-
摘要:
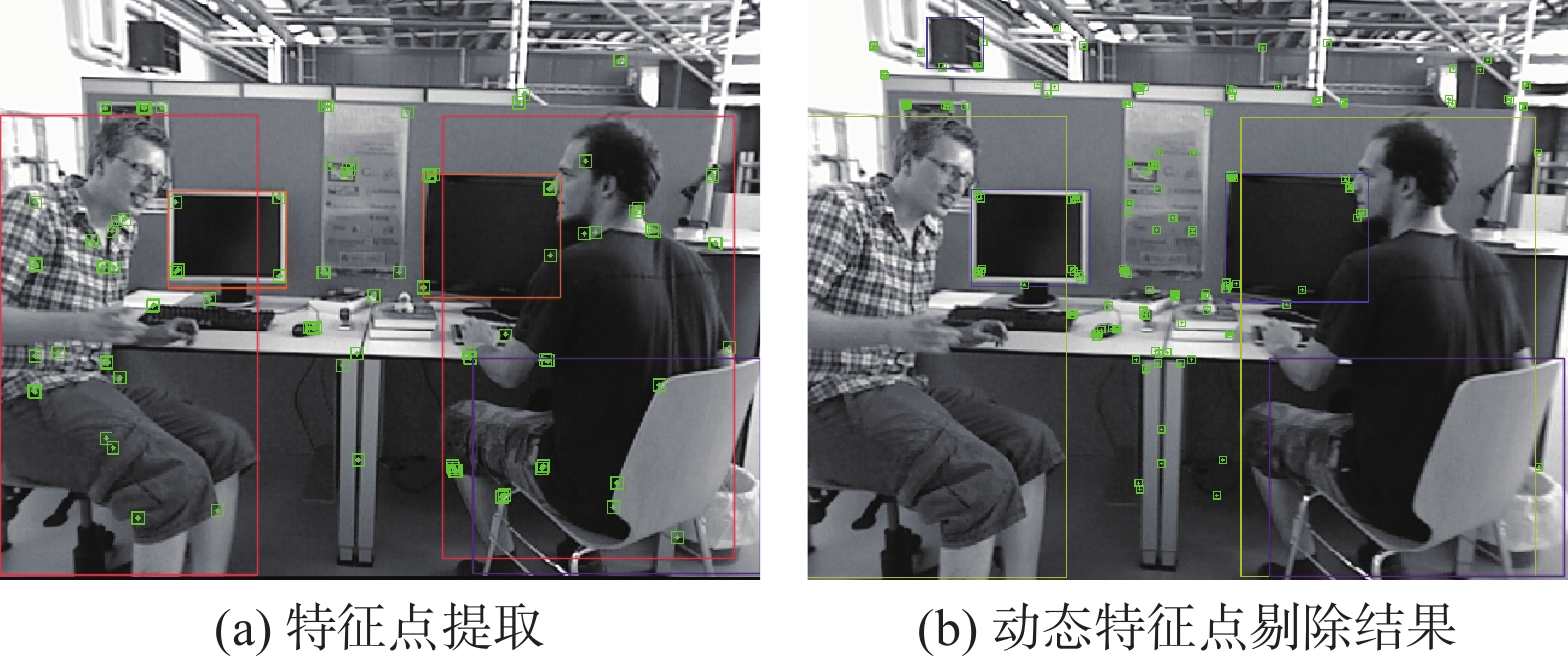
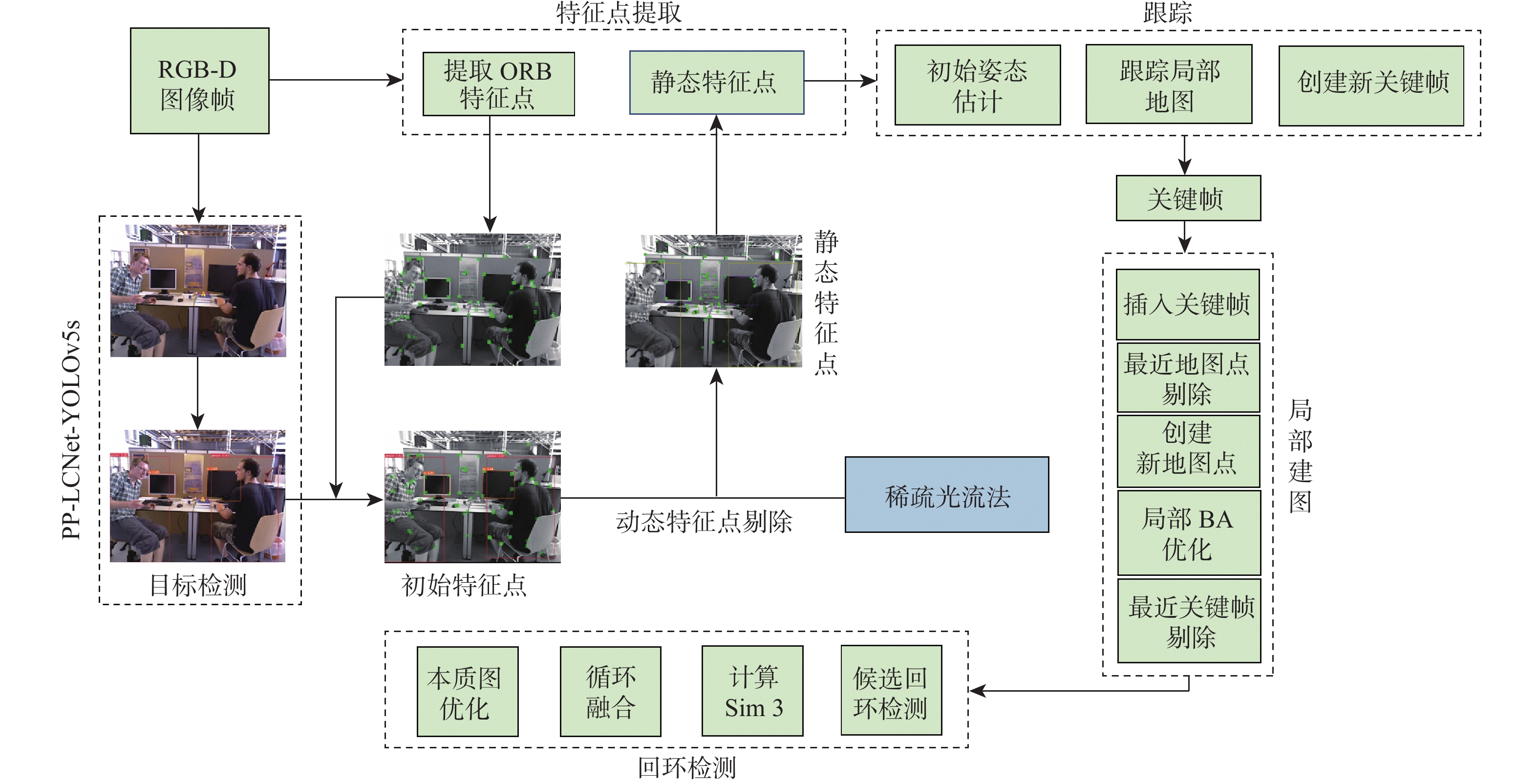
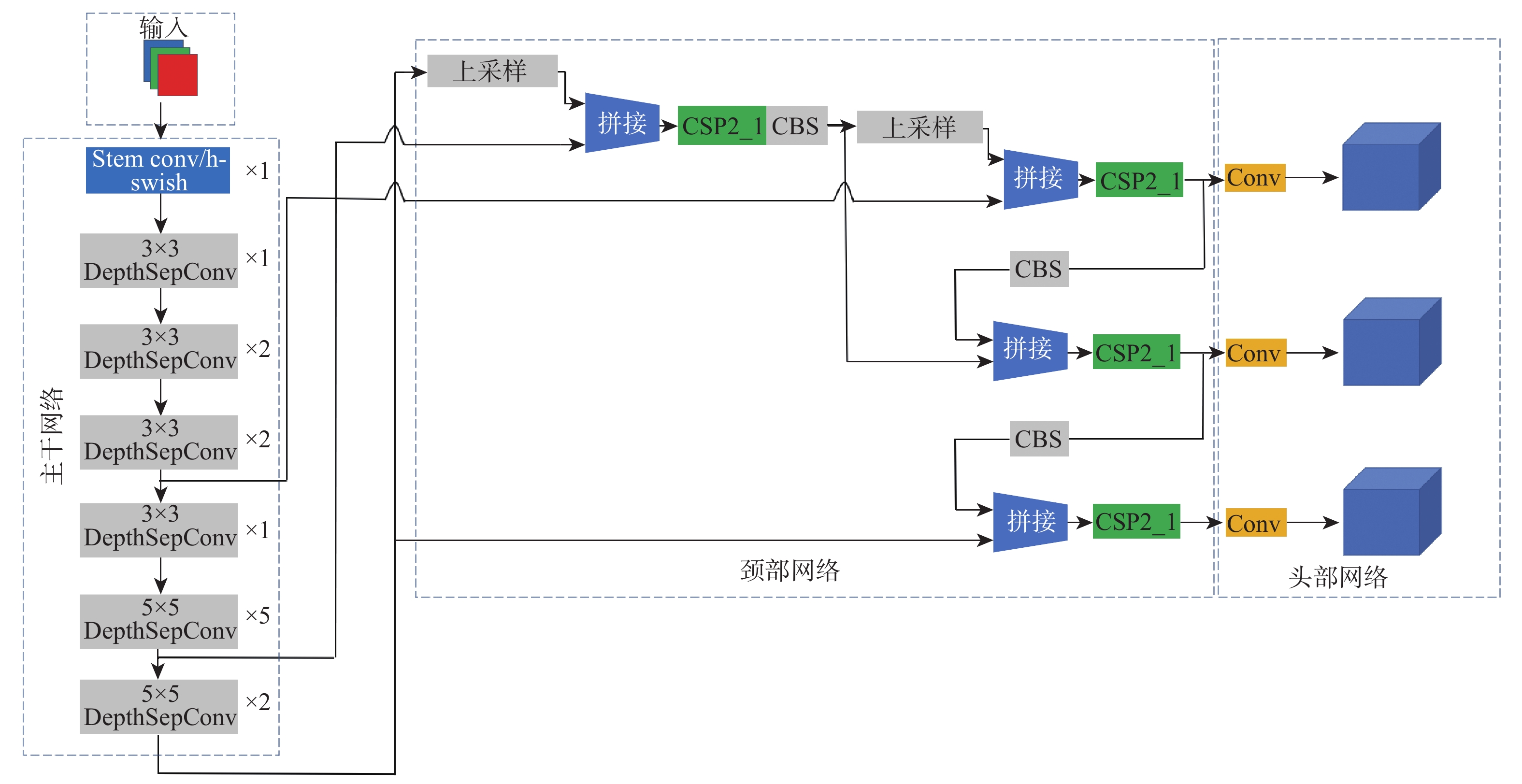
针对室内动态场景中存在的动态目标会降低同步定位与地图构建(SLAM)系统的鲁棒性和相机定位精度问题,提出了一种基于目标检测网络的动态视觉SLAM算法。选择YOLOv5系列中深度和特征图宽度最小的YOLOv5s作为目标检测网络,并将其主干网络替换为PP-LCNet轻量级网络,在VOC2007+VOC2012数据集训练后,由实验结果可知,PP-LCNet-YOLOv5s模型较YOLOv5s模型网络参数量减少了41.89%,运行速度加快了39.13%。在视觉SLAM系统的跟踪线程中引入由改进的目标检测网络和稀疏光流法结合的并行线程,用于剔除动态特征点,仅利用静态特征点进行特征匹配和相机位姿估计。实验结果表明,所提算法在动态场景下的相机定位精度较ORB-SLAM3提升了92.38%。
Abstract:A dynamic visual simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) algorithm based on an object detection network is proposed to address the robustness and camera localization accuracy issues caused by dynamic targets in indoor dynamic scenes. The lightweight network PP-LCNet replaces the YOLOv5 backbone network, and the YOLOv5s with the shortest depth and feature map width are chosen as the object detection network. After training on the VOC2007+VOC2012 dataset, experimental results show that the PP-LCNet-YOLOv5s model reduces the network parameters by 41.89% and improves the running speed by 39.13% compared to the YOLOv5s model. In order to eliminate dynamic feature points from the tracking thread of the visual SLAM system, a parallel thread that combines the enhanced object recognition network and sparse optical flow approach is implemented. Only static feature points are used for feature matching and camera position estimation. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm improves the camera localization accuracy in dynamic scenes by 92.38% compared to ORB-SLAM3.
-
表 1 室内目标的动态属性设定
Table 1. Dynamic property setting for indoor targets
目标 类别 目标 类别 人 动态目标 椅子 潜在动态目标 鸟 动态目标 tv 潜在动态目标 猫 动态目标 水杯 潜在动态目标 狗 动态目标 书 潜在动态目标 扫地机器人 动态目标 桌子 潜在动态目标 表 2 目标检测网络在CPU上的性能测试
Table 2. Performance test of object detection network on CPU
模型 算力要求 参数量 帧速率/(帧·ms−1) 精确率/% 召回率/% mAP@0.5/% PP-LCNet-YOLOv5s 8.7 GFLOPs 4.3×106 11.2 76.1 84.3 73.0 YOLOv5s 17.4 GFLOPs 7.4×106 18.4 78.9 87.5 75.6 YOLOv5m 37.4 GFLOPs 21.4×106 26.8 81.2 90.5 78.8 YOLOv5l 82.1 GFLOPs 47.1×106 43.9 83.2 91.1 80.7 YOLOv5x 141.8 GFLOPs 89.2×106 71.0 84.0 92.0 81.6 表 3 不同策略下的定位精度和每帧耗时
Table 3. Positioning accuracy(unit m) and time consuming per frame(unit s) under different strategies
数据集 均方根误差/m 标准偏差/m 每帧耗时/s 策略1 策略2 策略1 策略2 策略1 策略2 sitting_staic 0.007 9 0.010 3 0.004 3 0.006 7 0.081 3 0.063 1 walking_halfsphere 0.019 6 0.020 4 0.009 8 0.010 7 0.078 1 0.066 4 表 4 ORB-SLAM3算法与改进算法的绝对轨迹误差对比分析
Table 4. Comparison of ATE analysis between ORB-SLAM3 algorithm and improved algorithm
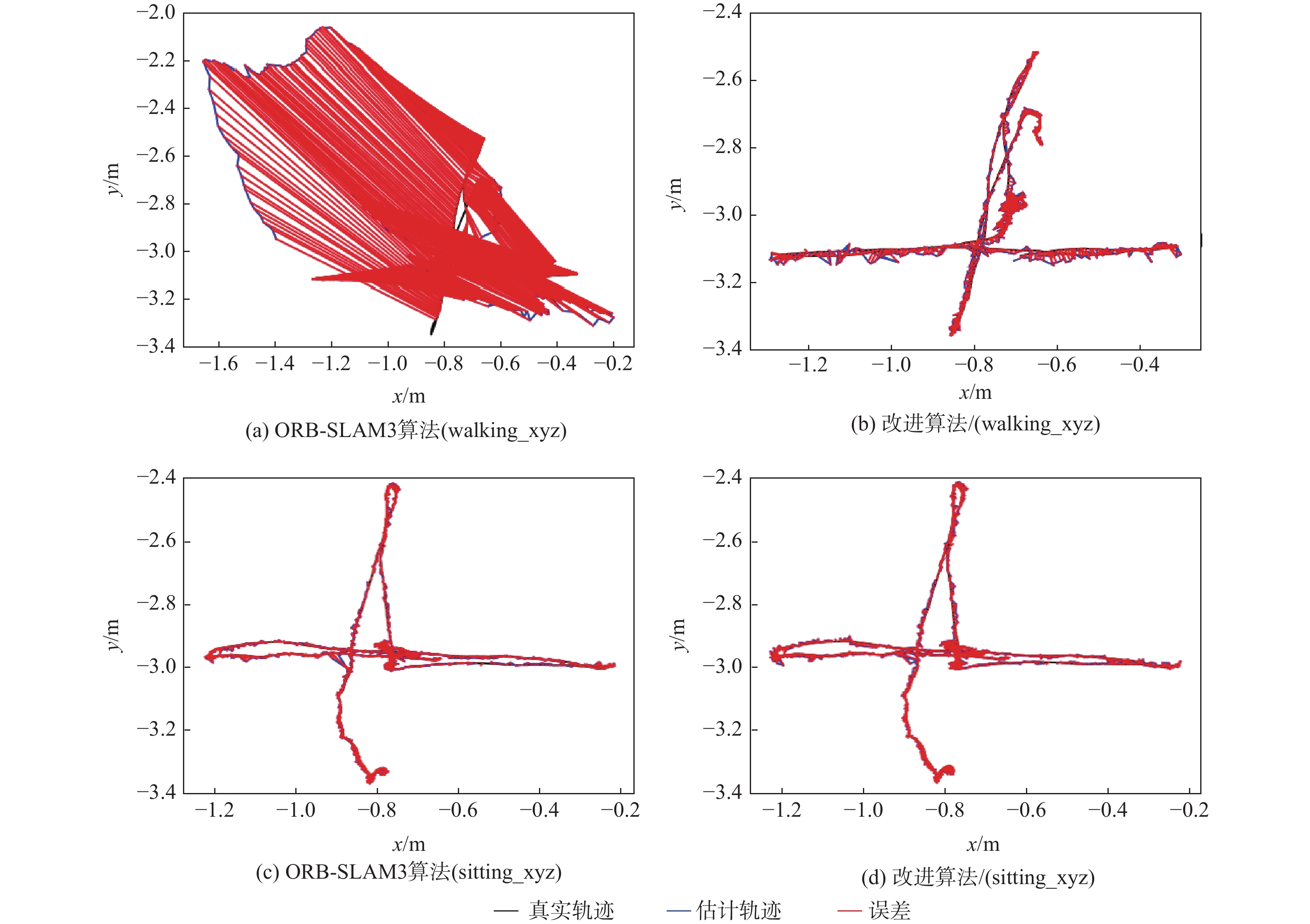
m 序列 均方根误差 标准偏差 平均误差 误差中位数 ORB-SLAM3算法 改进算法 ORB-SLAM3算法 改进算法 ORB-SLAM3算法 改进算法 ORB-SLAM3算法 改进算法 sitting_xyz 0.0092 0.0115 0.0053 0.0075 0.0079 0.0089 0.0073 0.0079 sitting_staic 0.0071 0.0103 0.0035 0.0067 0.0063 0.0072 0.0057 0.0063 walking_rpy 0.3571 0.0302 0.1717 0.0168 0.2983 0.0225 0.2846 0.0203 walking_halfsphere 0.2185 0.0204 0.0879 0.0107 0.1999 0.0174 0.1864 0.0161 walking_xyz 0.2831 0.0143 0.1263 0.0074 0.2534 0.0122 0.2278 0.0107 表 5 ORB-SLAM3与改进算法的相对姿态误差对比分析
Table 5. Comparison of RPE analysis between ORB-SLAM3 algorithm and improved algorithm
m 序列 均方根误差 标准偏差 平均误差 误差中位数 ORB-SLAM3算法 改进算法 ORB-SLAM3算法 改进算法 ORB-SLAM3算法 改进算法 ORB-SLAM3算法 改进算法 sitting_xyz 0.0096 0.0119 0.0061 0.0064 0.0084 0.0100 0.0075 0.0084 sitting_staic 0.0048 0.0074 0.0025 0.0046 0.0041 0.0067 0.0036 0.0059 walking_rpy 0.3741 0.0319 0.3316 0.0219 0.4213 0.0223 0.4113 0.0211 walking_halfsphere 0.1534 0.0143 0.0984 0.0087 0.1175 0.0113 0.1025 0.0105 walking_xyz 0.1497 0.0121 0.1257 0.0071 0.1371 0.0098 0.1224 0.0087 表 6 改进算法与其他动态SLAM算法的绝对轨迹误差对比分析
Table 6. Comparison of ATE analysis between improved algorithm and other dynamic SLAM algorithms
% 序列 DynaSLAM RTD-SLAM RDS-SLAM 改进算法 walking_rpy 93.64 92.46 90.68 91.54 walking_halfsphere 88.79 90.13 84.46 90.66 walking_xyz 93.31 95.57 91.68 94.95 表 7 改进算法和其他算法的跟踪线程耗时和每帧耗时
Table 7. Tracking thread time consumption and time consumption per frame of improved algorithm and other algorithms
算法 网络模型 跟踪线程耗时/ms 每帧消耗时间/ms ORB-SLAM3 26 DynaSLAM Mask R-CNN 200 230 RTD-SLAM YOLOv5s 43 82 改进算法 PP-LCNet-YOLOv5s 31 65 -
[1] 田野, 陈宏巍, 王法胜, 等. 室内移动机器人的SLAM算法综述[J]. 计算机科学, 2021, 48(9): 223-234.TIAN Y, CHEN H W, WANG F S, et al. Overview of SLAM algorithms for mobile robots[J]. Computer Science, 2021, 48(9): 223-234(in Chinese). [2] CAMPOS C, ELVIRA R, RODRÍGUEZ J J G, et al. ORB-SLAM3: an accurate open-source library for visual, visual-inertial, and multimap SLAM[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2021, 37(6): 1874-1890. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2021.3075644 [3] MUR-ARTAL R, TARDÓS J D. ORB-SLAM2: an open-source SLAM system for monocular, stereo, and RGB-D cameras[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2017, 33(5): 1255-1262. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2017.2705103 [4] GOMEZ-OJEDA R, MORENO F A, ZUÑIGA-NOËL D, et al. PL-SLAM: a stereo SLAM system through the combination of points and line segments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2019, 35(3): 734-746. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2019.2899783 [5] 张有全, 祁宇明, 邓三鹏, 等. 直接法和共视图优化的视觉惯性SLAM系统研究[J]. 自动化与仪器仪表, 2022(5): 197-203.ZHANG Y Q, QI Y M, DENG S P, et al. Research on visual-inertial SLAM system based on direct method and common view optimization[J]. Automation and Instrumentation, 2022(5): 197-203(in Chinese). [6] ENGEL J, STÜCKLER J, CREMERS D. Large-scale direct SLAM with stereo cameras[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 1935-1942. [7] ENGEL J, KOLTUN V, CREMERS D. Direct sparse odometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(3): 611-625. [8] LI H, JIANG Y H, FAN F Y, et al. RGB-D SLAM based on semantic and geometry for indoor dynamic environments[C]//Proceedings of the China Automation Congress. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2022: 5581-5586. [9] LONG X D, ZHANG W W, ZHAO B. PSPNet-SLAM: a semantic SLAM detect dynamic object by pyramid scene parsing network[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 214685-214695. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3041038 [10] BESCOS B, FÁCIL J M, CIVERA J, et al. DynaSLAM: tracking, mapping, and inpainting in dynamic scenes[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2018, 3(4): 4076-4083. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2018.2860039 [11] HE K, GKIOXARI G, DOLLAR P, et al. Mask R-CNN[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(2): 386-397. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2844175 [12] HAN S Q, XI Z H. Dynamic scene semantics SLAM based on semantic segmentation[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 43563-43570. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2977684 [13] YUAN X, CHEN S. SaD-SLAM: a visual SLAM based on semantic and depth information[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 4930-4935. [14] YU C, LIU Z X, LIU X J, et al. DS-SLAM: a semantic visual SLAM towards dynamic environments[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 1168-1174. [15] BADRINARAYANAN V, KENDALL A, CIPOLLA R. SegNet: a deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(12): 2481-2495. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2644615 [16] LIU Y B, MIURA J. RDS-SLAM: real-time dynamic SLAM using semantic segmentation methods[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 23772-23785. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3050617 [17] SU P, LUO S Y, HUANG X C. Real-time dynamic SLAM algorithm based on deep learning[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 87754-87766. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3199350 [18] ZHANG H, YE M, SUN X. Robust indoor visual-inertial SLAM with pedestrian detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2019, 68(10): 3897-3908. [19] MUR-ARTAL R, TARDÓS J D. Visual-inertial monocular SLAM with map reuse[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2017, 2(2): 796-803. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2017.2653359 -







 下载:
下载: