Low illumination image enhancement algorithm for UAV aerial photography with color consistency
-
摘要:
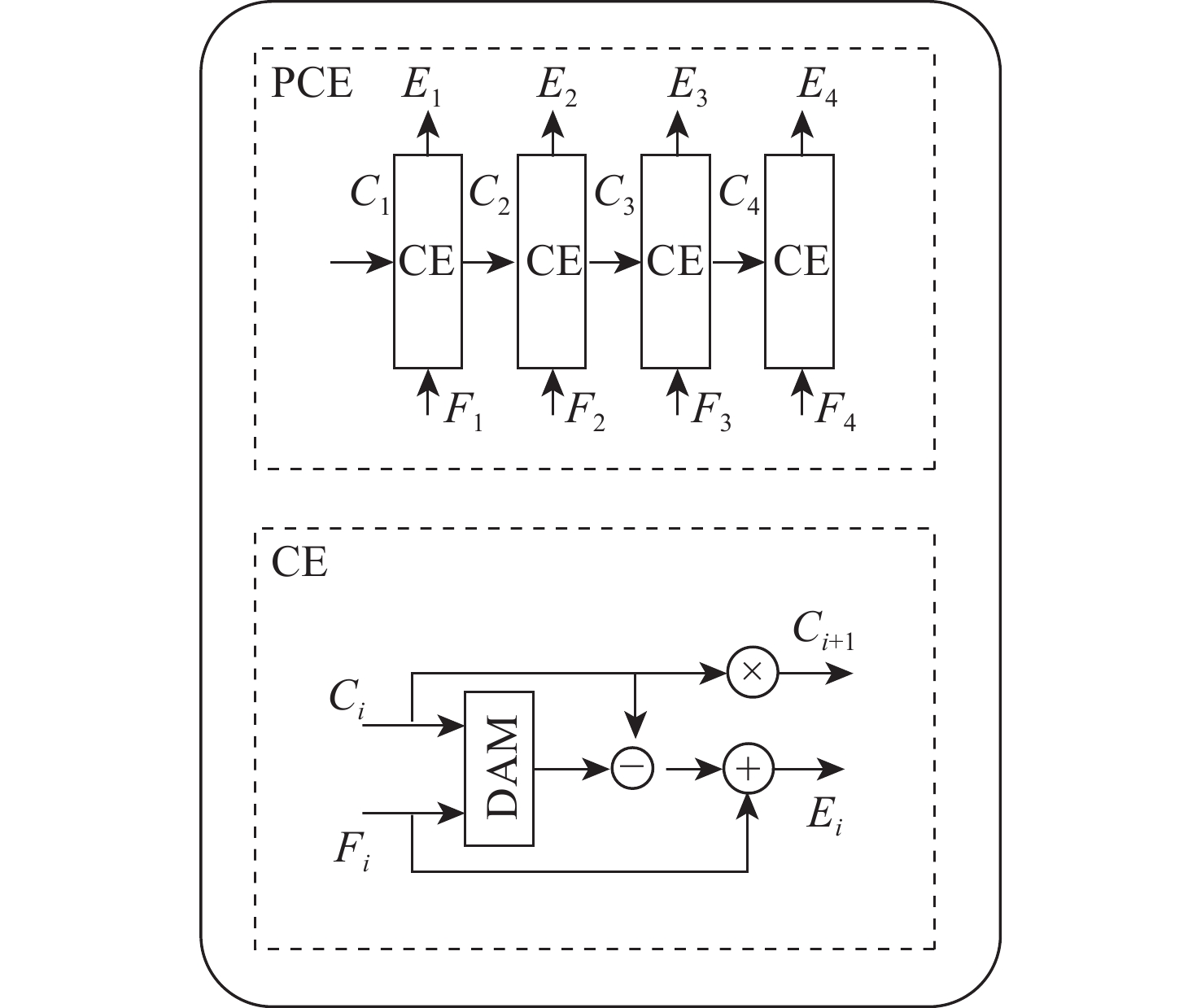
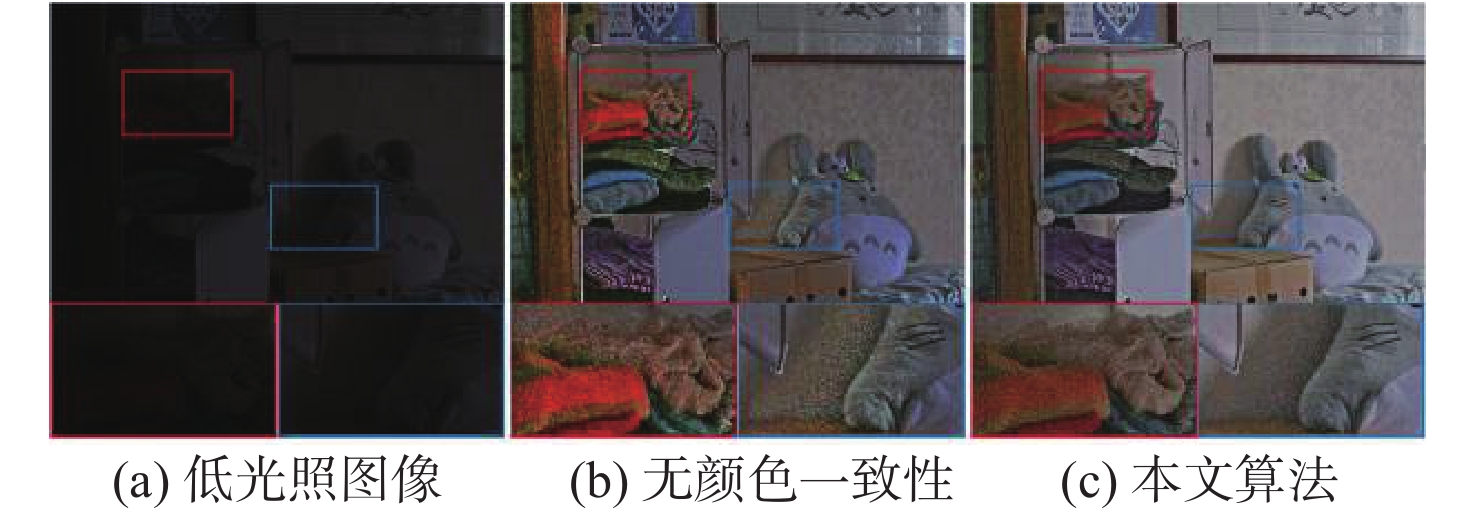
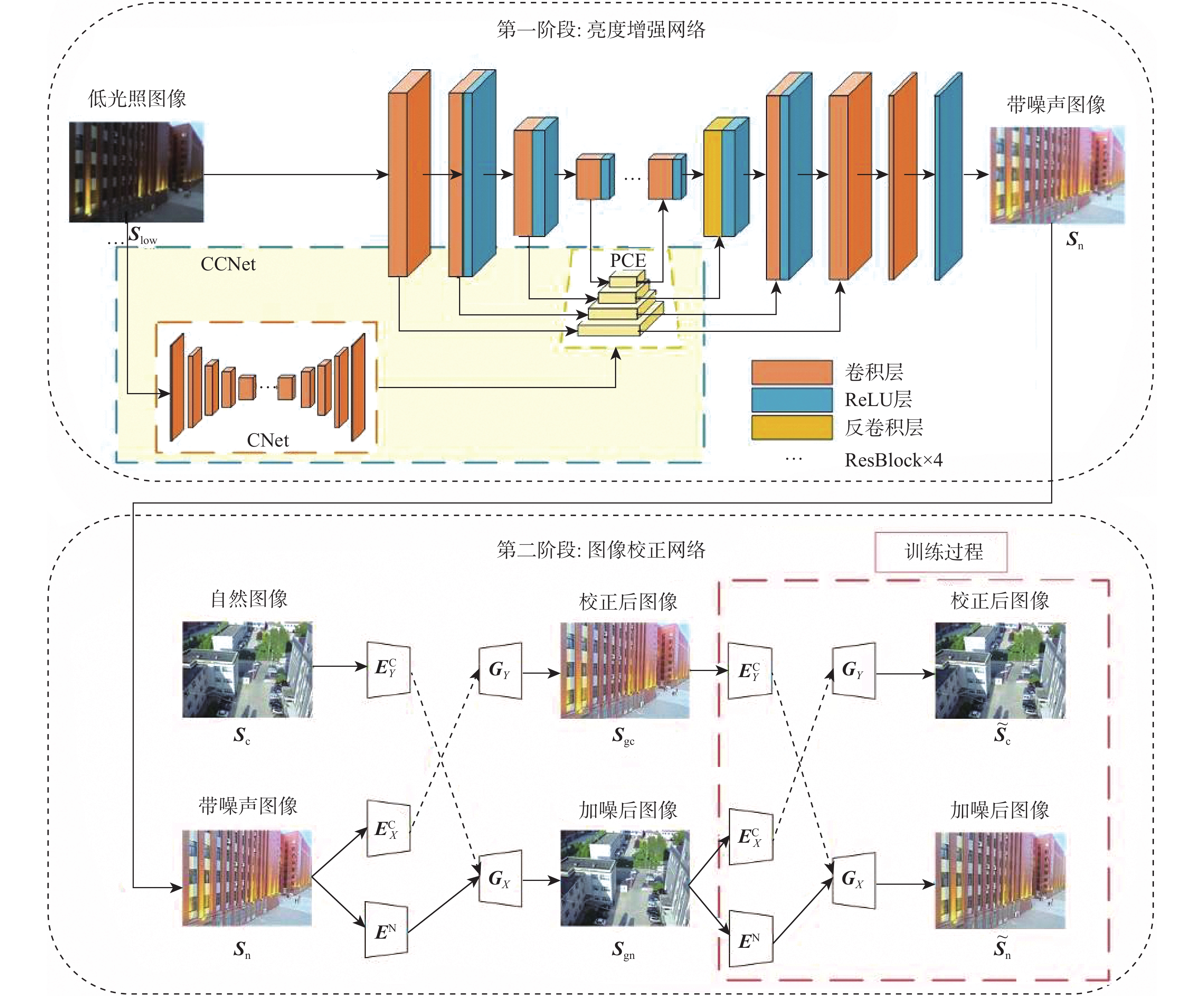
针对无人机(UAV)在低光照条件下拍摄的图像存在亮度低、视觉效果差等问题,建立了无人机航拍低光照数据集,提出了一种颜色一致性的无人机航拍低光照图像增强算法。在亮度增强阶段,构建亮度增强网络(BENet)来增强图像的亮度,利用颜色学习网络(CNet)模块和金字塔颜色嵌入(PCE)模块将图像的颜色特征和内容特征相结合,避免增强后的图像出现颜色失真;在图像校正阶段,构建基于域转移的校正网络,使用自建的数据集训练网络,借助光照良好图像来校正亮度增强阶段增强后的图像,减少噪声对图像的影响,得到增强后的图像。实验结果表明:所提算法可提升图像亮度,避免出现噪声放大和颜色失真的问题,在客观指标上,整体优于对比算法,同时还能提升目标检测算法在夜间的检测性能。
Abstract:To address the issue of low brightness and poor visual effect of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) in low illumination conditions, this paper established a low illumination dataset of UAV aerial photography and proposed a low illumination image enhancement algorithm for UAV aerial photography with color consistency. Firstly, in the brightness enhancement stage, this paper constructed a brightness enhancement network (BENet) to enhance the brightness of images and used the color network (CNet) module and the pyramid color embedding (PCE) module to combine the color features and content features of the images, which avoided color distortion in the enhanced image. In the image correction stage, this paper constructed a correction network based on domain transmission, trained the network with the self-built dataset, corrected the enhanced image after the first stage with the help of well-illuminated images, reduced the effect of noise on the image, and finally obtained the enhanced image. The experimental results show that the algorithm effectively avoids the problems of color distortion and noise amplification while enhancing the image brightness, and it outperforms other advanced algorithms in terms of objective indicators and improves the detection performance of the target detection algorithm at night.
-
表 1 无人机航拍低光照数据集
Table 1. Low illumination dataset of UAV photography
场景 图像数量/张 建筑 4000 街道 4000 野外 2000 表 2 不同算法在自建数据集上的客观评价指标
Table 2. Objective evaluation indicators for different algorithms on self-built dataset
算法 LOE BRISQUE NIQE 处理时间/s RetinexNet[5] 702.80 31.47 3.663 0.0270 DRBN[21] 462.32 28.69 3.250 0.0241 Zero-DCE++[22] 433.86 15.37 3.357 0.0012 EnlightenGAN[12] 408.01 17.63 3.247 0.0150 KinD++[7] 609.83 23.05 3.813 0.0220 URetinex-Net[23] 151.21 31.50 3.444 0.0281 SCI[24] 222.67 37.73 3.568 0.0067 本文算法 213.78 19.45 3.205 0.0232 表 3 不同算法在公开数据集上的NIQE值
Table 3. NIQE of different methods on public datasets
算法 LIME NPE MEF DICM RetinexNet[5] 4.907 4.080 4.904 4.674 DRBN[21] 4.133 4.112 3.356 3.431 Zero-DCE++[22] 3.762 4.253 3.283 3.362 EnlightenGAN[12] 3.608 3.425 3.121 2.846 KinD++[7] 4.206 3.551 3.374 2.965 URetinex-Net[23] 4.096 4.041 3.318 3.235 SCI[24] 4.138 4.160 3.433 3.709 本文算法 3.557 3.363 3.065 2.622 表 4 消融实验客观评价指标
Table 4. Objective evaluation indicators for ablation experiments
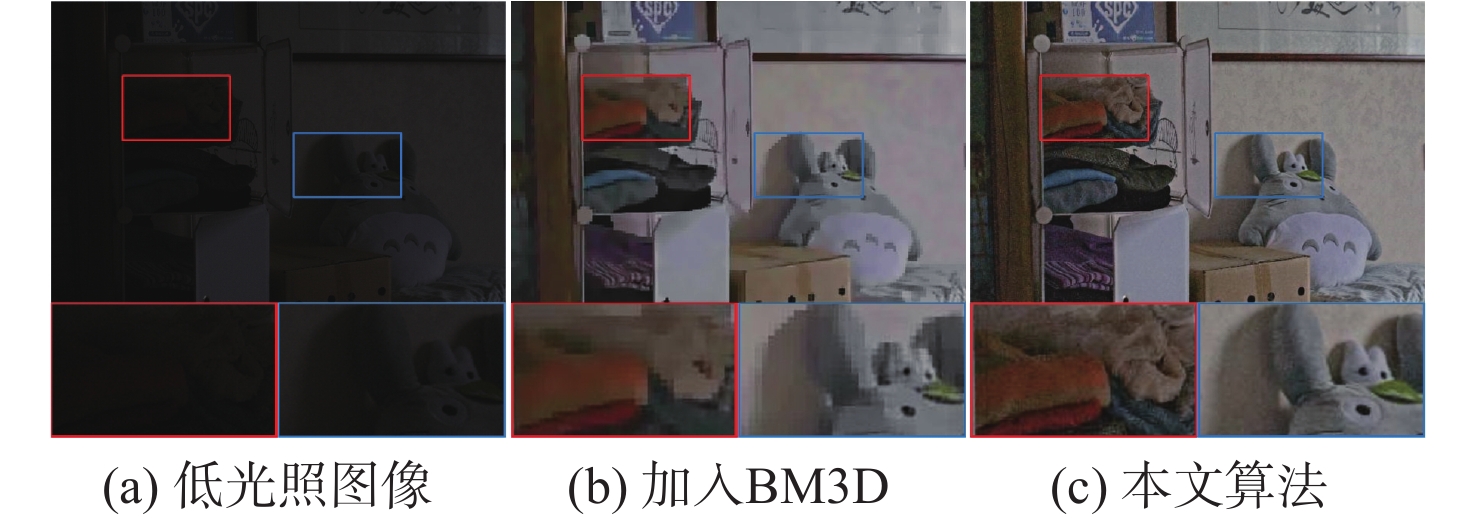
算法 PSNR/dB SSIM 无颜色一致性 20.138 0.769 加入BM3D 19.893 0.778 本文算法 21.221 0.791 表 5 图像增强前后算法检测结果平均精度对比
Table 5. Comparison of AP values of algorithm detection results before and after image enhancement
算法 主干网络 Person Bicycle Car Boat 增强前 增强后 增强前 增强后 增强前 增强后 增强前 增强后 SSD300 VGG-16 0.355 0.361 0.344 0.343 0.351 0.346 0.364 0.375 Deformable DETR ResNet-50 0.382 0.393 0.365 0.375 0.358 0.360 0.381 0.399 -
[1] 李可夫, 钟汇才, 高兴宇, 等. 显著性引导的低光照人脸检测[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2021, 47(3): 572-584.LI K F, ZHONG H C, GAO X Y, et al. Saliency guided low-light face detection[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2021, 47(3): 572-584(in Chinese). [2] PIZER S M, AMBURN E P, AUSTIN J D, et al. Adaptive histogram equalization and its variations[J]. Computer Vision, Graphics, and Image Processing, 1987, 39(3): 355-368. doi: 10.1016/S0734-189X(87)80186-X [3] LAND E H. The Retinex theory of color vision[J]. Scientific American, 1977, 237(6): 108-128. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican1277-108 [4] GUO X J, LI Y, LING H B. LIME: low-light image enhancement via illumination map estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(2): 982-993. [5] WEI C, WANG W J, YANG W H, et al. Deep Retinex decomposition for low-light enhancement[EB/OL]. (2018-08-14)[2023-04-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1808.04560v1. [6] ZHANG Y H, ZHANG J W, GUO X J. Kindling the darkness: a practical low-light image enhancer[C]//Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. New York: ACM, 2019: 1632-1640. [7] ZHANG Y H, GUO X J, MA J Y, et al. Beyond brightening low-light images[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2021, 129(4): 1013-1037. doi: 10.1007/s11263-020-01407-x [8] LV F F, LU F, WU J H, et al. MBLLEN: low-light image/video enhancement using CNNs[C]//Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference. [S. l. ]: BMVC, 2018. [9] 孙帮勇, 赵兴运, 吴思远, 等. 基于移位窗口多头自注意力U型网络的低照度图像增强方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(10): 3399-3408.SUN B Y, ZHAO X Y, WU S Y, et al. Low-light image enhancement method based on shifted window multi-head self-attention U-shaped network[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(10): 3399-3408(in Chinese). [10] XU K, YANG X, YIN B C, et al. Learning to restore low-light images via decomposition-and-enhancement[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 2278-2287. [11] 张雅荔, 李文元, 李昌禄, 等. 融合注意力引导的多尺度低照度图像增强方法[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报, 2023, 50(1): 129-136.ZHANG Y L, LI W Y, LI C L, et al. Method for enhancement of the multi-scale low-light image by combining an attention guidance[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 2023, 50(1): 129-136(in Chinese). [12] JIANG Y F, GONG X Y, LIU D, et al. EnlightenGAN: deep light enhancement without paired supervision[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 2340-2349. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3051462 [13] 向森, 王应锋, 邓慧萍, 等. 基于双重迭代的零样本低照度图像增强[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(10): 3379-3388.XIANG S, WANG Y F, DENG H P, et al. Zero-shot learning for low-light image enhancement based on dual iteration[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(10): 3379-3388(in Chinese). [14] 王殿伟, 刘旺, 房杰, 等. 受生物视觉启发的无人机航拍低照度图像增强算法[J]. 西北工业大学学报, 2023, 41(1): 144-152. doi: 10.1051/jnwpu/20234110144WANG D W, LIU W, FANG J, et al. Enhancement algorithm of low illumination image for UAV images inspired by biological vision[J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2023, 41(1): 144-152(in Chinese). doi: 10.1051/jnwpu/20234110144 [15] JIN Y Y, YANG W H, TAN R T. Unsupervised night image enhancement: when layer decomposition meets light-effects suppression[EB/OL]. (2022-09-17)[2023-04-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.10564v2. [16] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, BROX T. U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Berlin: Springer, 2015: 234-241. [17] ZHANG Z, ZHENG H, HONG R C, et al. Deep color consistent network for low-light image enhancement[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2022: 1889-1898. [18] ZHANG F, SHAO Y J, SUN Y S, et al. Unsupervised low-light image enhancement via histogram equalization prior[EB/OL]. (2021-11-03)[2023-04-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.01766v1. [19] DU W C, CHEN H, YANG H Y. Learning invariant representation for unsupervised image restoration[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 14471-14480. [20] WANG W J, WEI C, YANG W H, et al. GLADNet: low-light enhancement network with global awareness[C]//Proceedings of the 13th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 751-755. [21] YANG W H, WANG S Q, FANG Y M, et al. From fidelity to perceptual quality: a semi-supervised approach for low-light image enhancement[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 3060-3069. [22] LI C Y, GUO C L, LOY C C. Learning to enhance low-light image via zero-reference deep curve estimation[EB/OL]. (2021-03-01)[2023-04-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.00860v1. [23] WU W H, WENG J, ZHANG P P, et al. URetinex-Net: Retinex-based deep unfolding network for low-light image enhancement[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2022: 5891-5900. [24] MA L, MA T Y, LIU R S, et al. Toward fast, flexible, and robust low-light image enhancement[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2022: 5627-5636. [25] AHN H, KEUM B, KIM D, et al. Adaptive local tone mapping based on Retinex for high dynamic range images[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2013: 153-156. [26] MITTAL A, MOORTHY A K, BOVIK A C. No-reference image quality assessment in the spatial domain[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2012, 21(12): 4695-4708. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2012.2214050 [27] MITTAL A, SOUNDARARAJAN R, BOVIK A C. Making a “completely blind” image quality analyzer[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2012, 20(3): 209-212. [28] DABOV K, FOI A, KATKOVNIK V, et al. Image denoising by sparse 3-D transform-domain collaborative filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2007, 16(8): 2080-2095. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2007.901238 [29] LIU W, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: single shot multibox detector[C]//Proceedings of the Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 21-37. [30] ZHU X Z, SU W J, LU L W, et al. Deformable DETR: deformable Transformers for end-to-end object detection[EB/OL]. (2021-03-18)[2023-04-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.04159v4. [31] LOH Y P, CHAN C S. Getting to know low-light images with the exclusively dark dataset[J]. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2019, 178: 30-42. doi: 10.1016/j.cviu.2018.10.010 -







 下载:
下载: