-
摘要:
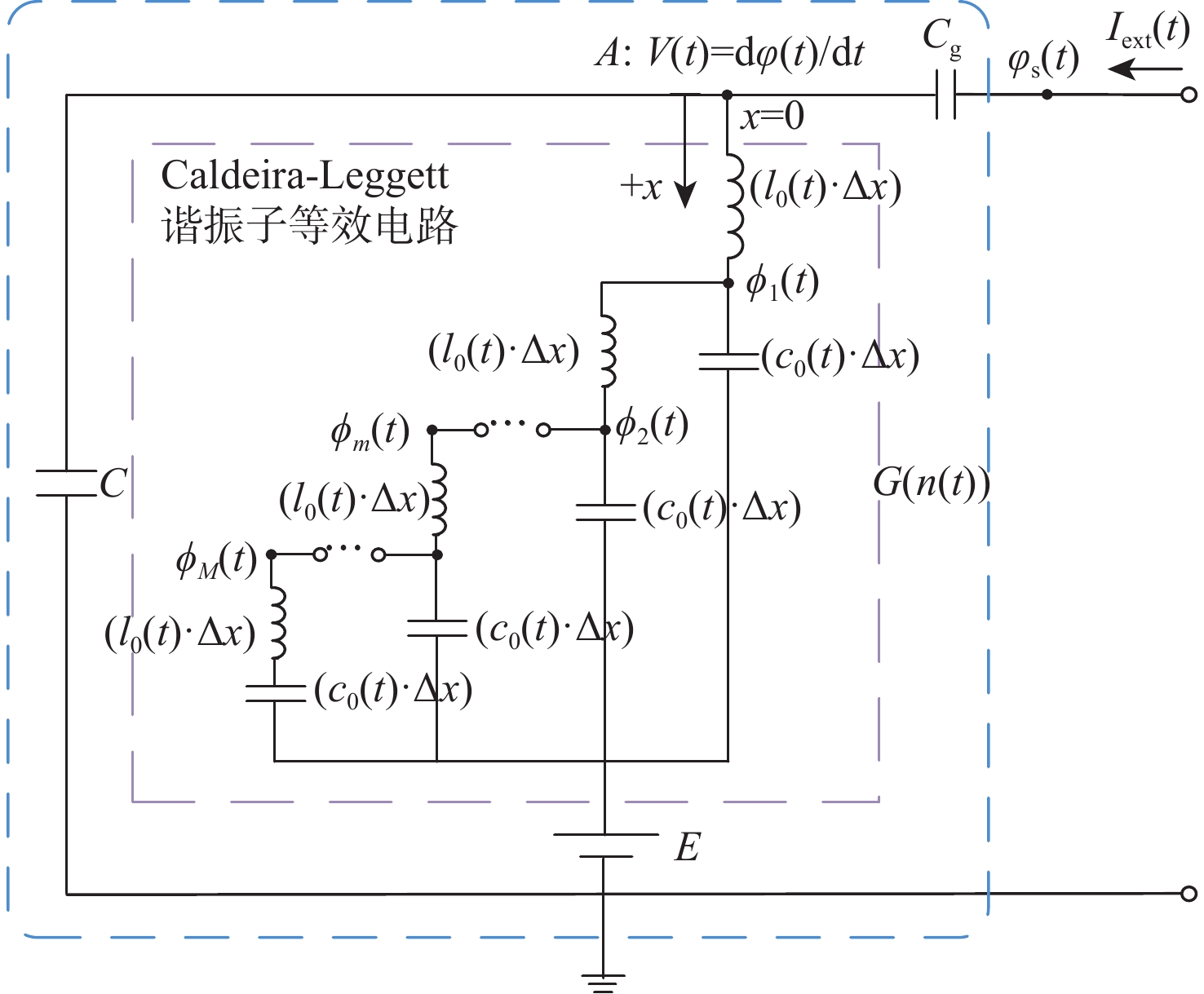
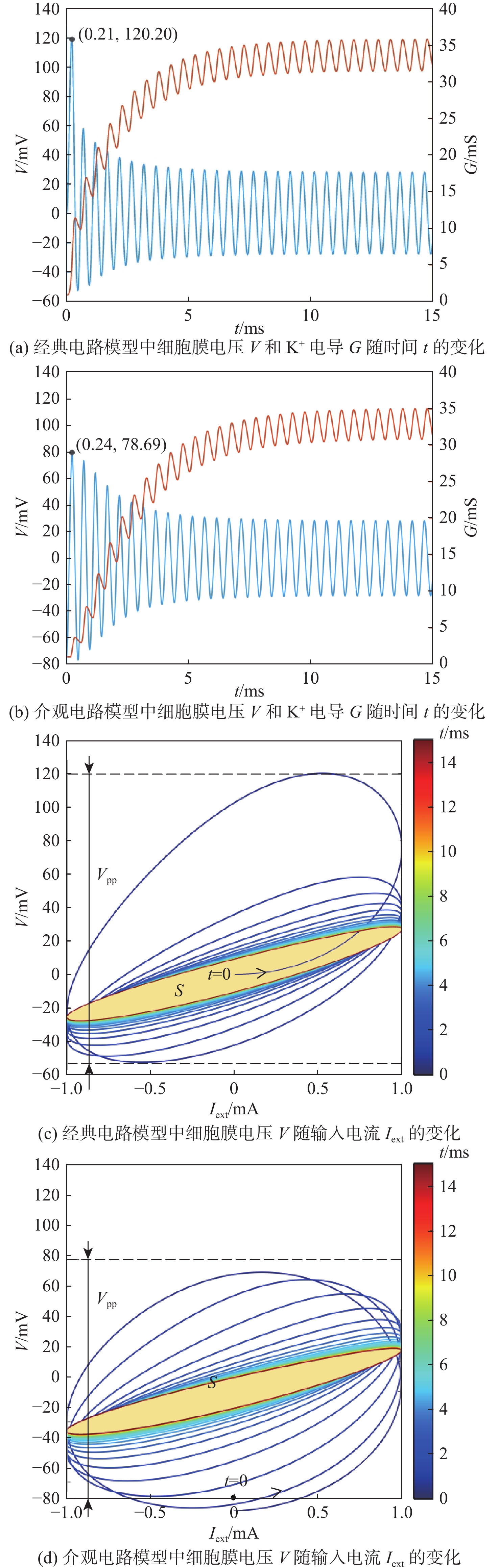
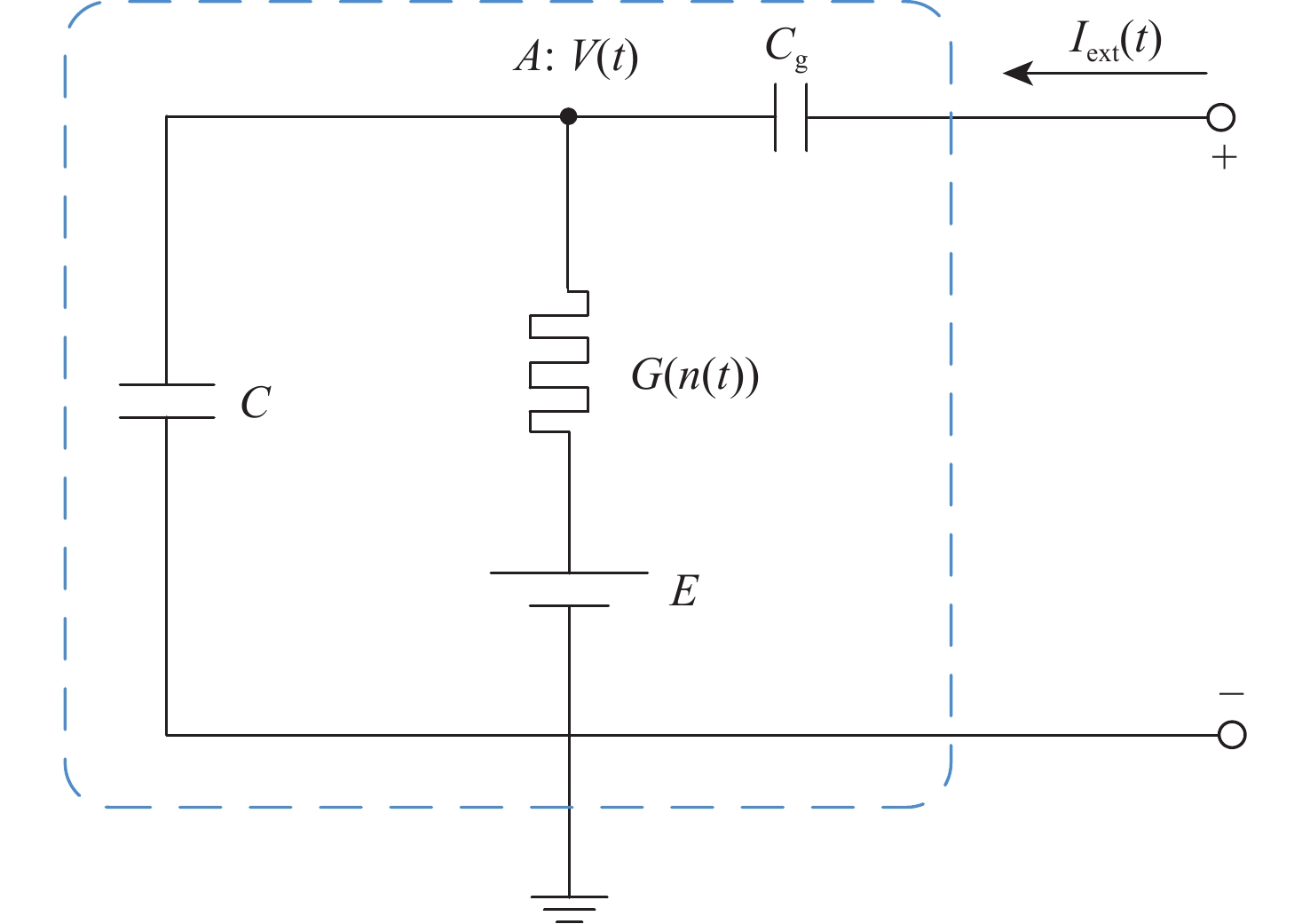
神经网络是由大量神经元通过突触联结而成的复杂网络系统,神经元的合理建模与分析是理解神经网络的功能及动力学特征的关键,对于推动脑科学与类脑科学研究具有重要价值。利用细胞膜电容和钾离子忆阻器分别表征神经元对电荷的存储和记忆特性,在Hodgkin-Huxley单离子通道神经元经典电路模型的基础上建立介观电路模型。使用经典电路理论和介观量子电路理论,在给予正弦激励下推导神经元细胞膜电压的响应表达式。计算结果表明:神经元细胞膜电压峰-峰值和迟滞回线的面积随激励频率的增大先增大后减小。在经典电路模型中,神经元细胞膜电压峰-峰值和迟滞回线面积达到最大值的频率与外部激励源的幅值有关,而在介观电路模型中,其仅与神经元电路参数有关,不依赖外部激励,更能表征神经元自身的特性。神经元的介观电路模型有益于揭示神经网络的动力学机理,推动脑科学理论体系的发展。
-
关键词:
- Hodgkin-Huxley 神经元 /
- 介观电路 /
- 忆阻器 /
- 量子理论 /
- 动力学响应
Abstract:By using a cellular membrane capacitor and a potassium ion memristor to characterize the charge storage and memory function of a neuron, this paper modified the classical circuit model and got the mesoscopic circuit model of the Hodgkin-Huxley single ion channel neuron. Based on the classical circuit theory and quantum theory of mesoscopic circuits, the response of membrane voltage of neurons under the sinusoidal excitation was derived. The calculation results show that with the increase in the frequency of the excitation source, the voltage peak-peak value of the membrane of the neuron and its steady-state hysteresis loop area first increase and then decrease. In the classical circuit model, the frequency at which the voltage peak-peak value and the hysteresis loop area reach the maximum depends on the amplitude of the external excitation source, while in the mesoscopic circuit model, it only depends on the circuit parameters of the neuron and is independent of the external excitation, which can better describe the characteristics of neurons. The mesoscopic circuit model of neurons is beneficial to reveal the dynamic mechanism of neural networks and promote the development of brain science theory systems.
-
Key words:
- Hodgkin-Huxley neuron /
- mesoscopic circuits /
- memristors /
- quantum theory /
- dynamic response
-
-
[1] 张帅, 崔琨, 史勋, 等. 经颅磁声电刺激参数对神经元放电模式的影响分析[J]. 电工技术学报, 2019, 34(18): 3741-3749.ZHANG S, CUI K, SHI X, et al. Effect analysis of transcranial magneto-acousto-electrical stimulation parameters on neural firing patterns[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2019, 34(18): 3741-3749(in Chinese). [2] 张帅, 许家悦, 李梦迪, 等. 基于皮层神经元模型的经颅磁声电刺激神经网络放电活动仿真分析[J]. 电工技术学报, 2021, 36(18): 3851-3859.ZHANG S, XU J Y, LI M D, et al. Simulation of the discharge activity of neural network under transcranial magneto-acousto-electrical stimulation based on cortical neuron model[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2021, 36(18): 3851-3859(in Chinese). [3] 朱海军, 尹晓楠, 丁冲, 等. 高频即时磁刺激对神经兴奋性与电压门控钠钾离子通道的影响[J]. 电工技术学报, 2021, 36(18): 3787-3798.ZHU H J, YIN X N, DING C, et al. Effects of high-frequency immediate magnetic stimulation on neuronal excitability and voltage-gated Na+ and K+ channels[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2021, 36(18): 3787-3798(in Chinese). [4] 徐泠风, 李传东, 陈玲. 神经元模型对比分析[J]. 物理学报, 2016, 65(24): 5-16. doi: 10.7498/aps.65.240701XU L F, LI C D, CHEN L. Contrastive analysis of neuron model[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2016, 65(24): 5-16(in Chinese). doi: 10.7498/aps.65.240701 [5] HODGKIN A L, HUXLEY A F. Currents carried by sodium and potassium ions through the membrane of the giant axon of Loligo[J]. The Journal of Physiology, 1952, 116(4): 449-472. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004717 [6] ANDREEV A V, FROLOV N S, PISARCHIK A N, et al. Chimera state in complex networks of bistable Hodgkin-Huxley neurons[J]. Physical Review E, 2019, 100(2-1): 022224. [7] BAYSAL V, SARAÇ Z, YILMAZ E. Chaotic resonance in Hodgkin-Huxley neuron[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2019, 97(2): 1275-1285. doi: 10.1007/s11071-019-05047-w [8] BOSSY M, FONTBONA J, OLIVERO H. Synchronization of stochastic mean field networks of Hodgkin-Huxley neurons with noisy channels[J]. Journal of Mathematical Biology, 2019, 78(6): 1771-1820. doi: 10.1007/s00285-019-01326-7 [9] CARLU M, CHEHAB O, DALLA PORTA L, et al. A mean-field approach to the dynamics of networks of complex neurons, from nonlinear integrate-and-fire to Hodgkin-Huxley models[J]. Journal of Neurophysiology, 2020, 123(3): 1042-1051. doi: 10.1152/jn.00399.2019 [10] KHODASHENAS M, BAGHDADI G, TOWHIDKHAH F. A modified Hodgkin-Huxley model to show the effect of motor cortex stimulation on the trigeminal neuralgia network[J]. The Journal of Mathematical Neuroscience, 2019, 9(1): 4. doi: 10.1186/s13408-019-0072-5 [11] LIU D, ZHAO S, LUO X Y, et al. Unidirectional synchronization of Hodgkin-Huxley neurons with prescribed performance under transcranial magneto-acoustical simulation[J]. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 2019, 13: 1061. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.01061 [12] ZHANG X J, GU H G, WU F Q. Memristor reduces conduction failure of action potentials along axon with Hopf bifurcation[J]. The European Physical Journal Special Topics, 2019, 228(10): 2053-2063. doi: 10.1140/epjst/e2019-900004-2 [13] 张帅, 史勋, 尹宁, 等. 基于H-H神经元模型的经颅磁声刺激对神经元放电活动的影响[J]. 高电压技术, 2019, 45(4): 1124-1130.ZHANG S, SHI X, YIN N, et al. Effects of transcranial magneto-acoustical stimulation on neuronal firing activities based on H-H neuron model[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2019, 45(4): 1124-1130(in Chinese). [14] HODGKIN A L, HUXLEY A F. The components of membrane conductance in the giant axon of Loligo[J]. The Journal of Physiology, 1952, 116(4): 473-496. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004718 [15] HODGKIN A L, HUXLEY A F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve[J]. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology, 1990, 52(1-2): 25-71. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8240(05)80004-7 [16] CHUA L. Memristor, Hodgkin-Huxley, and edge of chaos[J]. Nanotechnology, 2013, 24(38): 383001. doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/24/38/383001 [17] CHUA L, SBITNEV V, KIM H. Hodgkin-Huxley axon is made of memristors[J]. International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, 2012, 22(3): 1230011. doi: 10.1142/S021812741230011X [18] EBELING W. Stochastic processes in physics and chemistry[J]. Zeitschrift Für Physikalische Chemie, 1995, 188(1-2): 310-311. [19] PFEIFFER P, EGUSQUIZA I L, DI VENTRA M, et al. Quantum memristors[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 29507. doi: 10.1038/srep29507 [20] SALMILEHTO J, DEPPE F, DI VENTRA M, et al. Quantum memristors with superconducting circuits[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 42044. doi: 10.1038/srep42044 [21] SANZ M, LAMATA L, SOLANO E. Invited Article: Quantum memristors in quantum photonics[J]. APL Photonics, 2018, 3(8): 080801. doi: 10.1063/1.5036596 [22] NEOUIOUA B, BENAMIRA F, BENBITOUR M A. Quantum fluctuations of mesoscopic RLC circuit with sources and time-dependant resistances[J]. Modern Physics Letters B, 2015, 29(15): 1550077. doi: 10.1142/S0217984915500773 [23] 陈斌, 李有泉, 沙健, 等. 介观电路中电荷的量子效应[J]. 物理学报, 1997, 46(1): 129-133. doi: 10.7498/aps.46.129CHEN B, LI Y Q, SHA J, et al. Quantum effects of charge in the mesoscopic circuit[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 1997, 46(1): 129-133(in Chinese). doi: 10.7498/aps.46.129 [24] 康金平, 蔡绍洪, 张玉强. 介观电路系统的量子化及其量子涨落分析[J]. 江南大学学报(自然科学版), 2011(1): 86-92.KANG J P, CAI S H, ZHANG Y Q. Analysis of quantization and quantum fluctuations of mesoscopic circuit system[J]. Journal of Jiangnan University (Natural Science Edition), 2011(1): 86-92(in Chinese). [25] 孔令杰. 有源介观二阶RLC串并联电路的量子效应[J]. 河北师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 39(2): 117-122.KONG L J. Quantum effects of active mesoscopic second order RLC series and parallel circuit[J]. Journal of Hebei Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 39(2): 117-122(in Chinese). [26] GONZALEZ-RAYA T, CHENG X H, EGUSQUIZA I N L, et al. Quantized single-ion-channel Hodgkin-Huxley model for quantum neurons[J]. Physical Review Applied, 2019, 12(1): 014037. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.12.014037 [27] CALDEIRA A O, LEGGETT A J. Quantum tunnelling in a dissipative system[J]. Annals of Physics, 1983, 149(2): 374-456. doi: 10.1016/0003-4916(83)90202-6 -







 下载:
下载: