Semantic segmentation network of remote sensing images based on dual path supervision
-
摘要:
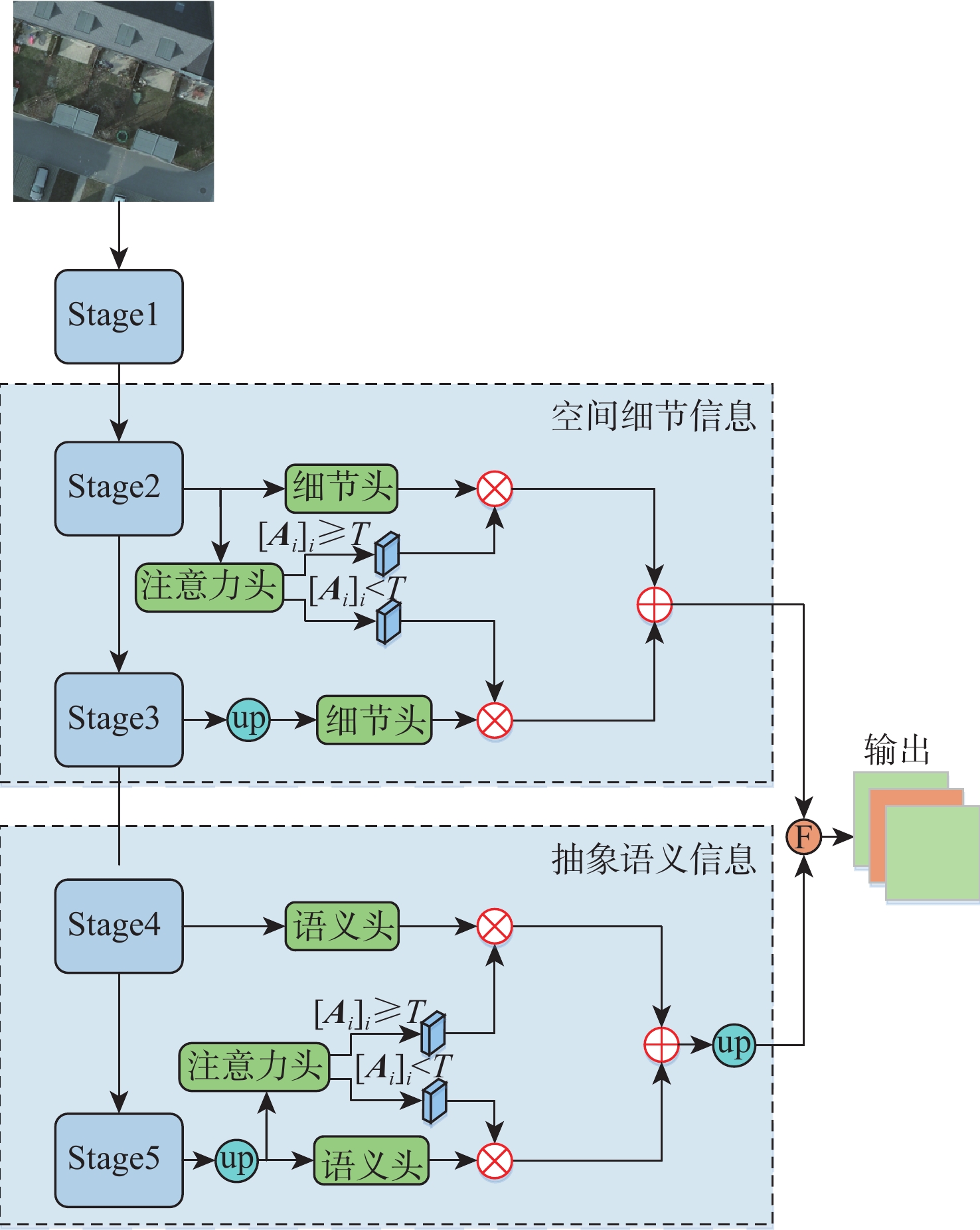
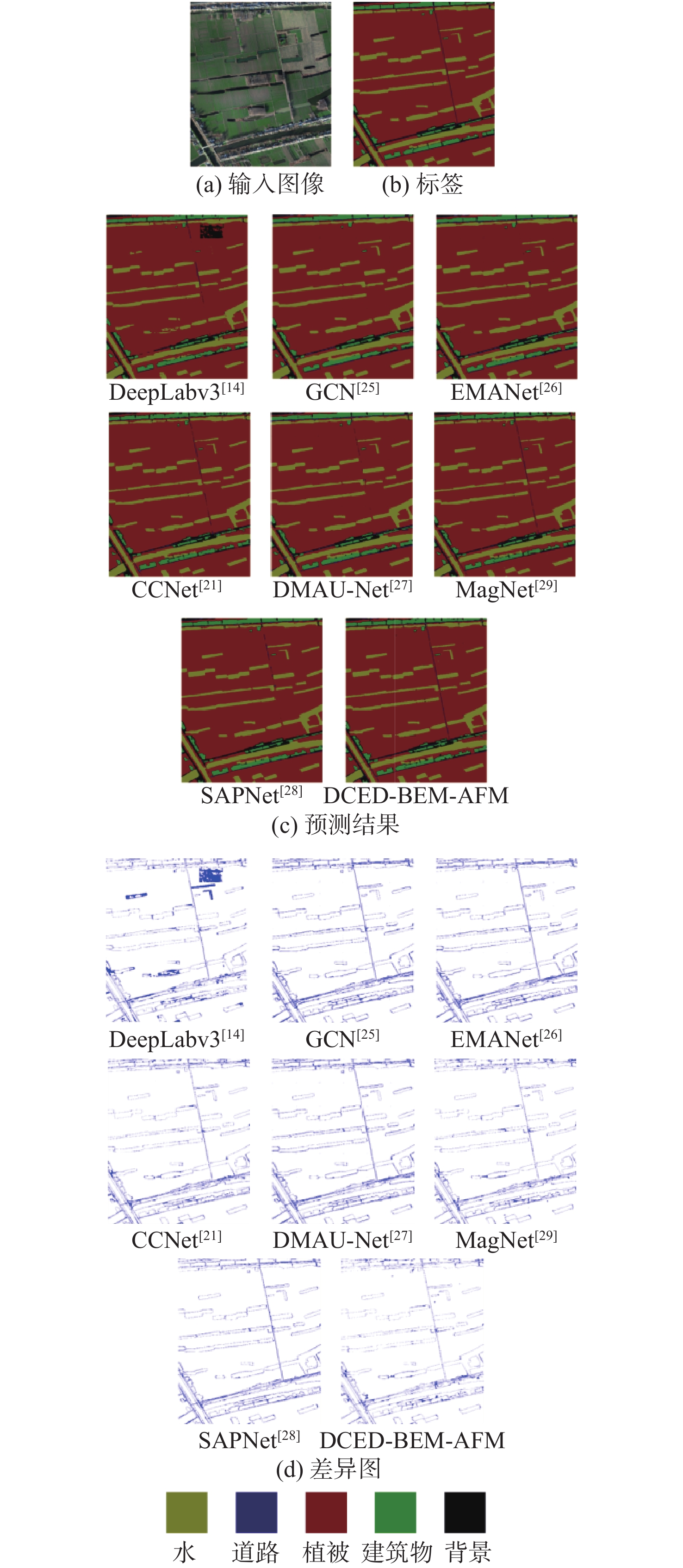
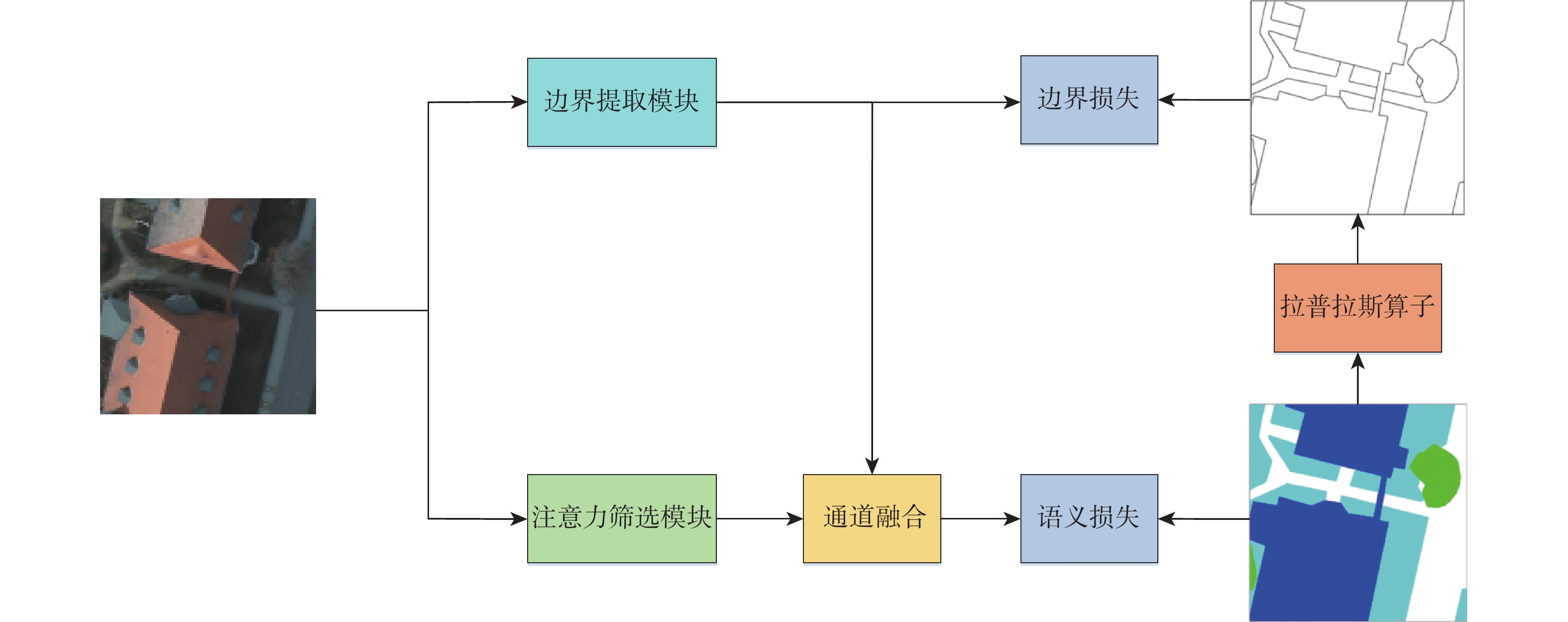
为解决遥感图像语义分割任务中目标物体边界分类模糊的问题,提出双路径监督与注意力筛选网络。引入可监督的边界提取模块来增加边界信息通道,提高边界信息在语义分割中的权重,增强对目标物体边界像素的注意力;引入注意力筛选模块,通过注意力图筛选出浅层网络中的空间细节信息和深层网络中的抽象语义信息,舍弃网络中的冗余信息,防止过拟合。双路径监督与注意力筛选网络在Potsdam数据集和Jiage数据集上的平均交并比分别为85.44%和86.07%,比次优网络MagNet和SAPNet分别提升了1.24%和1.28%、1.54%和1.27%。实验结果表明,所提网络能更精准地分割目标物体的边界。
Abstract:A dual path supervision and attention filtering network was proposed to solve the problem of blurry boundary classification of target objects in semantic segmentation tasks of remote sensing images. A supervised boundary extraction module was introduced to increase the channel of boundary information, improve the weight of boundary information in semantic segmentation, and enhance attention to the boundary pixels of the target object. The attention filtering module was introduced to filter out spatial details in shallow networks and abstract semantic information in deep networks through attention maps, discarding redundant information in the network to prevent overfitting. The mean intersection over union of the dual path supervision and attention filtering network on the Potsdam dataset and the Jiage dataset was 85.44% and 86.07% respectively, which increased by 1.24%, 1.28% and 1.54%, 1.27% compared with the suboptimal network MagNet and SAPNet. Experimental results show that the proposed network can more accurately segment the boundaries of target objects.
-
Key words:
- remote sensing images /
- semantic segmentation /
- supervision /
- boundary information /
- attention filtering
-
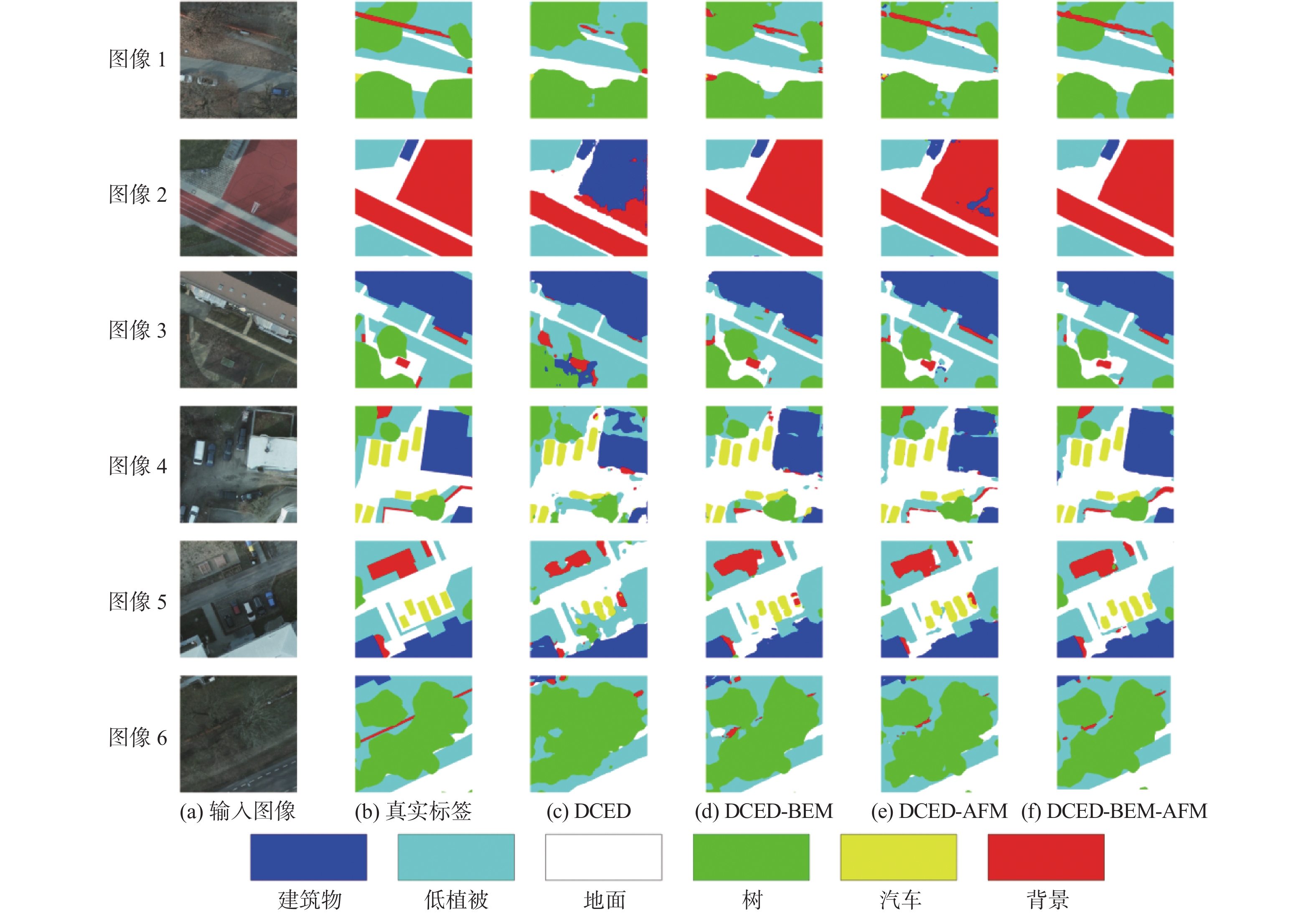
表 1 Potsdam数据集消融实验结果
Table 1. Results of ablation experiments on Potsdam dataset
% 网络模型 IoU F1 mIoU PA 背景 汽车 地面 树 低植被 建筑物 DCED 54.57 76.05 79.37 72.02 74.97 89.02 84.85 74.33 86.29 DCED-BEM 80.70 79.07 85.60 78.41 80.39 89.89 91.02 82.34 91.21 DCED-AFM 81.57 79.48 86.38 81.26 82.28 89.82 91.78 83.47 92.09 DCED-BEM-AFM 84.93 79.51 87.37 84.33 85.07 91.41 92.89 85.44 93.36 表 2 Jiage数据集消融实验结果
Table 2. Results of ablation experiments on Jiage dataset
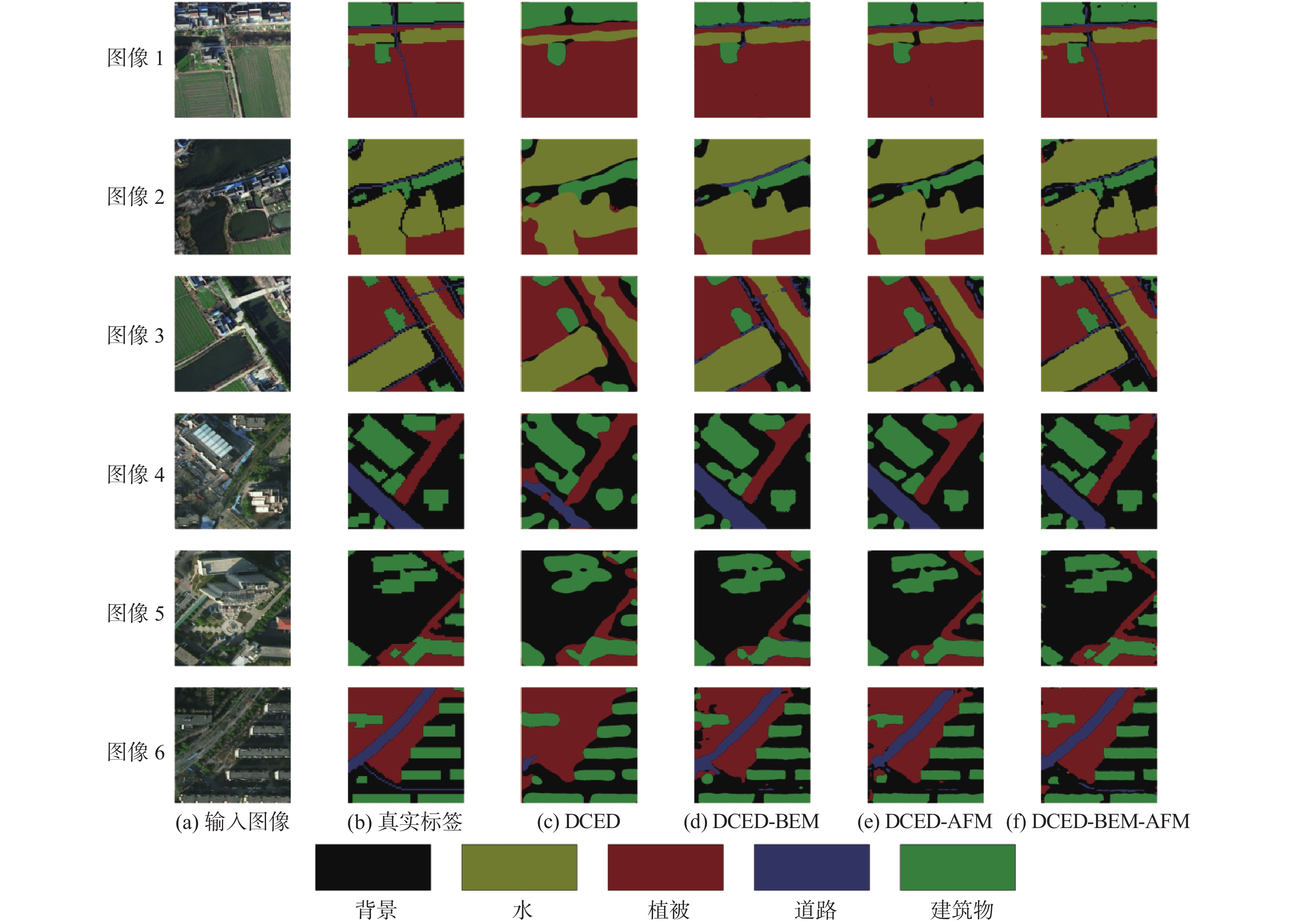
% 网络模型 IoU F1 mIoU PA 背景 植被 道路 水 建筑物 DCED 77.04 92.84 43.91 83.91 78.56 84.71 75.25 91.89 DCED-BEM 82.39 95.34 64.33 89.32 82.85 90.24 82.85 94.18 DCED-AFM 83.55 95.94 68.05 90.60 83.63 91.22 84.35 94.76 DCED-BEM-AFM 83.84 96.25 73.51 92.21 84.52 92.32 86.07 95.15 表 3 Potsdam数据集上对比实验结果
Table 3. Comparison of experimental results on Potsdam dataset
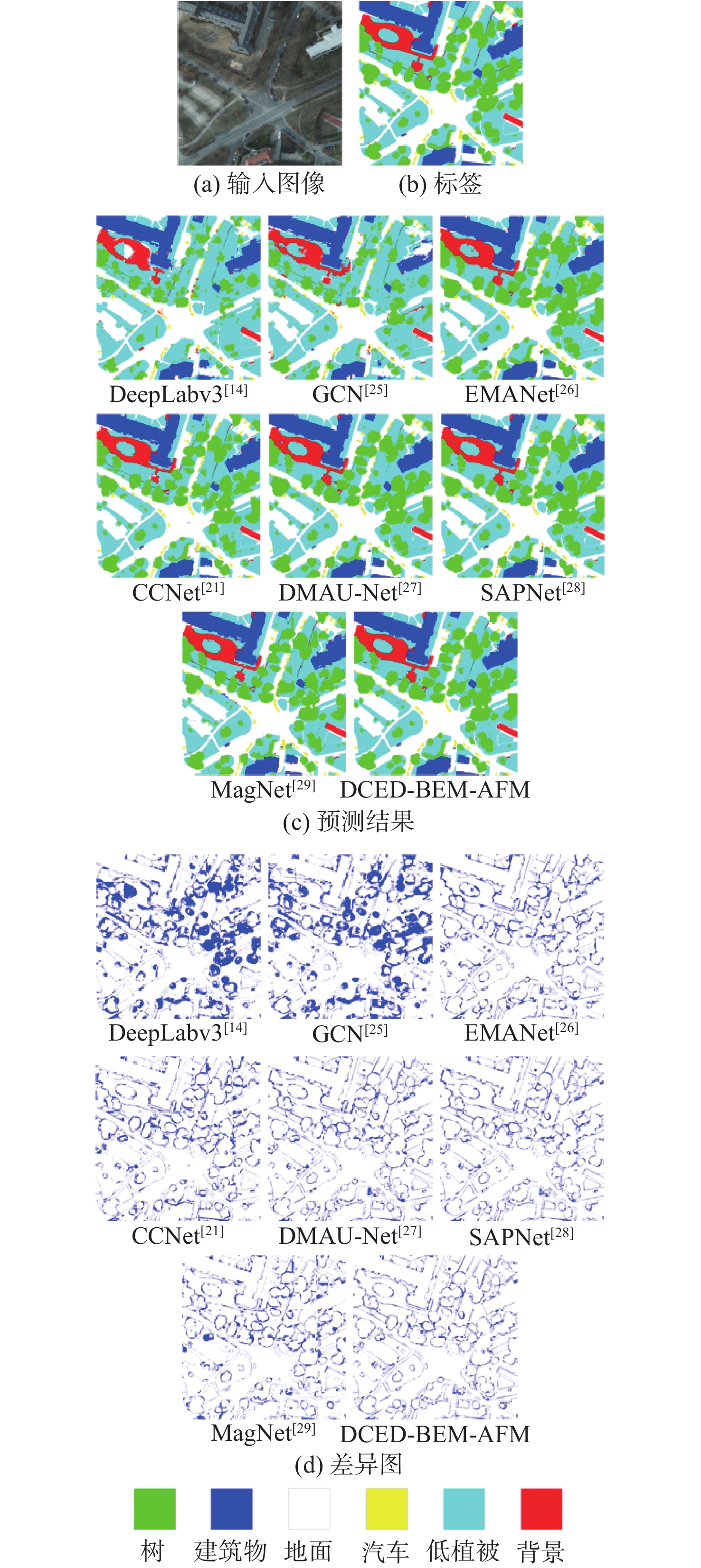
模型 IoU/% mIoU/% 参数量 预测时间/s 背景 汽车 地面 树 低植被 建筑物 SegNet[24] 69.49 59.85 83.44 52.97 79.26 80.36 70.90 15.62×106 0.12 PSPNet[15] 78.33 65.84 86.78 56.21 81.55 88.32 76.17 30.95×106 0.34 DeepLabv3[14] 78.86 67.57 85.63 60.38 80.57 87.51 76.75 59.24×106 0.41 GCN[25] 75.12 73.15 85.36 67.32 82.85 85.27 78.18 25.91×106 0.15 EMANet[26] 77.40 75.60 85.60 80.70 82.10 89.30 81.78 34.72×106 0.12 CCNet[21] 76.39 78.79 87.60 79.62 82.24 89.71 82.39 60.11×106 0.23 DMAU-Net[27] 80.69 76.54 86.76 80.87 82.15 92.55 83.26 36.42×106 0.19 SAPNet[28] 82.30 73.59 87.27 85.38 84.65 91.75 84.16 63.83×106 0.37 MagNet[29] 79.54 82.09 88.67 79.85 83.00 92.07 84.20 51.67×106 0.32 DCED-BEM-AFM 84.93 79.51 87.37 84.33 85.07 91.41 85.44 56.57×106 0.24 表 4 Jiage数据集上对比实验结果
Table 4. Comparison of experimental results on Jiage dataset
模型 IoU/% mIoU/% 背景 植被 道路 水 建筑物 SegNet[24] 61.42 91.44 45.42 87.27 66.58 70.43 PSPNet[15] 79.08 96.25 48.81 89.91 81.27 79.06 DeepLabv3[14] 80.83 95.27 56.51 88.67 78.66 79.99 GCN[25] 75.77 95.76 58.94 90.11 81.00 80.32 EMANet[26] 81.93 95.13 63.88 88.37 82.52 82.37 CCNet[21] 81.29 95.30 67.06 90.86 81.64 83.23 DMAU-Net[27] 82.02 95.55 67.79 89.77 82.20 83.47 MagNet[29] 82.37 95.70 70.47 91.31 82.78 84.53 SAPNet[28] 83.88 96.07 68.37 91.10 84.58 84.80 DCED-BEM-AFM 83.84 96.25 73.51 92.21 84.52 86.07 -
[1] FAN M, LAI S, HUAN G J, et al. Rethinking BiseNet for real-time semantic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 9716-9725. [2] LATHA P, RAJ T. Advanced deep learning method for aerial image segmentation of landscape changes in pre-and post-disaster scenarios[J]. Global NEST Journal, 2022, 24(3): 544-552. [3] GUO Z L, SHENGOKU H, WU G M, et al. Semantic segmentation for urban planning maps based on U-Net[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 6187-6190. [4] FAN R Y, LI F P, HAN W, et al. Fine-scale urban informal settlements mapping by fusing remote sensing images and building data via a Transformer-based multimodal fusion network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5630316. [5] ZHU Q Q, ZHANG Y N, WANG L Z, et al. A global context-aware and batch-independent network for road extraction from VHR satellite imagery[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2021, 175: 353-365. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2021.03.016 [6] ZHOU M T, SUI H G, CHEN S X, et al. BT-RoadNet: a boundary and topologically-aware neural network for road extraction from high-resolution remote sensing imagery[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2020, 168: 288-306. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2020.08.019 [7] LONG J, SHELHAMER E, DARRELL T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 3431-3440. [8] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, BROX T. U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-assisted Intervention. Berlin: Springer, 2015: 234-241. [9] WANG X, LI Z S, HUANG Y P, et al. Multimodal medical image segmentation using multi-scale context-aware network[J]. Neurocomputing, 2022, 486: 135-146. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.11.017 [10] LUO J, ZHAO L, ZHU L, et al. Multi-scale receptive field fusion network for lightweight image super-resolution[J]. Neurocomputing, 2022, 493: 314-326. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2022.04.038 [11] LIN D, SHEN D G, SHEN S T, et al. ZigZagNet: fusing top-down and bottom-up context for object segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 7482-7491. [12] 吴泽康, 赵姗, 李宏伟, 等. 遥感图像语义分割空间全局上下文信息网络[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2022, 56(4): 795-802.WU Z K, ZHAO S, LI H W, et al. Spatial global context information network for semantic segmentation of remote sensing image[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2022, 56(4): 795-802(in Chinese). [13] CHEN L C, PAPANDREOU G, KOKKINOS I, et al. DeepLab: semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(4): 834-848. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2699184 [14] CHEN L C, PAPANDREOU G, SCHROFF F, et al. Rethinkingatrous convolution for semantic image segmentation[EB/OL]. (2017-06-17)[2023-03-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.05587. [15] ZHAO H S, SHI J P, QI X J, et al. Pyramid scene parsing network[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 6230-6239. [16] HU J, SHEN L, SUN G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 7132-7141. [17] WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. CBAM: convolutional block attention module[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 3-19. [18] ZHOU Z, ZHOU Y, WANG D L, et al. Self-attention feature fusion network for semantic segmentation[J]. Neurocomputing, 2021, 453: 50-59. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.04.106 [19] 谭大宁, 刘瑜, 姚力波, 等. 基于视觉注意力机制的多源遥感图像语义分割[J]. 信号处理, 2022, 38(6): 1180-1191.TAN D N, LIU Y, YAO L B, et al. Semantic segmentation of multi-source remote sensing images based on visual attention mechanism[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2022, 38(6): 1180-1191(in Chinese). [20] FU J, LIU J, TIAN H J, et al. Dual attention network for scene segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 3141-3149. [21] HUANG Z L, WANG X G, HUANG L C, et al. CCNet: criss-cross attention for semantic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 603-612. [22] LIN T Y, DOLLÁR P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 936-944. [23] SIMONYAN K, ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[EB/OL]. (2014-09-04)[2023-03-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.1556. [24] BADRINARAYANAN V, KENDALL A, CIPOLLA R. SegNet: a deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(12): 2481-2495. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2644615 [25] PENG C, ZHANG X Y, YU G, et al. Large kernel matters—improve semantic segmentation by global convolutional network[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1743-1751. [26] LI X, ZHONG Z S, WU J L, et al. Expectation-maximization attention networks for semantic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 9166-9175. [27] YANG Y, DONG J W, WANG Y H, et al. DMAU-Net: an attention-based multiscale max-pooling dense network for the semantic segmentation in VHR remote-sensing images[J]. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15(5): 1328. doi: 10.3390/rs15051328 [28] LI X, XU F, LIU F, et al. A synergistical attention model for semantic segmentation of remote sensing images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5400916. [29] HUYNH C, TRAN A T, LUU K, et al. Progressive semantic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 16750-16759. -







 下载:
下载: