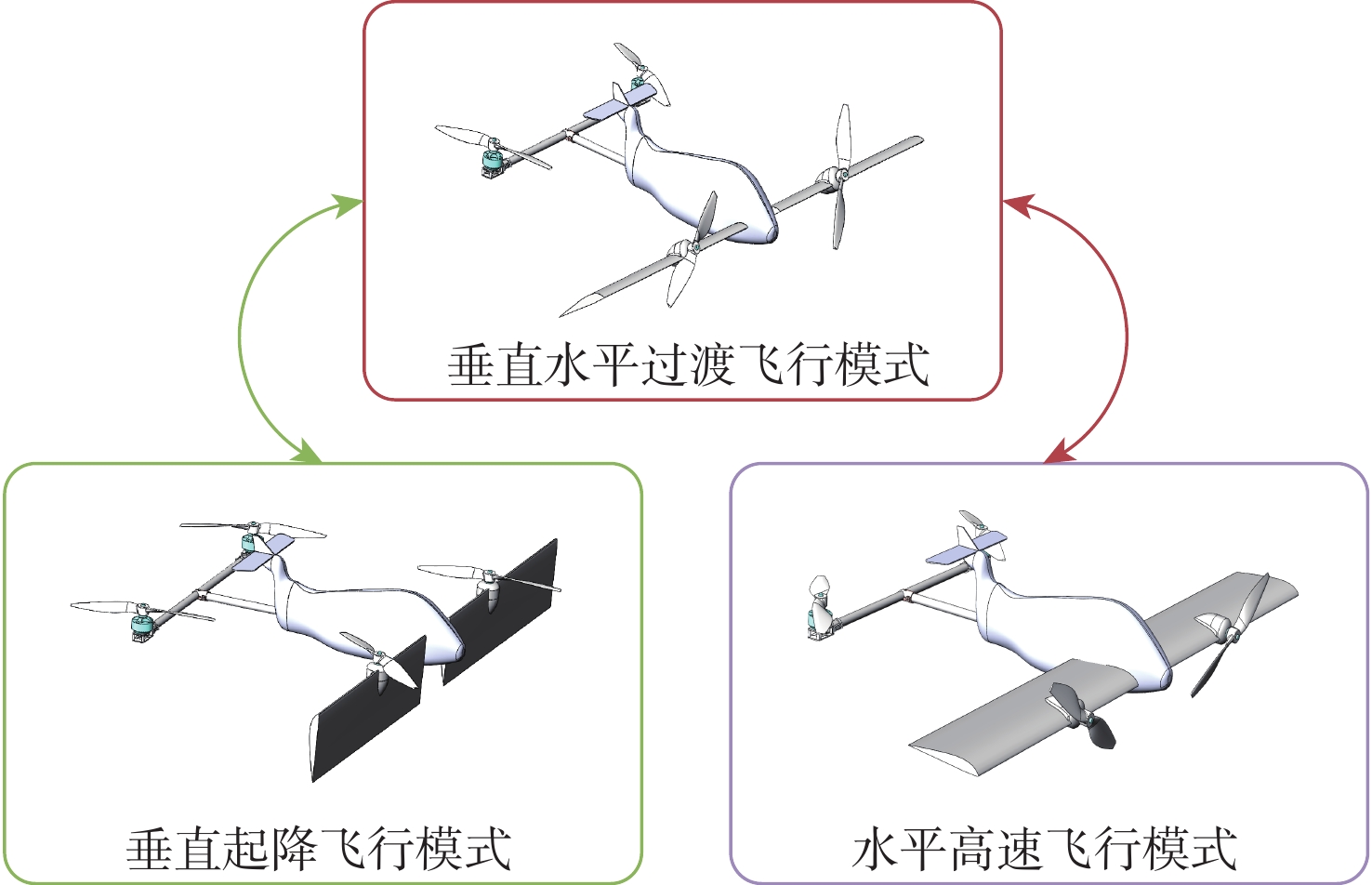
Fixed time trajectory tracking control of forward-tilting morphing aerospace vehicle
-
摘要:
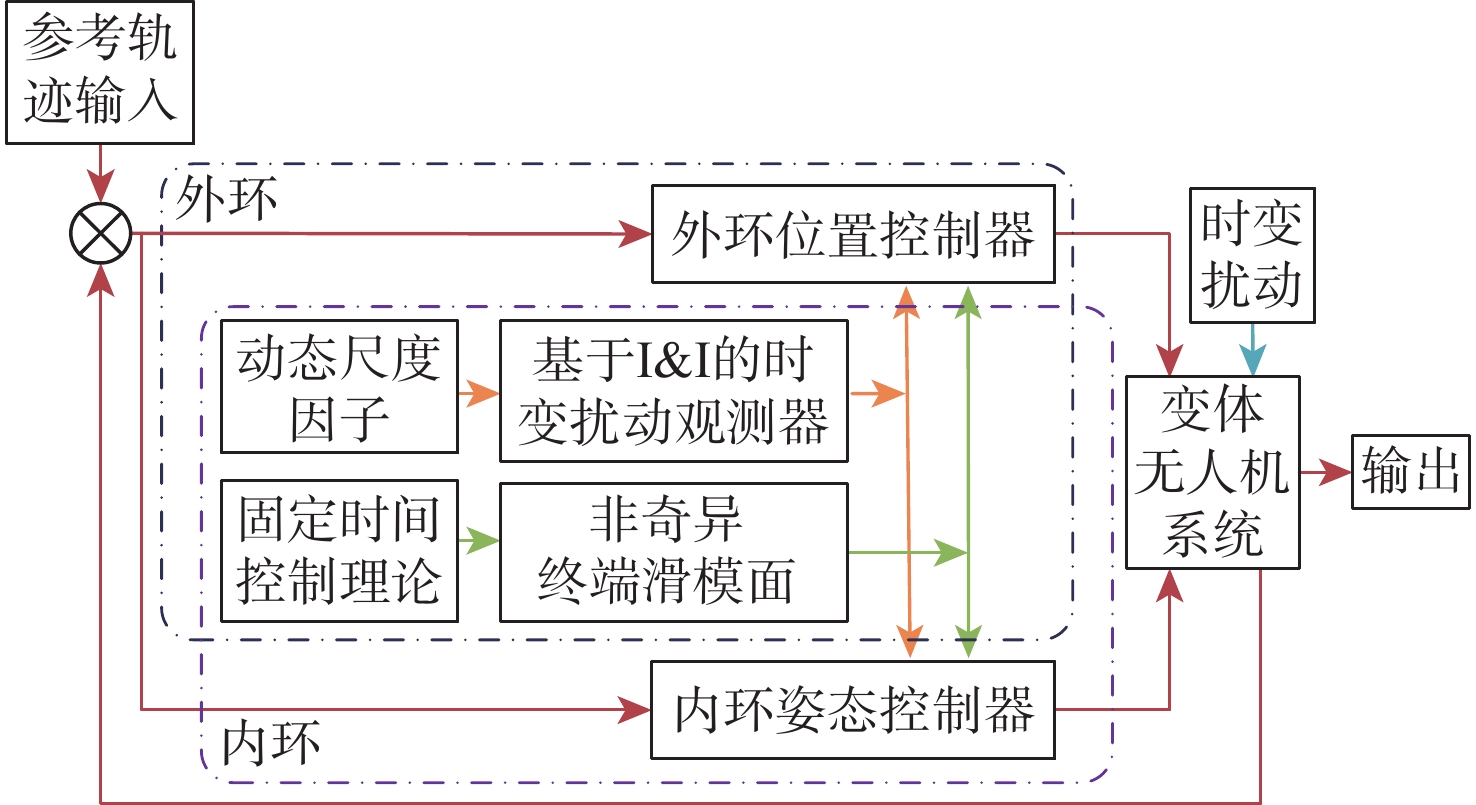
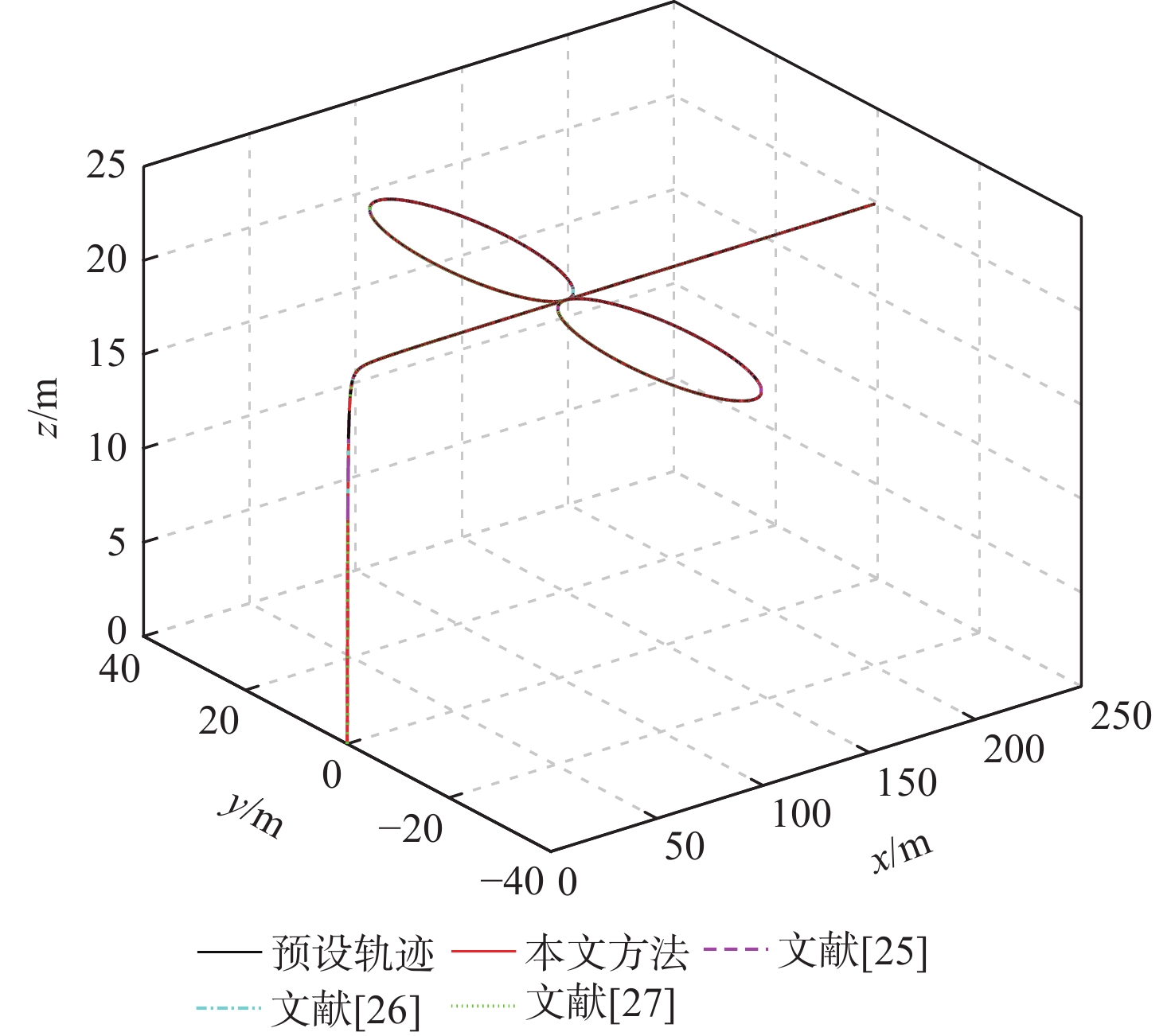
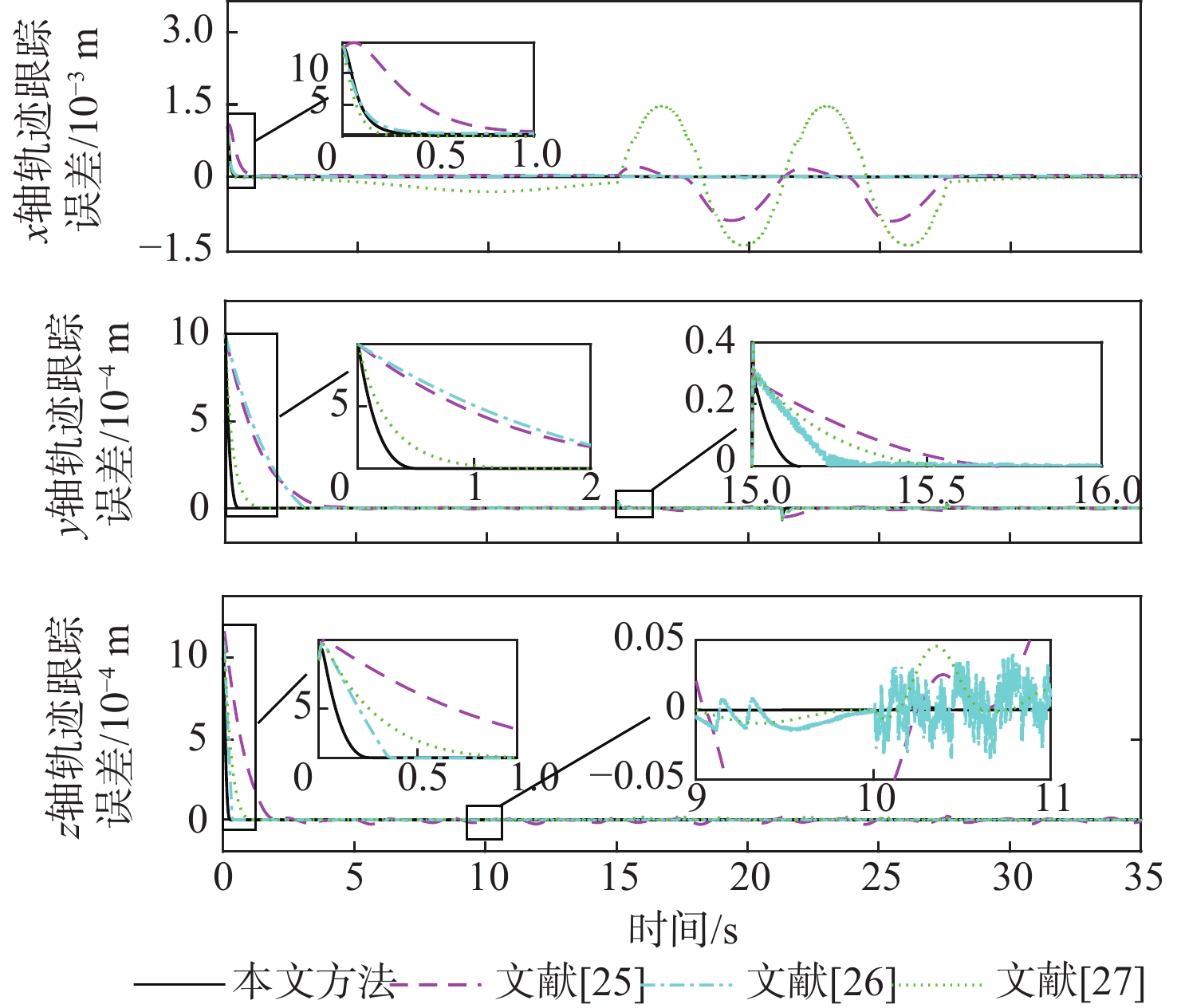
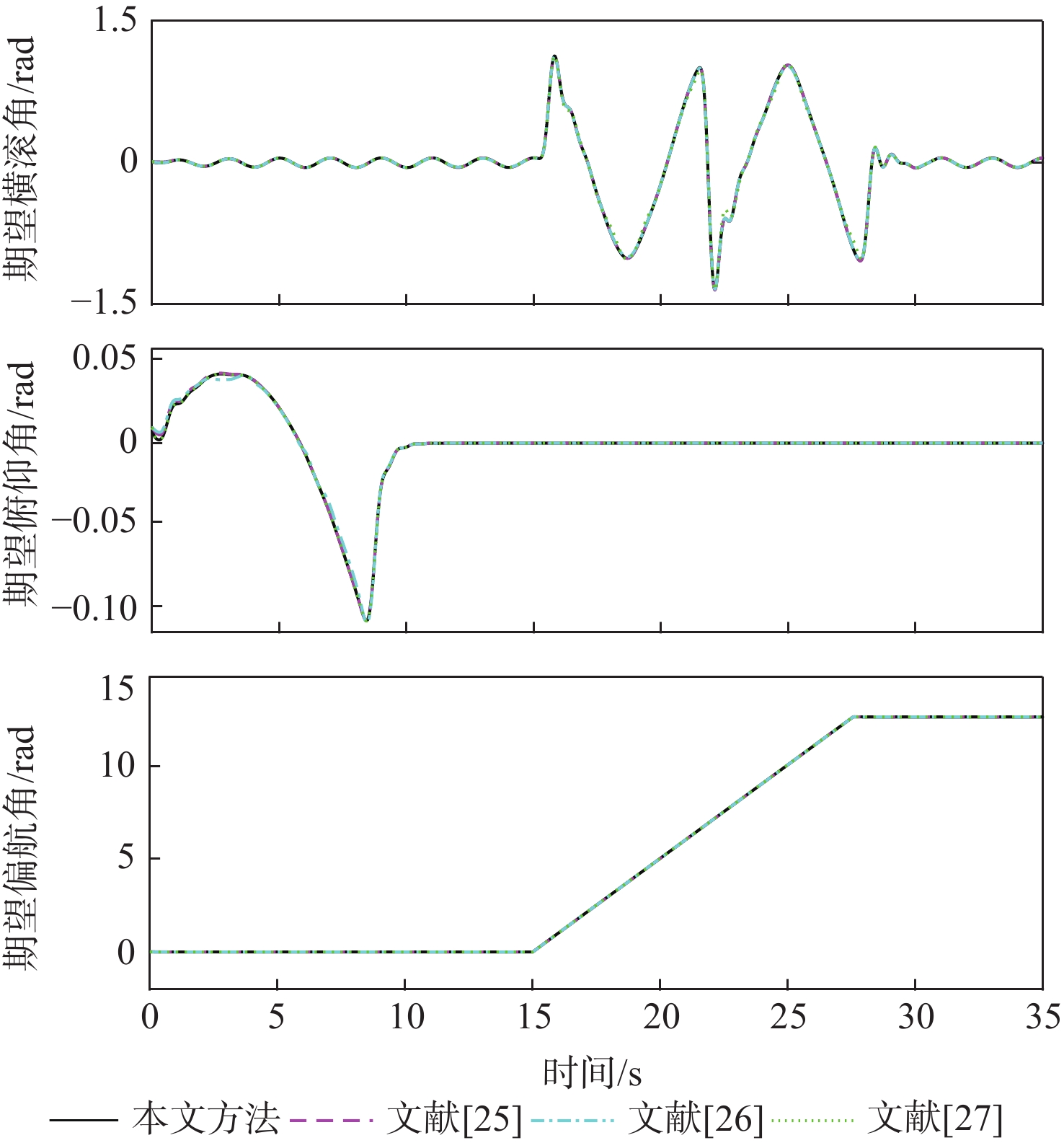
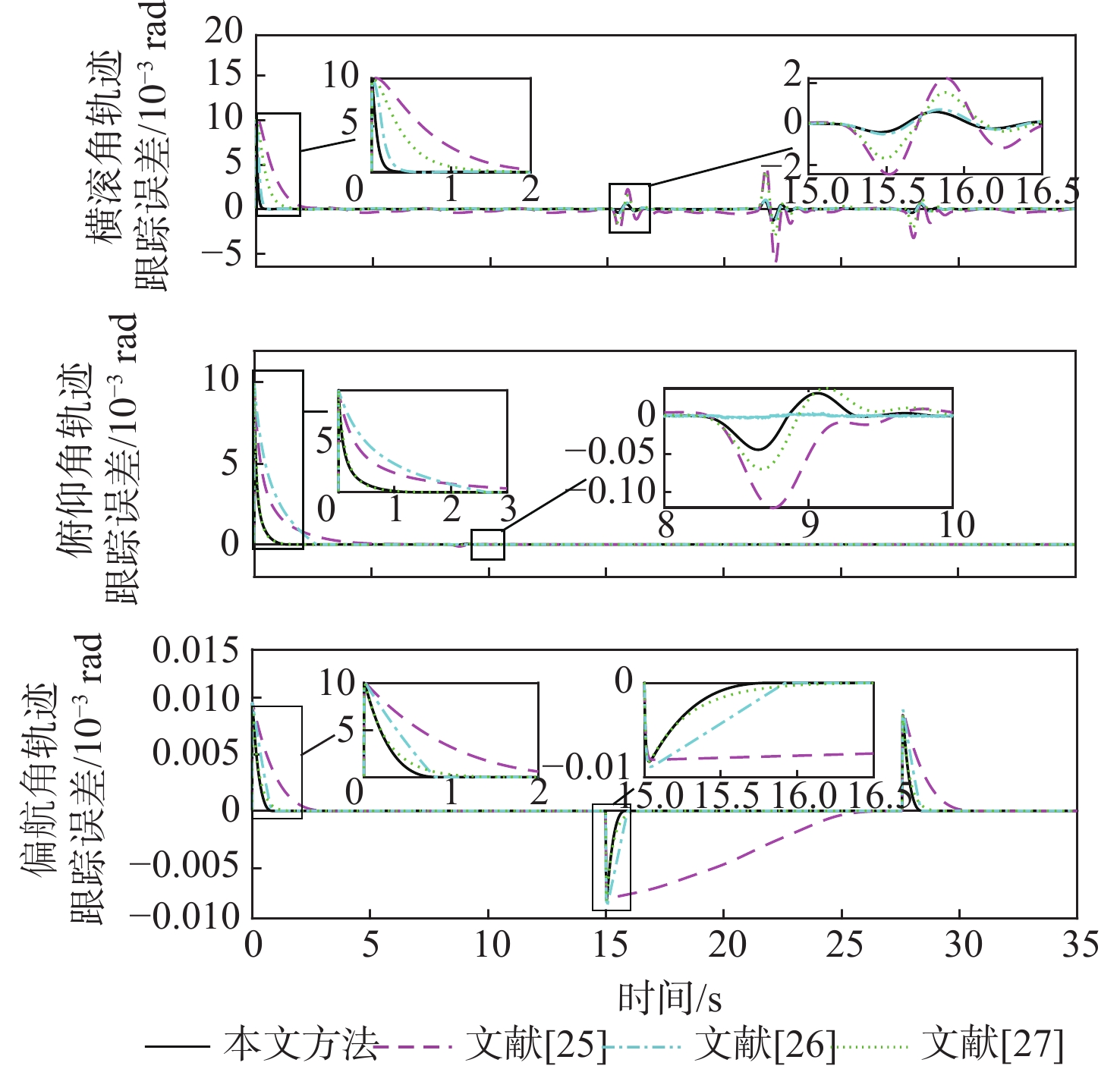
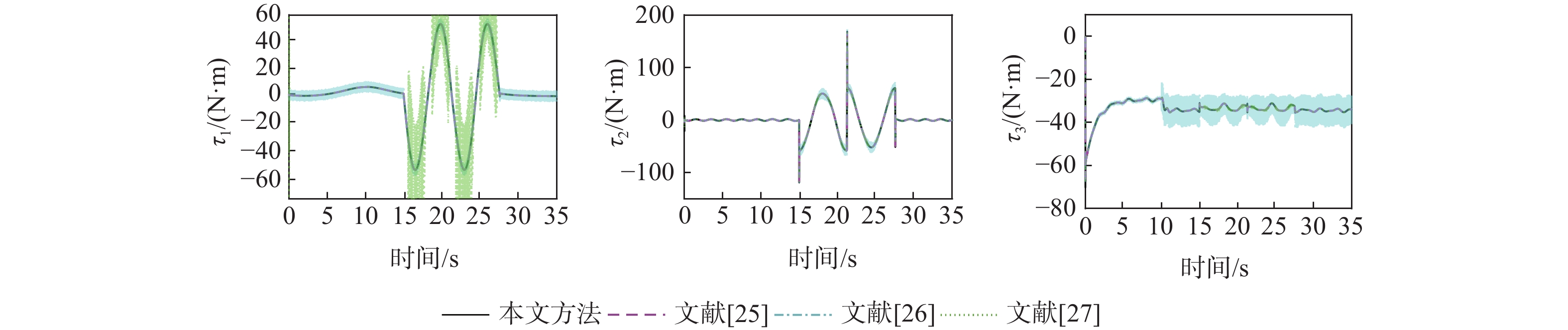
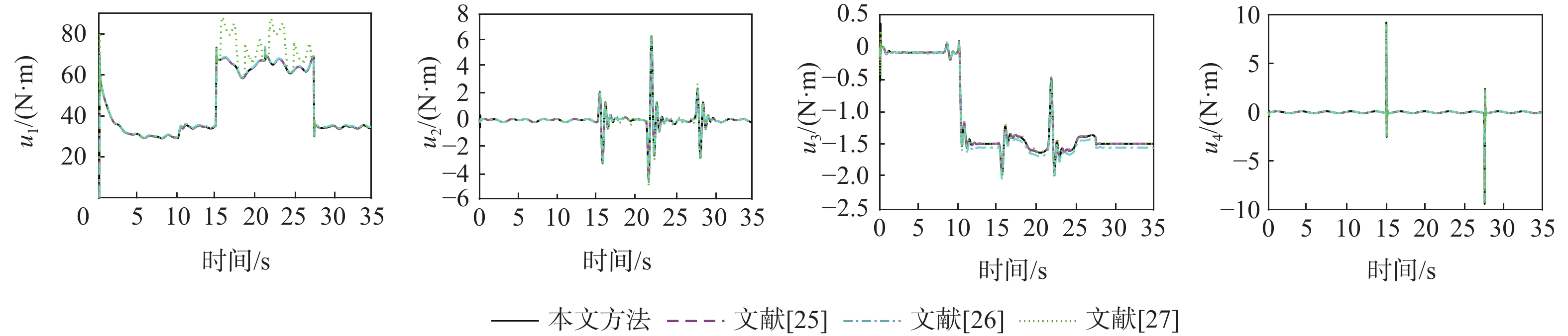
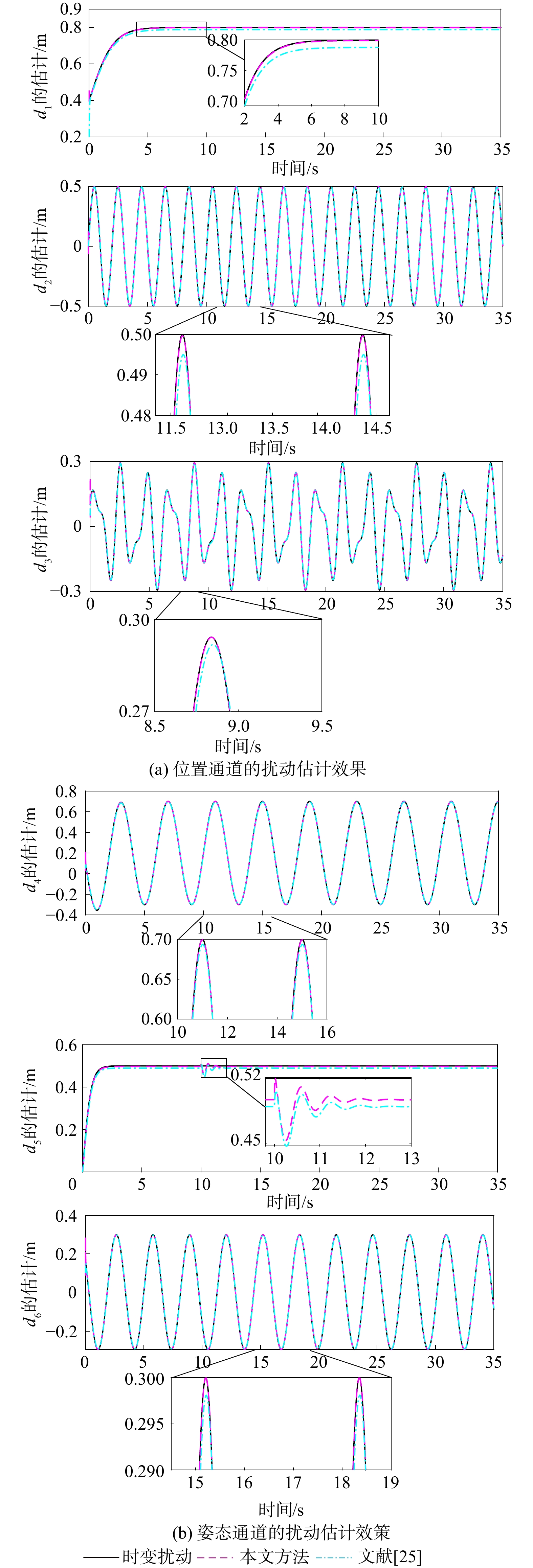
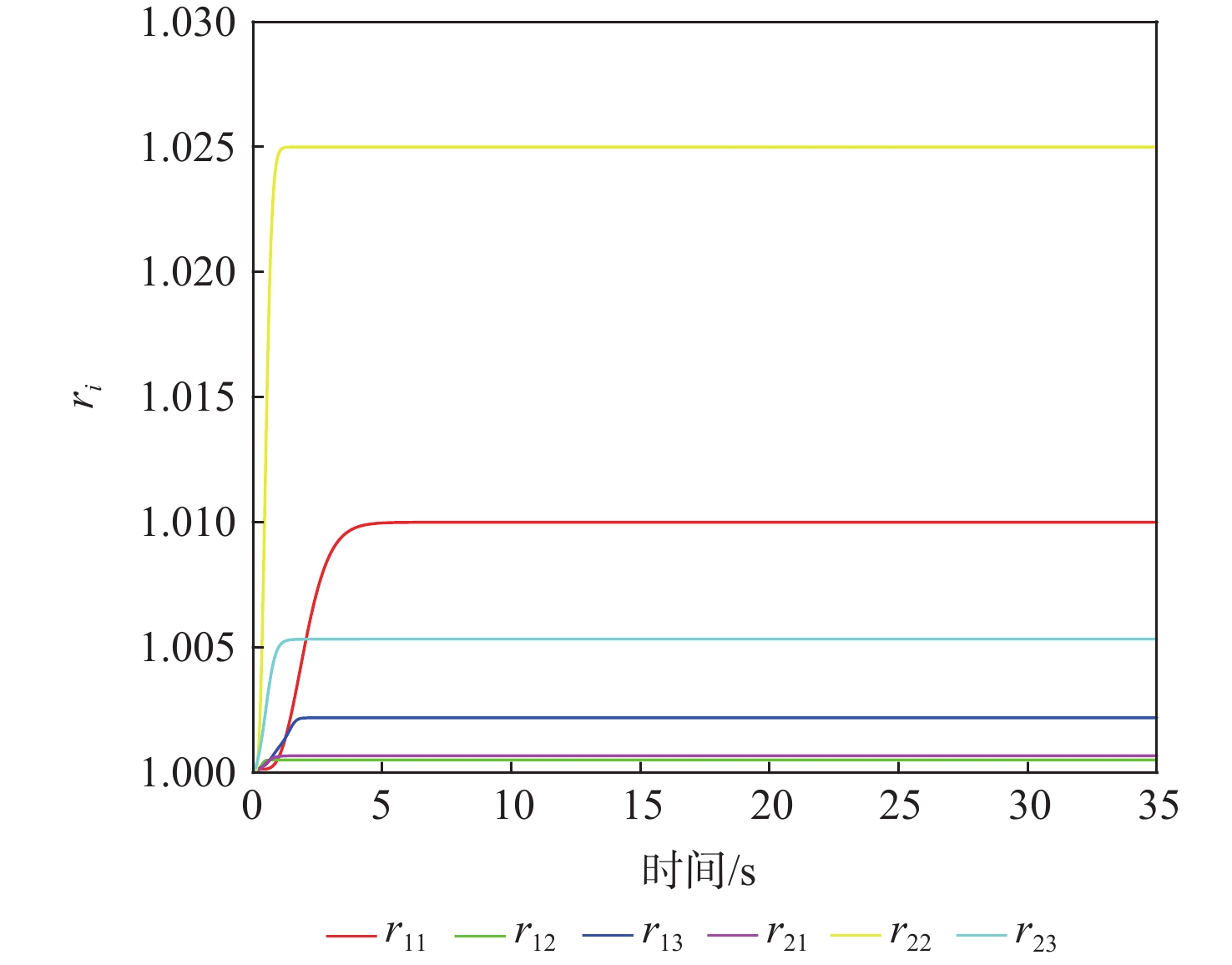
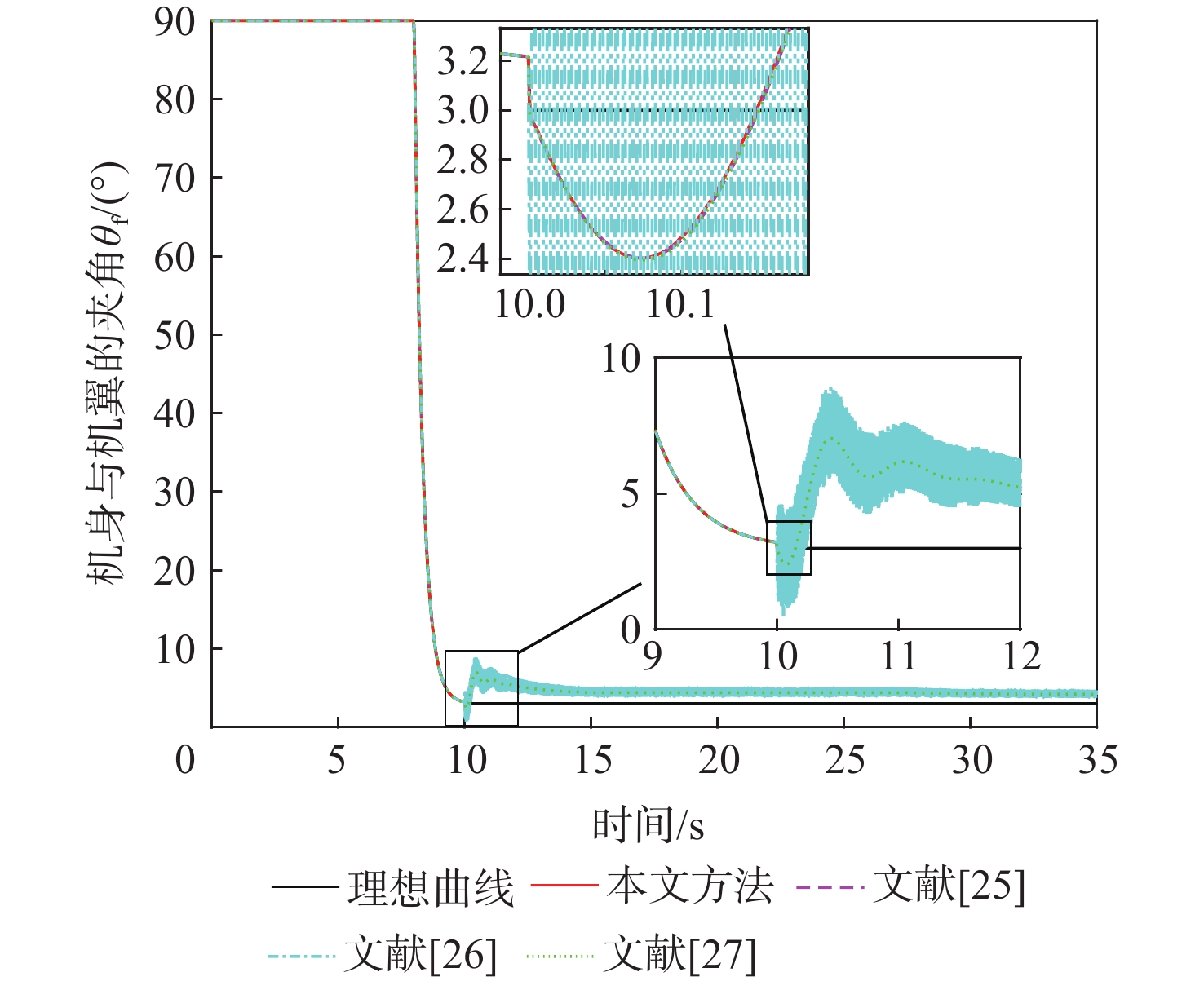
针对具有时变扰动的前倾转变体无人机轨迹跟踪控制问题,提出了一种基于浸入与不变(I&I)理论和固定时间收敛理论的非奇异终端滑模控制方案。融合动态尺度因子设计一种基于I&I的时变扰动观测器;构造一种分段式的固定时间非奇异终端滑模面,消除滑模面的奇异性,并使系统状态在固定时间内收敛到平衡点附近小邻域内,且收敛时间的上界与系统的初始状态无关;基于Lyapunov稳定性理论证明系统的全局固定时间稳定性,并给出其收敛时间的上界。在2种实验场景下验证了所提控制方案的有效性和优越性。与传统的控制方法相比,所提控制方案使系统的收敛速度更快,抗扰动能力更好。
Abstract:In view of the trajectory tracking problem of the forward-tilting morphing aerospace vehicle with time-varying disturbance, a non-singular terminal sliding mode control scheme based on immersion and invariance (I&I) theory and fixed time convergence theory was proposed. Firstly, a time-varying disturbance observer based on I&I was designed by combining dynamic scale factors. Secondly, a segmented fixed-time non-singular terminal sliding surface was constructed, which eliminated the singularity of the sliding mode surface and made the system state converge to any small neighborhood of the equilibrium point within a fixed time, and the upper bound of the convergence time had nothing to do with the initial state of the system. Finally, based on the Lyapunov stability theory, the global fixed-time stability of the system was proven, and the upper bound of its convergence time was given. The effectiveness and superiority of the proposed control scheme were verified in two experimental scenarios. Compared with the traditional control method, the control scheme proposed in this paper made the system converge faster and has better anti-disturbance ability.
-
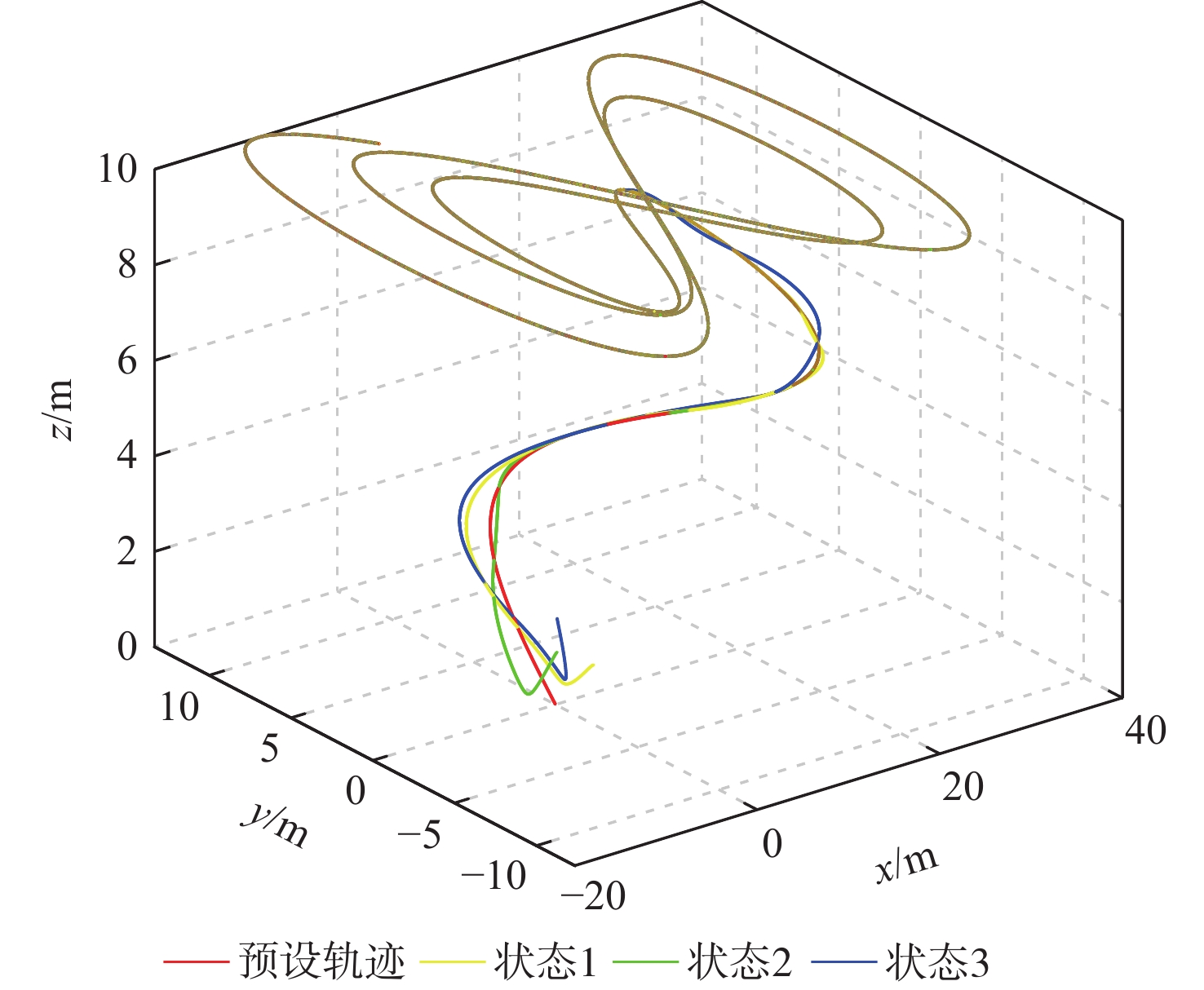
表 1 3种初始状态的选取
Table 1. Selection of three initial states
m 状态 x(0) y(0) z(0) ϕ(0) θ(0) ψ(0) 1 1.5 −0.5 −1.5 0 0 0 2 −2.5 −0.5 −1.5 0 0 π/6 3 2 −0.5 1 0 0 π/3 -
[1] 刘重, 何玉庆, 谷丰, 等. 四倾转旋翼无人机无源控制与飞行实验[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2021, 38(8): 1287-1298.LIU Z, HE Y Q, GU F, et al. Passivity-based control and flight experiment of quad-tilt rotor unmanned aerial vehicle[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2021, 38(8): 1287-1298(in Chinese). [2] 陈卓英, 陈怀民, 王永康. 飞翼布局矢量推力无人机容错控制研究[J]. 西北工业大学学报, 2022, 40(5): 990-996. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2758.2022.05.005CHEN Z Y, CHEN H M, WANG Y K. Study on tolerance control of flying-wing layout vectored thrust UAV[J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2022, 40(5): 990-996(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2758.2022.05.005 [3] ZHANG J M, LIU Y B, GAO L, et al. Bioinspired drone actuated using wing and aileron motion for extended flight capabilities[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2022, 7(4): 11197-11204. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2022.3192803 [4] 李新凯, 张宏立, 范文慧. 非匹配扰动下变体无人机预设性能控制[J]. 航空学报, 2022, 43(2): 325008.LI X K, ZHANG H L, FAN W H. Prescribed performance control for morphing aerospace vehicle under mismatched disturbances[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2022, 43(2): 325008(in Chinese). [5] ASTOLFI A, ORTEGA R. Immersion and invariance: a new tool for stabilization and adaptive control of nonlinear systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2003, 48(4): 590-606. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2003.809820 [6] ARBO M H, GRØTLI E I, GRAVDAHL J T. On the globally exponentially convergent immersion and invariance speed observer for mechanical systems[C]//Proceedings of the 2017 American Control Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 3294-3299. [7] YU L, HE G, ZHAO S L, et al. Immersion and invariance-based sliding mode attitude control of tilt tri-rotor UAV in helicopter mode[J]. International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, 2021, 19(2): 722-735. doi: 10.1007/s12555-020-0110-9 [8] HOSSEINI-PISHROBAT M, KEIGHOBADI J, PIRASTEHZAD A, et al. Immersion and invariance-based extended state observer design for a class of nonlinear systems[J]. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2021, 31(13): 6233-6254. doi: 10.1002/rnc.5607 [9] KARAGIANNIS D, SASSANO M, ASTOLFI A. Dynamic scaling and observer design with application to adaptive control[J]. Automatica, 2009, 45(12): 2883-2889. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2009.09.013 [10] XIA D D, YUE X K, WEN H W. Output feedback tracking control for rigid body attitude via immersion and invariance angular velocity observers[J]. International Journal of Adaptive Control and Signal Processing, 2020, 34(12): 1812-1830. doi: 10.1002/acs.3178 [11] XIA D D, YUE X K. Dynamic scaling-based adaptive control without scaling factor: with application to Euler-Lagrange systems[J]. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2021, 31(10): 4531-4552. doi: 10.1002/rnc.5492 [12] BHAT S P, BERNSTEIN D S. Geometric homogeneity with applications to finite-time stability[J]. Mathematics of Control, Signals and Systems, 2005, 17(2): 101-127. doi: 10.1007/s00498-005-0151-x [13] YU J P, SHI P, ZHAO L. Finite-time command filtered backstepping control for a class of nonlinear systems[J]. Automatica, 2018, 92: 173-180. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2018.03.033 [14] HOU H Z, YU X H, XU L, et al. Finite-time continuous terminal sliding mode control of servo motor systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2019, 67(7): 5647-5656. [15] POLYAKOV A. Nonlinear feedback design for fixed-time stabilization of linear control systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2012, 57(8): 2106-2110. [16] ZUO Z Y. Non-singular fixed-time terminal sliding mode control of non-linear systems[J]. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2015, 9(4): 545-552. [17] HUANG Y, JIA Y M. Fixed-time consensus tracking control for second-order multi-agent systems with bounded input uncertainties via NFFTSM[J]. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2017, 11(16): 2900-2909. [18] TIAN Y, CAI Y L, DENG Y F. A fast nonsingular terminal sliding mode control method for nonlinear systems with fixed-time stability guarantees[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 60444-60454. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2980044 [19] LI H J, CAI Y L. Fixed-time non-singular terminal sliding mode control with globally fast convergence[J]. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2022, 16(12): 1227-1241. [20] WANG X, GUO J, TANG S J, et al. Fixed-time disturbance observer based fixed-time back-stepping control for an air-breathing hypersonic vehicle[J]. ISA Transactions, 2019, 88: 233-245. doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2018.12.013 [21] SONG S, PARK J H, ZHANG B Y, et al. Event-triggered adaptive practical fixed-time trajectory tracking control for unmanned surface vehicle[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2020, 68(1): 436-440. [22] JIN X, DAI S L, LIANG J J. Fixed-time path-following control of an autonomous vehicle with path-dependent performance and feasibility constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2021, 8(1): 458-468. [23] ZOU A M, KUMAR K D, DE RUITER A H J. Fixed-time attitude tracking control for rigid spacecraft[J]. Automatica, 2020, 113: 108792. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2019.108792 [24] 李新凯, 张宏立, 范文慧. 基于时变障碍李雅普诺夫函数的变体无人机有限时间控制[J]. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(8): 2062-2074.LI X K, ZHANG H L, FAN W H. Finite-time control for morphing aerospace vehicle based on time-varying barrier Lyapunov function[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(8): 2062-2074(in Chinese). [25] NI J K, LIU L, LIU C X, et al. Fast fixed-time nonsingular terminal sliding mode control and its application to chaos suppression in power system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2016, 64(2): 151-155. [26] ZHANG Y, TANG S J, GUO J. Adaptive terminal angle constraint interception against maneuvering targets with fast fixed-time convergence[J]. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2018, 28(8): 2996-3014. doi: 10.1002/rnc.4067 [27] NEKOUKAR V, MAHDIAN DEHKORDI N. Robust path tracking of a quadrotor using adaptive fuzzy terminal sliding mode control[J]. Control Engineering Practice, 2021, 110: 104763. doi: 10.1016/j.conengprac.2021.104763 -







 下载:
下载: