A deep reinforcement learning based on discrete state transition algorithm for solving fuzzy flexible job shop scheduling problem
-
摘要:
柔性作业车间调度问题(FJSP)作为一种在实际生活中应用广泛的调度问题,对其智能算法具有重要价值。为了解决FJSP,以最小化最大完工时间为优化目标,提出了一种基于近端策略优化的离散状态转移算法(DSTA-PPO)。DSTA-PPO具有3个特点:考虑到FJSP需要同时对工序排序、机器分配同时进行调度安排,结合工序编码和机器编码,设计了一种能够充分表达当前调度问题的状态特征;针对工序排序、机器分配设计了多种基于关键路径的搜索操作;通过强化学习的训练,能够有效地引导智能体选择正确的搜索操作优化当前的调度序列。通过基于不同数据集的仿真实验,验证了算法各环节的有效性,同时在相同算例上以最小化最大完工时间为对比指标与现有算法进行了比较,对比结果表明了所提算法能够在多数算例上以更短的完工时间对算例完成求解,有效地求解了柔性作业车间调度问题。
Abstract:The study of the intelligent algorithms for the flexible job shop scheduling issue (FJSP), a scheduling problem with a broad range of application backgrounds, is very relevant both academically and practically. To address FJSP with the objective of minimizing the maximum completion time, this paper proposes a discrete state transfer algorithm based on proximal policy optimization (DSTA-PPO). DSTA-PPO has the following three characteristics. Considering that FJSP requires simultaneous scheduling arrangements for operation sequencing and machine assignment. This state feature can adequately express the current scheduling problem that was designed by combining operation coding and machine coding. Various critical path based search operations have been designed for operation sequencing and machine allocation. Reinforcement learning training is an efficient way to direct intelligence to choose the best search operation to maximize the current scheduling sequence.. The effectiveness of each component of the algorithm is verified through simulation experiments on different datasets. Furthermore, a comparison is conducted with existing algorithms using the objective of minimizing the maximum completion time in the same instances. The comparison results show that the suggested method successfully resolves the flexible job shop scheduling issue by typically achieving shorter completion times.
-
云制造作为工业4.0中下一代制造系统的新兴范式,在过去的数年中,受到了持续的关注[1]。云制造能够将分布式制造资源虚拟化并整合到云平台中,经过与网络物理系统、物流互联网和人工智能等先进技术的结合[2],达到按需提供灵活、优质的制造服务[3]。提供一个高效的资源调度更是其中的关键部分,其主要任务是在制造资源上对制造任务进行合理的安排,以达到充分发挥系统性能的目的。本文所研究的FJSP隶属于云制造资源调度任务中的一种[4,5],虽然其同作业车间调度问题一样都属于NP-hard问题中,但FJSP允许工件有一个或多个加工机器进行选择。因此,FJSP更切合高灵活性、高多样性的云制造模式,有着重要的应用价值[6]。因此,FJSP得到了广泛的关注。
近年来,许多方法已经被应用于解决FJSP。一些研究提出了精确算法,包括Choi等[7]提出的数学编程和混合整数目标编程。然而,由于FJSP的NP-hard特性,精确算法很耗时,而且即使对于小规模的实例也很难达到全局最优。因此,许多研究人员开始开发更有效的解决方法,以获得接近最优的解决方案。Zhang等[8]对粒子群算法和禁忌搜索算法相结合,用以解决FJSP。Nouiri等提出了一种两阶段粒子群算法[9]和基于多智能体的粒子群算法[10]用于解决该问题。Xing等[11]针对FJSP提出了一种基于知识模型的蚁群优化算法,其中,知识模型被用来指导当前的启发式搜索。Jiang等[12]首次将离散的灰狼优化法应用于解决FJSP,其中引入了自适应突变法,目标是最小化完工时间。尽管这些智能优化算法能够在合理的时间内解决FJSP,但并不能在更复杂的调度问题取得较好的表现。
状态转移算法是Zhou等[13]提出的一种智能型随机性全局优化算法,该算法同其他群智能算法相比具有结构简单、参数少、易理解等优点。董天雪等[14]提出了一种新的离散状态转移算法提高企业员工指派问题的成功率和稳定性。张凤雪等[15]采用状态转移算法对非线性规划问题进行了求解,并验证了算法的有效性。状态转移算法同其他优化算法相比,具有较快的收敛速率和较高的寻优精度,但是,在特定的复杂高维全局优化问题中,状态转移算法表现出较为缓慢的收敛速度和较低的收敛精度,且其在局部收敛方面的能力相对有限。
深度强化学习算法提供了一种可扩展的方法来解决具有共同特征的调度问题。Du等[16]提出了一种基于知识的强化学习同分布式估计算法结合的混合算法求解FJSP。Chen等[17]提出了一种自适应学习的遗传算法求解FJSP,通过强化学习自适应地学习遗传算法中的关键参数以提高求解性能。Lei等[18]提出了一种端到端的深度强化学习算法,利用图神经网络求解FJSP,并通过实验在大规模的FJSP中验证了算法的有效性。张凯等[19]提出一种集成式强化学习算法求解FJSP,通过设计调度规则完成求解。王凌等[20]提出一种协同群智能算法,通过基于信息交互的工序排序搜索和基于Q-learning的机器分配搜索求解分布式绿色柔性作业车间调度问题。可以看出深度强化学习算法已经广泛地应用在FJSP中,并取得较好的效果。
本文结合状态转移算法和深度强化学习算法的优点,提出了一种基于深度强化学习的离散状态转移算法。将离散状态转移算法的三种高效的变换算子添加到深度强化学习算法工件选择的动作中,并添加机器的邻域搜索结构用于确定加工机器。针对缩短柔性作业车间调度的最大完工时间问题,通过深度神经网络训练强化学习智能体在不同的状态下,能够自适应选择合适的离散状态转移动作和机器邻域搜索结构,改进了深度强化学习算法的策略搜索过程,增加了策略空间的多样性,提高了策略搜索的效果。
为了验证DSTA-PPO的有效性,本文在两种测试算例中进行了仿真实验,分别在低维和高维问题中同其他深度强化学习算法完成了对比实验。
1. 问题描述
1.1 问题定义
FJSP描述如下:n个工件在m台机器上加工,工件集和机器集分别记为Ji(i=1,2,⋯,n)和Mk(k=1,2,⋯,m)。每个工件都包含有多道不同的工序记为Ji={Oi1,Oi2,⋯,Oini},每道工序进行加工时须严格按照先后顺序,每个工件中至少包含一道工序具有多个可加工机器。在加工过程中,工件中的工序能够选择任意一台候选机器进行加工。FJSP需要对所有工件工序的加工机器进行选择,并合理地安排加工机器加工工序的顺序,在某些优化目标下合理地安排生产。本文以最小化最大完工时间Cmax为优化目标,即
{\text{min }}C = \min (\max \{ {C_i}|i = 1,2, \cdots ,n\} ) 式中: {C_i} 表示工件 {J_i} 的完工时间;最大完工时间 {C_{\max }} = \max \{ {C_i}|i = 1,2, \cdots ,n\} 。
不同的假设和约束条件会导致不同的柔性作业车间调度问题,本文作出如下假设:
1) 起始时刻所有机器为空闲状态,所有工件为待加工状态;
2) 同一机器同一时刻中只能加工一个工件;
3) 同一工件工序顺序确定不变,不同工件无优先级差别;
4) 任意一道工序开始加工后不能中断。
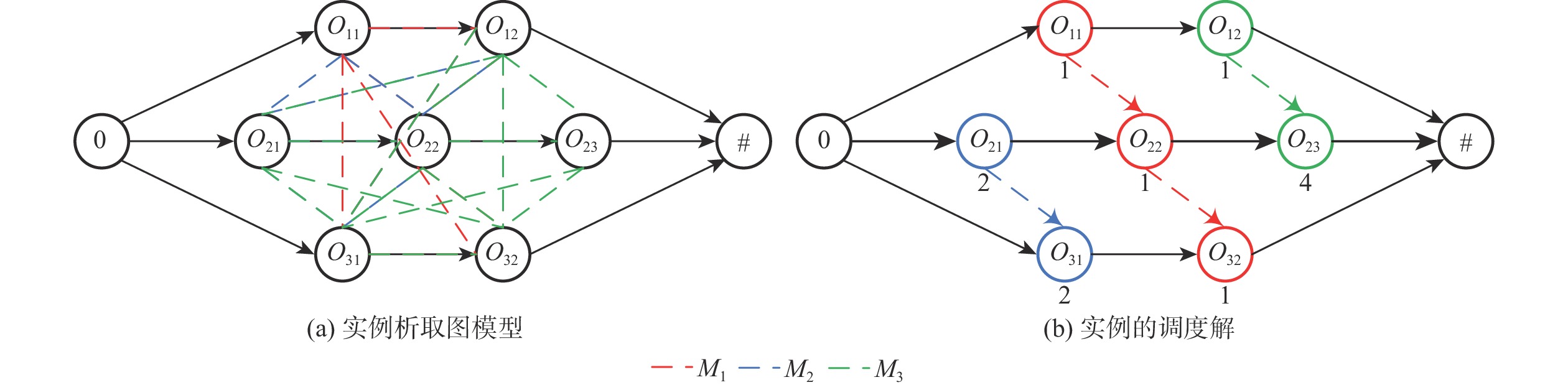
表1为三工件、三机器的FJSP实例。
表 1 3×3的FJSP实例Table 1. 3×3 FJSP instance工件 工序 工序号 工序和加工时间 M1 M2 M3 J1 O11 1 1 2 * O12 2 3 2 1 J2 O21 3 * 2 1 O22 4 1 2 4 O23 5 * * 4 J3 O31 6 3 2 2 O32 7 1 * 2 注:“*”表示该工序无法在该机器上进行加工。 1.2 调度问题的析取图描述
析取图以图的形式来表示FJSP的调度结果,能够更直观地了解工序的加工机器和加工顺序。一个FJSP析取图记为 G = (N,A,E) ,其中, N 是包含了调度问题中所有工件工序的顶点、开始顶点和结束顶点(0和#)的集合,即 N = \{ {O_{ij}}|i = 1,2, \cdots ,n;1 \leqslant j \leqslant {n_i}\} \cup \{ 0,\# \} , A = \{ ({O_{ij}},{O_{i,j + 1}})|i = 1,2, \cdots ,n;1 \leqslant j \leqslant {n_i} - 1\} \cup \{ (0,{O_{i1}})({O_{i{n_i}}},\# )|i = 1,2, \cdots ,n\} ,表示同一工件的两道连续工序之间的合取弧集合,反映了任意工件的工序之间的顺序约束关系; E 表示同一台机器上加工的相邻两道工序之间析取弧集合,反映了每台机器上的工序加工顺序和加工序列;对于任意一道工序 \omega ,将其在所选机器 {M_k} 上的加工时间 {p_{wk}} 作为该节点的权重 ({p_{wk}} > 0;{p_0} = {p_\# } = 0) ,当工序 \omega 的加工机器是确定的, {p_{wk}} 可简写为 {p_w} 。当图 G 为一个无环图时,图 G 能够表示为调度问题的一个可行解。
析取图 G 路径 ({\omega _1},{\omega _2}, \cdots ,{\omega _q}) 的长度为从最先开始加工的工序 {\omega _1} 到最后加工的工序 {\omega _q} 间加工花费时间总和,即 \displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 2}^{q - 1} {{p_{{w_i}}}} 。 L(i,j) 表示工序 i 到工序 j 之间的最长路径的长度。析取图 G 的关键路径为开始至结束顶点间加工时间最长的一段路径,在关键路径中加工的工序则为关键工序。用 L(0,\# ) 表示关键路径长度,则调度问题的最大完工时间可以表示为 {C_{\max }}(G) = L(0,\# ) 。
以表1中的FJSP实例为例,实例的析取图模型如图1所示。图1(a)所示的无向图表示未分配机器和工序时的析取图模型。图1(b)为实例的一个可行解,加粗实线表示关键路径,可以看出其长度为7,即最大完工时间 {C_{\max }}(G) = 7 ,且存在如图中加粗显示的一条关键路径,分别是 0 \to {O_{21}} \to {O_{22}} \to {O_{23}} \to \# ,工序 {O_{21}} 、 {O_{22}} 、 {O_{23}} 是关键工序。
2. 基础算法
2.1 编码和解码
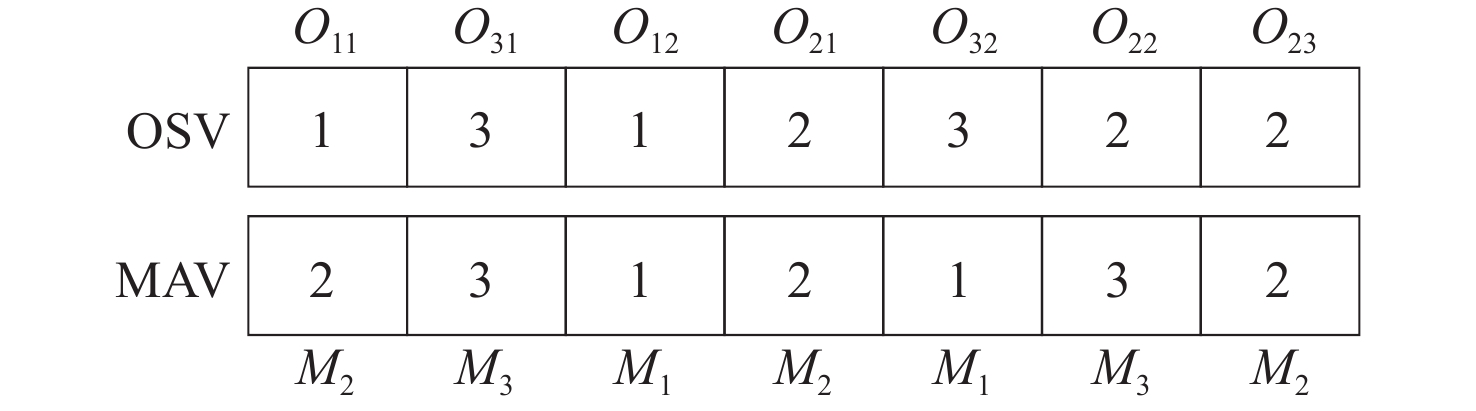
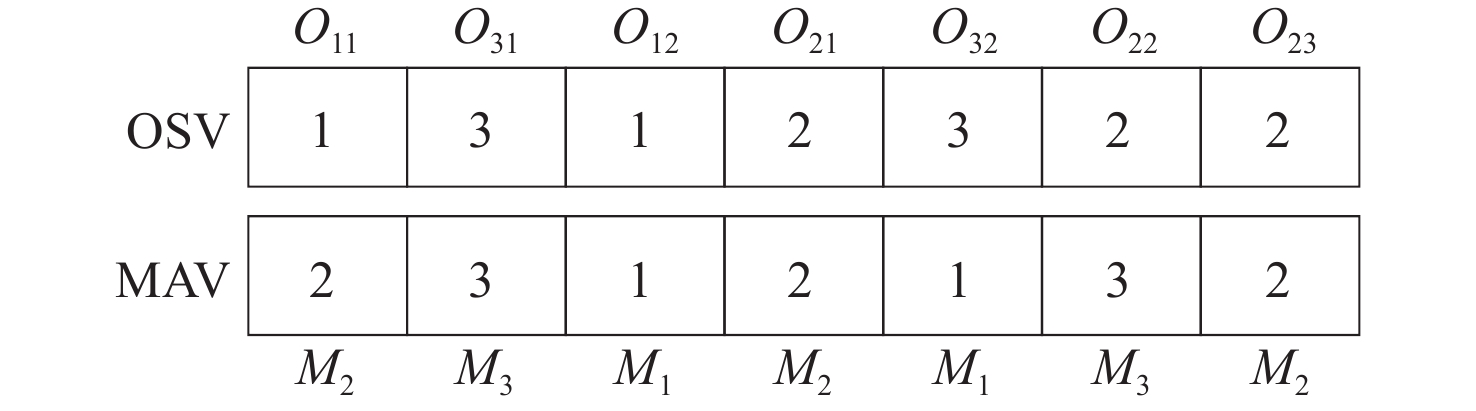
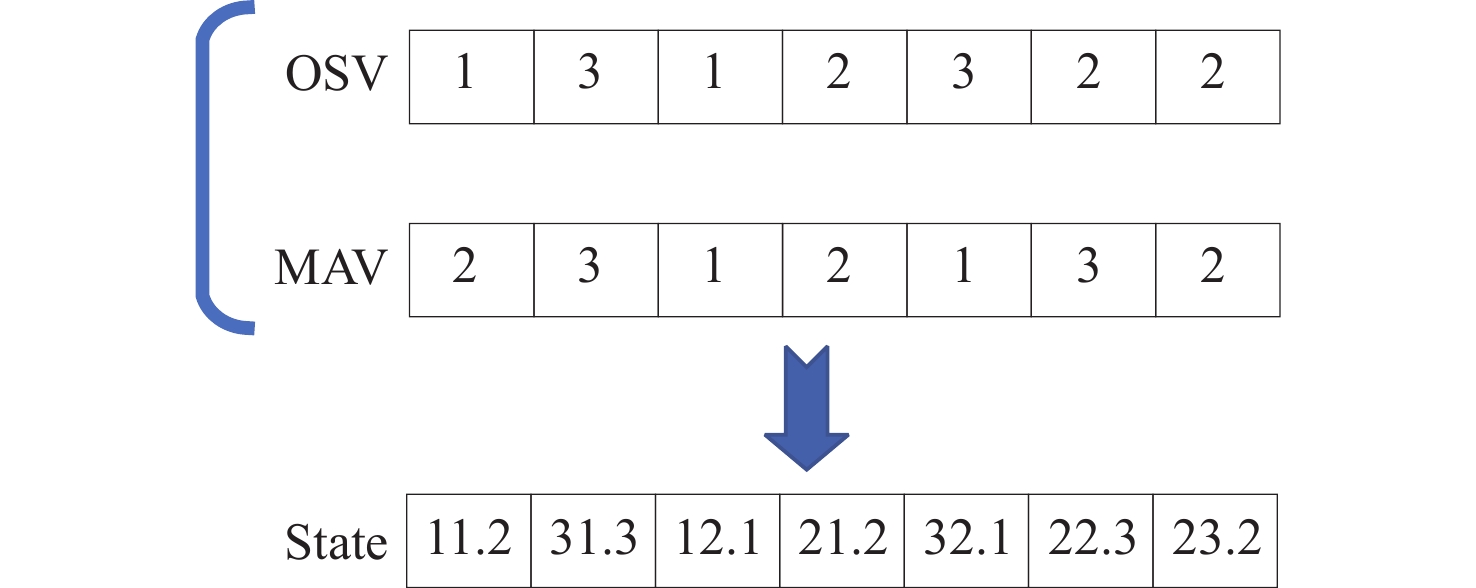
FJSP需要确定工序的加工机器、工序的加工顺序,因此分别采用表示工序排序(operation sequence,OS)和加工设备选择(machine assignment,MA)的两个向量(OSV,MAV)对解进行编码,如图2所示。OSV中的每个元素为工件序号,第p次出现表示该工件的第p道工序,MAV的每个元素对应于OSV中相应位置工序的加工机器。为保证解的可行性,MAV中每个元素的取值都从OSV中对应工序的可加工机器集合中选取。
为求得当前序列对应解的最大完工时间,需将编码解码为满足约束的调度方案。采用左插法的主动调度理论,将OSV中的工件工序按顺序安排至对应的MAV中的机器上,并遵循最早可加工时间安排,得到唯一的调度方案。
2.2 搜索算子
为提高算法的寻优能力及寻优策略,分别针对编码中OS的操作排序以及MA中的机器分配设计多种有效操作。
2.2.1 针对OS的操作设计
状态转移算法是一种创新性的随机性全局优化方法,其核心思想是将问题的可行解视为一种状态,并将可行解的更新过程看作从一个状态向另一个状态的变化,即状态之间发生转移。该算法产生候选解的基本框架如式(1)所示:
\left\{ \begin{gathered} {x_{k + 1}} = {A_k}{x_k} \oplus {B_k}{u_k} \\ {y_{k + 1}} = f({x_{k + 1}}) \\ \end{gathered} \right. (1) 为了保持状态转移算法在FJSP状态转移过程的可控性、高效性,使用了3种特殊的状态转移算子对OS序列中的关键路径上的关键工序序列进行操作。具体如下。
1) 交换变换算子
{x_{k + 1}} = A_k^{{\text{swap}}}{x_k} (2) 式中: A_k^{{\text{swap}}} \in {{\bf{R}}^{n \times n}} 称为交换变换矩阵,其具有交换变换功能。该算子能够交换 {x_k} 中随机两个位置元素。如下式所示:
\left[ \begin{gathered} 1 \\ 5 \\ 3 \\ 4 \\ 2 \\ \end{gathered} \right] = \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} 1&0&0&0&0 \\ 0&0&0&0&1 \\ 0&0&1&0&0 \\ 0&0&0&1&0 \\ 0&1&0&0&0 \end{array}} \right] \times \left[ \begin{gathered} 1 \\ 2 \\ 3 \\ 4 \\ 5 \\ \end{gathered} \right] (3) 对OS序列中第2号和第5号位置上的元素进行了交换。
2) 移动变换算子
{x_{k + 1}} = A_k^{{\text{shift}}}{x_k} (4) 式中: A_k^{{\text{shift}}} \in {\bf{R}^{n \times n}} 称为移动变换矩阵,其具有移动变换功能。该算子能够移动 {x_k} 中某个随机位置到另一个随机位置后面。比如:
\left[ \begin{gathered} 1 \\ 2 \\ 4 \\ 5 \\ 3 \\ \end{gathered} \right] = \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} 1&0&0&0&0 \\ 0&1&0&0&0 \\ 0&0&0&1&0 \\ 0&0&0&0&1 \\ 0&0&1&0&0 \end{array}} \right] \times \left[ \begin{gathered} 1 \\ 2 \\ 3 \\ 4 \\ 5 \\ \end{gathered} \right] (5) 将OS序列中第3号位置上的元素移动至第5号位置元素的后面。
3) 对称变换算子
{x_{k + 1}} = A_k^{{\text{sym}}}{x_k} (6) 式中: A_k^{{\text{sym}}} \in {\mathbf{R}^{n \times n}} 称为对称变换矩阵,是一个带有对称变换功能的随机0-1矩阵。该算子具有将 {x_k} 中随机两个位置之间所有元素对称或倒置的能力。比如:
\left[ \begin{gathered} 1 \\ 5 \\ 4 \\ 3 \\ 2 \\ \end{gathered} \right] = \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} 1&0&0&0&0 \\ 0&0&0&0&1 \\ 0&0&0&1&0 \\ 0&0&1&0&0 \\ 0&1&0&0&0 \end{array}} \right] \times \left[ \begin{gathered} 1 \\ 2 \\ 3 \\ 4 \\ 5 \\ \end{gathered} \right] (7) 将OS序列中第2、3、4、5号位置元素进行对称变换,其位置发生倒置。
2.2.2 针对MA的操作设计
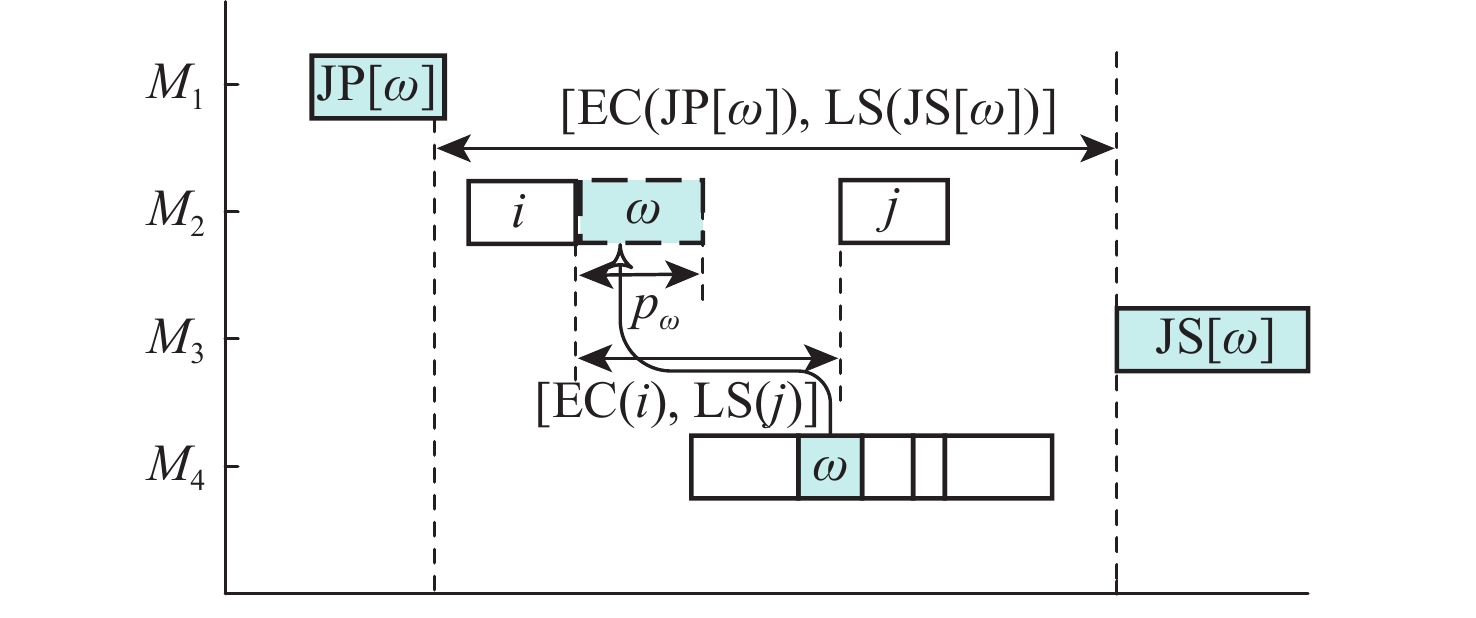
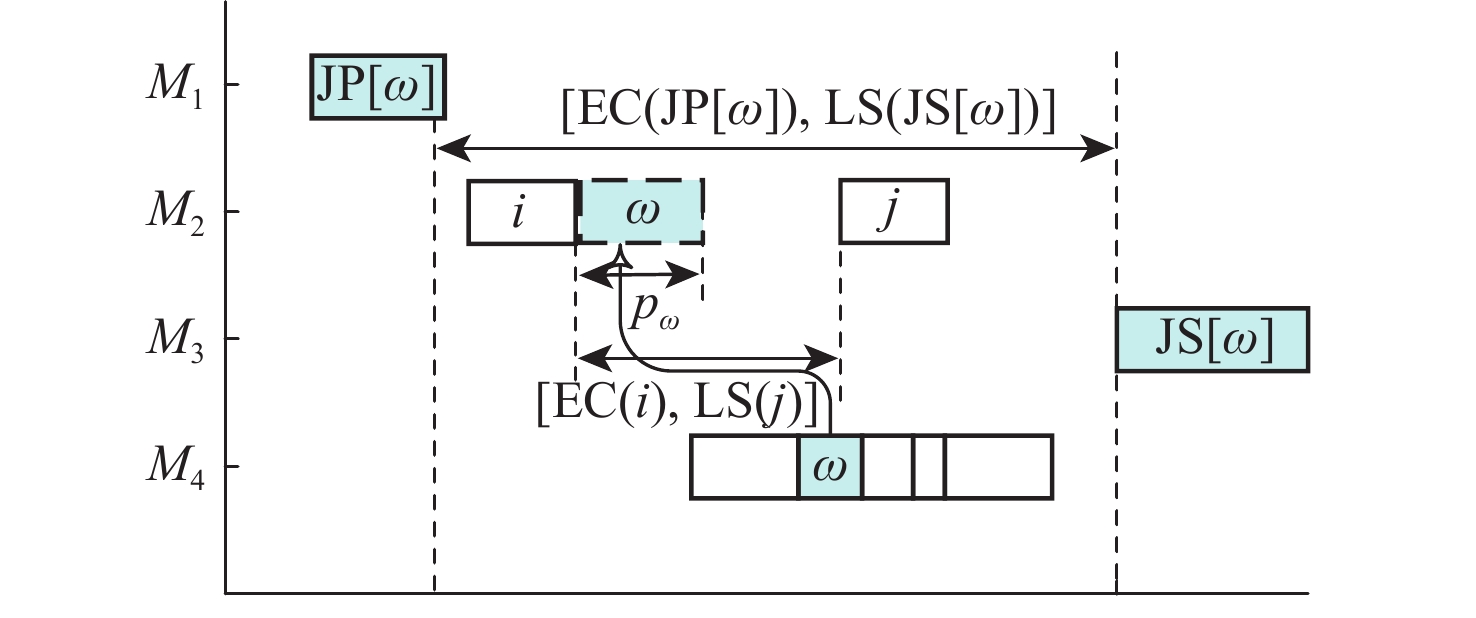
在每道工序均有一个或多个加工设备可选择的情况下,MA的搜索空间是巨大的,针对同一OSV的机器分配方案数量为 \displaystyle\prod\limits_{j = 1}^n {\displaystyle\prod\limits_{i = 1}^{{n_j}} {|{M_{j,i}}|} } 。不同的OSV的最优MAV仍有不同,若依靠随机性的迭代搜索,效率太低,无法寻找到较优的MAV。因此设计了一种关键工序的邻域搜索:跨机器移动工序。跨机器移动关键工序邻域结构示意图如图3所示。在图3所示情况下,对关键工序 \omega 进行跨机器移动,采用直接利用机器空闲时间的方式。由于工件的加工顺序要求,以工序 \omega 的前继工序 {\text{JP}}[\omega ] 的最早完工时间 {\text{EC(JP}}[\omega ]) 和后继工序 {\text{JS}}[\omega ] 的最晚开工时间 {\text{LS(JS}}[\omega ]) 为区间的范围内,在工序 \omega 的候选机器集中查找机器空闲时间。工序 \omega 能否跨机器移动,取决于移至机器位置的空闲时间,只有当式(8)满足时,跨机器移动关键工序 \omega 至 i 和 j 中间才不会增大关键路径长度。
\{{\text{EC(JP}}[\omega ]),{\text{LS(JS}}[\omega ])\} \cap \{{\text{EC}}(i),{\text{LS}}(j)\} > {p_\omega } (8) 2.3 强化学习和PPO
一般而言,强化学习算法能够处理马尔可夫过程。在这个过程中,智能体通过训练和试错与环境进行交互以达到最大化期望的累积长期奖励。一个典型的马尔可夫过程可以表示为一个五元组 (S,A,P,\gamma ,R) 。在每个决策点 t ,智能体获取当前时刻状态 {s_t} \in S 并根据策略 \pi (S \to A) 采取可行的动作。之后,根据状态转移概率 p({s_{t + 1}}|{s_t},{a_t}) \in P(S \times A \to S) 进入新的状态 {s_{t + 1}} 得到即时奖励 {r_t} \in R(S \times A \times S \to \bf{R}) 。 {Q_\pi }(s,a) 表示在状态 s 下根据给定策略 \pi 采取动作 a 时的期望累积奖励(也称为行动价值函数或 Q 函数),其定义如下:
{Q_{_\pi }}(s,a) = E\left[ {{r_t} + \gamma {r_{t + 1}} + {\gamma ^2}{r_{t + 2}} + \cdots |{s_t} = s,\pi } \right] (9) 强化学习算法中智能体的目标是从所有可能获取的状态中找到一个能使期望累积奖励最大化的最佳策略 {\pi ^*} ,其定义如下:
{\pi ^*} = \arg \max {E_{s|\pi }}\left[ {{V_\pi }(s)} \right] (10) 在基于深度强化学习的方法中,策略 \pi (\theta ) 总是以具有可微调参数 \theta 的深度神经网络表示。为了保证式(10)在参数更新后旧策略 {\pi _{{\text{old}}}}({\theta _{{\text{old}}}}) 和新策略 \pi (\theta ) 之间呈现单调递增,能够最大化智能体新旧策略间KL散度的信赖域策略优化被提出。而近端策略优化是信赖域策略优化的一种扩展,它保留了信赖域策略优化的稳定性和可靠性,且计算效率更高,实现起来也更简单。PPO使用了一个只需要计算似然的新目标来替代KL散度约束,将其定义为 {\text{rati}}{{\text{o}}_t}(\theta ) = (\pi ({s_t},{a_t};\theta ))/({\pi _{{\text{old}}}}({s_t},{a_t};{\theta _{{\text{old}}}})) ,PPO的目标如下所示:
{\max _\theta }{E_t}\min ({\text{ratio(}}\theta {\text{)}}{A_t},{\text{clip}}({\text{rati}}{{\text{o}}_t}(\theta ),1 - \varepsilon ,1 + \varepsilon ){A_t}) (11) 式中: {A_t} = {Q_{\pi {\text{old}}}}({s_t},{a_t}) - {V_{\pi {\text{old}}}}({s_t}) 为优势函数, \varepsilon \in (0,1) 为裁剪系数。由于PPO算法可以通过限制策略的更新来降低参数设置的敏感性,从而能够获得良好的性能,本文将采用它作为基本的学习算法。
3. 基于深度强化学习的离散状态转移算法
本节分别从状态定义、动作设计、奖励设计等方面对本文所提出的基于深度强化学习的智能优化算法进行介绍。
3.1 状态特征定义
状态特征描述了决策时刻下对当前调度问题解决的状态。因此,对于状态特征的设计应该能够反映出当前动作的影响,并有助于后续的动作选择。
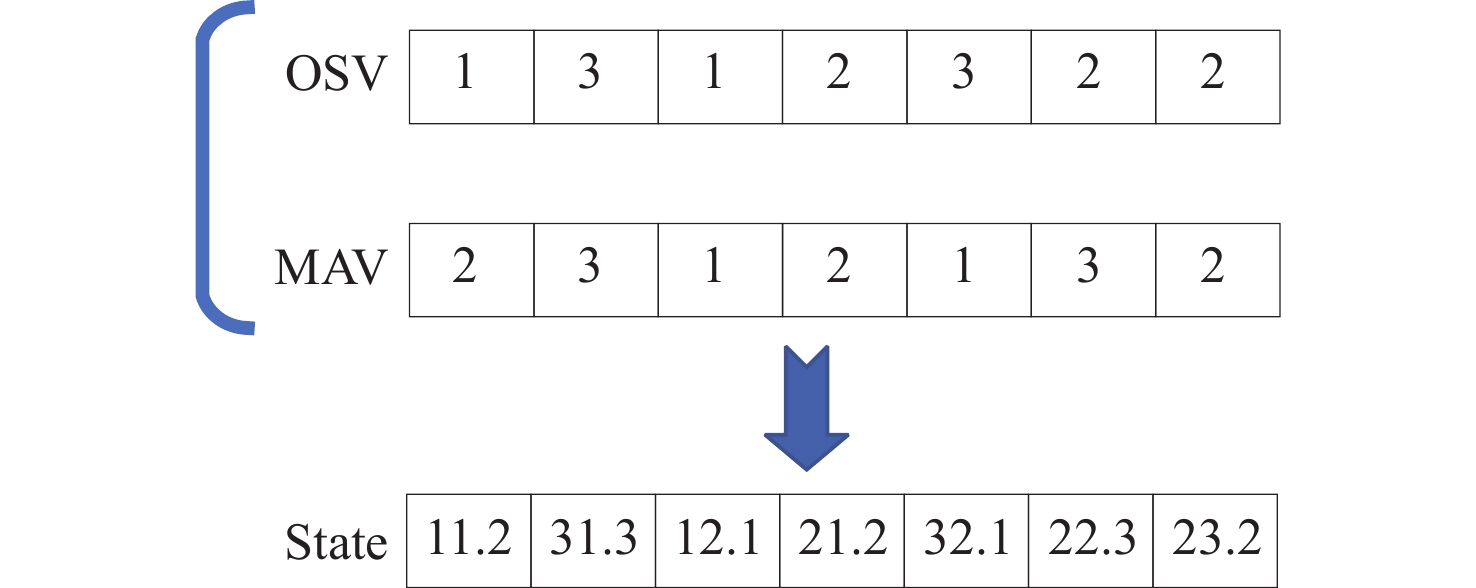
在DSTA算法中是以当前OSV作为状态进行候选解的选取,OSV与对应的MAV解码后,即可得到当前问题的一个对应调度解,不同的OSV则会产生不同的调度解,选用OSV作为状态是对FJSP很好的反应。因此本文所提出的DSTA-PPO将在当前OSV和MAV的基础上,进行状态特征设计。在决策时刻下状态特征中变化的工件序列,对OSV和MAV进行了如图4所示的处理,得到智能体的State列表内元素以 ijk 形式进行表示,其中 i 代表加工工件序号, j 代表加工工件的工序序号, k 代表加工机器的序号。状态特征列表作为深度神经网络的输入,为更有利于神经网络的训练,对当前状态列表进行标准化处理。标准化处理的核心在于,在同环境交互的过程中,维护一个动态的关于所有经历过的所有状态的mean和std,并对当前state进行标准化处理,使state符合mean=0,std=1的正态分布。具体状态标准化处理算法如算法1所示。
算法 1 状态标准化处理算法。
输入: {s_t} , t
输出: Normalized state list {s_{{\rm{t\_norm}}}}
1. Initialization t=0、Mean= 0、S=0、Std=sqrt(S)
2. if t=0 then
3. Mean=st
4. Std=st
5. end
6. if t > 0 then
7. {\text{Mean\_old = Mean}}
8. {\text{Mean = Mean\_old}} + ({s_t} - {\text{Mean\_old}})/t
9. S = S + ({s_t} - {\text{Mean\_old}})*({s_t} - {\text{Mean)}}
10. {\text{Std = sqrt}}(S/t)
11. end
12. {s_t} = ({s_t} - {\text{Mean)/(Std}} + 1{\text{e}} - 8)
13. t + = 1
3.2 动作空间设计
在DSTA-PPO算法中,基于FJSP问题的特点设计了4种动作来提高求解质量,4种动作都是针对关键路径上的关键工序进行操作的。
{a_1} 、 {a_2} 、 {a_3} 3种动作都是基于离散状态转移算法的3种算子进行设计的。原始的3种搜索算子是对关键工序直接进行操作变换,这种过程为一次状态转移,进行一次状态转移后,能够得到 C_n^2 种候选的关键工序。在基于一次状态转移所得候选关键工序集的基础上,使用相同的搜索算子再次进行状态转移变换,得到二次状态转移的候选关键工序集,此时,若忽略其中重复的候选解,可得 C_n^2 \times C_n^2 种候选解。通过此种方式能够提升3种动作的搜索空间,提高了智能体对关键工序的探索能力,其具体执行如算法2所示。以上3种动作在离散状态转移算法的思想上做了一定改进,在选定一种动作后执行SE次,得到大小为SE的OSV集合,计算所有该集合所对应的完工时间得到解集。此时不再要求解集中一定出现优于当前最优解的结果时才进行状态更新。而是选定解集中表现最好的OSV进行状态更新,即使此时的完工时间不一定优于已知的最优完工时间,从而避免算法陷入局部最优。
算法 2 {a_1} , {a_2} , {a_3} 。
输入: Critic path A , action a
输出: New OSV
1. for i in SE do
2. if a = {a_1} then
3. Swap( A )
4. Swap( A )
5. Update(OSV)
6. end
7. if a = {a_2} then
8. Shift( A )
9. Shift( A )
10. Update(OSV)
11. end
12. if then
13. Sysmmetry( A )
14. Sysmmetry( A )
15. Update(OSV)
16. end
17. end
{a_1} 、 {a_2} 、 {a_3} 3种动作的执行能够保证得到较优的OSV,但MAV在整个过程中是没有变换的,最终得到的调度解也只能保证是在当前MAV下的一种局部最优解。因此添加了跨机器邻域搜索的动作 {a_4} 。智能体通过执行 {a_4} 能够改变关键工序的加工机器。其具体执行如算法3所示。通过执行动作 {a_4} ,提升了智能体的全局寻优能力。
算法 3 a_{4} 。
输入: Critic path A ,action \boldsymbol{\alpha}
输出: New OSV
1. for critic operation O_{i j} in A do
2. for k in M_{k} do
3. if [{\mathrm{E C}}({\mathrm{J P}}[j], {\mathrm{L S}}({\mathrm{J S}}[f]]] \wedge[{\mathrm{E C}}(k), {\mathrm{L S}}(k)] >p_{j, \omega}
4. MAV[ O_{i j} ]=k
5. end
6. end
7. end
3.3 奖励设计
在每个决策点,通过对当前OSV、MAV解码后计算可得出最大完工时间,通过式(12)进行奖励计算,当最大完工时间减小时,奖励会相应变大。
{r_t} = 1/C{\text{ma}}{{\text{x}}_t} (12) 3.4 DSTA-PPO算法计算过程
DSTA-PPO算法被提出用以训练智能体解决FJSP,提高智能体对当前状态自适应选择动作的能力,提出的方法能够有效地处理工件调度排序问题,避免了处理调度问题时工件间的约束条件。该算法的具体流程如算法4所示。
算法 4 DSTA-PPO算法流程。
1. 初始化当前策略网络 \pi(\theta) 和价值网络 v(\omega)
2. for \text { apoch }=1: L do
3. 观察当前状态 s_{t} ,提取当前状态特征向量 \phi\left(s_{t}\right)
4. 选择一个动作 a_{1}=\pi\left(\theta_{2} \phi\left(s_{t}\right)\right)
5. if a_{1}=a_{1} or a_{1}=a_{2} or a_{1}=a_{3}
6. 通过算法2更新 OSV
7. end
8. if a_{1}=a_{4}
9. 通过算法3更新 MAV
10. end
11. 计算即时奖励 r_{t} 并产生新的状态 s_{t+1}
12. if t \% M=0
13. 通过算法5更新 \pi(\theta) , v(\omega)
14. end
15. end
算法 5 \pi(\theta) , v(\omega) 参数更新。
1.
2. for i = t - 1: - 1:t - M do
3. {R_i} = {r_i} + \gamma {R_{i + 1}}
4. {A_i} = {R_i} - {v_m}({\phi _i};\omega )
5. {\text{ratio}}(\theta ) = \dfrac{{\pi ({\phi _i},{a_i};\theta )}}{{{\pi _{{\text{old}}}}({\phi _i},{a_i};{\theta _{{\text{old}}}})}}
6. end
7. {\text{PPO}}(\theta ) = - \displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = t - M}^{t - 1} \min ({\text{rati}}{{\text{o}}i}(\theta ){A_i},{\text{clip(rati}}{{\text{o}}i}(\theta ), 1 - \varepsilon , 1 + \varepsilon ){A_i})
8. {\text{MSE}}(\omega ) = \displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = t - M}^{t - 1} {{{({R_i} - v({\phi _i};\omega ))}^2}}
9. 通过梯度下降法更新 \theta 、 {\text{PPO}}(\theta )
10. 通过梯度下降法更新 \omega 、 {\text{MSE}}(\omega )
11. 返回 \theta 、 \omega
4. 实例仿真
4.1 实验设置
本文使用Python编程语言在Windows11系统上运行Pycharm实现了所提出的DSTA-PPO算法。硬件条件为AMD Ryzen 5 4600H 3.00 GHz,16 GB RAM。为验证算法性能,使用了2类不同规模大小的FJSP测试集。第1类测试集为Brdata测试集,包括了10个不同规模的算例。第2类测试集为Hurink测试集,包括了40个不同规模的算例。
4.2 参数设置
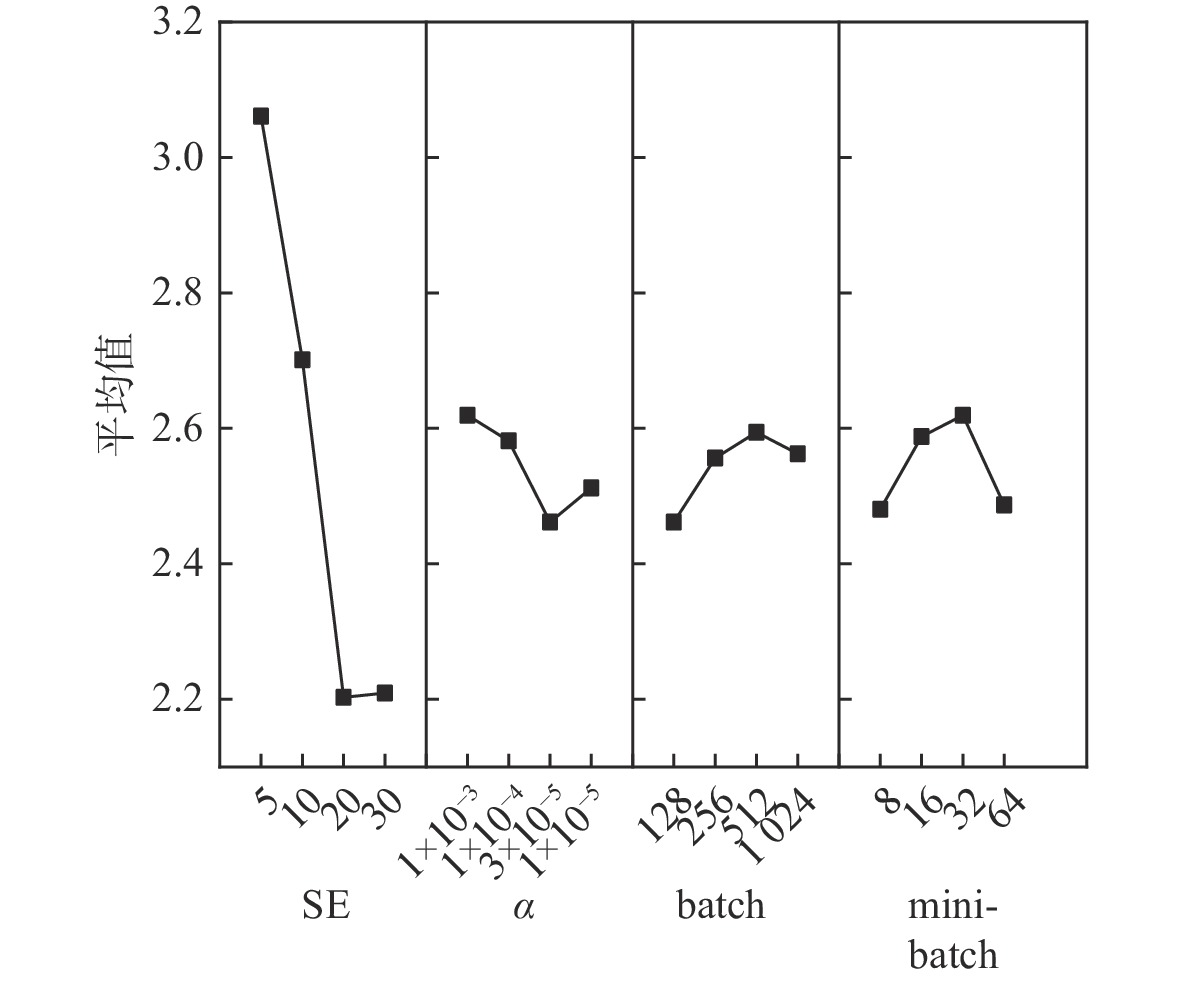
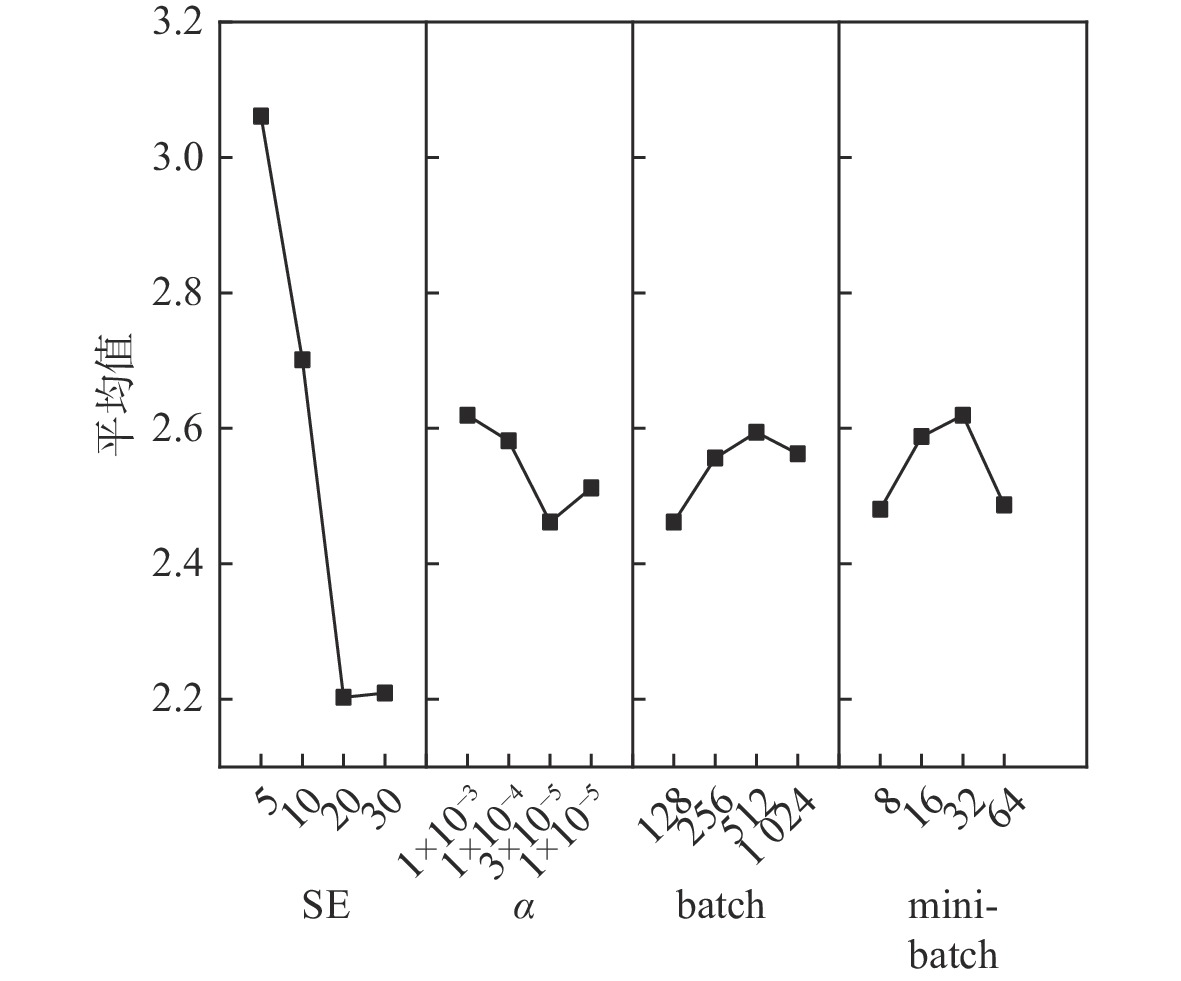
本文所提出算法包含4个关键参数:①候选解集大小SE;②动作网络和评价网络学习率 \alpha ;③batchsize(batch)表示一次完整的训练迭代所收集的经验轨迹;④mibi-batchsize(minibatch)表示从batch中随机选取的小部分样本个数,用于更新网络参数。采用实验设计(design-of-experiment,DOE)方法分析参数对算法性能的影响。为综合参数在不同规模算例上的影响,选取第2类测试集中Vdata_la1、Vdata_la6、Vdata_la11、Vdata_la16、Vdata_la21等5个不同规模的算例进行分析。每个参数设置4个水平, \text{SE}\in \{5,10,20,30\},\alpha \in \{{\mathrm{1e}}-3,1{\mathrm{e}}-4, 3{\mathrm{e}}-5,1{\mathrm{e}}-5\} , {\text{batch}} \in \{ 128,256,512,1024\} , {\text{mini\_batch}} \in \{ 8,16,32,64\} 。选择正交数组 {L_{16}}({4^4}) ,包含16组参数水平组合。对于每个组合计算同算例最优解之间的误差,算法运行10次并取最优的一次作为该组参数水平的解。运行16个参数水平组合可得解集 {E_i}(i = 1,2, \cdots ,16) 。计算所有算例的参数水平组合的平均误差作为响应值(response value,RV),如表2所示。对表2中的数据进行极差分析可得表3,通过极差分析,能够分析各因子间的优势及因子间具体水平的优劣。表3中K值为某因子某水平时试验数据求和;Kavg为对应的平均值;最佳水平指某因子的最佳Kavg对应的水平标号;R指因子的极差值,该值越小则该因素对于算法性能影响越大。因子的趋势变化如图5所示。
表 2 正交试验表及各参数组合的响应值Table 2. Orthogonal test table and response values of various parameter combinations编号 参数因子组合 RV SE α batch mini-batch 1 1 1 1 1 3.054784 2 1 2 2 2 3.181015 3 1 3 3 3 3.08003 4 1 4 4 4 2.928553 5 2 1 2 3 2.802323 6 2 2 1 4 2.575107 7 2 3 4 1 2.600353 8 2 4 3 2 2.827569 9 3 1 3 4 2.2974 10 3 2 4 3 2.398384 11 3 3 1 2 2.019692 12 3 4 2 1 2.09543 13 4 1 4 2 2.322646 14 4 2 3 1 2.171169 15 4 3 2 4 2.145923 16 4 4 1 3 2.196415 根据表3以及图5可以看出,SE对于算法性能影响最大, \alpha 、batch、mini-batch次之。合适的SE能够影响算法的多样性和收敛性。过小的 \alpha 则会使算法收敛过快,较小的batch、mini-batch会使算法性能得到提升。根据以上实验结果和分析, 设置 {\text{SE}} = 20 , \alpha = 3\times10^{ - 5 }, {\text{batch}} = 128 , {\text{mini\_batch}} = 8 。
4.3 与现有算法比较
为了验证DSTA-PPO算法在求解柔性作业车间调度问题的有效性和先进性,首先在第一类测试集Brdata中进行了算法实例仿真,在第一类测试集中,同目前已有的使用了相同算例的最新深度强化学习算法SLGA[17]和集成强化学习算法[19]进行了比较,SLGA算法的相关参数为:学习率为0.75,折扣因子为0.2,初始奖励为1,贪婪率为0.85。为了显示算法改进的有效性,也同DSTA算法进行了比较。如表4所示,其中加黑显示的数据代表了4种算法在各个算例上求得的最优解,带星号的表示目前已知的算法所能求得的最优解。在求解最优解方面,DSTA-PPO算法在7个算例中都找到了目前算例所能求得的最优解,虽然有3个算例未能找到所能求得的最优解,所得解的效果略差于当前的启发式算法,但深度强化学习算法的优势主要在于当完成训练后,即可在整个测试集上直接进行应用,无须像启发式算法一般需要对每个算例分别进行求解。
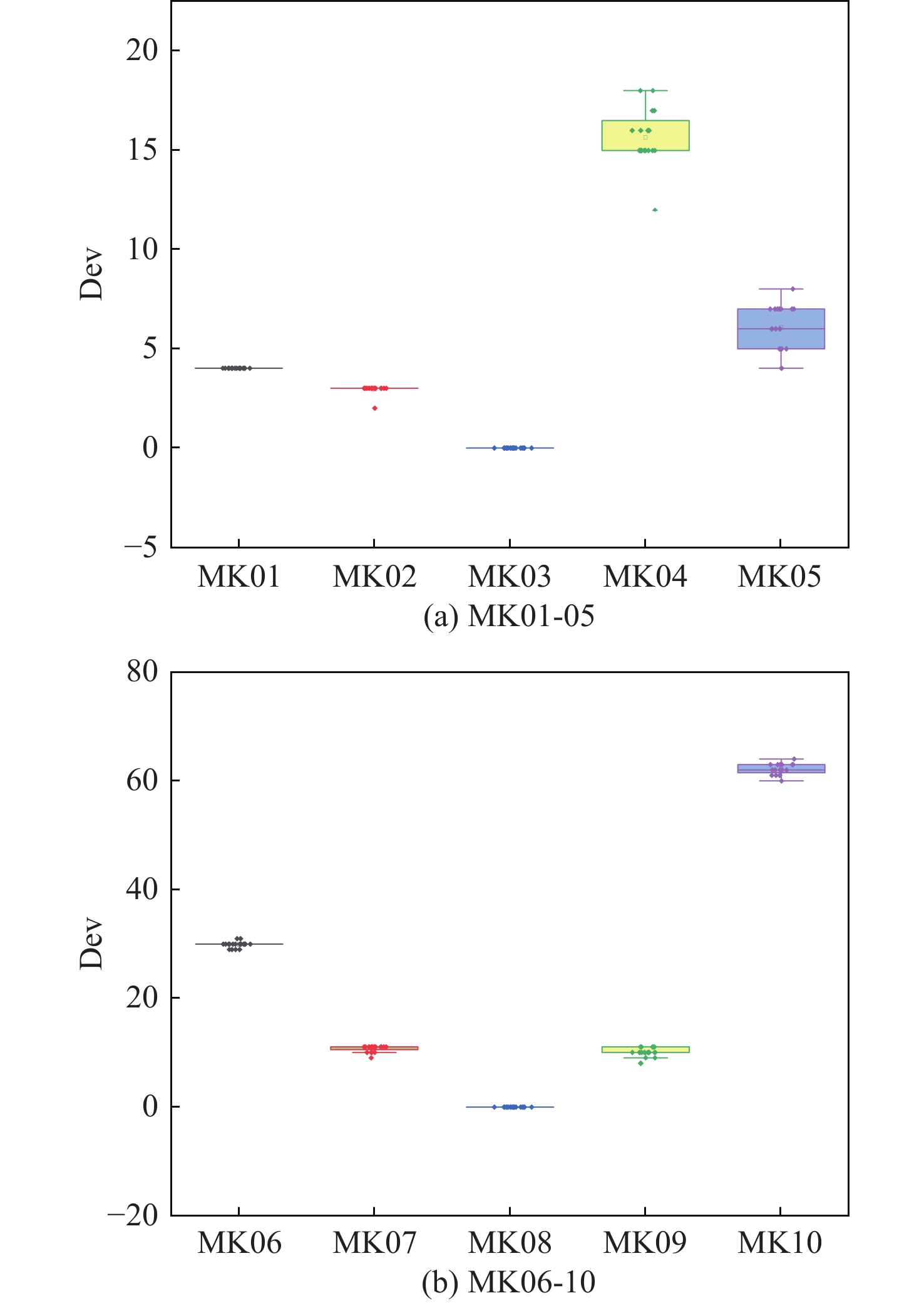
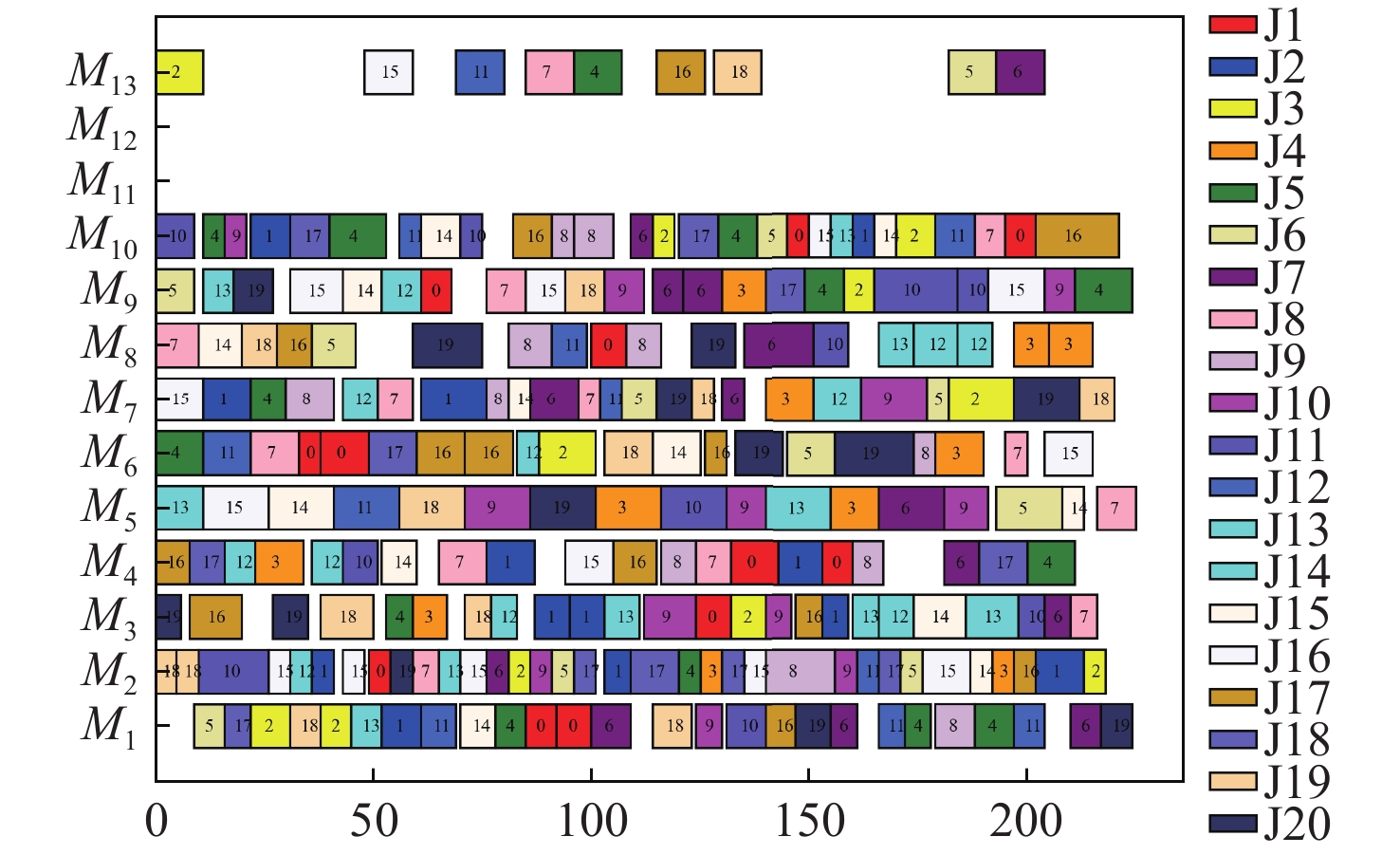
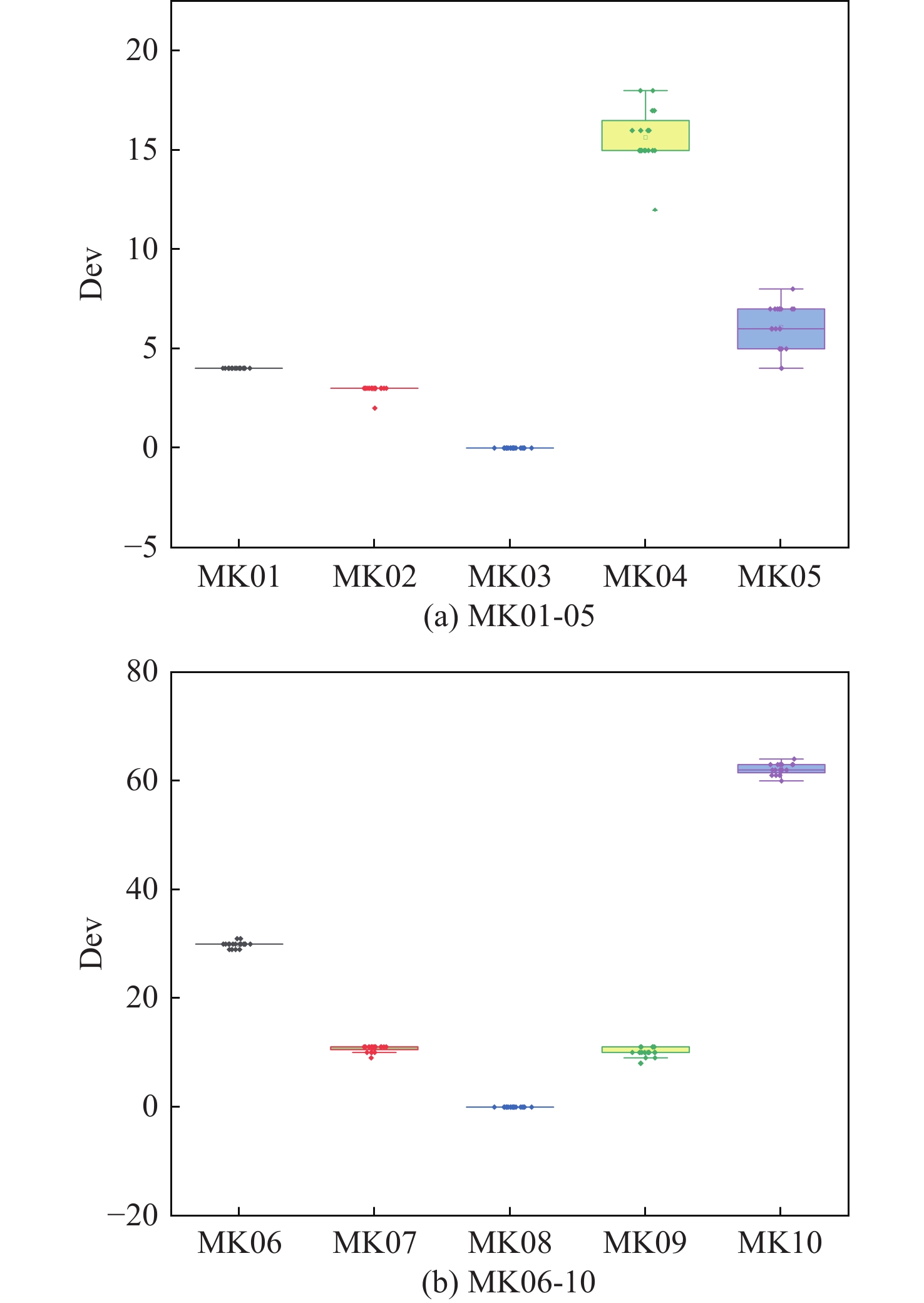
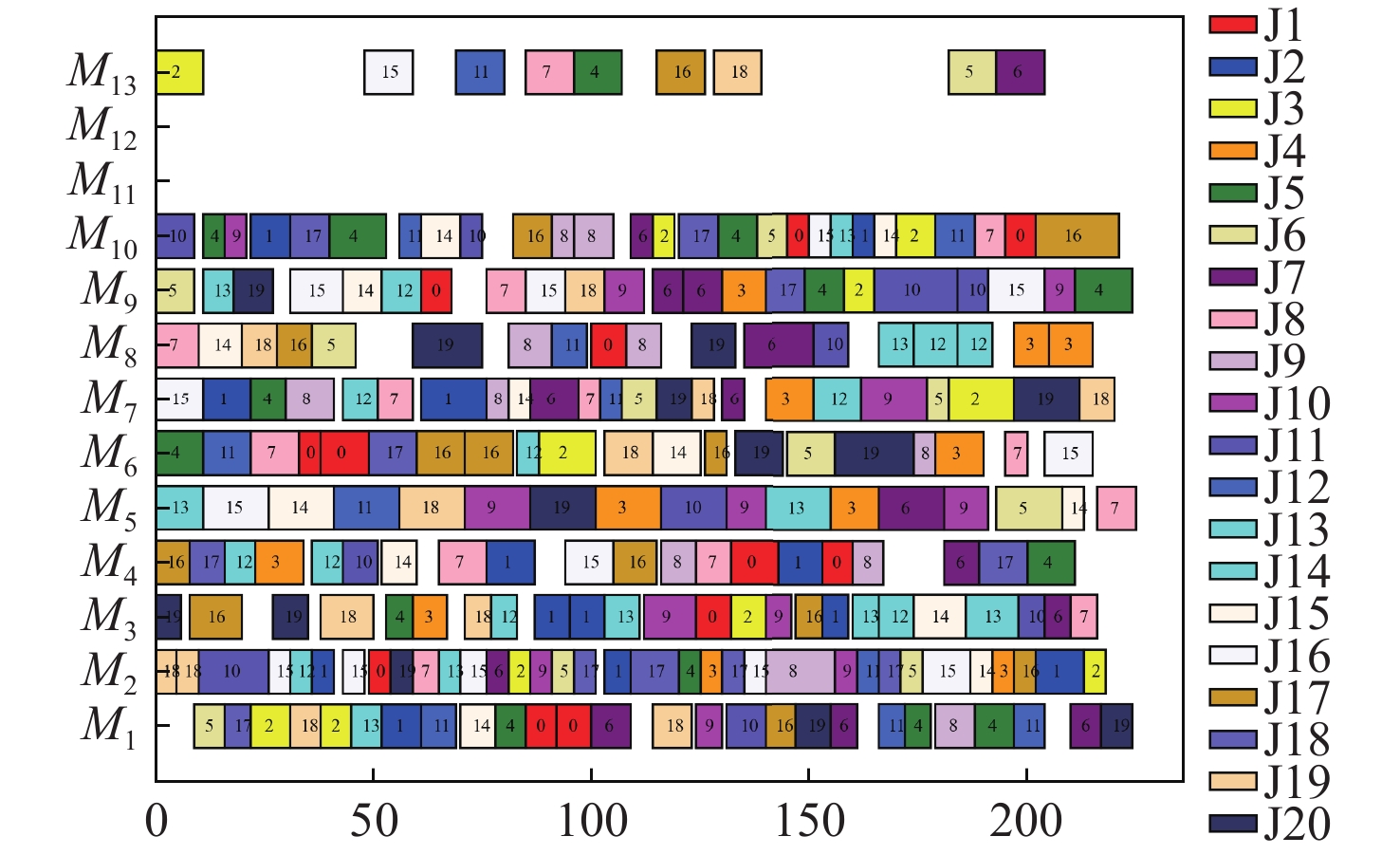
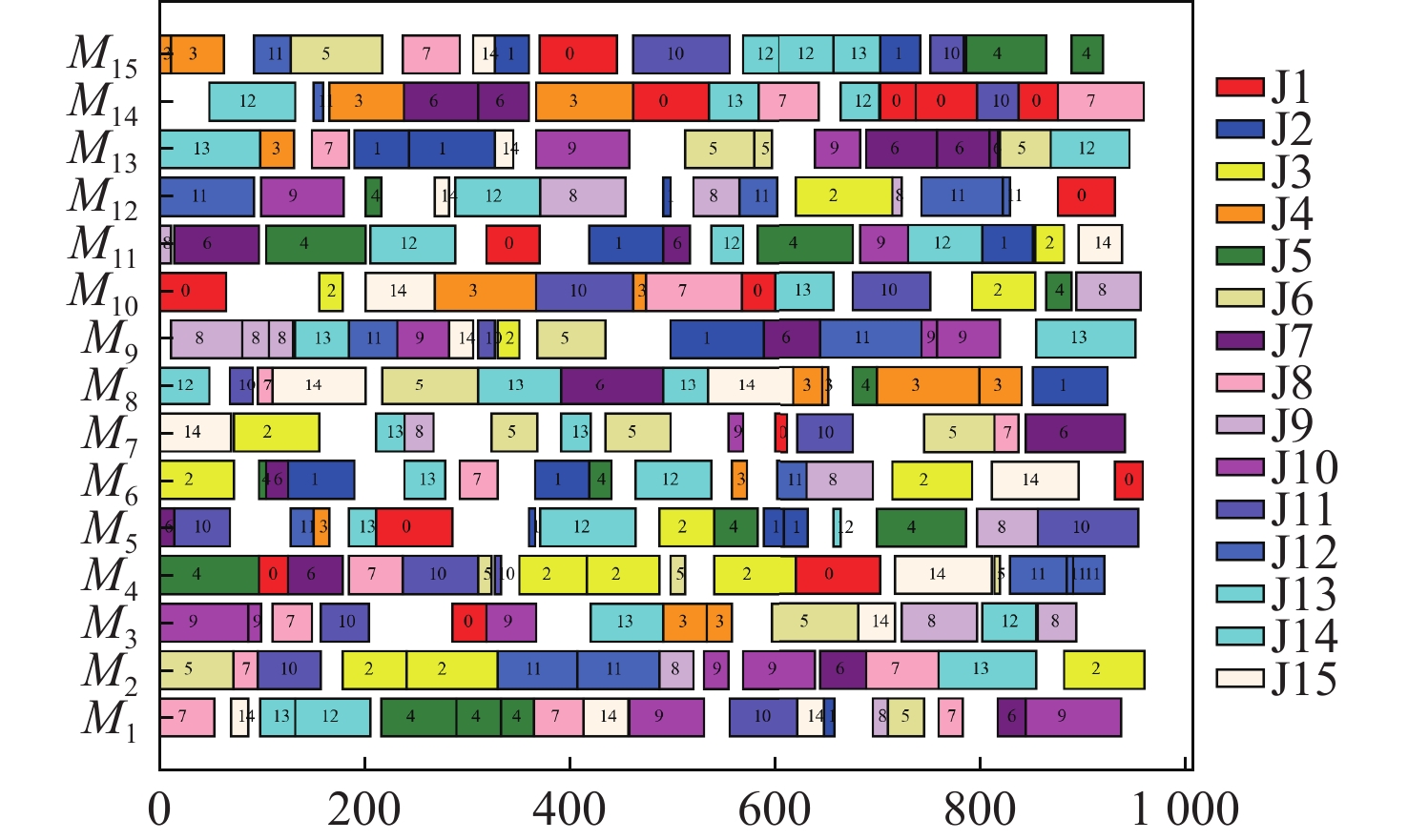
表 3 参数各水平的极差分析Table 3. Extreme variance analysis of parameters at different levels参数因子 K值 Kavg值 最佳水平 R 水平数量 每水平重复数 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 SE 12.24 10.81 8.81 8.84 3.06 2.7 2.2 2.21 3 −0.86 4 4 α 10.48 10.33 9.85 10.05 2.62 2.58 2.46 2.51 3 −0.16 4 4 batch 9.85 10.22 10.38 10.25 2.46 2.56 2.59 2.56 1 −0.13 4 4 mini-batch 9.92 10.35 10.48 9.95 2.48 2.59 2.62 2.49 1 −0.14 4 4 表 4 第一类测试集对比Table 4. Comparison of the first type of dataset数据集 最优解 DSTA SLGA 集成强化学习 DSTA-PPO Mk01 36 40* 40* 42 40* Mk02 24 28 27 31 26* Mk03 204 204 204* 204* 204* Mk04 48 66 60* 69 60* Mk05 168 178 172* 180 172* Mk06 33 73 69 68 62 Mk07 133 147 144 153 142 Mk08 523 523* 523* 523* 523* Mk09 299 327 320 315 307* Mk10 165 263 254 230 225 如图6所示,为DSTA-PPO算法在10个算例上运行20次所得结果与算例下界求得的差值所做的箱线图,可以看出,DSTA-PPO算法在各个算例中的波动程度都很小,均值与最优值差距很小。这表明DSTA-PPO在求解FJSP问题相较其余3种算法会有着更好的统计效果。图7给出了算法在MK10算例上的调度甘特图。
在第2类测试集上,以Multi-PPO[19]为基准在8组不同规模的算例中进行算法先进性的对比,Multi-PPO算法参数为:学习率为0.001,裁剪系数为0.2。对比包括每个算例的调度结果、其同最优解的差距。结果如表5所示。表中加黑部分为该算例中表现最好的算法。可以看出,DSTA-PPO和Multi-PPO算法表现明显优于DSTA算法。DSTA-PPO算法在28个算例上都取得了比Multi-PPO更优的值。在机器数为10的算例中,随着机器数的增加,DSTA-PPO算法的寻优能力相较Multi-PPO算法变弱,但在最终的平均差距中,DSTA-PPO相较Multi-PPO的值提升了约39%。能够发现,虽然在部分算例上DSTA-PPO算法测试时的效果略差于Multi-PPO,但整体的性能明显优于Multi-PPO。图8给出了算法在Vdata_la40上的调度甘特图。
表 5 第二类测试集对比Table 5. Comparison of the second type of datasetDataset Val gap/% DSTA Multi-PPO DSTA-PPO UB DSTA Multi-PPO DSTA-PPO 10×5 Vdata_la1 613 610 573 570 7.54 7.02 0.53 Vdata_la2 557 555 536 529 5.29 4.91 1.32 Vdata_la3 531 532 487 477 11.32 11.53 2.10 Vdata_la4 538 530 510 502 7.17 5.58 1.59 Vdata_la5 490 507 467 457 7.22 10.94 2.19 15×5 Vdata_la6 824 820 802 799 3.13 2.63 0.38 Vdata_la7 788 757 755 749 5.21 1.07 0.80 Vdata_la8 791 782 765 765 3.40 2.22 0.00 Vdata_la9 925 879 859 853 8.44 3.05 0.70 Vdata_la10 830 862 808 804 3.23 7.21 0.50 20×5 Vdata_la11 1102 1101 1074 1071 2.89 2.80 0.28 Vdata_la12 960 950 939 936 2.56 1.50 0.32 Vdata_la13 1070 1053 1042 1038 3.08 1.45 0.39 Vdata_la14 1095 1086 1071 1070 2.34 1.56 0.09 Vdata_la15 1117 1111 1092 1089 2.57 2.02 0.28 10×10 Vdata_la16 717 717 717 717 0.00 0.00 0.00 Vdata_la17 646 647 646 646 0.00 0.15 0.00 Vdata_la18 714 663 663 663 7.69 0.00 0.00 Vdata_la19 705 626 644 617 14.26 1.46 4.38 Vdata_la20 756 756 756 756 0.00 0.00 0.00 15×10 Vdata_la21 903 887 870 804 12.31 10.32 8.21 Vdata_la22 849 793 798 736 15.35 7.74 8.42 Vdata_la23 970 858 888 815 19.02 5.28 8.96 Vdata_la24 891 883 834 775 14.97 13.94 7.61 Vdata_la25 896 883 820 756 18.52 16.80 8.47 20×10 Vdata_la26 1195 1089 1100 1054 13.38 3.32 4.36 Vdata_la27 1231 1123 1133 1084 13.56 3.60 4.52 Vdata_la28 1249 1106 1121 1070 16.73 3.36 4.77 Vdata_la29 1121 1049 1048 994 12.78 5.53 5.43 Vdata_la30 1256 1117 1122 1069 17.49 4.49 4.96 30×10 Vdata_la31 1688 1561 1553 1520 11.05 2.70 2.17 Vdata_la32 1837 1693 1697 1658 10.80 2.11 2.35 Vdata_la33 1630 1531 1530 1497 8.88 2.27 2.20 Vdata_la34 1731 1562 1565 1537 12.62 1.63 1.82 Vdata_la35 1711 1574 1582 1549 10.46 1.61 2.13 15×15 Vdata_la36 1100 985 967 948 16.03 3.90 2.00 Vdata_la37 1171 1028 1035 986 18.76 4.26 4.97 Vdata_la38 1061 948 943 943 12.51 0.53 0.00 Vdata_la39 1109 976 959 922 20.28 6.18 4.01 Vdata_la40 1041 968 955 955 9.01 1.36 0.00 注:Ave.Gap: DSTA、Multi-ppo、DSTA-PPO分别为9.55、4.20、2.58。 5. 结 论
本文将深度强化学习算法同状态转移算法结合,提出了一种基于深度强化学习的状态转移算法,针对不同规模的FJSP,以最小化最大完工时间为调度目标进行了算例测试和算法对比。结果表明:本文提出的DSTA-PPO能够有效地解决FJSP,并在大多数测试算例中提升效果显著。经过设计的状态特征和动作空间能够有效地使智能体在经过训练后高效地完成调度操作,产生合适的调度策略。该算法不足之处在于:首先2种算法的结合增加了整体算法的复杂性,其次2种算法结合后参数增多,增加了调参和训练的难度。进一步工作将在此基础上继续改进,优化代码结构,以提高DSTA-PPO的训练效率,对其动作空间继续优化,以提高其在更大规模调度问题中的泛化性和鲁棒性。
-
表 1 3×3的FJSP实例
Table 1. 3×3 FJSP instance
工件 工序 工序号 工序和加工时间 M1 M2 M3 J1 O11 1 1 2 * O12 2 3 2 1 J2 O21 3 * 2 1 O22 4 1 2 4 O23 5 * * 4 J3 O31 6 3 2 2 O32 7 1 * 2 注:“*”表示该工序无法在该机器上进行加工。 表 2 正交试验表及各参数组合的响应值
Table 2. Orthogonal test table and response values of various parameter combinations
编号 参数因子组合 RV SE α batch mini-batch 1 1 1 1 1 3.054784 2 1 2 2 2 3.181015 3 1 3 3 3 3.08003 4 1 4 4 4 2.928553 5 2 1 2 3 2.802323 6 2 2 1 4 2.575107 7 2 3 4 1 2.600353 8 2 4 3 2 2.827569 9 3 1 3 4 2.2974 10 3 2 4 3 2.398384 11 3 3 1 2 2.019692 12 3 4 2 1 2.09543 13 4 1 4 2 2.322646 14 4 2 3 1 2.171169 15 4 3 2 4 2.145923 16 4 4 1 3 2.196415 表 3 参数各水平的极差分析
Table 3. Extreme variance analysis of parameters at different levels
参数因子 K值 Kavg值 最佳水平 R 水平数量 每水平重复数 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 SE 12.24 10.81 8.81 8.84 3.06 2.7 2.2 2.21 3 −0.86 4 4 α 10.48 10.33 9.85 10.05 2.62 2.58 2.46 2.51 3 −0.16 4 4 batch 9.85 10.22 10.38 10.25 2.46 2.56 2.59 2.56 1 −0.13 4 4 mini-batch 9.92 10.35 10.48 9.95 2.48 2.59 2.62 2.49 1 −0.14 4 4 表 4 第一类测试集对比
Table 4. Comparison of the first type of dataset
数据集 最优解 DSTA SLGA 集成强化学习 DSTA-PPO Mk01 36 40* 40* 42 40* Mk02 24 28 27 31 26* Mk03 204 204 204* 204* 204* Mk04 48 66 60* 69 60* Mk05 168 178 172* 180 172* Mk06 33 73 69 68 62 Mk07 133 147 144 153 142 Mk08 523 523* 523* 523* 523* Mk09 299 327 320 315 307* Mk10 165 263 254 230 225 表 5 第二类测试集对比
Table 5. Comparison of the second type of dataset
Dataset Val gap/% DSTA Multi-PPO DSTA-PPO UB DSTA Multi-PPO DSTA-PPO 10×5 Vdata_la1 613 610 573 570 7.54 7.02 0.53 Vdata_la2 557 555 536 529 5.29 4.91 1.32 Vdata_la3 531 532 487 477 11.32 11.53 2.10 Vdata_la4 538 530 510 502 7.17 5.58 1.59 Vdata_la5 490 507 467 457 7.22 10.94 2.19 15×5 Vdata_la6 824 820 802 799 3.13 2.63 0.38 Vdata_la7 788 757 755 749 5.21 1.07 0.80 Vdata_la8 791 782 765 765 3.40 2.22 0.00 Vdata_la9 925 879 859 853 8.44 3.05 0.70 Vdata_la10 830 862 808 804 3.23 7.21 0.50 20×5 Vdata_la11 1102 1101 1074 1071 2.89 2.80 0.28 Vdata_la12 960 950 939 936 2.56 1.50 0.32 Vdata_la13 1070 1053 1042 1038 3.08 1.45 0.39 Vdata_la14 1095 1086 1071 1070 2.34 1.56 0.09 Vdata_la15 1117 1111 1092 1089 2.57 2.02 0.28 10×10 Vdata_la16 717 717 717 717 0.00 0.00 0.00 Vdata_la17 646 647 646 646 0.00 0.15 0.00 Vdata_la18 714 663 663 663 7.69 0.00 0.00 Vdata_la19 705 626 644 617 14.26 1.46 4.38 Vdata_la20 756 756 756 756 0.00 0.00 0.00 15×10 Vdata_la21 903 887 870 804 12.31 10.32 8.21 Vdata_la22 849 793 798 736 15.35 7.74 8.42 Vdata_la23 970 858 888 815 19.02 5.28 8.96 Vdata_la24 891 883 834 775 14.97 13.94 7.61 Vdata_la25 896 883 820 756 18.52 16.80 8.47 20×10 Vdata_la26 1195 1089 1100 1054 13.38 3.32 4.36 Vdata_la27 1231 1123 1133 1084 13.56 3.60 4.52 Vdata_la28 1249 1106 1121 1070 16.73 3.36 4.77 Vdata_la29 1121 1049 1048 994 12.78 5.53 5.43 Vdata_la30 1256 1117 1122 1069 17.49 4.49 4.96 30×10 Vdata_la31 1688 1561 1553 1520 11.05 2.70 2.17 Vdata_la32 1837 1693 1697 1658 10.80 2.11 2.35 Vdata_la33 1630 1531 1530 1497 8.88 2.27 2.20 Vdata_la34 1731 1562 1565 1537 12.62 1.63 1.82 Vdata_la35 1711 1574 1582 1549 10.46 1.61 2.13 15×15 Vdata_la36 1100 985 967 948 16.03 3.90 2.00 Vdata_la37 1171 1028 1035 986 18.76 4.26 4.97 Vdata_la38 1061 948 943 943 12.51 0.53 0.00 Vdata_la39 1109 976 959 922 20.28 6.18 4.01 Vdata_la40 1041 968 955 955 9.01 1.36 0.00 注:Ave.Gap: DSTA、Multi-ppo、DSTA-PPO分别为9.55、4.20、2.58。 -
[1] THAMES L, SCHAEFER D. Software-defined cloud manufacturing for industry 4.0[J]. Procedia CIRP, 2016, 52: 12-17. doi: 10.1016/j.procir.2016.07.041 [2] GOLPÎRA H, KHAN S A R, SAFAEIPOUR S. A review of logistics Internet-of-things: current trends and scope for future research[J]. Journal of Industrial Information Integration, 2021, 22: 100194. doi: 10.1016/j.jii.2020.100194 [3] LIU Y K, WANG L H, WANG X V, et al. Scheduling in cloud manufacturing: state-of-the-art and research challenges[J]. International Journal of Production Research, 2019, 57(15-16): 4854-4879. doi: 10.1080/00207543.2018.1449978 [4] FANG Y L, PENG C, LOU P, et al. Digital-twin-based job shop scheduling toward smart manufacturing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2019, 15(12): 6425-6435. doi: 10.1109/TII.2019.2938572 [5] ZHANG Y F, WANG J, LIU S C, et al. Game theory based real‐time shop floor scheduling strategy and method for cloud manufacturing[J]. International Journal of Intelligent Systems, 2017, 32(4): 437-463. doi: 10.1002/int.21868 [6] GAO K Z, CAO Z G, ZHANG L, et al. A review on swarm intelligence and evolutionary algorithms for solving flexible job shop scheduling problems[J]. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2019, 6(4): 904-916. doi: 10.1109/JAS.2019.1911540 [7] CHOI I C, CHOI D S. A local search algorithm for jobshop scheduling problems with alternative operations and sequence-dependent setups[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2002, 42(1): 43-58. [8] ZHANG G H, SHAO X Y, LI P G, et al. An effective hybrid particle swarm optimization algorithm for multi-objective flexible job-shop scheduling problem[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2009, 56(4): 1309-1318. [9] NOUIRI M, BEKRAR A, JEMAI A, et al. Two stage particle swarm optimization to solve the flexible job shop predictive scheduling problem considering possible machine breakdowns[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2017, 112: 595-606. [10] NOUIRI M, BEKRAR A, JEMAI A, et al. An effective and distributed particle swarm optimization algorithm for flexible job-shop scheduling problem[J]. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 2018, 29(3): 603-615. doi: 10.1007/s10845-015-1039-3 [11] XING L N, CHEN Y W, WANG P, et al. A knowledge-based ant colony optimization for flexible job shop scheduling problems[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2010, 10(3): 888-896. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2009.10.006 [12] JIANG T H, ZHANG C. Application of grey wolf optimization for solving combinatorial problems: job shop and flexible job shop scheduling cases[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 26231-26240. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2833552 [13] ZHOU X J, YANG C H, GUI W H. State transition algorithm[J]. Journal of Industrial & Management Optimization, 2012, 8(4): 1039-1056. [14] 董天雪, 阳春华, 周晓君, 等. 一种求解企业员工指派问题的离散状态转移算法[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2016, 33(10): 1378-1388. doi: 10.7641/CTA.2016.50982DONG T X, YANG C H, ZHOU X J, et al. A novel discrete state transition algorithm for staff assignment problem[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2016, 33(10): 1378-1388(in Chinese). doi: 10.7641/CTA.2016.50982 [15] 张凤雪, 阳春华, 周晓君, 等. 基于控制周期计算的锌液净化除铜过程优化控制[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2017, 34(10): 1388-1395. doi: 10.7641/CTA.2017.60621ZHANG F X, YANG C H, ZHOU X J, et al. Optimal control based on control period calculation for copper removal process of zinc solution purification[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2017, 34(10): 1388-1395(in Chinese). doi: 10.7641/CTA.2017.60621 [16] DU Y, LI J Q, CHEN X L, et al. Knowledge-based reinforcement learning and estimation of distribution algorithm for flexible job shop scheduling problem[J]. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computational Intelligence, 2022, 7(4): 1036-1050. [17] CHEN R H, YANG B, LI S, et al. A self-learning genetic algorithm based on reinforcement learning for flexible job-shop scheduling problem[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2020, 149: 106778. [18] LEI K, GUO P, ZHAO W C, et al. A multi-action deep reinforcement learning framework for flexible Job-shop scheduling problem[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2022, 205: 117796. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2022.117796 [19] 张凯, 毕利, 焦小刚. 集成强化学习算法的柔性作业车间调度问题研究[J]. 中国机械工程, 2023, 34(2): 201-207. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2023.02.010ZHANG K, BI L, JIAO X G. Research on flexible job-shop scheduling problems with integrated reinforcement learning algorithm[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2023, 34(2): 201-207(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2023.02.010 [20] 王凌, 王晶晶. 考虑运输时间的分布式绿色柔性作业车间调度协同群智能优化[J]. 中国科学: 技术科学: 1-15. -







 下载:
下载:








 下载:
下载: