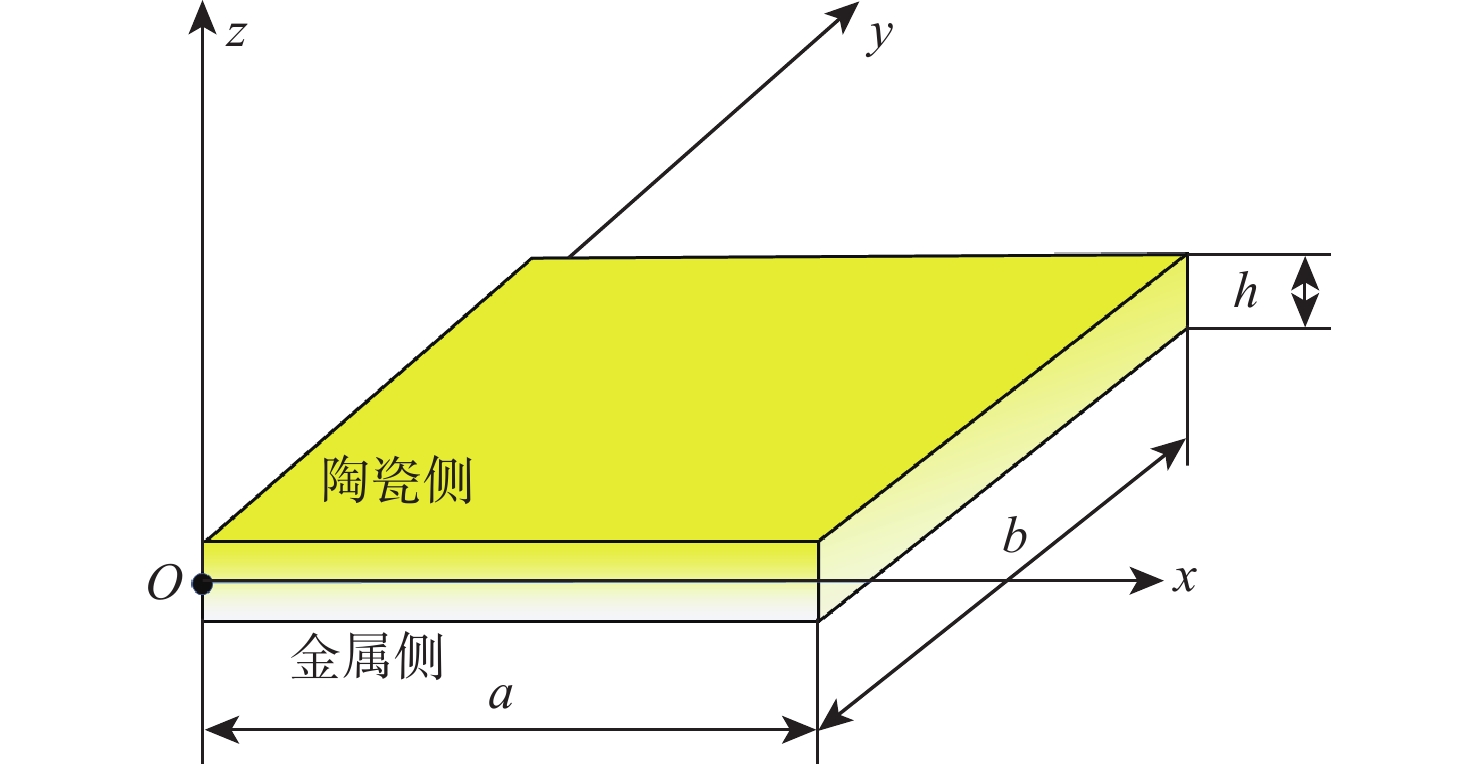
Buckling characteristics of metal-ceramic functionally graded plates in thermal loading environments
-
摘要:
功能梯度材料(FGM)是一种新型材料,由2种及以上的材料组分连续变化混合而成,由于其优秀的力学性能,被广泛应用于航空航天、生物医学、汽车等领域。但热载荷环境对FGM影响的解析理论研究还很少。针对功能梯度板的力学特性,提出一种基于里兹法和经典板理论的解析方法。重点分析了热载荷环境的影响,主要研究了热应力引起的刚度降低,以及材料属性随温度变化对FGM的影响。通过能量法表示应变能、热应变能,利用哈密顿原理建立运动微分方程,分析功能梯度板在均匀温度场、线性温度场和非线性温度场下的热屈曲特性。分析了梯度指数、温度场和宽厚比、宽长比等几何参数对功能梯度板屈曲特性的影响。结果表明:梯度指数对功能梯度板屈曲特性的影响呈复杂非线性,且温度场分布及材料属性随温度变化特性影响显著。
Abstract:Because of its exceptional mechanical qualities, functionally graded material (FGM)— a unique material made up of a constantly changing mixture of two or more components—has earned respect in both academics and industry. Nonetheless, there are limited studies on the analytical approach to the impact of thermal loading on FGM. In this paper, a mechanical characterization method applicable to functionally graded plates is proposed, which is based on the Ritz method and classical plate theory. The study focuses on investigating the effects of thermal loading on the reduction of stiffness caused by thermal stresses, and the effects of material property changes at different temperatures on FGM. The thermal buckling of functionally graded plates is analyzed under the uniform, linear, and nonlinear temperature fields. Strain energy and thermal strain energy are used to establish differential equations of motion through the energy method and Hamilton’s principle. Furthermore, the functionally graded plates’ mechanical characteristics are examined in connection with the width-to-thickness ratio, temperature field, gradient index, and width-to-length ratio. The results indicate that the gradient index exerts a complex nonlinear influence on the buckling characteristics of functionally graded plates, with significant effects arising from the temperature field distribution and the temperature-dependent properties.
-
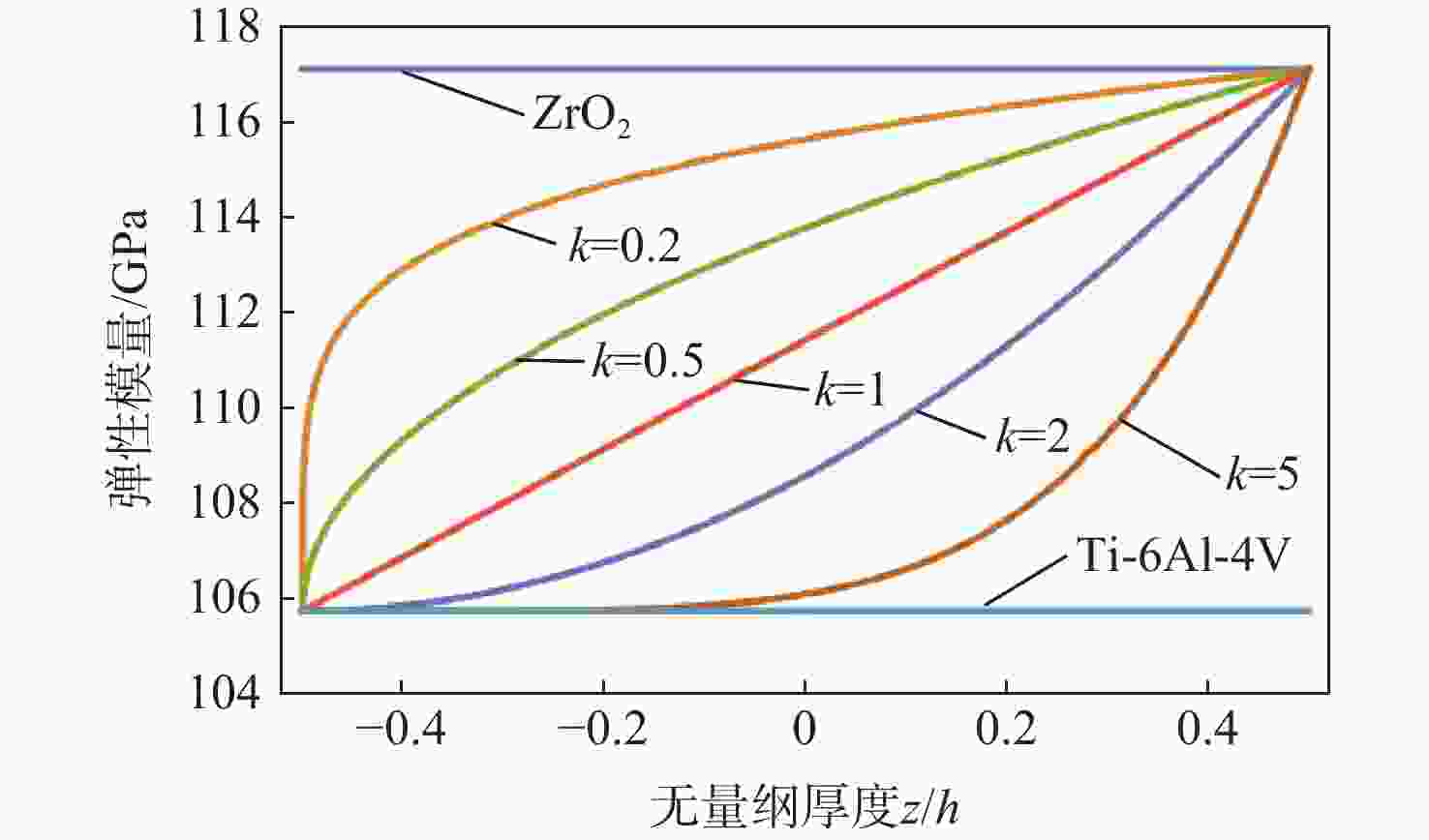
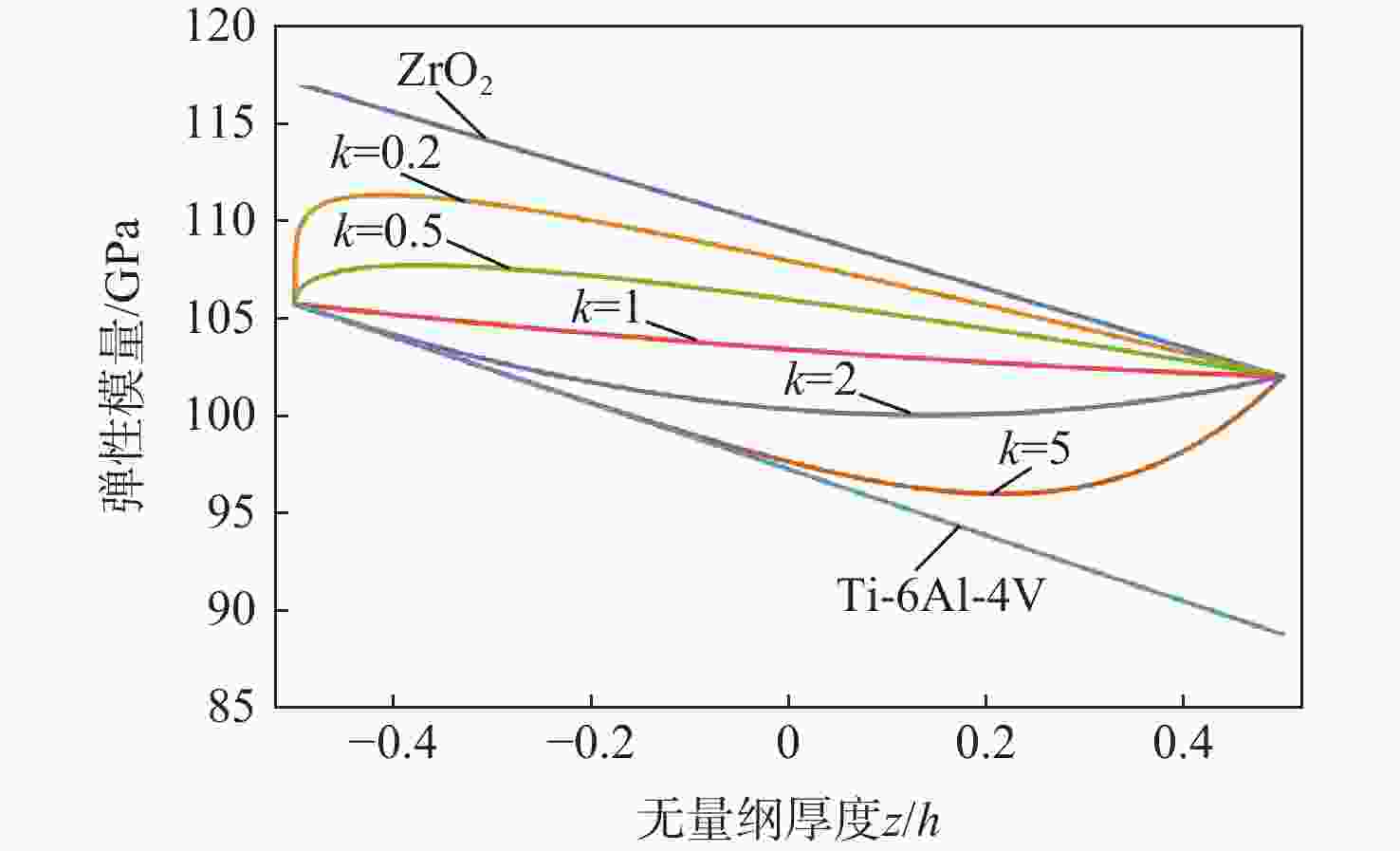
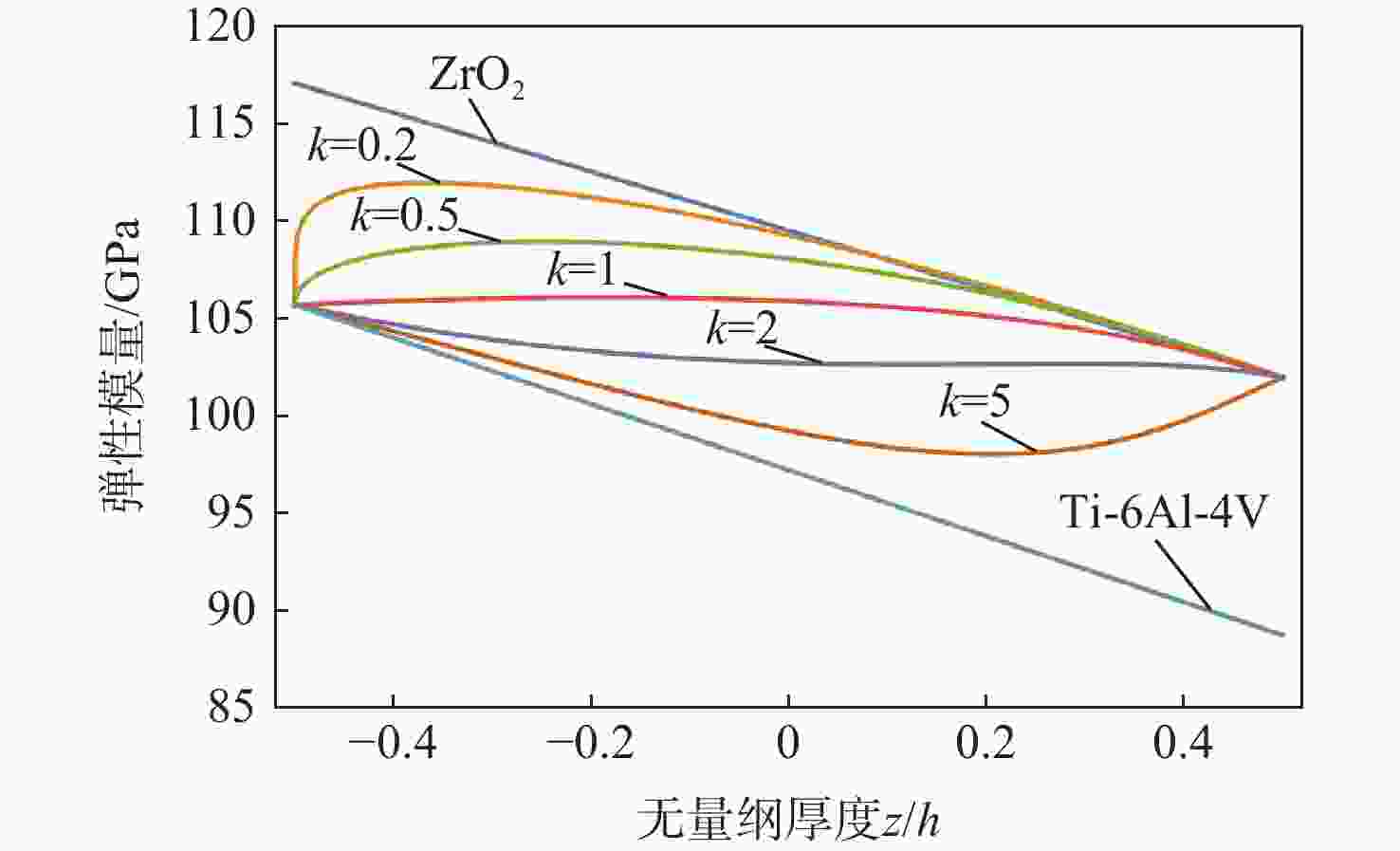
表 1 Ti-6Al-4V和ZrO2的材料性能
Table 1. Material properties for Ti-6Al-4V and ZrO2
材料 弹性模量/Pa 热膨胀系数 密度/(kg·m−3) 热传导系数/(W·(m·K)−1)) 常数项 1次项 常数项 1次项 常数项 1次项 常数项 1次项 Ti-6Al-4V 122.70×109 −4.605×10−4 7.430 ×10−67.483×10−4 4429 0 7.82 0 ZrO2 132.20×109 −3.805×10−4 13.300×10−6 −1.421×10−3 3000 0 1.8 0 表 2 线性/非线性温度场下功能梯度板的临界屈曲温升
Table 2. Critical buckling temperature difference of functionally graded plates under linear and nonlinear temperature field
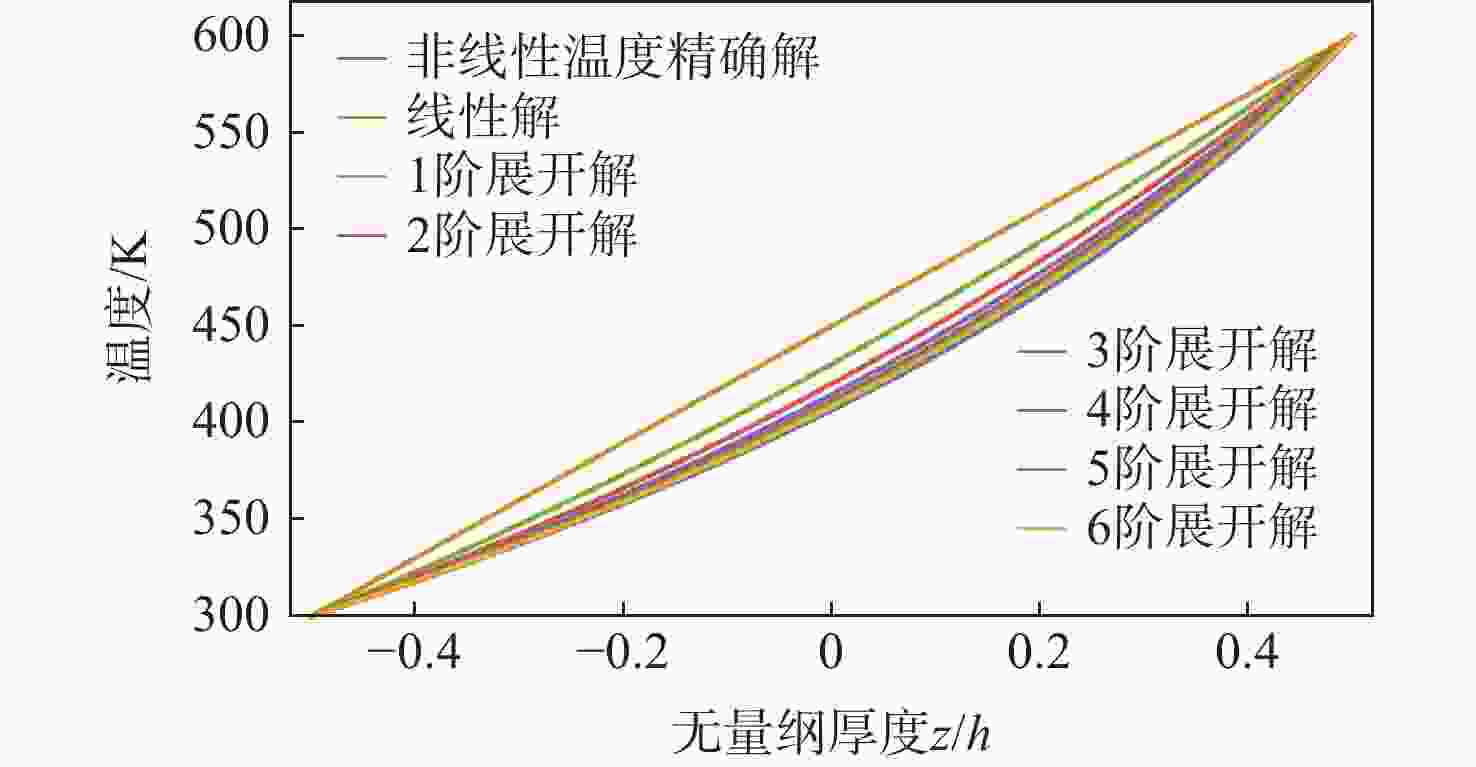
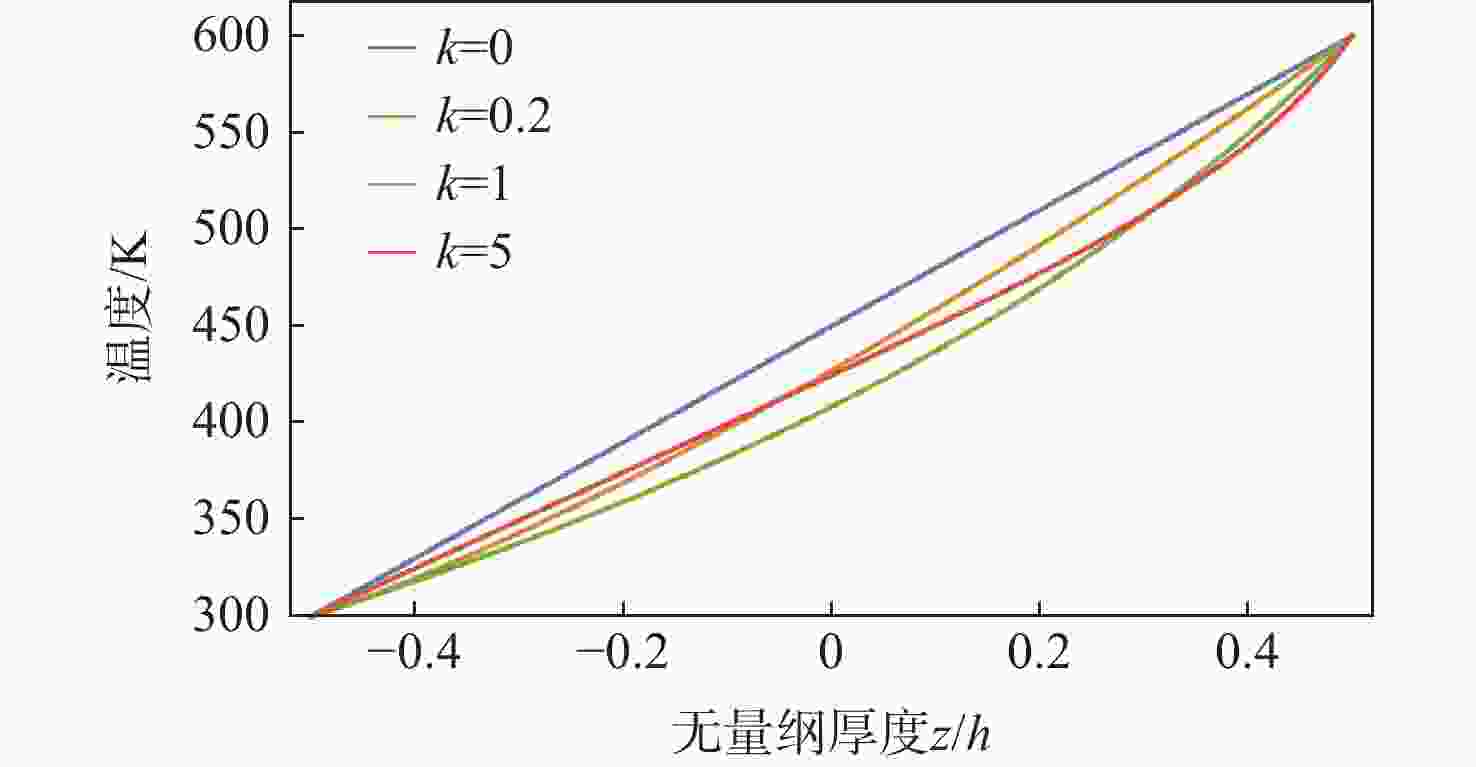
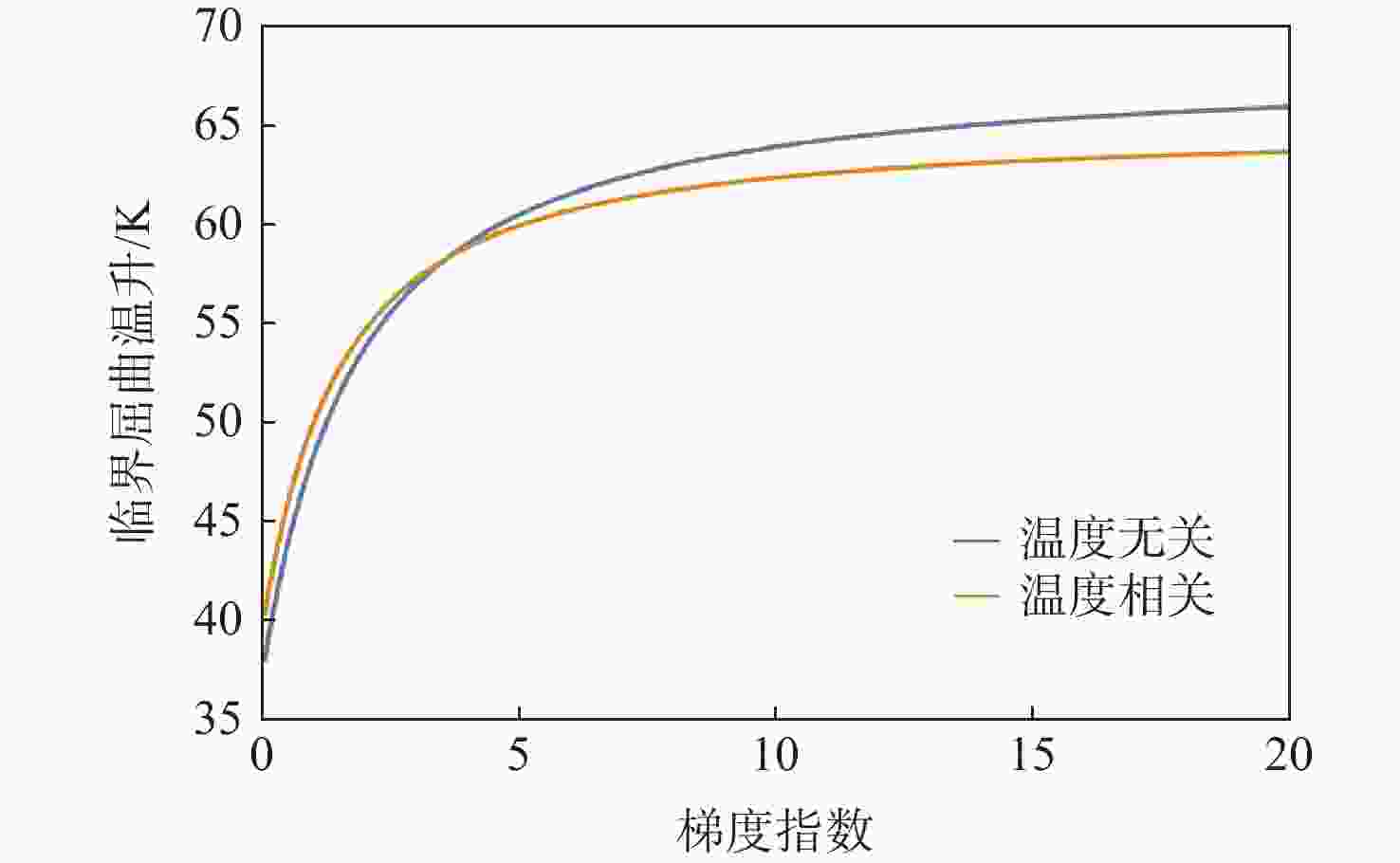
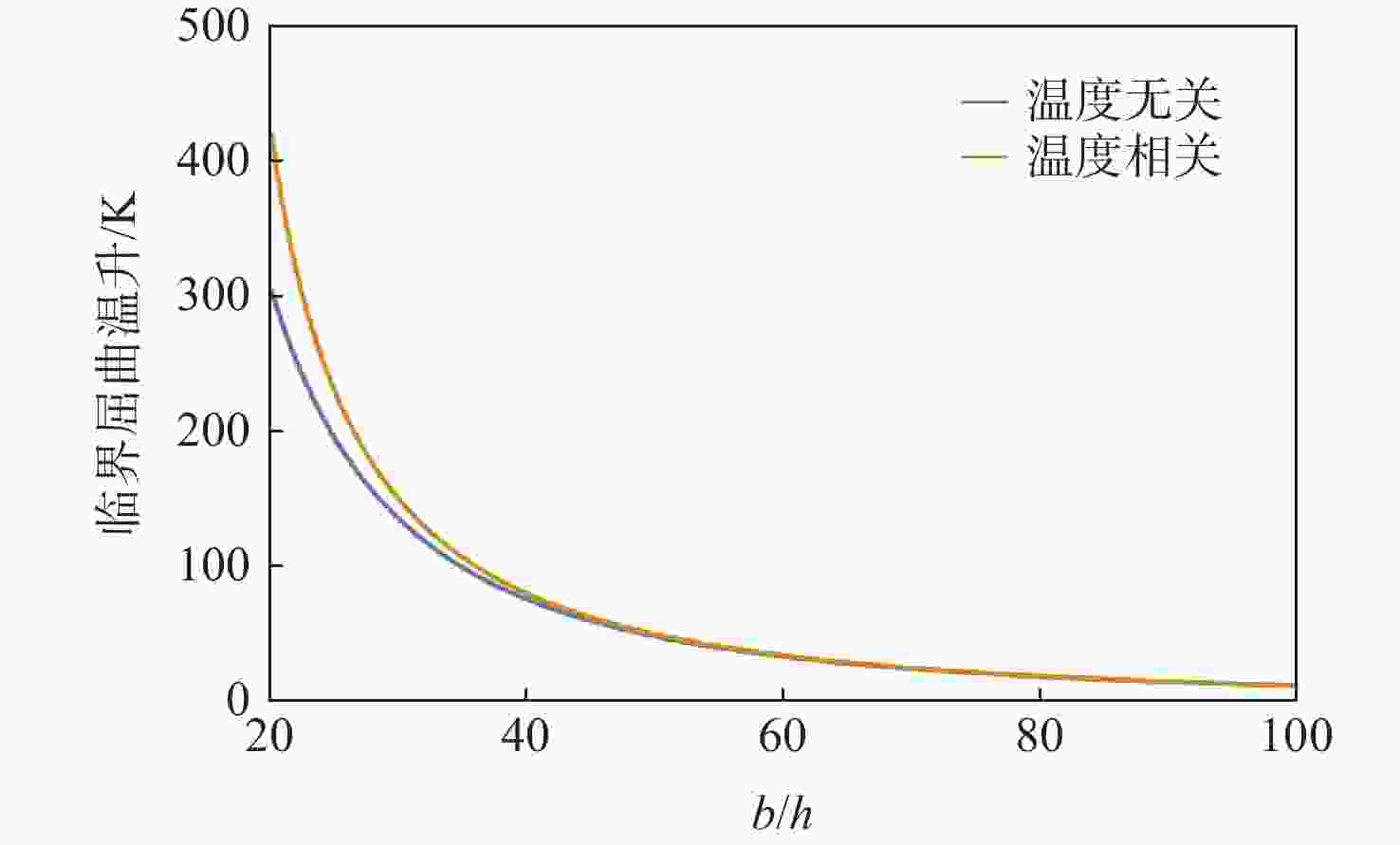
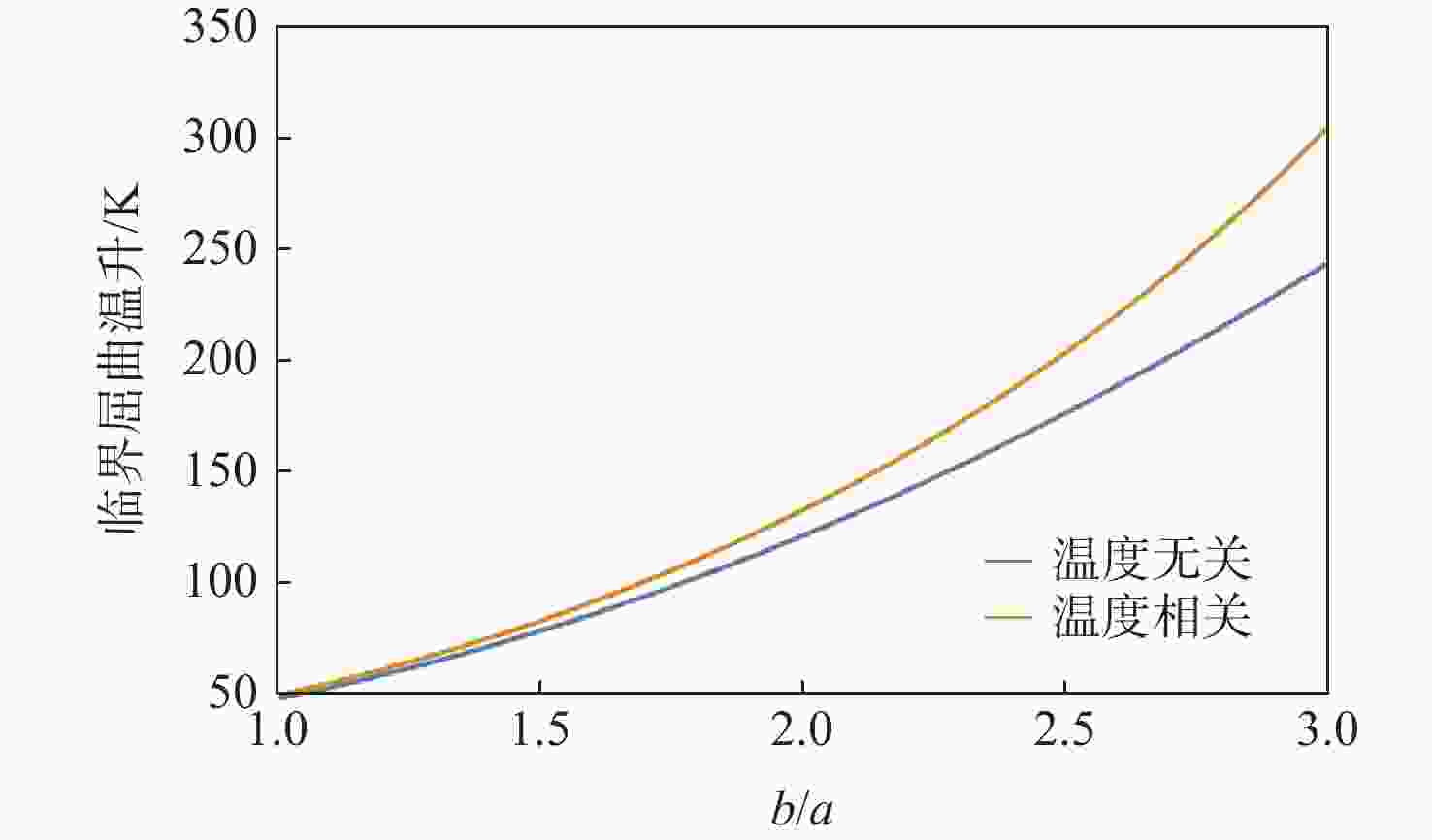
梯度指数 b/h 温度场类型 临界屈曲温升/℃ 计算值 文献值[21] 0 20 线性 844.9553 844.9553 非线性 844.9553 844.9553 40 线性 203.7388 203.7388 非线性 203.7388 203.7388 100 线性 24.1982 24.1982 非线性 24.1982 24.1982 1 20 线性 363.0796 363.0796 非线性 493.9125 503.9879 40 线性 83.7369 83.7369 非线性 113.9108 116.2345 100 线性 5.5209 5.5209 非线性 7.5104 7.6635 5 20 线性 304.0540 304.0540 非线性 372.0301 380.2613 40 线性 69.5587 69.5586 非线性 85.1096 86.9926 100 线性 3.9000 3.8999 非线性 4.7719 4.8774 表 3 不同温度场下的临界屈曲温升(k=1)
Table 3. Critical buckling temperature difference under various temperature fields (k=1)
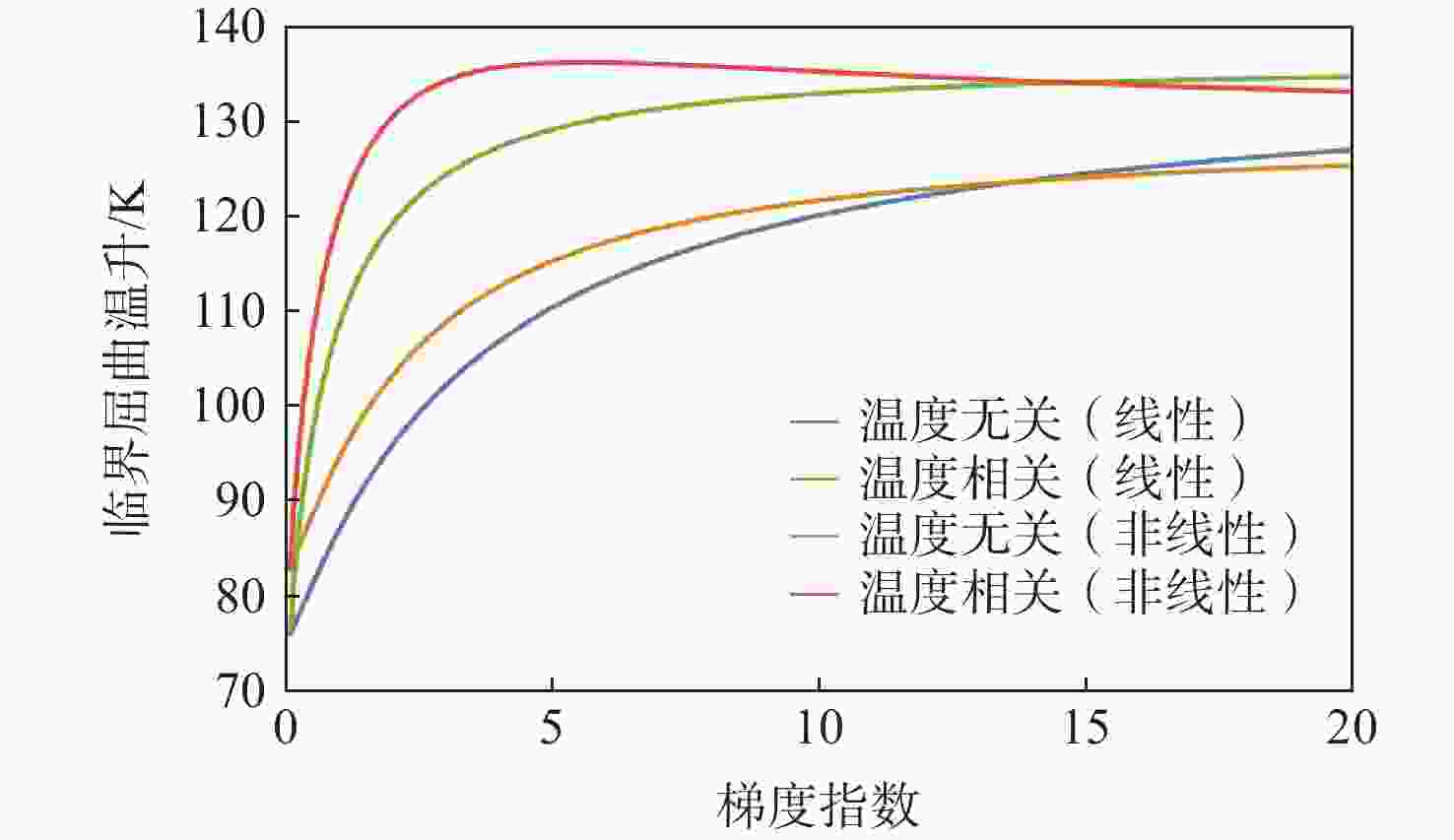
温度场类型 临界屈曲温升/K 均匀温度场(温度无关) 48.6373 均匀温度场(温度相关) 50.2855 线性温度场(温度无关) 87.9170 线性温度场(温度相关) 95.4877 非线性温度场(温度无关) 109.7937 非线性温度场(温度相关) 122.9446 -
[1] DAIKH A A, HOUARI M S A, BELARBI M O, et al. Static and dynamic stability responses of multilayer functionally graded carbon nanotubes reinforced composite nanoplates via quasi 3D nonlocal strain gradient theory[J]. Defence Technology, 2022, 18(10): 1778-1809. doi: 10.1016/j.dt.2021.09.011 [2] LIEW K M, PAN Z Z, ZHANG L W. The recent progress of functionally graded CNT reinforced composites and structures[J]. Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy, 2019, 63(3): 234601. [3] WANG P, GAO Z J, PAN F, et al. A couple of GDQM and iteration techniques for the linear and nonlinear buckling of bi-directional functionally graded nanotubes based on the nonlocal strain gradient theory and high-order beam theory[J]. Engineering Analysis with Boundary Elements, 2022, 143: 124-136. doi: 10.1016/j.enganabound.2022.06.007 [4] KIANI Y, ŻUR K K. Free vibrations of graphene platelet reinforced composite skew plates resting on point supports[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2022, 176: 109363. [5] LI Z C, ZHANG Q, SHEN H, et al. Buckling performance of the encased functionally graded porous composite liner with polyhedral shapes reinforced by graphene platelets under external pressure[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2023, 183: 110370. [6] VAN VINH P, VAN CHINH N, TOUNSI A. Static bending and buckling analysis of bi-directional functionally graded porous plates using an improved first-order shear deformation theory and FEM[J]. European Journal of Mechanics-A/Solids, 2022, 96: 104743. doi: 10.1016/j.euromechsol.2022.104743 [7] GHATAGE P S, KAR V R, SUDHAGAR P E. On the numerical modelling and analysis of multi-directional functionally graded composite structures: a review[J]. Composite Structures, 2020, 236: 111837. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2019.111837 [8] GAYEN D, TIWARI R, CHAKRABORTY D. Static and dynamic analyses of cracked functionally graded structural components: a review[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2019, 173: 106982. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.106982 [9] VAN VINH P, HUY L Q. Finite element analysis of functionally graded sandwich plates with porosity via a new hyperbolic shear deformation theory[J]. Defence Technology, 2022, 18(3): 490-508. doi: 10.1016/j.dt.2021.03.006 [10] CHO J R. Numerical study on the thermal buckling of functionally graded sandwich plates[J]. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2023, 37(4): 1913-1922. doi: 10.1007/s12206-023-0328-6 [11] 仲政, 吴林志, 陈伟球. 功能梯度材料与结构的若干力学问题研究进展[J]. 力学进展, 2010, 40(5): 528-541.ZHONG Z, WU L Z, CHEN W Q. Progress in the study on mechanics problems of functionally graded materials and structures[J]. Advances in Mechanics, 2010, 40(5): 528-541(in Chinese). [12] REDDY J N, WANG C M. An overview of the relationships between solutions of the classical and shear deformation plate theories[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2000, 60(12-13): 2327-2335. doi: 10.1016/S0266-3538(00)00028-2 [13] ABRATE S. Free vibration, buckling, and static deflections of functionally graded plates[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2006, 66(14): 2383-2394. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2006.02.032 [14] THAI H T, KIM S E. A review of theories for the modeling and analysis of functionally graded plates and shells[J]. Composite Structures, 2015, 128: 70-86. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2015.03.010 [15] ZHANG D G, ZHOU Y H. A theoretical analysis of FGM thin plates based on physical neutral surface[J]. Computational Materials Science, 2008, 44(2): 716-720. doi: 10.1016/j.commatsci.2008.05.016 [16] ZAHARI K, HILALI Y, MESMOUDI S, et al. Review and comparison of thin and thick FGM plate theories using a unified buckling formulation[J]. Structures, 2022, 46: 1545-1560. doi: 10.1016/j.istruc.2022.10.115 [17] EL MEICHE N, TOUNSI A, ZIANE N, et al. A new hyperbolic shear deformation theory for buckling and vibration of functionally graded sandwich plate[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2011, 53(4): 237-247. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2011.01.004 [18] REDDY J N. Analysis of functionally graded plates[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2000, 47(1-3): 663-684. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0207(20000110/30)47:1/3<663::AID-NME787>3.0.CO;2-8 [19] SHAHRJERDI A, MUSTAPHA F, BAYAT M, et al. Free vibration analysis of solar functionally graded plates with temperature-dependent material properties using second order shear deformation theory[J]. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2011, 25(9): 2195-2209. doi: 10.1007/s12206-011-0610-x [20] EL-HAINA F, BAKORA A, BOUSAHLA A A, et al. A simple analytical approach for thermal buckling of thick functionally graded sandwich plates[J]. Structural Engineering and Mechanics, 2017, 63(5): 585-595. [21] JAVAHERI R, ESLAMI M R. Thermal buckling of functionally graded plates[J]. AIAA Journal, 2002, 40(1): 162-169. doi: 10.2514/2.1626 [22] 夏巍, 赵东伟, 冯宇鹏. 基于Mindlin横剪变形理论的功能梯度板热屈曲分析[J]. 应用力学学报, 2016, 33(1): 13-18.XIA W, ZHAO D W, FENG Y P. Thermal buckling analysis of functionally graded plates based on Mindlin transverse shear deformable theory[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2016, 33(1): 13-18(in Chinese). -






 下载:
下载: