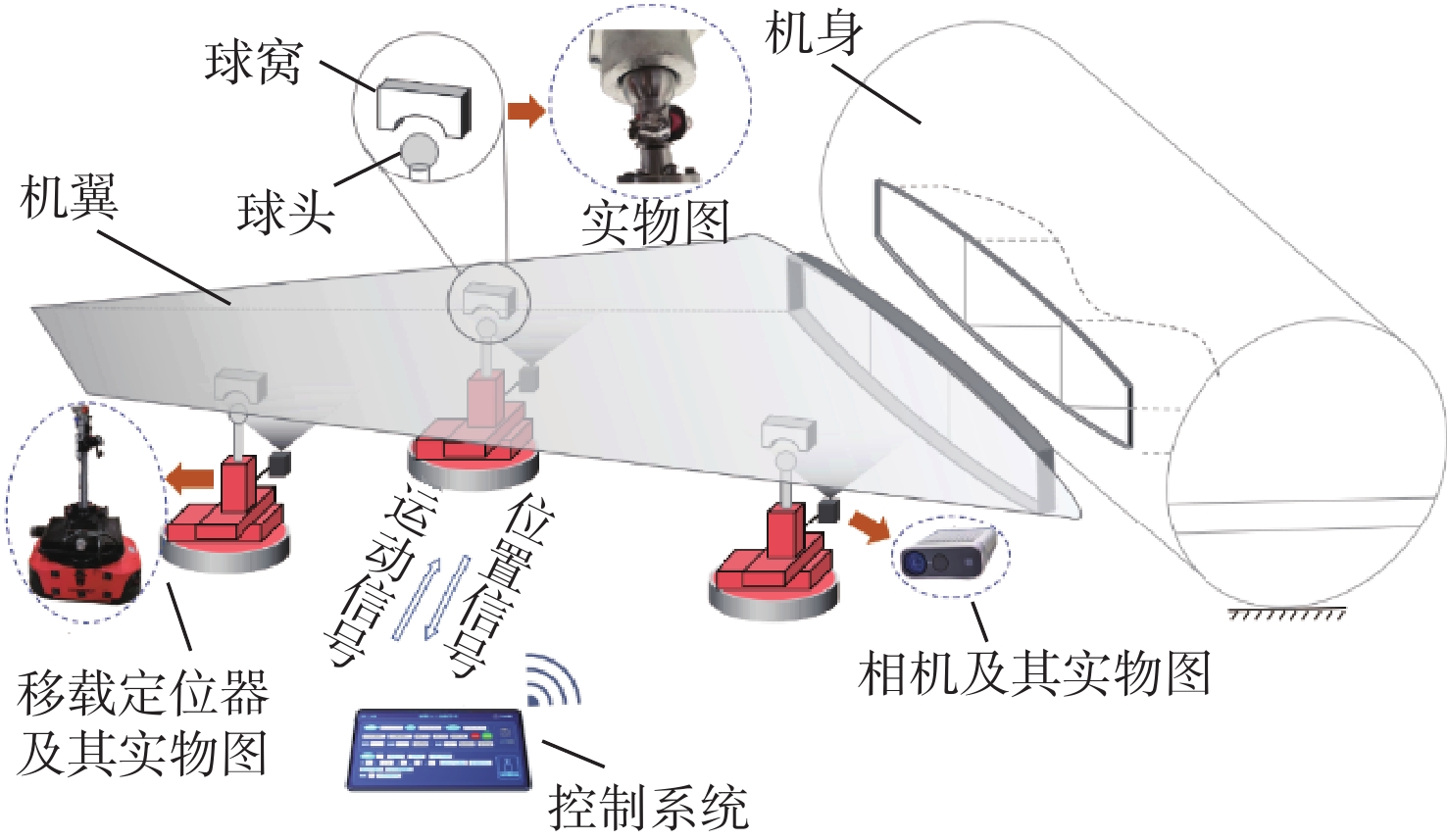
Vision-based mobile positioner insertion method for pose alignment of large components
-
摘要:
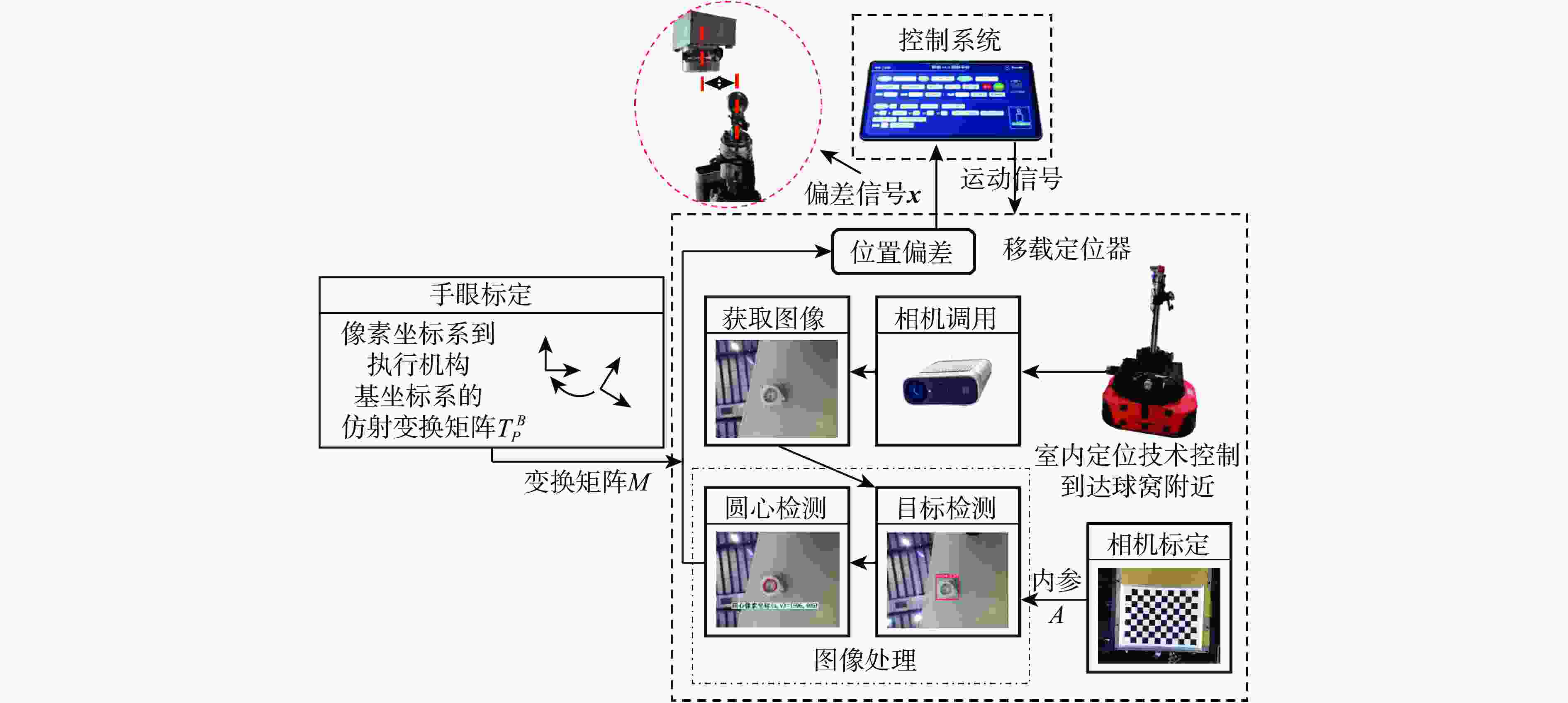
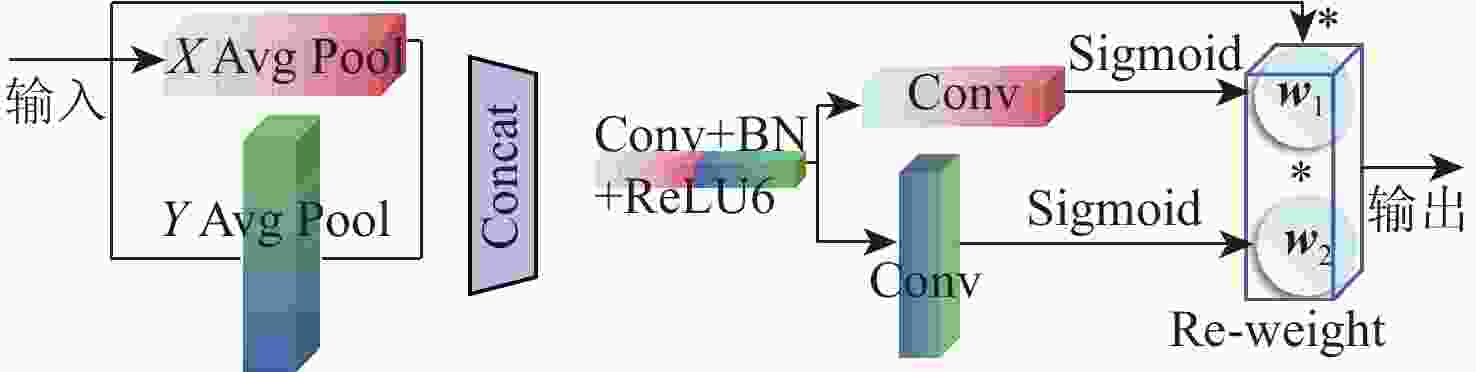
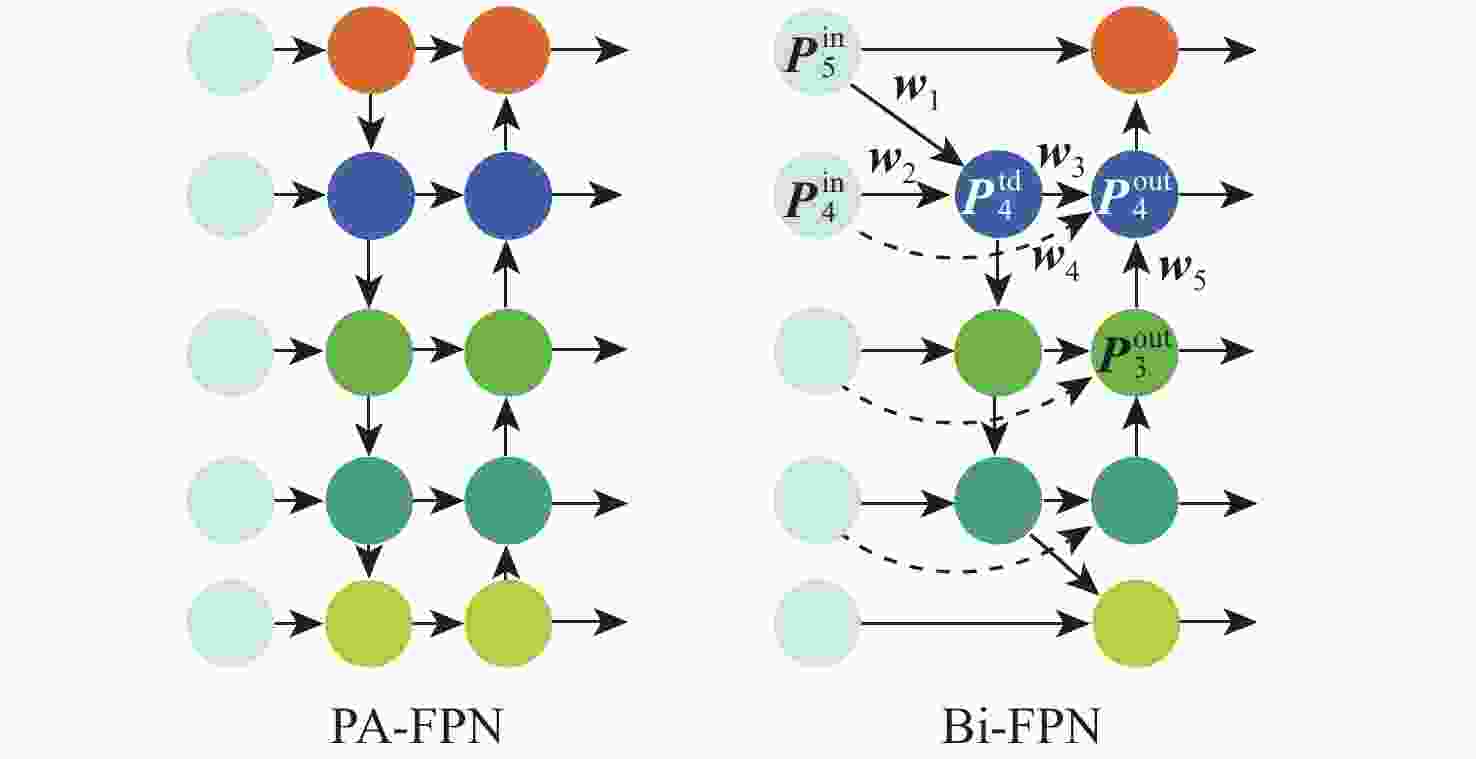
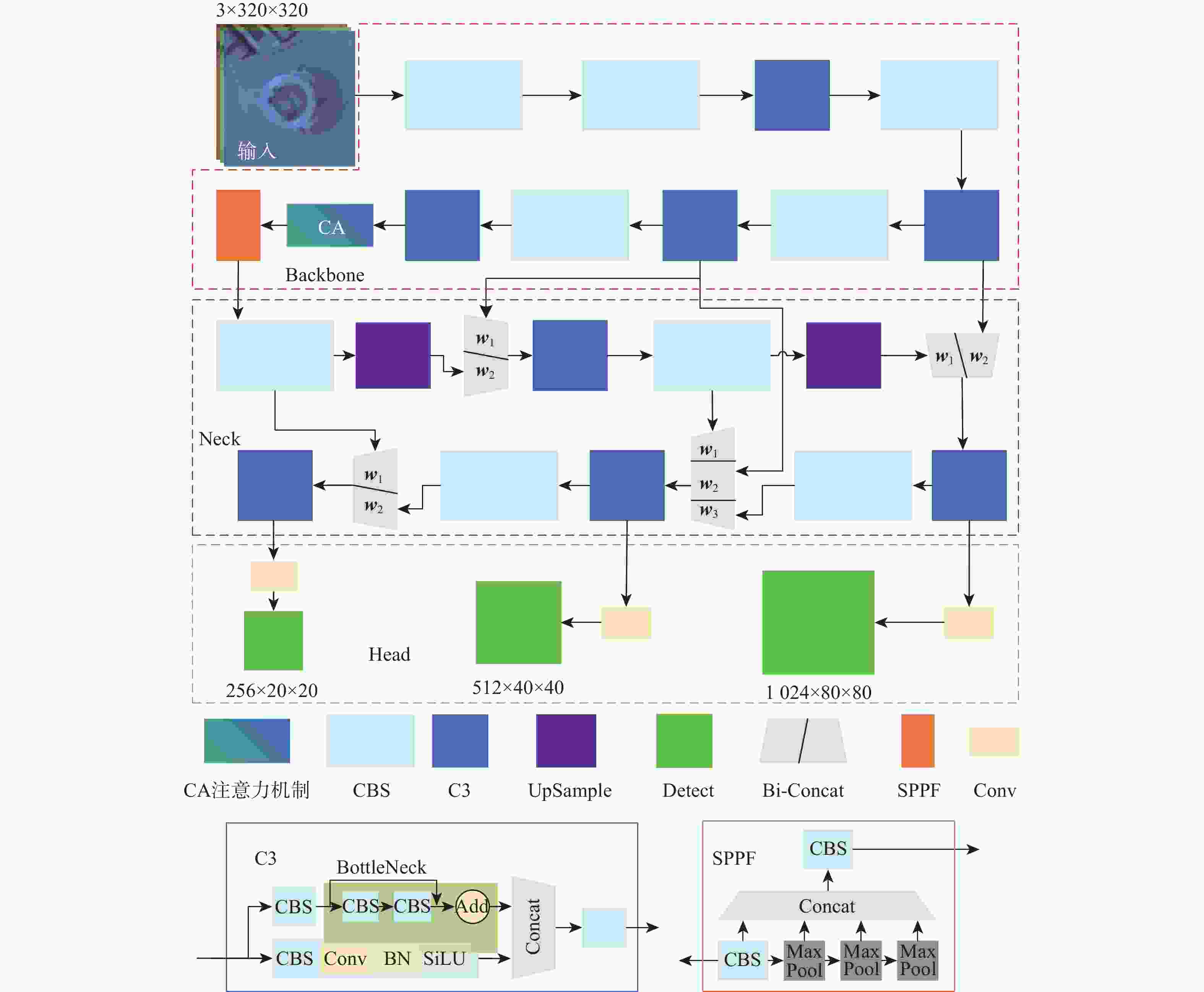
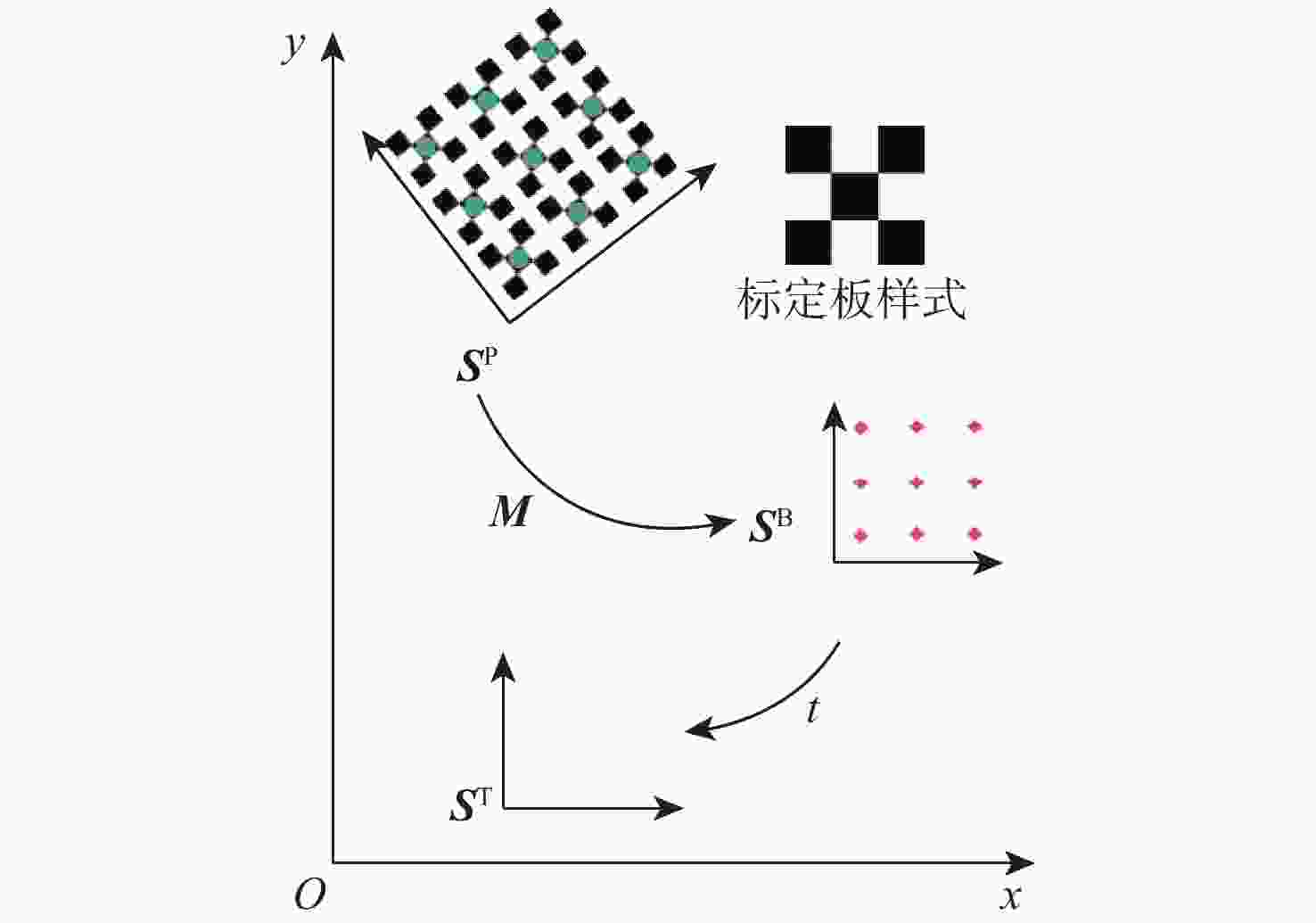
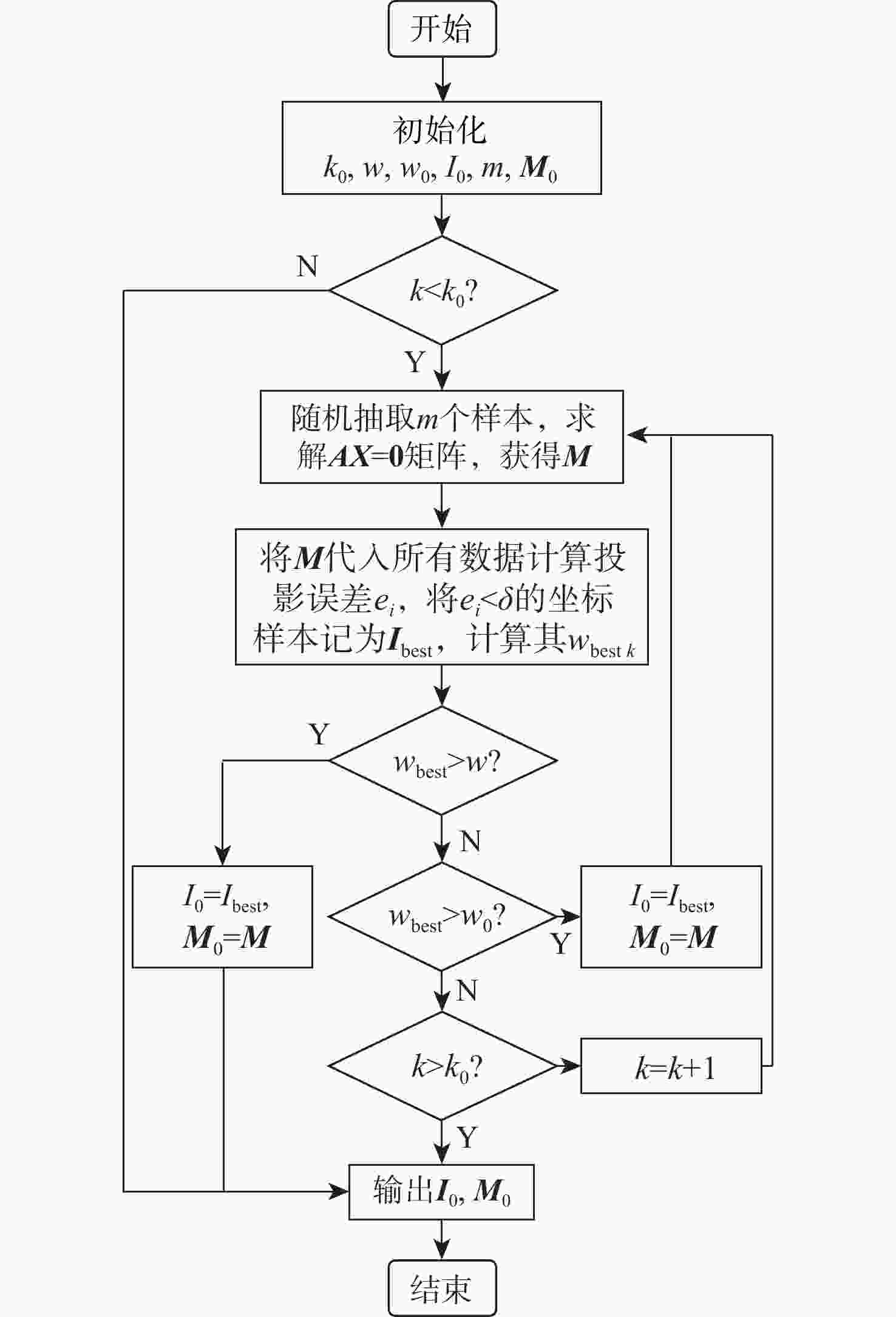
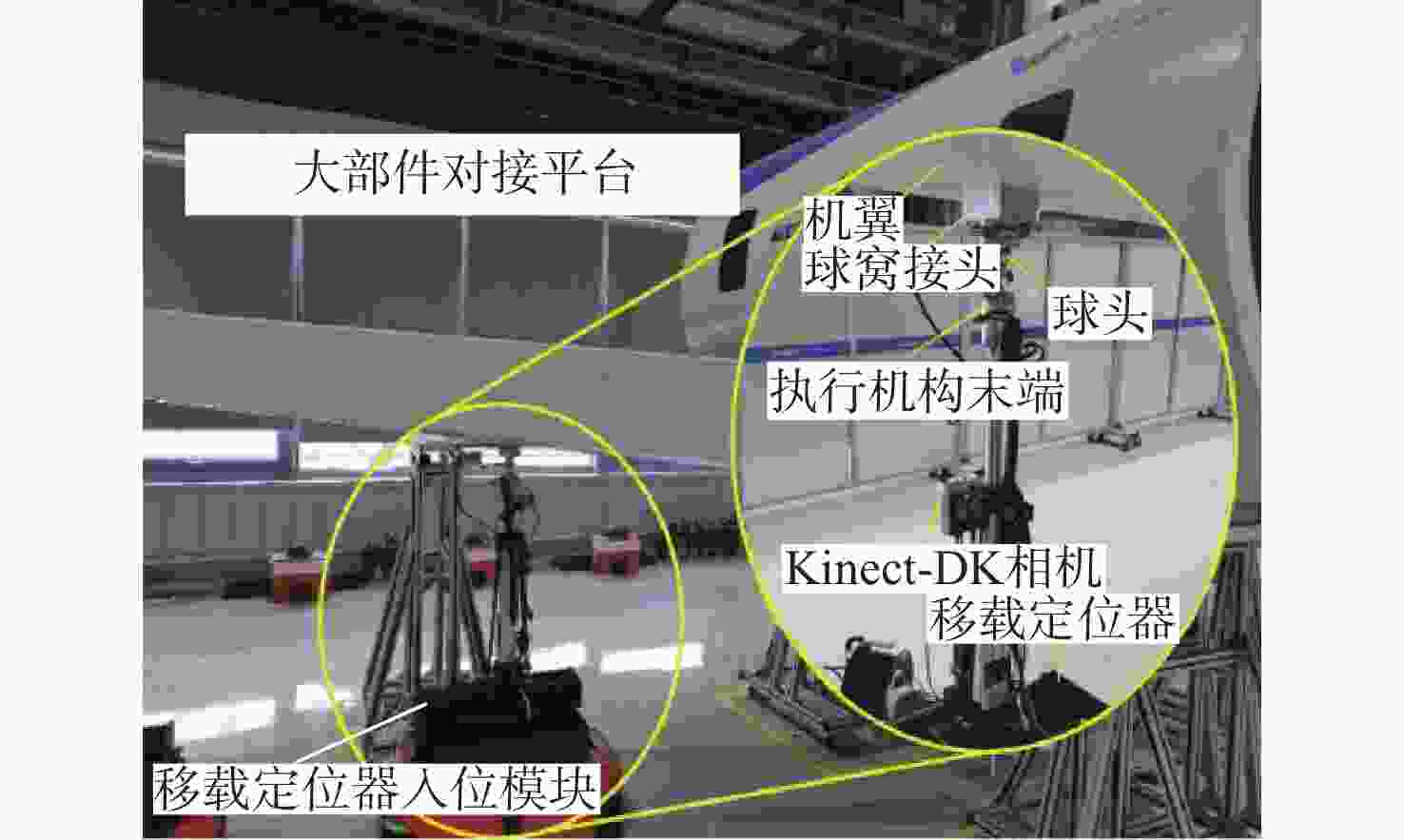
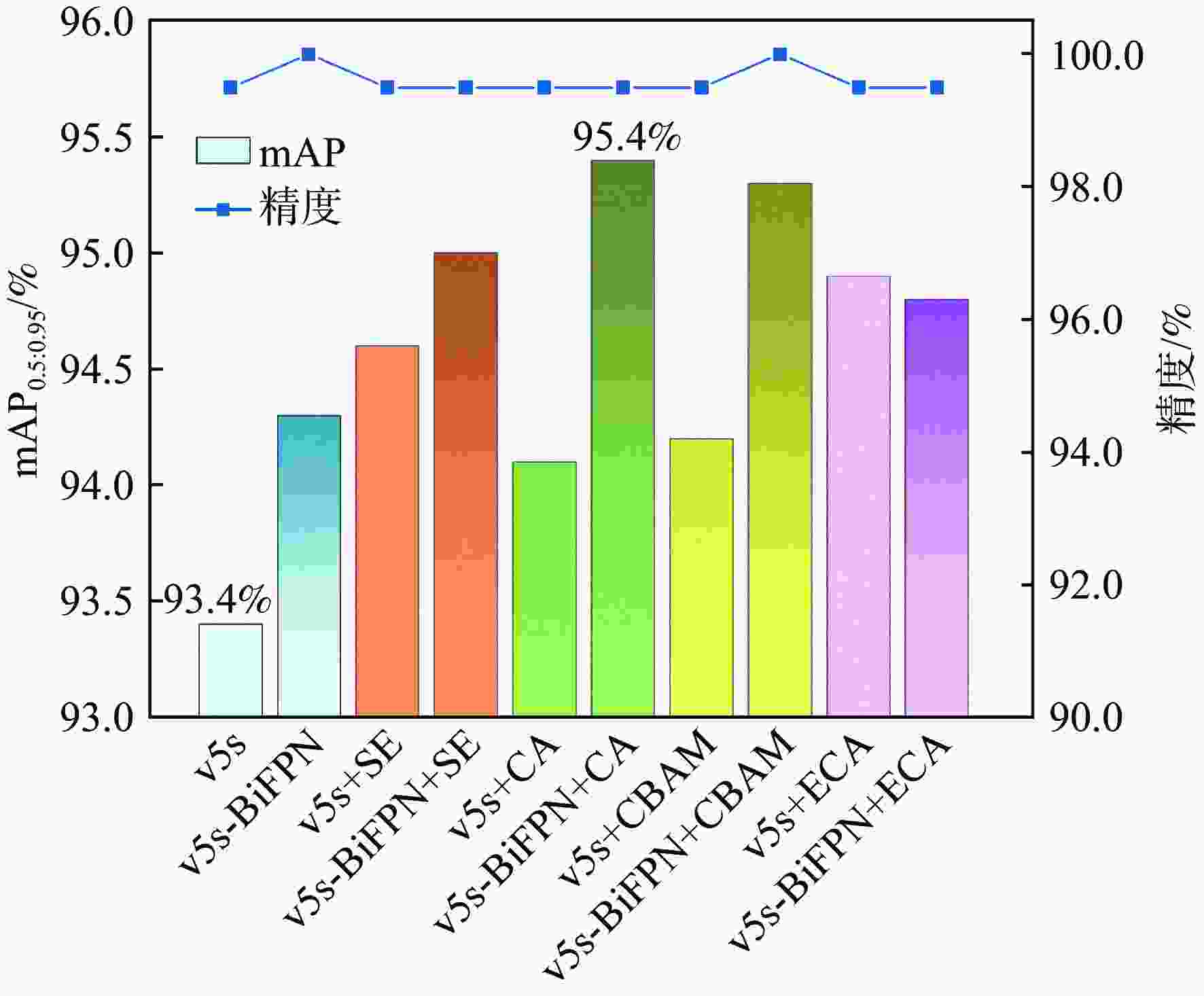
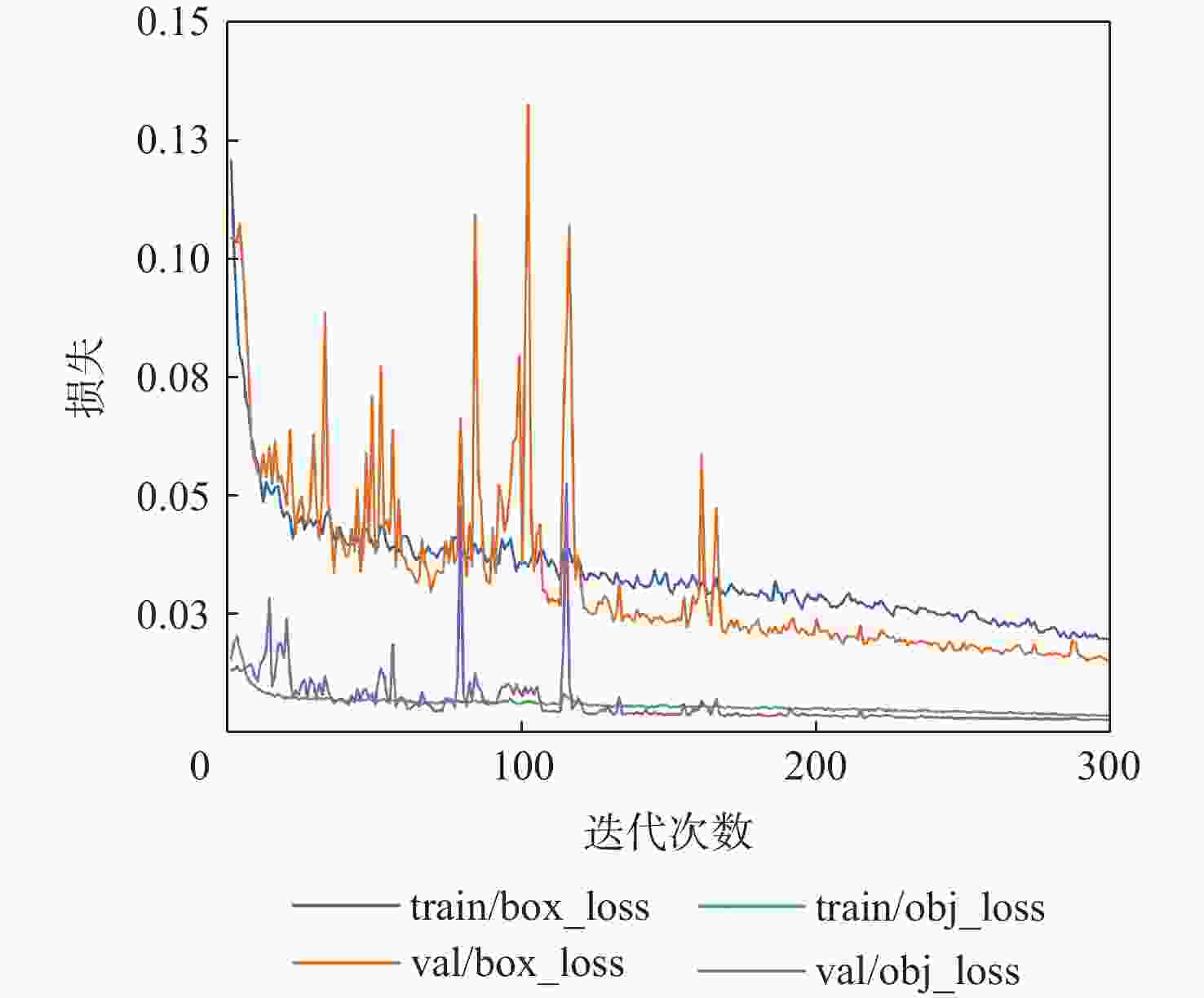
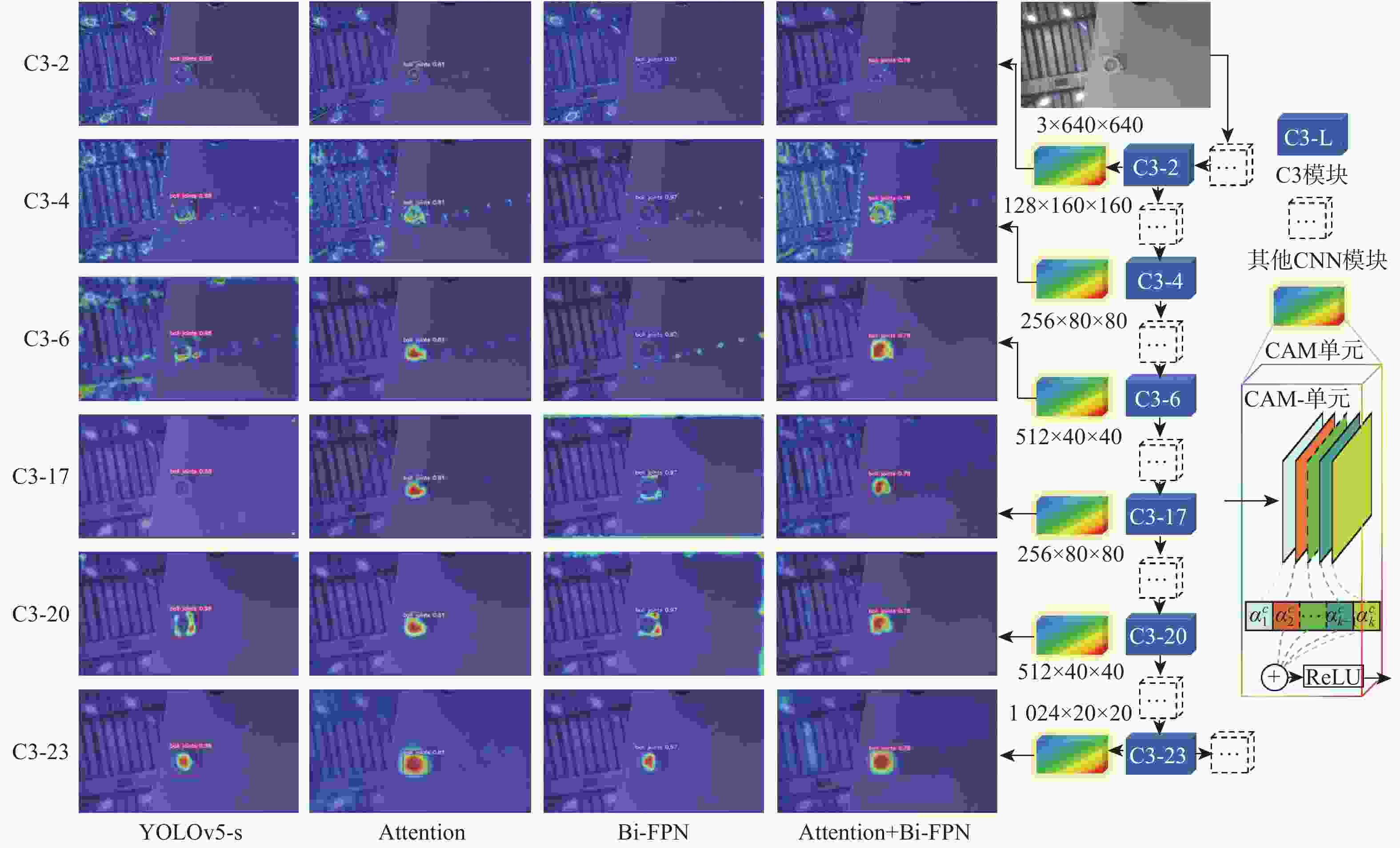
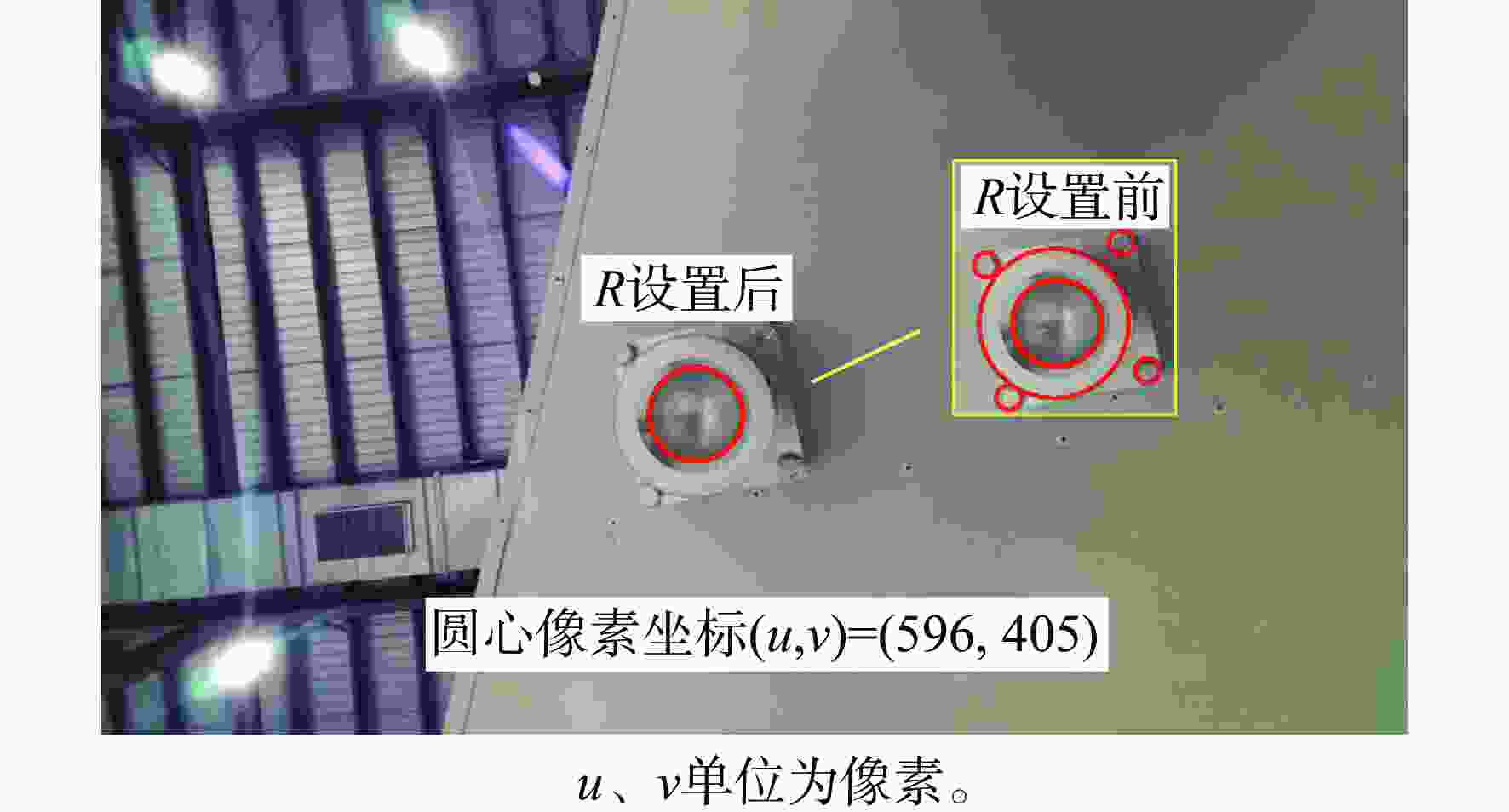
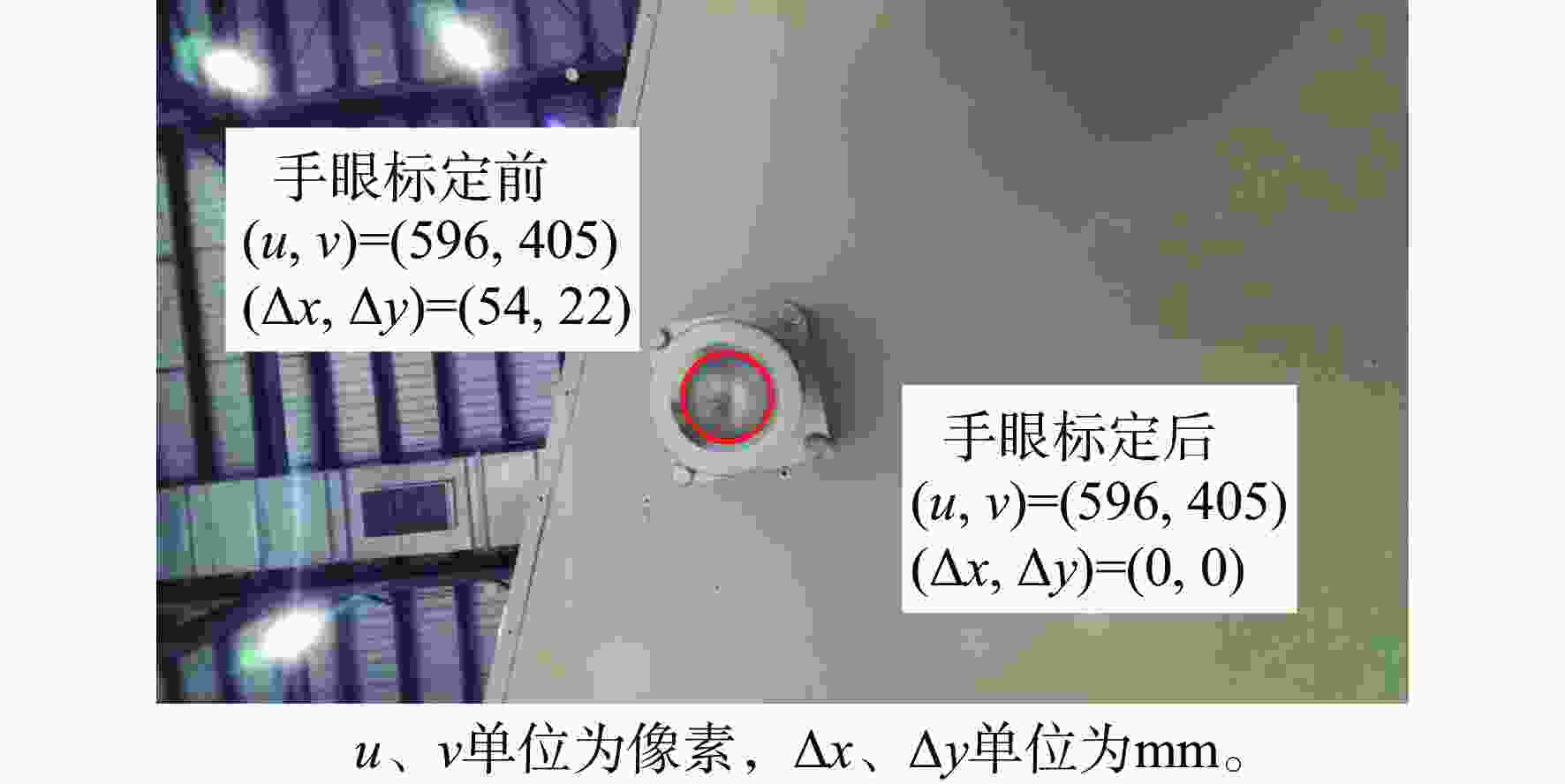
大部件对接是飞机装配的重要一环。在大部件对接前,需要将移载定位器球头插入部件上的支撑球窝接头。目前移载定位器末端球头插入球窝主要通过人工引导,定位器入位误差大、效率低,且仍存在一定安全风险。提出了一种基于视觉引导的移载式定位器入位方法。为了获取球窝位置,使用YOLO-v5s模型实现了球窝接头目标检测并对模型做出了改进:在主干网络与颈部网络之间加入CA注意力机制模块,将加权双向特征金字塔网络(Bi-FPN)作为颈部网络,使用Grad-CAM技术对模型运行过程进行了可视化,结果表明:改进后YOLO-v5s模型的mAP0.5:0.95增长了2%,改进后模型精确度保持在99.5%以上,帧率可达到30。通过手眼标定技术统一坐标系,设计了融合随机采样一致性(RANSAC)算法的线性模型用于求解变换矩阵,与传统手眼标定算法相比精度提高了22.0%~77.2%。基于大部件移载对接实验平台,开展了移载定位器视觉引导入位实验,实验结果表明:入位引导误差在1 mm以内,满足大部件对接移载定位器引导入位的精度要求。
Abstract:The pose alignment of large components is a critical step in aircraft assembly. Prior to the assembly of large components, it is necessary to insert the ball-head of the positioner into the ball socket to support the component. Currently, the state-of-the-art process is primarily guided by manual operation, resulting in significant positioning errors, low efficiency, and potential safety risks. This paper proposes a vision-based mobile positioner insertion method. Firstly, a modified YOLO-v5s object detection model is applied to obtain the position of the ball socket. Then, a coordinate attention (CA) attention mechanism module is added between the backbone network and neck network. The Bidirectional feature pyramid network (Bi-FPN) was adopted as the neck network, and the gradient-weighted class activation mapping (Grad-CAM) is used to visualize the operation of the model. The results show that up to 30 frames per second, the precision of the updated YOLO-v5s model surpasses 99.5%, with a 2% increase in mAP0.5:0.95. The coordinate system unification is then accomplished via hand-eye calibration methods, and the transformation matrix is calculated using a linear model that incorporates the random sample consensus (RANSAC) algorithm. Compared to traditional hand-eye calibration algorithms, the accuracy is improved by 22.0%−77.2%. Finally, the experimental validation of the proposed method is conducted, which demonstrates that the error of insertion is within 1mm, which fulfills the precision requirements of the insertion in the pose alignment of large components.
-
Key words:
- aircraft assembly /
- mobile positioner /
- computer vision /
- attention mechanism /
- deep learning
-
表 1 实验工作站硬件配置
Table 1. Hardware configuration of experimental workstation
项目 信息 GPU GeForce RTX3070Ti,显存8 GB CPU Intel(R)Core(TM) i7-10700,
主频2.90 GHz,内存32 GBPython版本 Python 3.8 IDE PyCharm CUDA版本 11.3 CUDNN版本 8.9.2 深度学习框架 PyTorch-1.10.1 表 2 各模型评估结果
Table 2. Evaluation results for each model
模型 P R mAP0.5:0.95/% 参数量 帧率/(帧·s−1) YOLOv7-tiny 1 1 92.9 6.01×106 250 YOLOX-s 1 1 95.1 8.97×106 20 YOLOv5-s 1 1 93.4 7.23×106 30 本文 1 1 95.4 7.32×106 30 表 3 不同模型手眼标定结果
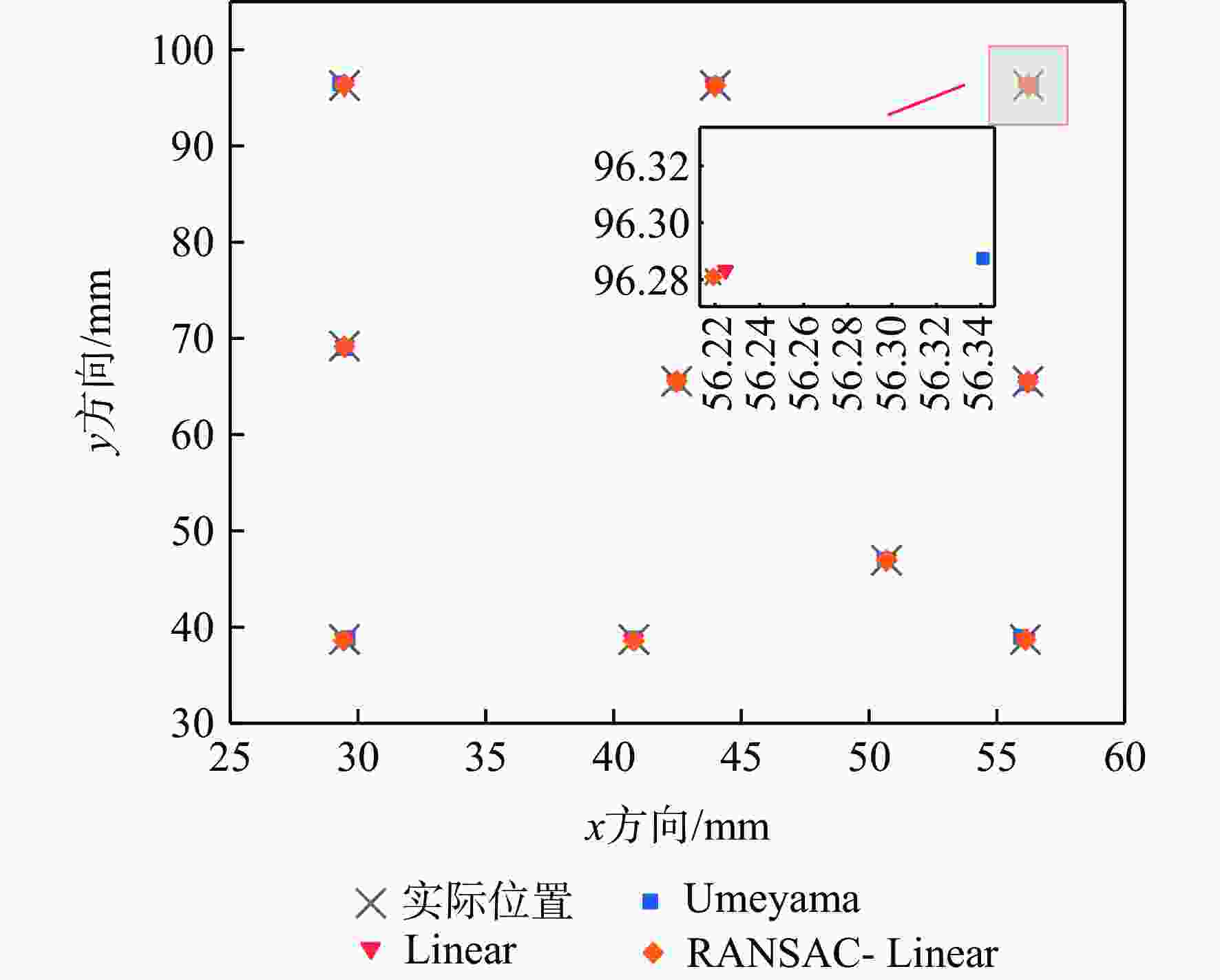
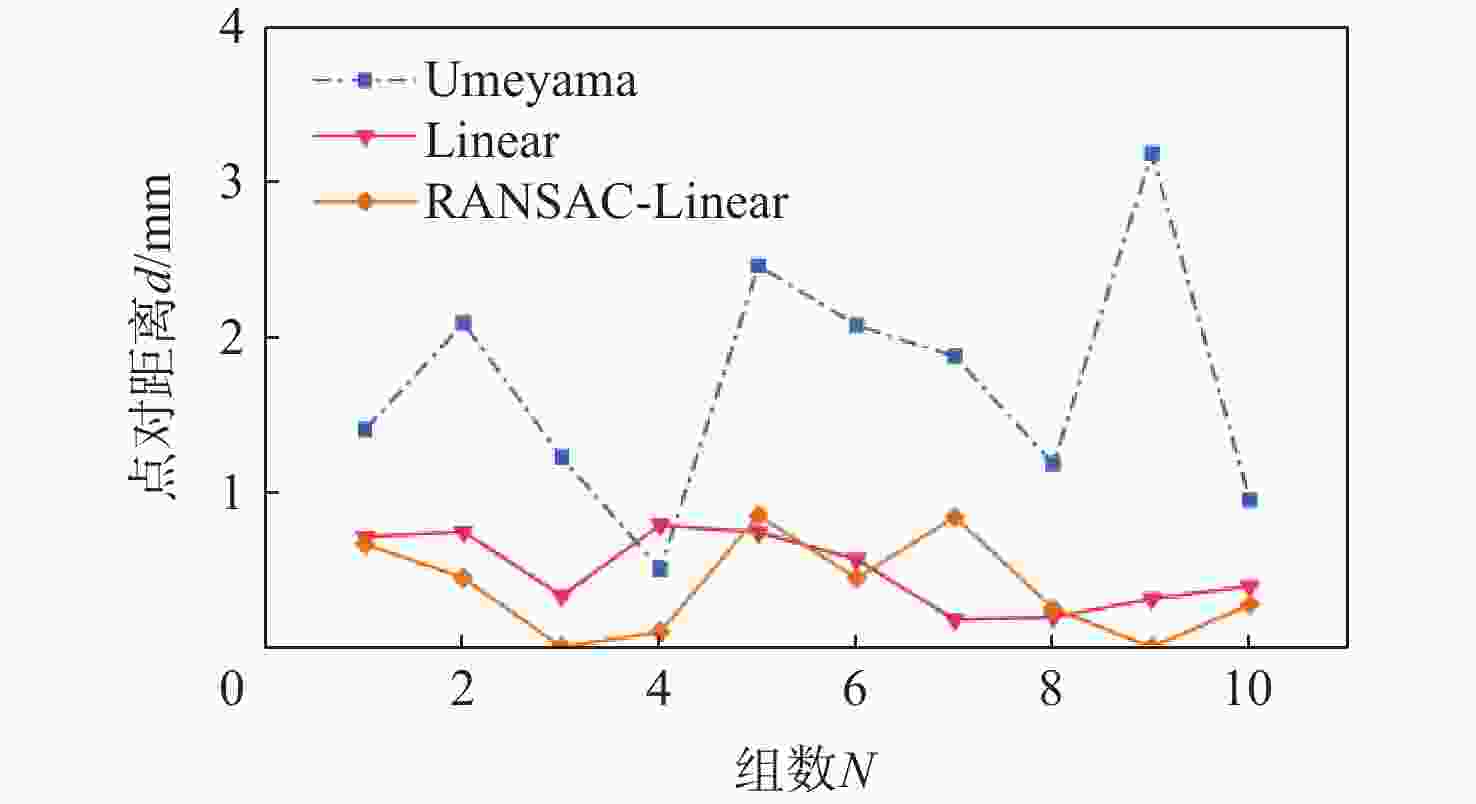
Table 3. Hand-eye calibration results for different models
mm 算法 均值 标准差 方差 Umeyama 1.694 0.868 0.754 Linear 0.496 0.478 0.229 RANSAC- Linear 0.387 0.550 0.303 表 4 入位误差测量
Table 4. Insertion error measurement
位置
序号定位器
坐标$({X_i},{Y_i})$/mm三维扫描仪拟合
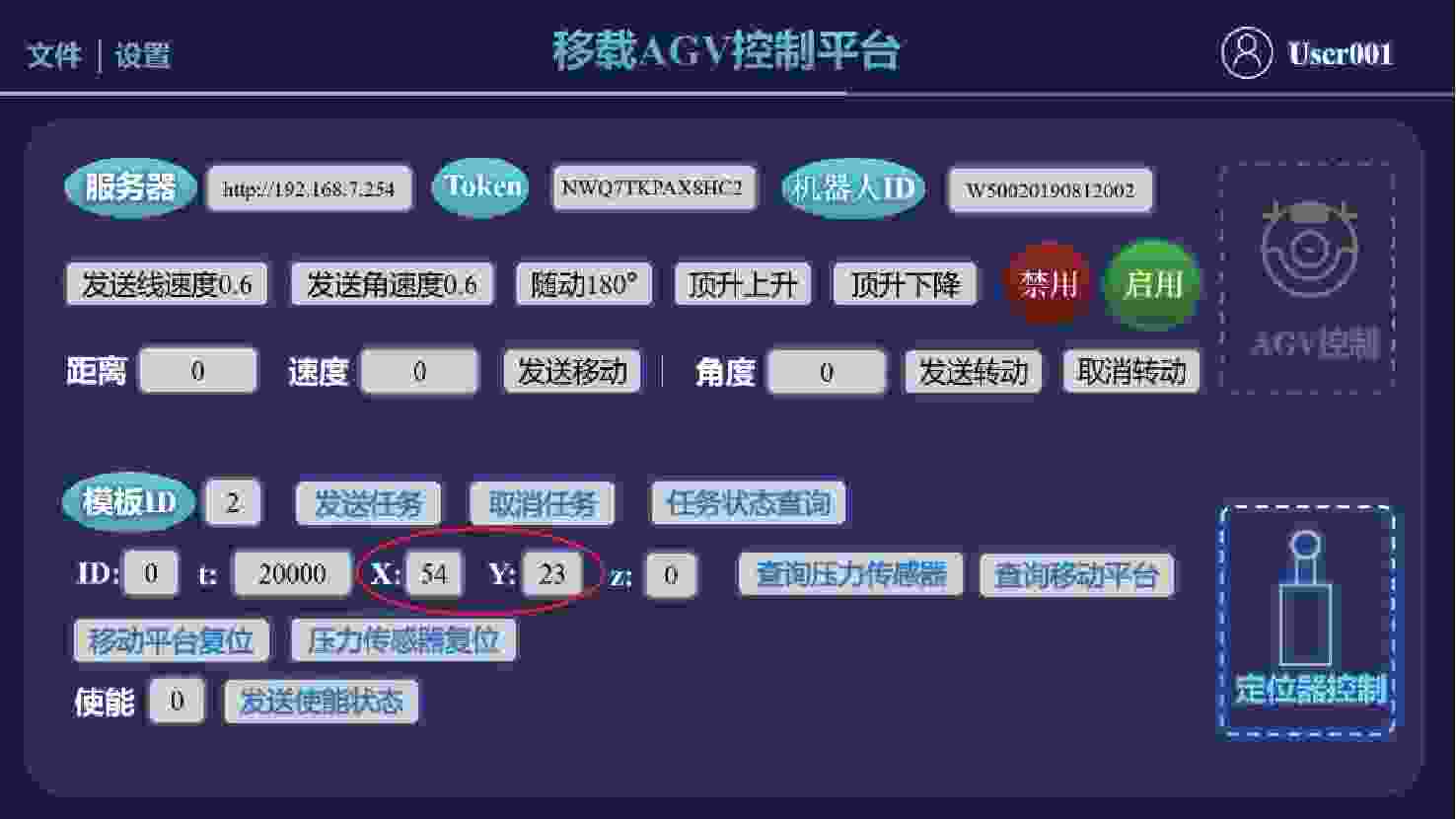
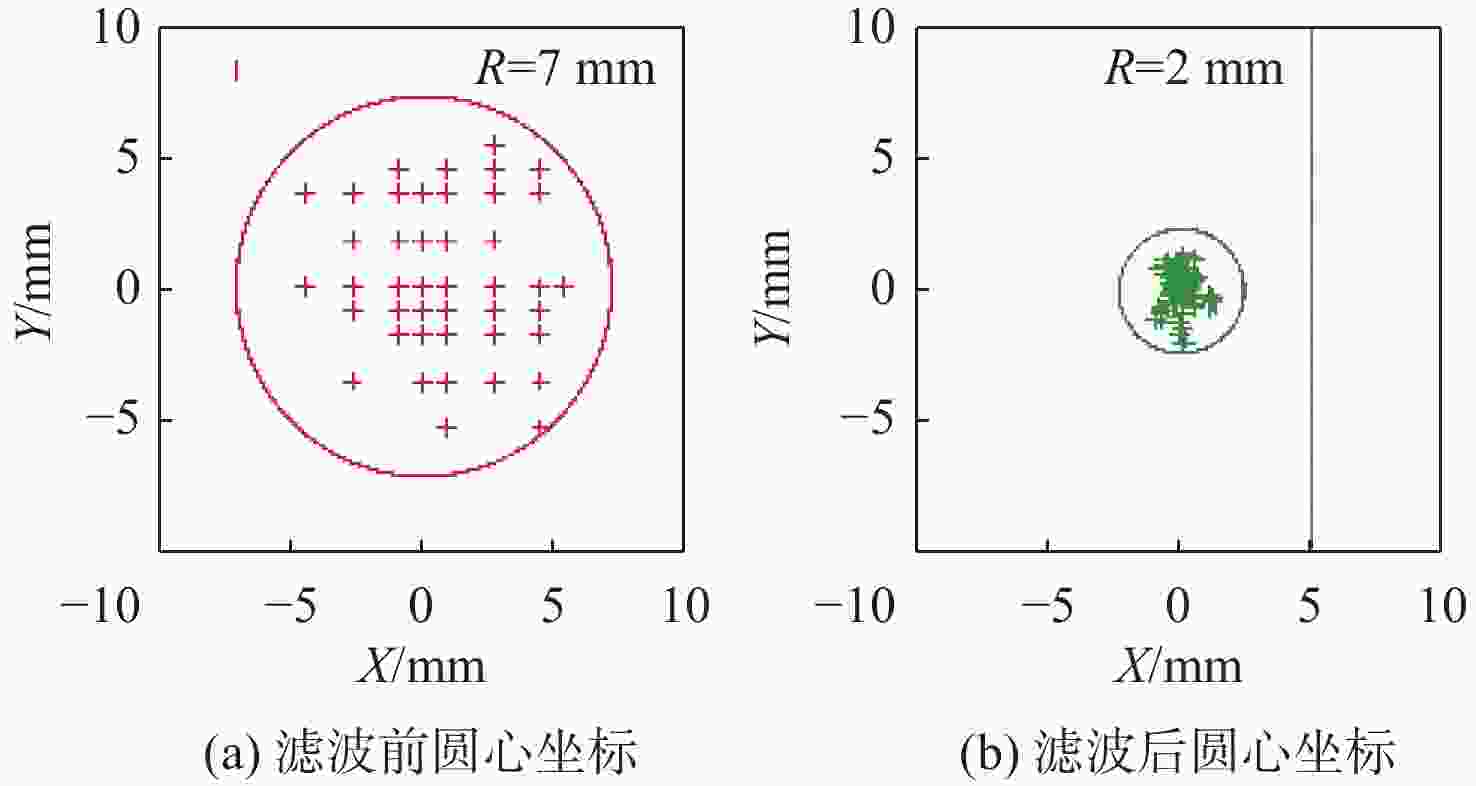
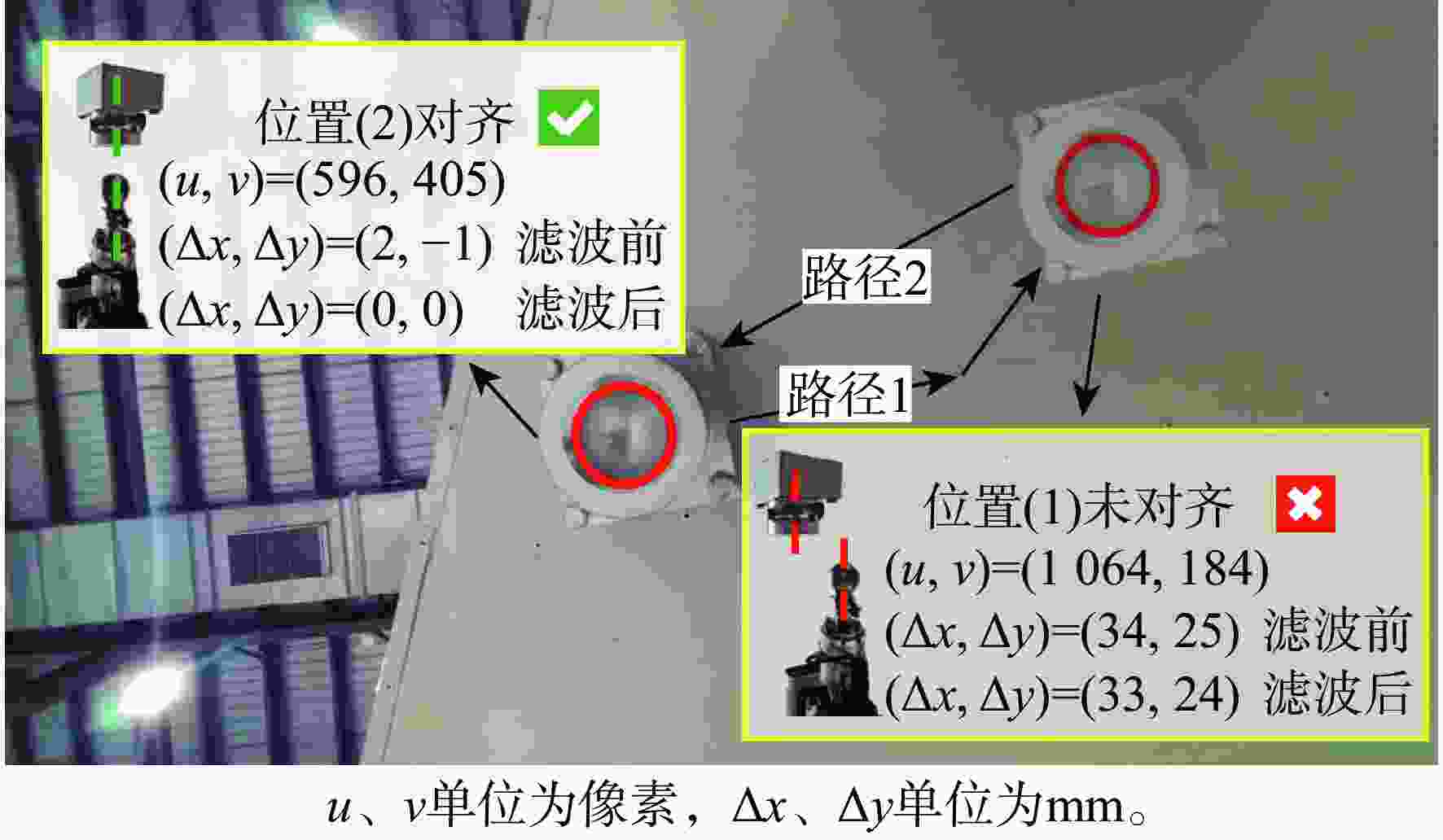
坐标$ ({x_i},{y_i}) $/mm偏差${e_1}$/mm 1 (53,23) (933.87,4 046.29) 0.908 2 (54,22) (933.84,4 046.37) 0.859 3 (55,22) (932.9,4 046.29) 0.279 4 (54,22) (934.9,4 046.31) 1.915 5 (53,23) (933.9,4 046.29) 0.937 6 (53,23) (932.91,4 046.29) 0.275 7 (54,24) (933.95,4 046.30) 0.982 8 (54,23) (932.91,4 046.44) 0.142 9 (54,23) (933.96,4 046.31) 0.990 10 (54,23) (933.96,4 046.29) 0.995 注:${e_1}$均值为0.828 mm,${e_1} $标准差为0.512 mm,${e_1} $方差为0.262 mm。 -
[1] 薛红前. 飞机装配工艺学[M]. 西安: 西北工业大学出版社, 2015: 1-2.XUE H Q. Aircraft assembly technology[M]. Xi’an: Northwestern Polytechnical University Press, 2015: 1-2(in Chinese). [2] 刘华. 视觉定位关键技术及其在飞机装配中的应用研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2019: 1-2.Liu H. Study on key techniques of visual positioning and its application in aircraft assembly[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2019: 1-2(in Chinese). [3] 陶永, 高赫, 王田苗, 等. 移动工业机器人在飞机装配生产线中的应用研究[J]. 航空制造技术, 2021, 64(5): 32-41,67.TAO Y, GAO H, WANG T M, et al. Application of mobile industrial robot in aircraft assembly production line[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology, 2021, 64(5): 32-41,67(in Chinese). [4] 杨应科, 李东升, 沈立恒, 等. 大型复合材料机身壁板多机器人协同装配调姿控形方法[J]. 航空学报, 2023, 44(14): 428006.YANG Y K, LI D S, SHEN L H, et al. Pose and shape adjustment method for CFRP fuselage panel based on multi-robot collaboration[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2023, 44(14): 428006(in Chinese). [5] 董正建, 杨森, 王平, 等. 一种用于飞机装配的移载定位器: CN216509183U[P]. 2022-05-13.DONG Z J, YANG S, WANG P, et al. Transfer positioner for aircraft assembly: CN216509183U[P]. 2022-05-13(in Chinese). [6] 于勇, 陶剑, 范玉青. 波音787飞机装配技术及其装配过程[J]. 航空制造技术, 2009, 52(14): 44-47.YU Y, TAO J, FAN Y Q. Assembly technology and process of boeing 787 jet[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology, 2009, 52(14): 44-47(in Chinese). [7] 柯臻铮, 柯岩, 朱伟东. 飞机大部件对接及精加工系统研究[J]. 航空制造技术, 2022, 65(20): 92-102.KE Z Z, KE Y, ZHU W D. Research on docking and finishing system of large aircraft parts[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology, 2022, 65(20): 92-102(in Chinese). [8] SCHMIDT B, WANG L H. Automatic work objects calibration via a global−local camera system[J]. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2014, 30(6): 678-683. doi: 10.1016/j.rcim.2013.11.004 [9] WU C H, JIANG S Y, SONG K T. CAD-based pose estimation for random Bin-picking of multiple objects using a RGB-D camera[C]// Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 1645-1649. [10] 刘红帝, 吕睿, 田林雳, 等. 用于引导机器人定位的汇聚式双目视觉算法实现[J]. 机械工程学报, 2022, 58(14): 161-169. doi: 10.3901/JME.2022.14.161LIU H D, LÜ R, TIAN L L, et al. Realization of convergent binocular vision algorithm for guiding robot localization[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2022, 58(14): 161-169(in Chinese). doi: 10.3901/JME.2022.14.161 [11] 王营华, 宋光明, 刘盛松, 等. 一种视觉引导的作业型飞行机器人设计[J]. 机器人, 2019, 41(3): 353-361.WANG Y H, SONG G M, LIU S S, et al. Design of a vision-guided aerial manipulator[J]. Robot, 2019, 41(3): 353-361(in Chinese). [12] SUSEMIHL H, MOELLER C, KOTHE S, et al. High accuracy mobile robotic system for machining of large aircraft components[J]. SAE International Journal of Aerospace, 2016, 9(2): 231-238. [13] 季旭全, 王君臣, 赵江地, 等. 基于机器人与视觉引导的星载设备智能装配方法[J]. 机械工程学报, 2018, 54(23): 63-72. doi: 10.3901/JME.2018.23.063JI X Q, WANG J C, ZHAO J D, et al. Intelligent robotic assembly method of spaceborne equipment based on visual guidance[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2018, 54(23): 63-72(in Chinese). doi: 10.3901/JME.2018.23.063 [14] 王稼祥, 陈坤勇, 江录春, 等. 基于视觉引导的航空发动机低压涡轮轴自动化装配系统研究[J]. 机械设计与研究, 2021, 37(3): 94-100,104.WANG J X, CHEN K Y, JIANG L C, et al. Research on automatic assembly system of aero engine low pressure turbine shaft based on visual guidance[J]. Machine Design & Research, 2021, 37(3): 94-100,104(in Chinese). [15] ZHANG P, KAI Z, LI Z W, et al. High dynamic range 3D measurement based on structured light: a review[J]. Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Science and Technology, 2021, 1(2): 2021004. doi: 10.51393/j.jamst.2021004 [16] 胡占义, 吴福朝. 基于主动视觉摄像机标定方法[J]. 计算机学报, 2002, 25(11): 1149-1156. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-4164.2002.11.004HU Z Y, WU F C. A review on some active vision based camera calibration techniques[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2002, 25(11): 1149-1156(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-4164.2002.11.004 [17] ZHANG Z. A flexible new technique for camera calibration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2000, 22(11): 1330-1334. doi: 10.1109/34.888718 [18] REDMON J, DIVVALA S, GIRSHICK R, et al. You only look once: unified, real-time object detection[C]//Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 779-788. [19] GIRSHICK R, DONAHUE J, DARRELL T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]// Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2014: 580-587. [20] HU J, SHEN L, SUN G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]//Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 7132-7141. [21] WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. CBAM: convolutional block attention module[C]//Proceedings of the Computer Vision−ECCV 2018. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2018: 3-19. [22] HOU Q B, ZHOU D Q, FENG J S. Coordinate attention for efficient mobile network design[C]//Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 13708-13717. [23] WANG Q L, WU B G, ZHU P F, et al. ECA-net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks[C]//Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 11531-11539. [24] TAN M X, PANG R M, LE Q V. EfficientDet: scalable and efficient object detection[C]//Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 10778-10787. [25] ZHOU B L, KHOSLA A, LAPEDRIZA A, et al. Learning deep features for discriminative localization[C]//Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 2921-2929. [26] SELVARAJU R R, COGSWELL M, DAS A, et al. Grad-CAM: visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2020, 128(2): 336-359. doi: 10.1007/s11263-019-01228-7 [27] FU J H, LIU H D, HE M Q, et al. A hand-eye calibration algorithm of binocular stereo vision based on multi-pixel 3D geometric centroid relocalization[J]. Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Science and Technology, 2021, 1(1): 51-60. doi: 10.51393/j.jamst.2022005 [28] PEI H N, ZHOU W J, ZHANG P Y, et al. A review of point set registration: from fundamental algorithms to geometric quality inspection of aviation complex parts[J]. Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Science and Technology, 2023, 3(4): 2023012. doi: 10.51393/j.jamst.2023012 [29] UMEYAMA S. Least-squares estimation of transformation parameters between two point patterns[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1991, 13(4): 376-380. doi: 10.1109/34.88573 [30] FISCHLER M A, BOLLES R C. Random sample consensus: a paradigm for model fitting with applications to image analysis and automated cartography[J]. Readings in Computer Vision, 1987, 24(6): 726-740. -






 下载:
下载: