-
摘要:
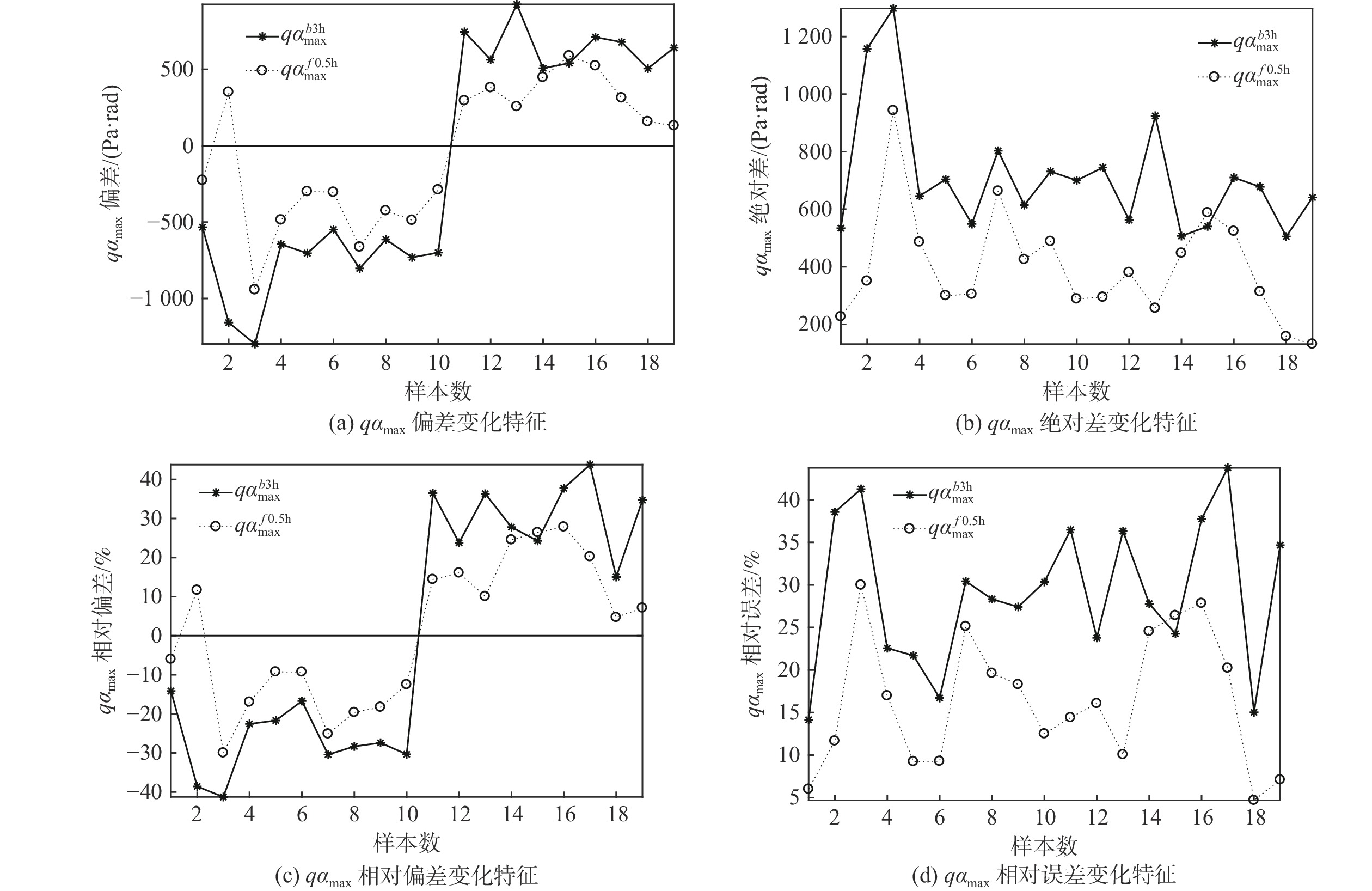
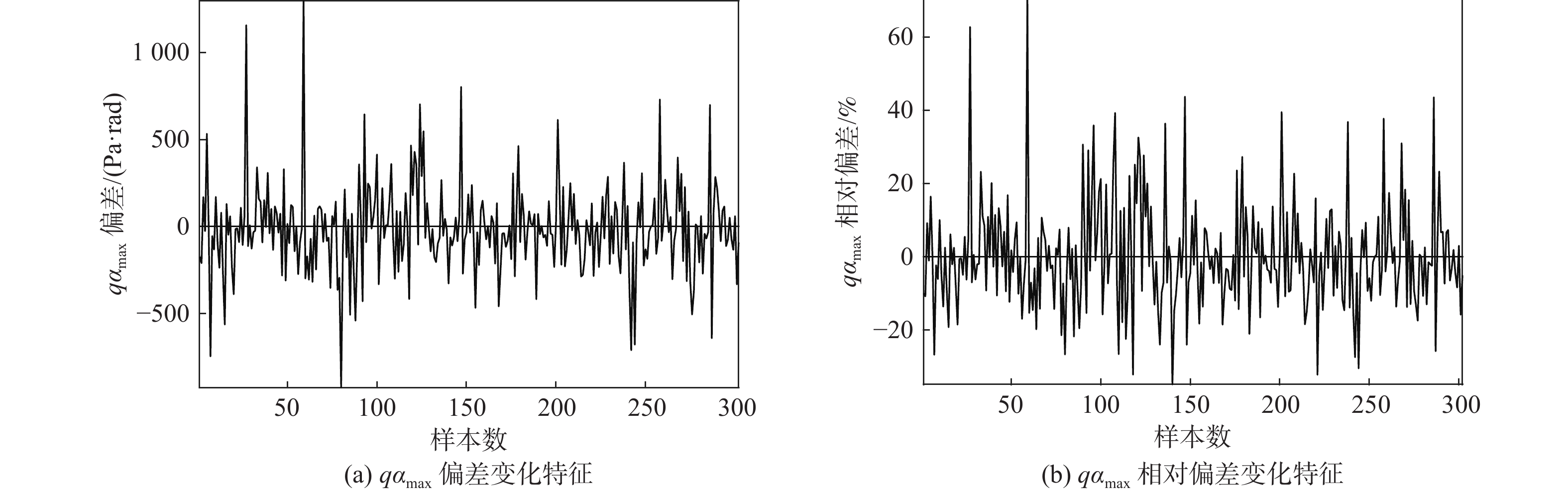
火箭发射前3 h的最大气动载荷是决定能否按计划发射的重要指标之一,该值与发射时刻的最大气动载荷差异特征研究极少。通过对2014年12月—2019年12月的时间间隔3.5 h内最大气动载荷差异特征进行分析,发现6.29%样本数的最大气动载荷绝对差超过了500 Pa∙rad,主要是由于3.5 h内高空风出现异常增大、异常减小导致的,若未提前发现该变化特征,则可能会影响火箭的飞行安全。针对绝对差超过500 Pa∙rad的样本,通过建模订正可得到更接近发射后0.5 h最大气动载荷值,绝对差由713.08 Pa∙rad减小到398.22 Pa∙rad,相对误差由29.02%减小到16.32%,相关系数由0.27增大到0.71,表明该建模方法有一定的改进作用,有利于提高火箭安全飞行的保障能力。
Abstract:The maximum aerodynamic load 3 h before the launch of the rocket is one of the important data to determine whether the rocket launch can be carried out as planned, and the different characteristics between 3 h before rocket launch and launch time have rarely been studied. The maximum aerodynamic load absolute difference of the 6.29% sample size surpasses 500 Pa∙rad, according to an analysis of the features of the maximum aerodynamic load difference during 3.5 hours between December 2014 and December 2019. This is mainly due to the anomalous increase and decrease of the upper wind. If the changing characteristics are not detected in advance, it may affect the safe flight of the rocket; for samples with an absolute difference of more than 500 Pa∙rad. The correlation coefficient rose from 0.27 to 0.71, the relative error dropped from 29.02% to 16.32%, and the absolute difference dropped from 713.08 Pa∙rad to 398.22 Pa∙rad. It shows that the modeling method has a certain improvement effect, which is conducive to improving the guaranteed ability of rocket safety flight.
-
表 1 qαmax偏差值超过500 Pa∙rad、−500 Pa∙rad时,火箭发射前3 h、发射后0.5 h的大气环境差异特征
Table 1. When the qαmax deviation value exceeds 500 Pa∙rad and −500 Pa∙rad, the atmospheric environment difference characteristics of 3 h before rocket launch and 0.5 h after launch
qαmax偏差值/(Pa∙rad) Vb3h Va0.5h 数值范围/(m·s−1) 对应高度/km 平均值/(m·s−1) 数值范围/(m·s−1) 对应高度/km 平均值/(m·s−1) >500 0.80~45.19 1.50~13.00 24.59 2.00~52.50 1.50~11.30 26.68 <−500 1.11~54.15 1.50~12.00 30.55 1.67~47.44 1.50~13.50 27.65 qαmax偏差值/(Pa·rad) 风速偏差 ρb3h 数值范围/(m·s−1) 对应高度/km 平均值/(m·s−1) 数值范围/(kg·m−3) 对应高度/km 平均值/(kg·m−3) >500 −2.30~9.80 5.10~11.10 2.09 0.07~1.04 21.50~1.50 0.51 <−500 −7.21~2.22 12.00~21.50 −2.90 0.07~1.09 21.50~1.50 0.51 qαmax偏差值/(Pa·rad) ρa0.5h 大气密度偏差 数值范围/(kg·m−3) 对应高度/km 平均值/(kg·m−3) 数值范围/(kg·m−3) 对应高度/km 平均值/(kg·m−3) >500 0.07~1.04 21.50~1.50 0.51 − 0.0038 ~0.0029 6.50~5.10 −1.2×10−4 <−500 0.07~1.08 21.50~1.50 0.51 − 0.0092 ~0.0071 3.10~7.90 2.9×10−4 表 2 WRF模式中的参数化方案设计
Table 2. Parametric scheme design in WRF model
参数化方案 方案设计 微物理过程方案 WDM 5-class scheme 长波辐射方案 rrtm scheme 短波辐射方案 Goddard short wave 近地面层方案 Monin-Obukhov(Janjic) scheme 陆面过程方案 unified Noah land-surface model 边界层方案 Mellor-Yamada-Janjic TKE scheme 积云参数化方案 Betts-Miller-Janjic scheme 表 3 qαmax偏差值超过500 Pa∙rad、−500 Pa∙rad时,Vb3h、Vf0.5h,与Va0.5h之间的偏差和绝对差特征
Table 3. When the qαmax deviation value exceeds 500 Pa∙rad, −500 Pa∙rad, the deviation between Vb3h, Vf0.5h, and Va0.5h and the absolute difference characteristics
qαmax偏差值/(Pa∙rad) Vb3h偏差/(m·s−1) Vf0.5h偏差/(m·s−1) Vb3h偏差/(m·s−1) Vf0.5h偏差/(m·s−1) 数值范围 平均值 数值范围 平均值 数值范围 平均值 数值范围 平均值 >500 −10.57~2.71 −2.61 −6.24~1.87 −0.83 1.14~14.29 5.19 1.13~7.42 3.52 <−500 −1.28~8.85 3.50 −4.64~5.78 1.34 2.14~10.00 5.17 1.28~6.61 3.33 注:所有偏差均为与Va 0.5h相比较。 表 4 qαmax绝对差值超过500 Pa∙rad时,qαb3hmax、qαf0.5hmax与qαa0.5hmax之间的数理统计
Table 4. When the qαmax absolute difference exceeds500 Pa∙rad, Mathematical statistics between qαb3hmax、qαf0.5hmax and qαa0.5hmax
参数 数值范围 平均值 qαb3hmax偏差/(Pa∙rad) − 1297.62 ~924.43−101.24 qαb3hmax绝对差/(Pa∙rad) 504.98~ 1297.62 713.08 qαb3hmax相对偏差/% −41.27~43.76 0.44 qαb3hmax相对误差/% 14.15~43.76 29.02 qαf0.5hmax偏差/(Pa∙rad) −942.95~587.99 −35.95 qαf0.5hmax绝对差/(Pa∙rad) 131.21~942.95 398.22 qαf0.5hmax相对偏差/% −29.99~27.84 0.84 qαf0.5hmax相对误差/% 4.69~29.99 16.32 注:所有偏差、绝对差、相对偏差、相对误差均为与qαa0.5hmax相比较。 -
[1] 李东, 杨云飞, 胡鹏翔, 等. 运载火箭多体动力学建模与仿真技术研究[J]. 宇航学报, 2021, 42(2): 141-149. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2021.02.001LI D, YANG Y F, HU P X, et al. Research on multibody dynamic modeling and simulation technology for launch vehicles[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2021, 42(2): 141-149(in Chinese). doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2021.02.001 [2] PIAO S Y, ZHANG Y H. Frequency-domain response prediction of a launch vehicle coupled with new payloads[J]. Journal of Spacecraft and Rockets, 2021, 58(5): 1557-1562. doi: 10.2514/1.A35047 [3] 李新田, 陈新民, 陈世立, 等. 固体火箭冲压发动机设计点性能优化分析[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2021, 47(10): 1989-1995.LI X T, CHEN X M, CHEN S L, et al. Optimal analysis of design point performance of ducted rocket[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2021, 47(10): 1989-1995(in Chinese). [4] 吴杰, 张成, 李淼, 等. 基于凸优化和LQR的火箭返回轨迹跟踪制导[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2022, 48(11): 2270-2280.WU J, ZHANG C, LI M, et al. Rocket return trajectory tracking guidance based on convex optimization and LQR[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2022, 48(11): 2270-2280(in Chinese). [5] 王伟龙, 张会强. 预混C2H4/N2O推力室喷注面板热反侵着火现象数值模拟[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 60(3): 206-211.WANG W L, ZHANG H Q. Numerical simulations of ignition by soak-back heat through the injection panel in a premixed C2H4/N2O thruster[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University(Science and Technology), 2020, 60(3): 206-211(in Chinese). [6] WANG Y B, XU M, AN X M, et al. Numerical study on the trajectory of a long-range flexible rocket with large slenderness ratio[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2021, 117(3): 106959. [7] 冯瑞, 刘宇, 张章, 等. 火箭整流罩半罩再入过程连续流区气动特性数值研究[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 63(3): 414-422.FENG R, LIU Y, ZHANG Z, et al. Numerical study on the aerodynamics of a rocket fairing half in the continuum regime of the reentry process[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University(Science and Technology), 2023, 63(3): 414-422(in Chinese). [8] 程镇煌. 大型火箭风载试验[J]. 上海航天, 1996, 13(4): 3-9.CHENG Z H. Wind load test for large rocket[J]. Aerospace Shanghai (Chinese & English), 1996, 13(4): 3-9(in Chinese). [9] 赵人濂, 陈振官, 付维贤. 风切变与运载火箭设计[J]. 宇航学报, 1998, 19(2): 105-108.ZHAO R L, CHEN Z G, FU W X. Wind shear and rocket design[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 1998, 19(2): 105-108(in Chinese). [10] 余梦伦. CZ-2E火箭高空风弹道修正[J]. 导弹与航天运载技术, 2001, 249(1): 9-15.YU M L. CZ-2E ballistic correction for high altitude wind[J]. Missiles and Space Vehicles, 2001, 249(1): 9-15(in Chinese). [11] 李效明, 许北辰, 陈存芸. 一种运载火箭减载控制工程方法[J]. 上海航天, 2004, 21(6): 7-9.LI X M, XU B C, CHEN C Y. An engineering method on the control of decreasing load for a launch vehicle[J]. Aerospace Shanghai, 2004, 21(6): 7-9(in Chinese). [12] 耿光有, 李东. 由火箭一级飞行弹道分析底部力等动力参数[J]. 导弹与航天运载技术, 2014, 335(5): 10-13.GENG G Y, LI D. Analysis of dynamic parameters such as base-force for 1st stage of a launch vehicle via the trajectory[J]. Missiles and Space Vehicles, 2014, 335(5): 10-13(in Chinese). [13] 程胡华, 王益柏, 蔡其发, 等. 大气密度对运载火箭飞行的qαmax精度影响及建模分析[J]. 宇航学报, 2021, 42(3): 378-389.CHENG H H, WANG Y B, CAI Q F, et al. Influence of atmospheric density on qαmax accuracy of launch vehicle flight and modeling analysis[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2021, 42(3): 378-389(in Chinese). [14] 程胡华, 李娟, 肖云清, 等. 风偏差对火箭最大气动载荷精度的影响与分析[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2021, 47(10): 2034-2042.CHENG H H, LI J, XIAO Y Q, et al. Influence and analysis of wind deviation on rocket maximum aerodynamic load accuracy[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2021, 47(10): 2034-2042(in Chinese). [15] 董欣心, 刘莉, 葛佳昊, 等. 捆绑火箭气动载荷分布不确定性分析[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2022, 48(3): 464-472.DONG X X, LIU L, GE J H, et al. Uncertainty analysis of aerodynamic load distribution on strap-on launch vehicle[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2022, 48(3): 464-472(in Chinese). [16] 程胡华, 张军军, 王益柏, 等. 火箭最大气动载荷预报精度及建模订正分析[J]. 航天控制, 2023, 41(4): 77-83.CHENG H H, ZHANG J J, WANG Y B, et al. Analysis of the precision of the maximum aerodynamic load forecast for rockets and modeling revisions[J]. Aerospace Control, 2023, 41(4): 77-83 (in Chinese). [17] 全美兰, 刘海文, 朱玉祥, 等. 高空急流在北京“7.21”暴雨中的动力作用[J]. 气象学报, 2013, 71(6): 1012-1019.QUAN M L, LIU H W, ZHU Y X, et al. Study of the dynamic effects of the upper-level jet stream on the Beijing rainstorm of 21 July 2012[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 2013, 71(6): 1012-1019(in Chinese). [18] 孙颖姝, 周玉淑, 王咏青. 一次双高空急流背景下南疆强降水事件的动力过程和水汽源分析[J]. 大气科学, 2019, 43(5): 1041-1054. doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.1812.18168SUN Y S, ZHOU Y S, WANG Y Q. Analysis of dynamic process and moisture source on a heavy precipitation event in southern Xinjiang associated with the double upper-level jet[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 2019, 43(5): 1041-1054(in Chinese). doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.1812.18168 [19] 程胡华, 成巍, 沈洪标, 等. 火箭发射前后3.5 h内高空风差异特征及预报[J]. 应用气象学报, 2022, 33(4): 400-413.CHENG H H, CHENG W, SHEN H B, et al. Upper wind difference characteristics and forecast within 3.5 hours before and after rocket launch[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science, 2022, 33(4): 400-413(in Chinese). [20] 朱莉, 王曼, 李华宏, 等. 基于WRF模式的云南短时强降水物理量特征[J]. 大气科学学报, 2019, 42(5): 755-768.ZHU L, WANG M, LI H H, et al. Analysis of physical quantity features of Yunnan short-time severe rainfall based on WRF model[J]. Transactions of Atmospheric Sciences, 2019, 42(5): 755-768(in Chinese). [21] 刘郁珏, 苗世光, 刘磊, 等. 修正WRF次网格地形方案及其对风速模拟的影响[J]. 应用气象学报, 2019, 30(1): 70-81.LIU Y J, MIAO S G, LIU L, et al. Effects of a modified sub-grid-scale terrain parameterization scheme on the simulation of low-layer wind over complex terrain[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science, 2019, 30(1): 70-81(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: