-
摘要:
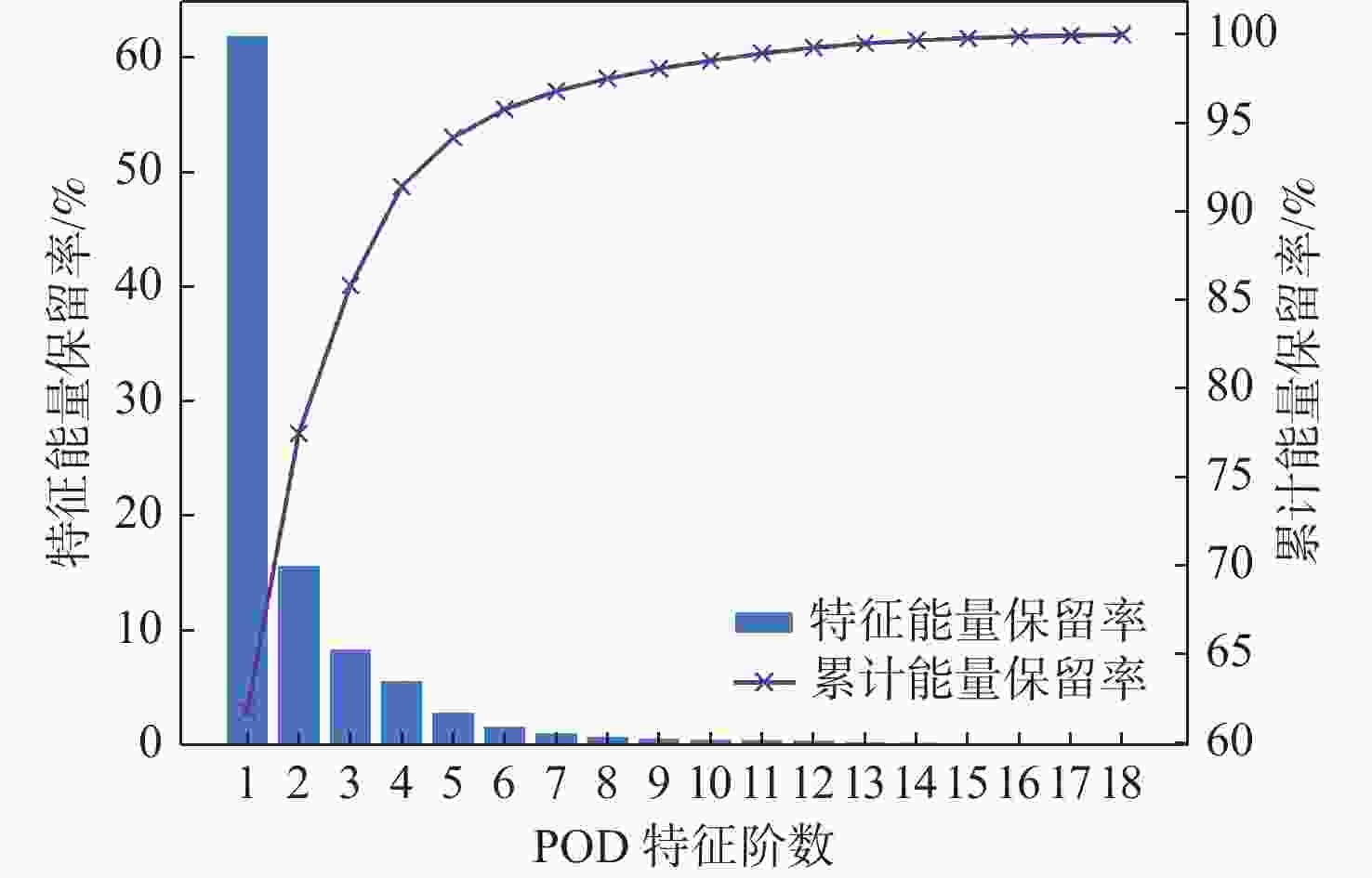
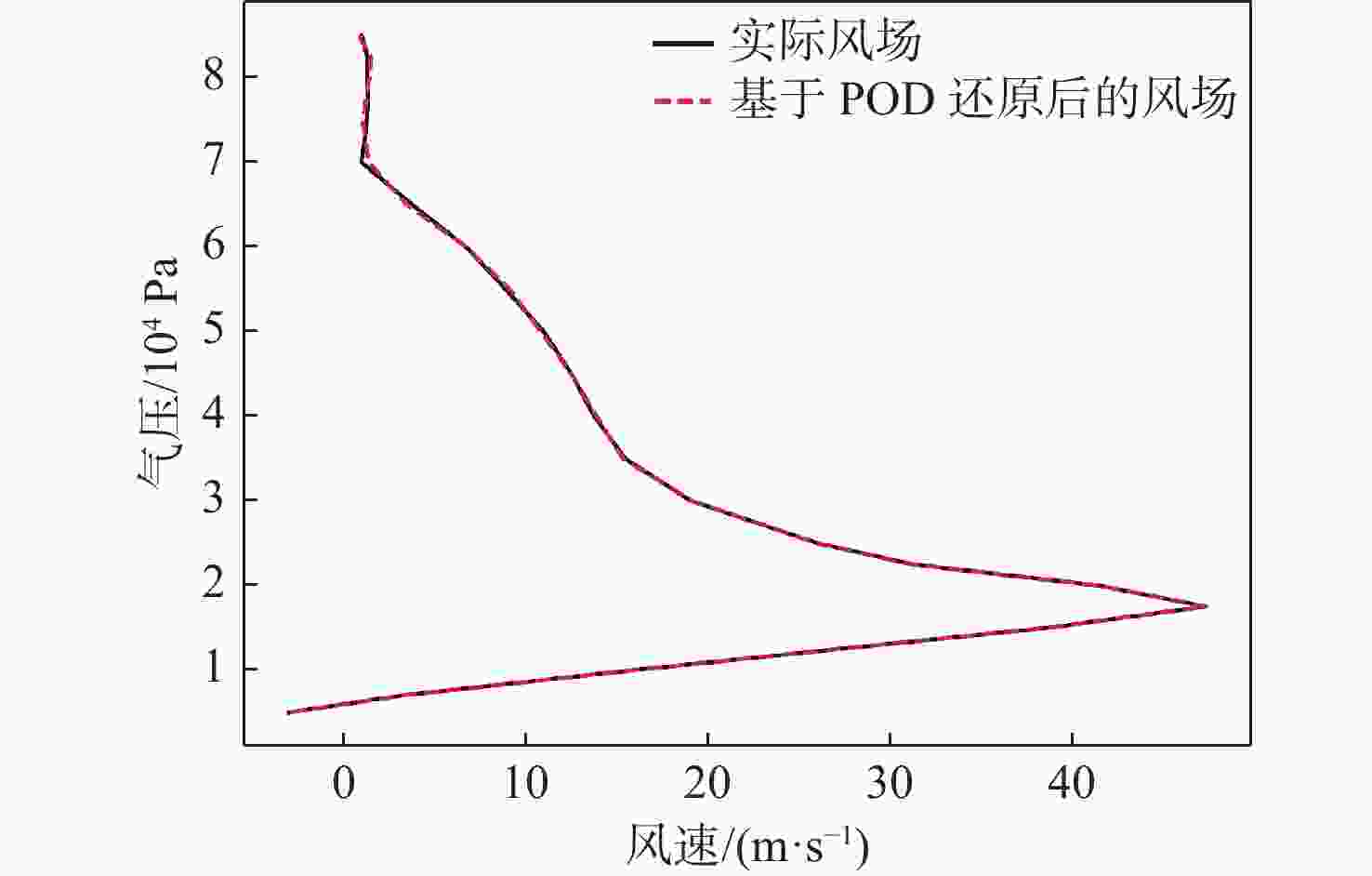
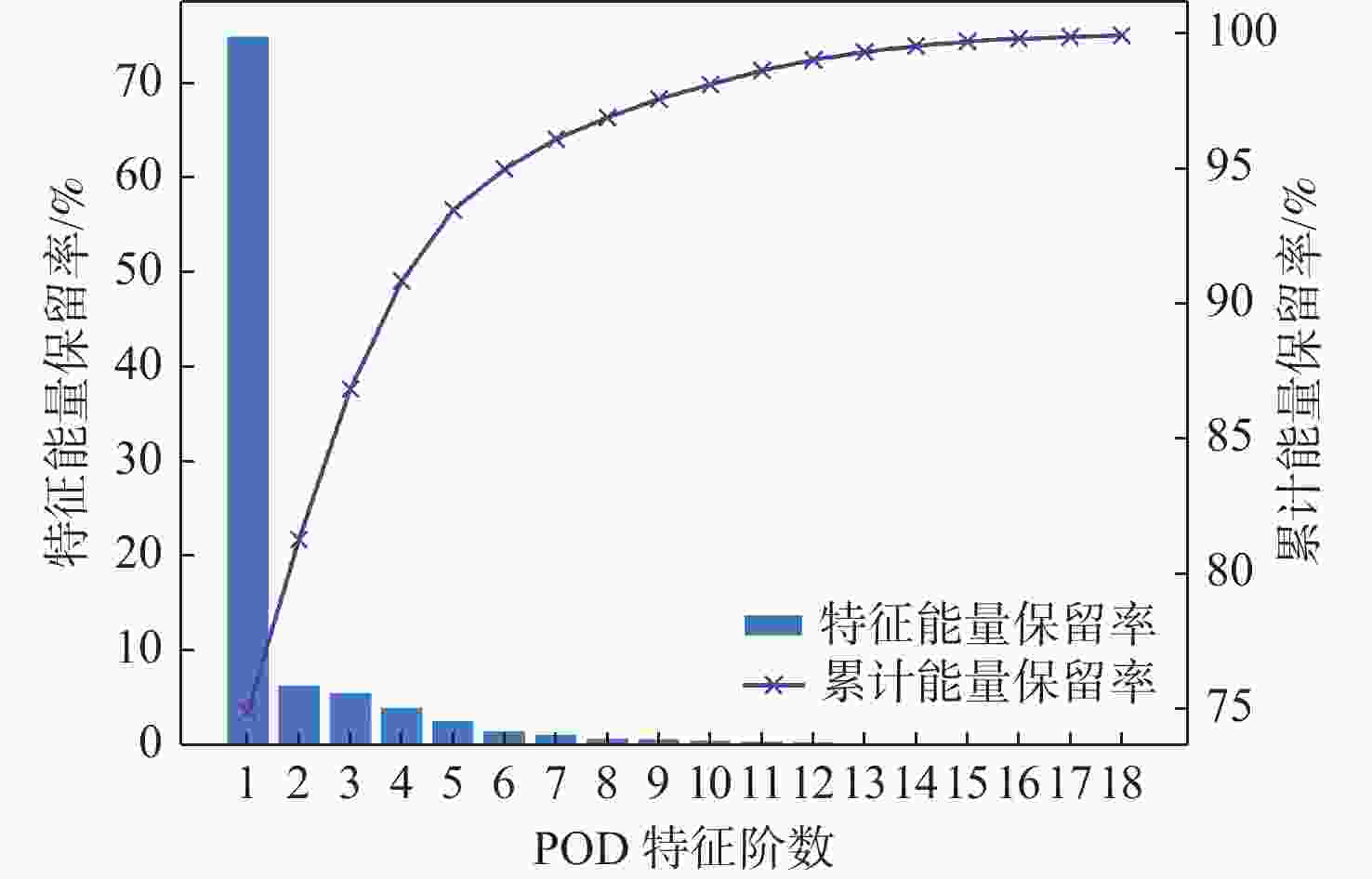
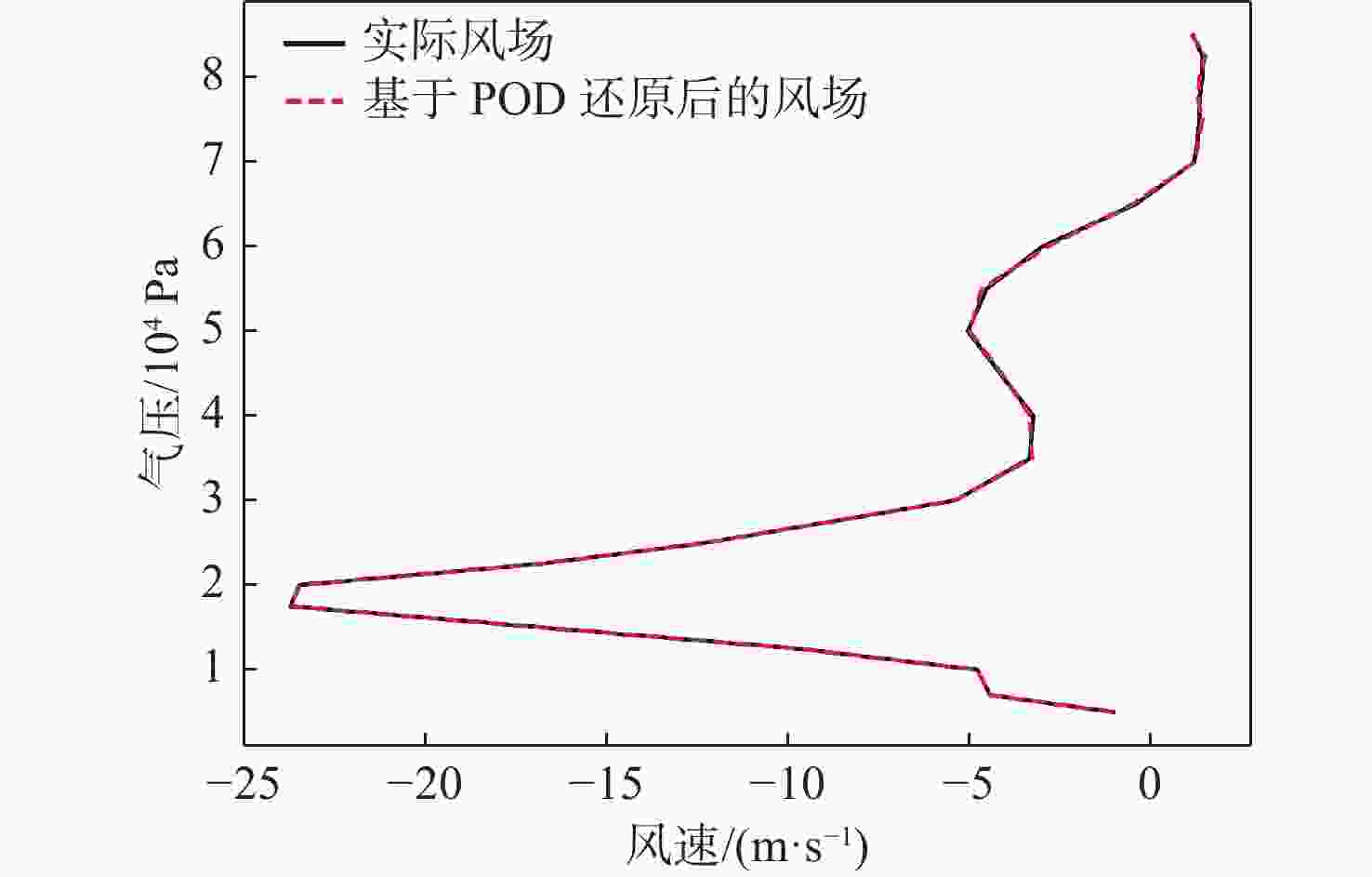
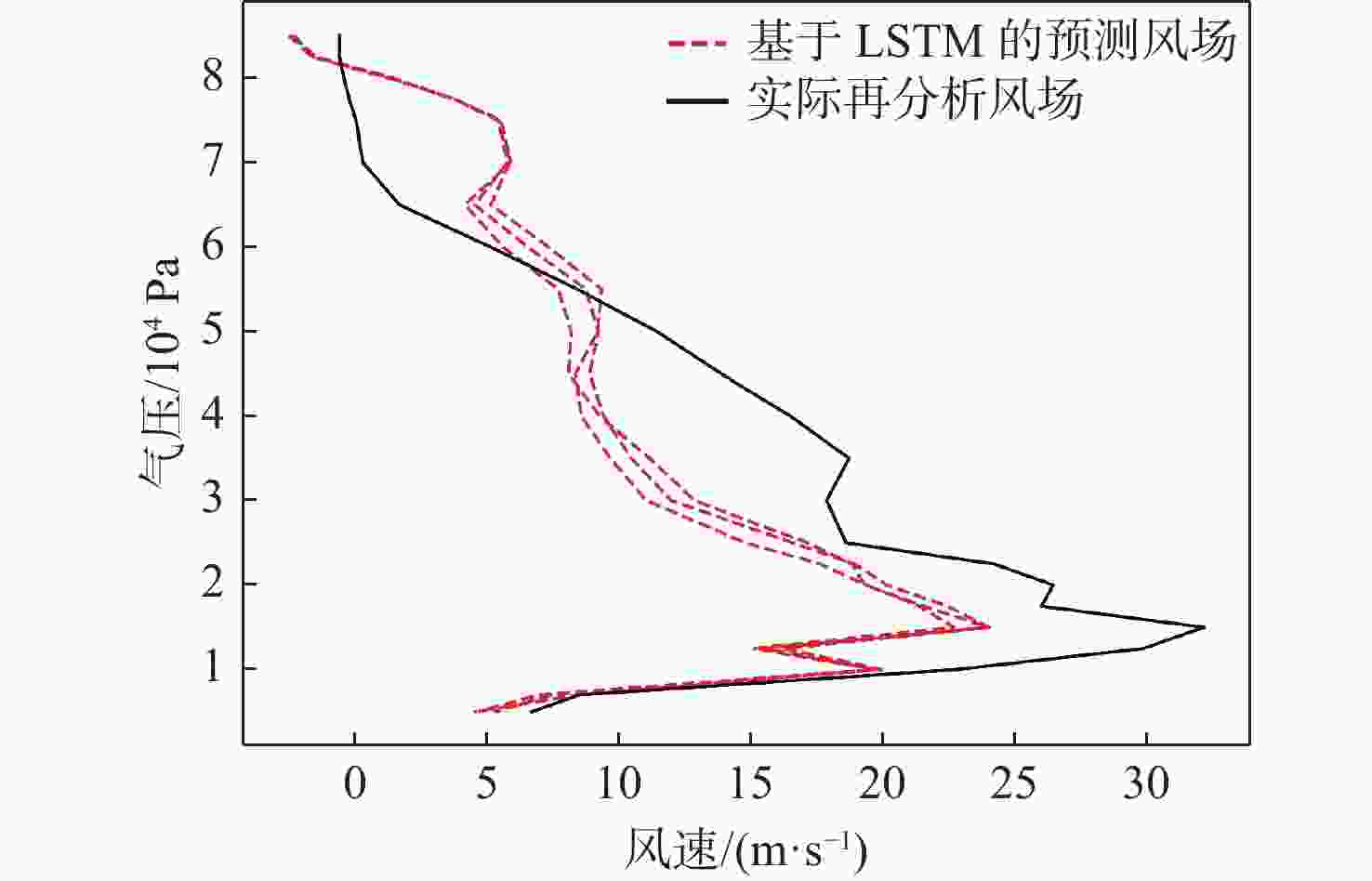
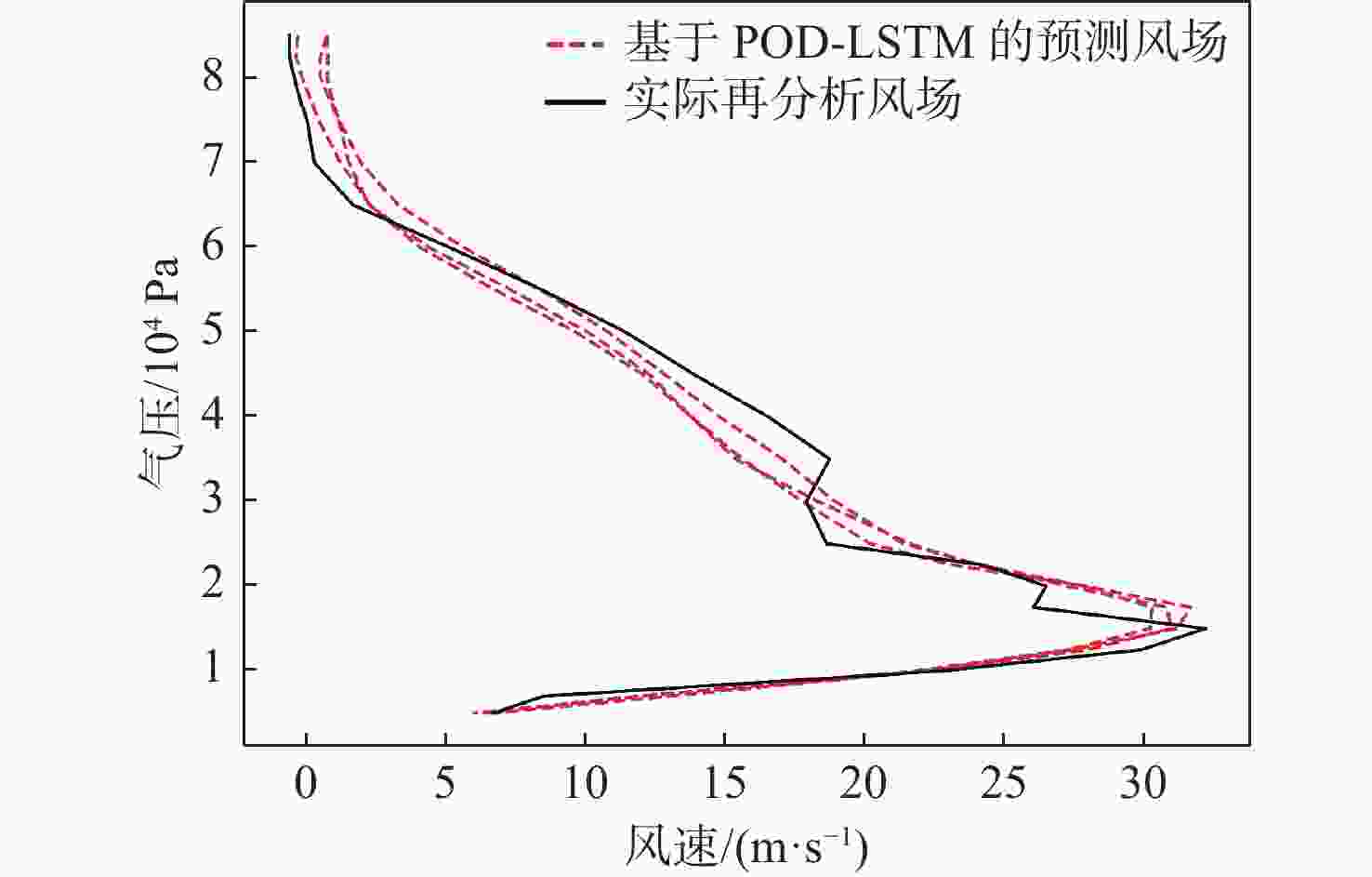
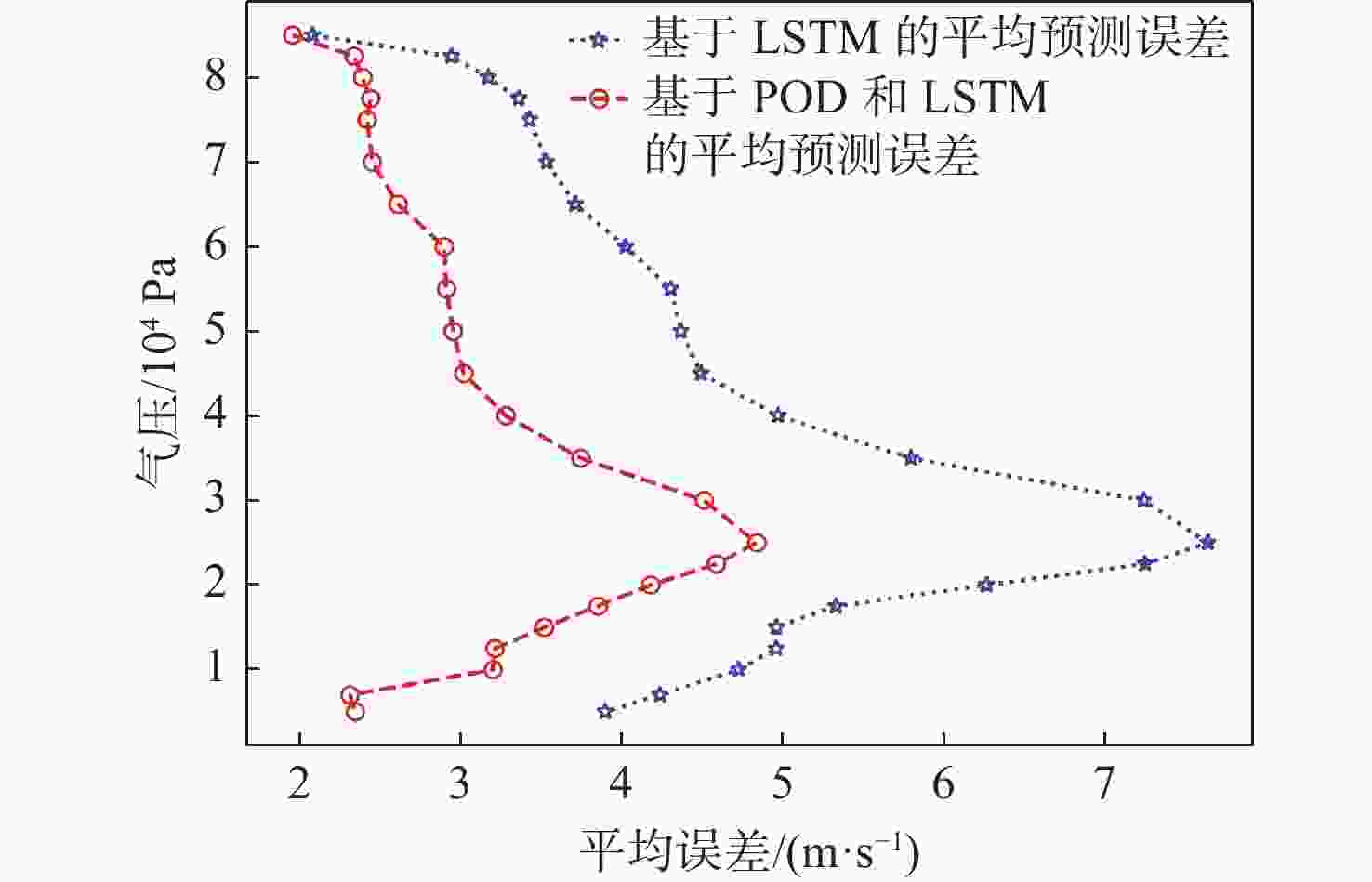
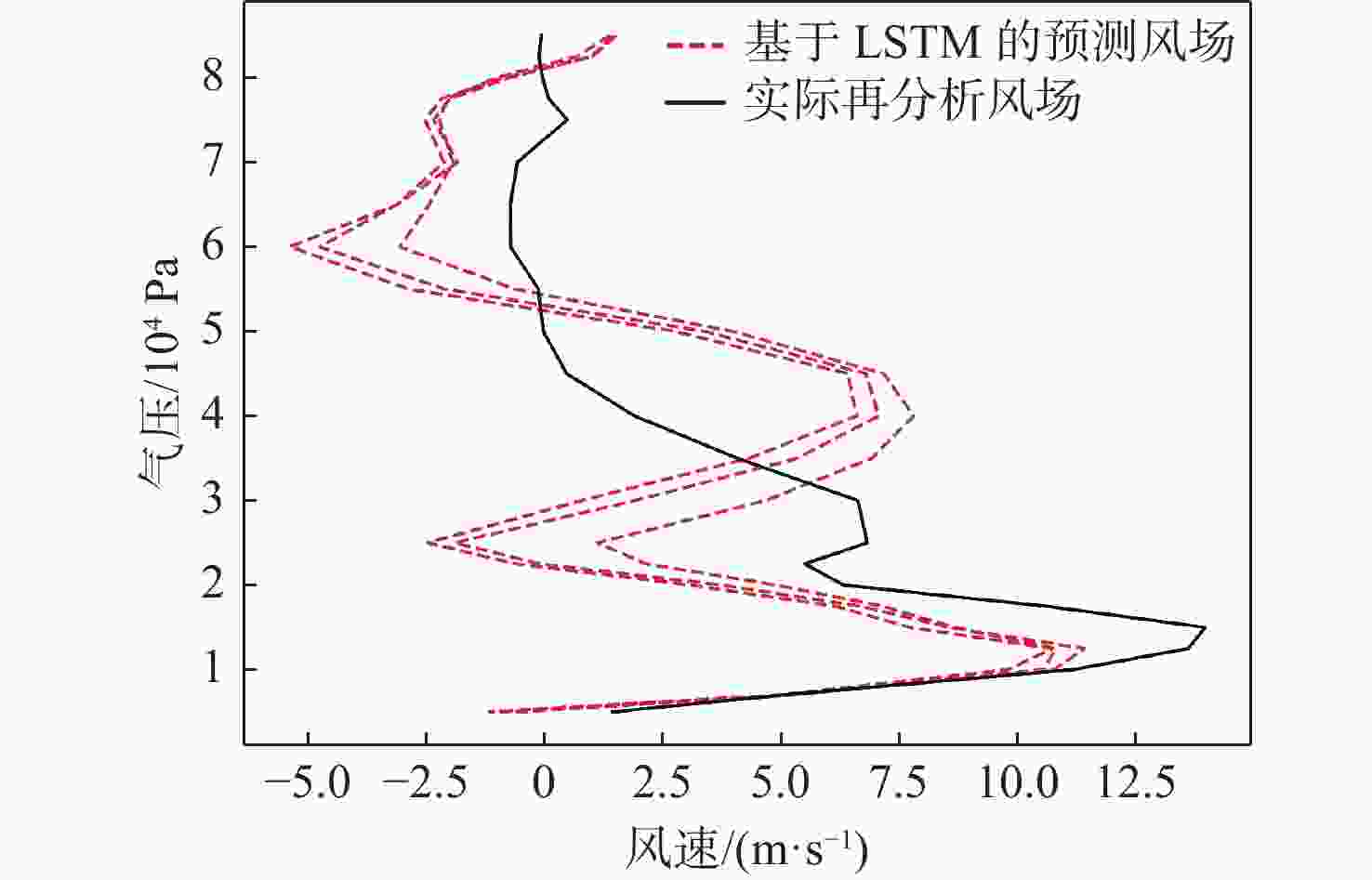
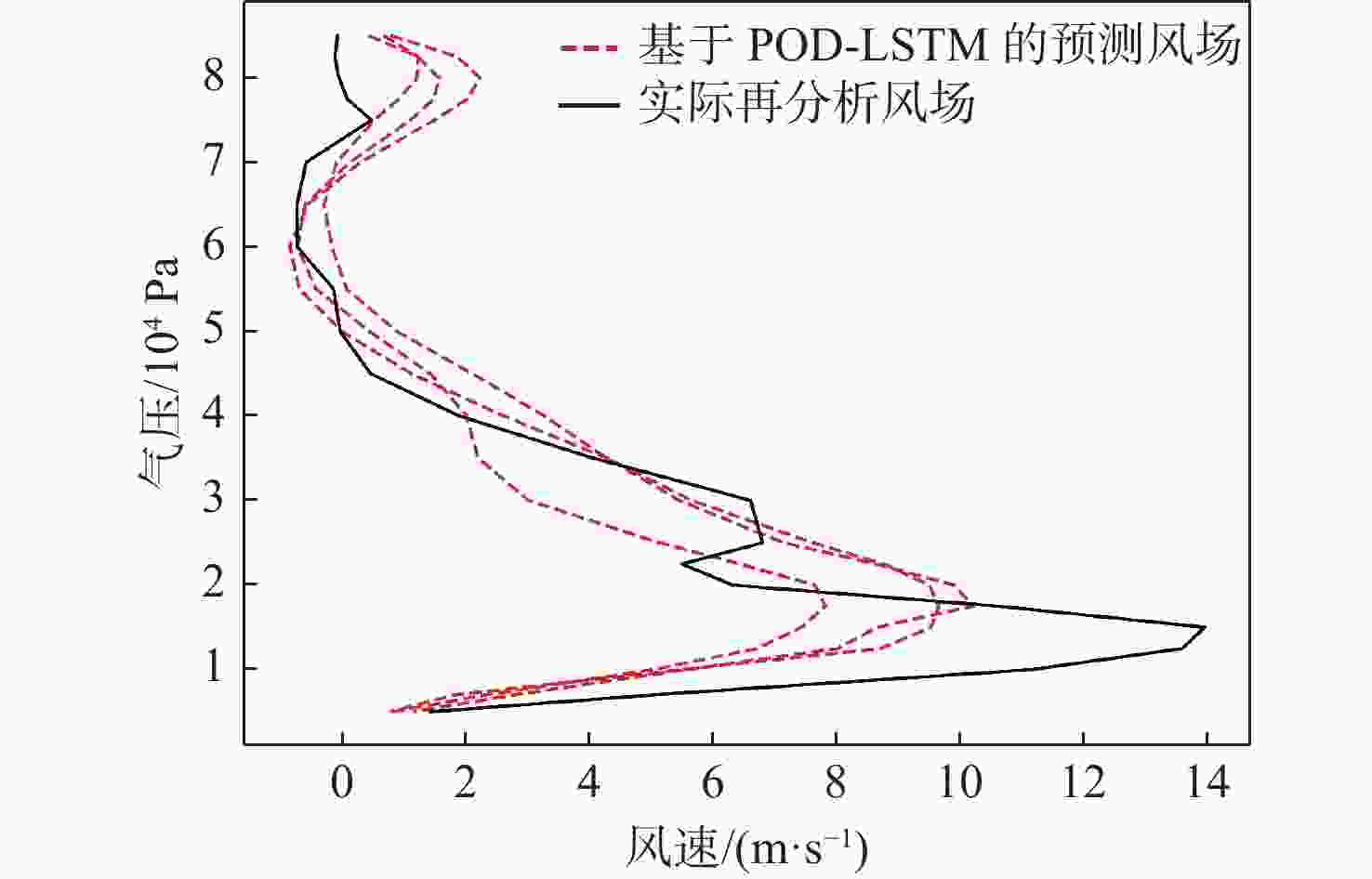
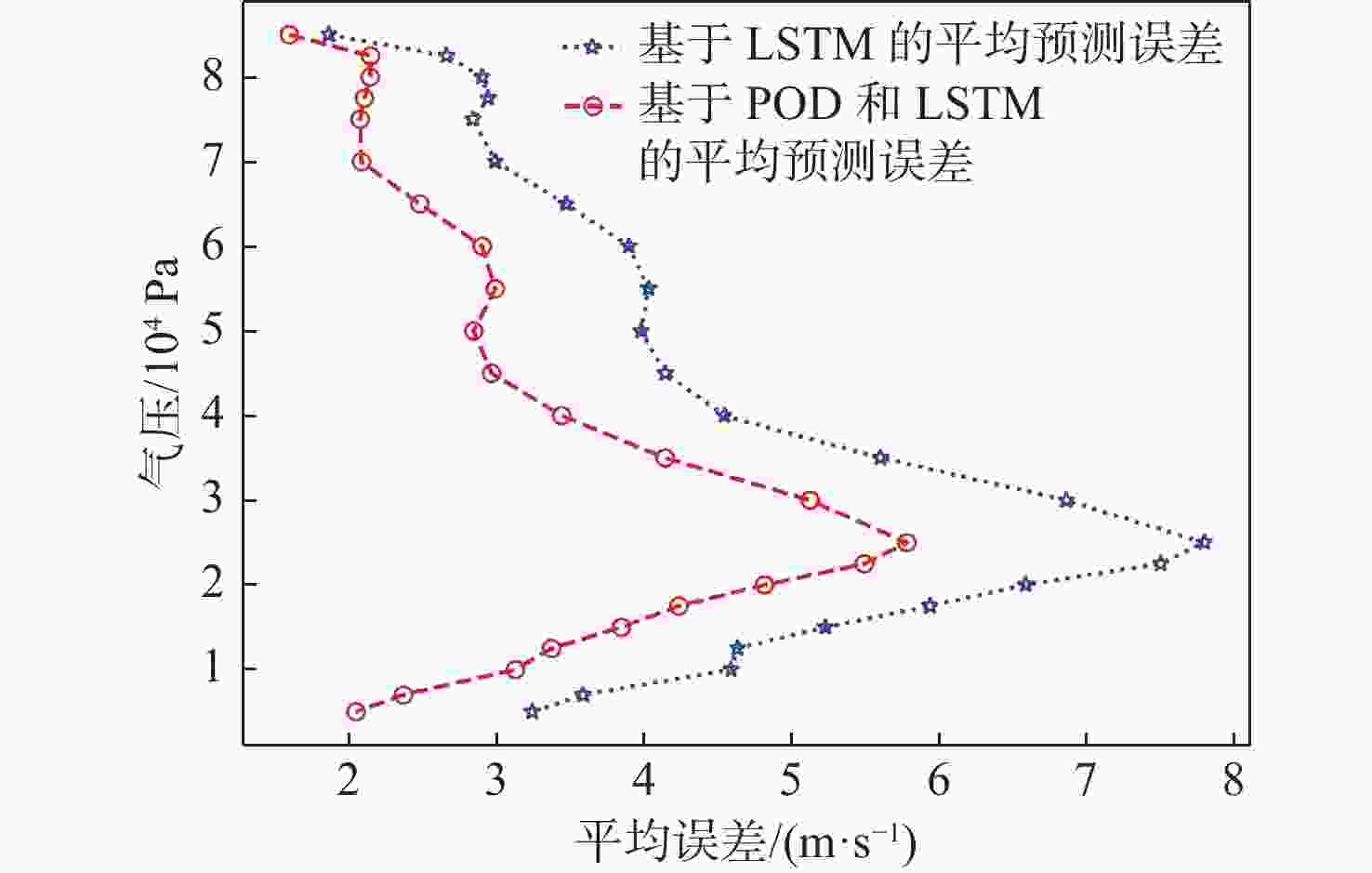
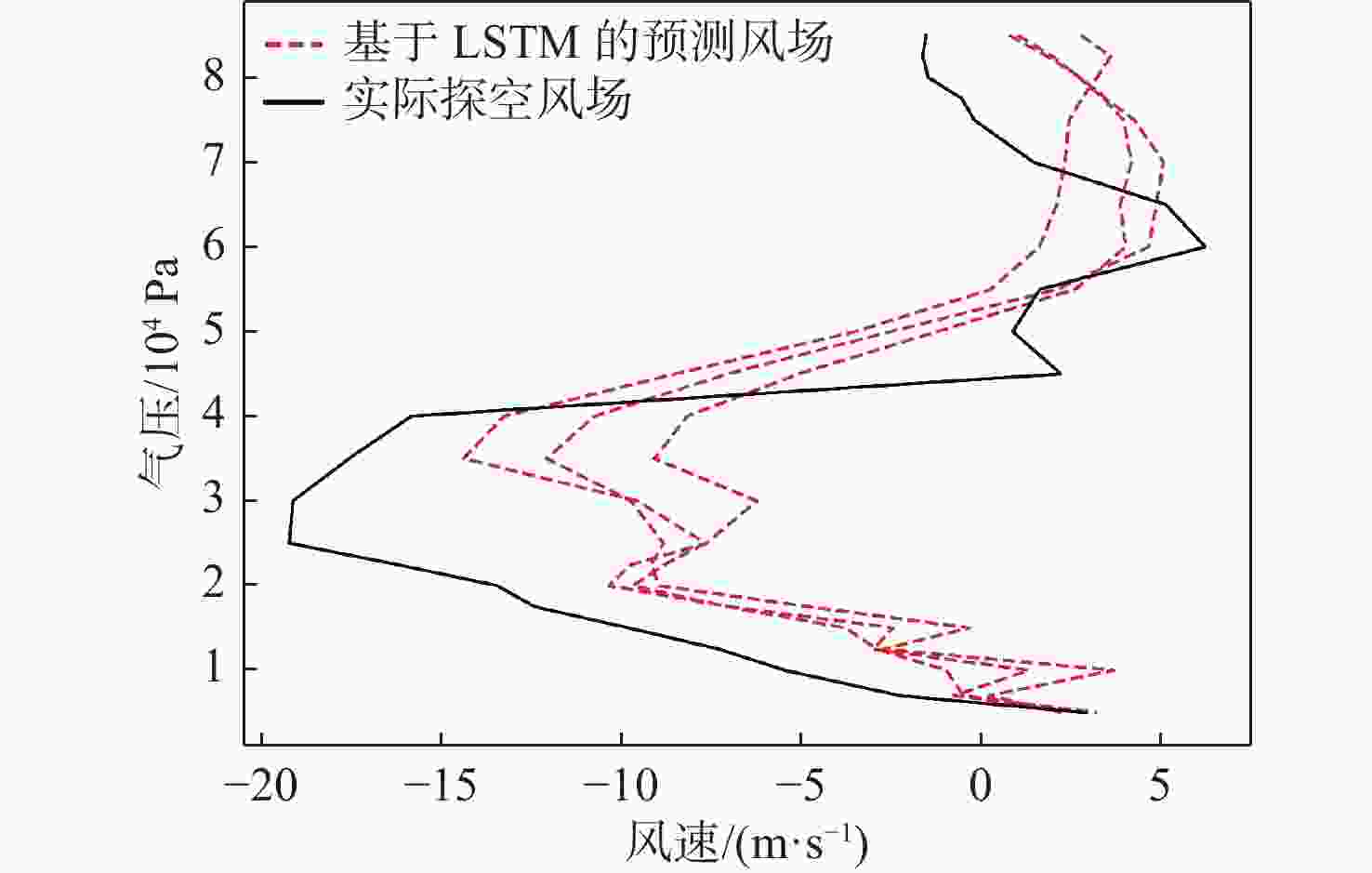
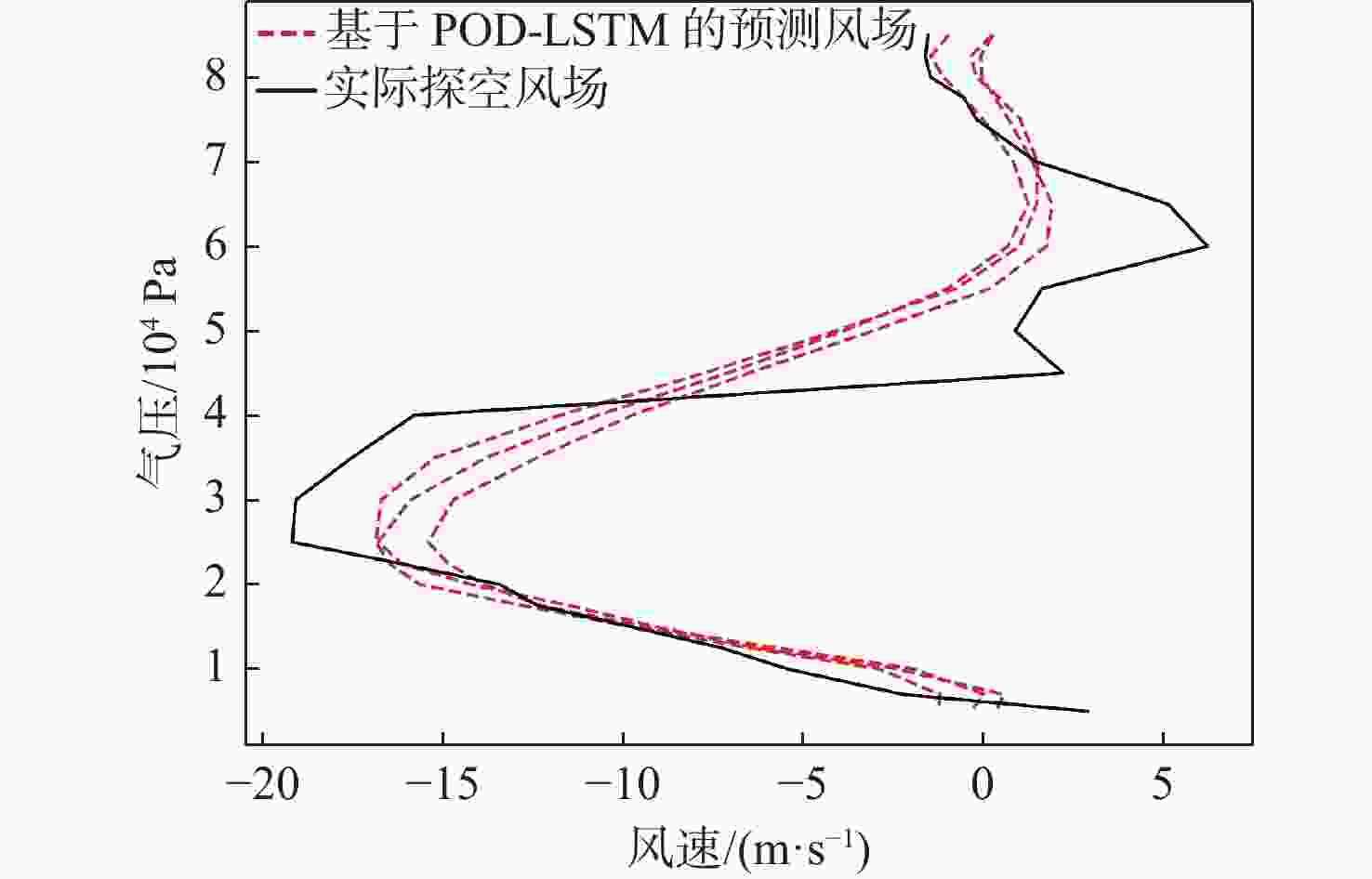
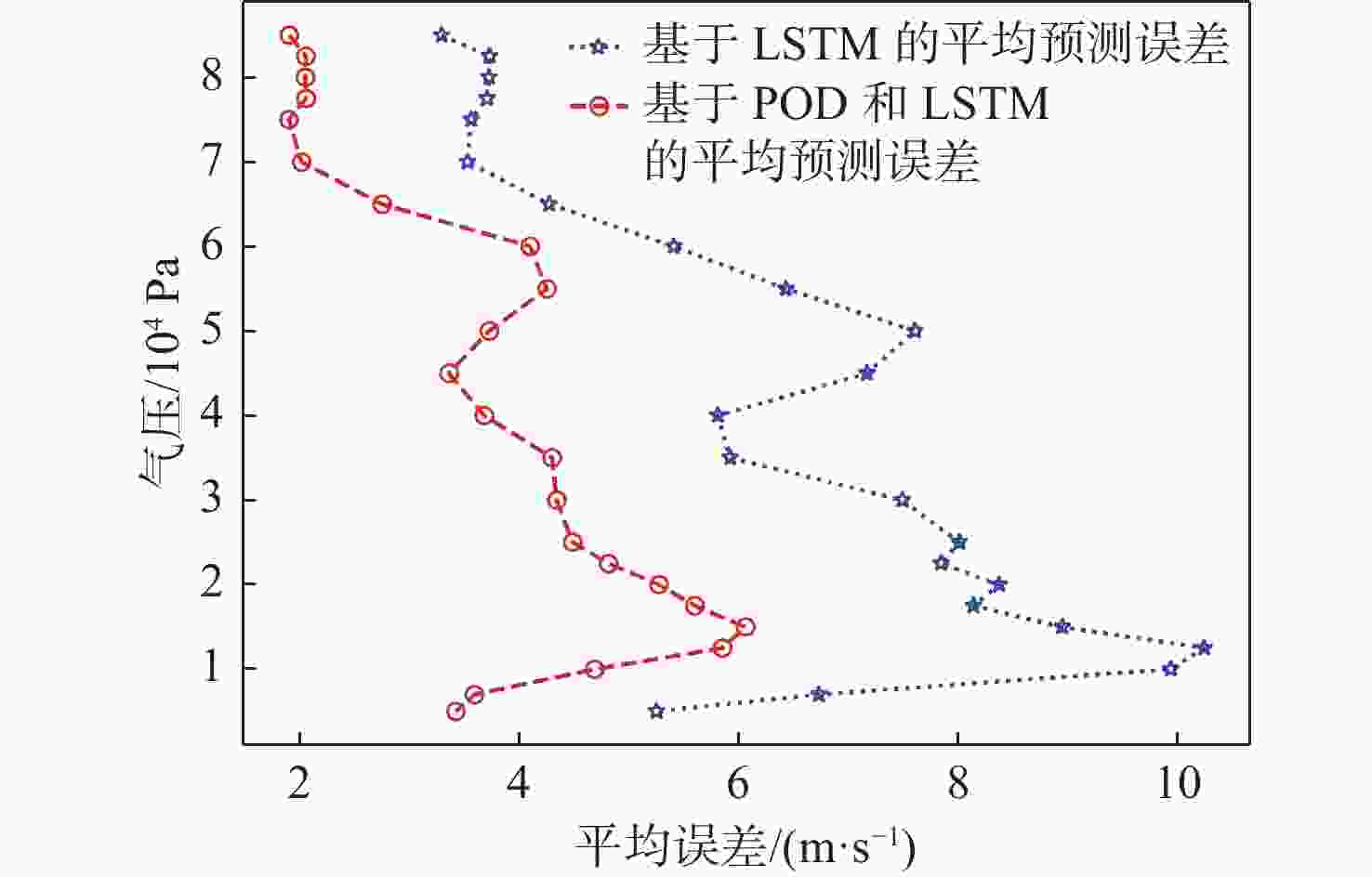
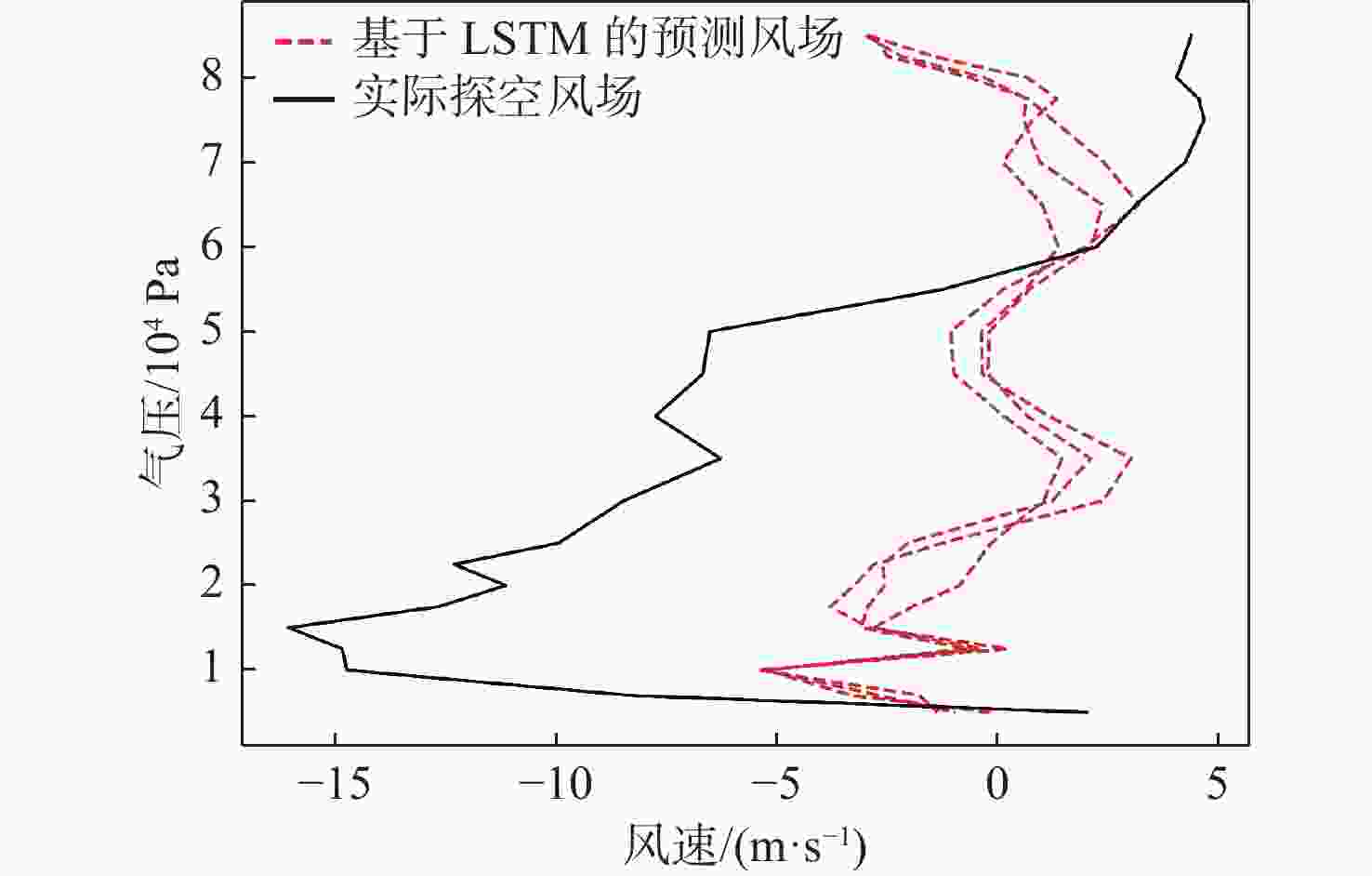
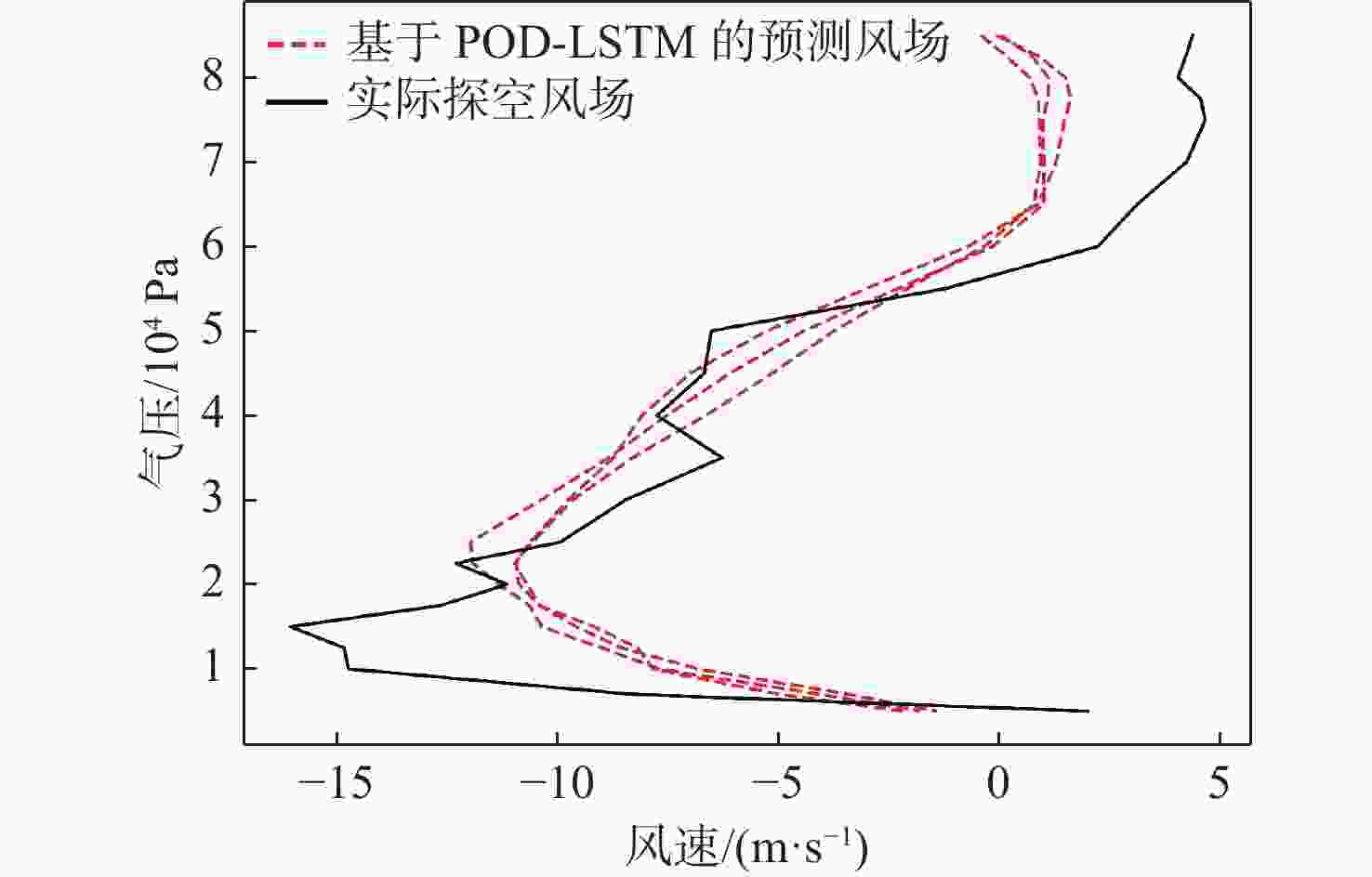
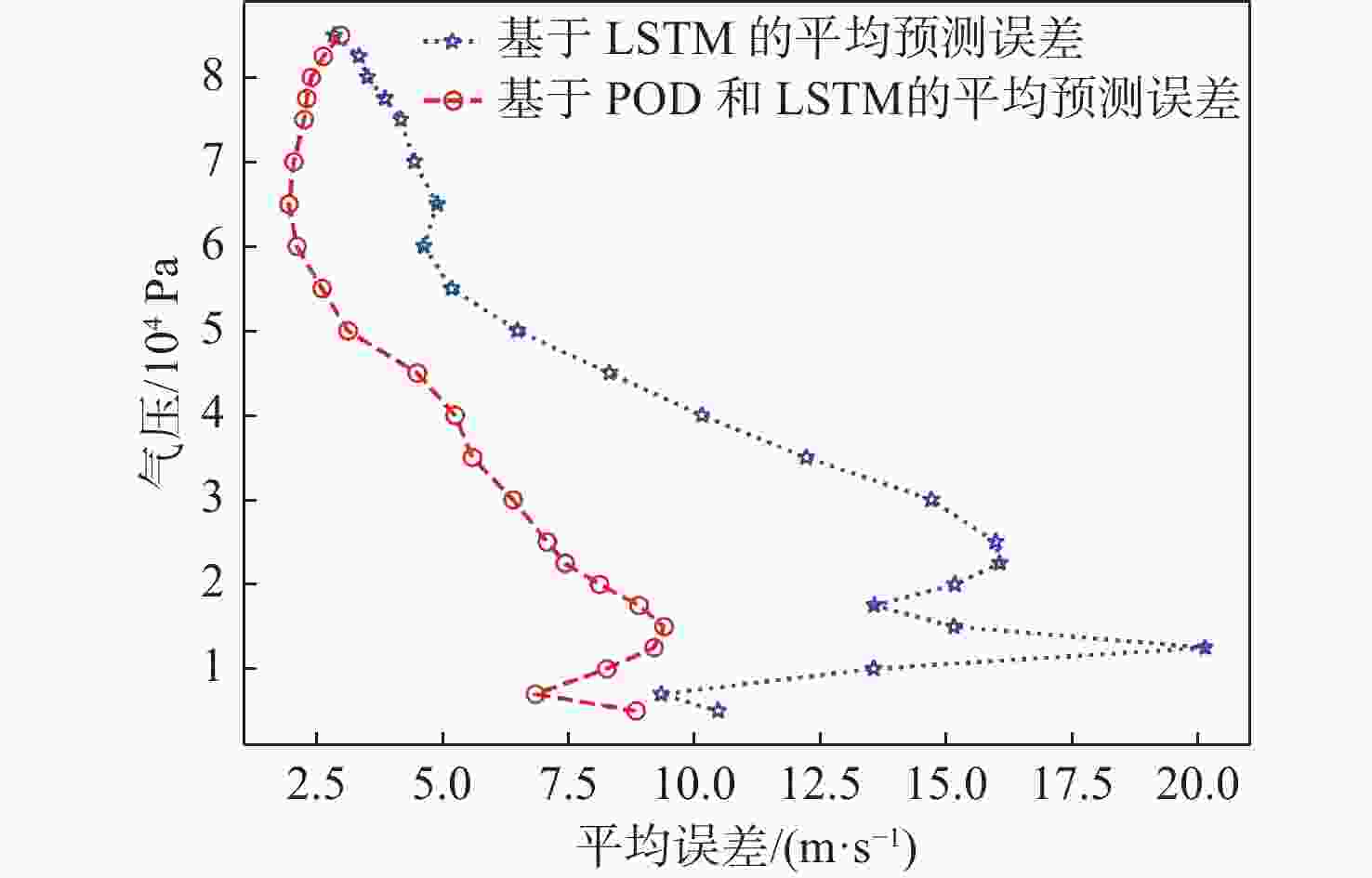
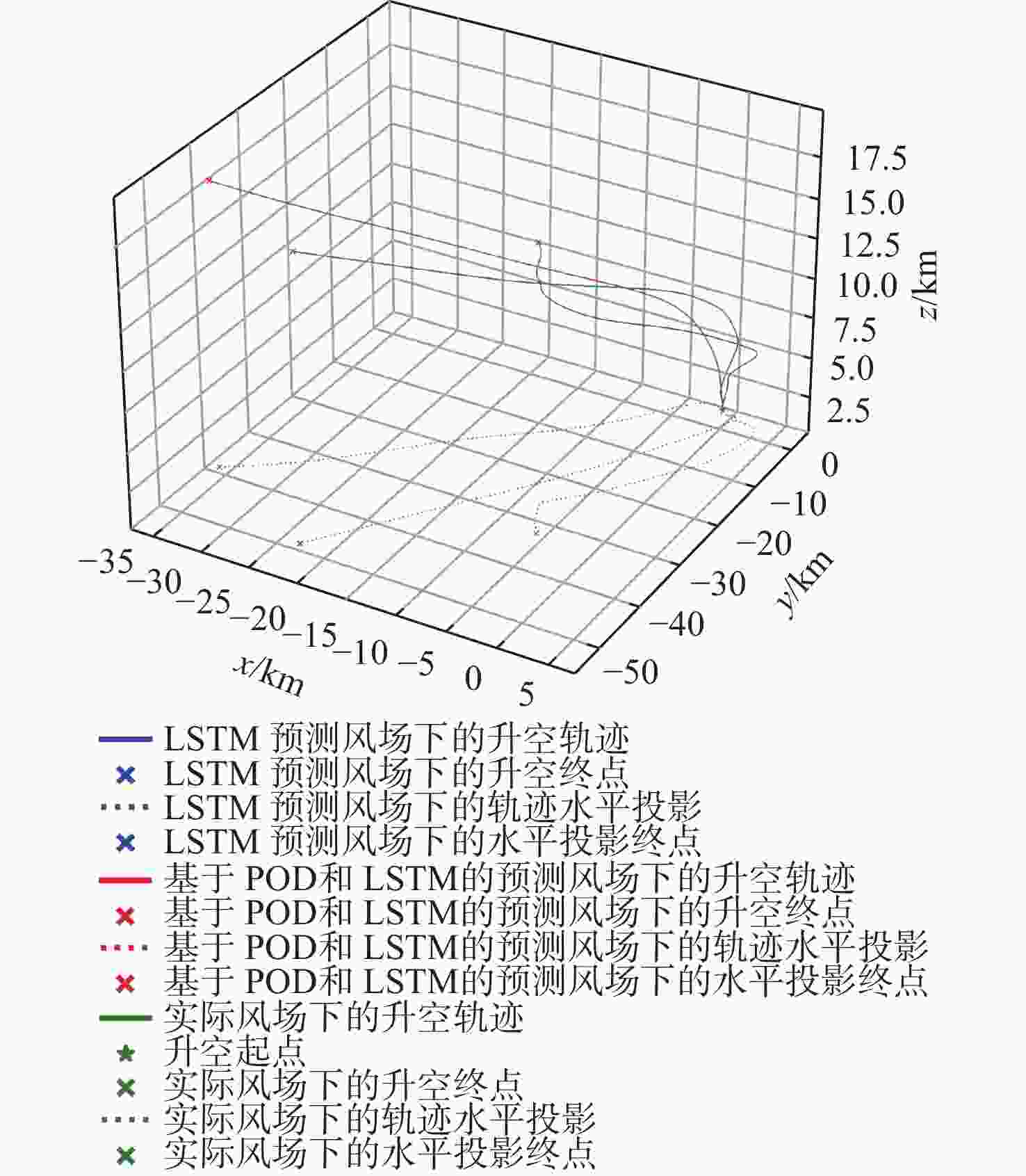
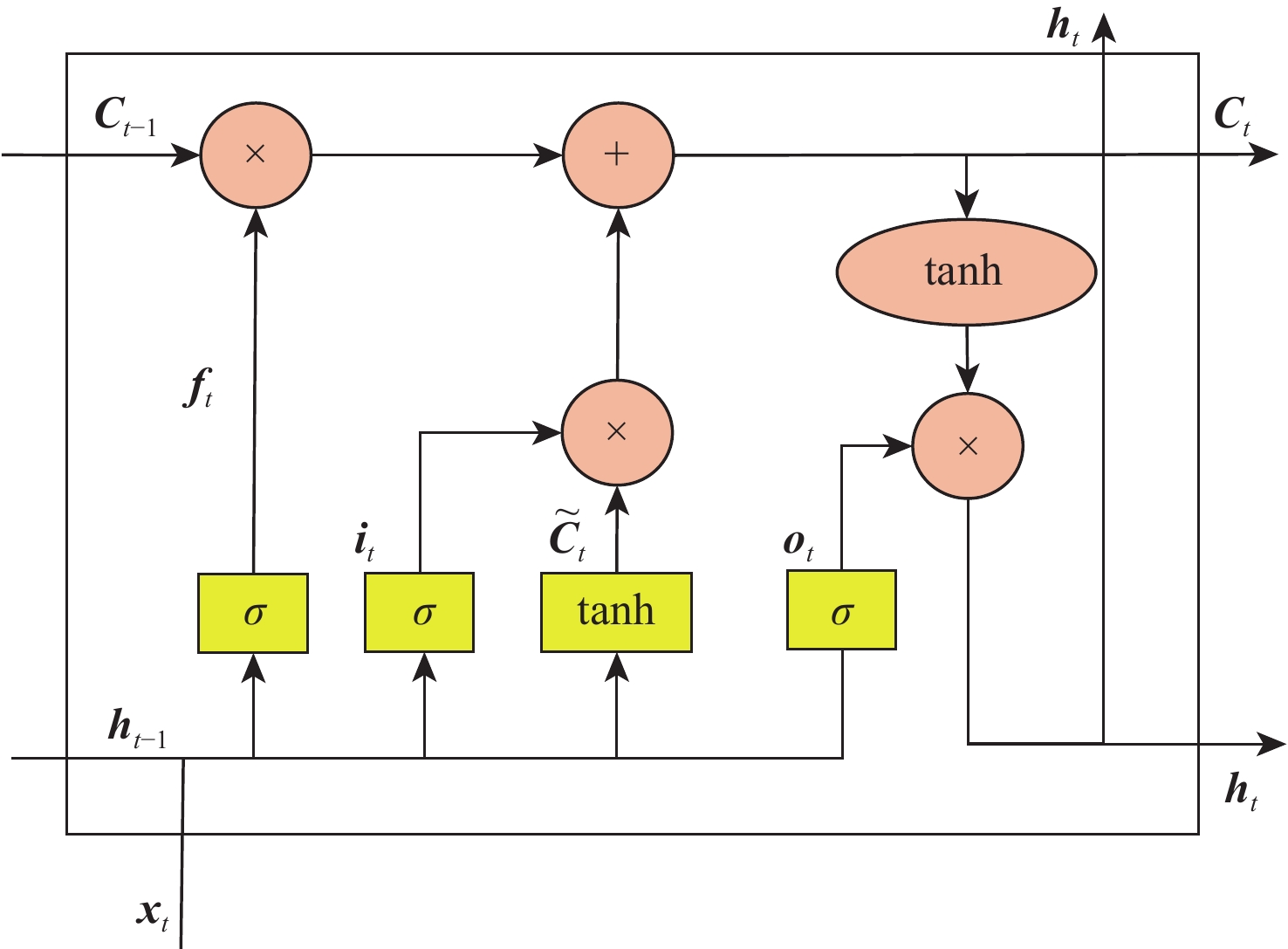
平流层风场对平流层浮空器的升空及长航时驻空有重要影响。利用再分析数据,建立基于长短期记忆(LSTM)网络的再分析风场预测模型,利用本征正交分解(POD)对风场进行特征分解,提升模型对风场特征的检测和提取能力,在实际探空数据上检测再分析风场预测模型的泛化性。以喀什地区连续4年的再分析风场数据为研究对象,对比分析仅基于LSTM的预测模型与基于POD-LSTM的预测模型。结果表明:基于POD-LSTM的预测模型能有效检测到风场特征,提供更准确的风场预测;同时,基于POD-LSTM的预测模型对于探空风场具有更为显著的预测泛化性。研究结果可以在缺少历史实际风场数据的背景下,为实现准确的平流层风场短期预测提供解决途径。
Abstract:The stratospheric wind field has an important effect on the liftoff and long-endurance station-keeping of stratospheric aerostats. By using the reanalysis data, a wind field prediction model based on long short-term memory (LSTM) network is built. Proper orthogonal decomposition (POD) is applied to extract key features of the wind field, enhancing the model’s ability to detect and represent wind field characteristics. The generalization ability of the reanalysis-based prediction model is evaluated using actual radiosonde data. Taking four consecutive years of reanalysis wind field data from the Kashgar region as a case study, a comparative analysis is conducted between the LSTM-based model and the POD-LSTM-based model. The results show that the POD-LSTM model effectively captures wind field features and provides more accurate predictions. Moreover, the POD-LSTM model demonstrates stronger generalization ability when predicting real wind field conditions. These findings offer a practical approach for accurate short-term stratospheric wind field prediction in scenarios where historical real wind data are limited.
-
-
[1] 田文寿, 黄金龙, 郄锴, 等. 平流层大气环流的典型系统及变化特征综述[J]. 气象科学, 2020, 40(5): 628-638.TIAN W S, HUANG J L, QIE K, et al. Review of the general atmospheric circulation in the stratosphere and its variation features[J]. Journal of the Meteorological Sciences, 2020, 40(5): 628-638(in Chinese). [2] 杨燕初, 张航悦, 赵荣. 零压式高空气球球形设计与参数敏感性分析[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2019, 41(1): 58-64. doi: 10.11887/j.cn.201901009YANG Y C, ZHANG H Y, ZHAO R. Shape design of zero pressure high altitude balloon and sensitivity analysis of key parameters[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2019, 41(1): 58-64(in Chinese). doi: 10.11887/j.cn.201901009 [3] 郭建国, 周军. 临近空间低动态飞行器控制研究综述[J]. 航空学报, 2014, 35(2): 320-331.GUO J G, ZHOU J. Review of the control of low dynamic vehicles in near space[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2014, 35(2): 320-331(in Chinese). [4] 曾庆存. 大气运动的特征参数和动力学方程[J]. 气象学报, 1963, 21(4): 472-483.ZENG Q C. Characteristic parameters and dynamic equations of atmospheric motion[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 1963, 21(4): 472-483(in Chinese). [5] CHARNEY J G, FJÖRTOFT R, VON NEUMANN J. Numerical integration of the barotropic vorticity equation[J]. Tellus, 1950, 2(4): 237-254. doi: 10.3402/tellusa.v2i4.8607 [6] 张晨阳, 马志强, 刘利民, 等. Hadoop下基于粗糙集与贝叶斯的气象数据挖掘研究[J]. 计算机应用与软件, 2015, 32(4): 72-76.ZHANG C Y, MA Z Q, LIU L M, et al. Research on rough set and Bayes-based meteorological data mining on hadoop platform[J]. Computer Applications and Software, 2015, 32(4): 72-76(in Chinese). [7] 蔡舒平, 孙华辰. 短期负荷预测中气象因素的Fisher信息建模方法[J]. 科学技术创新, 2018(17): 35-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1328.2018.17.020CAI S P, SUN H C. Fisher information modeling method of meteorological factors in short-term load forecasting[J]. Scientific and Technological Innovation, 2018(17): 35-36(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1328.2018.17.020 [8] REMSBERG E, LINGENFELSER G, HARVEY V L, et al. On the verification of the quality of SABER temperature, geopotential height, and wind fields by comparison with Met Office assimilated analyses[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2003, 108(D20): 4628. [9] 徐熙超, 杨铮, 马廷淮. 基于HBase的气象结构化数据查询优化[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2017, 53(9): 80-84.XU X C, YANG Z, MA T H. Optimization of meteorological structured data based on HBase[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2017, 53(9): 80-84(in Chinese). [10] KWONG K M, WONG M H Y, LIU J N K, et al. An artificial neural network with chaotic oscillator for wind shear alerting[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 2012, 29(10): 1518-1531. doi: 10.1175/2011JTECHA1501.1 [11] 黄豪南, 郑祥, 韦勇凤. 基于BP神经网络-SARIMA组合模型对气象要素预测与天气多因子期权的估值[J]. 投资研究, 2018, 37(5): 82-97.HUANG H N, ZHENG X, WEI Y F. Forecasting of meteorological elements time series and pricing of weather multi-factor options: integrating BP neural network and SARIMA model[J]. Review of Investment Studies, 2018, 37(5): 82-97(in Chinese). [12] 任才溶, 谢刚. 基于随机森林和气象参数的PM2.5浓度等级预测[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2019, 55(2): 213-220. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1709-0378REN C R, XIE G. Prediction of PM2.5 concentration level based on random forest and meteorological parameters[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2019, 55(2): 213-220(in Chinese). doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1709-0378 [13] BI K F, XIE L X, ZHANG H H, et al. Accurate medium-range global weather forecasting with 3D neural networks[J]. Nature, 2023, 619(7970): 533-538. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06185-3 [14] 王怡婷, 陈曦, 鞠兴旺, 等. 基于GRU网络的气象要素预测算法[J]. 计算机仿真, 2021, 38(7): 419-423.WANG Y T, CHEN X, JU X W, et al. A meteorological element prediction algorithm based on GRU network[J]. Computer Simulation, 2021, 38(7): 419-423(in Chinese). [15] GAO S, ZHAO P, PAN B, et al. A nowcasting model for the prediction of typhoon tracks based on a long short term memory neural network[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2018, 37(5): 8-12. doi: 10.1007/s13131-018-1219-z [16] ANINDYA C. An introduction to the proper orthogonal decomposition[J]. Current Science, 2000, 78(7): 808-817. -







 下载:
下载: