-
摘要:
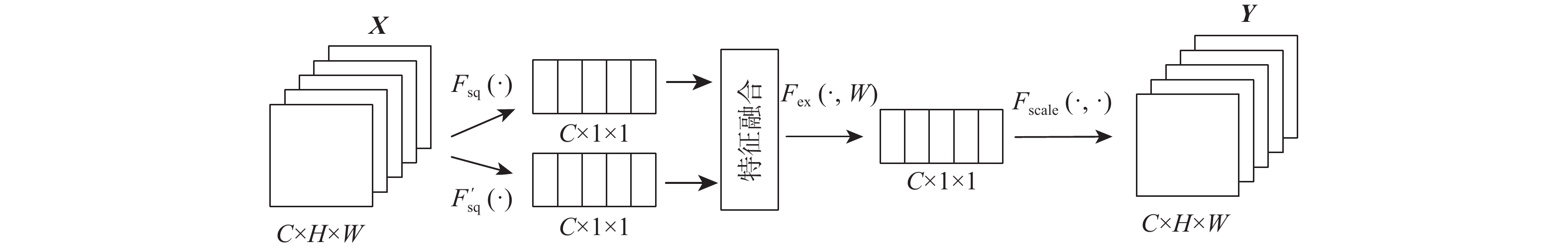
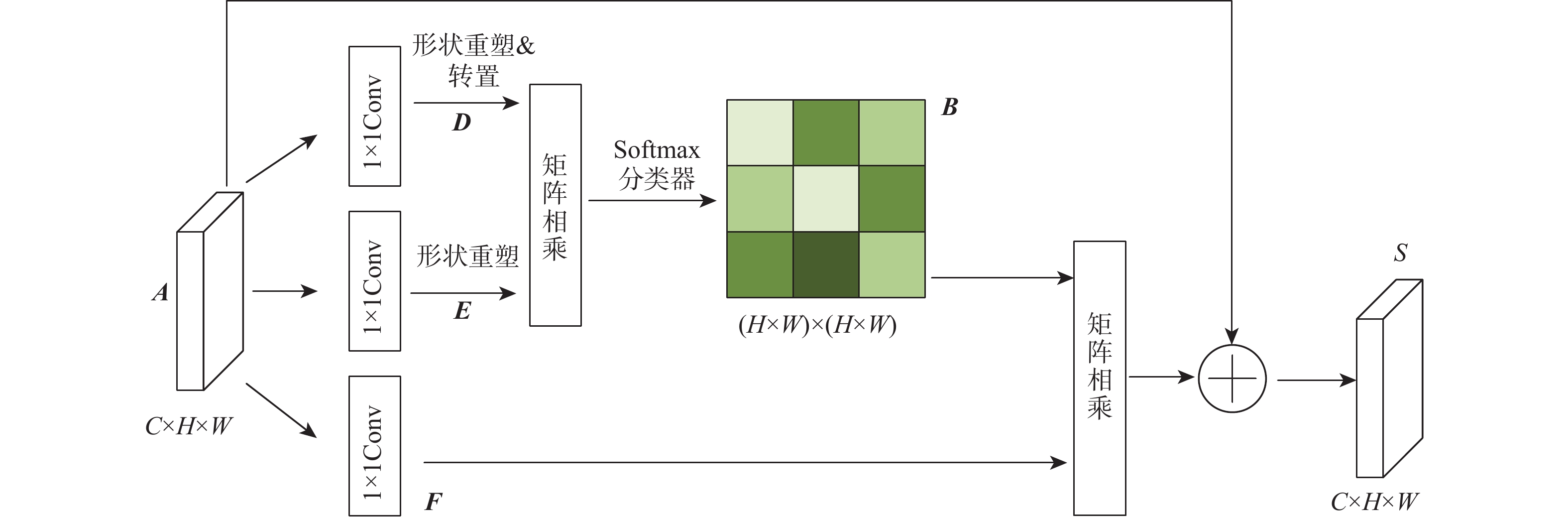
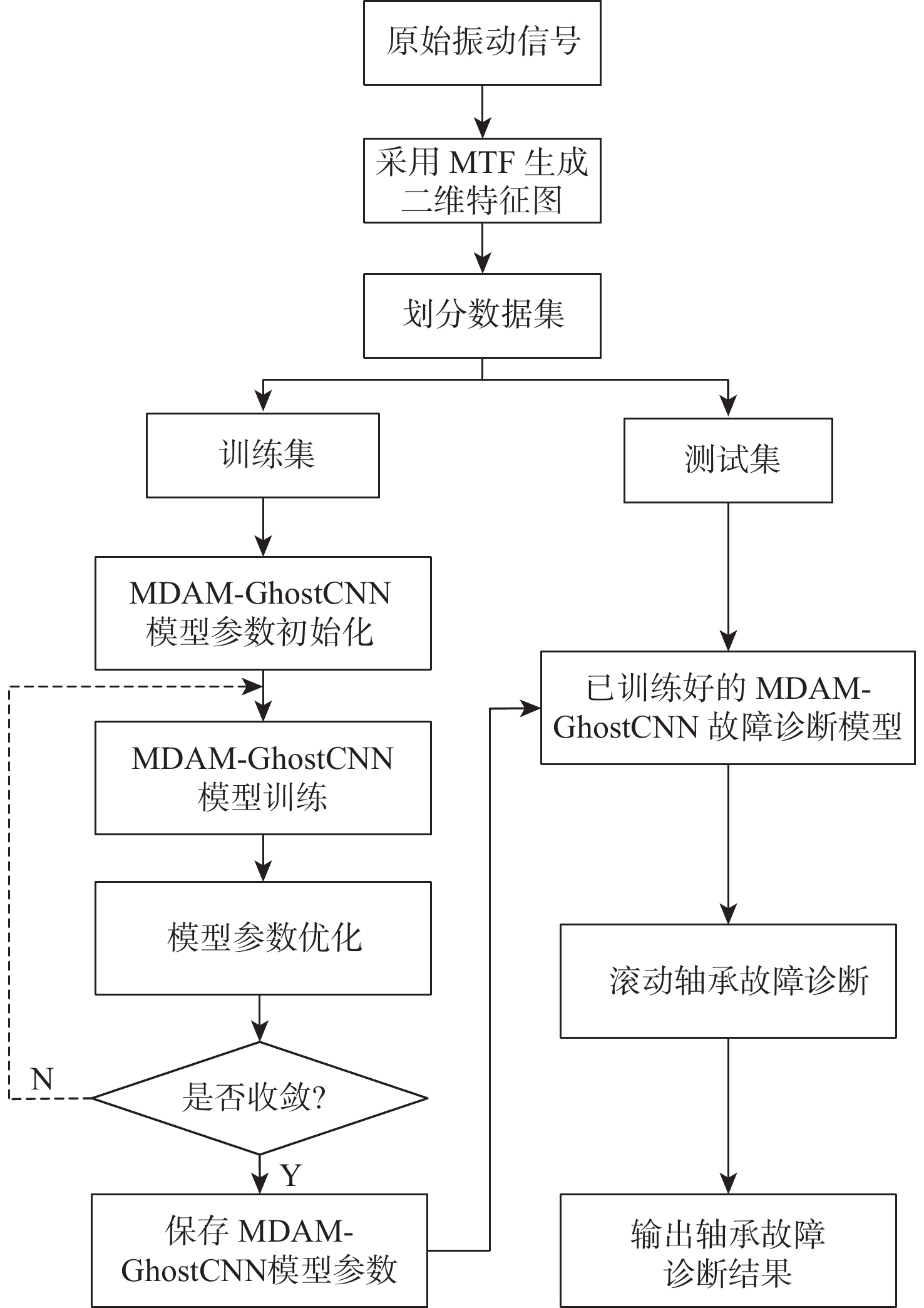
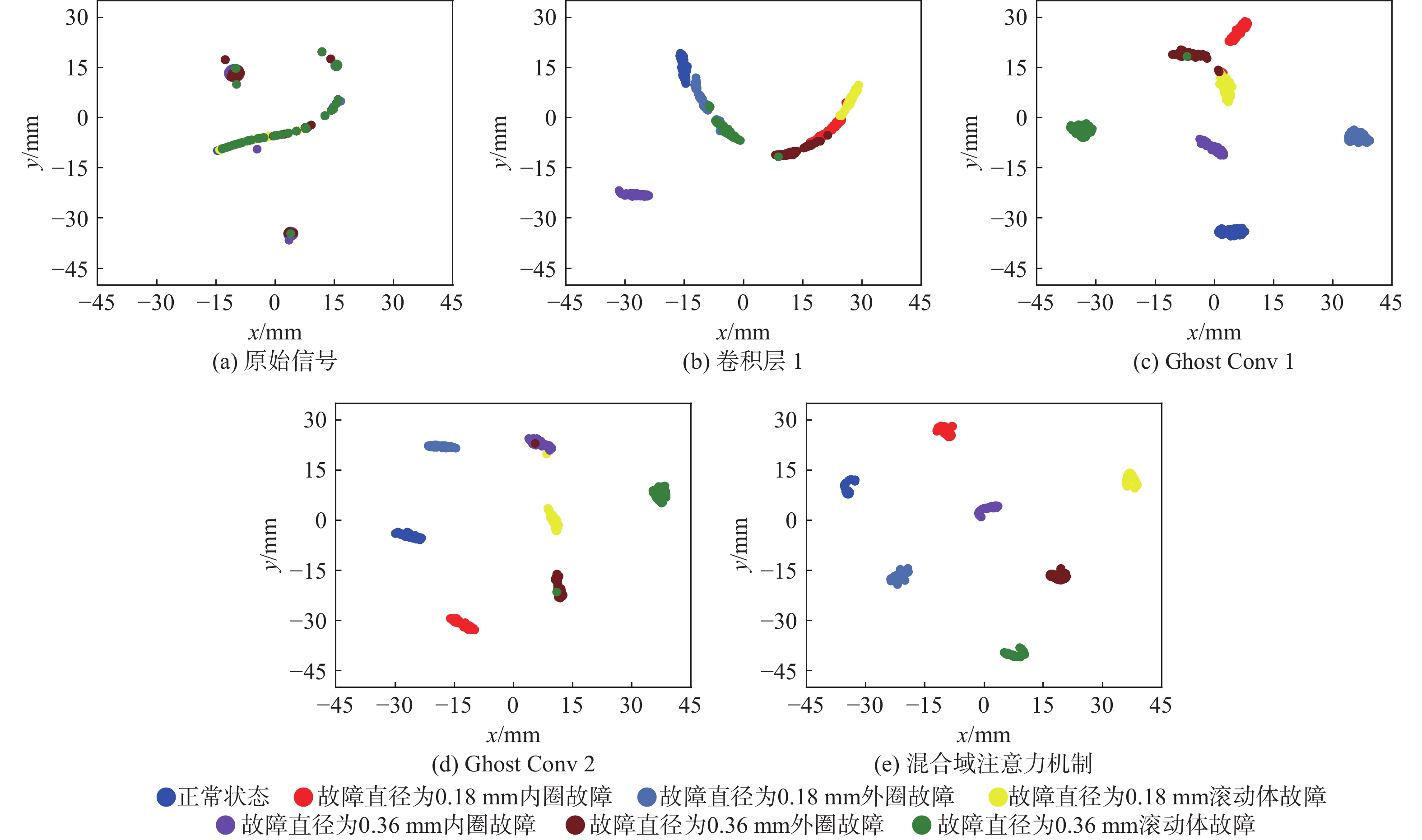
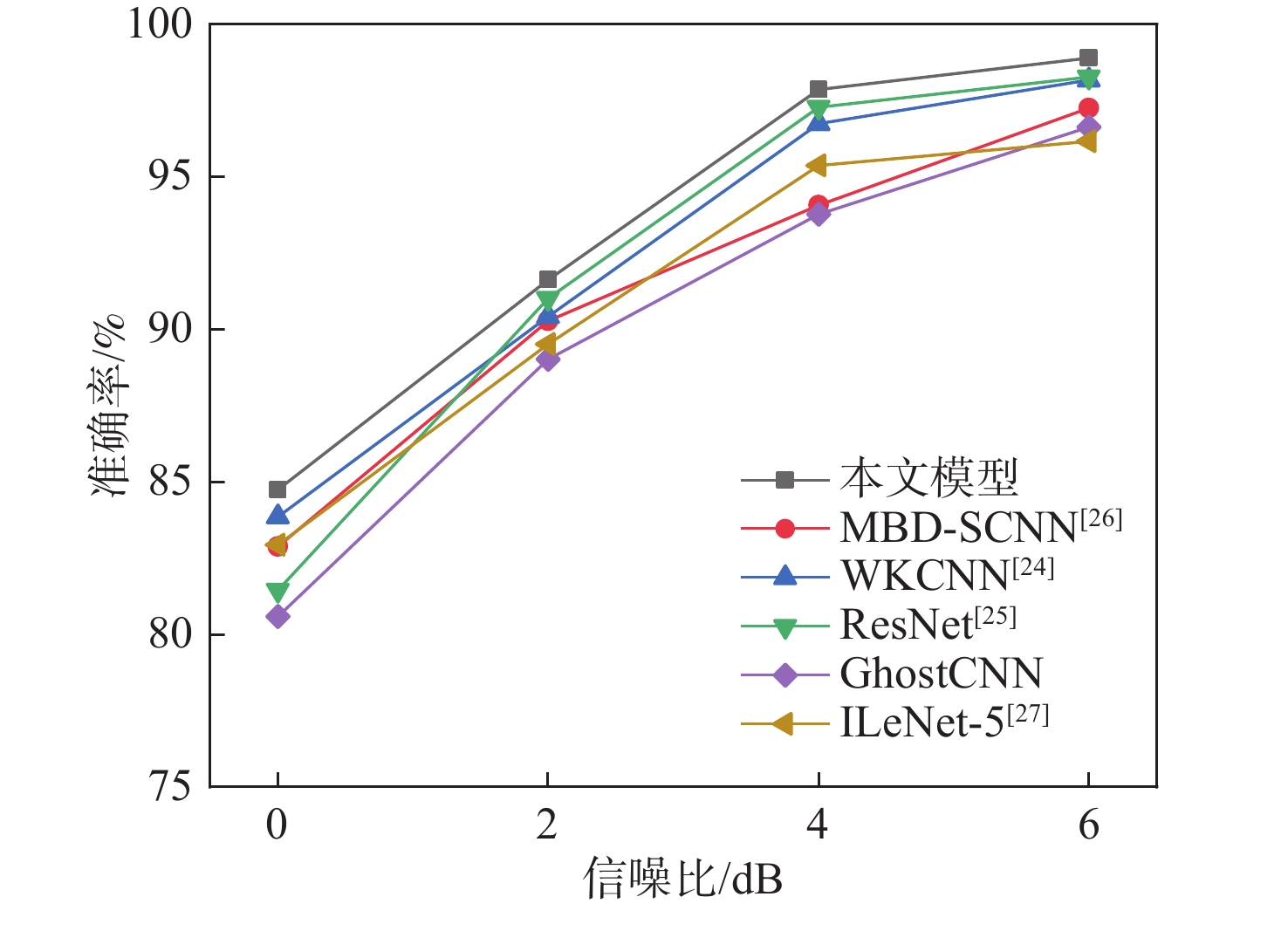
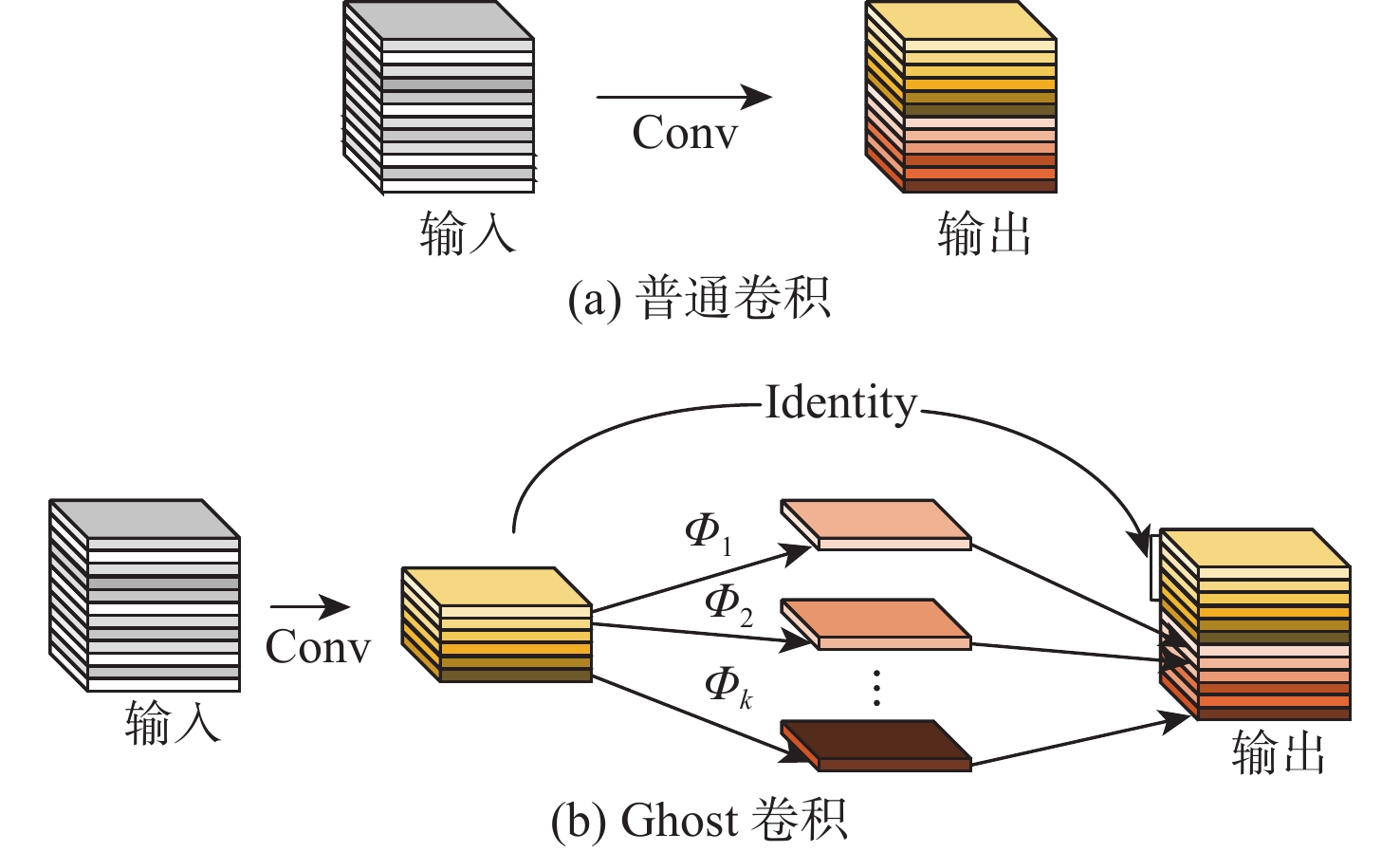
针对传统故障诊断方法特征提取不充分、计算复杂及在变工况下识别准确率低的问题,提出一种基于混合域注意力机制(MDAM)-GhostCNN的滚动轴承故障诊断方法。采用马尔可夫转移场(MTF)将轴承振动信号转化为具有时间相关性的二维特征图;利用Ghost卷积计算精简的优点,构造出GhostCNN;设计一种MDAM,使网络从通道和空间2个维度充分捕获特征信息,实现特征通道间相互依赖的同时让网络有效关注特征空间信息。由此,构建出MDAM-GhostCNN模型。将MTF二维特征图输入到MDAM-GhostCNN模型中进行训练并输出诊断结果。采用凯斯西储大学和江南大学(JNU)轴承数据集进行实验验证,并对其数据集进行加噪处理。结果表明:在变工况下,所建模型有着更高的识别准确率、抗噪性能和泛化性能。
Abstract:A rolling bearing fault diagnostic approach based on mixture domain attention mechanism (MDAM)-GhostCNN is developed to address the issues of inadequate feature extraction, complicated computation, and low recognition accuracy under varied working conditions in conventional fault detection methods. First of all, the Markov transfer field (MTF) is used to transform the bearing vibration signal into a two-dimensional feature graph with time correlation. Secondly, taking advantage of the simplification of Ghost convolution calculation, GhostCNN is constructed. Then, a MDAM is designed, which makes the network fully capture the feature information from the two dimensions of channel and space, and makes the network pay attention to the feature space information effectively while realizing the interdependence between the feature channels, and construct the MDAM-GhostCNN model. Finally, the MTF two-dimensional feature map is input into the MDAM-GhostCNN model for training and output diagnosis results. Experimental verification and noise processing were performed on the bearing data sets from Jiang Nan University (JNU) and Case Western Reserve University. The results show that under variable working conditions, the constructed model has higher recognition accuracy, noise immunity and generalization performance.
-
Key words:
- rolling bearing /
- fault diagnosis /
- Markov transfer field /
- Ghost convolution /
- attention mechanism
-
表 1 MDAM-GhostCNN结构
Table 1. MDAM-GhostCNN structure
特征层 卷积核数量 卷积核大小 输出大小 输入 (128,128,1) 卷积层 32 5×5 (128,128,32) GN (128,128,32) 最大池化1 32 2×2 (64,64,32) Ghost Conv 1 32 3×3 (64,64,32) GN (64,64,32) 最大池化2 32 2×2 (32,32,32) Ghost Conv 2 32 3×3 (32,32,32) GN (32,32,32) 最大池化3 2×2 (16,16,32) MDAM (16,16,32) 全局平均池化 (1,1,32) 分类器 7 (7) 损伤位置 标签 损伤直径/mm 样本数量 数据集A 数据集B 数据集C 训练集 测试集 训练集 测试集 训练集 测试集 正常 0 0 240 100 240 100 240 100 内圈 1 0.18 240 100 240 100 240 100 2 0.36 240 100 240 100 240 100 外圈 3 0.18 240 100 240 100 240 100 4 0.36 240 100 240 100 240 100 滚动体 5 0.18 240 100 240 100 240 100 6 0.36 240 100 240 100 240 100 表 3 不同模型参数量和训练时间
Table 3. Number of Different model parameters and training time
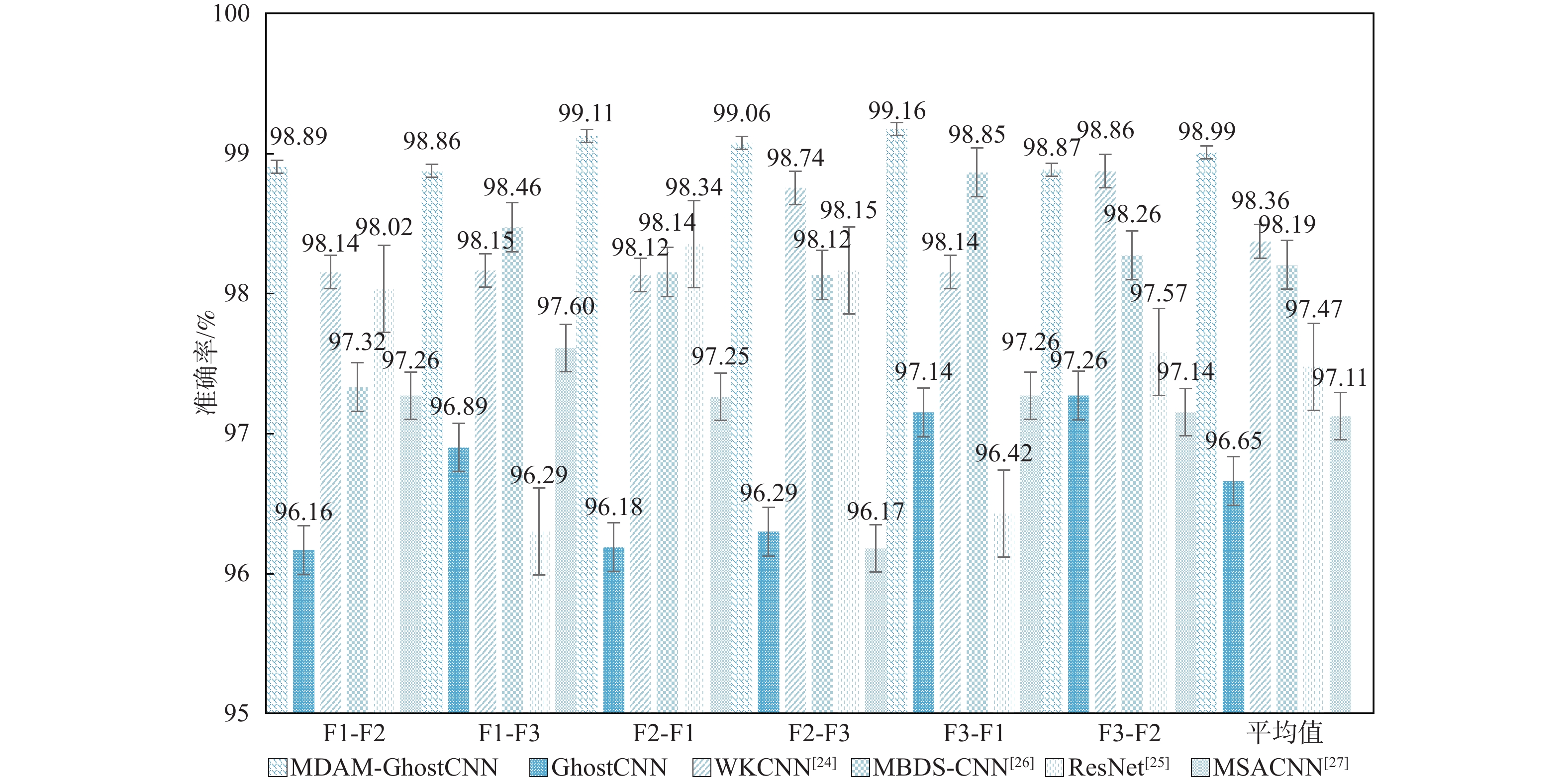
表 4 JNU轴承数据集说明
Table 4. JNU rolling bearing data set description
损伤位置 标签 样本数量 工况F1 工况F2 工况F3 训练集 测试集 训练集 测试集 训练集 测试集 正常 0 240 100 240 100 240 100 内圈 1 240 100 240 100 240 100 外圈 2 240 100 240 100 240 100 滚动体 3 240 100 240 100 240 100 -
[1] HAN T, LIU C, YANG W G, et al. Deep transfer network with joint distribution adaptation: a new intelligent fault diagnosis framework for industry application[J]. ISA Transactions, 2020, 97: 269-281. doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2019.08.012 [2] HE S Y, HU D Y, YU G, et al. Trackside acoustic detection of axle bearing fault using wavelet domain moving beamforming method[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2022, 195: 108851. doi: 10.1016/j.apacoust.2022.108851 [3] HOU M X, SHI H T. Stator-winding incipient shorted-turn fault detection for motor system in motorized spindle using modified interval observers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2021, 70: 3505716. [4] LIU R N, YANG B Y, ZIO E, et al. Artificial intelligence for fault diagnosis of rotating machinery: a review[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2018, 108: 33-47. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2018.02.016 [5] 袁彩艳, 孙洁娣, 温江涛, 等. 多域信息融合结合改进残差密集网络的轴承故障诊断[J]. 振动与冲击, 2022, 41(4): 200-208.YUAN C Y, SUN J D, WEN J T, et al. Bearing fault diagnosis based on information fusion and improved residual dense networks[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2022, 41(4): 200-208(in Chinese). [6] HOANG D T, KANG H J. A survey on deep lelarning based bearing fault diagnosis[J]. Neurocomputing, 2019, 335: 327-335. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2018.06.078 [7] SCHOLARPEDIA G E H. Deep belief networks[J]. Scholarpedia the Peer-Reviewed Open-Access Encyclopedia, 2009, 4(5): 5947. [8] RUMELHART D E, HINTON G E, WILLIAMS R J. Learning representations by back-propagating errors[J]. Nature, 1986, 323: 533-536. doi: 10.1038/323533a0 [9] XU Y, LI Z X, WANG S Q, et al. A hybrid deep-learning model for fault diagnosis of rolling bearings[J]. Measurement, 2021, 169: 108502. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2020.108502 [10] ZHANG Z Q, YANG Q Y, ZI Y Y. Multi-scale and multi-pooling sparse filtering: a simple and effective representation learning method for intelligent fault diagnosis[J]. Neurocomputing, 2021, 451: 138-151. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.04.066 [11] CHEN Z Y, MAURICIO A, LI W H, et al. A deep learning method for bearing fault diagnosis based on cyclic spectral coherence and convolutional neural networks[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2020, 140: 106683. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2020.106683 [12] XU Z F, LI C, YANG Y. Fault diagnosis of rolling bearing of wind turbines based on the variational mode decomposition and deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2020, 95: 106515. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106515 [13] YE M Y, YAN X A, CHEN N, et al. Intelligent fault diagnosis of rolling bearing using variational mode extraction and improved one-dimensional convolutional neural network[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2023, 202: 109143. [14] 刘俊锋, 俞翔, 万海波, 等. 基于 MFMD 和 Transformer-CNN 的滚动轴承故障诊断方法[J]. 航空动力学报, 2023, 38(6): 1446-1456.LIU J F, YU X, WAN H B, et al. Fault diagnosis method of rolling bearing using MFMD and Transformer-CNN[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2023, 38(6): 1446-1456(in Chinese) . [15] FU W L, JIANG X H, LI B L, et al. Rolling bearing fault diagnosis based on 2D time-frequency images and data augmentation technique[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2023, 34(4): 045005. doi: 10.1088/1361-6501/acabdb [16] 金江涛, 许子非, 李春, 等. 基于卷积双向长短期记忆网络与混沌理论的滚动轴承故障诊断[J]. 振动与冲击, 2022, 41(17): 160-169.JIN J T, XU Z F, LI C, et al. Fault diagnosis of rolling bearing based on CCNN-BiLSTMN method[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2022, 41(17): 160-169(in Chinese). [17] MAO G, ZHANG Z Z, QIAO B, et al. Fusion domain-adaptation CNN driven by images and vibration signals for fault diagnosis of gearbox cross-working conditions[J]. Entropy, 2022, 24(1): 119. doi: 10.3390/e24010119 [18] WANG M J, WANG W J, ZHANG X N, et al. A new fault diagnosis of rolling bearing based on Markov transition field and CNN[J]. Entropy, 2022, 24(6): 751. doi: 10.3390/e24060751 [19] HAN K, WANG Y H, TIAN Q, et al. GhostNet: more features from cheap operations[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 1577-1586. [20] HU J, SHEN L, SUN G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 7132-7141. [21] HUANG Z L, WANG X G, HUANG L C, et al. CCNet: criss-cross attention for semantic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 603-612. [22] XU G W, LIU M, JIANG Z F, et al. Online fault diagnosis method based on transfer convolutional neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2020, 69(2): 509-520. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2019.2902003 [23] Case Western Reserve University. Case Western Reserve University bearing data[EB/OL]. (2018-05-22) [2023-04-28]. https://gitcode.com/open-source-toolkit/1cd2d/?utm_source=tools_gitcode&index=bottom&type=card&webUrl. [24] SONG X D, CONG Y Y, SONG Y F, et al. A bearing fault diagnosis model based on CNN with wide convolution kernels[J]. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 2022, 13(8): 4041-4056. doi: 10.1007/s12652-021-03177-x [25] HAO X Y, ZHENG Y, LU L, et al. Research on intelligent fault diagnosis of rolling bearing based on improved deep residual network[J]. Applied Sciences, 2021, 11(22): 10889. doi: 10.3390/app112210889 [26] 刘恒畅, 姚德臣, 杨建伟, 等. 基于多分支深度可分离卷积神经网络的滚动轴承故障诊断研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2021, 40(10): 95-102.LIU H C, YAO D C, YANG J W, et al. Fault diagnosis of rolling bearings based on multi-branch deep separable convolutional neural networks[J]. Vibration and Shock, 2021, 40(10): 95-102(in Chinese) . [27] 吴晨芳, 杨世锡, 黄海舟, 等. 一种基于改进的LeNet-5模型滚动轴承故障诊断方法研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2021, 40(12): 55-61.WU C F, YANG S X, HUANG H Z, et al. An improved fault diagnosis method of rolling bearings based on LeNet-5[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2021, 40(12): 55-61(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: