-
摘要:
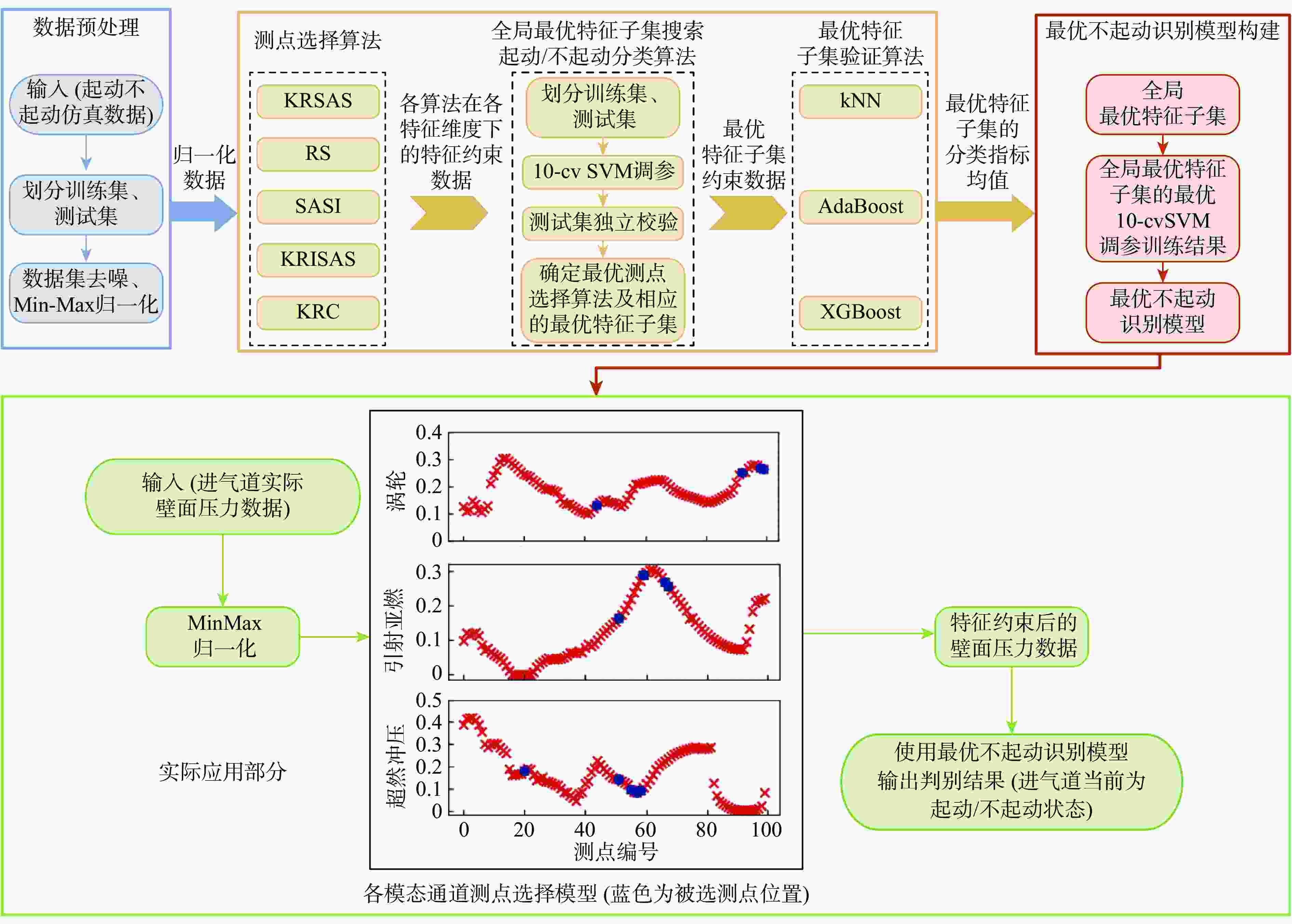
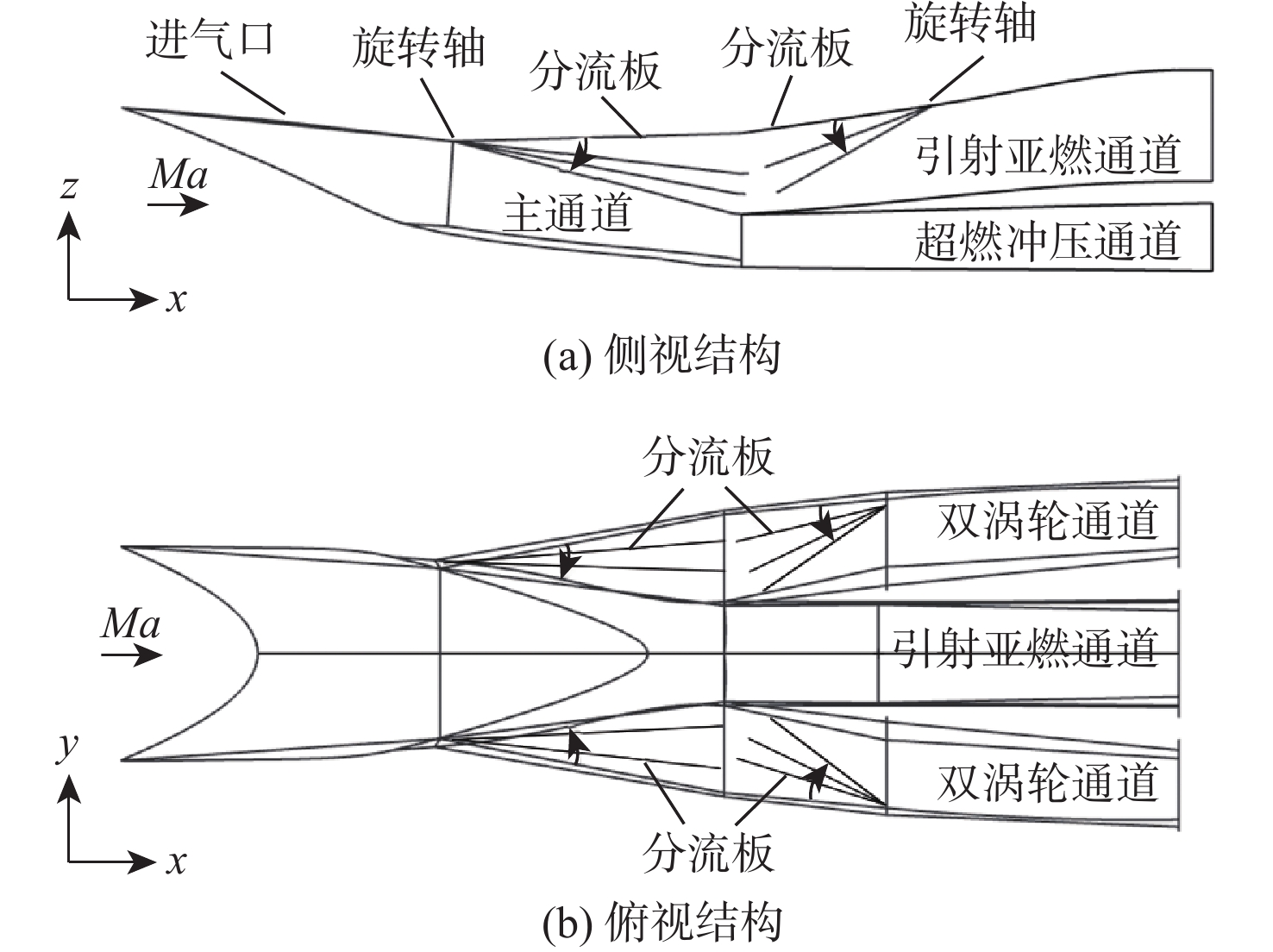
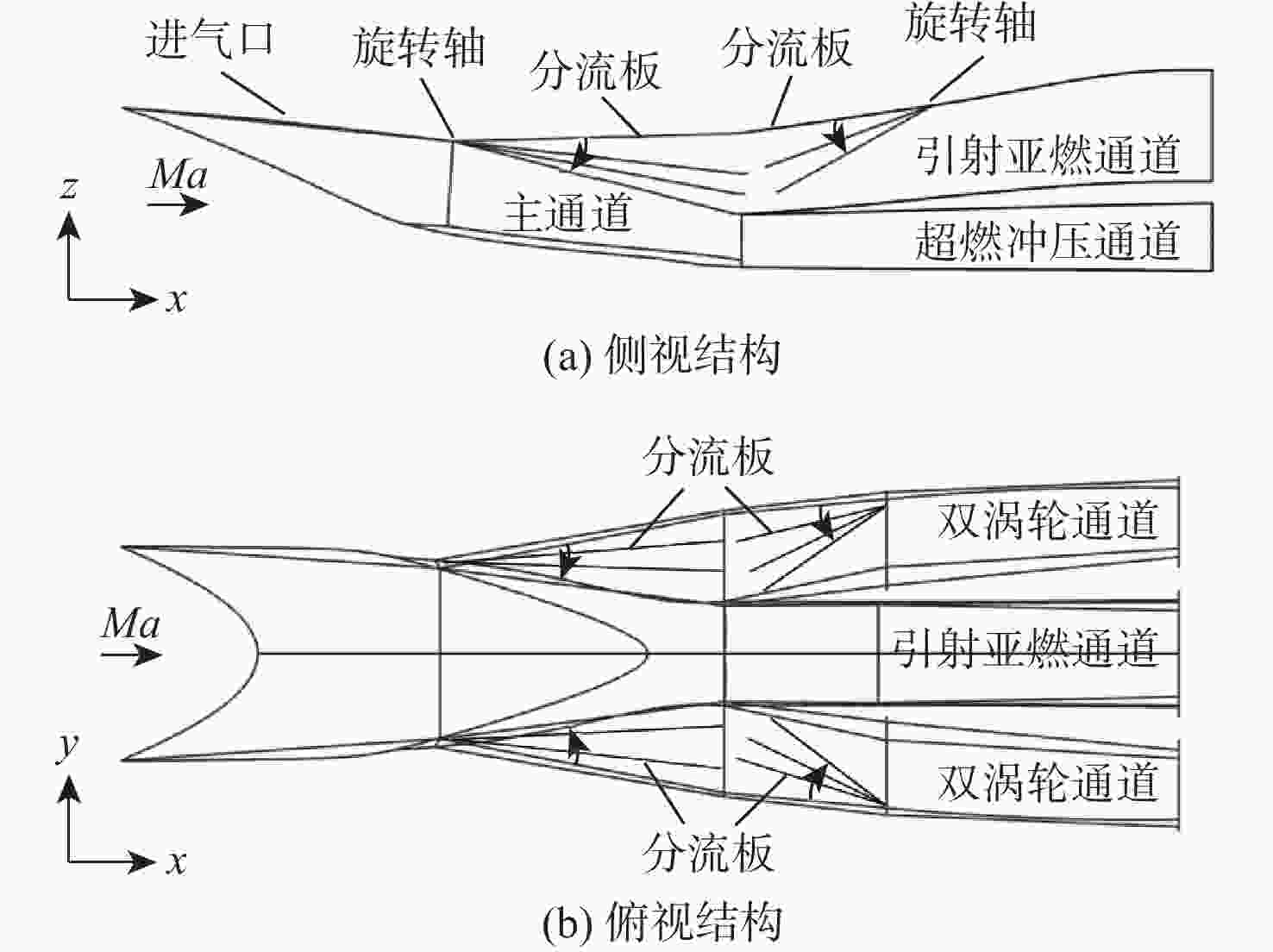
进气道不起动会严重影响到高超声速发动机的正常运行。基于稳态压力信息的模式分类方法,以某高超声速三维内转式组合进气道为研究对象,通过提取关键可靠的壁面压力测点并构建高精度的分类模型,以解决不起动识别问题。在不同马赫数和背压条件下,通过数值模拟获得了若干起动/不起动沿程壁面压力数据。在测点选择算法设计上,提出了一种
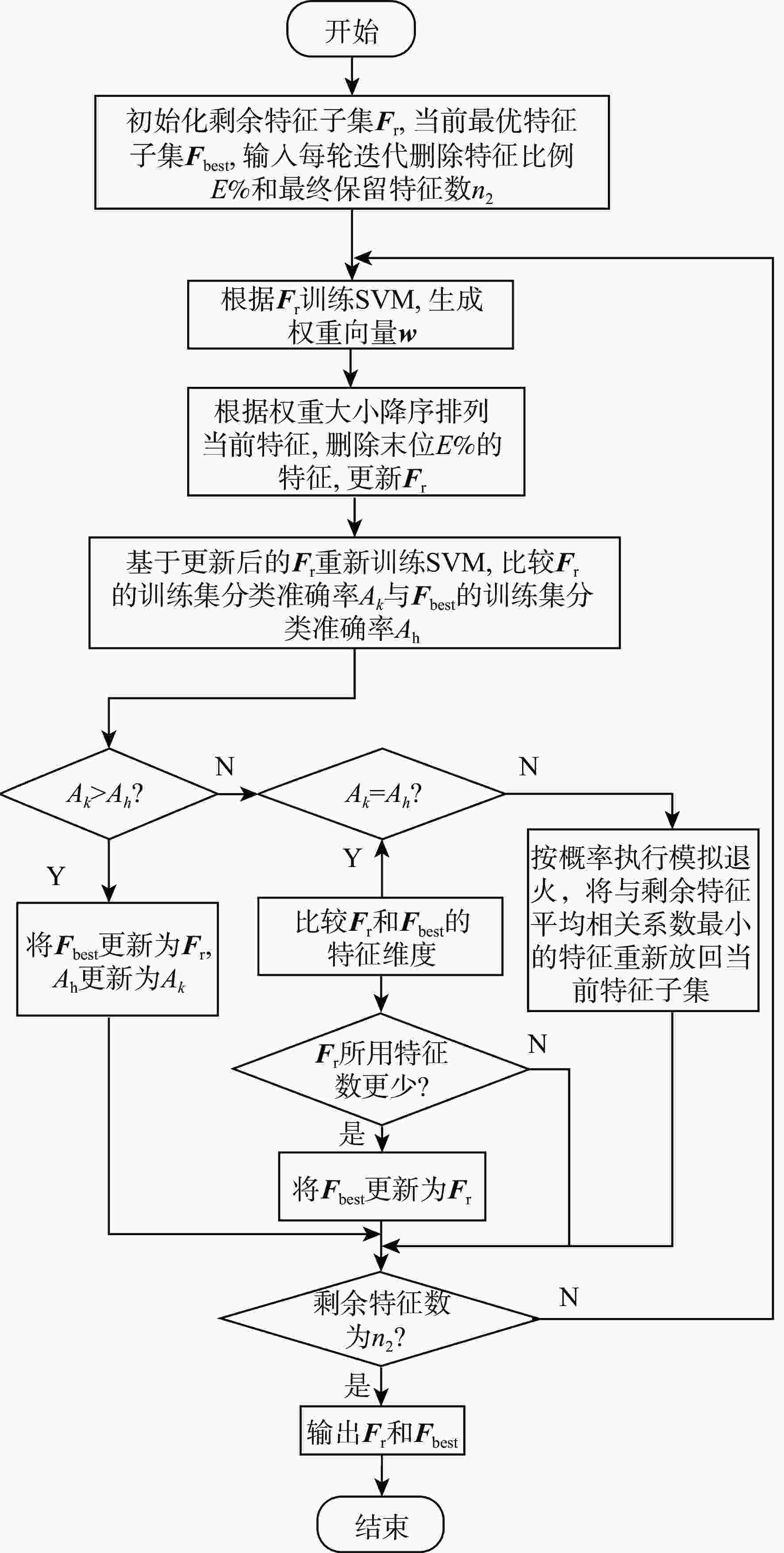
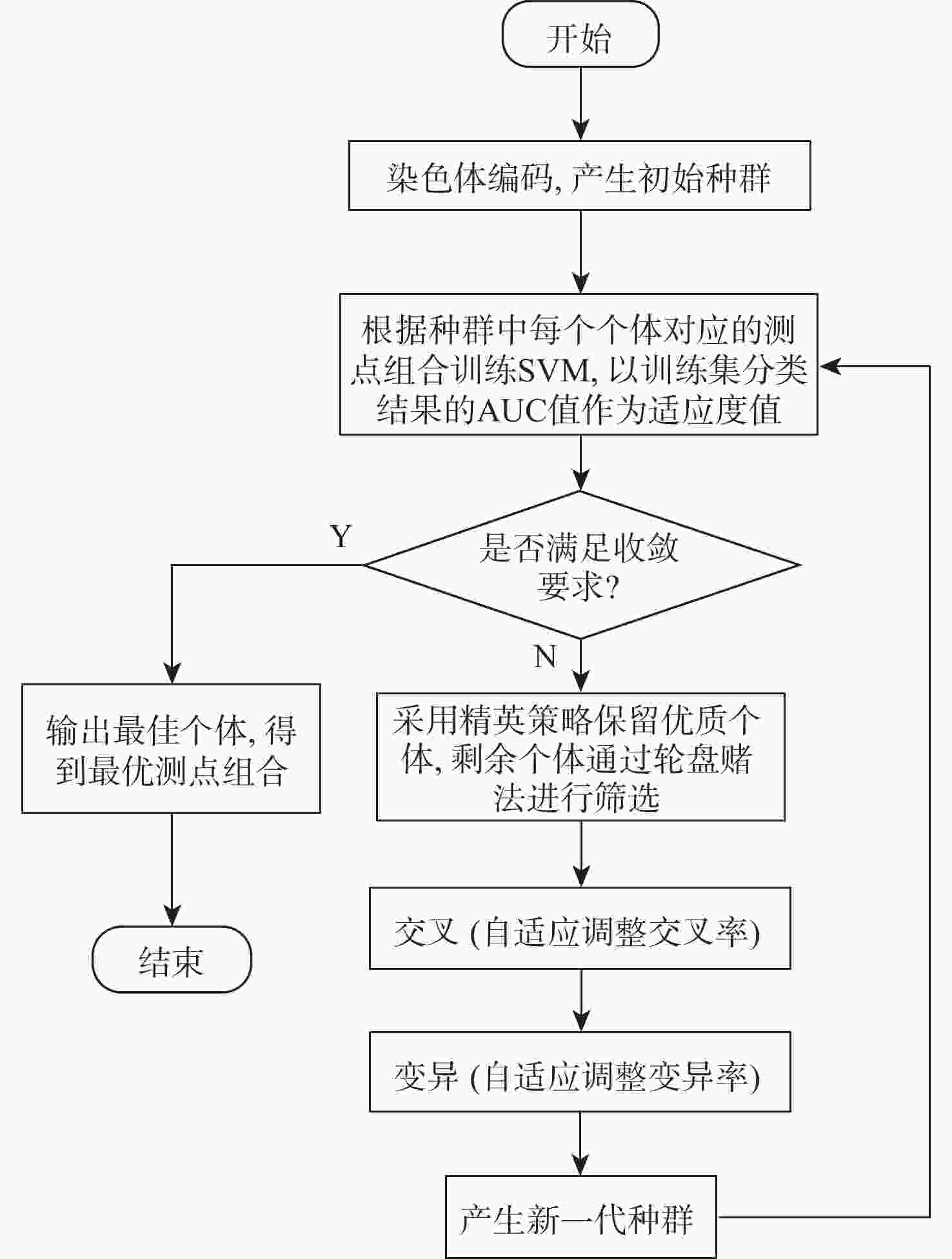
k -均值聚类与ReliefF相结合的算法,在解决原数据集起动/不起动类别不平衡的同时充分考虑了联合特征对的权重信息;为兼顾特征权重和全局分类精度,提出了一种引入模拟退火策略的改进支持向量机递归特征消除算法。将二者进行组合式设计,先采用KMMS-ReliefF算法快速剔除不相关测点,在剩余测点子集中通过SA-SVMRFE算法删除冗余测点,并与其他4种组合算法进行对比。实验结果表明:所提组合算法在最优特征子集维度上明显低于其他算法,利用十折交叉验证支持向量机(10-cv SVM)训练的不起动识别模型,在各模态通道测试集的平均分类准确率均达到99%以上,且具备较高运行效率。此外,通过k最近邻(kNN)、AdaBoost等其他分类算法验证了最优测点组合的可靠性。Abstract:Inlet unstart state can seriously affect the normal operation of hypersonic engines. Based on the pattern classification method of steady state pressure information, a hypersonic three-dimensional internal rotary combined inlet is taken as the research object to solve the unstart state recognition problem by extracting the key reliable wall pressure measurement points and constructing a high-accuracy classification model. Firstly, a number of along-track wall pressure data are obtained for several start/unstart states by numerical simulation, under different Mach numbers and back pressure conditions. Secondly, an algorithm integrating ReliefF (KMMS-ReliefF) and k-means clustering is proposed for the construction of the measurement points selection methods; this algorithm solves the imbalance of start/unstart categories of the dataset while completely considering the weight information of the joint feature pairs. Besides, in order to take into account the feature weights and the global classification accuracy, an improved SVM Recursive Feature Elimination Algorithm with simulated annealing strategy is proposed (SA-SVMRFE). Finally, the two algorithms are combined into a two-stage algorithm (KRSAS). A significant number of unnecessary measurement points are swiftly eliminated from the original dataset in the first stage using the KMMS-ReliefF algorithm. In the second stage, the SA-SVMRFE algorithm eliminates the redundant measurement points from the remaining subset of points. Then the comparison is made with the other four combined algorithms. The experimental results show that the combinatorial algorithm proposed in this paper is significantly lower than other algorithms in terms of optimal feature subset dimension. The unstart recognition model trained by 10-fold cross-validation SVM (10-cv SVM) has an average classification accuracy of more than 99% in the test set of each model tunnel, and has high operational efficiency. In addition, other classification algorithms such as kNN and AdaBoost are used to verify the reliability of the optimal measurement point combinations.
-
Key words:
- hypersonic inlet /
- unstart state recognition /
- feature selection /
- ReliefF /
- k-means clustering /
- SVM-RFE
-
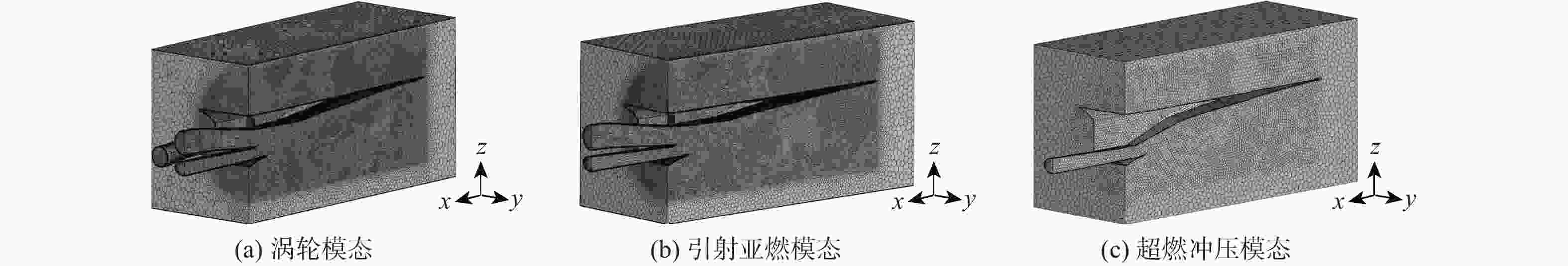
表 1 不同工作点的数值条件
Table 1. Numerical conditions for different operating points
$ {M_a} $ H/km 模态 背压比 1.5 9.1 涡轮 1,1.2,1.4,1.8,2,2.2,2.4,2.6 2.0 13 涡轮 1,1.5,2,2.5,3,3.5,4.25,4.5,4.75,5 2.5 15.5 涡轮 1,2,3,4,6,7,8,9 2.5 15.5 引射亚燃 1,4,6,7,8 3.0 18.5 引射亚燃 1,2,4,5,6,7,8.5,9.5,11 4.0 22.7 引射亚燃 1,3,6,9,12,15,16,17,18 4.0 22.7 超燃冲压 1,5,10,20,30,40,50 4.5 24 超燃冲压 1,10,20,30,40,50,60,70,80 5.0 26 超燃冲压 1,10,20,30,40,60,80,90,100,110,115 6.0 28 超燃冲压 1,10,20,40,70,80,90,95,110,120,130,135 表 2 各模态起动/不起动样本信息
Table 2. Start/Unstart sample information for each model
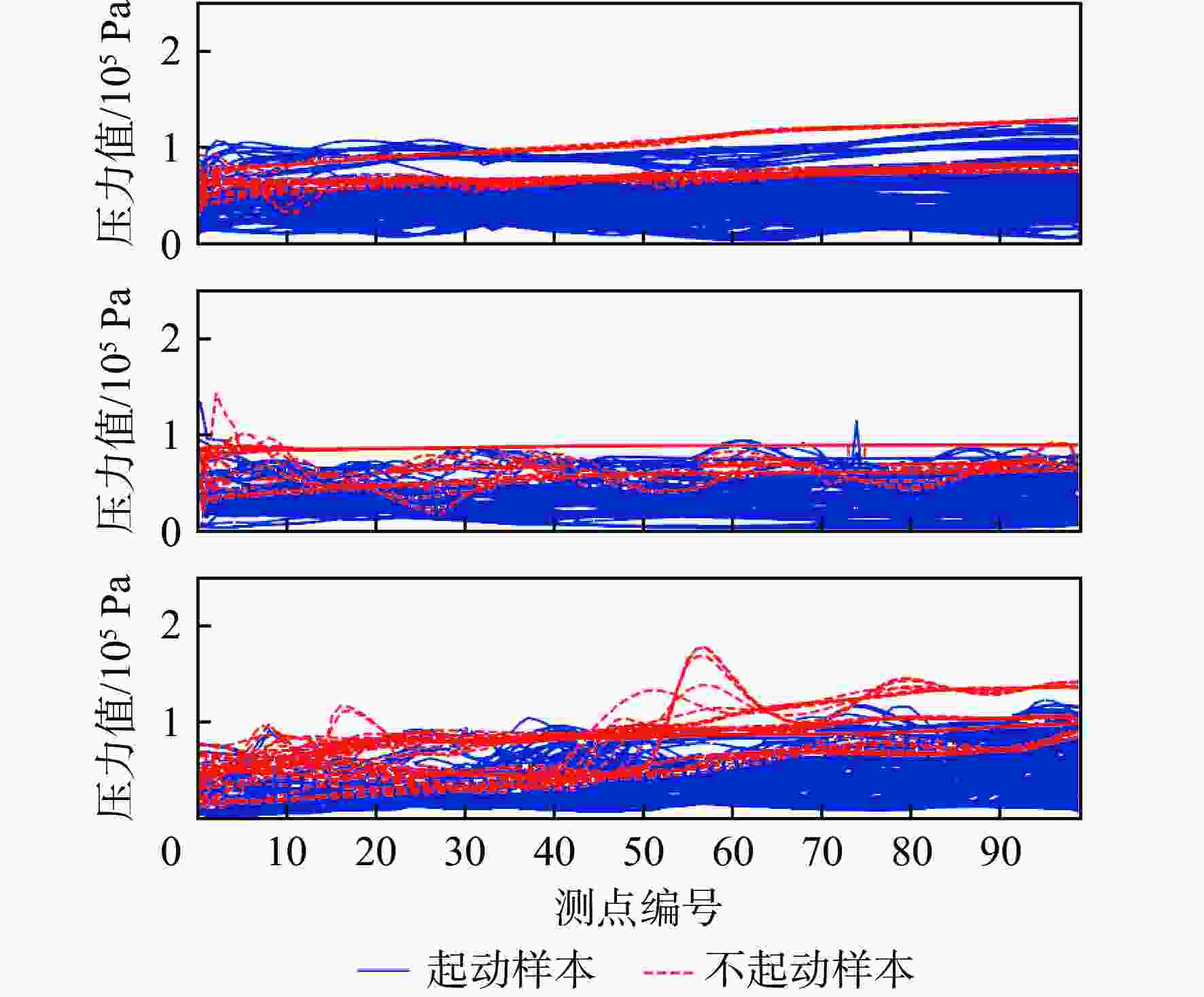
模态 总样本数 起动样本数 不起动样本数 特征数 涡轮 513 465 48 100 引射亚燃 556 498 58 100 超燃冲压 420 380 40 100 表 3 各组合特征选择算法在最优特征维度下的分类性能指标
Table 3. Classification performance metrics of each combined feature selection algorithm under optimal feature dimensions
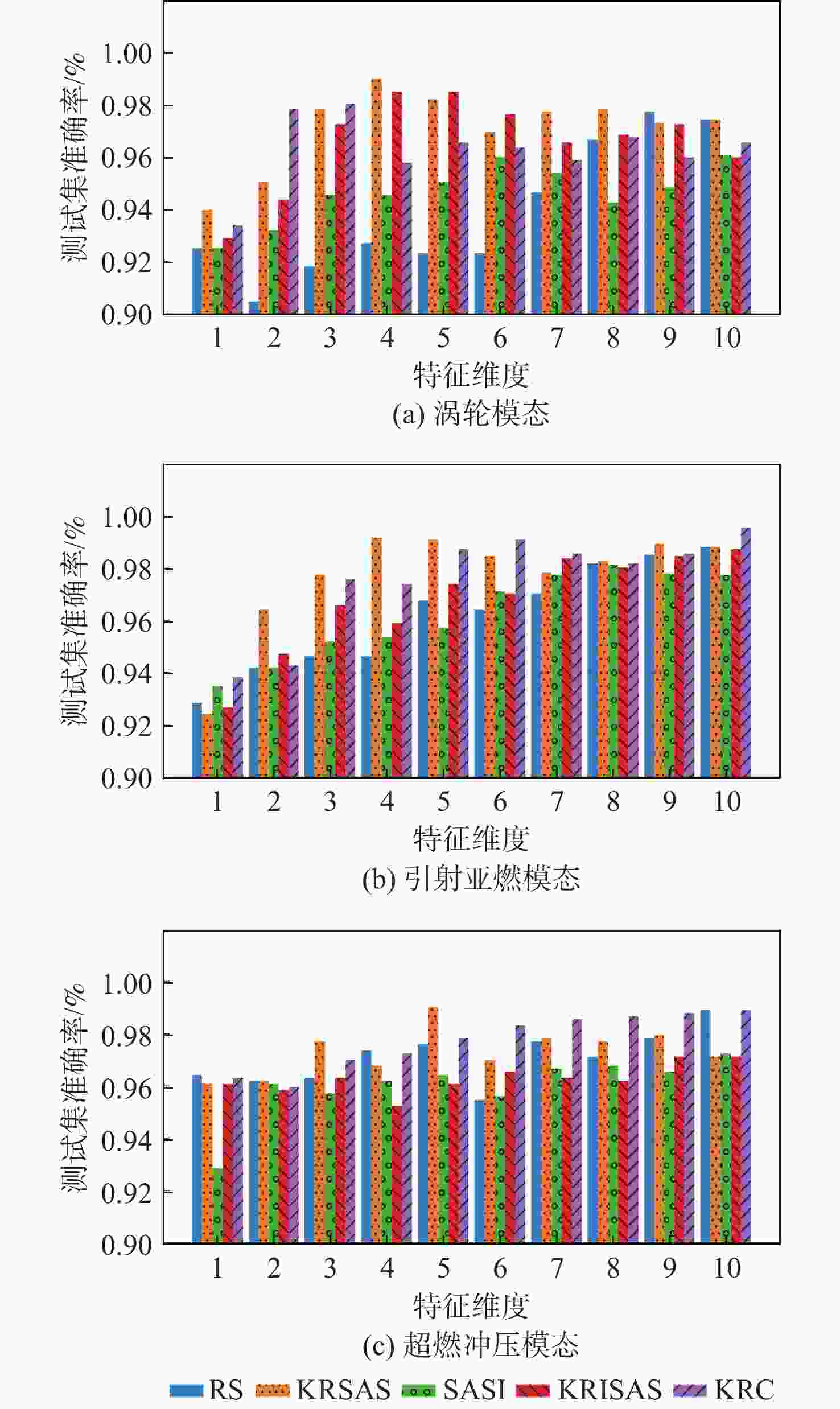
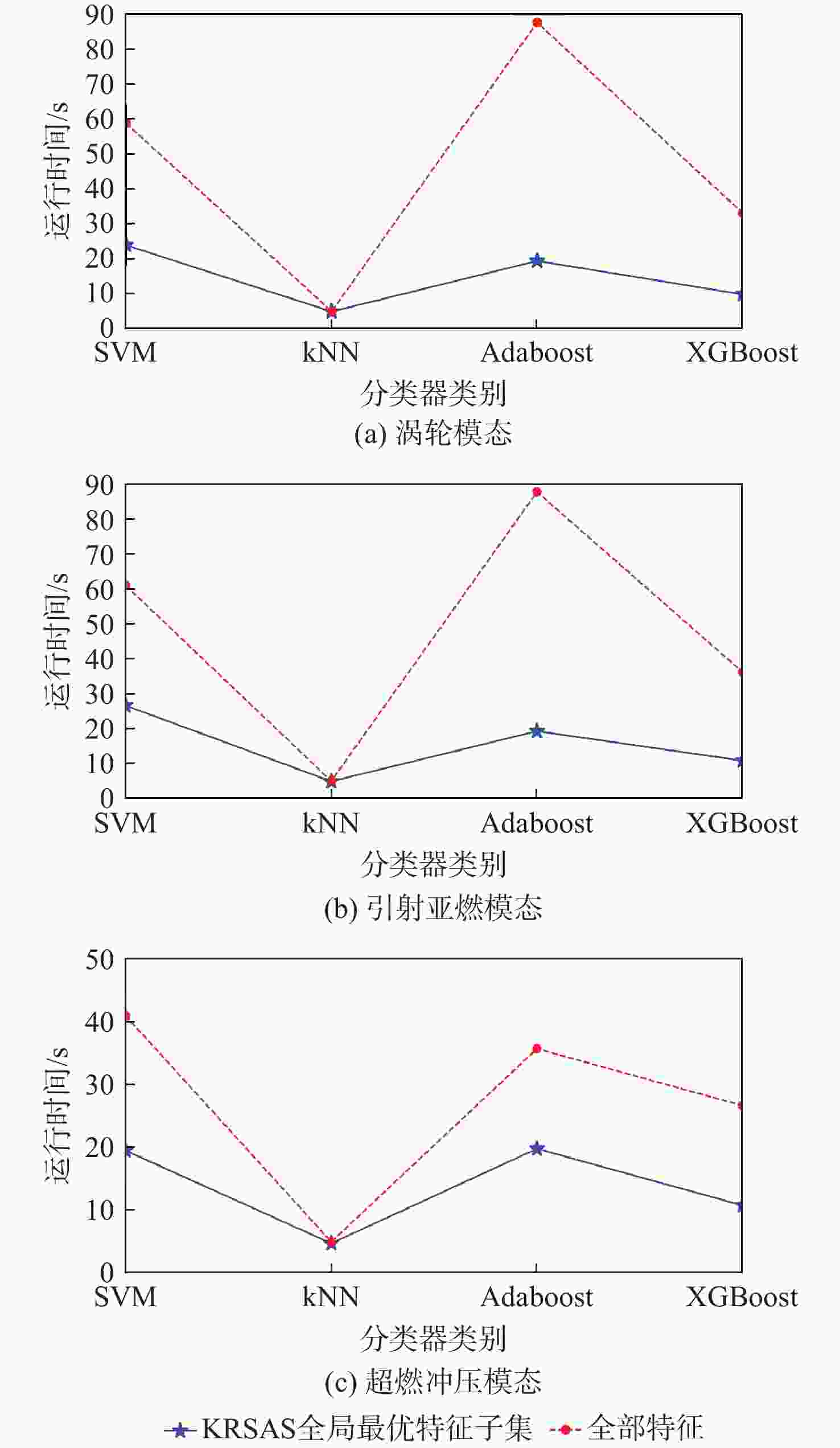
模态 算法 最优特征维度 训练集准确率 测试集准确率 F1-Score AUC 平均耗时/s 涡轮 RS 9 0.998 05 0.977 67 0.987 69 0.956 45 15.334 KRSAS 4 0.993 17 0.990 29 0.995 21 0.987 96 24.358 SASI 10 0.992 68 0.961 17 0.978 33 0.988 49 124.870 KRISAS 4 0.989 51 0.985 44 0.991 87 0.997 42 161.290 KRC 3 0.972 68 0.980 58 0.989 34 0.902 26 16.751 引射亚燃 RS 10 1.000 00 0.988 39 0.993 55 1.000 00 16.339 KRSAS 4 0.997 30 0.991 96 0.995 51 0.998 67 25.773 SASI 8 0.995 27 0.981 25 0.989 61 0.985 42 117.040 KRISAS 10 0.997 52 0.987 50 0.993 05 0.999 33 152.822 KRC 10 1.000 00 0.995 54 0.997 51 0.999 92 16.504 超燃冲压 RS 10 0.994 31 0.989 29 0.994 04 1.000 00 15.139 KRSAS 5 0.989 82 0.990 48 0.994 72 0.993 26 28.104 SASI 10 0.982 63 0.972 62 0.984 94 0.928 62 111.710 KRISAS 9 0.989 22 0.971 43 0.984 31 0.991 12 158.230 KRC 10 0.991 92 0.989 29 0.994 11 1.000 00 16.651 表 4 各算法在最优特征维度下的最优特征子集
Table 4. Optimal feature subsets for each algorithm under the optimal feature dimension
模态 算法 最优特征子集 训练集准确率 测试集准确率 出现次数 涡轮 KRSAS [37, 42, 92, 98] 1.000 00 1.000 00 1 [44, 92, 98, 99] 0.990 24 1.000 00 3 KRISAS [37, 43, 92, 98] 1.000 00 1.000 00 1 引射亚燃 KRSAS [51, 59, 66, 67] 1.000 00 1.000 00 2 [19, 48, 67, 76] 1.000 00 1.000 00 1 KRC [36, 41, 45, 53, 60, 68, 72, 75, 88, 93] 1.000 00 1.000 00 3 超燃冲压 RS [27, 30, 33, 34, 38, 39, 49, 56, 57, 58] 0.99 401 1.000 00 1 KRSAS [20, 51, 56, 57, 58] 0.991 02 1.000 00 2 [20, 51, 55, 57, 58] 0.991 02 1.000 00 2 KRC [22, 24, 27, 32, 44, 46, 54, 65, 81, 82] 1.000 00 1.000 00 1 表 5 KRSAS算法最优特征子集的F1-Score验证结果
Table 5. F1-Score validation results for the optimal feature subsets of the KRSAS algorithm
通道 最优特征子集
和所有特征F1-Score F1-Score平均值 SVM kNN AdaBoost XGBoost 涡轮 [37, 42, 92, 98] 1.000 00 0.994 59 1.000 00 0.978 72 0.993 33 [44, 92, 98, 99] 1.000 00 1.000 00 1.000 00 0.983 78 0.995 95 所有特征 0.989 25 0.978 02 0.978 49 0.972 68 0.979 61 引射亚燃 [51, 59, 66, 67] 1.000 00 0.990 00 0.990 10 0.985 22 0.991 33 [19, 48, 67, 76] 1.000 00 0.979 59 0.975 37 0.965 52 0.980 12 所有特征 0.995 02 0.994 97 0.995 02 0.970 30 0.988 83 超燃冲压 [20, 51, 56, 57, 58] 1.000 00 0.980 39 0.993 38 0.986 84 0.990 15 [20, 51, 55, 57, 58] 1.000 00 0.980 39 0.993 46 0.993 46 0.991 83 所有特征 0.980 65 0.979 87 0.993 46 1.000 00 0.988 50 -
[1] 谭慧俊, 卜焕先, 张启帆, 等. 高超声速进气道不起动问题的研究进展[J]. 南京航空航天大学学报, 2014, 46(4): 501-508. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2615.2014.04.003TAN H J, BU H X, ZHANG Q F, et al. Review of hypersonic inlet unstart phenomenon[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics, 2014, 46(4): 501-508(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2615.2014.04.003 [2] 张启帆, 谭慧俊, 陈昊. 基于滑动多缝板的高超声速进气道不起动振荡流态控制实验研究[J]. 推进技术, 2017, 38(7): 1450-1458.ZHANG Q F, TAN H J, CHEN H. Experimental study of unstart oscillatory flow control of hypersonic inlet with movable slot-plate[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology, 2017, 38(7): 1450-1458(in Chinese). [3] 常军涛, 于达仁, 鲍文. 攻角引起的高超声速进气道不起动/再起动特性分析[J]. 航空动力学报, 2008, 23(5): 816-821.CHANG J T, YU D R, BAO W. Characteristic analysis of unstart/restart of hypersonic inlets caused by variations of attack angle of freestream[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2008, 23(5): 816-821(in Chinese). [4] 刘振皓, 任方, 郭静, 等. 基于LES的超声速进气道不起动流场分析[C]//北京力学会第21届学术年会暨北京振动工程学会第22届学术年会论文集. 北京: 北京力学会, 2015: 1327-1329.LIU Z H, REN F, GUO J, et al. LES-based analysis of unstart flow field in supersonic intakes[C]//Proceeding of the 21st Annual Conference of the Beijing Society of Theoretical and Applied Mechanic and the 22nd Annual Conference of the Beijing Society of Vibration Engineering. Beijing: BSTAM, 2015: 1327-1329(in Chinese). [5] 王晨曦, 谭慧俊, 张启帆, 等. 高超声速进气道低马赫数不起动和再起动试验[J]. 航空学报, 2017, 38(11): 43-54.WANG C X, TAN H J, ZHANG Q F, et al. Test of low Mach number unstart and restart processes of hypersonic inlet[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2017, 38(11): 43-54(in Chinese). [6] CHANG J T, LI N, XU K J, et al. Recent research progress on unstart mechanism, detection and control of hypersonic inlet[J]. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 2017, 89: 1-22. doi: 10.1016/j.paerosci.2016.12.001 [7] 贺理浩, 张启帆, 岳连捷, 等. 高速进气道低马赫数不起动特性及马赫数影响规律[J]. 推进技术, 2021, 42(10): 2207-2217.HE L H, ZHANG Q F, YUE L J, et al. Unstart characteristics of high speed inlet at low Mach number and influence law of Mach number[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology, 2021, 42(10): 2207-2217(in Chinese). [8] 袁化成, 梁德旺. 高超声速侧压式模型进气道不起动特性分析[J]. 南京航空航天大学学报, 2004, 36(6): 683-687. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2615.2004.06.003YUAN H C, LIANG D W. Characteristic analysis of unstart performance for hypersonic side-wall inlet model[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics, 2004, 36(6): 683-687(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2615.2004.06.003 [9] YU D R, CHANG J T, BAO W, et al. Optimal classification criterions of hypersonic inlet start/unstart[J]. Journal of Propulsion and Power, 2007, 23(2): 310-316. doi: 10.2514/1.24640 [10] CHANG J, YU D, BAO W, et al. A CFD assessment of classifications for hypersonic inlet start/unstart phenomena[J]. The Aeronautical Journal, 2009, 113(1142): 263-271. doi: 10.1017/S0001924000002931 [11] 胡清华, 常军涛, 鲍文, 等. 高超声速发动机进气道起动/不起动模式分析[C]//第二十九届中国控制会议论文集. 北京: 中国控制会议, 2010: 5939-5944.HU Q H, CHANG J T, BAO W, et al. Pattern analysis on hypersonic inlet state of start/unstart[C]//Proceedings of the 29th Chinese Control Conference. Beijing: CCC, 2010: 5939-5944(in Chinese). [12] ZHENG R S, CHANG J T, HE H X, et al. Optimal classification of hypersonic inlet start/unstart based on manifold learning[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2013, 274: 200-203. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.274.200 [13] 刘欢, 黄俊, 张勇, 等. Relief和SVMRFE在高超声速进气道不起动预测中的应用[J]. 计算机测量与控制, 2018, 26(4): 183-186, 190.LIU H, HUANG J, ZHANG Y, et al. Application of relief and SVMRFE in predicting unstart of hypersonic inlet[J]. Computer Measurement & Control, 2018, 26(4): 183-186, 190. [14] 刘欢. 高超声速进气道起动/不起动分类研究与实现[D]. 绵阳: 西南科技大学, 2018: 33-35.LIU H. Research and implementation of classification of hypersonic inlet start/unstart[D]. Mianyang: Southwest University of Science and Technology, 2018: 33-35(in Chinese). [15] 王祥. 基于改进的自适应遗传算法与多模型融合的信贷风险预测模型研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2021: 41-45.WANG X. Research on credit risk forecasting model based on improved adaptive genetic algorithm and multi-model fusion[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2021: 41-45(in Chinese). [16] ZHU C X, ZHANG X, KONG F, et al. Design of a three-dimensional hypersonic inward-turning inlet with tri-ducts for combined cycle engines[J]. International Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 2018(1): 7459141. [17] ZHU C X, ZHANG H F, HU Z C, et al. Analysis on the low speed performance of an inward-turning multiduct inlet for turbine-based combined cycle engines[J]. International Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 2019(1): 6728387. [18] 蔡泽君, 胡占仓, 余联郴, 等. XTER内收缩组合进气道设计理念及气动特性[J]. 空气动力学学报, 2022, 40(1): 218-231. doi: 10.7638/kqdlxxb-2021.0393CAI Z J, HU Z C, YU L C, et al. Design concept and aerodynamic characteristics of XTER TBCC inlet[J]. Acta Aerodynamica Sinica, 2022, 40(1): 218-231(in Chinese). doi: 10.7638/kqdlxxb-2021.0393 [19] ROBNIK-ŠIKONJA M, KONONENKO I. Theoretical and empirical analysis of ReliefF and RReliefF[J]. Machine Learning, 2003, 53(1): 23-69. [20] TIWARI D. Handling class imbalance problem using feature selection[J]. International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science & Technology, 2014, 2(2): 516-520. [21] 尹欢一. 一种改进的多阶段ReliefF特征选择算法[J]. 信息与电脑, 2019, 16: 45-47.YIN H Y. An improved multi-stage ReliefF feature selection algorithm[J]. China Computer & Communication, 2019, 16: 45-47(in Chinese). [22] GUYON I, WESTON J, BARNHILL S. Gene selection for cancer classification using support vector machines[J]. Machine Learning, 2001, 46(1-3): 389-422. [23] 张学工, 汪小我. 模式识别: 模式识别与机器学习[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2021: 137-156.ZHANG X G, WANG X W. Pattern recognition: pattern recognition and machine learning[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2021: 137-156(in Chinese). [24] 王君. 基于SVM-RFE的特征选择方法研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2015: 13-17.WANG J. The research of feature selection algorithm based on SVM-RFE[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2015: 13-17(in Chinese). -






 下载:
下载: