Dehazing network based on residual global contextual attention and cross-layer feature fusion
-
摘要:
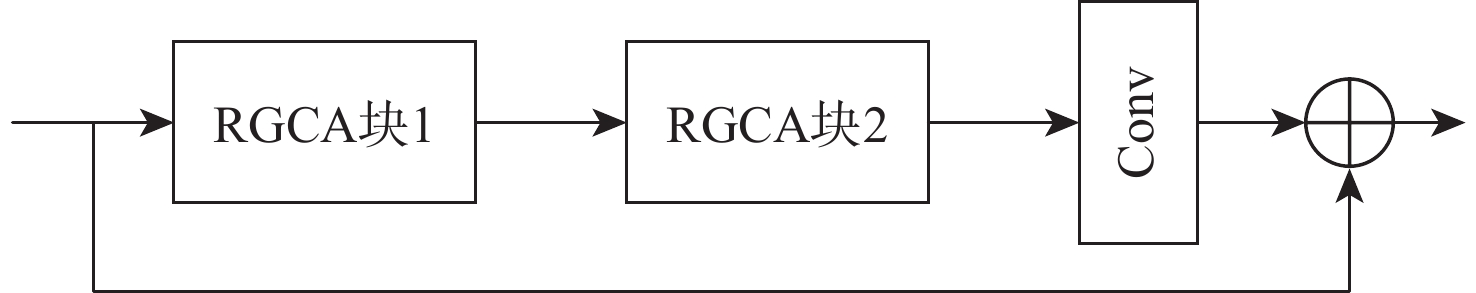
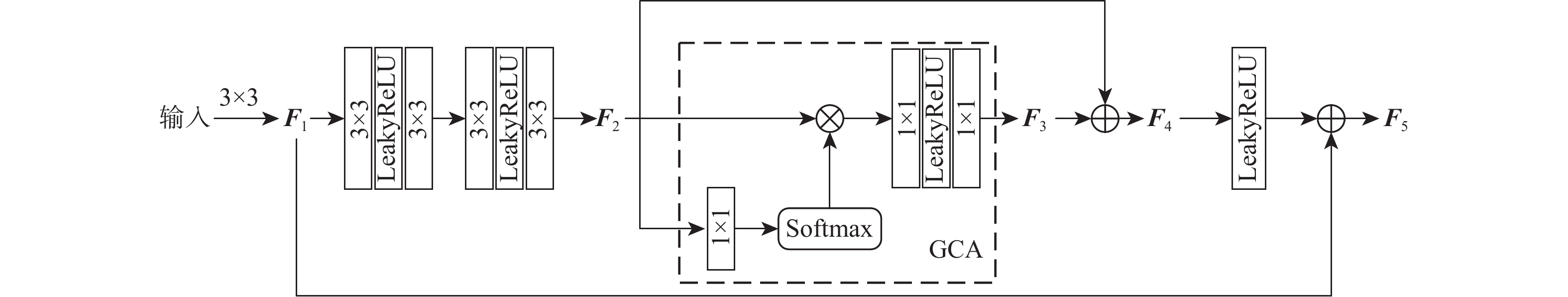
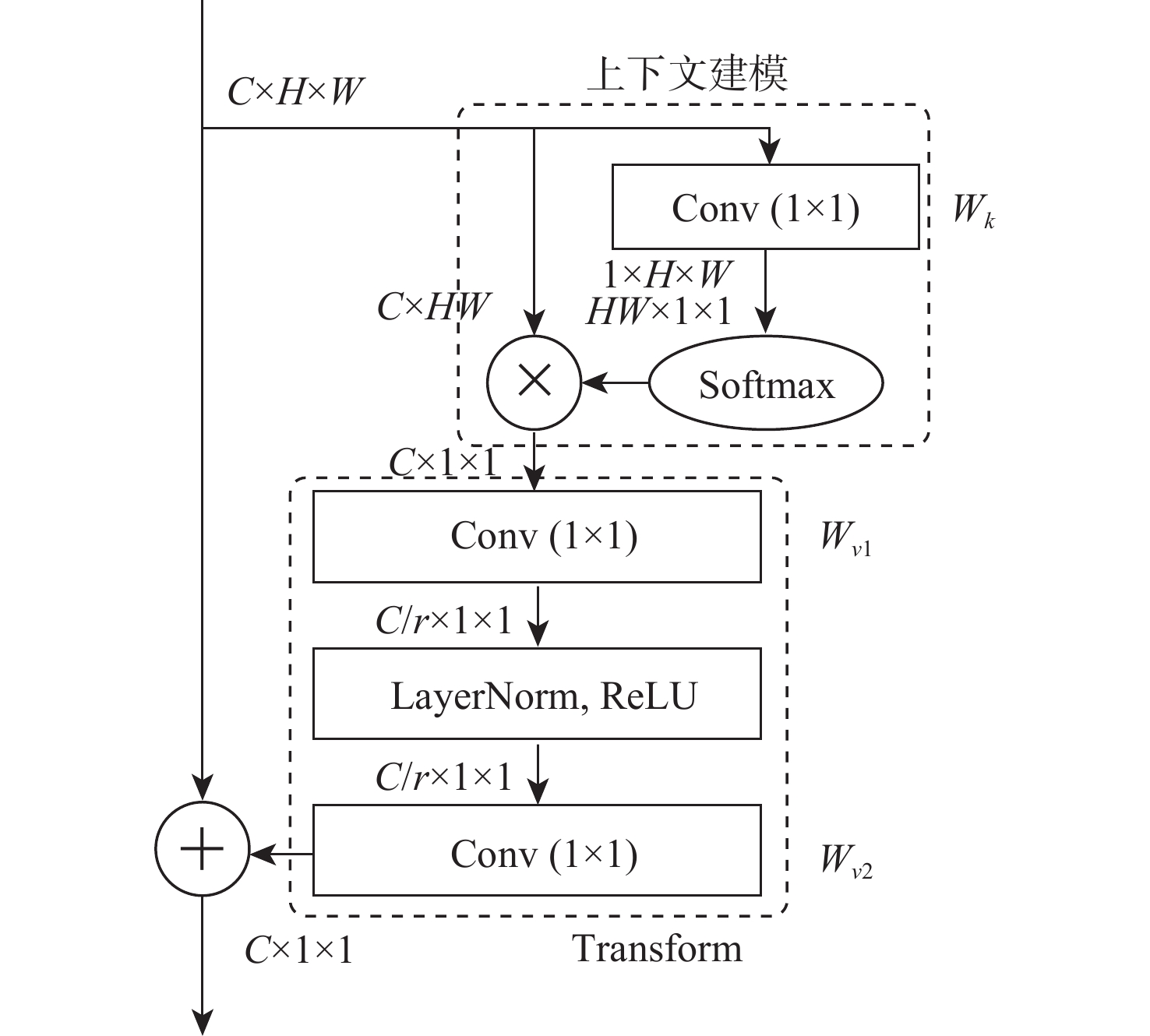
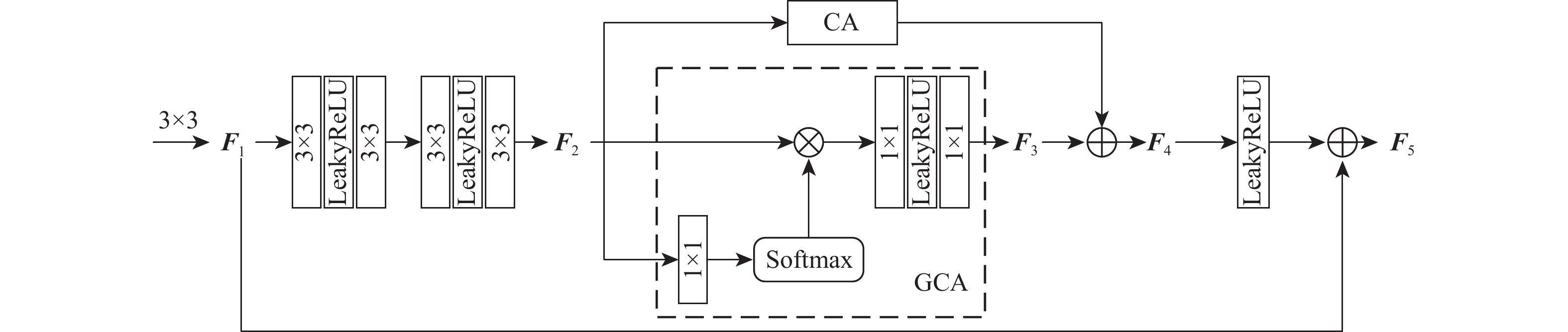
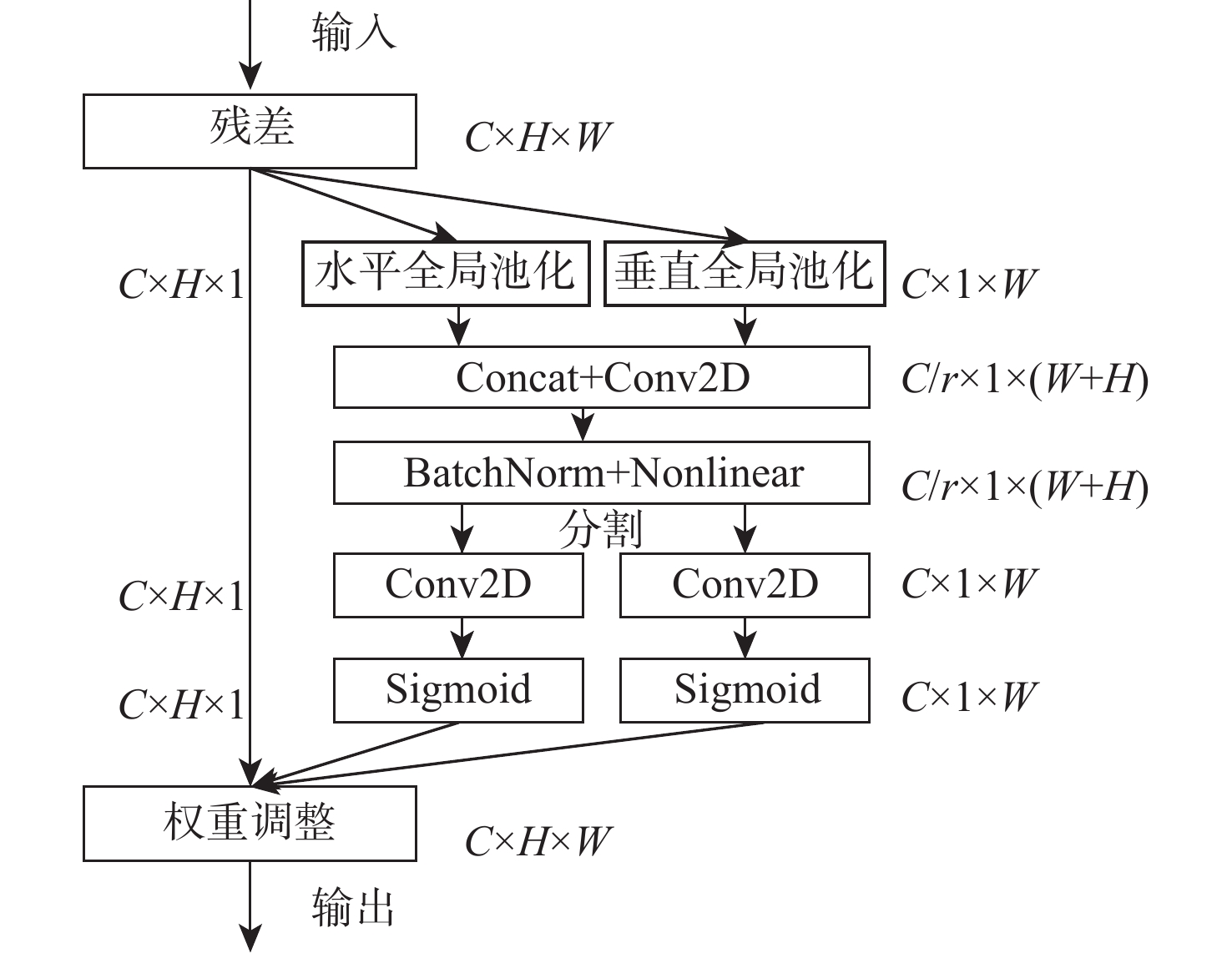
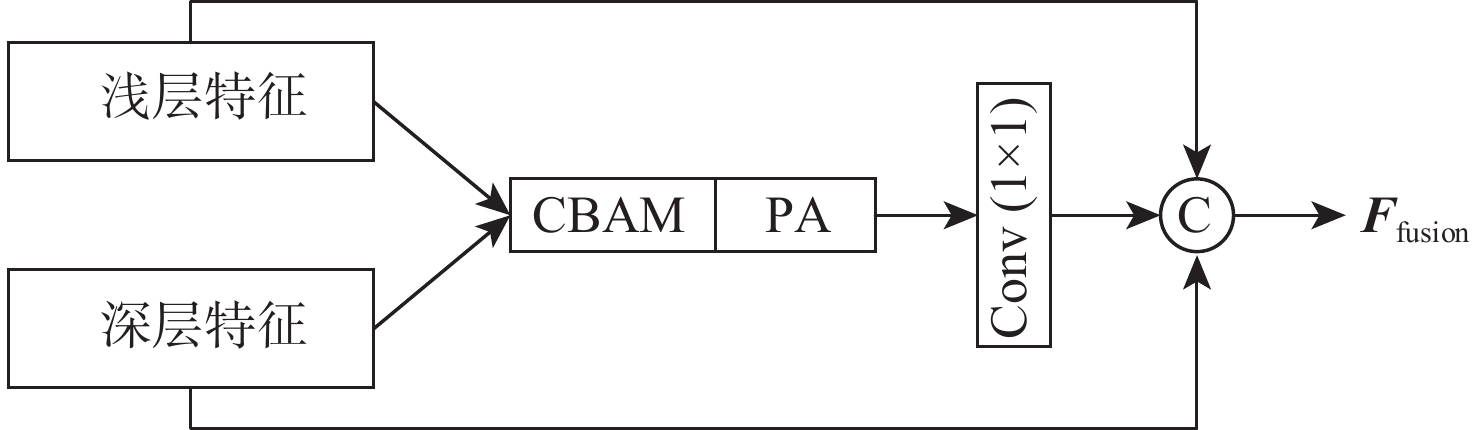
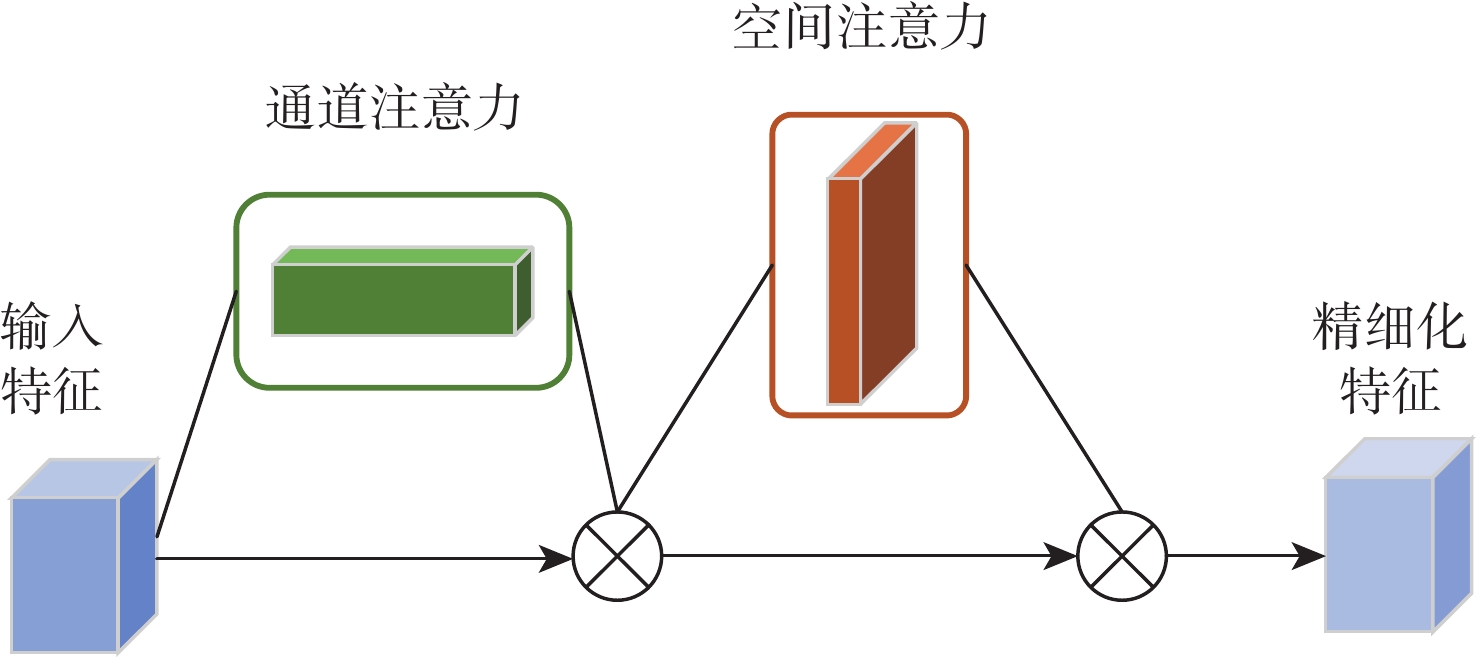
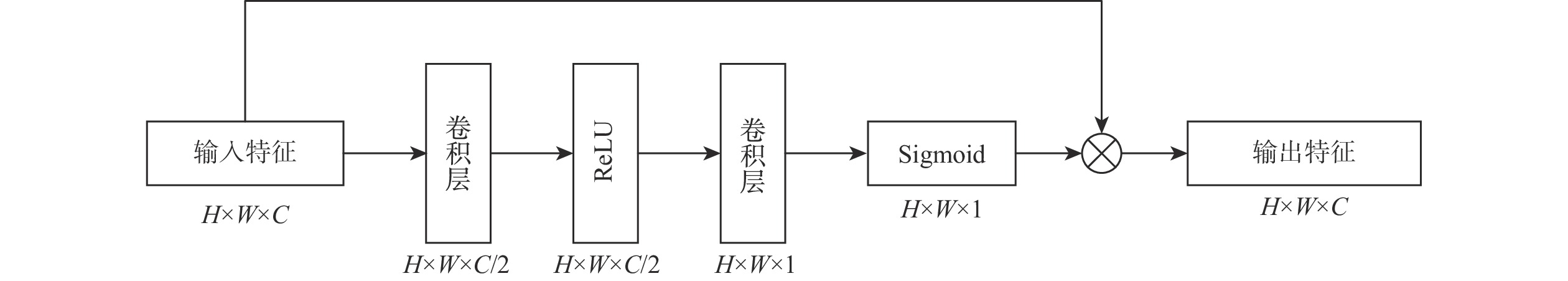
基于深度学习的图像去雾算法通常在提取特征时使用传统的卷积层,容易造成图像的细节和边缘等信息丢失,提取特征时忽略图像的位置信息,融合特征时忽略图像原始信息,不能恢复出结构完整、清晰的高质量无雾图像。针对该问题,提出了一种基于残差全局上下文注意和跨层特征融合的去雾算法。对提出的残差全局上下文注意块串行得到残差组结构,并对网络的前2层(即浅层)进行特征提取,得到浅层丰富的上下文信息;引入坐标注意力,建立具有位置信息的注意力图,并将其应用于残差上下文特征提取,放置在网络的第3层(即深层),提取更深层次的语义信息;在网络中间层,通过跨层融合来自不同分辨率流的特征信息,增强深浅层的信息交换,达到特征增强的目的;聚合网络得到具有丰富语义信息的特征与原始输入特征,提升复原效果。在RESIDE和Haze4K数据集上的实验结果表明:所提算法在视觉效果与客观指标上都取得了较好的效果。
Abstract:Current deep learning-based image dehazing algorithms usually use traditional convolutional layers when extracting features, which easily cause loss of information, such as details and edges of the image, ignore the location information of the image in feature extraction, and neglect the original information of the image in feature fusion, and they thus fail to recover a high-quality dehazing image with complete and clear structure. To address this problem, a dehazing algorithm based on residual contextual attention and cross-layer feature fusion was proposed. Firstly, the residual group structure was obtained by serializing the proposed residual contextual blocks, and feature extraction was performed on the first two layers of the network, i.e. the shallow layers, to obtain rich contextual information in the shallow layers; secondly, coordinate attention was introduced to build an attention graph with location information and apply it to the residual contextual feature extraction, which was placed in the third layer of the network, i.e. the deep layer, to extract deeper semantic information; then, by fusing feature information from different resolution streams across layers in the middle layer of the network, the information exchange between the deep and shallow layers was enhanced to achieve feature enhancement; finally, the semantic information-rich features obtained from the network were combined with the original input, thus enhancing the recovery effect. Experimental results on the RESIDE dataset and the Haze4K dataset show that the proposed algorithm achieves better results in terms of visual effects and objective metrics.
-
Key words:
- image dehazing /
- deep learning /
- residual structure /
- attention mechanism /
- feature fusion
-
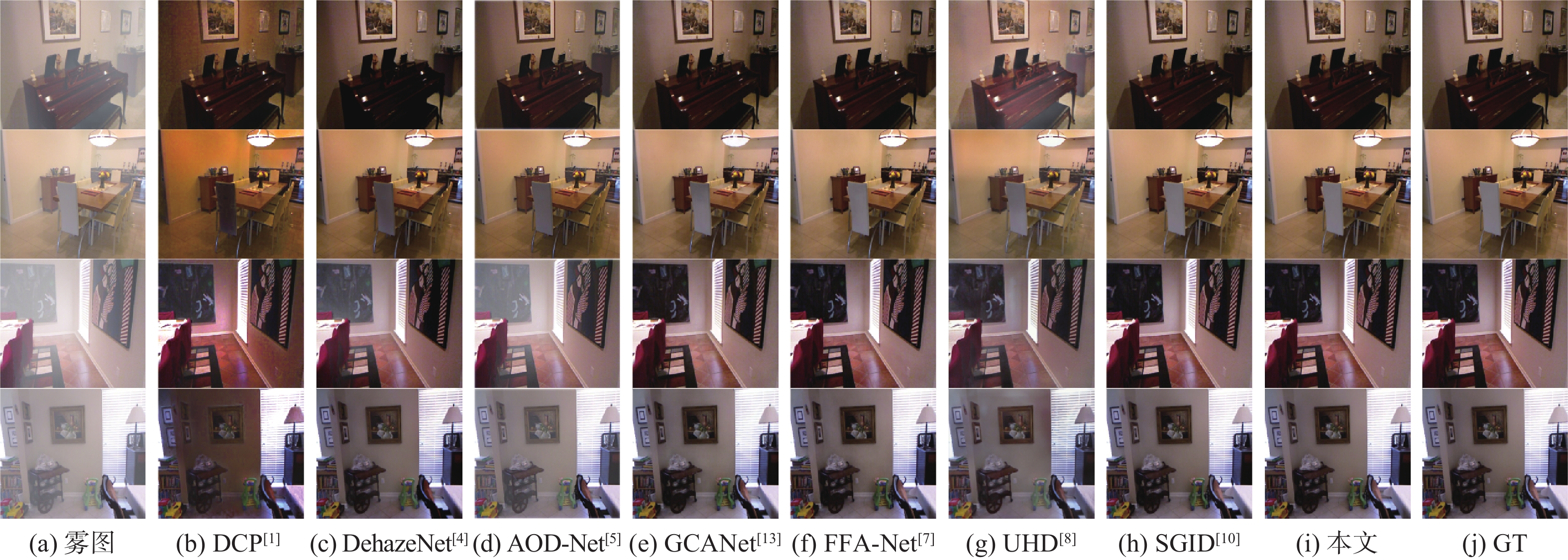
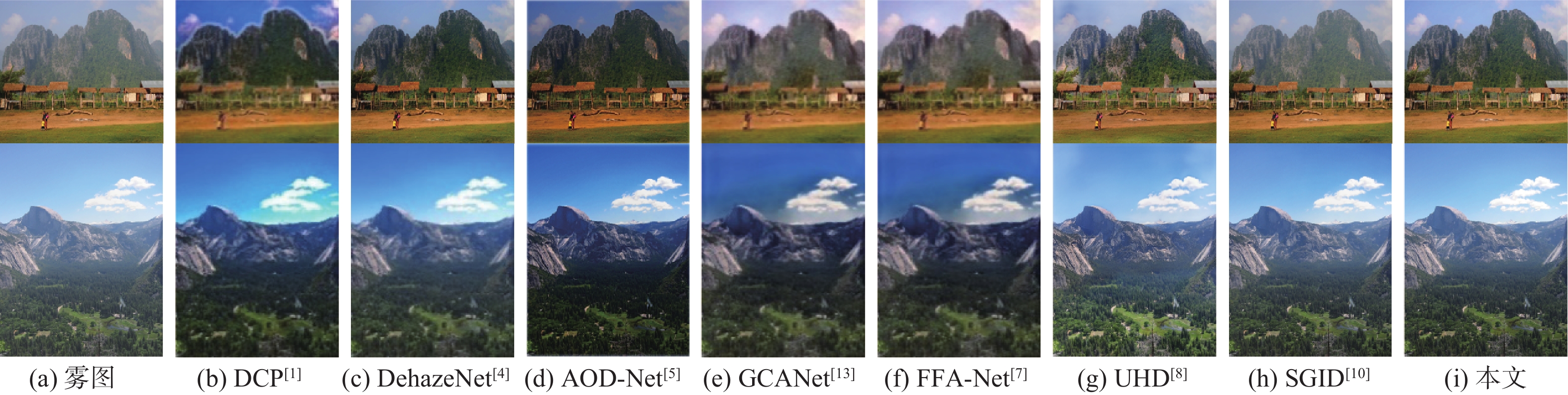
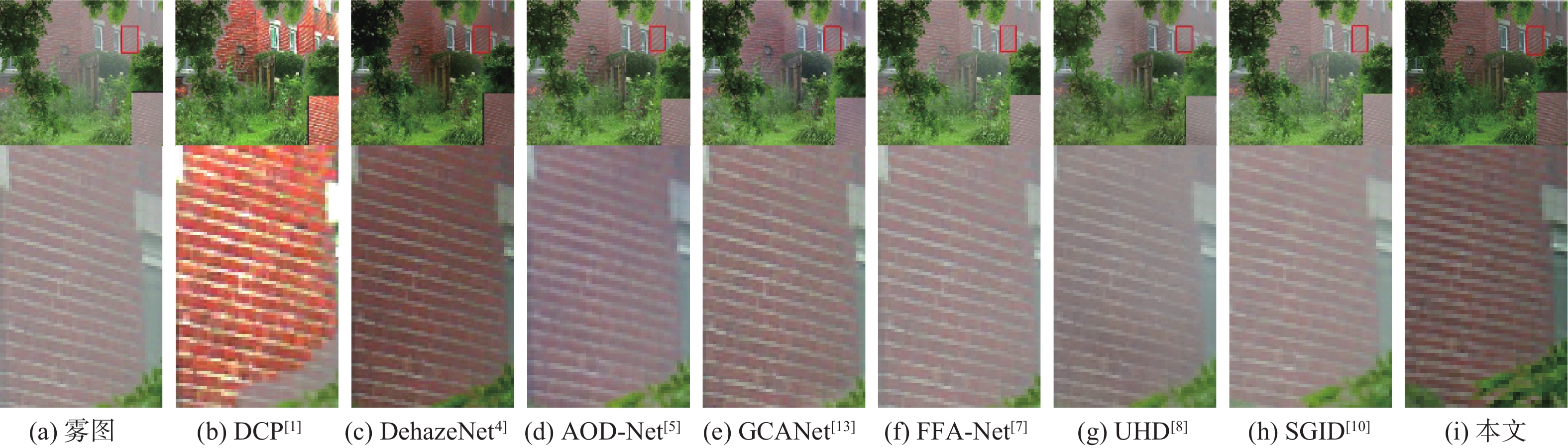
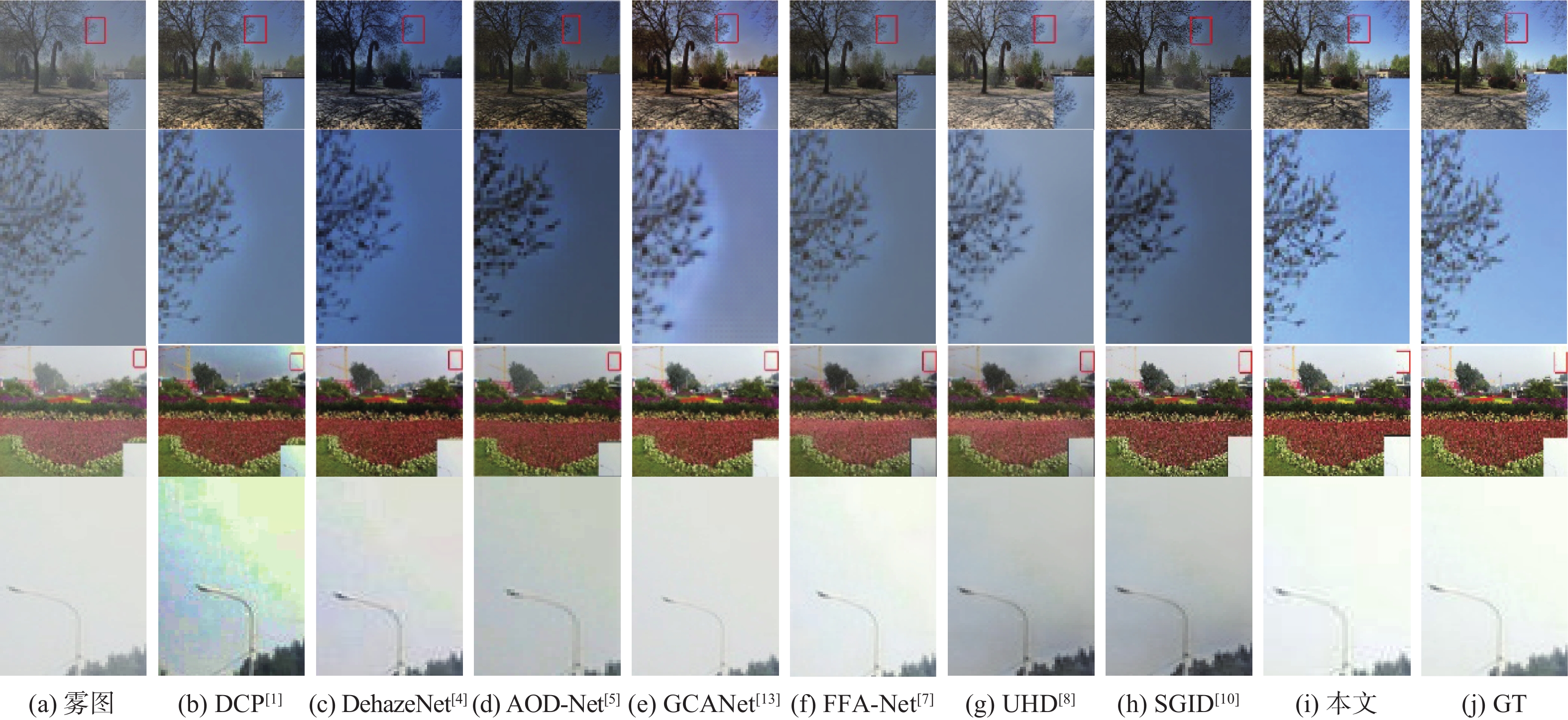
表 1 不同算法在不同测试集上的评测指标
Table 1. Evaluation metrics for different algorithms on different test sets
算法 PSNR/dB SSIM SOTS室内 Haze4K SOTS室外 SOTS室内 Haze4K SOTS室外 DCP[1] 16.52 14.21 19.03 0.8186 0.7246 0.8216 DehazeNet[4] 20.13 19.24 22.16 0.8457 0.8428 0.8233 AOD-Net[5] 19.08 17.18 19.15 0.8503 0.8349 0.8458 GCANet[13] 30.20 23.57 30.14 0.9806 0.9492 0.9521 FFA-Net[7] 33.29 24.97 30.79 0.9764 0.9514 0.9342 UHD[8] 21.59 13.28 25.80 0.8679 0.7457 0.9639 SGID[10] 33.45 21.25 29.98 0.9856 0.9291 0.9780 本文 34.14 25.53 31.29 0.9830 0.9624 0.9808 表 2 平均运行时间对比
Table 2. Average runtime comparison
表 3 消融实验
Table 3. Ablation experiment
模块 PSNR/dB SSIM Base 27.25 0.9562 Base+RGCA 28.89 0.9619 Base+RGCA+RG-C 28.85 0.9761 Base+RG-C+LHFF 31.17 0.9792 Base+RGCA+LHFF 30.61 0.9780 本文 33.08 0.9814 -
[1] HE K M, SUN J, TANG X O. Single image haze removal using dark channel prior[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2011, 33(12): 2341-2353. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2010.168 [2] ZHU Q S, MAI J M, SHAO L. A fast single image haze removal algorithm using color attenuation prior[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(11): 3522-3533. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2446191 [3] 杨燕, 张金龙, 张浩文. 基于区间估计与透射率自适应约束的去雾算法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2022, 48(1): 15-26.YANG Y, ZHANG J L, ZHANG H W. Dehazing algorithm based on interval estimation and adaptive constraints of transmittance[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2022, 48(1): 15-26(in Chinese) . [4] CAI B L, XU X M, JIA K, et al. DehazeNet: an end-to-end system for single image haze removal[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(11): 5187-5198. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2598681 [5] LI B Y, PENG X L, WANG Z Y, et al. AOD-Net: all-in-one dehazing network[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 4780-4788. [6] DONG H, PAN J S, XIANG L, et al. Multi-scale boosted dehazing network with dense feature fusion[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 2154-2164. [7] QIN X, WANG Z L, BAI Y C, et al. FFA-Net: feature fusion attention network for single image dehazing[C]//Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Palo Alto: AAAI Press, 2020: 11908-11915. [8] ZHENG Z R, REN W Q, CAO X C, et al. Ultra-high-definition image dehazing via multi-guided bilateral learning[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 16180-16189. [9] WU H Y, QU Y Y, LIN S H, et al. Contrastive learning for compact single image dehazing[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 10546-10555. [10] BAI H R, PAN J S, XIANG X G, et al. Self-guided image dehazing using progressive feature fusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2022, 31: 1217-1229. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2022.3140609 [11] LIU X H, MA Y R, SHI Z H, et al. GridDehazeNet: attention-based multi-scale network for image dehazing[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 7313-7322. [12] LI R D, PAN J S, LI Z C, et al. Single image dehazing via conditional generative adversarial network[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 8202-8211. [13] CHEN D D, HE M M, FAN Q N, et al. Gated context aggregation network for image dehazing and deraining[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 1375-1383. [14] CAO Y, XU J R, LIN S, et al. GCNet: non-local networks meet squeeze-excitation networks and beyond[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 1971-1980. [15] HOU Q B, ZHOU D Q, FENG J S. Coordinate attention for efficient mobile network design[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 13708-13717. [16] WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 3-19. [17] GIRSHICK R. Fast R-CNN[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 1440-1448. [18] WANG Z, BOVIK A C, SHEIKH H R, et al. Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2004, 13(4): 600-612. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2003.819861 [19] LI B Y, REN W Q, FU D P, et al. Benchmarking single image dehazing and beyond[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(1): 492-505. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2867951 [20] LIU Y, ZHU L, PEI S D, et al. From synthetic to real: image dehazing collaborating with unlabeled real data[C]//Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. New York: ACM, 2021: 50-58. [21] HE T, ZHANG Z, ZHANG H, et al. Bag of tricks for image classification with convolutional neural networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 558-567. [22] HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 770-778. [23] HU J, SHEN L, SUN G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 7132-7141. -








 下载:
下载: