Investigation on unsteady flow characteristics of a supersonic inlet with exit blocked
-
摘要:
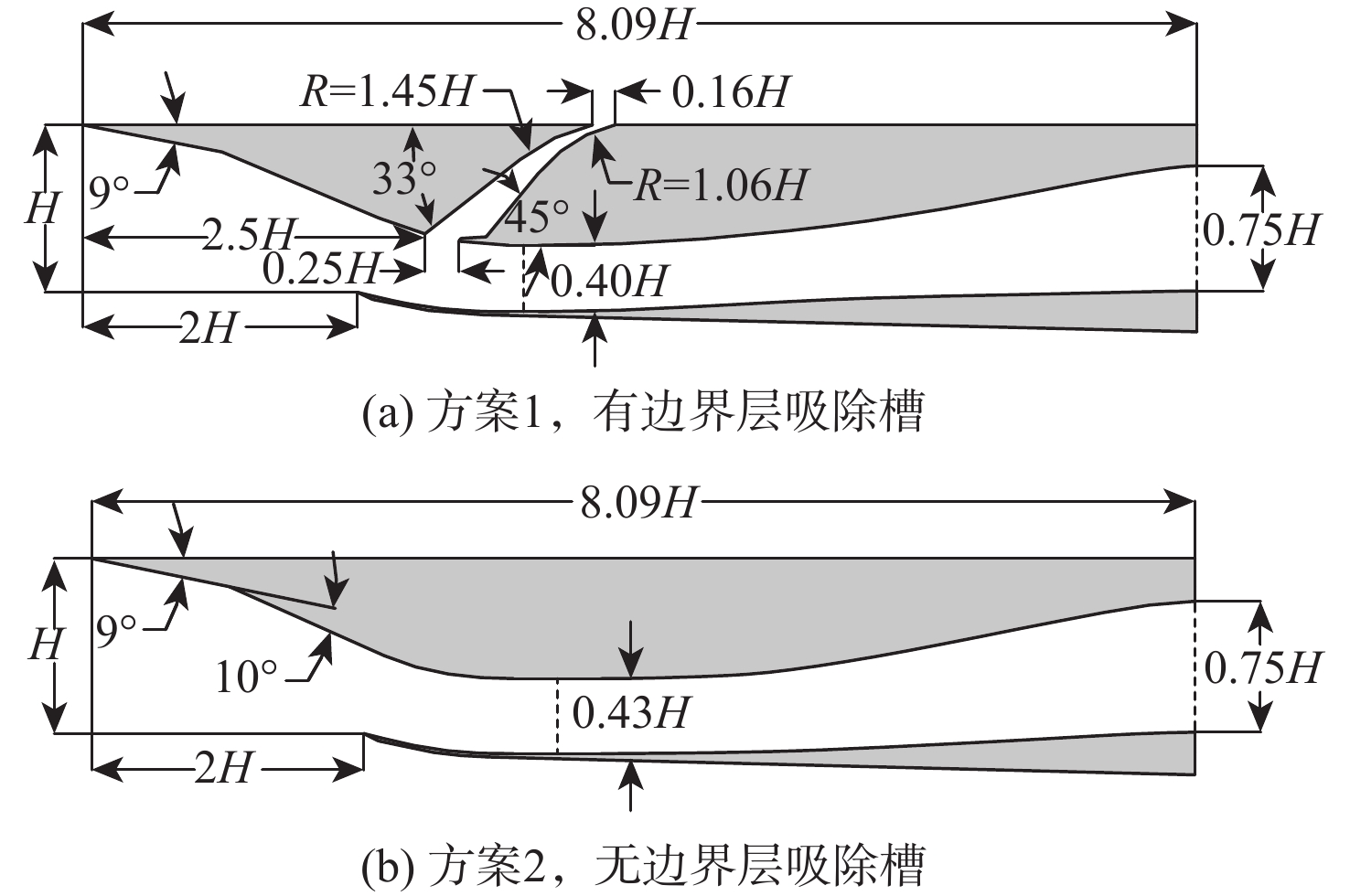
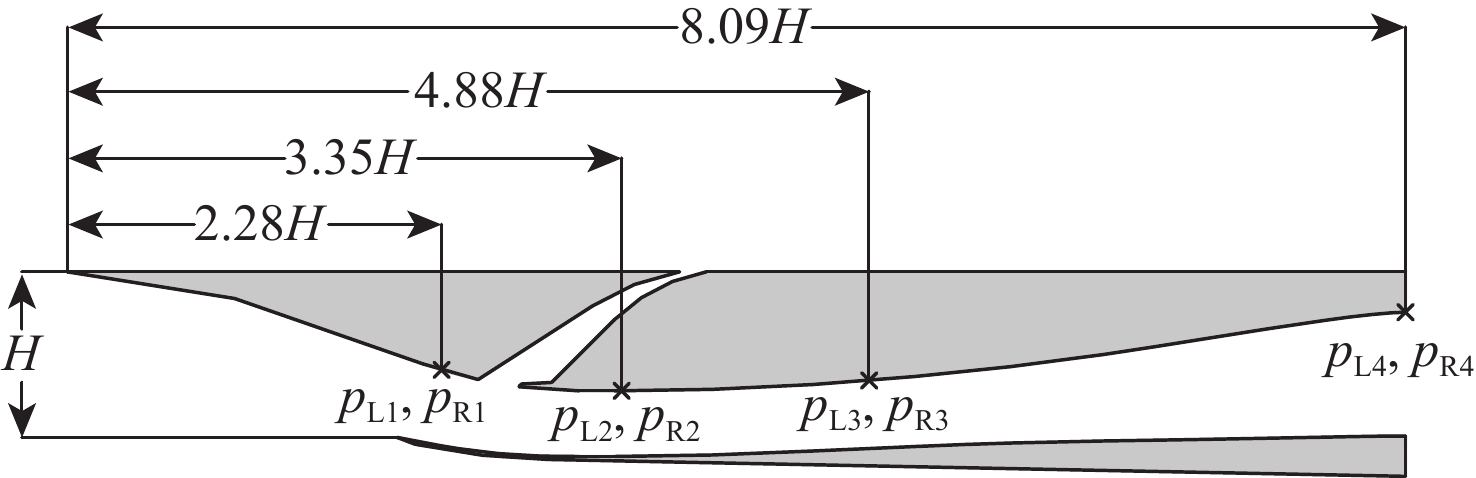
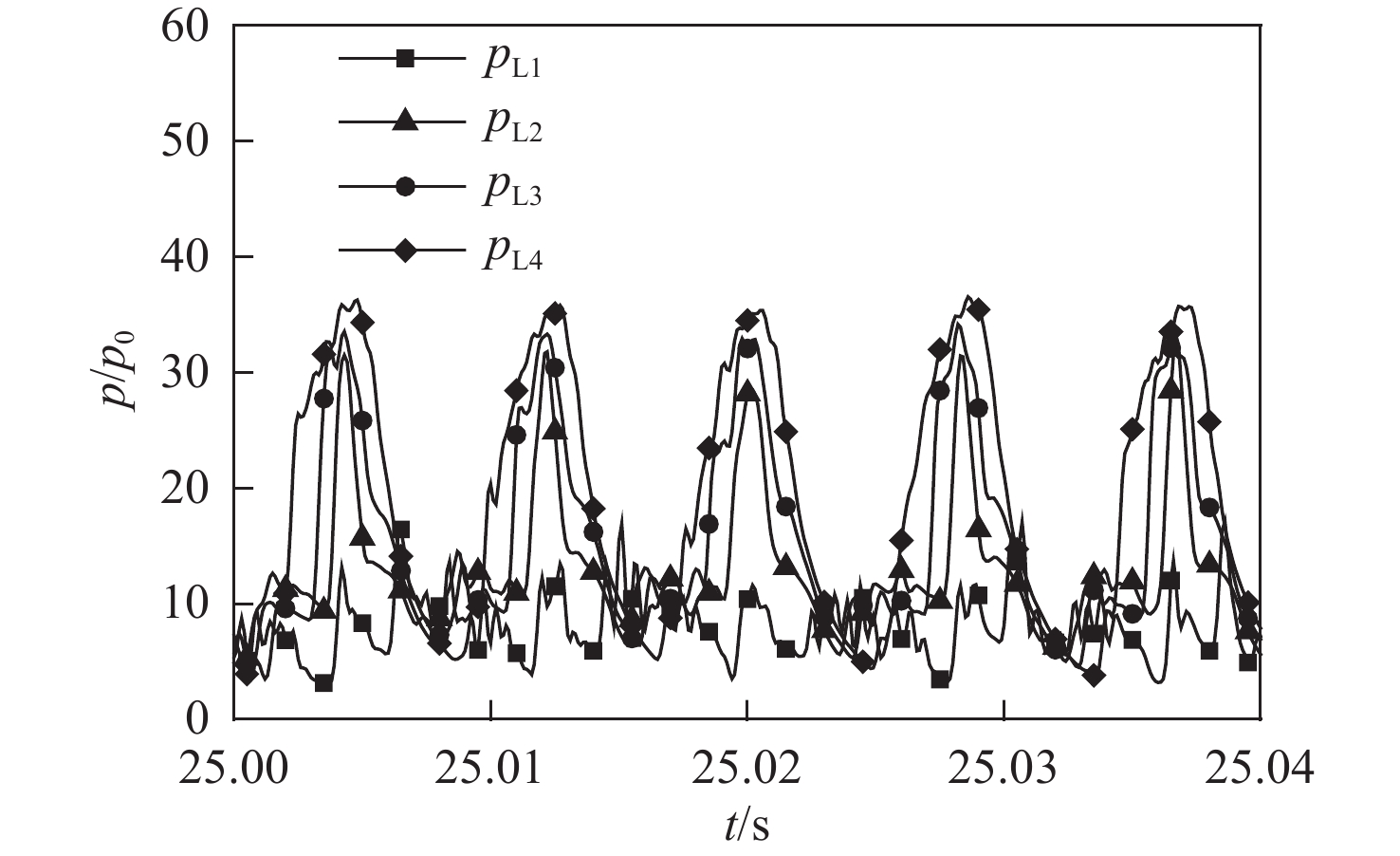
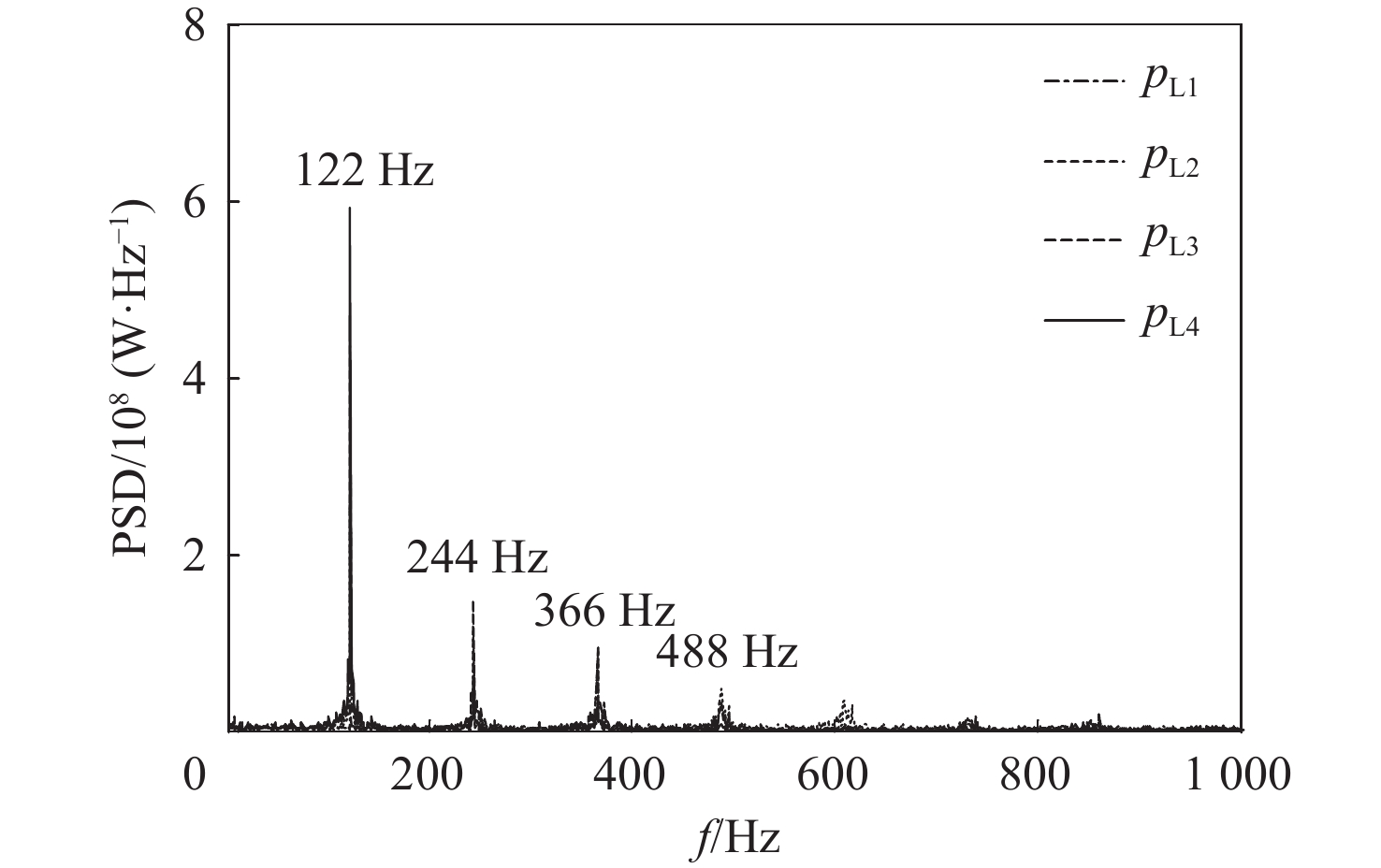
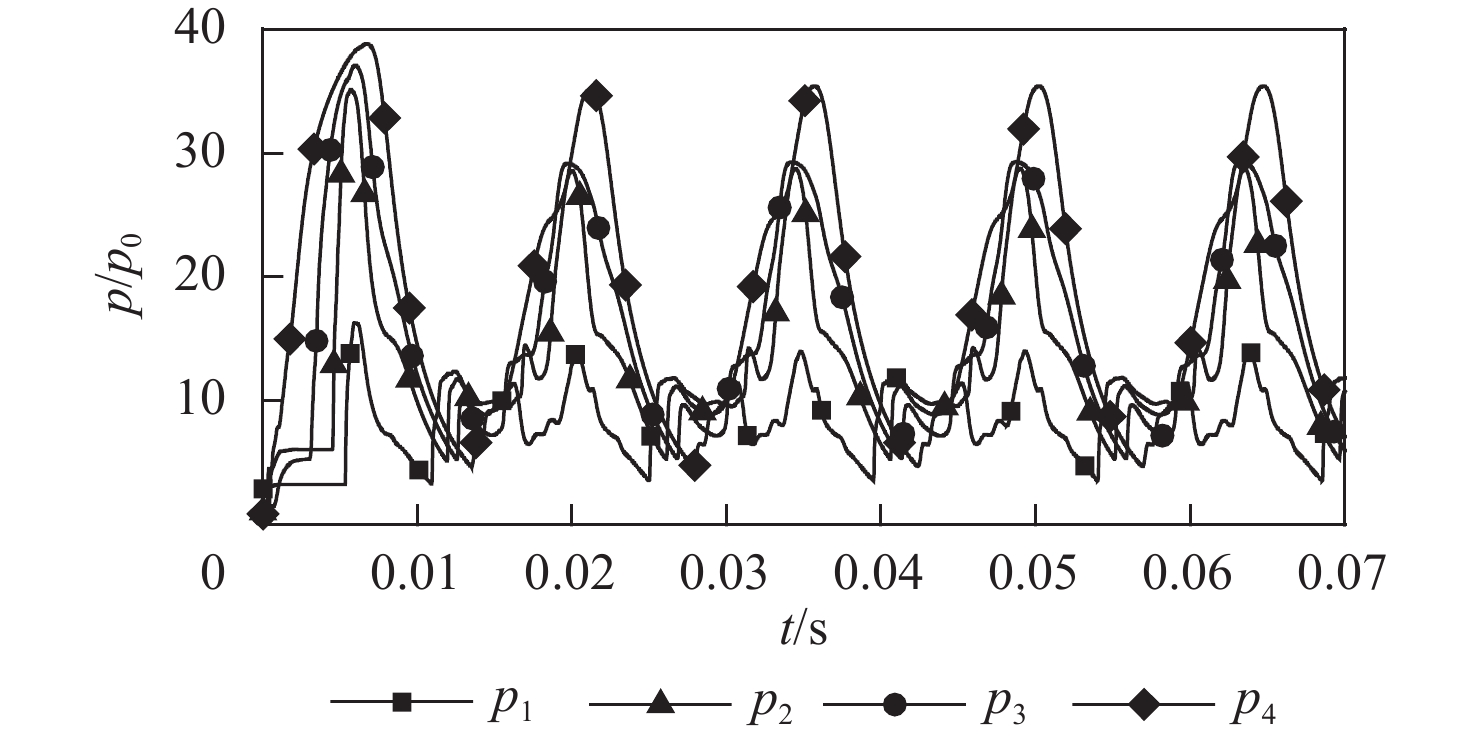
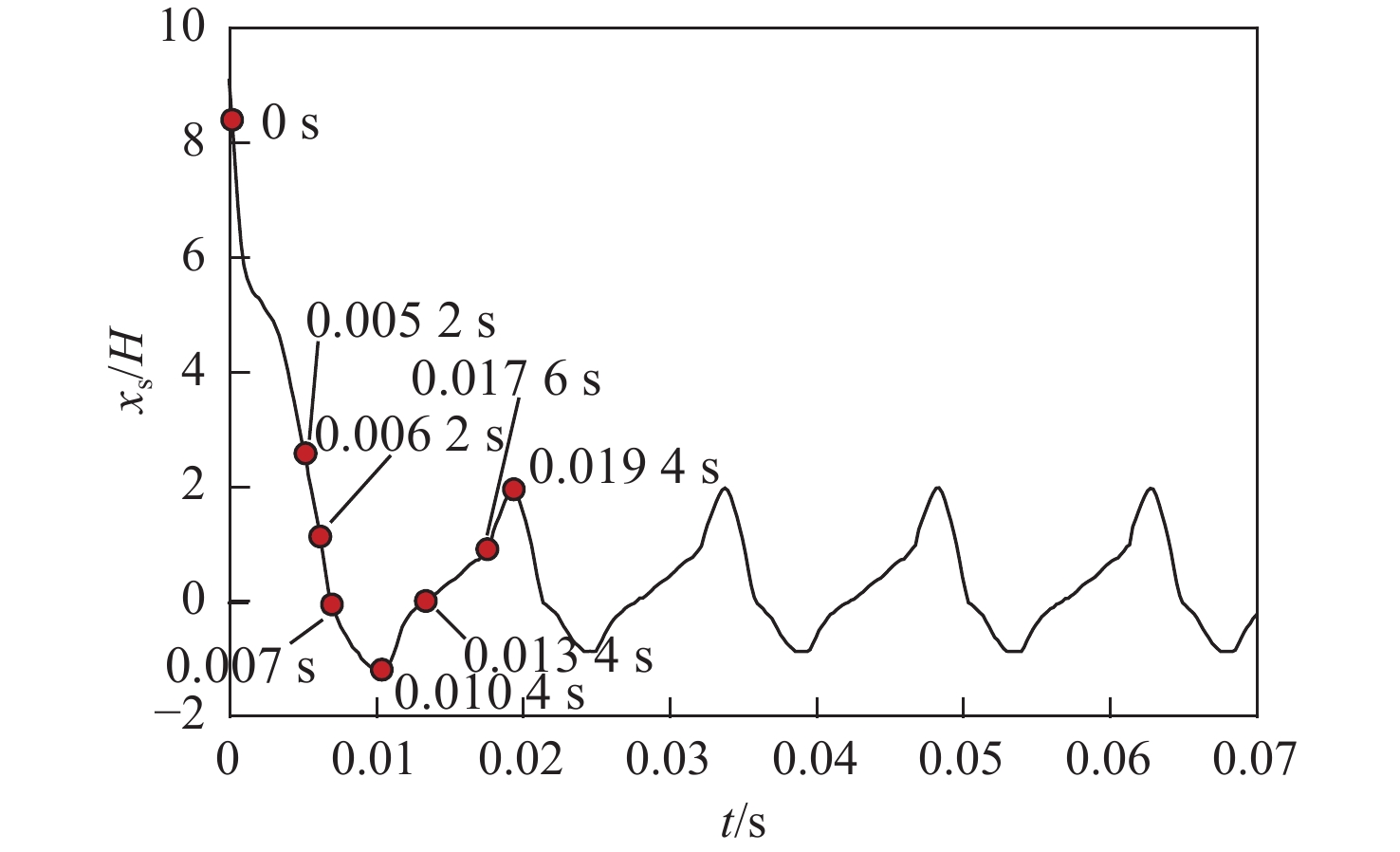
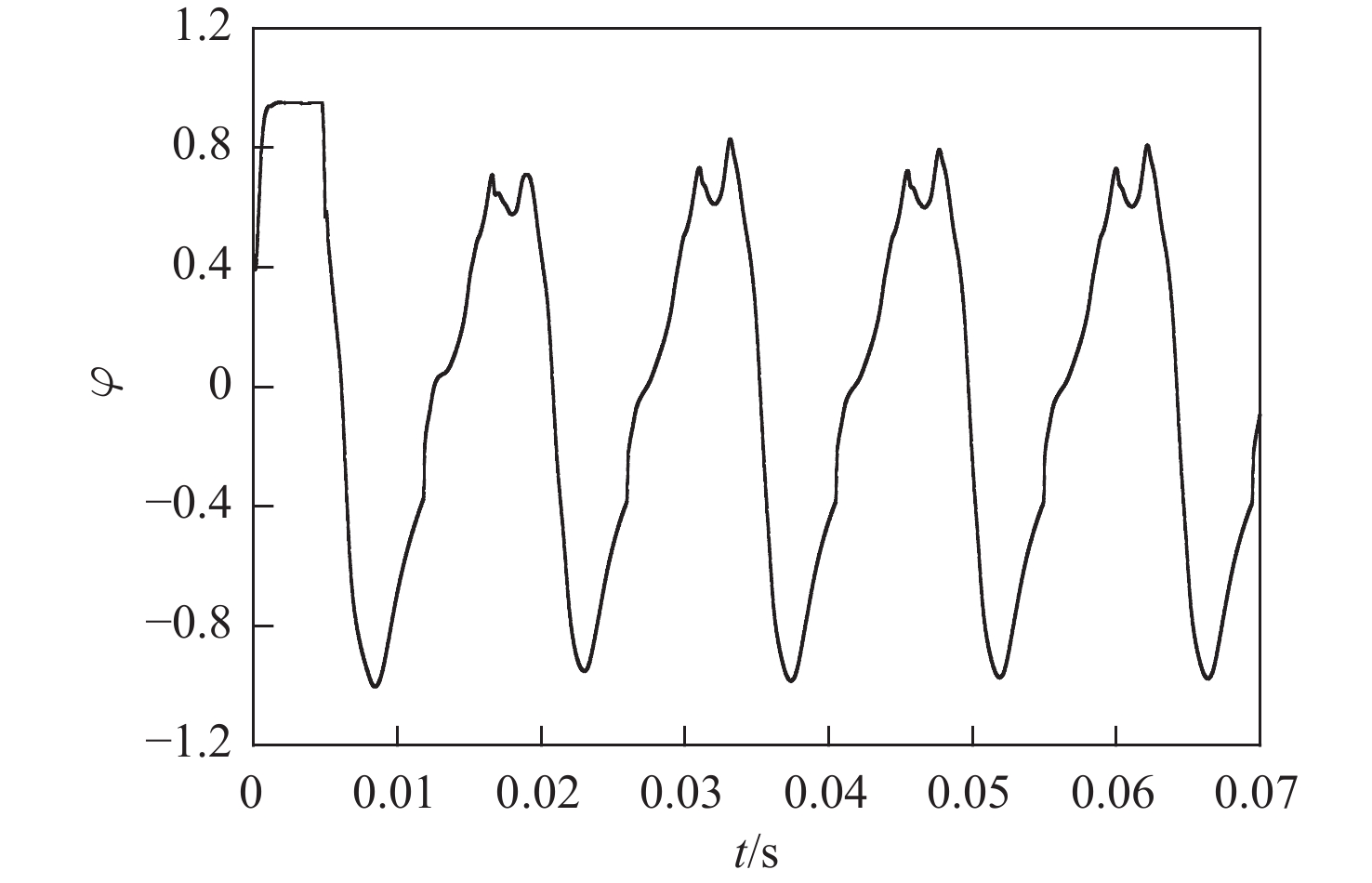
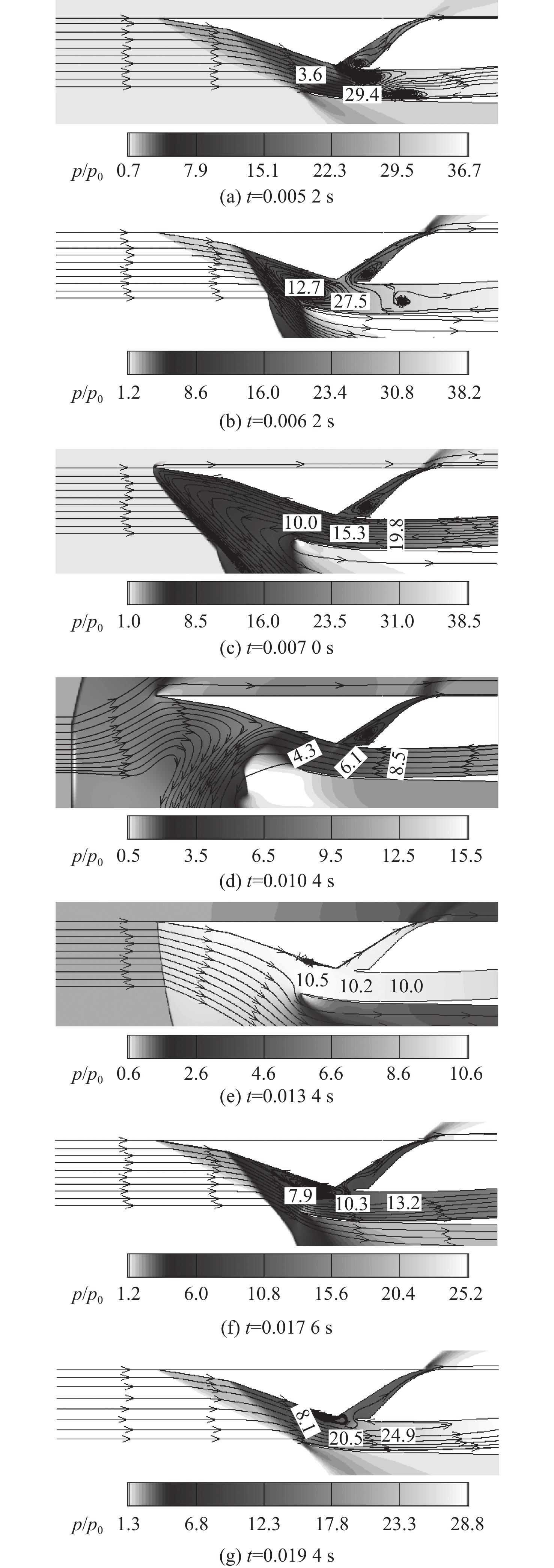
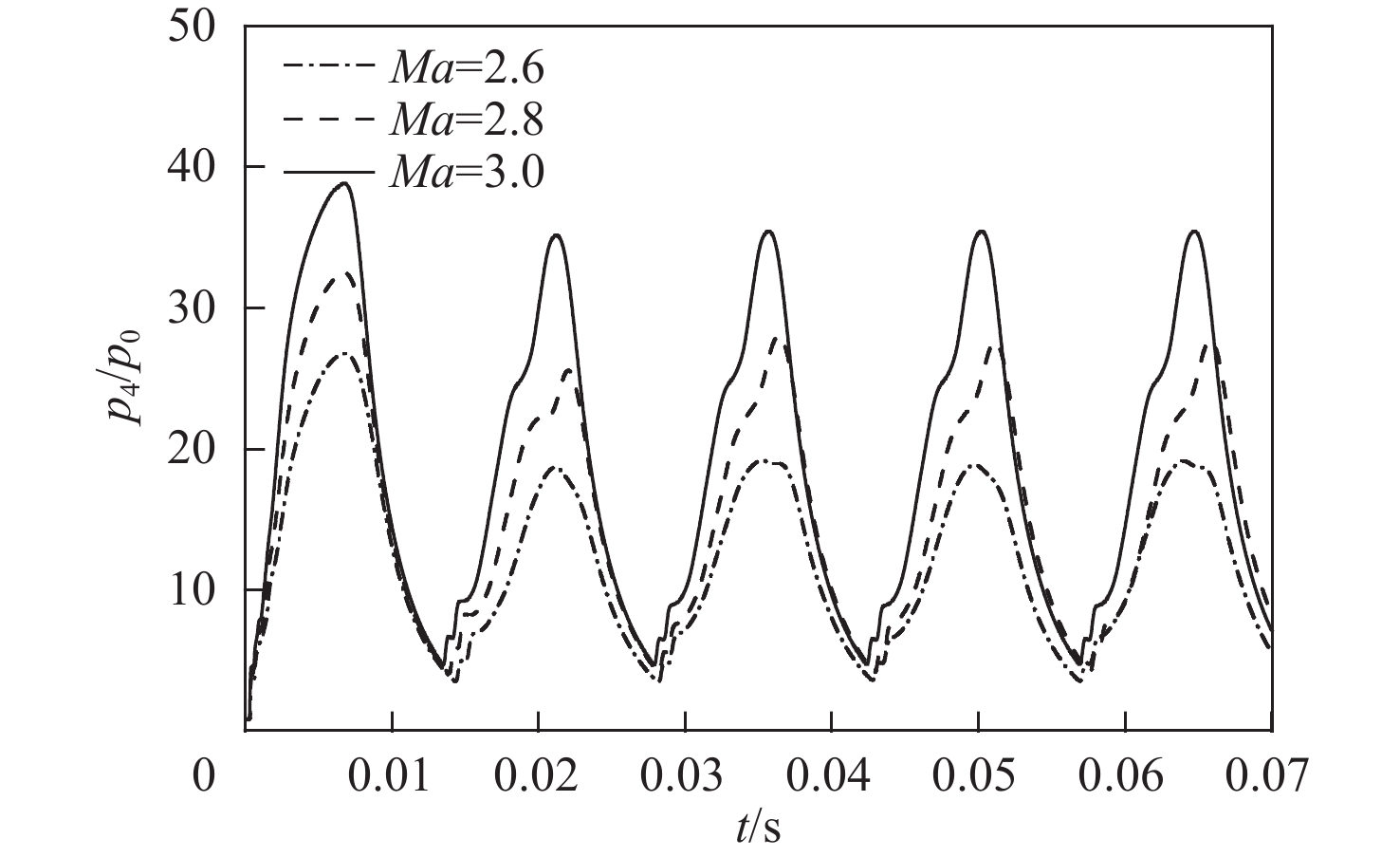
冲压发动机转级过程中可能会出现进气道入口通流、出口封闭的盲腔流动现象,使得进气道发生大幅气流振荡,飞行器面临姿态失稳和结构破坏的风险。针对进气道的气流振荡问题,对一种超声速双侧布局进气道在出口封闭状态下的非定常流动特性开展风洞试验和数值仿真研究,获得了模型尺寸、来流马赫数及边界层吸除对进气道压强振荡特性的影响。结果表明:出口封闭时,进气道发生周期性的流动振荡现象,气流振荡频率与来流声速成正比,与进气道长度成反比,压强振荡峰值与来流总压接近,且随着来流马赫数的增大显著上升。采用的数值仿真方法较好地模拟了进气道出口封闭状态下的非定常流动,数值仿真结果与风洞试验结果吻合良好。非定常仿真结果进一步表明:在气流振荡过程中,进气道内收缩段的边界层吸除槽可以起到泄压作用,使得进气道头部斜激波系在回退过程中达到封口状态,捕获的流量系数较无边界层吸除槽时明显增大,从而导致了进气道压强振荡峰值上升49.47%,频率下降21.78%。
Abstract:Cavity flow oscillation phenomenon would occur during the transiton of ramjet with the inlet entrance unobstructed while its exit blocked. As the flow oscillating dramatically, the flight vehicle would face a crisis of instability attitude controlling and structural failure. Due to the problem of fluctuation flow, the unsteady flow characteristics of a supersonic twin-duct inlet with its exit blocked were studied by wind tunnel test and numerical simulation. The effects of the model scale, Mach number of the incoming flow, and boundary layer suction on the characteristics of oscillating pressure of the inlet were acquired. The results indicate that periodic oscillating flow is observed when the exit of the inlet is blocked. The frequency of the oscillating flow is positively correlated to the acoustic velocity of the incoming flow but inversely correlated to the length of the inlet. The oscillating pressure peak is found to approximate the total pressure value of the incoming flow, and it raises obviously with the increment of the Mach number of the incoming flow. The unsteady flow of the inlet with its exit blocked is approximately simulated by the numerical method adopted in this paper, and the numerical simulation result agrees well with that of the wind tunnel test. Furthermore, unsteady simulation results show that the inlet’s pressure is relieved in the duration of flow oscillation by conducting the boundary layer suction method at the internal contracted region, which results in a shock-on-lip state during the backward movement of the shock wave system. A rise of captured flow coefficient is observed when compared to the inlet without boundary layer suction, leading to a 49.47% increase of amplitude peak while 21.78% descending of the frequency for the oscillating pressure.
-
Key words:
- supersonic inlet /
- oscillating pressure /
- boundary layer suction /
- unsteady /
- wind tunnel test
-
表 1 风洞试验参数
Table 1. Parameters of wind tunnel test
Ma α/(°) β/(°) P∗0/Pa T∗0/K 3.0 0 0 390000 300 表 2 数值计算工况及模拟参数
Table 2. Numerical calculation conditions and simulated parameters
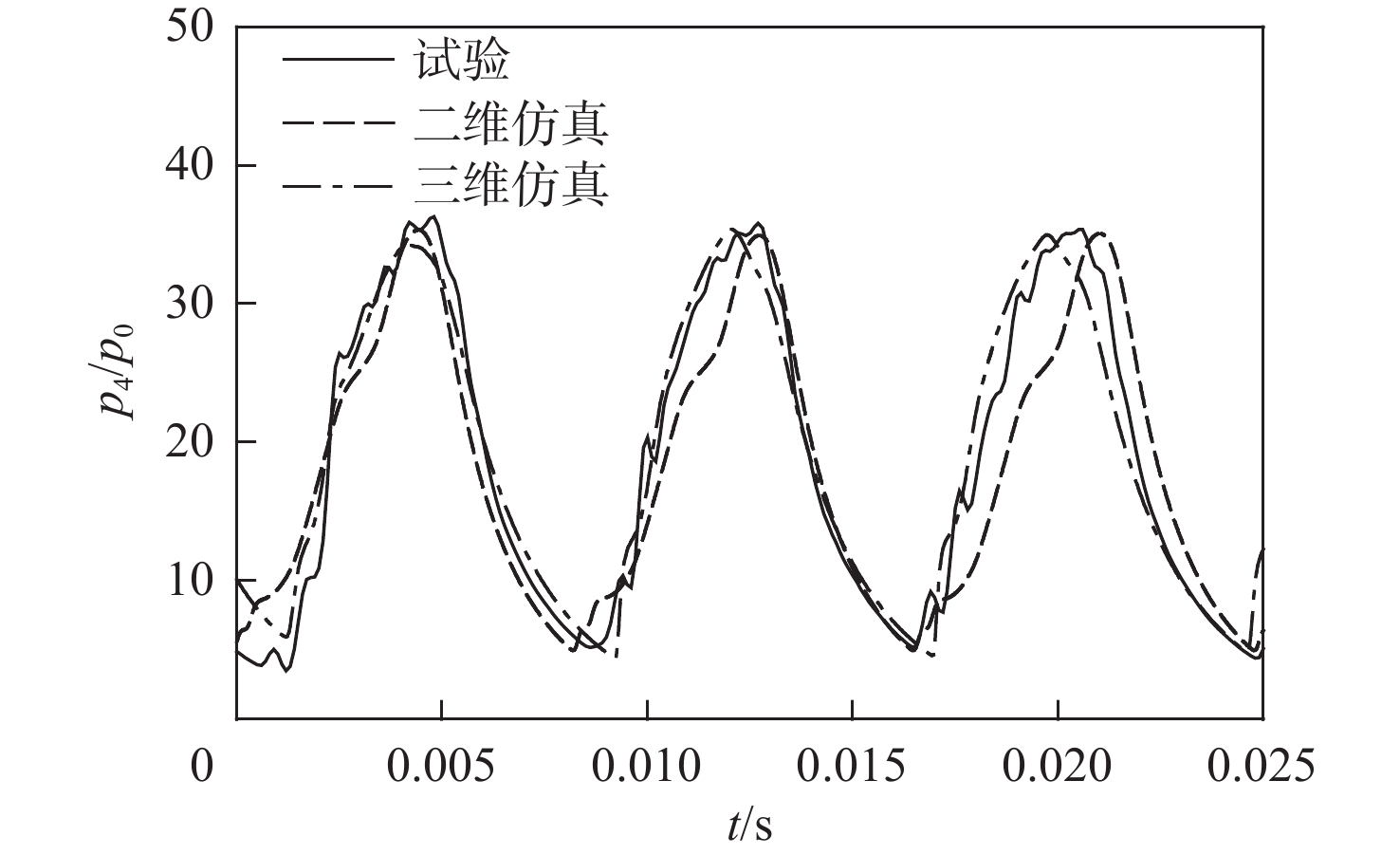
工况 方案 h/km Ma p0/Pa T/K ξ 维度 1 1 3.0 10617.2 107.14 1∶2.5 三维 2 1 3.0 10617.2 107.14 1∶2.5 二维 3 1 15 3.0 12111.8 216.65 1∶1 二维 4 1 12 2.8 19399.4 216.65 1∶1 二维 5 1 12 2.6 19399.4 216.65 1∶1 二维 6 2 15 3.0 12111.8 216.65 1∶1 二维 表 3 方案1进气道扩张段出口的压强振荡幅值和频率试验值与仿真值对比
Table 3. Comparison of experimental and simulated inlet’s oscillating pressure amplitudes and frequencies at exit of diffuser for option 1
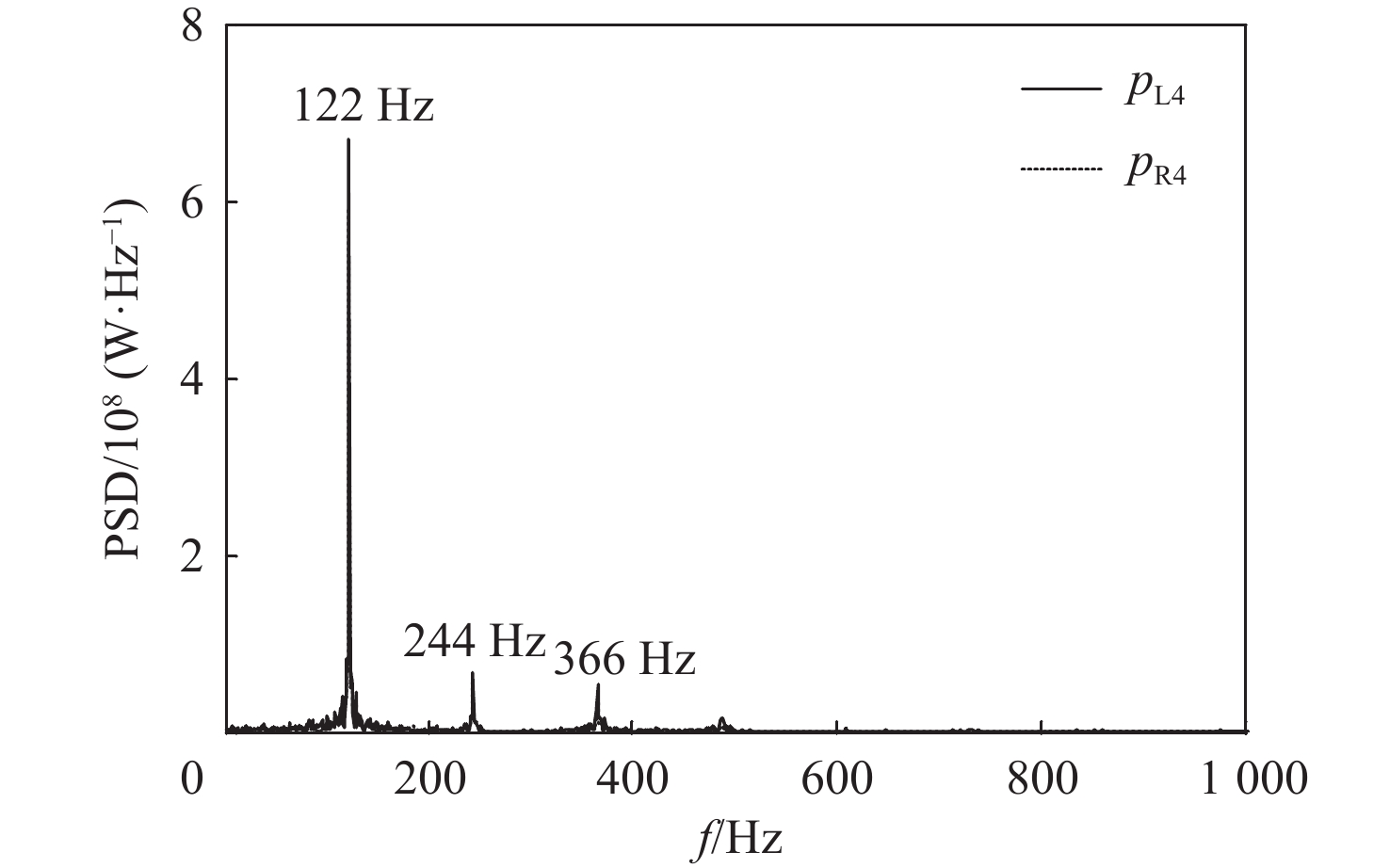
参数来源 f/Hz pmax/p0 Δf/% Δ(pmax/p0)/% 试验 122.00 36.06 二维仿真 120.47 35.40 −1.25 −1.83 三维仿真 121.99 34.87 −0.008 −3.30 表 4 方案1进气道进口前方的气流参数与来流参数对比(h=15 km)
Table 4. Comparison of flow parameters and incoming flow parameters ahead of inlet entrance for option 1 (h = 15 km)
位置 Ma P∗0/Pa T/K 自由来流 3.0 444899.38 216.65 进气道进口前方 2.992 434888.47 217.40 表 5 不同尺寸模型进气道扩张段出口位置的压强振荡峰值和频率对比
Table 5. Comparison of inlet’s oscillating pressure peaks and frequencies at exit of diffuser for models of different sizes
尺寸模型 f/Hz pmax/p0 1∶1(工况3) 69.00 35.41 1∶2.5(工况2) 120.47 35.40 表 6 不同马赫数下进气道p4监测点的压强振荡频率仿真值与理论值对比
Table 6. Comparison of simulated and theoretical frequencies of inlet’s oscillating pressure at monitoring point p4 for different Mach numbers
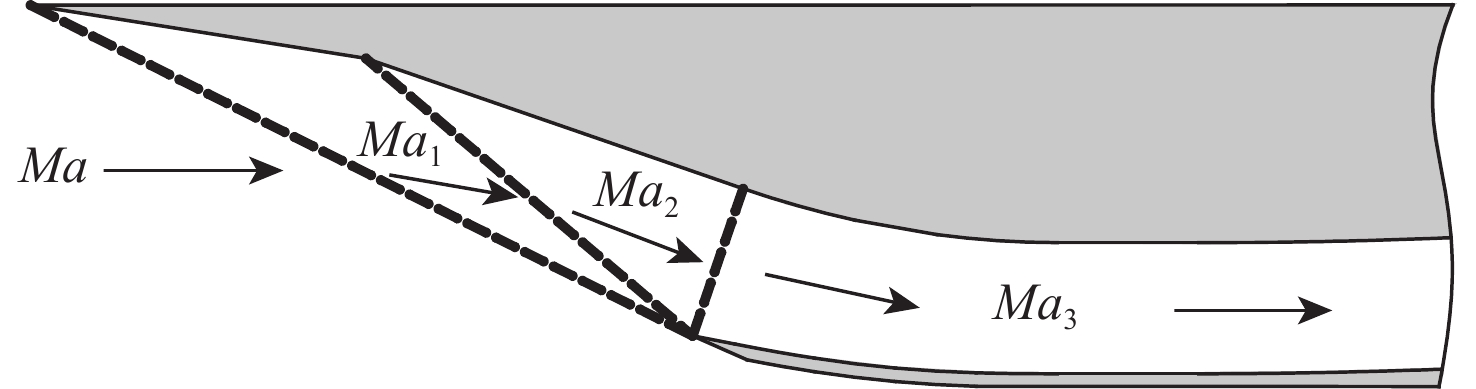
Ma Ma3 ¯Ma c/(m·s−1) 理论f/Hz 仿真f/Hz f相对
误差/%2.6 0.608 0.304 295.07 71.03 69.08 2.75 2.8 0.580 0.290 295.07 71.69 68.44 4.53 3.0 0.556 0.278 295.07 72.22 69.00 4.07 表 7 不同方案进气道p4监测点的压强振荡峰值和频率对比
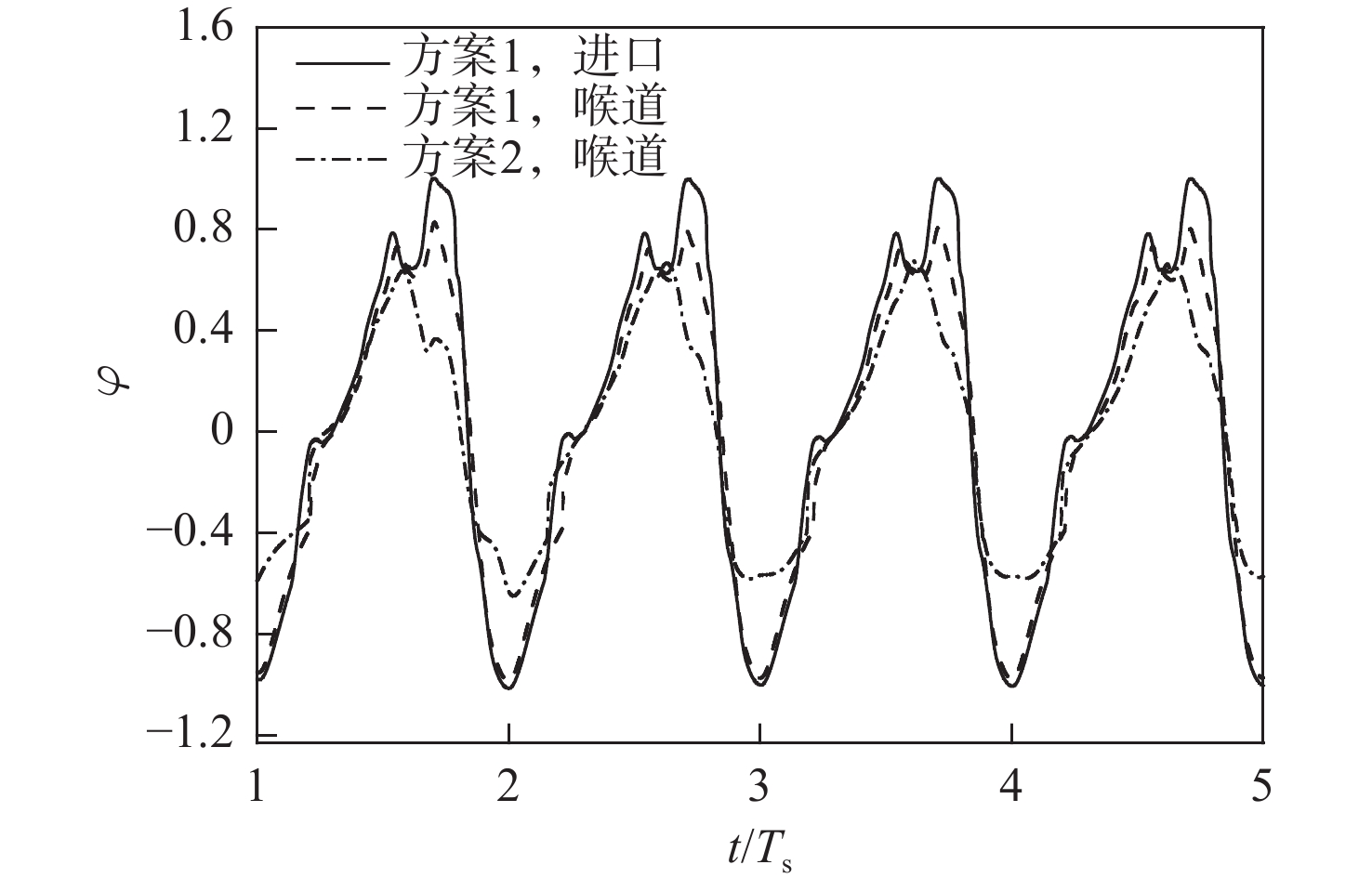
Table 7. Comparison of inlet’s oscillating pressure peaks and frequencies at monitoring point p4 of inlet for different options
方案 f/Hz pmax/p0 方案1 69.00 35.41 方案2 88.21 23.69 -
[1] NISHIZAWA U, KAMEDA M, WATANABE Y, et al. Computational simulation of shock oscillation around a supersonic air-intake[C]//Proceedings of the 36th AIAA Fluid Dynamics Conference and Exhibit. Reston: AIAA, 2006. [2] NAKAYAMA T, SATO T, AKATSUKA M, et al. Investigation on shock oscillation phenomenon in a supersonic air inlet[C]//Proceedings of the 41st AIAA Fluid Dynamics Conference and Exhibit. Reston: AIAA, 2011. [3] LU P J, JAIN L T. Numerical investigation of inlet buzz flow[J]. Journal of Propulsion and Power, 1998, 14(1): 90-100. doi: 10.2514/2.5254 [4] FUJIWARA H, MURAKAMI A, WATANABE Y. Numerical analysis on shock oscillation of two-dimensional external compression intakes[C]//Proceedings of the 32nd AIAA Fluid Dynamics Conference and Exhibit. Reston: AIAA, 2002. [5] 王玉峰, 杨宝娥. 超声速进气道喘振的机理研究[J]. 火箭推进, 2008, 34(1): 17-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9374.2008.01.004WANG Y F, YANG B E. Study of the buzz mechanism of supersonic inlets[J]. Journal of Rocket Propulsion, 2008, 34(1): 17-22(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9374.2008.01.004 [6] OH J Y, MA F H, HSIEH S Y, et al. Interactions between shock and acoustic waves in a supersonic inlet diffuser[J]. Journal of Propulsion and Power, 2005, 21(3): 486-495. doi: 10.2514/1.9671 [7] 刘占生, 张云峰, 田新. 冲压发动机超声速进气道流动自激振荡研究[J]. 航空动力学报, 2008, 23(9): 1595-1602.LIU Z S, ZHANG Y F, TIAN X. Research on self-excited oscillation flows in inlet of ramjet[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2008, 23(9): 1595-1602(in Chinese). [8] SAUNDERS J, KEITH T. Results from computational analysis of a mixed compression supersonic inlet[C]//Proceedings of the 27th Joint Propulsion Conference. Reston: AIAA, 1991. [9] SAJBEN M, BOGAR T J, KROUTIL J C. Experimental study of flows in a two-dimensional inlet model[J]. Journal of Propulsion and Power, 1985, 1(2): 109-117. doi: 10.2514/3.22767 [10] 李强, 刘佩进, 李江, 等. 冲压发动机助推段压强振荡现象数值分析[J]. 推进技术, 2008, 29(6): 673-676. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4055.2008.06.007LI Q, LIU P J, LI J, et al. Numerical simulation of boosting stage pressure oscillation in ramjet[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology, 2008, 29(6): 673-676(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4055.2008.06.007 [11] 孙振华, 吴催生. 冲压发动机加速阶段进气道内动态特性[J]. 固体火箭技术, 2011, 34(3): 285-289. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2793.2011.03.005SUN Z H, WU C S. Dynamic characteristics in ramjet inlet during acceleration phase[J]. Journal of Solid Rocket Technology, 2011, 34(3): 285-289(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2793.2011.03.005 [12] 白晓征, 刘君, 郭正, 等. 冲压发动机进气道压力振荡过程的数值研究[J]. 推进技术, 2008, 29(5): 562-565. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4055.2008.05.010BAI X Z, LIU J, GUO Z, et al. Numerical simulation of pressure oscillation in ramjet inlet[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology, 2008, 29(5): 562-565(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4055.2008.05.010 [13] 刘志伟, 马高建, 崔金平. 附面层吸除对二元混压式进气道起动影响分析[J]. 弹箭与制导学报, 2009, 29(3): 149-152. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9728.2009.03.044LIU Z W, MA G J, CUI J P. Influence of boundary layers bleed sew to start[J]. Journal of Projectiles, Rockets, Missiles and Guidance, 2009, 29(3): 149-152(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9728.2009.03.044 [14] 贺永杰, 马高建, 刘志伟. 通过附面层泄除提高定几何混压式进气道性能的方法研究[J]. 航空兵器, 2010(2): 28-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5048.2010.02.007HE Y J, MA G J, LIU Z W. Study on improving the performance of mixed-compression inlet with fixed-geometry through boundary-layer bleed[J]. Aero Weaponry, 2010(2): 28-31(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5048.2010.02.007 [15] HARLOFF G J, SMITH G E. Supersonic-inlet boundary-layer bleed flow[J]. AIAA Journal, 1996, 34(4): 778-785. doi: 10.2514/3.13140 [16] SYBERG J, KONCSEK J L. Experimental evaluation of an analytically derived bleed system for a supersonic inlet[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 1976, 13(10): 792-797. doi: 10.2514/3.58712 [17] FUJIMOTO A, NIWA N, SAWADA K. Numerical investigation of supersonic inlet with realistic bleed andbypass systems[J]. Journal of Propulsion and Power, 1992, 8(4): 857-861. doi: 10.2514/3.23560 [18] HERRMANN D, BLEM S, GULHAN A. Experimental study of boundary-layer bleed impact on ramjet inlet performance[J]. Journal of Propulsion and Power, 2011, 27(6): 1186-1195. doi: 10.2514/1.B34223 [19] 翁小侪, 郭荣伟. 一种二元定几何混压式超声速进气道流场控制概念研究[J]. 航空动力学报, 2012, 27(11): 2492-2498.WENG X C, GUO R W. Study of novel flow control concept for fix-geometry two-dimensional mix-compression supersonic inlet[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2012, 27(11): 2492-2498(in Chinese). [20] WAN D W, GUO R W. Experimental investigation of a fixed-geometry two-dimensional mixed-compression supersonic inlet with sweep-forward high- light and bleed slot in an inverted “X”-type layout[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2007, 20(4): 304-312. doi: 10.1016/S1000-9361(07)60048-X [21] 麻肖妃, 谢旅荣, 郭荣伟. 双下侧布局带泄流腔二元进气道试验[J]. 航空动力学报, 2010, 25(8): 1818-1824.MA X F, XIE L R, GUO R W. Investigation of two-dimensional supersonic twin inlet with slot-coupled cavity in 90° configuration at venter[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2010, 25(8): 1818-1824(in Chinese). [22] SCHÜLEIN E. Skin friction and heat flux measurements in shock/boundary layer interaction flows[J]. AIAA Journal, 2006, 44(8): 1732-1741. doi: 10.2514/1.15110 -








 下载:
下载: