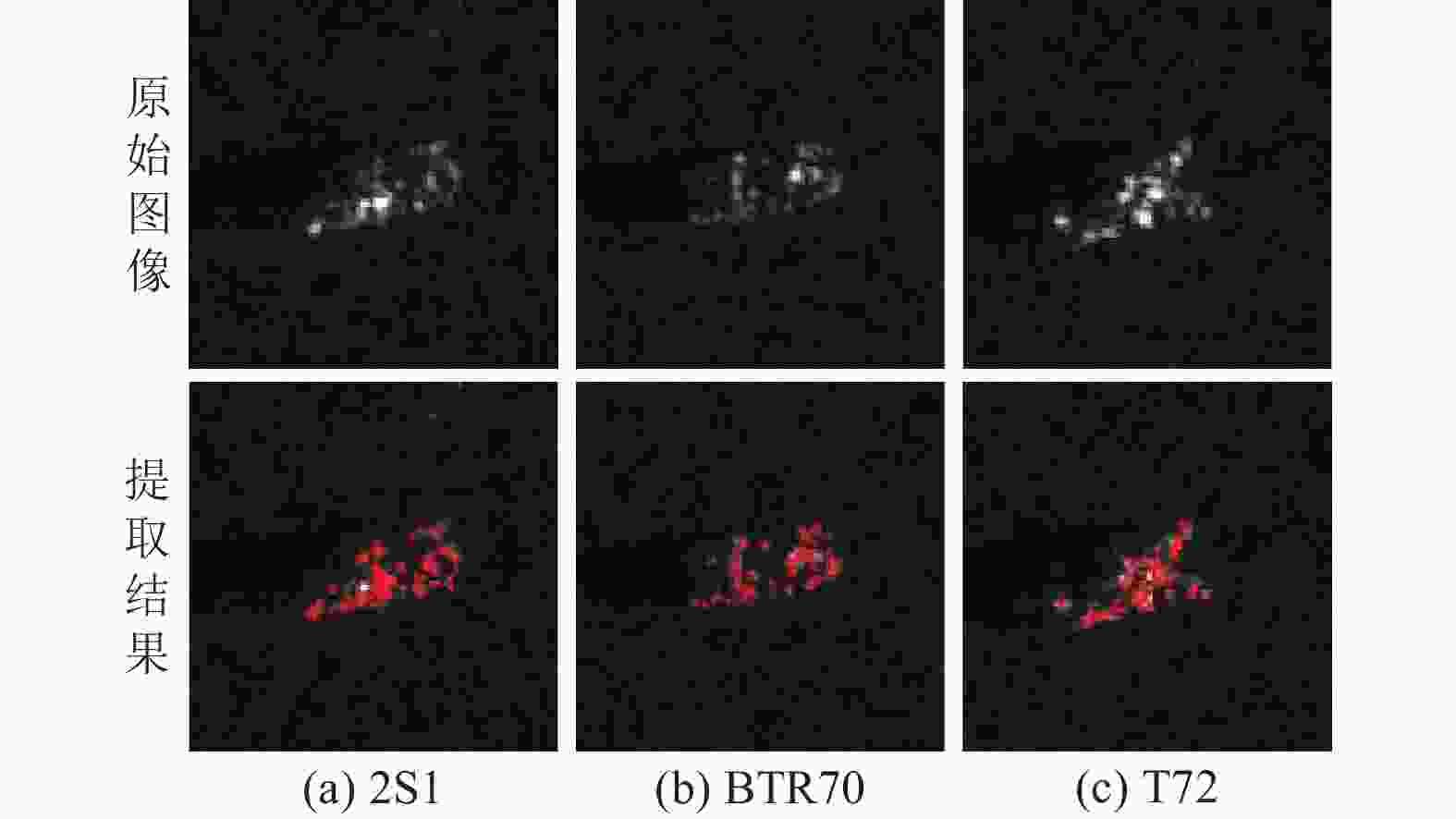
-
摘要:
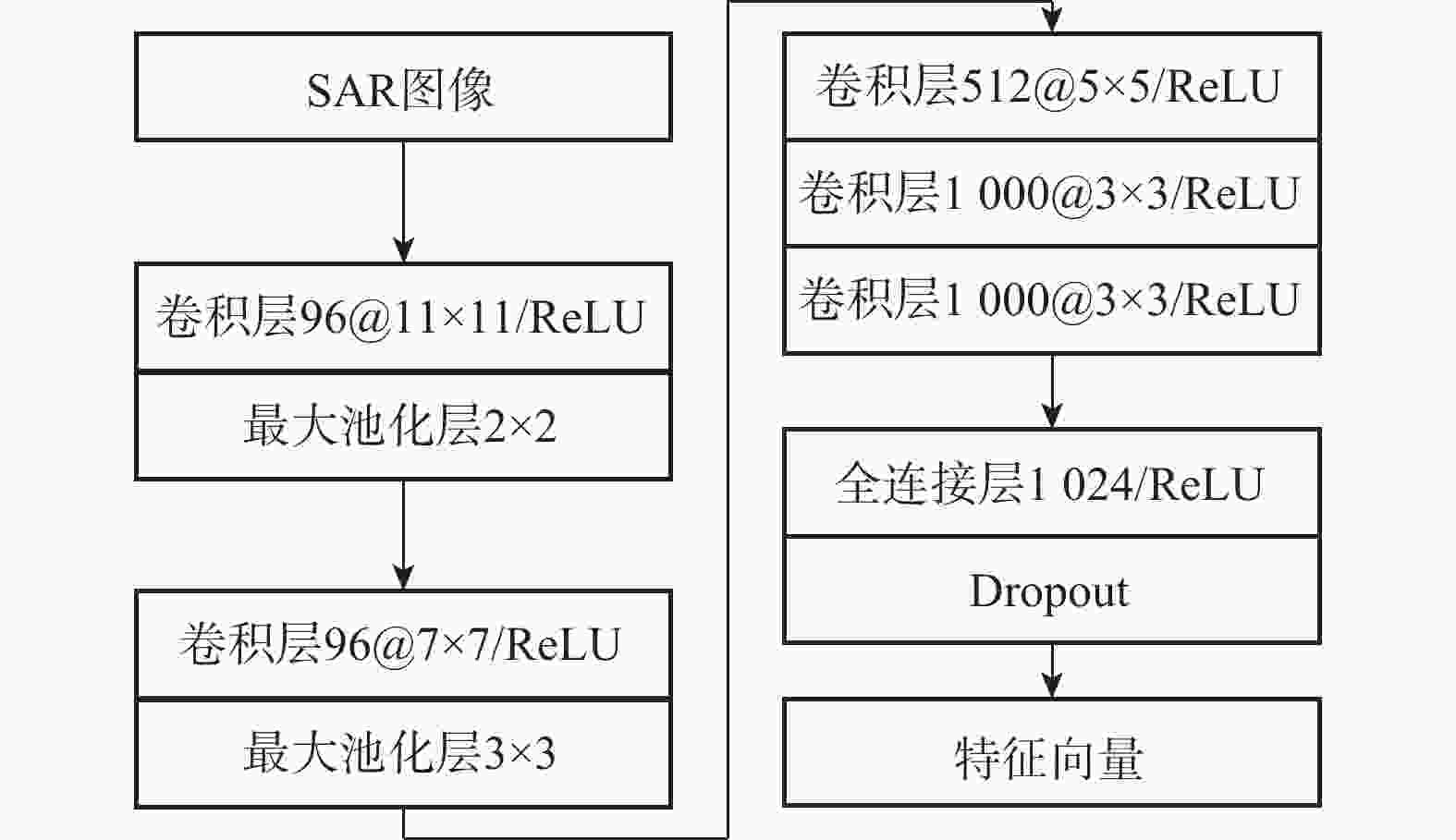
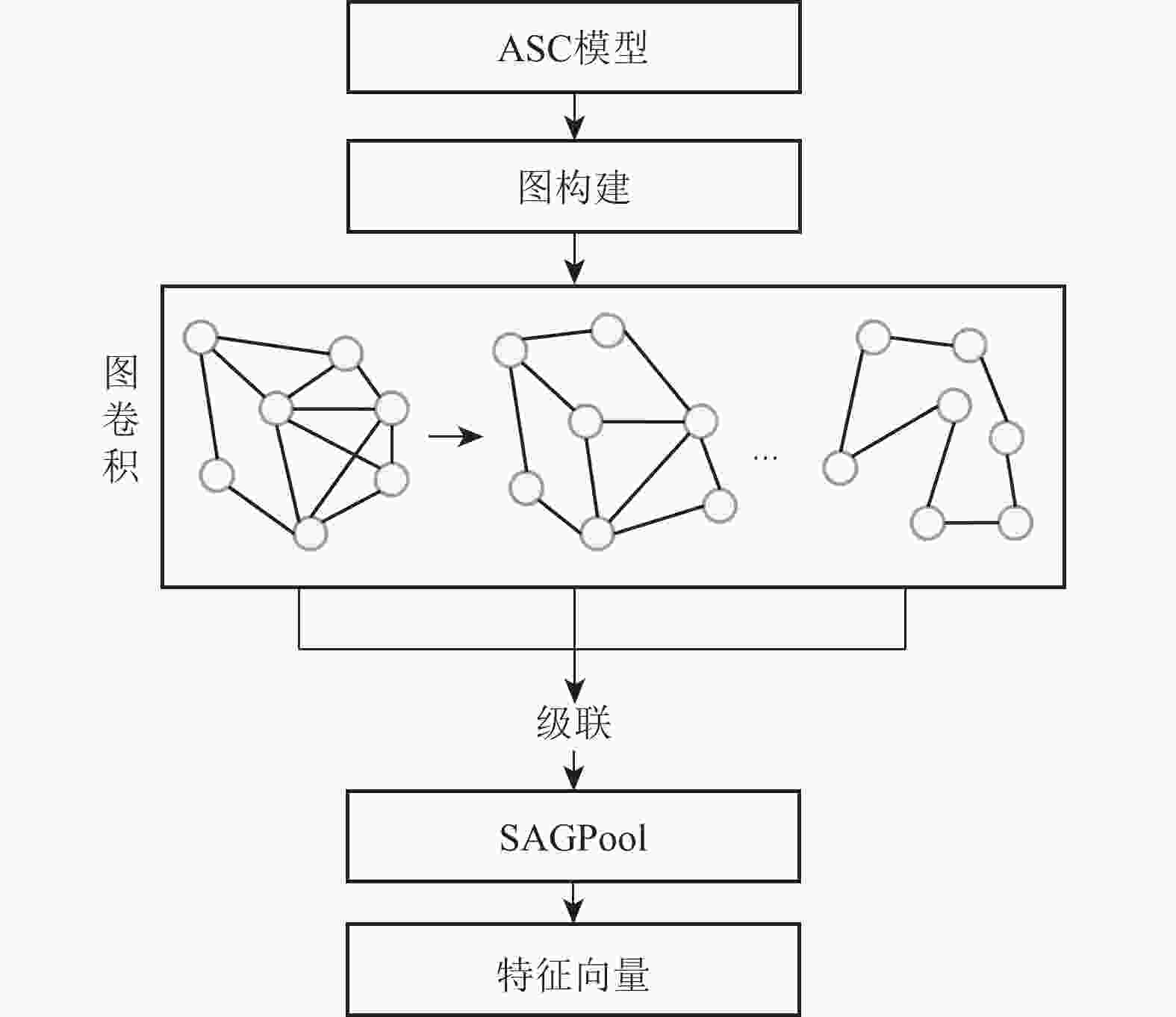
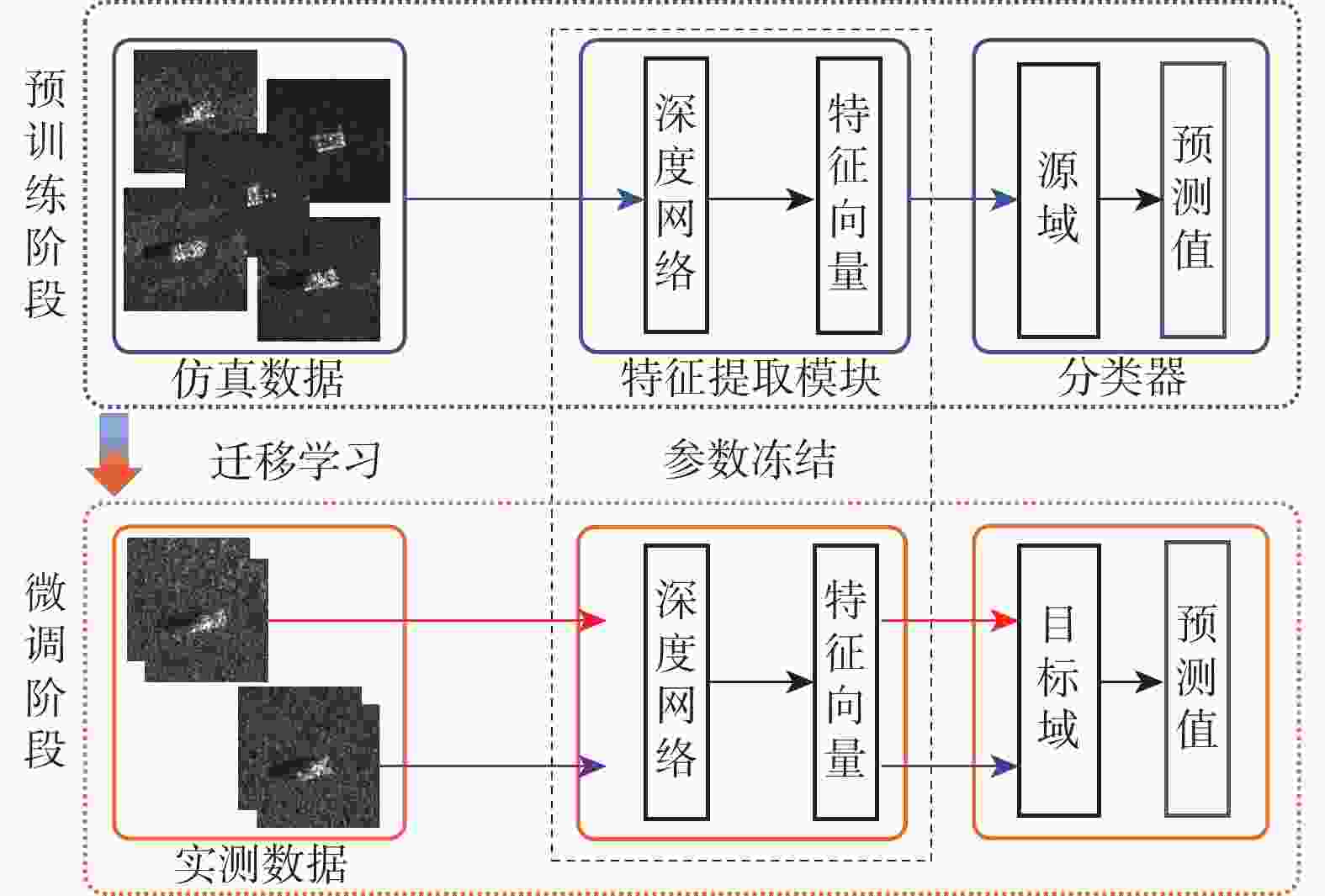
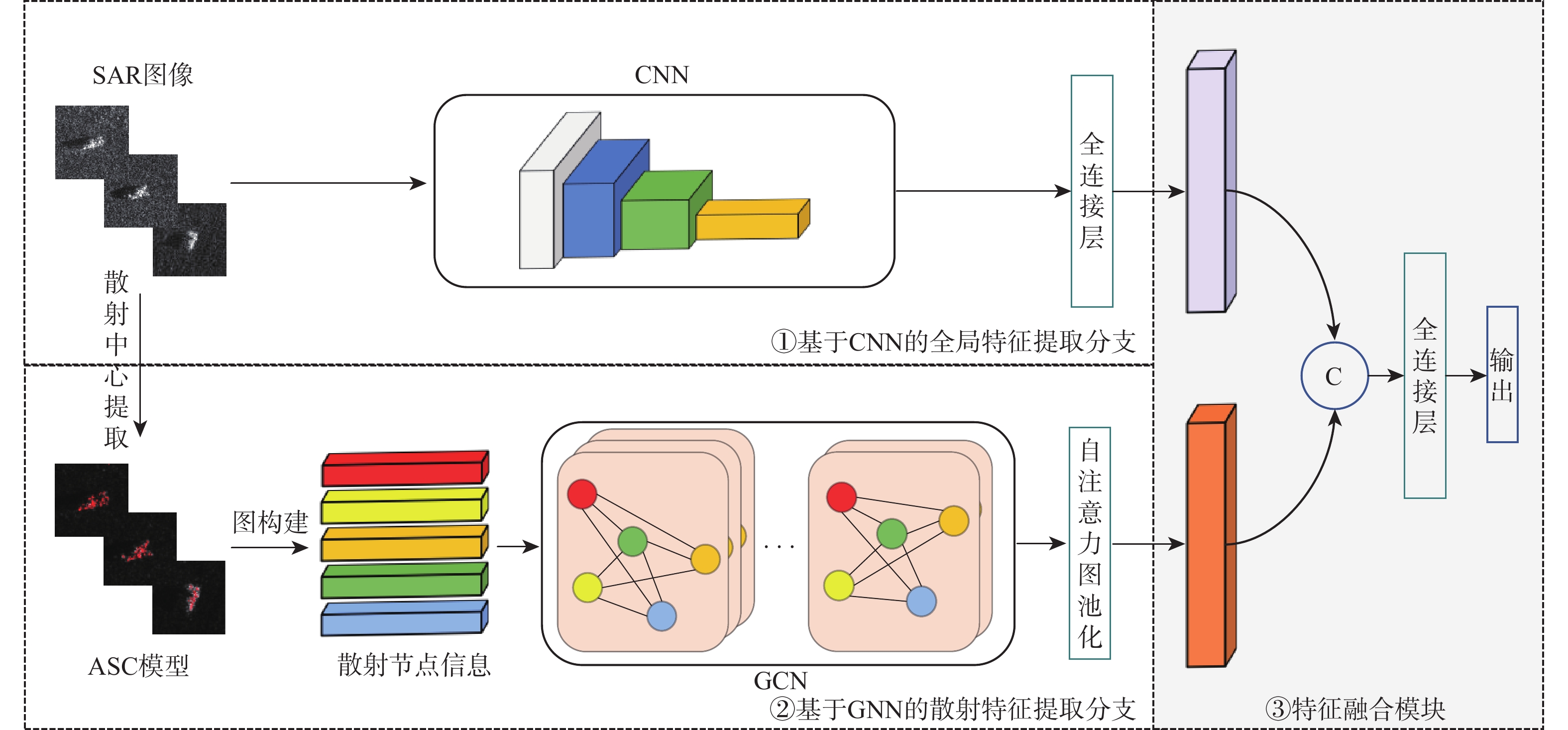
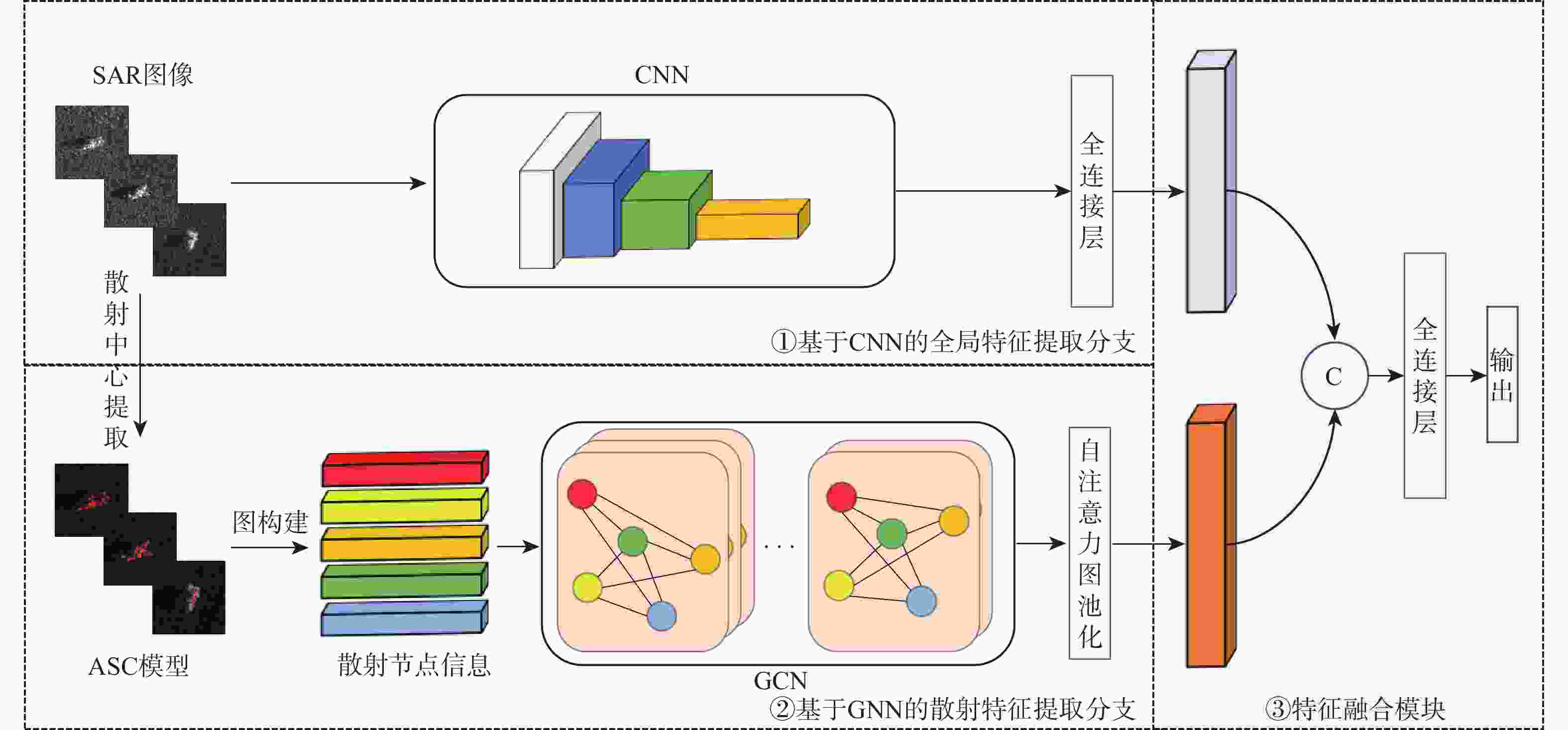
深度学习在合成孔径雷达(SAR)自动目标识别(ATR)领域中应用广泛。针对SAR图像的成像特点及标记样本有限的问题,提出基于深度特征融合模型的迁移学习方法。利用卷积神经网络(CNN)和图神经网络(GNN)分别提取图像域上的全局特征和属性散射特征,将2支网络提取得到的特征进行融合,融合后的特征能充分利用SAR图像的幅值和相位信息来完成SAR目标的识别分类。通过全仿真SAR数据预训练得到网络的模型参数,在训练阶段采用投影梯度下降的对抗训练算法来提升模型的对抗鲁棒性。结合迁移学习的思想,利用有限实测数据对预训练模型进行迭代微调。实验结果表明:所提方法在完全缺少实测样本条件下达到94.43%的识别率,同时所提方法能有效提升有限实测样本条件下SAR目标识别的精度。
Abstract:Deep learning is widely applied in the field of automatic target recognition (ATR) for synthetic aperture radar (SAR). The lack of annotated samples and the distinct imaging properties of SAR images are addressed in this work by proposing a transfer learning method based on a deep feature fusion model. The proposed algorithm fuses the globally extracted features from the convolutional neural networks (CNN) branch and the attribute scattering features from the graph neural networks (GNN) branch, thereby fully utilizing both the amplitude and phase information of SAR images for target recognition. The model parameters are pre-trained using fully simulated SAR data, and an adversarial training algorithm based on projected gradient descent is employed during the training phase. Lastly, a small amount of measured data is used to iteratively refine the pre-trained model in line with the principles of transfer learning. According to experimental data, the proposed method successfully improves the accuracy of SAR target recognition in the limited measured sample situation and reaches a recognition rate of 94.43% in the case of a complete lack of measured samples.
-
表 1 不同参数对应的几何散射体
Table 1. Geometric scattering types corresponding to different parameters
几何散射类型 $(\alpha ,L)$ 示意图 二面角 $ \alpha =1,L > 0 $ 
三面角 $ \alpha =1,L=0 $ 
圆柱 $ \alpha =0.5,L > 0 $ 
球 $ \alpha =0,L=0 $ 
边缘侧向 $ \alpha =0,L > 0 $ 
边缘绕射 $ \alpha =-0.5,L > 0 $ 
角绕射 $ \alpha =-1,L=0 $ 
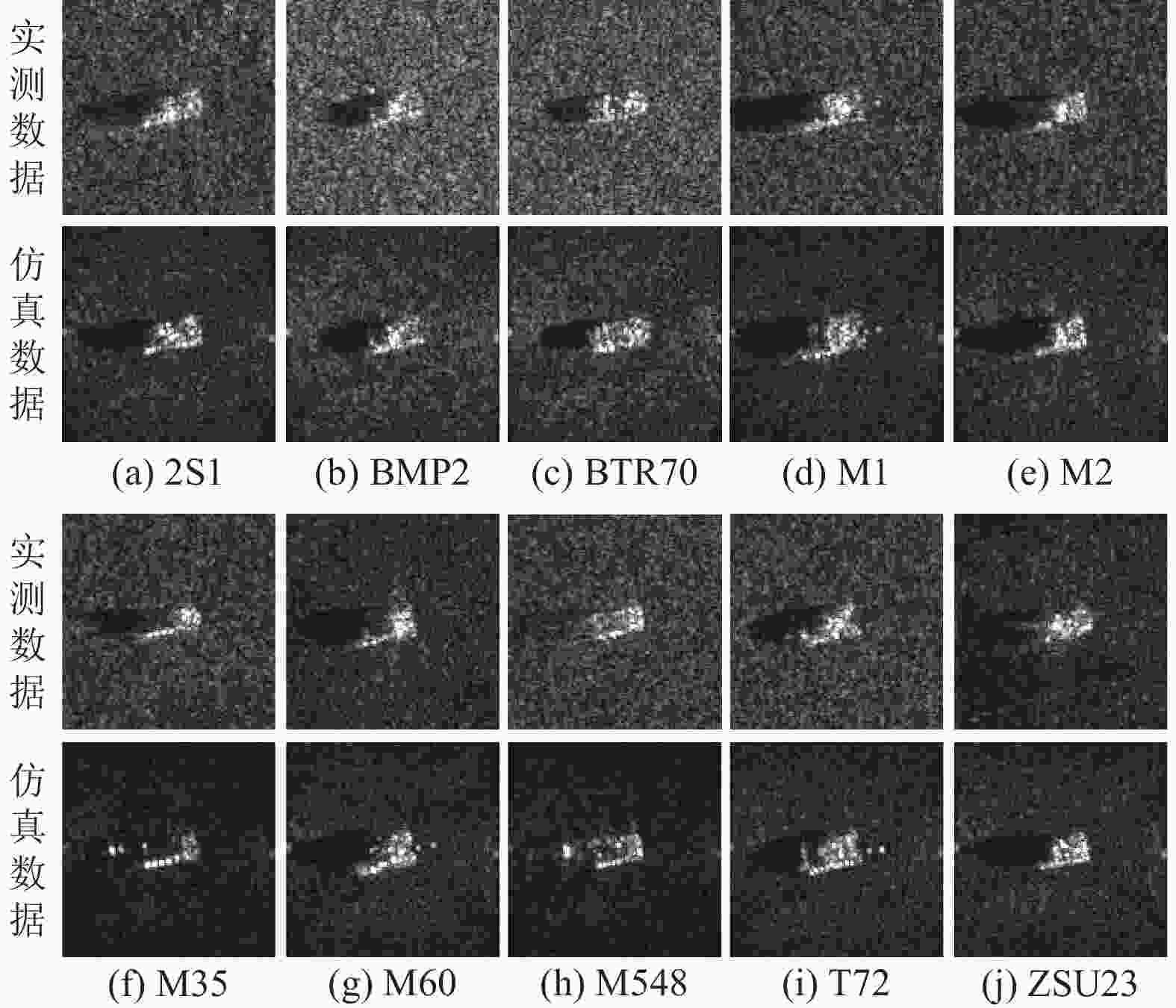
表 2 SAMPLE 数据集10类样本数量
Table 2. Details of SAMPLE ten-target dataset
目标
类别训练样本
数量测试样本
数量目标
类别训练样本
数量测试样本
数量2S1 116 58 M35 76 53 BMP2 55 52 M548 75 53 BTR70 43 49 M60 116 60 M1 78 51 T72 56 52 M2 75 53 ZSU23 116 58 表 3 SAMPLE数据集10类目标识别结果的混淆矩阵
Table 3. Confusion matrix of ten types of target recognition results on SAMPLE dataset
类别 混淆矩阵元素 识别率/% BTR70 M548 M35 T72 M2 M1 M60 ZSU23 2S1 BMP2 BTR70 49 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 100 M548 0 49 4 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 92.45 M35 0 0 52 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 98.11 T72 0 0 0 51 0 0 0 0 0 1 98.07 M2 0 0 0 0 40 0 2 5 1 5 75.47 M1 0 0 0 0 0 51 0 0 0 0 100 M60 0 0 0 0 0 1 59 0 0 0 98.33 ZSU23 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 48 9 0 82.76 2S1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 58 0 100 BMP2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 52 100 表 4 不同方法在SAMPLE数据集上的识别率对比
Table 4. Comparison of recognition rates between different methods on SAMPLE dataset
表 5 不同实测数据量下的各类目标识别率比较
Table 5. Comparison of various targets recognition performance under different measured data volumes
类别 识别率/% 实测
数据量为0%实测
数据量为20%实测
数据量为50%BTR70 100 100 100 M548 92.45 98.11 100 M35 98.11 96.23 100 T72 98.07 100 100 M2 75.47 98.11 94.34 M1 100 100 100 M60 98.33 100 100 ZSU23 82.76 98.28 100 2S1 100 100 100 BMP2 100 100 100 表 6 有限实测数据下的识别率比较
Table 6. Comparison of recognition performance under limited measured data
实测数据量/% 识别率/% CycleGAN[23] 本文方法 0 88.45 94.43 20 97.58 99.07 50 99.83 99.44 表 7 对抗训练有效性验证的消融实验
Table 7. Ablation study for verifying the effectiveness of adversarial training
表 8 双分支网络有效性验证的消融实验
Table 8. Ablation study for verifying effectiveness of dual-branch networks
网络结构 识别率/% 实测
数据量为0%实测
数据量为20%实测
数据量为50%CNN 89.42 95.36 98.87 CNN-GNN 94.43 99.07 99.44 -
[1] KECHAGIAS-STAMATIS O, AOUF N. Automatic target recognition on synthetic aperture radar imagery: a survey[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2021, 36(3): 56-81. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2021.3049857 [2] 郭炜炜, 张增辉, 郁文贤, 等. SAR图像目标识别的可解释性问题探讨[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(3): 462-476. doi: 10.12000/JR20059GUO W W, ZHANG Z H, YU W X, et al. Perspective on explainable SAR target recognition[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(3): 462-476(in Chinese). doi: 10.12000/JR20059 [3] MORGAN D A E. Deep convolutional neural networks for ATR from SAR imagery[C]//Proceedings of the Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery XXII. Bellingham: SPIE, 2015: 116-128. [4] CHEN S Z, WANG H P, XU F, et al. Target classification using the deep convolutional networks for SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(8): 4806-4817. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2551720 [5] ZHAO P F, LIU K, ZOU H, et al. Multi-stream convolutional neural network for SAR automatic target recognition[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(9): 1473. doi: 10.3390/rs10091473 [6] ZHANG Z M, WANG H P, XU F, et al. Complex-valued convolutional neural network and its application in polarimetric SAR image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(12): 7177-7188. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2743222 [7] ZENG Z Q, SUN J P, HAN Z, et al. SAR automatic target recognition method based on multi-stream complex-valued networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5228618. [8] MALMGREN-HANSEN D, KUSK A, DALL J, et al. Improving SAR automatic target recognition models with transfer learning from simulated data[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(9): 1484-1488. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2717486 [9] LIU M, PENG L J, LIU X H, et al. SAR image classification based on CNN in real and simulation datasets[C]//Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Graphic and Image Processing. Bellingham: SPIE, 2018: 820-827. [10] 霍鑫怡, 李焱磊, 陈龙永, 等. 基于卷积注意力和胶囊网络的SAR少样本目标识别方法[J]. 中国科学院大学学报, 2022, 39(6): 783-792.HUO X Y, LI Y L, CHEN L Y, et al. SAR few-sample target recognition method based on convolutional block attention module and capsule network[J]. Journal of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2022, 39(6): 783-792(in Chinese). [11] ZHANG L B, LENG X G, FENG S J, et al. Domain knowledge powered two-stream deep network for few-shot SAR vehicle recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 60: 5215315. [12] LI L P, LIU J, SU L Y, et al. A novel graph metalearning method for SAR target recognition[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2021, 19: 4015705. [13] YANG M J, BAI X R, WANG L, et al. HENC: hierarchical embedding network with center calibration for few-shot fine-grained SAR target classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2023, 32: 3324-3337. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2023.3283065 [14] HUANG Z L, PAN Z X, LEI B. What, where, and how to transfer in SAR target recognition based on deep CNNs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 58(4): 2324-2336. [15] POTTER L C, MOSES R L. Attributed scattering centers for SAR ATR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1997, 6(1): 79-91. doi: 10.1109/83.552098 [16] PATI Y C, REZAIIFAR R, KRISHNAPRASAD P S. Orthogonal matching pursuit: recursive function approximation with applications to wavelet decomposition[C]//Proceedings of the 27th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 1993: 40-44. [17] LEE J, LEE I, KANG J. Self-attention graph pooling[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning. Long Beach: PMLR, 2019: 3734-3743. [18] LEWIS B, CAI K, BULLARD C. Adversarial training on SAR images[C]//Proceedings of the Automatic Target Recognition XXX. Bellingham: SPIE, 2020: 83-90. [19] LEWIS B, SCARNATI T, SUDKAMP E, et al. A SAR dataset for ATR development: the synthetic and measured paired labeled experiment (SAMPLE)[C]//Proceedings of the Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery XXVI. Bellingham: SPIE, 2019: 39-54. [20] WRIGHT J, YANG A Y, GANESH A, et al. Robust face recognition via sparse representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2008, 31(2): 210-227. [21] 康志强, 张思乾, 封斯嘉, 等. 稀疏先验引导CNN学习的SAR图像目标识别方法[J]. 信号处理, 2023, 39(4): 737-750.KANG Z Q, ZHANG S Q, FENG S J, et al. Sparse prior-guided CNN learning for SAR images target recognition[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2023, 39(4): 737-750 (in Chinese). [22] INKAWHICH N, INKAWHICH M J, DAVIS E K, et al. Bridging a gap in SAR-ATR: training on fully synthetic and testing on measured data[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 2942-2955. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3059991 [23] JENNISON A, LEWIS B, DELUNA A, et al. Convolutional and generative pairing for SAR cross-target transfer learning[C]//Proceedings of the Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery XXVIII. Bellingham: SPIE, 2021: 13-19. [24] RUDER S. An overview of gradient descent optimization algorithms[EB/OL]. (2017-06-15)[2023-09-30]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1609.04747v2. [25] SIMONYAN K, ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[EB/OL]. (2015-04-10)[2023-09-30]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.1556. -






 下载:
下载: