-
摘要:
针对现有的网络时间可靠性评估方法往往只考虑固有不确定性的影响,而忽略由于故障信息不足而导致的认知不确定性对可靠性评估结果影响的问题,提出一种基于不确定理论的新方法。根据网络可靠性关注的节点范围,设计了单节点对和多节点对时间可靠度两类度量参数,提出了扩展不确定网络模型可直接实现对节点和链路上的认知不确定性特征建模,并进一步设计了基于最可靠路径和最可靠扩展不确定子网络的单节点和多节点对时间可靠度算法。分别以一个六节点网络、中国教育和科研计算机网(CERNET)骨干网络为例,应用所提方法实现了2种时间可靠性指标的评估,验证了所提方法的正确性和有效性。
Abstract:The current network time reliability evaluation methods only consider the effect of inherent uncertainty but ignore the impact of epistemic uncertainty due to a lack of failure information on reliability evaluation results. To address this issue, a new method based on uncertainty theory was proposed. Based on the node range for network reliability, two metric parameters including single-node-pair time reliability and multi-node-pair time reliability were designed. An extended uncertain network model was proposed, which could directly model the epistemic uncertainty features on both nodes and links. Two algorithms were proposed to compute single-node-pair and multi-node-pair time reliability based on the most reliable path and the most reliable extended uncertain subnetwork. Finally, the proposed method was proposed to evaluate two time reliability metrics with a six-node network and the China education and research network (CERNET) backbone network as the example, and the results verify the correctness and effectiveness of the method.
-
表 1 节点和链路信息
Table 1. Node and link information
节点
编号节点时间/
ms节点不确定
测度链路
编号节点时间/
ms节点不确定
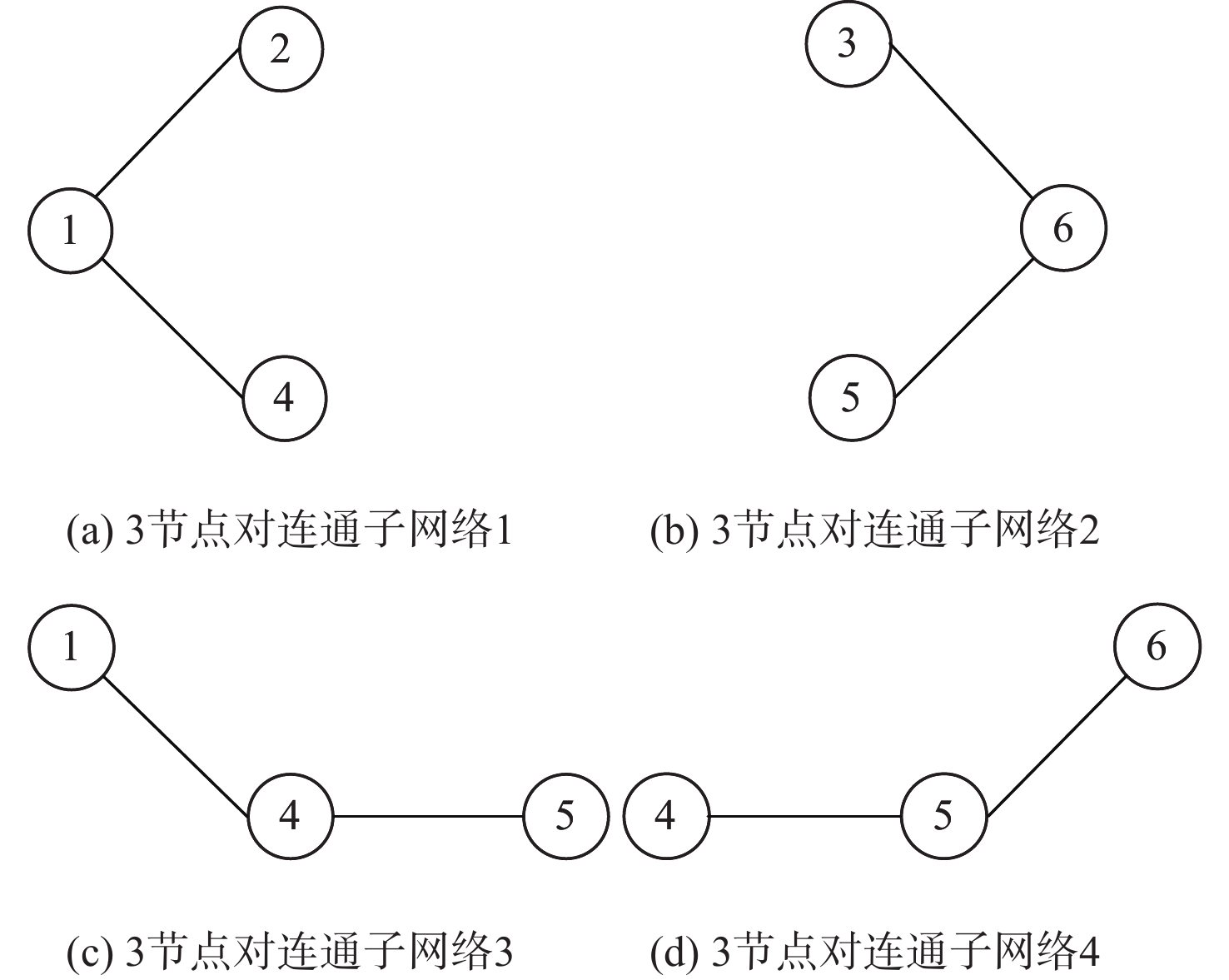
测度1 1 0.99 e1,2 1.5 0.96 2 1.9 0.97 e1,4 1 0.92 3 1.9 0.94 e2,3 1 0.93 4 1.9 0.96 e2,5 1 0.98 5 1.9 0.95 e3,4 1.5 0.91 6 1 0.98 e3,6 1.5 0.95 e4,5 2 0.97 e5,6 1 0.94 表 2 满足节点1和节点6传输时间要求的子网络信息
Table 2. Subnetwork information meeting transmission time requirement of node 1 and node 6
编号 子网络 子网络可靠度 1 
0.99∧0.96∧0.97∧0.93∧0.94∧0.95∧0.98=0.93 ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ 4 
0.99∧0.96∧0.97∧0.98∧0.95∧0.94∧0.98=0.94 ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ 95 
0.99∧0.96∧0.97∧0.93∧0.94∧0.95∧0.98∧0.94∧0.95∧0.91∧0.97∧0.96∧0.98∧0.92=0.91 表 3 满足10个节点对传输时间要求的子网络信息
Table 3. Subnetwork information meeting transmission time requirement of 10 node pairs
编号 子网络 子网络可靠度 1 
0.99∧0.96∧0.97∧0.93∧0.94∧0.98∧0.92∧0.96∧0.97∧0.95∧0.91=0.91 ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ 4 
0.99∧0.96∧0.97∧0.98∧0.95∧0.94∧0.97∧0.96∧0.94∧0.98∧0.95=0.94 ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ 79 
0.99∧0.96∧0.97∧0.93∧0.94∧0.95∧0.98∧0.94∧0.95∧0.91∧0.97∧0.96∧0.98∧0.92=0.91 表 4 节点信息
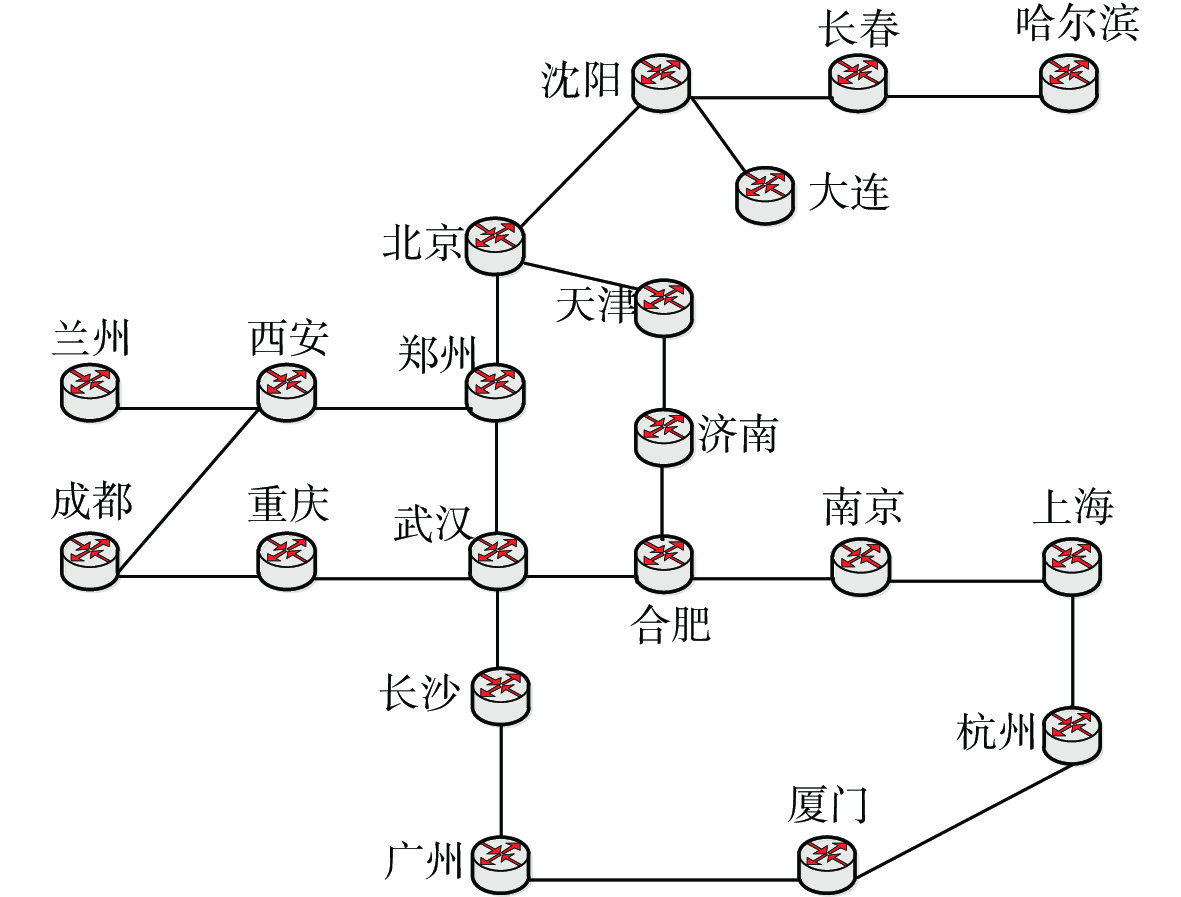
Table 4. Node information
节点 时延/ms 不确定
测度节点 时延/ms 不确定
测度哈尔滨 2 0.983 杭州 2 0.991 长春 2 0.988 厦门 2 0.989 沈阳 2 0.995 广州 2 0.986 大连 2 0.987 长沙 2 0.989 北京 1 0.991 武汉 2 0.980 天津 2 0.986 郑州 2 0.986 济南 2 0.987 重庆 2 0.987 合肥 2 0.983 成都 2 0.992 南京 2 0.988 西安 2 0.996 上海 2 0.994 兰州 2 0.989 表 5 链路信息
Table 5. Link information
链路 时延/ms 不确定
测度链路 时延/ms 不确定
测度哈尔滨-长春 1 0.986 上海-杭州 0.5 0.981 长春-沈阳 1 0.983 杭州-厦门 3 0.985 沈阳-大连 1 0.978 厦门-广州 2 0.991 沈阳-北京 2 0.986 广州-长沙 2 0.984 北京-天津 0.5 0.987 长沙-武汉 1 0.989 北京-郑州 2 0.987 武汉-郑州 1.5 0.976 天津-济南 1 0.988 武汉-重庆 3 0.982 济南-合肥 1 0.986 郑州-西安 1.5 0.979 合肥-南京 0.5 0.983 重庆-成都 1 0.993 合肥-武汉 1.5 0.979 成都-西安 2.5 0.988 表 6 不同节点对之间的单节点对时间可靠度
Table 6. Single-node-pair time reliability between different node pairs
节点对 可靠度 最可靠路径 哈尔滨-广州 0.979 哈尔滨-长春-沈阳-北京-天津-济南-
合肥-武汉-长沙-广州成都-上海 0.983 成都-重庆-武汉-合肥-南京-上海 兰州-合肥 0.981 兰州-西安-郑州-北京-天津-济南-合肥 表 7 不同时延阈值下的单节点对时间可靠度
Table 7. Single-node-pair time reliability under different delay thresholds
时延
阈值/ms可靠度 最可靠路径 30 0.976 哈尔滨-长春-沈阳-北京-郑州-武汉-长沙-广州 35 0.979 哈尔滨-长春-沈阳-北京-天津-济南-
合肥-武汉-长沙-广州40 0.981 哈尔滨-长春-沈阳-北京-天津-济南-
合肥-南京-上海-杭州-厦门-广州表 8 多节点对时间可靠度
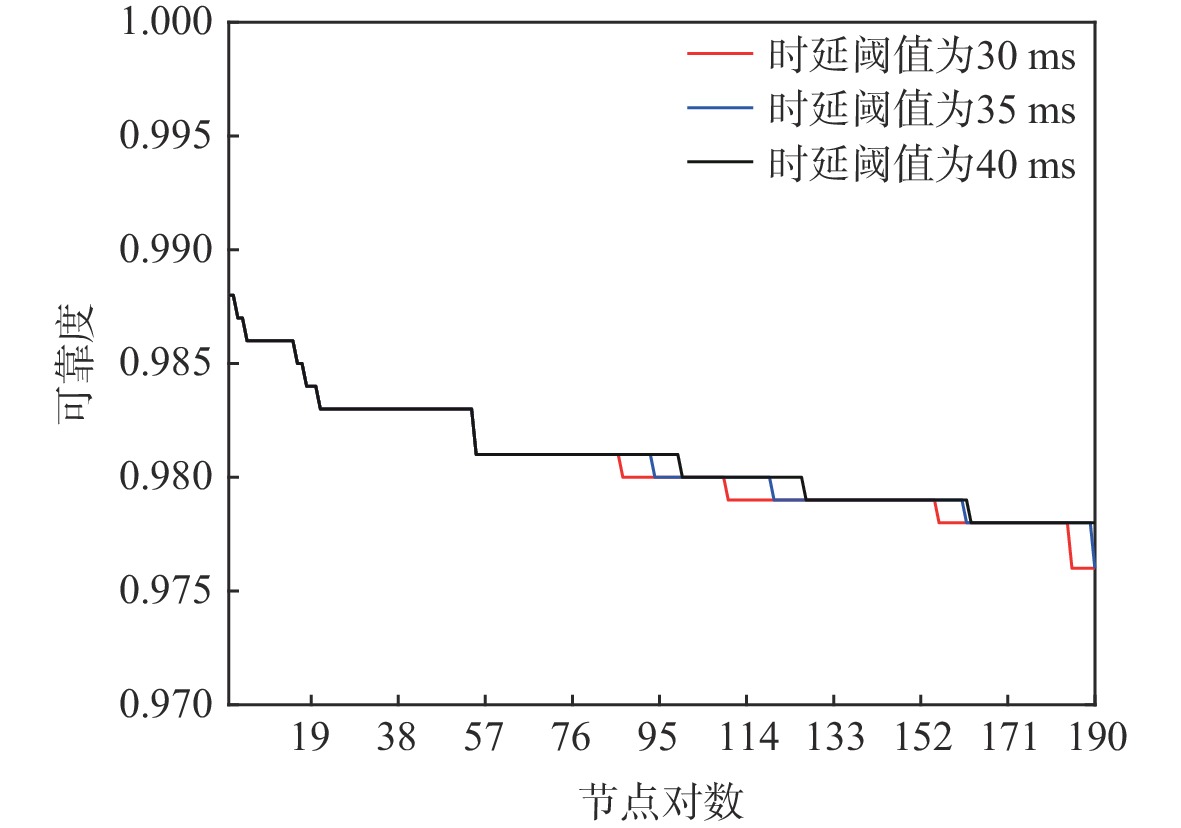
Table 8. Multi-node-pair time reliability
要求节点对数 可靠度 要求节点对数 可靠度 19 0.984 114 0.980 38 0.983 133 0.979 57 0.981 152 0.979 76 0.981 171 0.978 95 0.980 190 0.976 注:可靠度指要求达到传输时间要求的节点对数占网络总节点对数的比例。 表 9 2种算法的运行时间
Table 9. Running time of two algorithms
算法 运行时间/ms 单节点对时间可靠度算法 2.689 多节点对时间可靠度算法 93.61 -
[1] GAUR V, YADAV O P, SONI G, et al. A literature review on network reliability analysis and its engineering applications[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part O: Journal of Risk and Reliability, 2021, 235(2): 167-181. doi: 10.1177/1748006X20962258 [2] HONG S, LV C, ZHAO T D, et al. Cascading failure analysis and restoration strategy in an interdependent network[J]. Journal of Physics A: Mathematical and Theoretical, 2016, 49(19): 195101. doi: 10.1088/1751-8113/49/19/195101 [3] HONG S, ZHU J X, BRAUNSTEIN L A, et al. Cascading failure and recovery of spatially interdependent networks[J]. Journal of Statistical Mechanics: Theory and Experiment, 2017, 2017(10): 103208. doi: 10.1088/1742-5468/aa8c36 [4] 黄宁, 伍志韬. 网络可靠性评估模型与算法综述[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2013, 35(12): 2651-2660. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2013.12.32HUANG N, WU Z T. Survey of network reliability evaluation models and algorithms[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2013, 35(12): 2651-2660(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2013.12.32 [5] LIU Z, HUANG N, LI D P. An algorithm for delay-reliability in communication networks based on probabilistic user equilibrium model[C]// Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Science and Cloud Computing Companion. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2013: 135-141. [6] WU Z T, HUANG N, LI R Y, et al. A delay reliability estimation method for avionics full duplex switched ethernet based on stochastic network calculus[J]. Eksploatacja i Niezawodnosc-Maintenance and Reliability, 2015, 17(2): 288-296. doi: 10.17531/ein.2015.2.17 [7] WANG W X, GUO R J. Travel time reliability of highway network under multiple failure modes[J]. Sustainability, 2022, 14(12): 7256. doi: 10.3390/su14127256 [8] ZHANG X X, ZHAO M, APPIAH J, et al. Prediction of travel time reliability on interstates using linear quantile mixed models[J]. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2023, 2677(2): 774-791. doi: 10.1177/03611981221108380 [9] JUNG Y, JO H, CHOO J, et al. Statistical model calibration and design optimization under aleatory and epistemic uncertainty[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2022, 222: 108428. [10] BAUDRIT C, DUBOIS D. Practical representations of incomplete probabilistic knowledge[J]. Computational Statistics & Data Analysis, 2006, 51(1): 86-108. [11] SIMON C, WEBER P. Imprecise reliability by evidential networks[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part O: Journal of Risk and Reliability, 2009, 223(2): 119-131. doi: 10.1243/1748006XJRR190 [12] MUSHARRAF M, BRADBURY-SQUIRES D, KHAN F, et al. A virtual experimental technique for data collection for a Bayesian network approach to human reliability analysis[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2014, 132: 1-8. [13] FILIPPI G, VASILE M, KRPELIK D, et al. Space systems resilience optimisation under epistemic uncertainty[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2019, 165: 195-210. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2019.08.024 [14] BEER M, FERSON S, KREINOVICH V. Imprecise probabilities in engineering analyses[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2013, 37(1-2): 4-29. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2013.01.024 [15] ZADEH L A. Fuzzy sets as a basis for a theory of possibility[J]. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 1999, 100: 9-34. doi: 10.1016/S0165-0114(99)80004-9 [16] MOORE R E. Methods and applications of interval analysis[M]. Philadelphia: Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, 1979. [17] MI J H, LU N, LI Y F, et al. An evidential network-based hierarchical method for system reliability analysis with common cause failures and mixed uncertainties[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2022, 220: 108295. [18] QI X J, CHENG Q. Imprecise reliability assessment of generating systems involving interval probability[J]. IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution, 2017, 11(17): 4332-4337. [19] ZHANG X F, LI R M, LIU M, et al. Evaluating travel time reliability based on fuzzy logic[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2011, 97-98: 952-955. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.97-98.952 [20] KANG R, ZHANG Q Y, ZENG Z G, et al. Measuring reliability under epistemic uncertainty: review on non-probabilistic reliability metrics[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2016, 29(3): 571-579. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2016.04.004 [21] LIU B D. Uncertainty theory[M]. 2nd ed. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 2007: 205-234. [22] ZHANG Q Y, KANG R, WEN M L. Belief reliability for uncertain random systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2018, 26(6): 3605-3614. doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2018.2838560 [23] 康锐. 确信可靠性理论与方法[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2020: 63-65.KANG R. Belief reliability theory and methodology[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2020: 63-65 (in Chinese). [24] LIU Y H. Uncertain random variables: a mixture of uncertainty and randomness[J]. Soft Computing, 2013, 17(4): 625-634. doi: 10.1007/s00500-012-0935-0 [25] WANG S, YANG D, LU J. A connectivity reliability-cost approach for path selection in the maritime transportation of China’s crude oil imports[J]. Maritime Policy & Management, 2018, 45(5): 567-584. [26] HOSSEINI A, PISHVAEE M S. Capacity reliability under uncertainty in transportation networks: an optimization framework and stability assessment methodology[J]. Fuzzy Optimization and Decision Making, 2022, 21(3): 479-512. doi: 10.1007/s10700-021-09374-9 [27] ZENG Z G, KANG R, WEN M L, et al. A model-based reliability metric considering aleatory and epistemic uncertainty[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 15505-15515. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2733839 [28] KARGER D R. A randomized fully polynomial time approximation scheme for the all-terminal network reliability problem[J]. IAM Review, 2001, 43(3): 499-522. [29] YEH W C. An improved sum-of-disjoint-products technique for symbolic multi-state flow network reliability[J]. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2015, 64(4): 1185-1193. [30] LIU W. Uncertain programming models for shortest path problem with uncertain arc lengths[C]//Proceedings of the First International Conference on Uncertainty Theory. Urumchi: Journal of the Operations Research Society of China, 2010: 148-153. [31] 高原. 不确定图与不确定网络[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2013: 21-26.GAO Y. Uncertain graph and uncertain network[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2013: 21-26 (in Chinese). [32] 李瑞莹, 李枚楠. 基于Monte Carlo和启发式算法的网络可靠性分配[J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2014, 34(7): 695-700.LI R Y, LI M N. Network reliability allocation based on Monte Carlo and heuristic algorithm[J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2014, 34(7): 695-700 (in Chinese). -








 下载:
下载: