Friction and heat flux prediction of lift body under different gas models and slip boundary models
-
摘要:
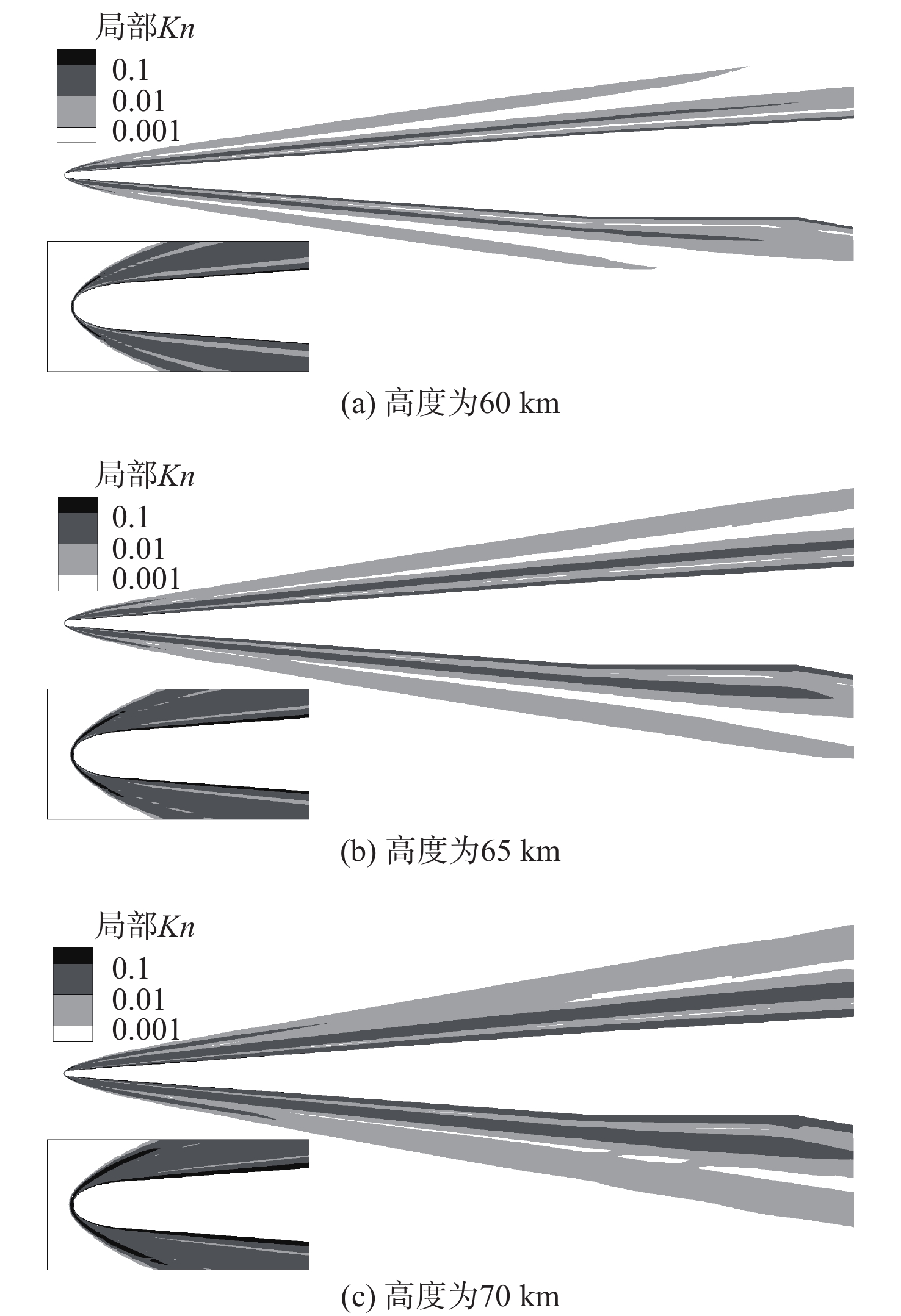
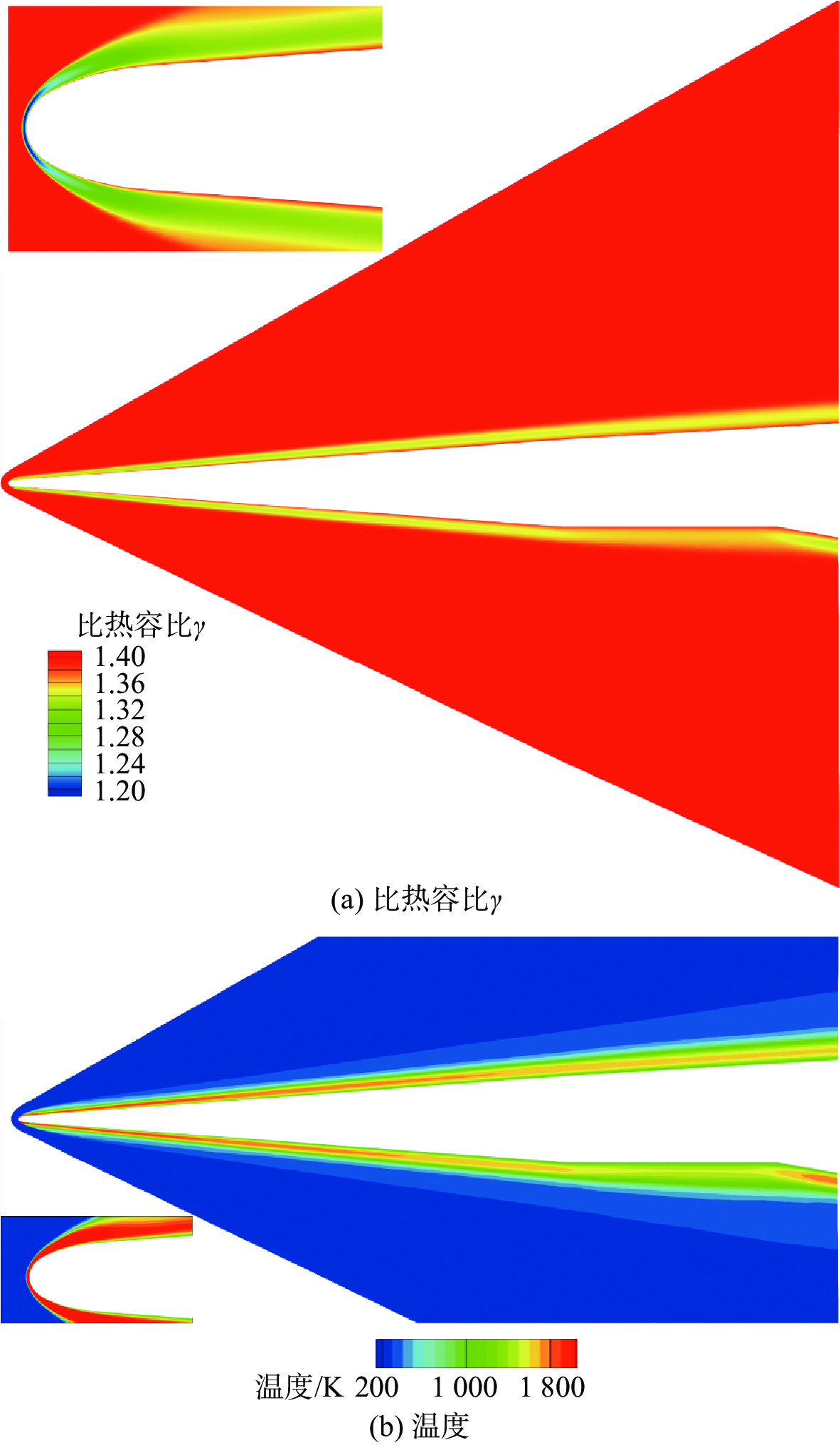
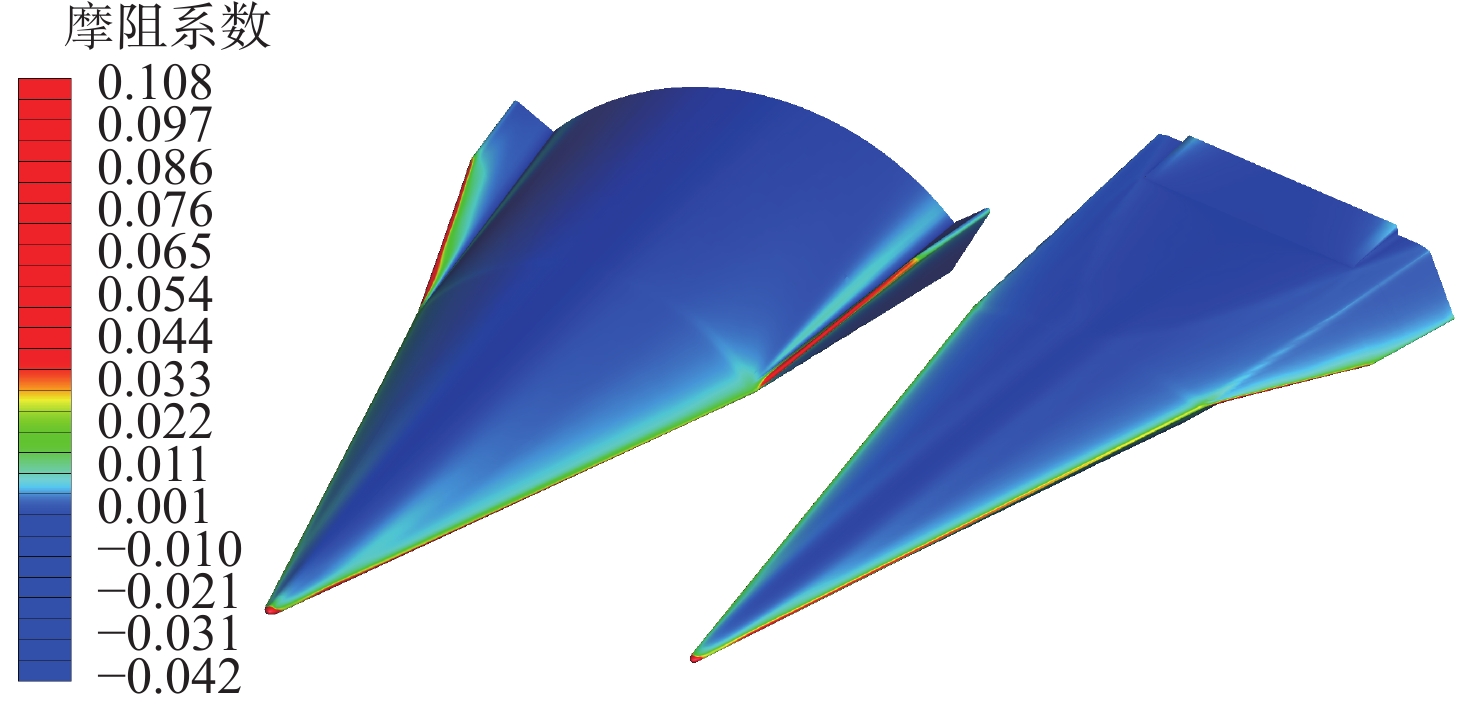
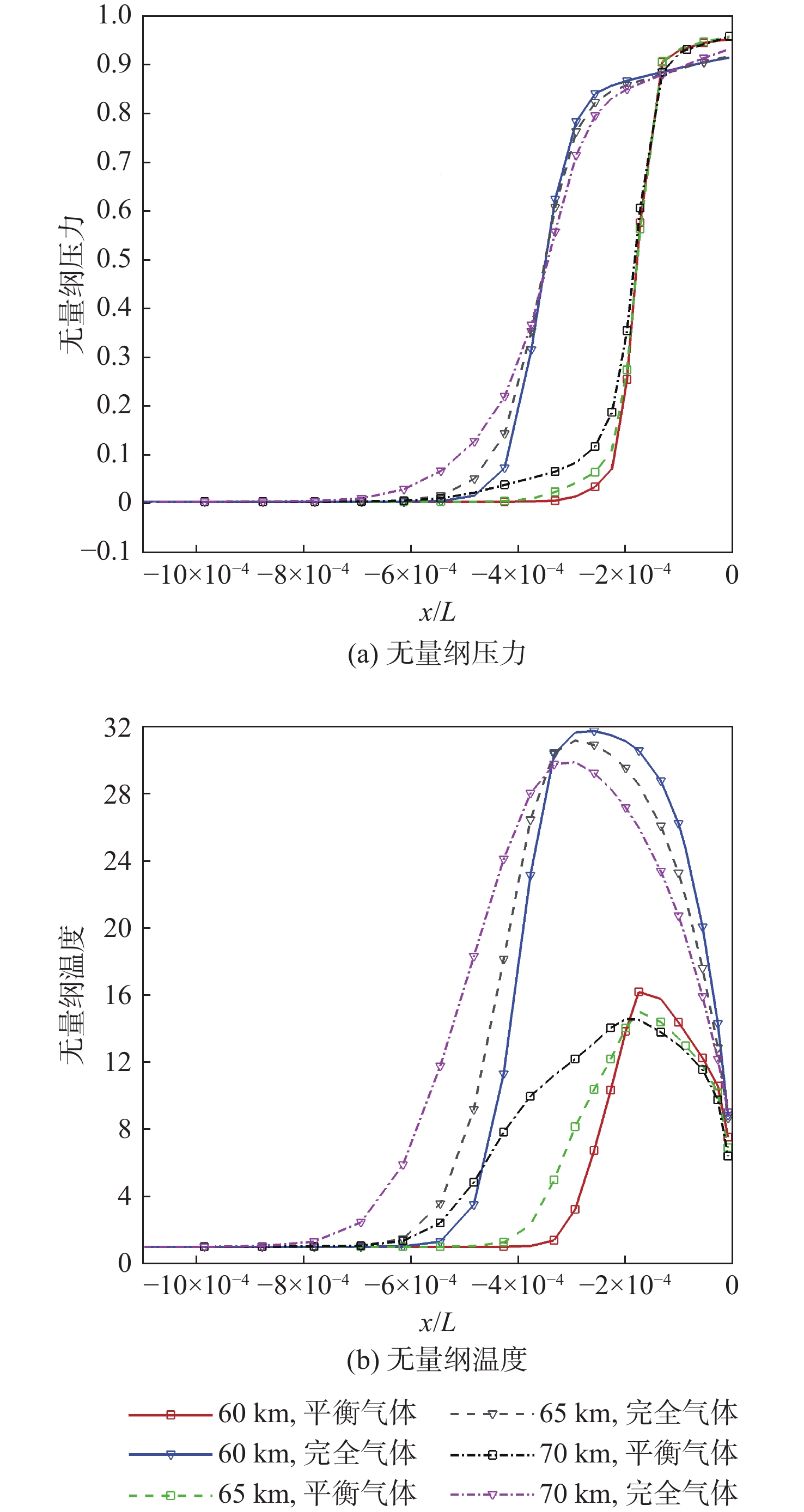
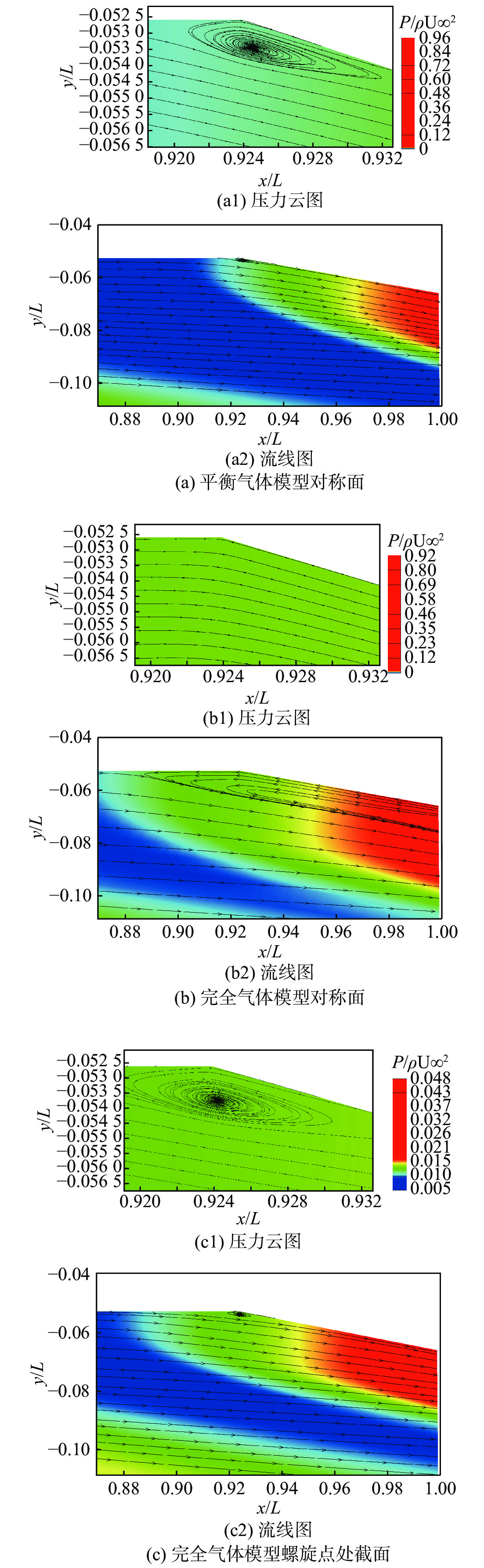
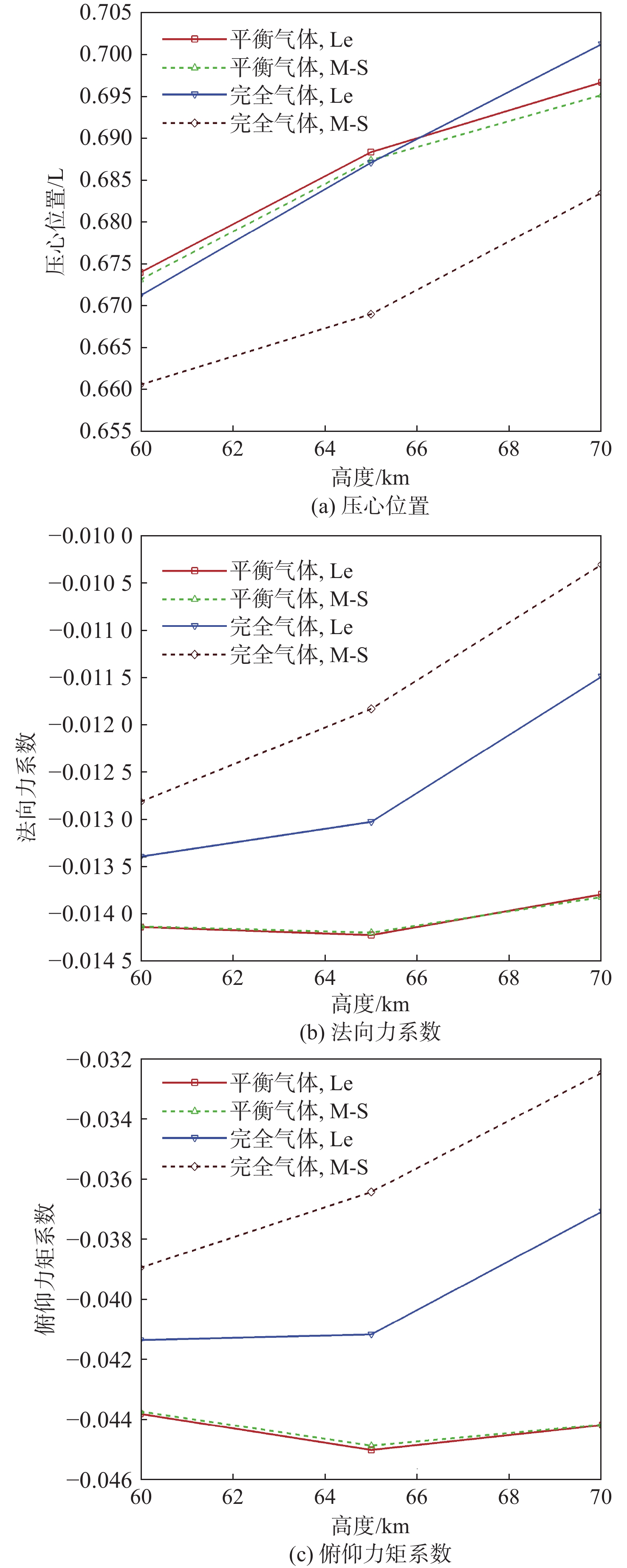
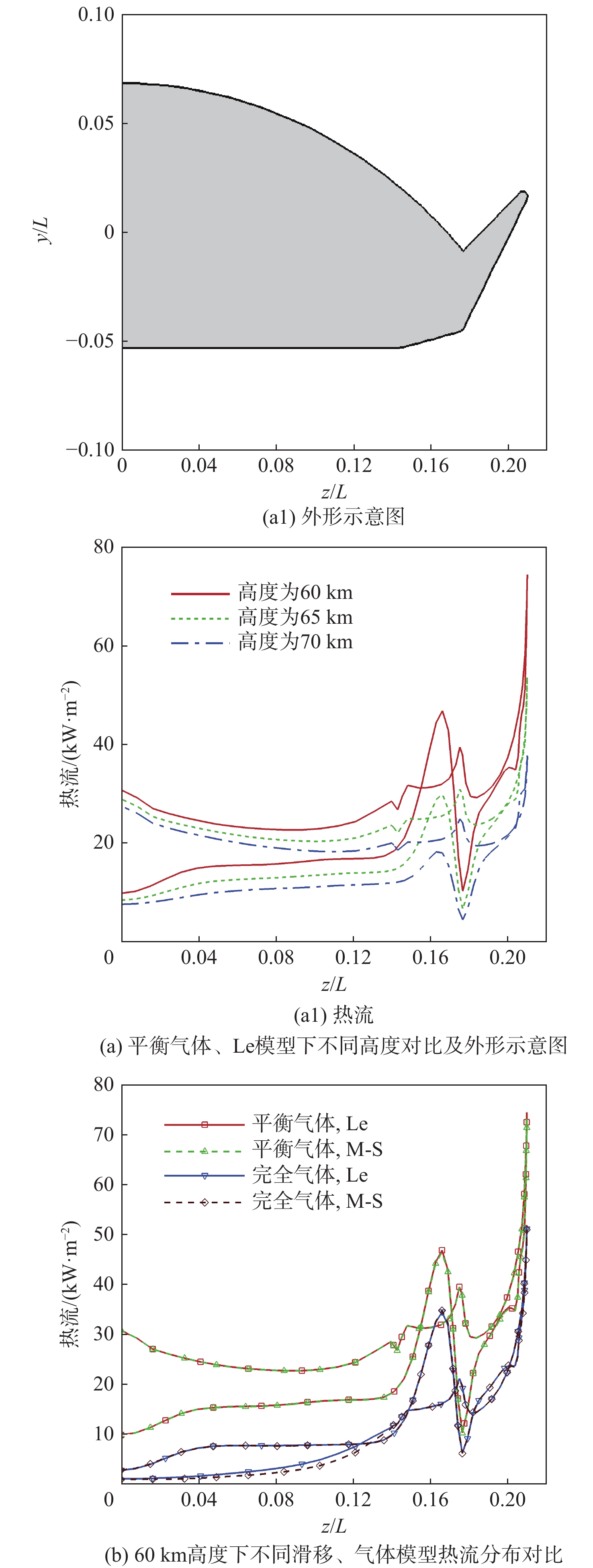
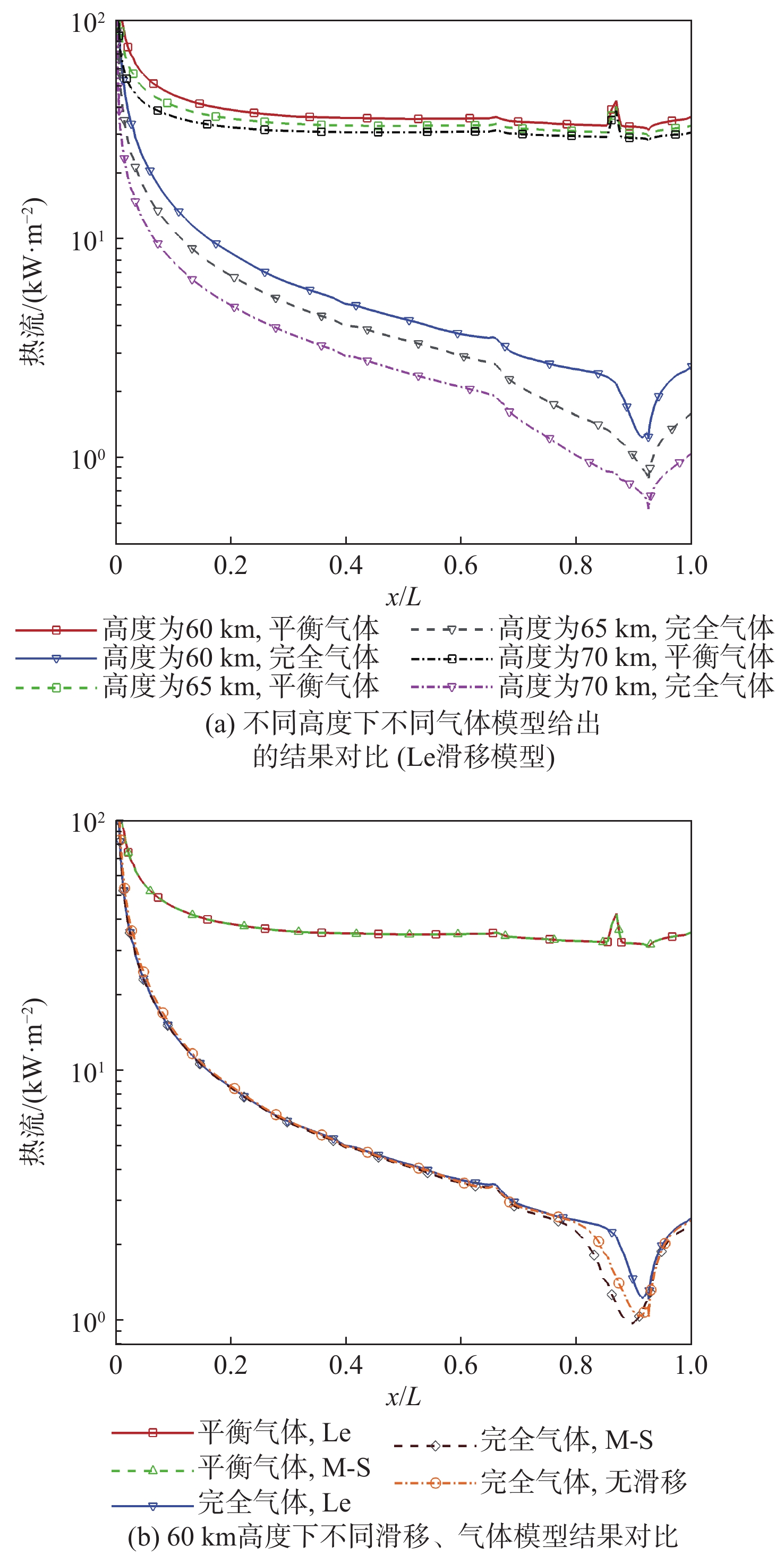
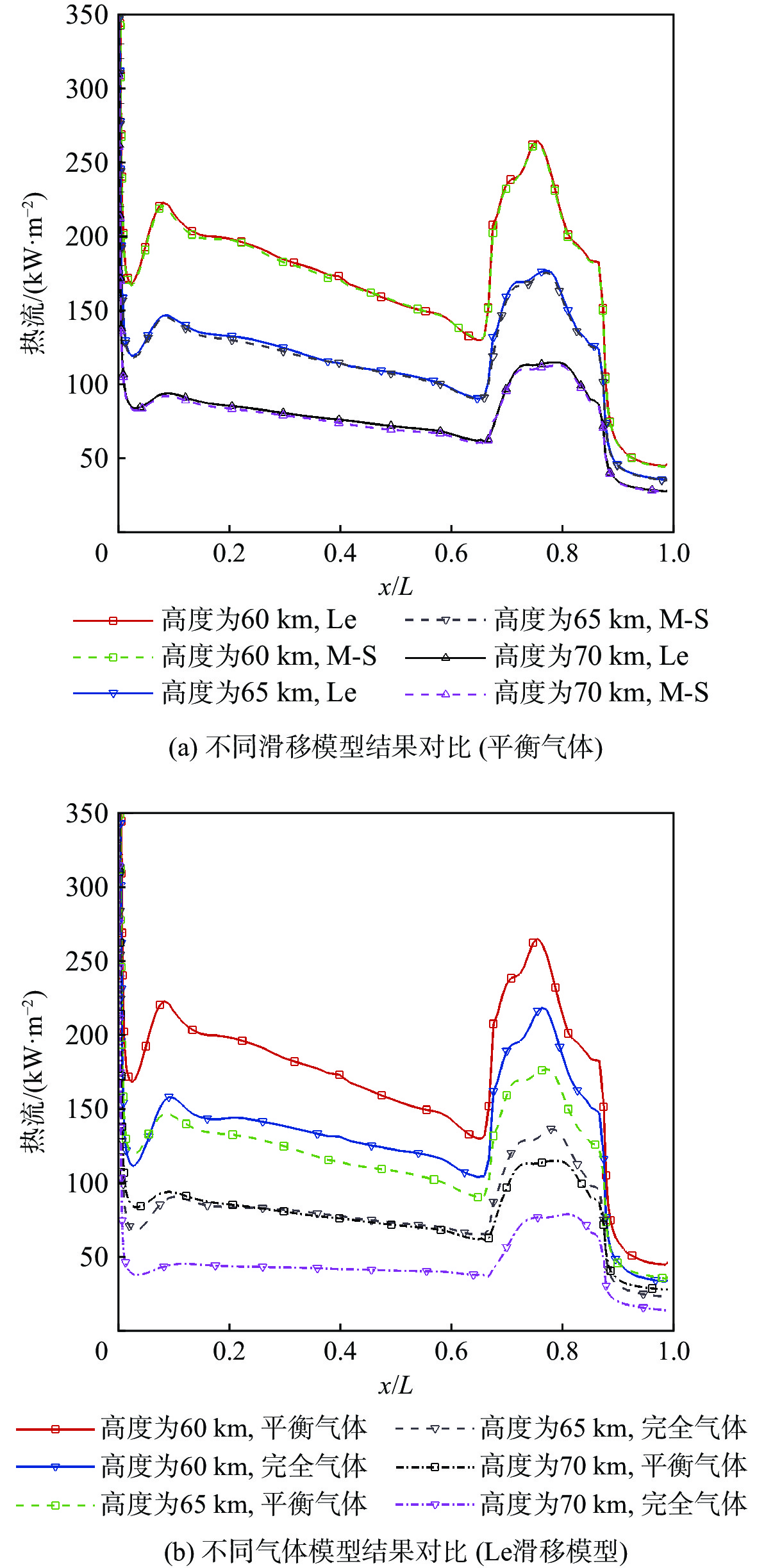
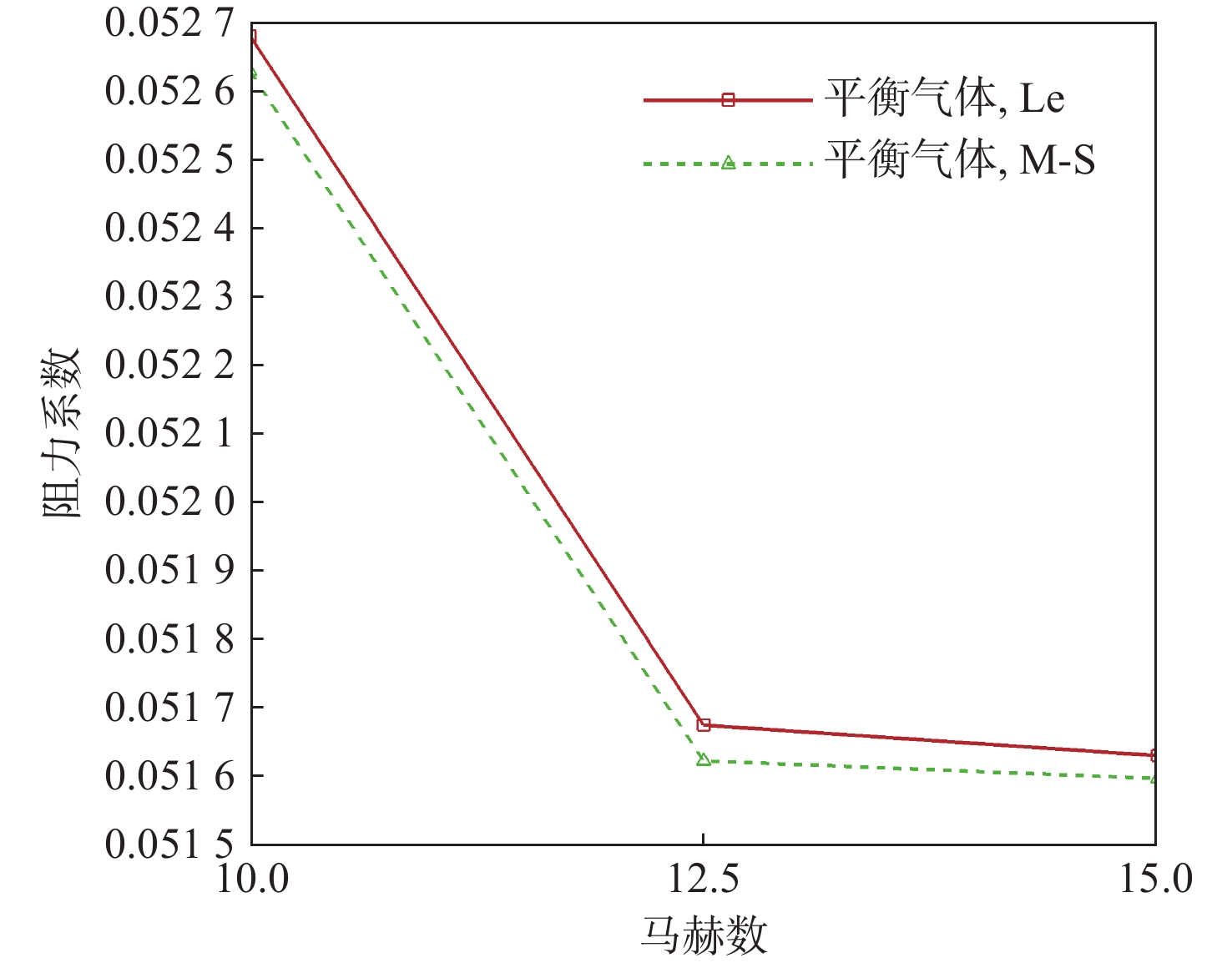
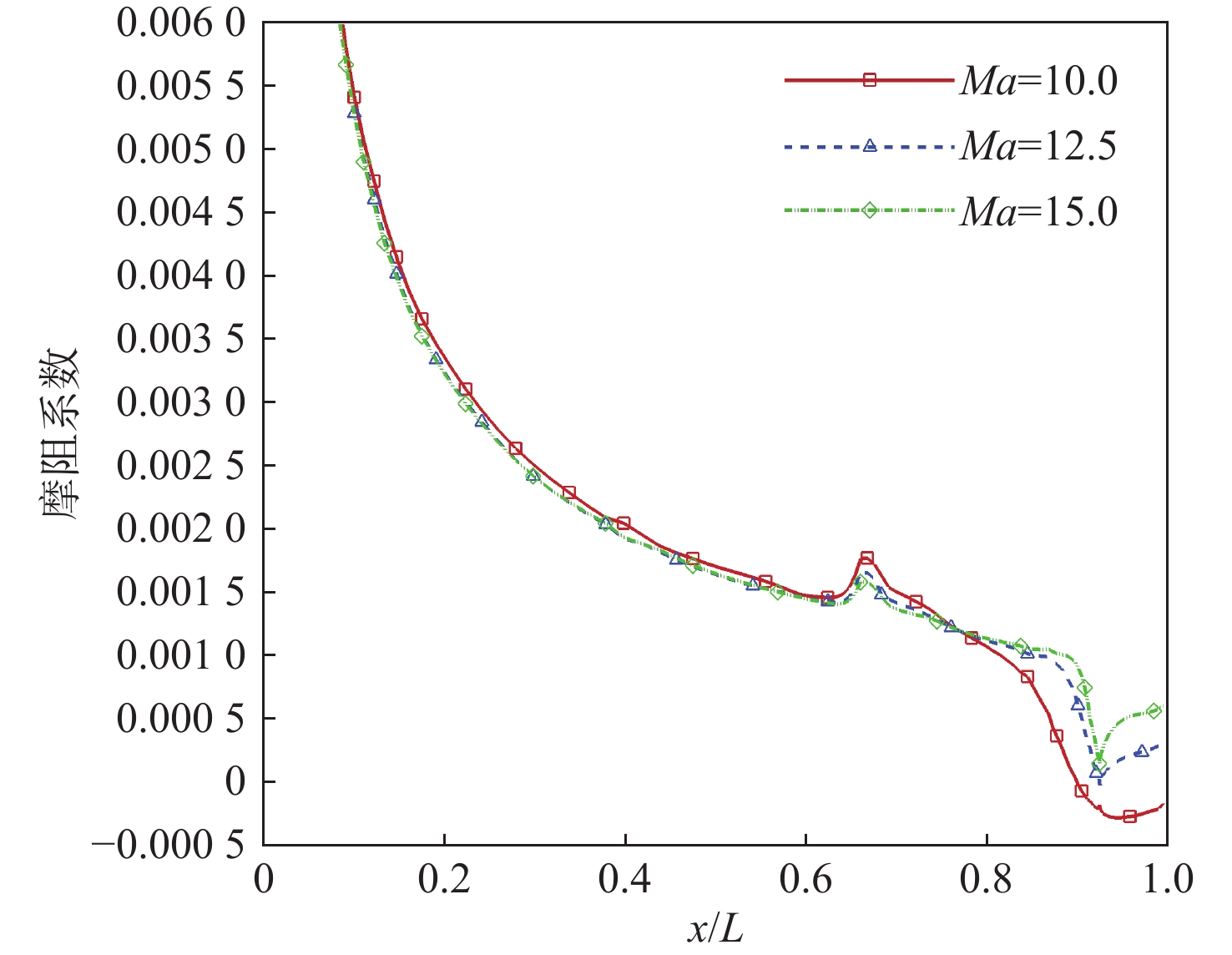
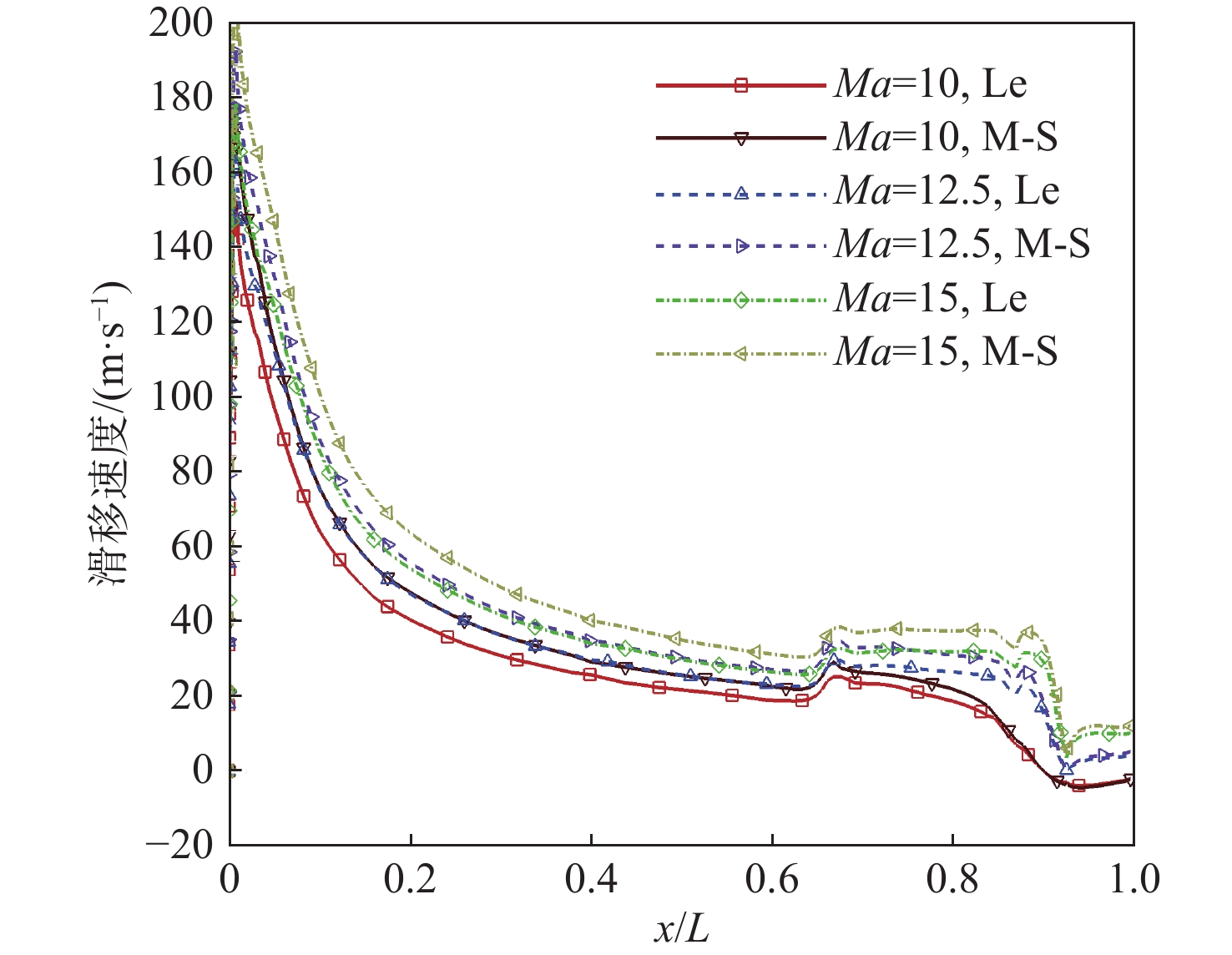
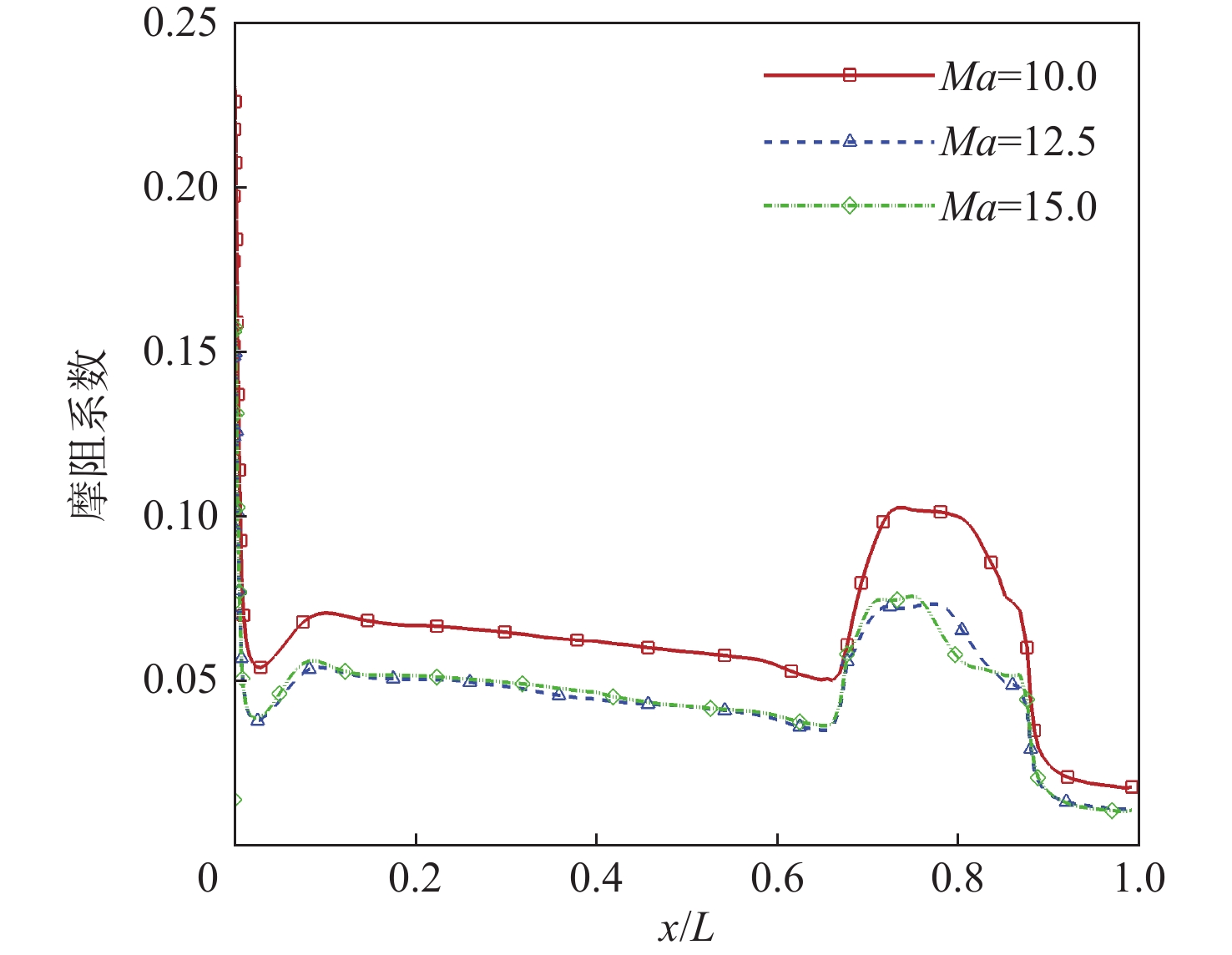
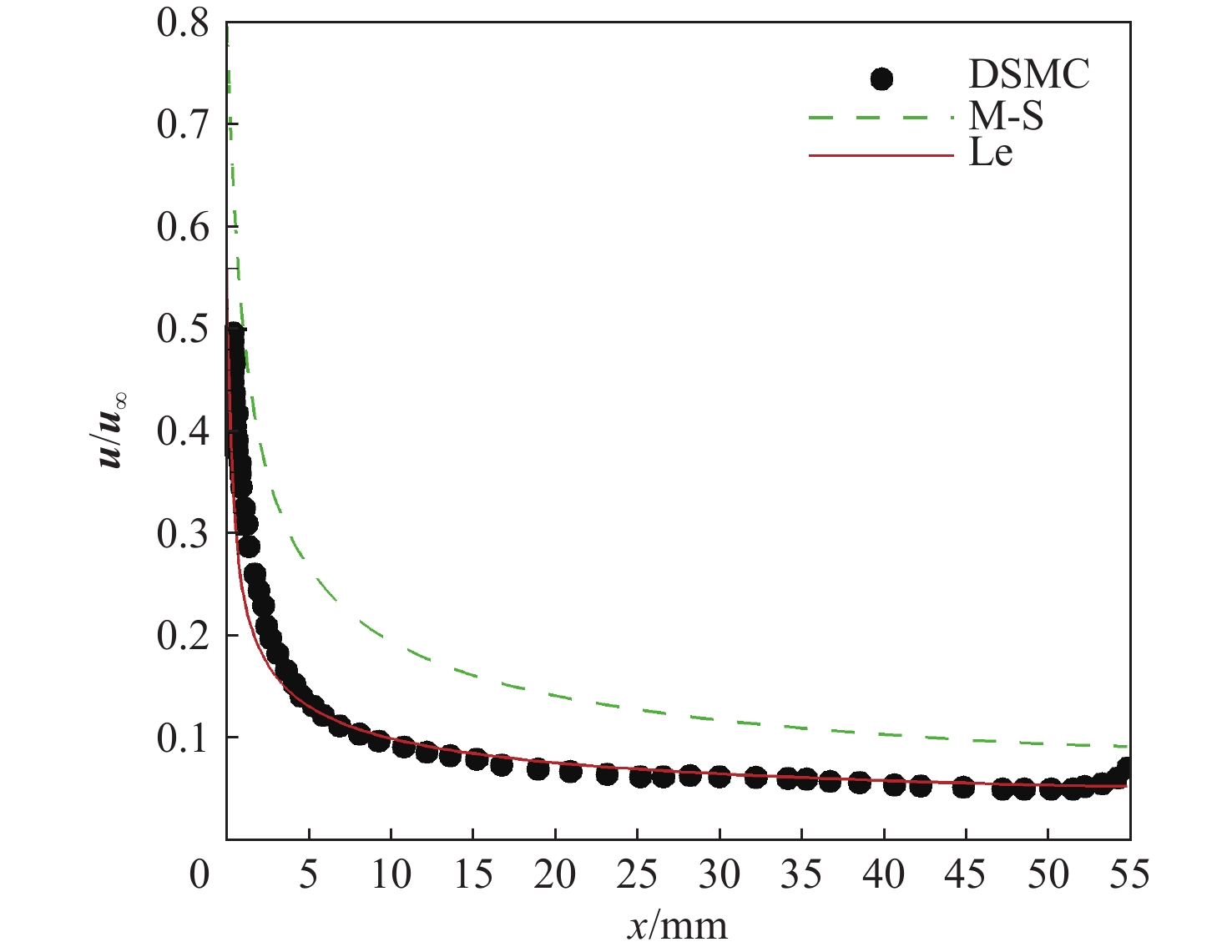
针对高超声速升力体外形的摩阻、热流预测问题,采用所发展的三阶精度本质无波动格式,研究了不同气体模型(完全气体、平衡气体)、滑移边界模型(M-S、Le)和来流条件(高度、马赫数和壁面温度)对摩阻、热流等预测的影响。研究采用不同滑移边界模型和气体模型,对双马赫反射问题及典型高超声速绕流问题绕流进行了数值模拟与分析。结果表明:高保真气体模型、滑移边界模型和高精度计算格式能够使高超声速问题计算具有更好的精度。在此基础上,开展了不同高度、马赫数和壁温的高超声速升力体绕流数值模拟与分析,综合分析了滑移边界模型和气体模型对摩阻、热流等预测的影响。结果表明:不同气体模型之间的结果存在较大差异,平衡气体模型预示的边界层温度更低、边界层厚度更小、壁面热流更大、摩阻系数与总阻力系数稍大,二者差异随高度增加而增大;完全气体模型下,不同滑移边界模型总阻力系数、压心位置和热流分布均存在差异且随高度增加差异有所增大;采用平衡气体模型时,不同滑移模型之间预测结果相近。
Abstract:In view of the friction and heat flux prediction problems in the hypersonic flows around a lift body, the influence of different gas models (perfect gas and equilibrium gas), slip boundary models (M-S and Le), and incoming flow conditions (height, Mach number, and wall temperature) on the prediction of friction and heat flux was studied with the developed third-order weighted essentially non-oscillatory scheme. Firstly, numerical simulation and analysis of double Mach reflection problem and typical hypersonic examples were carried out by different slip boundary models and gas models. The results show that high-fidelity gas models, slip boundary models, and high-precision schemes show better accuracy in the calculation of hypersonic problems. On this basis, numerical simulation and analysis of hypersonic flows around a lift body at different heights, Mach numbers, and wall temperatures are carried out. The effects of slip boundary models and gas models on the prediction of friction and heat flux are comprehensively analyzed. The results show that different gas models are quite different, and the equilibrium gas model gets lower temperature in the boundary layer, smaller thickness of the boundary layer, greater wall heat flux, and slightly larger friction coefficient and total drag coefficient. The difference between the two gas models increases with the increase in height. Under the perfect gas model, the total drag coefficient, position of the center of pressure, and heat flux distribution of different slip boundary models show greater difference, which increases with the increase in height. Under the equilibrium gas model, the results of different slip boundary models are similar.
-
Key words:
- hypersonic flow /
- lift body /
- slip boundary condition /
- equilibrium gas /
- heat flux /
- friction
-
表 1 高超声速圆锥绕流计算条件
Table 1. Calculation conditions of hypersonic flow around a cone
气体 Ma T∞/K P∞/Pa Re∞ 空气 25.3 252.6 20.35 1.29×105 表 2 Ma=11.35绕中空圆柱-长裙流动计算条件[17]
Table 2. Calculation condition of Ma=11.35 flow around a hollow cylinder-flare[17]
气体 Ma Re/m T∞/K Tw/K N2 11.35 3.596×105 79 294 表 3 不同高度下不同气体、滑移模型给出的升力体驻点热流
Table 3. Stagnation point heat flux of lift body by different gas and slip models at different heights
kW/m2 气体 滑移 高度为60 km 高度为65 km 高度为70 km 平衡 M-S 2397.25 1647.80 1042.67 Le 2383.09 1639.62 1092.05 完全 M-S 1800.28 1178.63 761.17 Le 1775.83 1192.44 759.53 -
[1] SRINIVASAN S, TANNEHILL J C, WEILMUENSTER K. Simplified curve fits for the thermodynamic properties of equilibrium air. NASA RP-1181[R]. Washington, D. C. : NASA, 1987. [2] SRINIVASAN S, TANNEHILL J C, WEILMUENSTER K J. Simplified curve fits for the transport properties of equilibrium Air: NASA CR-178411[R]. Washington, D. C. : NASA, 1987. [3] MAXWELL J C. On stresses in rarified gases arising from inequalities of temperature[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, 1879, 170: 231-256. doi: 10.1098/rstl.1879.0067 [4] VON SMOLAN M S. Ueber Wärmeleitung in verdünnten gasen[J]. Annalen der Physik, 1898, 300(1): 101-130. doi: 10.1002/andp.18983000110 [5] JIANG G S, SHU C W. Efficient implementation of weighted ENO schemes[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1996, 126(1): 202-228. doi: 10.1006/jcph.1996.0130 [6] HENRICK A K, ASLAM T D, POWERS J M. Mapped weighted essentially non-oscillatory schemes: achieving optimal order near critical points[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2005, 207(2): 542-567. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2005.01.023 [7] BORGES R, CARMONA M, COSTA B, et al. An improved weighted essentially non-oscillatory scheme for hyperbolic conservation laws[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2008, 227(6): 3191-3211. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2007.11.038 [8] LI Q, YAN P, HUANG X, et al. On developing piecewise rational mapping with fine regulation capability for WENO schemes[J]. Journal of Scientific Computing, 2021, 88(3): 75. doi: 10.1007/s10915-021-01559-z [9] LI Q, YAN P, HUANG X, et al. Improvements to enhance robustness of third-order scale-independent WENO-Z schemes[J]. Advances in Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2024, 17(2): 373-406. [10] LE N T P, WHITE C, REESE J M, et al. Langmuir–Maxwell and Langmuir–Smoluchowski boundary conditions for thermal gas flow simulations in hypersonic aerodynamics[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2012, 55(19-20): 5032-5043. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2012.04.050 [11] LE N T P, VU N A, LOC L T. New type of Smoluchowski temperature jump condition considering the viscous heat generation[J]. AIAA Journal, 2017, 55(2): 474-483. doi: 10.2514/1.J055058 [12] LE N T, TRAN N H, TRAN T N, et al. New slip boundary condition in high-speed rarefied gas flow simulations[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part G: Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 2020, 234(3): 840-856. doi: 10.1177/0954410019886955 [13] LE N T P, TRAN N H, TRAN T N. Modified Patterson temperature jump condition considering viscous heat generation[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2018, 126: 1267-1274. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2018.06.046 [14] KARNIADAKIS G, BESKOK A, ALURU N, et al. Microflows and nanoflows: fundamentals and simulation[M]. New York: Springer New York, 2001: 59-66. [15] BECKER, M. Flat plate flow files and surface measurements from merged layer into transition regime[C]// Proceedings of the seventh International Symposium on Rarefied Gas Dynamics. Pisa: University of Pisa, 1969 : 515–528. [16] TANNEHILL J C, BUELOW P E, LEVALTS J O, et al. Three-dimensional upwind parabolized Navier-Stokes code for real gasflows[J]. Journal of Spacecraft and Rockets, 1990, 27(2): 150-159. doi: 10.2514/3.26119 [17] JOHN K H, HOLDEN M S, WADHAMS T P. Code validation study of laminarshock/boundary layer and shock/shock interactions in hypersonic flow[C]//Proceedings of the 39th Aerospace Science Meeting and Exhibit. Reston: AIAA, 2001-1031. -







 下载:
下载: