A search for mechanism and preventability measure of the aircraft tire hydroplaning[J]. Aircraft Design, 2015, 35(5): 46-51(in Chinese). [2] 蔡靖, 许诤. 沟槽磨损对飞机轮胎滑水影响仿真分析[J]. 中国民航大学学报, 2020, 38(2): 38-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5590.2020.02.008CAI J, XU Z. Simulation analysis on influence of groove abrasion on aircraft hydroplaning[J]. Journal of Civil Aviation University of China, 2020, 38(2): 38-43(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5590.2020.02.008 [3] 许诤. 考虑道面平整度的飞机轮胎滑水安全问题研究[D]. 天津: 中国民航大学, 2019: 10-23.XU Z. Study on water skiing safety of aircraft tires considering pavement smoothness[D]. Tianjin: Civil Aviation University of China, 2019: 10-23(in Chinese). [4] 张恒. 轮胎与湿滑道面相互作用下的飞机滑水行为研究[D]. 天津: 中国民航大学, 2018: 62-66.ZHANG H. Study on aircraft water skiing behavior under the interaction between tire and wet road surface[D]. Tianjin: Civil Aviation University of China, 2018: 62-66(in Chinese). [5] 朱兴一, 庞亚凤, 杨健, 等. 湿滑条件下基于真实纹理道面的机轮着陆滑水行为解析[J]. 中国公路学报, 2020, 33(10): 159-170. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2020.10.010ZHU X Y, PANG Y F, YANG J, et al. Analysis on the hydroplaning of aircraft tire under real texture pavement conditions[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2020, 33(10): 159-170(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2020.10.010 [6] 刘芳兵. 湿滑跑道飞机侧风着陆滑行安全研究[D]. 天津: 中国民航大学, 2020: 45-47.LIU F B. Study on the safety of aircraft landing and taxiing in crosswind on wet runway[D]. Tianjin: Civil Aviation University of China, 2020: 45-47(in Chinese). [7] TREMBLAY L, METIVET M, MEUNIER F, et al. Method and system for aircraft sideslip guidance: US11054437[P]. 2021-07-06. [8] 李岳, 宗辉杭, 蔡靖, 等. 飞机轮组滑水行为与道面积水附加阻力[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2023, 49(5): 1099-1107.LI Y, ZONG H H, CAI J, et al. Hydroplaning behavior of aircraft wheel group and additional resistance due to accumulated water on pavement[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2023, 49(5): 1099-1107(in Chinese). [9] 李岳, 胡宇祺, 蔡靖, 等. 湿滑道面飞机着陆滑水风险量化分析[J]. 南京航空航天大学学报, 2022, 54(6): 1138-1144.LI Y, HU Y Q, CAI J, et al. Quantification analysis of hydroplaning risks of aircraft landing on wet pavement[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics, 2022, 54(6): 1138-1144(in Chinese). [10] FWA T F, PASINDU H R, ONG G P. Critical rut depth for pavement maintenance based on vehicle skidding and hydroplaning consideration[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 2012, 138(4): 423-429. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)TE.1943-5436.0000336 [11] 张兆宁, 石峰. 基于组合赋权云模型的塔台管制系统运行安全评估[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2024, 24(4): 1254-1265.ZHANG Z N, SHI F. Operational safety assessment of tower control system based on combined weighted cloud model[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2024, 24(4): 1254-1265(in Chinese). [12] 史佳辉, 徐吉辉, 陈玉金, 等. 基于交互作用矩阵多维云模型的飞机重着陆风险评估方法研究[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2021, 43(10): 3026-3032. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.10.39SHI J H, XU J H, CHEN Y J, et al. Research on risk assessment method of aircraft heavy landing based on interaction matrix-multidimensional cloud model[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(10): 3026-3032(in Chinese). doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.10.39 [13] 唐家文, 董兵, 王超峰. 基于云模型的空管安全运行保障能力评价[J]. 航空工程进展, 2021, 12(4): 59-67.TANG J W, DONG B, WANG C F. Evaluation on safe operation support ability of air traffic management based on cloud model[J]. Advances in Aeronautical Science and Engineering, 2021, 12(4): 59-67(in Chinese). [14] 李岳, 胡宇祺, 蔡靖, 等. 基于变权重-正态云模型的飞机轮胎滑水风险研究[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2023, 49(9): 2299-2305.LI Y, HU Y Q, CAI J, et al. Hydroplaning risk of aircraft tire based on variable weight theory-normal cloud model[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2023, 49(9): 2299-2305(in Chinese). [15] 周义蛟, 郭基联, 周舟. 基于云模型与组合赋权法的飞机保障性评估研究[C]//2017年首届航空保障设备发展论坛. 北京: 中国航空航天工具协会, 中国航空学会航空维修工程专业分会, 2017: 142-148.ZHOU Y J, GUO J L, ZHOU Z. A study on military aircraft supportability assessment based on cloud model and game theory[C]//Proceedings of the 2017 1st Aviation Support Equipment Development Forum. Beijing: China Aerospace Tools Association, Aviation Maintenance Engineering Branch of the Chinese Aerospace Society, 2017: 142-148(in Chinese). [16] 叶琼, 李绍稳, 张友华, 等. 云模型及应用综述[J]. 计算机工程与设计, 2011, 32(12): 4198-4201.YE Q, LI S W, ZHANG Y H, et al. Cloud model and application overview[J]. Computer Engineering and Design, 2011, 32(12): 4198-4201(in Chinese). [17] 李德毅, 刘常昱. 论正态云模型的普适性[J]. 中国工程科学, 2004, 6(8): 28-34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2004.08.006LI D Y, LIU C Y. Study on the universality of the normal cloud model[J]. Engineering Science, 2004, 6(8): 28-34(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2004.08.006 [18] 刘俊杰, 张瑞瑞, 叶英豪, 等. 基于云模型的航空器地面滑行错误事件风险分析[J]. 中国民航飞行学院学报, 2022, 33(5): 51-56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-4288.2022.05.011LIU J J, ZHANG R R, YE Y H, et al. Risk analysis of aircraft ground taxiing error event based on cloud model[J]. Journal of Civil Aviation Flight University of China, 2022, 33(5): 51-56(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-4288.2022.05.011 [19] 汪明武, 王霄, 龙静云, 等. 基于多维联系正态云模型的泥石流危险性评价[J]. 应用基础与工程科学学报, 2021, 29(2): 368-375.WANG M W, WANG X, LONG J Y, et al. Risk assessment of debris flow based on multidimensional connection normal cloud model[J]. Journal of Basic Science and Engineering, 2021, 29(2): 368-375(in Chinese). [20] 汪明武, 朱其坤, 赵奎元, 等. 基于有限区间联系云的围岩稳定性评价模型[J]. 岩土力学, 2016, 37(增刊1): 140-144.WANG M W, ZHU Q K, ZHAO K Y, et al. Stability evaluation model of surrounding rock based on limited interval connection cloud[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2016, 37(Sup 1): 140-144(in Chinese). [21] 马丽叶, 张涛, 卢志刚, 等. 基于变权可拓云模型的区域综合能源系统综合评价[J]. 电工技术学报, 2022, 37(11): 2789-2799.MA L Y, ZHANG T, LU Z G, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of regional integrated energy system based on variable weight extension cloud model[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2022, 37(11): 2789-2799(in Chinese). [22] 蔡文, 杨春燕, 何斌. 可拓学基础理论研究的新进展[J]. 中国工程科学, 2003, 5(2): 80-87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2003.02.013CAI W, YANG C Y, HE B. New development of the basic theory of extenics[J]. Engineering Science, 2003, 5(2): 80-87(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2003.02.013 [23] 关晓吉. 基于可拓联系云模型的隧道塌方风险等级评价方法[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2018, 14(11): 186-192. doi: 10.11731/j.issn.1673-193x.2018.11.030GUAN X J. Evaluation method on risk grade of tunnel collapse based on extension connection cloud model[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2018, 14(11): 186-192(in Chinese). doi: 10.11731/j.issn.1673-193x.2018.11.030 [24] 牛亚东, 张思祥, 田广军, 等. 机场跑道摩擦系数影响因素研究[J]. 应用力学学报, 2021, 38(2): 715-720. doi: 10.11776/cjam.38.02.D158NIU Y D, ZHANG S X, TIAN G J, et al. Research on influencing factors of friction coefficient in airport runway[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2021, 38(2): 715-720(in Chinese). doi: 10.11776/cjam.38.02.D158 [25] 王迎超, 靖洪文, 张强, 等. 基于正态云模型的深埋地下工程岩爆烈度分级预测研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2015, 36(4): 1189-1194.WANG Y C, JING H W, ZHANG Q, et al. A normal cloud model-based study of grading prediction of rockburst intensity in deep underground engineering[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2015, 36(4): 1189-1194(in Chinese). [26] 宗一鸣. 湿滑道面条件下轮胎力学行为与飞机着陆安全问题研究[D]. 天津: 中国民航大学, 2017: 19-30.ZONG Y M. Research on tire mechanical behavior and aircraft landing safety under wet road surface conditions[D]. Tianjin: Civil Aviation University of China, 2017: 19-30(in Chinese). [27] OH C W, KIM T W, JEONG H Y, et al. Hydroplaning simulation for a straight-grooved tire by using FDM, FEM and an asymptotic method[J]. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2008, 22(1): 34-40. doi: 10.1007/s12206-007-1004-y -







 下载:
下载: