A method for calculating reachability regions of lift re-entry vehicles with multiple constraints
-
摘要:
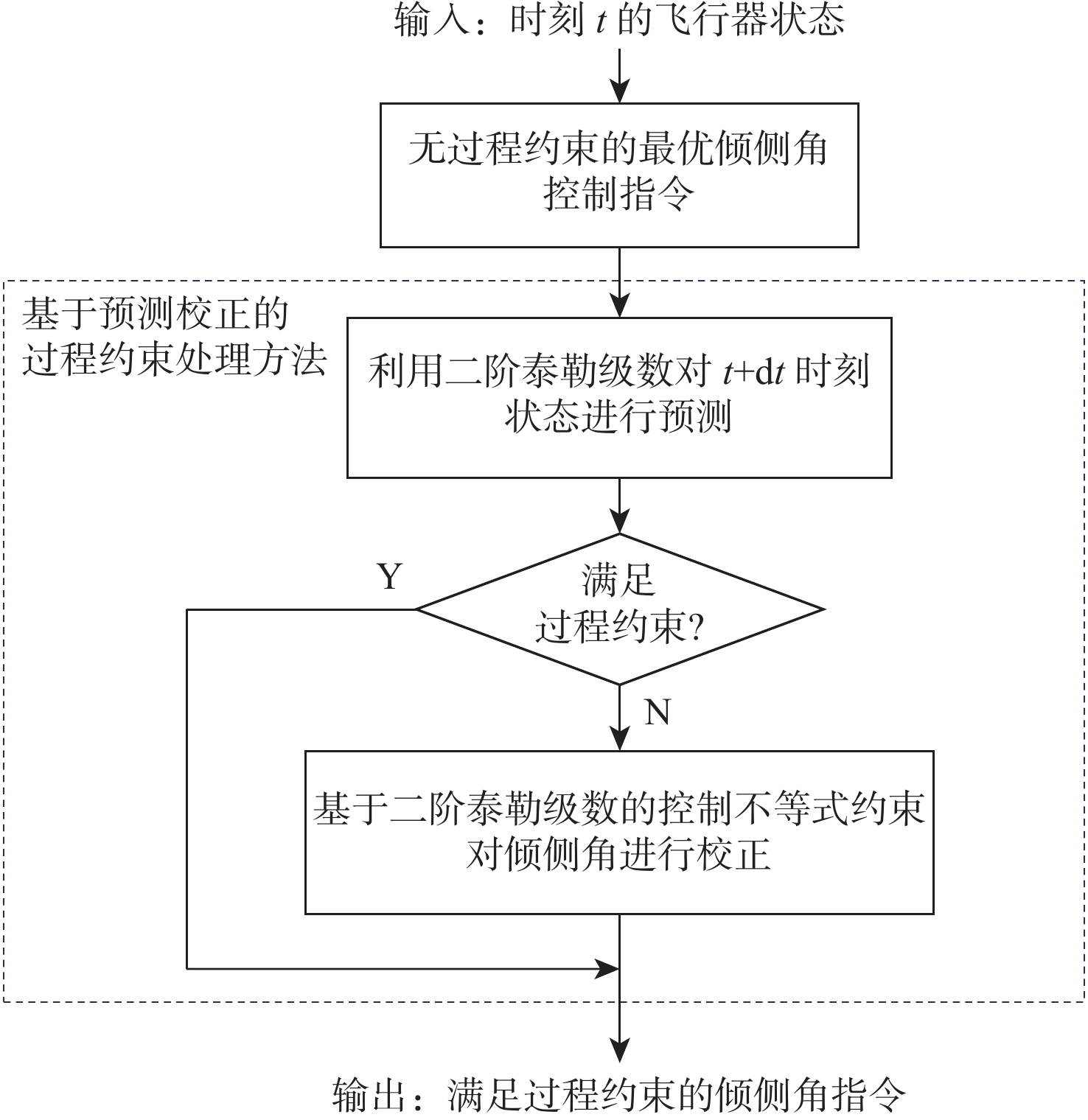
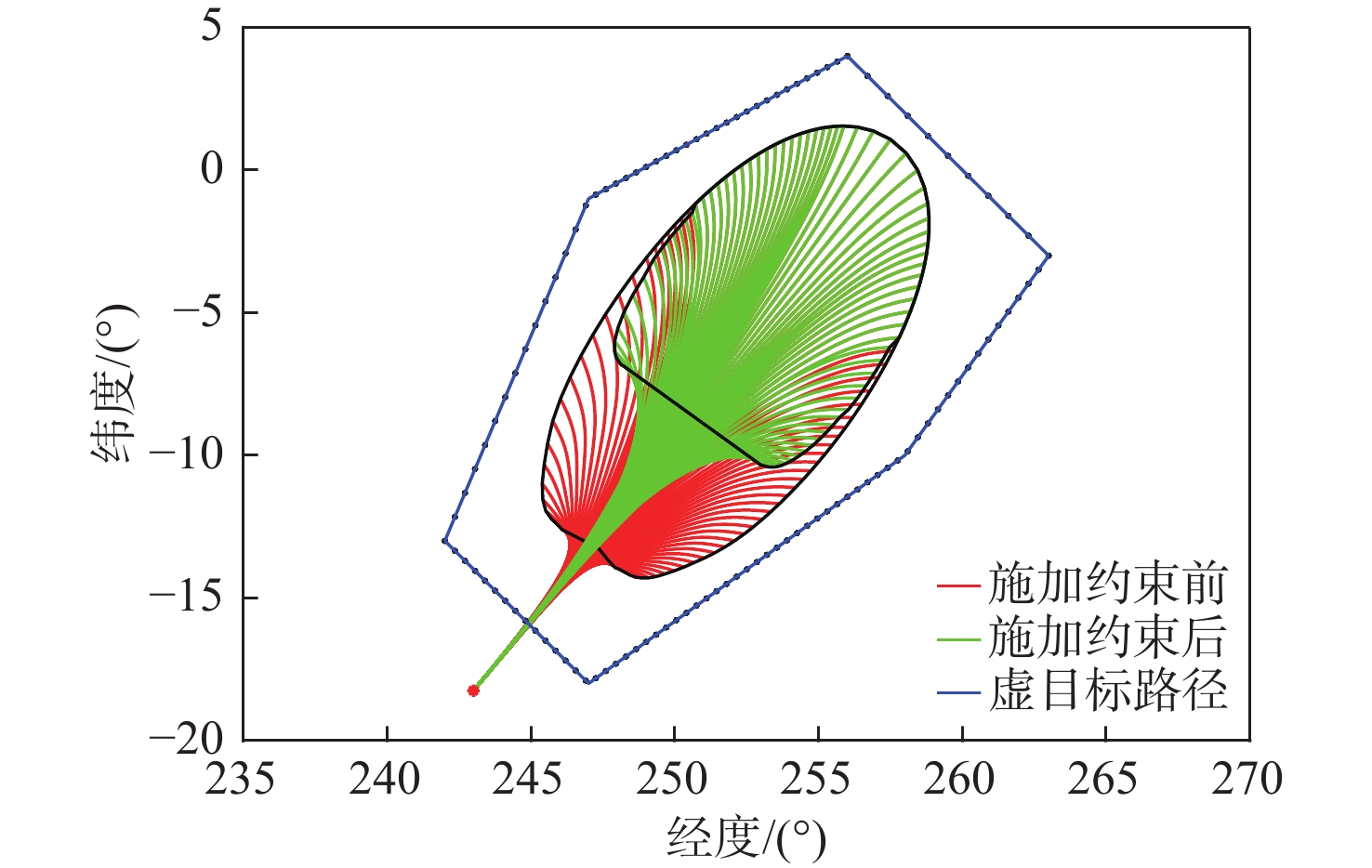
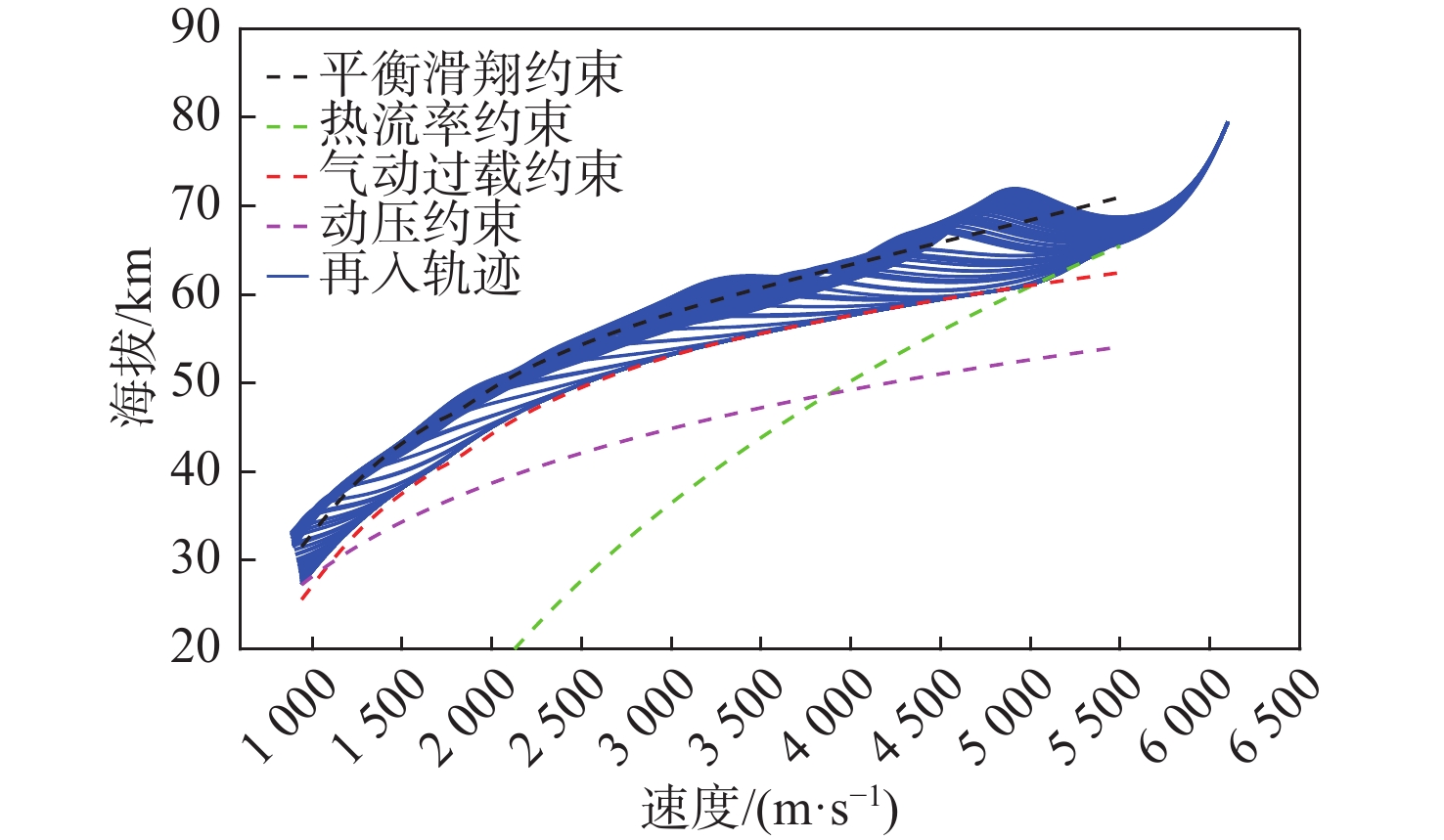
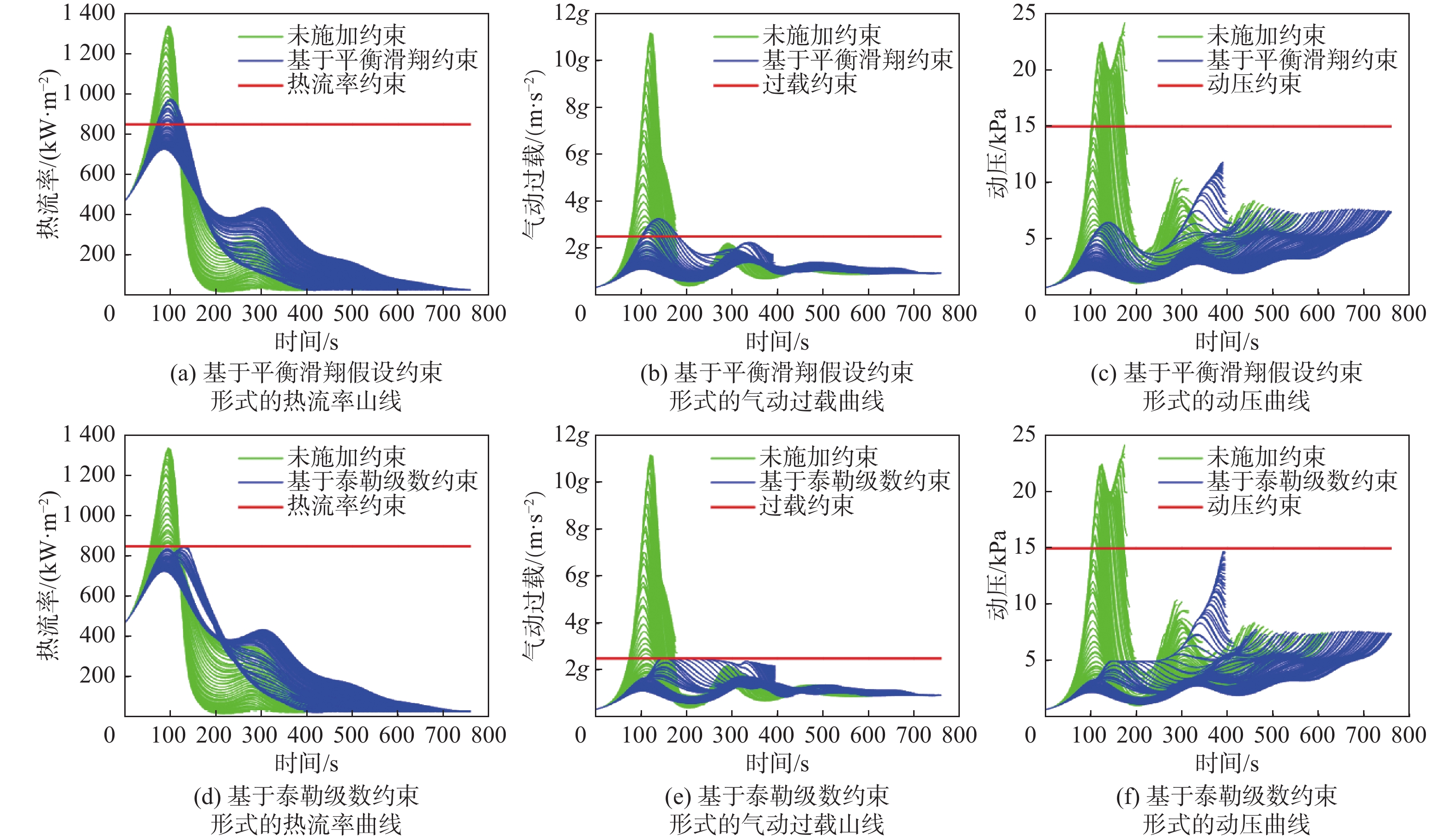
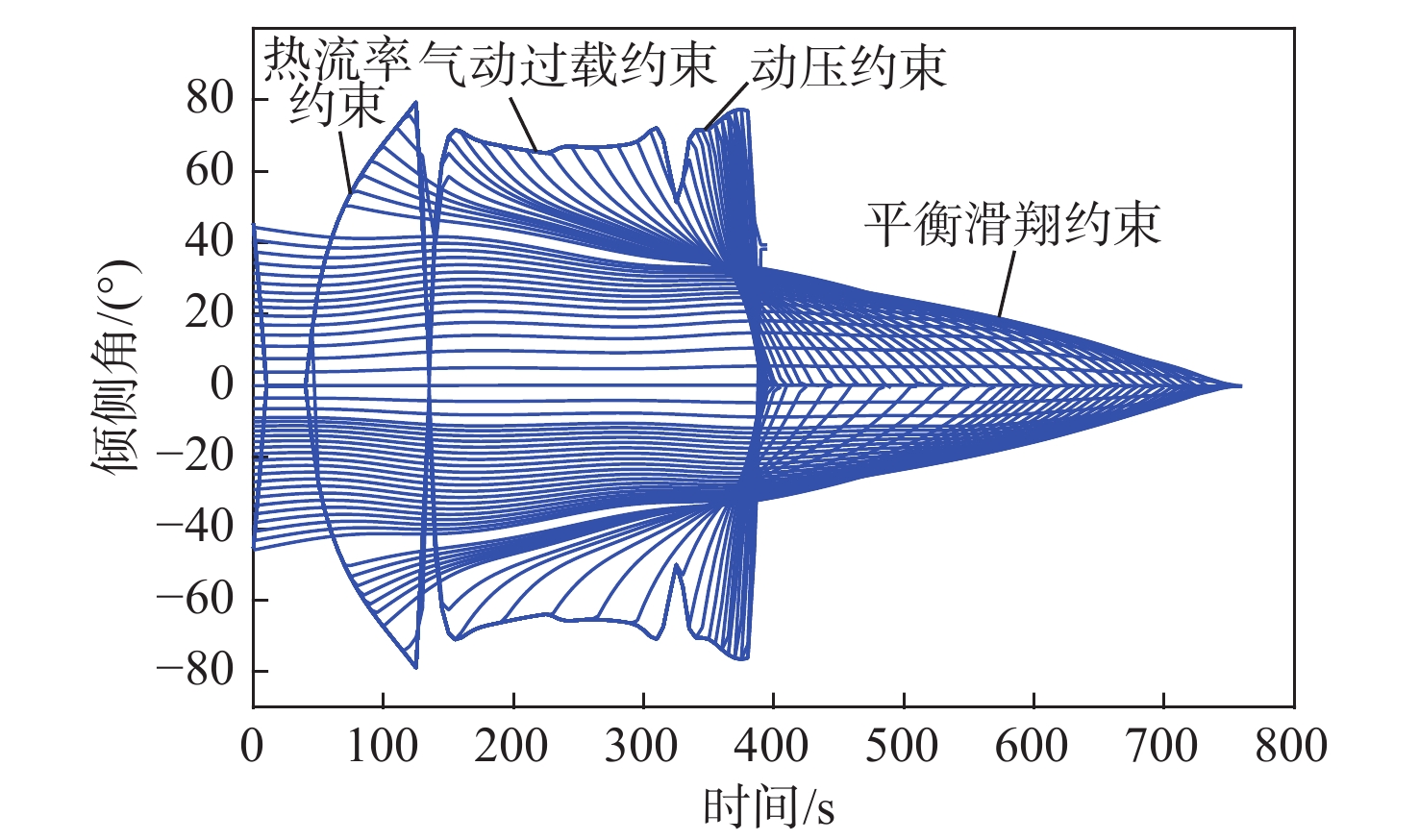
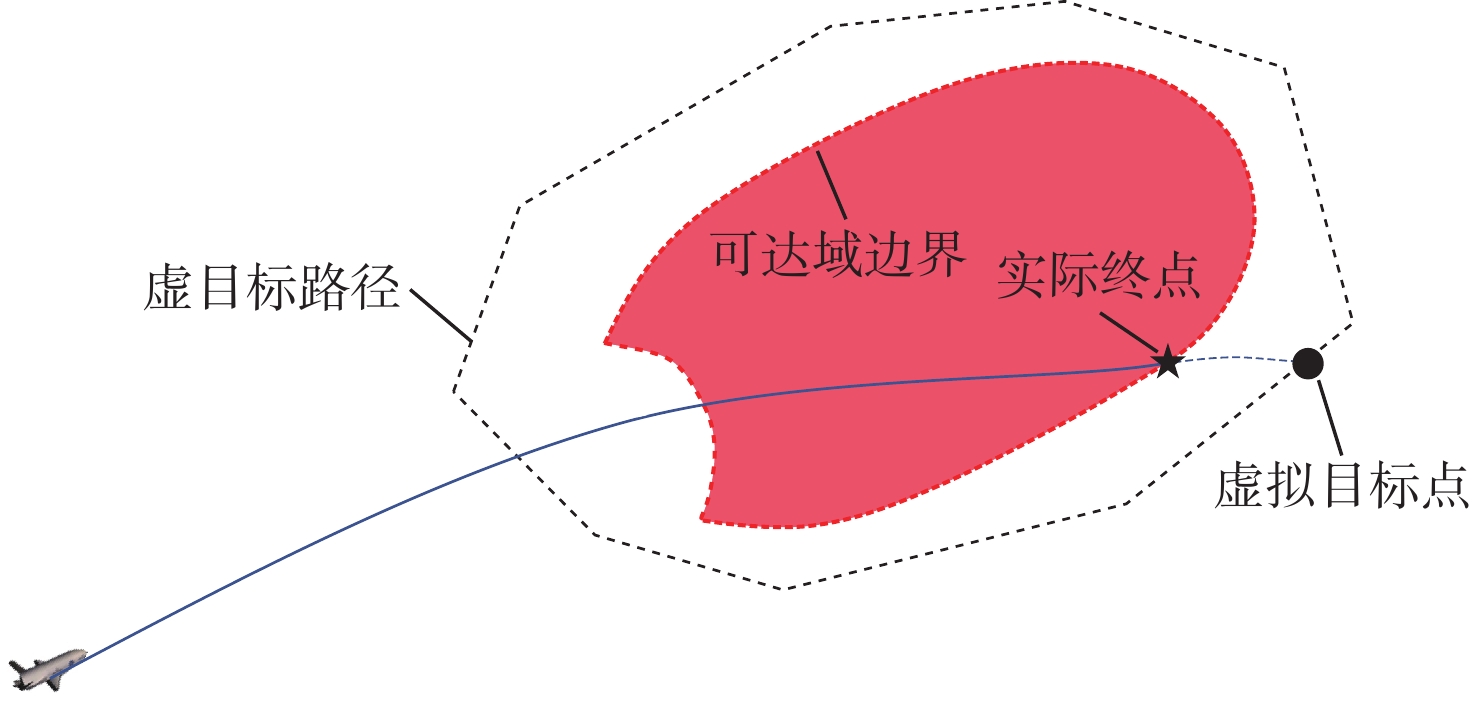
针对升力式再入飞行器再入过程中的热流率、过载和动压受约束问题,提出一种多约束条件下的再入可达域计算方法。基于虚目标法建立了不考虑状态不等式过程约束的再入可达域最优控制模型;基于无过程约束问题的最优控制设计预测校正方法,将状态不等式约束转换为控制不等式约束;以X-33再入飞行器为对象完成数值仿真验证。数值仿真结果表明:与传统的依赖于平衡滑翔假设的“软约束”方法相比,所提方法可实现“硬约束”,即使飞行器在短时间内进行大幅度机动,各项过程约束仍能严格满足。
Abstract:In view of the heat flow, overload, and dynamic pressure constraint problems during the reentry process of the lift reentry vehicle, a calculation method of the reentry reachability region under multiple constraints is designed. Using the virtual target method, an optimal control model for the reentry reachability region is developed without the state inequality restrictions. A predictive correction method is designed based on the optimal control without process constraints, which converts state inequality constraints into control inequality constraints. The numerical simulation of the X-33 is completed. The results of the numerical simulation demonstrate that, in contrast to the conventional "soft constraint" method, which depends on the quasi-equilibrium glide conditions, the suggested method is capable of achieving “hard constraint,” meaning that all process constraints can still be strictly satisfied even in the event that the aircraft makes large maneuvers quickly.
-
Key words:
- reachable region /
- reentry vehicle /
- process constraints /
- balanced glide /
- indirect method
-
表 1 再入飞行器初始状态
Table 1. Initial state of re-entry vehicle
高度/km 速度/(m·s−1) 经度/(°) 纬度/(°) 速度倾角/(°) 速度方向角/(°) 79.5 6100.0 243.1 −18.3 −1.0 38.3 -
[1] GUO H C, HUANG H B, YANG Y. Reentry trajectory planning and guidance method with no-fly zone constraints[C]//Proceedings of the China Automation Congress. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 4633-4638. [2] SARAF A, LEAVITT J, FERCH M, et al. Landing footprint computation for entry vehicles[C]//Proceedings of the AIAA Guidance, Navigation, and Control Conference and Exhibit. Reston: AIAA, 2004. [3] FU S N, LU T Y, YIN J, et al. Rapid algorithm for generating entry landing footprints satisfying the No-fly zone constraint[J]. International Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 2021, 2021: 8827377. [4] PENG Q, GUO J G, YANG S J. Genetic algorithm-based re-entry trajectory optimization and footprint determination for lifting body spacecraft[M]// Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering. Berlin: Springer, 2021: 1369-1379. [5] ZHOU C J, LI M J, SHAO L, et al. An improved predictor-corrector guidance algorithm for reentry glide vehicle based on fast landing points position prediction[M]// Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering. Berlin: Springer, 2023: 639-649. [6] 吴楠, 王锋, 赵敏, 等. 高超声速滑翔再入飞行器的可达区快速预测[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2021, 43(1): 1-6. doi: 10.11887/j.cn.202101001WU N, WANG F, ZHAO M, et al. Fast prediction for footprint of hypersonic glide reentry vehicle[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2021, 43(1): 1-6(in Chinese). doi: 10.11887/j.cn.202101001 [7] 冯必鸣, 聂万胜, 李柯. 再入飞行器可达区域近似算法及地面覆盖研究[J]. 航天控制, 2012, 30(6): 43-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3242.2012.06.008FENG B M, NIE W S, LI K. Research on closest-aproach of footprint and coverage for reentry vehicle[J]. Aerospace Control, 2012, 30(6): 43-49(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3242.2012.06.008 [8] VINH N . Optimal trajectories in atmospheric flight[J]. Space Mankinds Fourth Environment, 1982: 449-468. [9] ZHAO J, ZHOU R. Reentry trajectory optimization for hypersonic vehicle satisfying complex constraints[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2013, 26(6): 1544-1553. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2013.10.009 [10] PEI P, FAN S P, WANG W, et al. Online reentry trajectory optimization using modified sequential convex programming for hypersonic vehicle[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 23511-23525. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3056517 [11] 蔺君, 何英姿, 黄盘兴. 基于差分进化算法的再入可达域快速计算[J]. 中国空间科学技术, 2020, 40(4): 54-60.LIN J, HE Y Z, HUANG P X. Fast reentry landing footprint calculation using differential evolution algorithm[J]. Chinese Space Science and Technology, 2020, 40(4): 54-60(in Chinese). [12] 肖翔, 杨业, 郭涛, 等. 升力式再入飞行器两种可达区域计算方法的探讨[J]. 航天控制, 2015, 33(2): 39-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3242.2015.02.007XIAO X, YANG Y, GUO T, et al. Discussion of two algorithms for generating landing footprint for lifting reentry vehicles[J]. Aerospace Control, 2015, 33(2): 39-43(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3242.2015.02.007 [13] LU P. Asymptotic analysis of quasi-equilibrium glide in lifting entry flight[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2006, 29(3): 662-670. doi: 10.2514/1.15789 [14] LU P, XUE S B. Rapid generation of accurate entry landing footprints[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2010, 33(3): 756-767. [15] 李惠峰, 谢陵. 基于预测校正方法的RLV再入制导律设计[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2009, 35(11): 1344-1348.LI H F, XIE L. Reentry guidance law design for RLV based on predictor-corrector method[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2009, 35(11): 1344-1348(in Chinese). [16] LU P. Non-linear systems with control and state constraints[J]. Optimal Control Applications and Methods, 1997, 18(5): 313-326. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1099-1514(199709/10)18:5<313::AID-OCA605>3.0.CO;2-K -







 下载:
下载: