A micro expression recognition method integrating LBP and parallel attention mechanism
-
摘要:
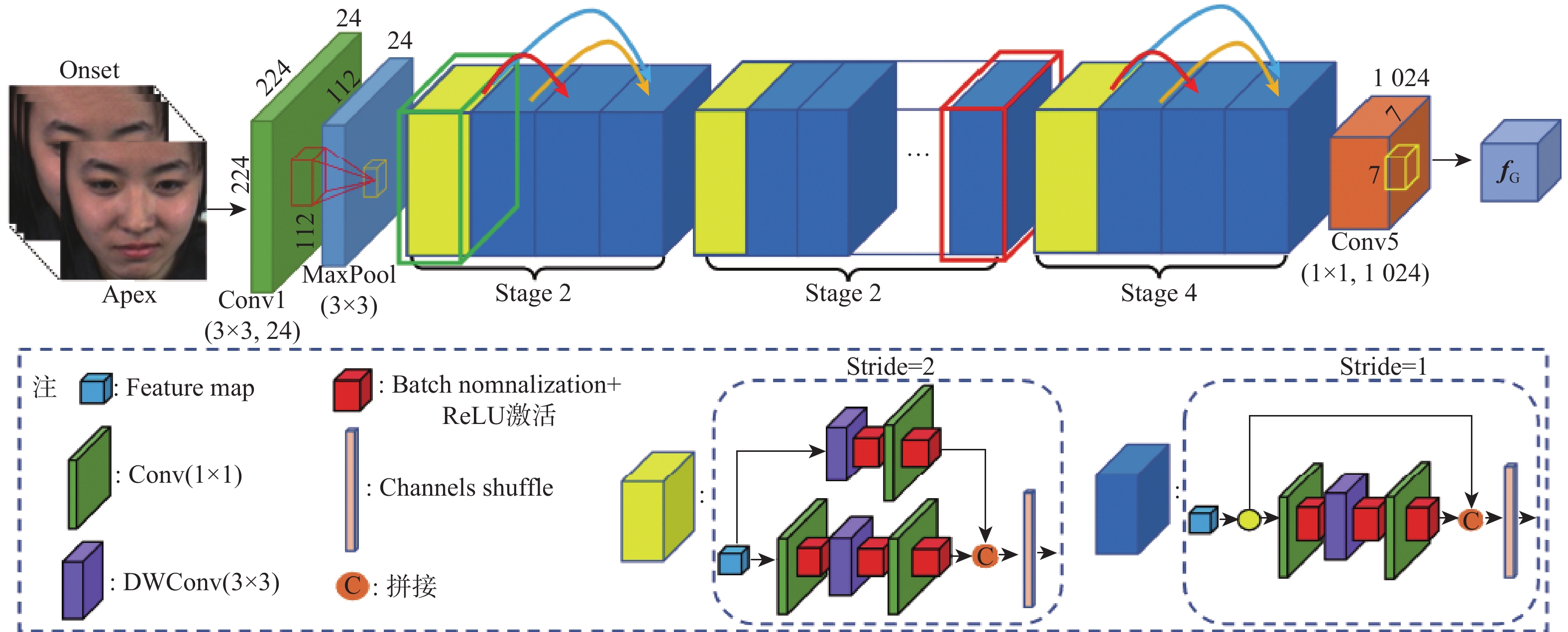
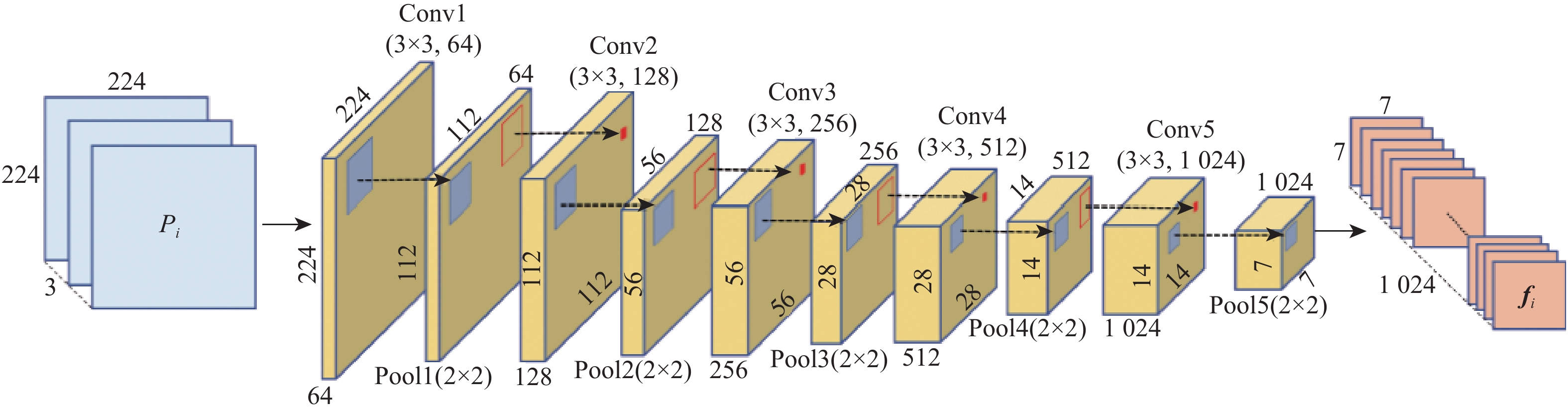
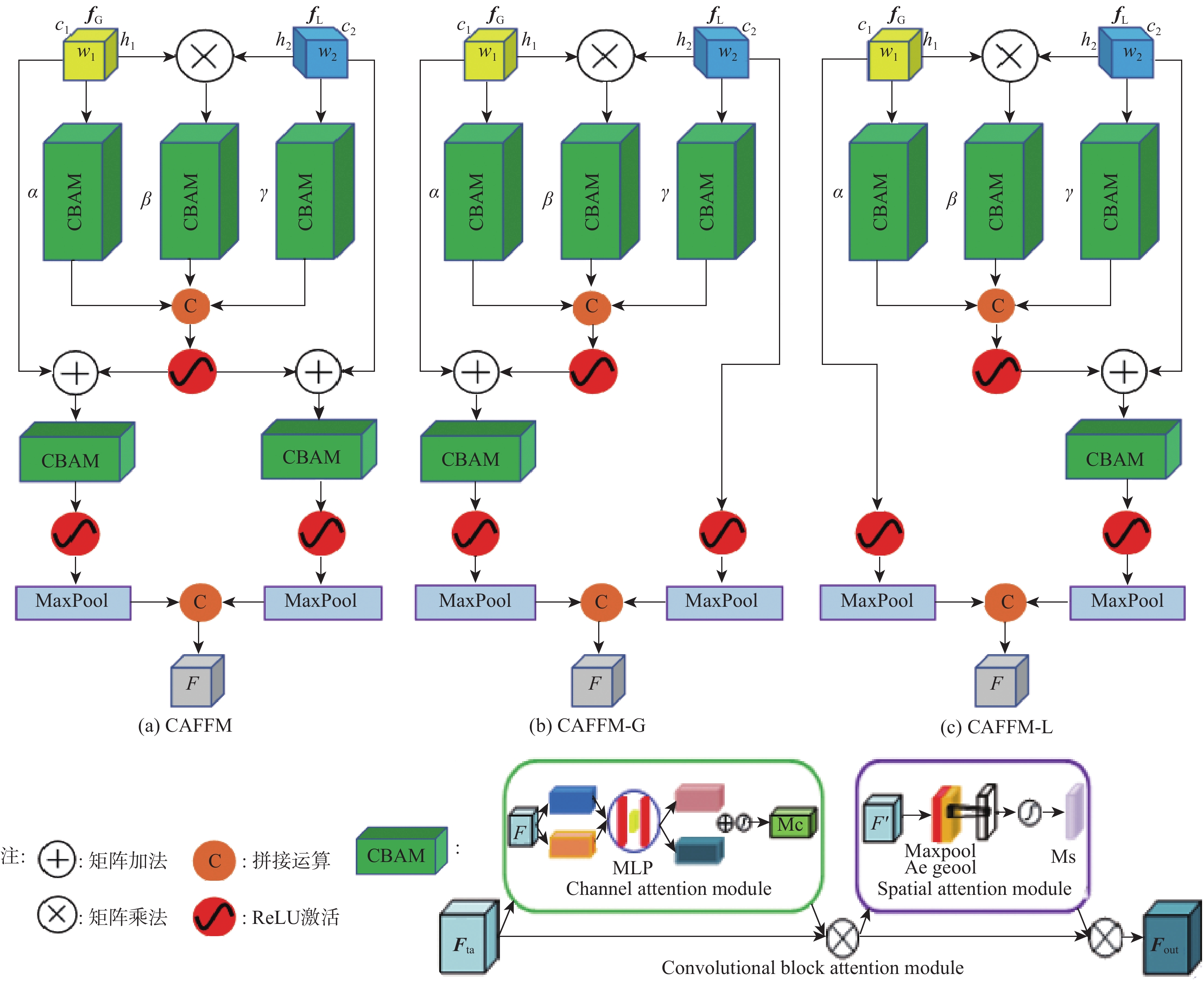
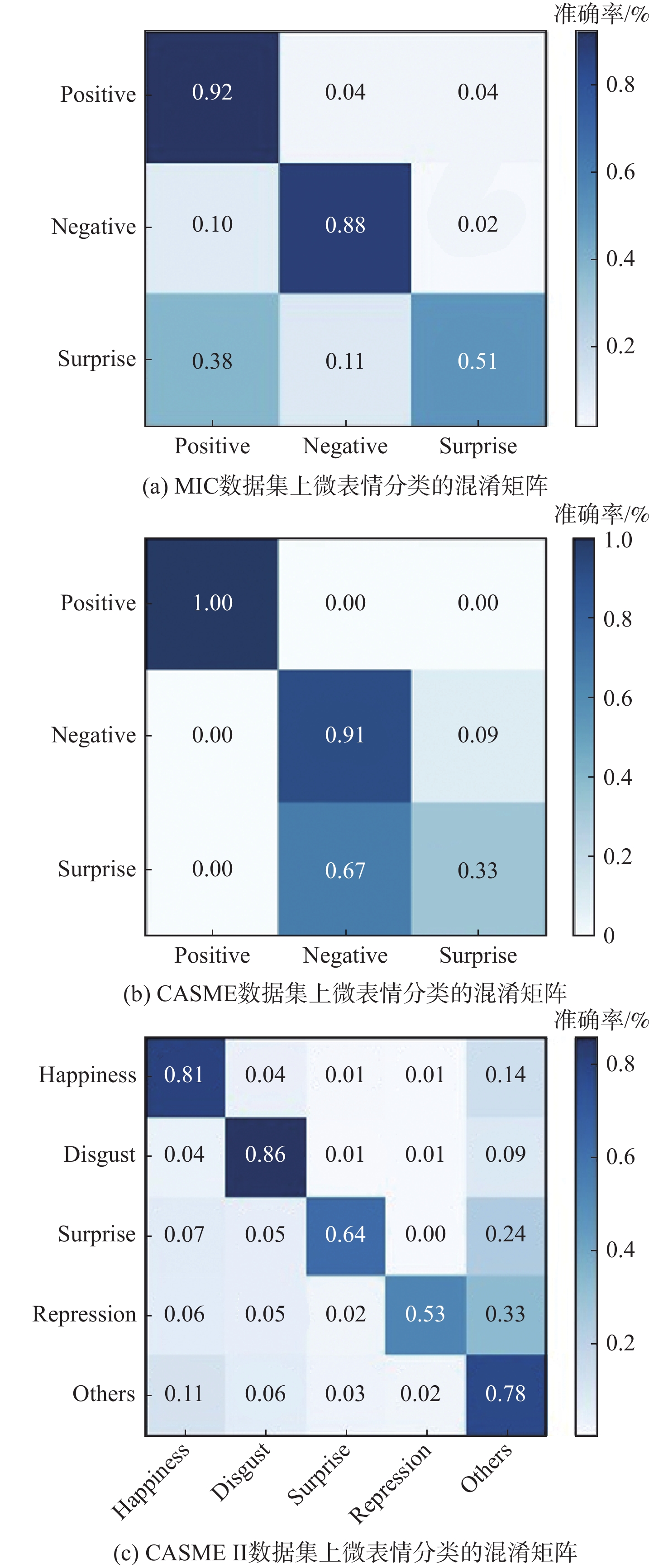
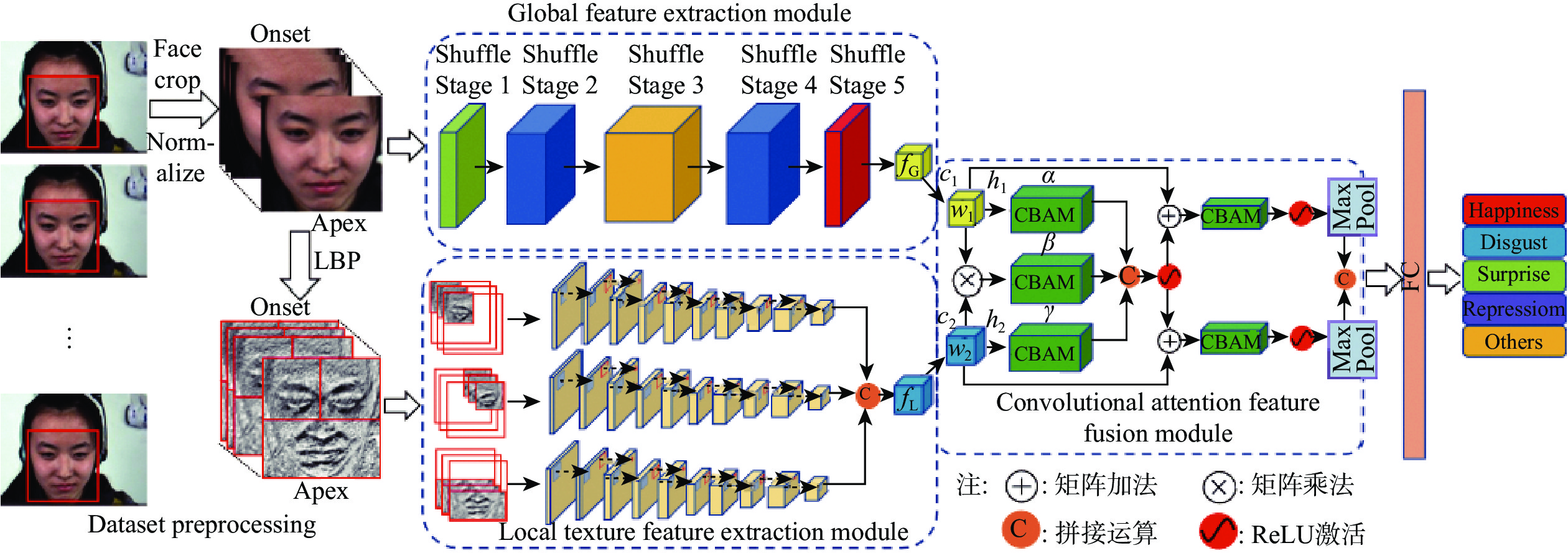
针对面部微表情变化强度弱、背景噪声干扰及特征区分度较小等问题,提出了一种融合LBP与并行注意力机制的微表情识别网络。该网络将RGB图像输入密集连接改进的Shuffle Stage分支提取面部全局特征,增强上下文语义信息关联;将LBP图像输入多尺度分层卷积神经网络构成的局部纹理特征分支,提取细节信息;双分支特征提取后,在网络后端引入并行注意力机制提高特征融合能力,抑制背景干扰,专注微表情特征兴趣区域;所提方法在CASME、CASME II和SMIC等3个公开数据集上进行了测试,识别准确率分别达到了85.18%、74.53%和81.19%;实验结果表明,所提方法有效提高了微表情识别准确率,优于当前诸多先进方法。
-
关键词:
- 微表情识别 /
- 密集连接 /
- Shuffle Stage分支 /
- 多尺度分层卷积 /
- 并行注意力机制
Abstract:This research proposes a micro expression recognition network that incorporates LBP and parallel attention method to address the issues of small feature discrimination, background noise interference, and weak intensity of facial micro-expression changes. The network inputs the RGB image into the densely connected improved Shuffle Stage branch to extract the global features of the face and enhance the association of contextual semantic information. The LBP image is input into the local texture feature branch composed of a multi-scale layered convolutional neural network to extract detailed information. Following extraction of the dual-branch feature, the network backend implements a parallel attention technique to enhance feature fusion capabilities, reduce background noise, and concentrate on the micro-expression feature's interest region. The proposed method is tested on three public data sets including CASME, CASME II and SMIC, and the recognition is accurate The rates reached 85.18%, 74.53% and 81.19% respectively. The experimental results show that the proposed method effectively improves the accuracy of micro expression recognition, which is better than many current advanced methods.
-
表 1 CASME数据集识别准确率
Table 1. CASME dataset recognition accuracy
表 2 CASME II和SMIC数据集识别准确率
Table 2. CASME II and SMIC dataset recognition accuracy
方法 SMIC
准确率/%CASME II
准确率/%MSMMT[37] 78.30 71.31 AMAN[38] 79.87 75.40 KTGSL[39] 72.58 75.64 Later[40] 73.17 70.68 SLSTT-Mean[41] 73.17 73.79 STLBP-IIP[42] 60.37 62.75 DISTLBP-IIP[42] 63.41 64.78 3D-CNNs (with transfer learning)[43] 66.30 65.90 DSSN[44] 63.40 70.78 SSSN[44] 63.41 71.19 AKMNet[35] 72.56 67.06 TSCNN-I[26] 72.74 74.05 KFC-MER[21] 65.85 72.76 FR[17] 57.90 62.85 Knowledge Distillation[45] 76.06 72.61 本文 81.19 74.53 表 3 CASME、CASME II和SMIC数据集上的消融实验
Table 3. Ablation experimental research on CASME, CASME II and SMIC datasets
方法 CASME
准确率/%CASME II
准确率/%SMIC
准确率/%参数量/M 浮点运算量/G 推理速度/(帧·s−1) GFEM 77.50 66.31 73.38 2.59 1.778 111.5 LTFEM 76.53 62.69 76.90 6.26 3.287 106.3 GFEM+LTFEM 81.41 66.34 76.47 8.13 4.927 104.5 GFEM+LTFEM+DEN 83.49 71.19 77.39 8.17 5.073 102.2 GFEM+LTFEM+CAFFM 82.81 74.67 79.76 8.46 5.165 97.3 GFEM+LTFEM+DEN+CAFFM 85.18 74.33 81.19 8.97 5.258 95.8 GFEM+LTFEM+CAFFM-L 84.52 74.52 79.71 8.49 5.140 97.3 GFEM+LTFEM+DEN+CAFFM-L 84.14 74.55 77.81 8.78 5.232 95.7 GFEM+LTFEM + CAFFM-G 81.63 72.23 77.76 8.50 5.151 97.5 GFEM+LTFEM +DEN+CAFFM-G 83.26 74.05 77.52 8.79 5.243 95.8 表 4 CAFFM不同权重比在3个数据集上的准确率
Table 4. Accuracy of different weight ratios of CAFFM on 3 datasets
α∶β∶γ CASME
准确率/%CASME II
准确率/%SMIC
准确率/%1∶1∶1 82.82 74.67 80.19 2∶1∶1 80.78 72.71 80.76 1∶2∶1 78.37 73.67 79.71 1∶1∶2 79.56 73.28 79.90 表 5 CAFFM-L不同权重比在3个数据集上的准确率
Table 5. Accuracy of different weight ratios of CAFFM-L on 3 datasets
α∶β∶γ CASME
准确率/%CASME II
准确率/%SMIC
准确率/%1∶1∶1 83.53 74.53 79.71 2∶1∶1 84.15 74.47 78.86 1∶2∶1 82.96 74.36 78.81 1∶1∶2 82.44 74.22 77.76 表 6 CAFFM-G不同权重比在3个数据集上的准确率
Table 6. Accuracy of different weight ratios of CAFFM-G on 3 datasets
α∶β∶γ CASME
准确率/%CASME II
准确率/%SMIC
准确率/%1∶1∶1 82.96 72.23 77.76 2∶1∶1 82.96 73.86 78.38 1∶2∶1 81.63 74.56 79.57 1∶1∶2 82.44 73.61 80.24 -
[1] PORTER S, TEN BRINKE L. Reading between the lies: identifying concealed and falsified emotions in universal facial expressions[J]. Psychological Science, 2008, 19(5): 508-514. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9280.2008.02116.x [2] HAGGARD E A, ISAACS K S. Micromomentary facial expressions as indicators of ego mechanisms in psychotherapy[M]// Methods of Research in Psychotherapy. Boston: Springer US, 1966: 154-165. [3] EKMAN P, FRIESEN W V. The repertoire of nonverbal behavior: categories, origins, usage, and coding[J]. Semiotica, 1969, 1(1): 49-98. doi: 10.1515/semi.1969.1.1.49 [4] FRANK M, HERBASZ M, SINUK K, et al. I see how you feel: Training laypeople and professionals to recognize fleeting emotions[C]//The Annual Meeting of the International Communication Association. New York: Academic Press, 2009: 1-35. [5] EKMAN P, FRIESEN W V. Facial action coding system: a technique for the measurement of facial actions[J]. Rivista Di Psichiatria, 1978, 47(2): 126-138. [6] OJALA T, PIETIKÄINEN M, HARWOOD D. A comparative study of texture measures with classification based on featured distributions[J]. Pattern Recognition, 1996, 29(1): 51-59. doi: 10.1016/0031-3203(95)00067-4 [7] PFISTER T, LI X B, ZHAO G Y, et al. Recognising spontaneous facial micro-expressions[C]// 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2011: 1449-1456. [8] LIU Y J, ZHANG J K, YAN W J, et al. A main directional mean optical flow feature for spontaneous micro-expression recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2015, 7(4): 299-310. [9] WU Q, SHEN X B, FU X L. The machine knows what you are hiding: an automatic micro-expression recognition system[M]// D’MELLO S, GRAESSER A, SCHULLER B, et al. eds. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2011: 152-162. [10] MA H Y, AN G Y, WU S J, et al. A Region Histogram of Oriented Optical Flow (RHOOF) feature for apex frame spotting in micro-expression[C]// 2017 International Symposium on Intelligent Signal Processing and Communication Systems (ISPACS). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 281-286. [11] HUANG G, LIU Z, VAN DER MAATEN L, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks[C]// 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 2261-2269. [12] MA N N, ZHANG X Y, ZHENG H T, et al. ShuffleNet V2: practical guidelines for efficient CNN architecture design[M]// Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2018: 122-138. [13] WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. CBAM: convolutional block attention module[M]// Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2018: 3-19. [14] CHENG R, RAZANI R, TAGHAVI E, et al. (AF)2-S3Net: attentive feature fusion with adaptive feature selection for sparse semantic segmentation network[C]// 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 12542-12551. [15] LIU S H, REN Y S, LI L T, et al. Micro-expression recognition based on SqueezeNet and C3D[J]. Multimedia Systems, 2022, 28(6): 2227-2236. doi: 10.1007/s00530-022-00949-z [16] ZHAO S R, TANG H Y, LIU S F, et al. ME-PLAN: a deep prototypical learning with local attention network for dynamic micro-expression recognition[J]. Neural Networks, 2022, 153: 427-443. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2022.06.024 [17] ZHOU L, MAO Q R, HUANG X H, et al. Feature refinement: an expression-specific feature learning and fusion method for micro-expression recognition[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2022, 122: 108275. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2021.108275 [18] LI J T, WANG T, WANG S J. Facial micro-expression recognition based on deep local-holistic network[J]. Applied Sciences, 2022, 12(9): 4643. doi: 10.3390/app12094643 [19] LI J, JIN K, ZHOU D L, et al. Attention mechanism-based CNN for facial expression recognition[J]. Neurocomputing, 2020, 411: 340-350. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2020.06.014 [20] RODRÍGUEZ P, VELAZQUEZ D, CUCURULL G, et al. Pay attention to the activations: a modular attention mechanism for fine-grained image recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2019, 22(2): 502-514. [21] SU Y T, ZHANG J Q, LIU J, et al. Key facial components guided micro-expression recognition based on first & second-order motion[C]// 2021 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 1-6. [22] GAJJALA V R, REDDY S P T, MUKHERJEE S, et al. MERANet: facial micro-expression recognition using 3D residual attention network[C]// Proceedings of the Twelfth Indian Conference on Computer Vision, Graphics and Image Processing. New York: ACM, 2021: 1-10. [23] YAN W J, QI W, LIU Y J, et al. CASME database: a dataset of spontaneous micro-expressions collected from neutralized faces[C]// 2013 10th IEEE International Conference and Workshops on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2013: 1-7. [24] YAN W J, LI X B, WANG S J, et al. CASME II: an improved spontaneous micro-expression database and the baseline evaluation[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(1): e86041. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0086041 [25] LI X B, PFISTER T, HUANG X H, et al. A spontaneous micro-expression database: inducement, collection and baseline[C]// 2013 10th IEEE International Conference and Workshops on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2013: 1-6. [26] SONG B L, LI K, ZONG Y, et al. Recognizing spontaneous micro-expression using a three-stream convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 184537-184551. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2960629 [27] WANG Y, HAN J F, GUO Z Q. RETRACTED: LCBP-STGCN: a local cube binary pattern spatial temporal graph convolutional network for micro-expression recognition[J]. Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems, 2023, 44(2): 1601-1611. [28] CEN S X, YU Y, YAN G, et al. Multi-task Facial Activity Patterns Learning for micro-expression recognition using Joint Temporal Local Cube Binary Pattern[J]. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 2022, 103: 116616. doi: 10.1016/j.image.2021.116616 [29] VERMA M, VIPPARTHI S K, SINGH G, et al. LEARNet: Dynamic imaging network for micro expression recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 29: 1618-1627. [30] HUANG X H, ZHAO G Y, HONG X P, et al. Spontaneous facial micro-expression analysis using Spatiotemporal Completed Local Quantized Patterns[J]. Neurocomputing, 2016, 175: 564-578. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2015.10.096 [31] LI X B, HONG X P, MOILANEN A, et al. Towards reading hidden emotions: a comparative study of spontaneous micro-expression spotting and recognition methods[J]. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2017, 9(4): 563-577. [32] HAPPY S L, ROUTRAY A. Fuzzy histogram of optical flow orientations for micro-expression recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2017, 10(3): 394-406. [33] PENG M, WU Z, ZHANG Z H, et al. From macro to micro expression recognition: deep learning on small datasets using transfer learning[C]// 2018 13th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2018). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 657-661. [34] XIA Z Q, HONG X P, GAO X Y, et al. Spatiotemporal recurrent convolutional networks for recognizing spontaneous micro-expressions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2019, 22(3): 626-640. [35] PENG M, WANG C, GAO Y, et al. Recognizing micro-expression in video clip with adaptive key-frame mining[EB/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2009.09179, 2020. [36] GONG W J, ZHANG Y, WANG W, et al. Meta-MMFNet: meta-learning-based multi-model fusion network for micro-expression recognition[J]. ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications, and Applications, 2023, 20(2): 39. [37] WANG F, LI J, QI C, et al. Multi-scale multi-modal micro-expression recognition algorithm based on transformer[EB/OL]. arXiv abs/: 2301.02969, 2023. [38] WEI M T, ZHENG W M, ZONG Y, et al. A novel micro-expression recognition approach using attention-based magnification-adaptive networks[C]// ICASSP 2022 - 2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2022: 2420-2424. [39] WEI J S, LU G M, YAN J J, et al. Learning two groups of discriminative features for micro-expression recognition[J]. Neurocomputing, 2022, 479: 22-36. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.12.088 [40] HONG J, LEE C, JUNG H. Late fusion-based video transformer for facial micro-expression recognition[J]. Applied Sciences, 2022, 12(3): 1169. doi: 10.3390/app12031169 [41] ZHANG L F, HONG X P, ARANDJELOVIĆ O, et al. Short and long range relation based spatio-temporal transformer for micro-expression recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2022, 13(4): 1973-1985. doi: 10.1109/TAFFC.2022.3213509 [42] HUANG X H, WANG S J, ZHAO G Y, et al. Facial micro-expression recognition using spatiotemporal local binary pattern with integral projection[C]// 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop (ICCVW). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 1-9. [43] ZHI R C, XU H R, WAN M, et al. Combining 3D convolutional neural networks with transfer learning by supervised pre-training for facial micro-expression recognition[J]. IEICE Transactions on Information and Systems, 2019, 102(5): 1054-1064. [44] KHOR H Q, SEE J, LIONG S T, et al. Dual-stream shallow networks for facial micro-expression recognition[C]// 2019 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 36-40. [45] SUN B, CAO S M, LI D L, et al. Dynamic micro-expression recognition using knowledge distillation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2020, 13(2): 1037-1043. -







 下载:
下载: