-
摘要:
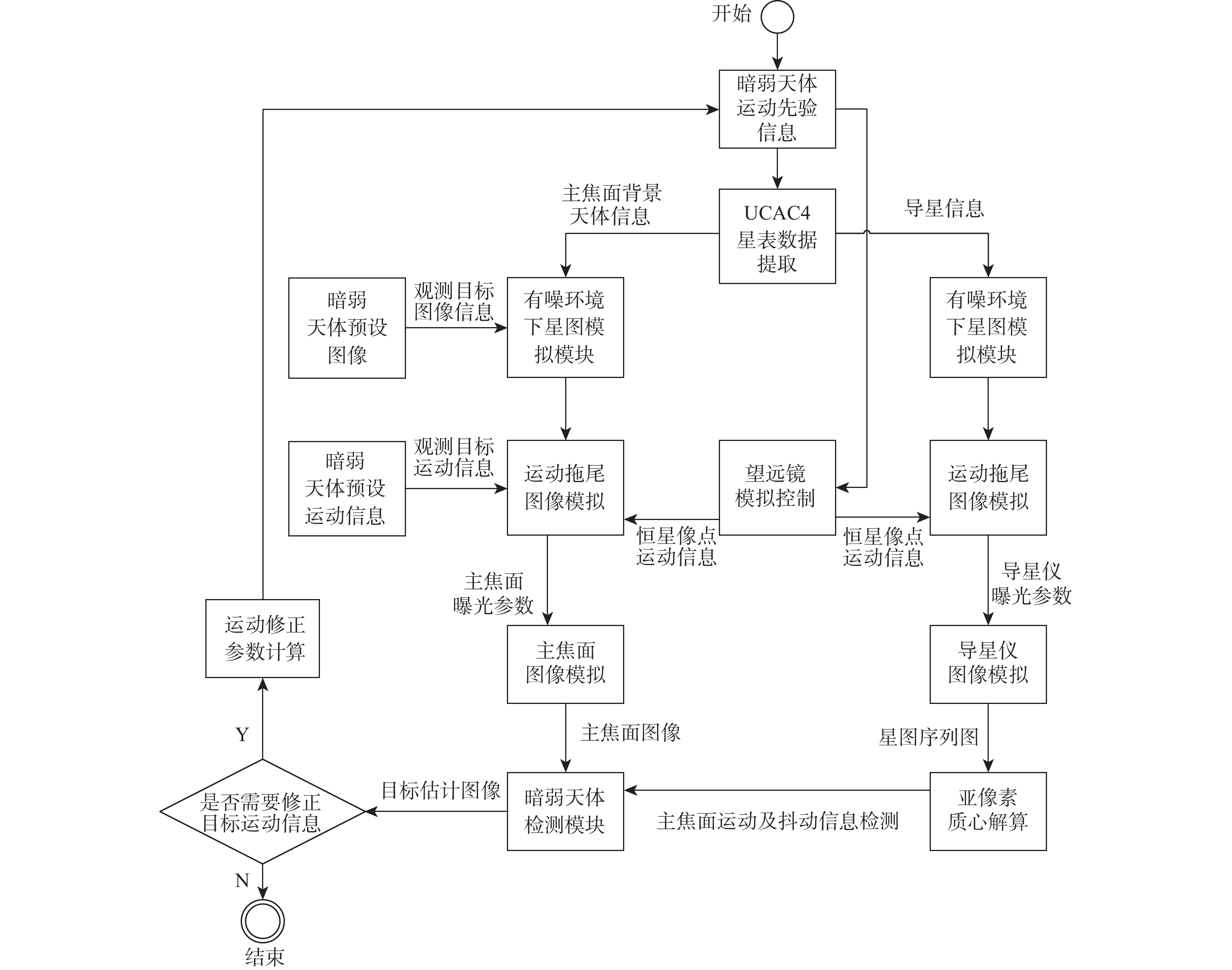
暗弱空间运动小目标检测在航天及军事领域有着广泛的应用,为提高空间目标监视系统的探测能力,提出并设计了导星辅助运动暗弱天体检测系统,该系统由星图模拟、图像去噪、质心解算、运动先验信息反向传播和主焦面成像组成。对星表及星空环境进行研究,确保星点坐标和噪声模拟的准确性;通过引入抖动误差、噪声误差和运动先验误差,更真实地模拟望远镜所处星空环境造成的误差影响,同时设计导星辅助的方法消除上述误差,并通过运动先验信息反向传播模块调整系统。实验证明:所设计的系统不仅可以模拟真实星图,而且可以减弱星空环境对望远镜的误差影响。
-
关键词:
- 暗弱目标 /
- 空间目标检测 /
- 美国海军天文台导航星表 /
- 误差分析 /
- 系统仿真
Abstract:The detection of faint moving objects in space is widely used in aerospace and military fields. In order to improve the detection capability of the space object monitoring system, a guide star assisted detection system for moving faint objects is proposed and designed. The system consists of star map simulation, image denoising, centroid calculation, motion backpropagation and main focal plane imaging. Firstly, the star catalog and the starry sky environment are studied to ensure the accuracy of the star point position and noise simulation. Secondly, to realistically simulate the starry sky environment where the telescope is located, jitter errors, noise errors, and motion prior errors are introduced. At the same time, a guide star assisted method is designed to eliminate the above errors, and the system is adjusted through the motion back-transmission module. Experiments prove that the designed system can not only simulate the real star map, but also slow down the error influence of the star environment on the telescope.
-
Key words:
- faint object /
- space object detection /
- USNO CCD astrograph catalog /
- error analysis /
- system simulation
-
表 1 残差背景噪声统计
Table 1. Residual background noise statistics
图像 均值/像素 标准差/像素 原始图像 63.25 18.73 背景消除图像 0.56 0.77 表 2 单导星多帧消融实验结果
Table 2. Results of ablation experiment for single guide star with multiple frames
导星帧数/帧 运动先验误差/(像素·帧−1) 抖动误差/(像素·帧−1) 2 1.37 0.631 3 1.37 0.562 4 1.37 0.560 表 3 多导星2帧消融实验结果
Table 3. Results of ablation experiment for multiple guide stars with two frames
导星数/个 运动先验误差/(像素·帧−1) 抖动误差/(像素·帧−1) 1 1.37 0.631 2 1.37/0.751 0.491 3 1.37/0.751/−0.107 0.412 表 4 条状目标端点定位结果
Table 4. Positioning results of strip target endpoints
目标 坐标 精确坐标 检测坐标 修正坐标 原始定位误差/像素 修正定位误差/像素 定位误差降低量/像素 目标1 x坐标 116.03 110.21 119.25 5.82 3.22 2.60 y坐标 89.29 83.51 90.13 5.78 0.84 4.94 目标2 x坐标 330.57 340.68 338.51 10.11 7.94 2.17 y坐标 230.41 240.72 237.16 10.31 6.75 3.56 目标3 x坐标 793.15 810.35 802.57 17.20 9.42 7.78 y坐标 701.36 715.69 703.86 14.33 2.50 11.83 -
[1] 王传军. 丽江2.4米望远镜观测控制系统关键技术研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院云南天文台), 2019.WANG C J. Research on key technologies of observation and control system of Lijiang 2.4 m telescope[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Yunnan Observatories, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2019(in Chinese). [2] 赵玥皎. 12 mag精细导星星库构建及解算方法研究[D]. 上海: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院上海技术物理研究所), 2017: 10-15.ZHAO Y J. Study on the construction and calculation method of 12 mag fine guide star library[D]. Shanghai: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Shanghai Institute of Technical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2017: 10-15(in Chinese). [3] 崔祥祥, 王宏力, 陆敬辉, 等. 适用于小视场星敏感器的导航星表构建方法[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2015, 44(4): 1249-1253.CUI X X, WANG H L, LU J H, et al. Guide star selection method for star tracker with thin field of view[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2015, 44(4): 1249-1253(in Chinese). [4] ZACHARIAS N, FINCH C T, GIRARD T M, et al. The fourth USNO CCD astrograph catalog (UCAC4)[J]. The Astronomical Journal, 2013, 145(2): 44. doi: 10.1088/0004-6256/145/2/44 [5] ZACHARIAS N, URBAN S E, ZACHARIAS M I, et al. The second US Naval Observatory CCD astrograph catalog (UCAC2)[J]. The Astronomical Journal, 2004, 127(5): 3043-3059. doi: 10.1086/386353 [6] BERRIMAN G B. The NASA/IPAC infrared science archive (IRSA) as a resource in supporting observatory operations[C]//Observatory Operations: Strategies, Processes, and Systems II. Bellingham: SPIE, 2008, 7016: 379-387. [7] 朱长征, 居永忠, 杜晓辉. 导航星库制定方法研究[J]. 宇航学报, 2010, 31(5): 1327-1330.ZHU C Z, JU Y Z, DU X H. Approach to founding a guide star catalogue[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2010, 31(5): 1327-1330(in Chinese). [8] 王松林, 蒋峥. 改进的自适应加权中值滤波算法[J]. 传感器与微系统, 2016, 35(11): 128-131.WANG S L, JIANG Z. Improved adaptive weighted median filtering algorithm[J]. Transducer and Microsystem Technologies, 2016, 35(11): 128-131(in Chinese). [9] 邹永宁, 姚功杰. 自适应窗口形状的中值滤波[J]. 光学 精密工程, 2018, 26(12): 3028-3039. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20182612.3028ZOU Y N, YAO G J. Median filtering algorithm for adaptive window shape[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2018, 26(12): 3028-3039(in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/OPE.20182612.3028 [10] 宿德志. 一种快速稳定的星图识别方法及单星模拟器的调校[D]. 长沙: 国防科学技术大学, 2010: 15-20.SU D Z. A fast and stable star map recognition method and the adjustment of single star simulator[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2010: 15-20(in Chinese). [11] 雍杨, 王敬儒, 张启衡. 基于多特征融合的弱小运动目标识别[J]. 量子电子学报, 2006, 23(5): 594-598. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5461.2006.05.003YONG Y, WANG J R, ZHANG Q H. Small moving target recognition based on multi-feature fusion[J]. Chinese Journal of Quantum Electronics, 2006, 23(5): 594-598(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5461.2006.05.003 [12] 张兵. 光学图像末制导中的点目标检测与识别算法研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科学技术大学, 2005: 20-25.ZHANG B. Research on point target detection and recognition algorithm in optical image terminal guidance[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2005: 20-25(in Chinese). [13] 赵玥皎, 尹达一, 许春, 等. 16 mv精细导星星库构建与评价[J]. 应用光学, 2017, 38(3): 385-391.ZHAO Y J, YIN D Y, XU C, et al. Construction and evaluation of 16 mv fine guide star catalog[J]. Journal of Applied Optics, 2017, 38(3): 385-391(in Chinese). [14] 刘南南, 徐抒岩, 曹小涛, 等. 自适应加权质心算法在高精度星点定位中的应用[J]. 光学学报, 2016, 36(8): 121-126.LIU N N, XU S Y, CAO X T, et al. Application of adaptive weighted centroid algorithm in high accuracy star localization[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2016, 36(8): 121-126(in Chinese). [15] 庞文. 天基可见光空间目标检测识别研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科学技术大学, 2014: 35-45.PANG W. Research on detection and recognition of space-based visible light space targets[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2014: 35-45(in Chinese). [16] 韩思奇, 王蕾. 图像分割的阈值法综述[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2002, 24(6): 91-94.HAN S Q, WANG L. A survey of thresholding methods for image segmentation[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2002, 24(6): 91-94(in Chinese). [17] 任剑峰, 饶长辉, 李明全. 一种Hartmann-Shack波前传感器图像的自适应阈值选取方法[J]. 光电工程, 2002, 29(1): 1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2002.01.001REN J F, RAO C H, LI M Q. An adaptive threshold selection method for Hartmann-Shack wavefront sensor[J]. Opto-electronic Engineering, 2002, 29(1): 1-5(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2002.01.001 [18] YANG J, LIANG B, ZHANG T, et al. A novel systematic error compensation algorithm based on least squares support vector regression for star sensor image centroid estimation[J]. Sensors, 2011, 11(8): 7341-7363. doi: 10.3390/s110807341 [19] 贾辉. 高精度星敏感器星点提取与星图识别研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科技大学, 2011: 25-35.JIA H. Research on star point extraction and star map identification of high-precision star sensors[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2011: 25-35(in Chinese). [20] 张己化, 范如玉, 赵宁, 等. 强背景下光电系统空间目标探测能力[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2014, 43(1): 212-216. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2014.01.038ZHANG J H, FAN R Y, ZHAO N, et al. Electro-optic system detection ability to space-object in strong background[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2014, 43(1): 212-216(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2014.01.038 -







 下载:
下载: