Structural design and aerodynamic performance analysis of gradient hexagonal deformable wing ribs
-
摘要:
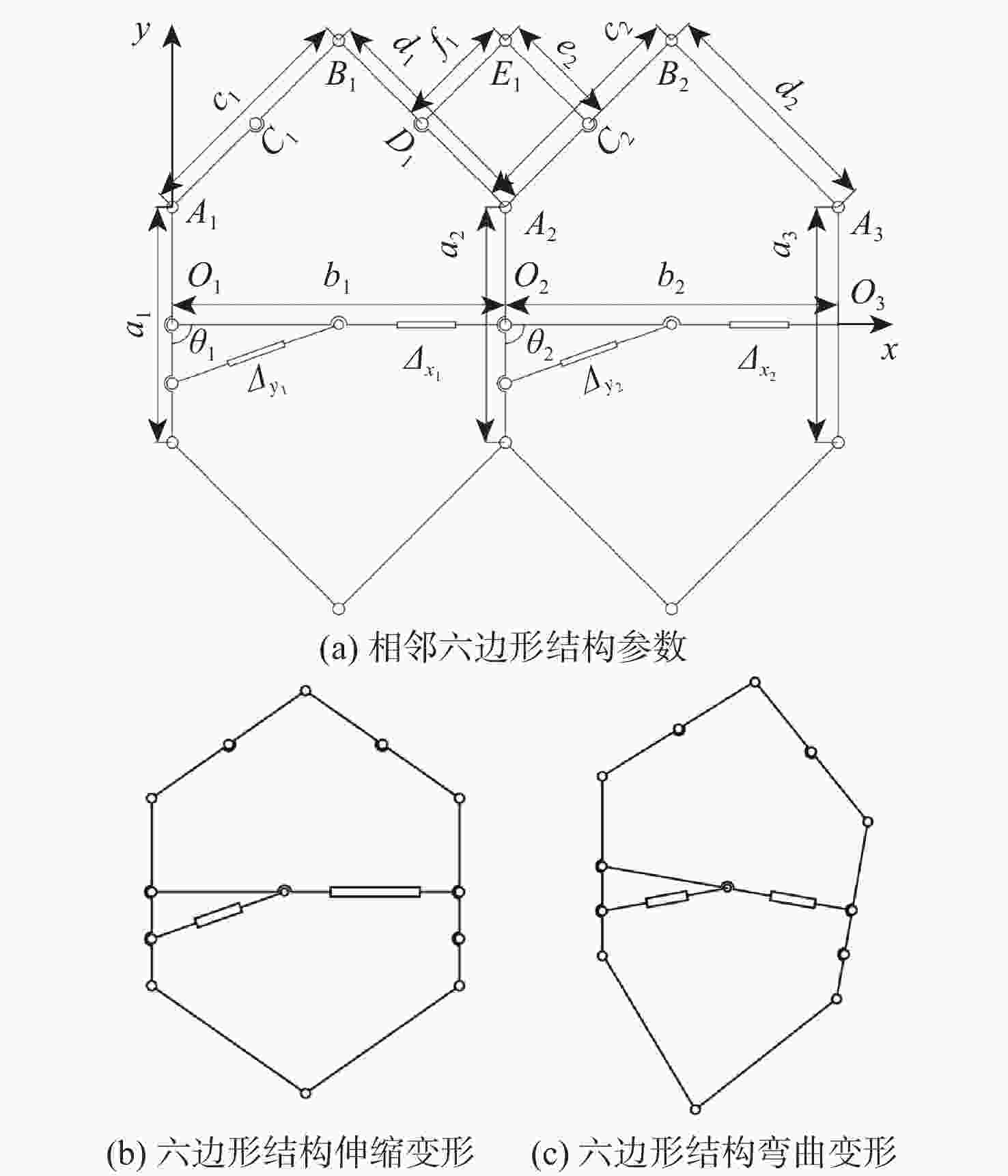
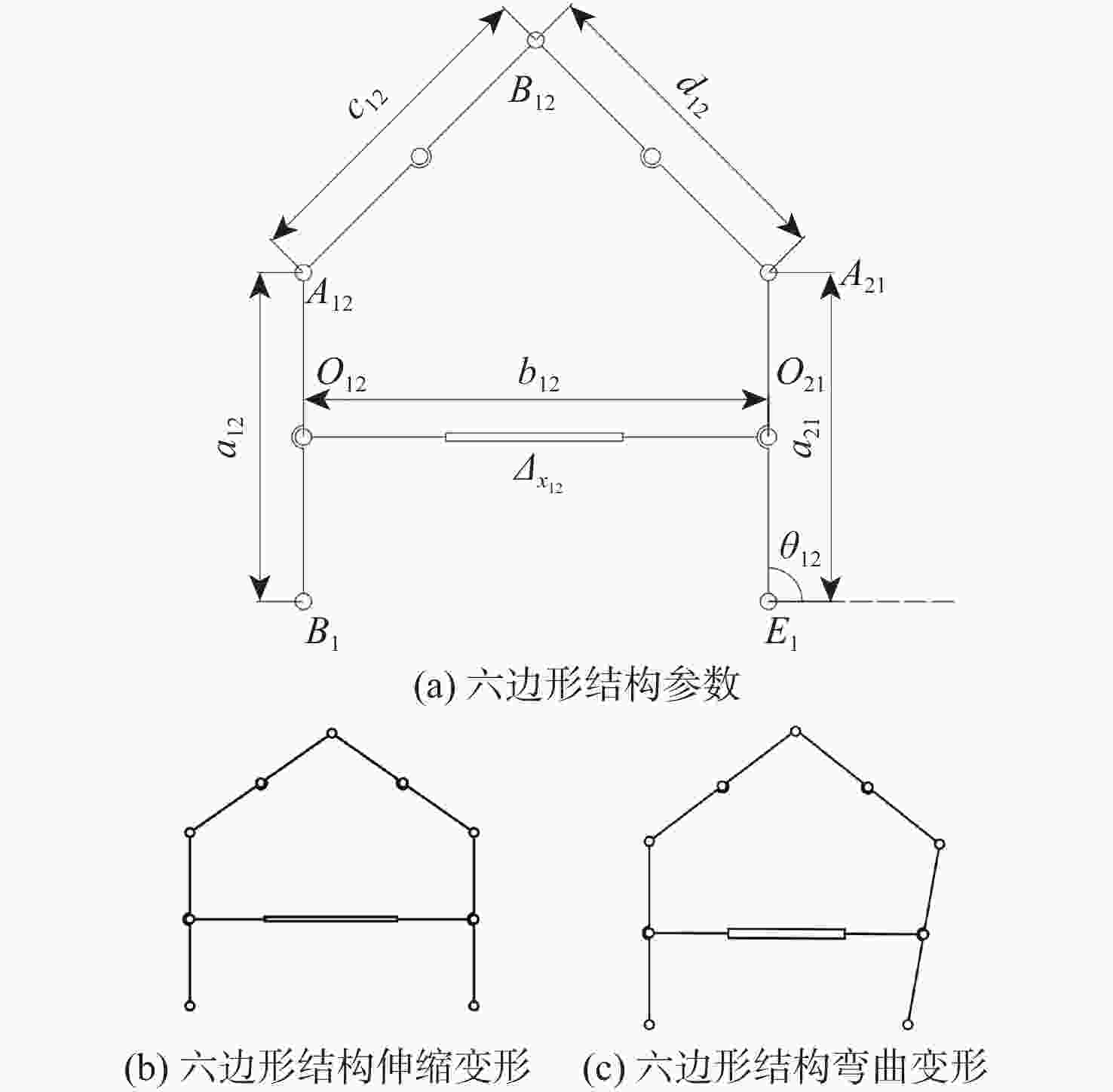
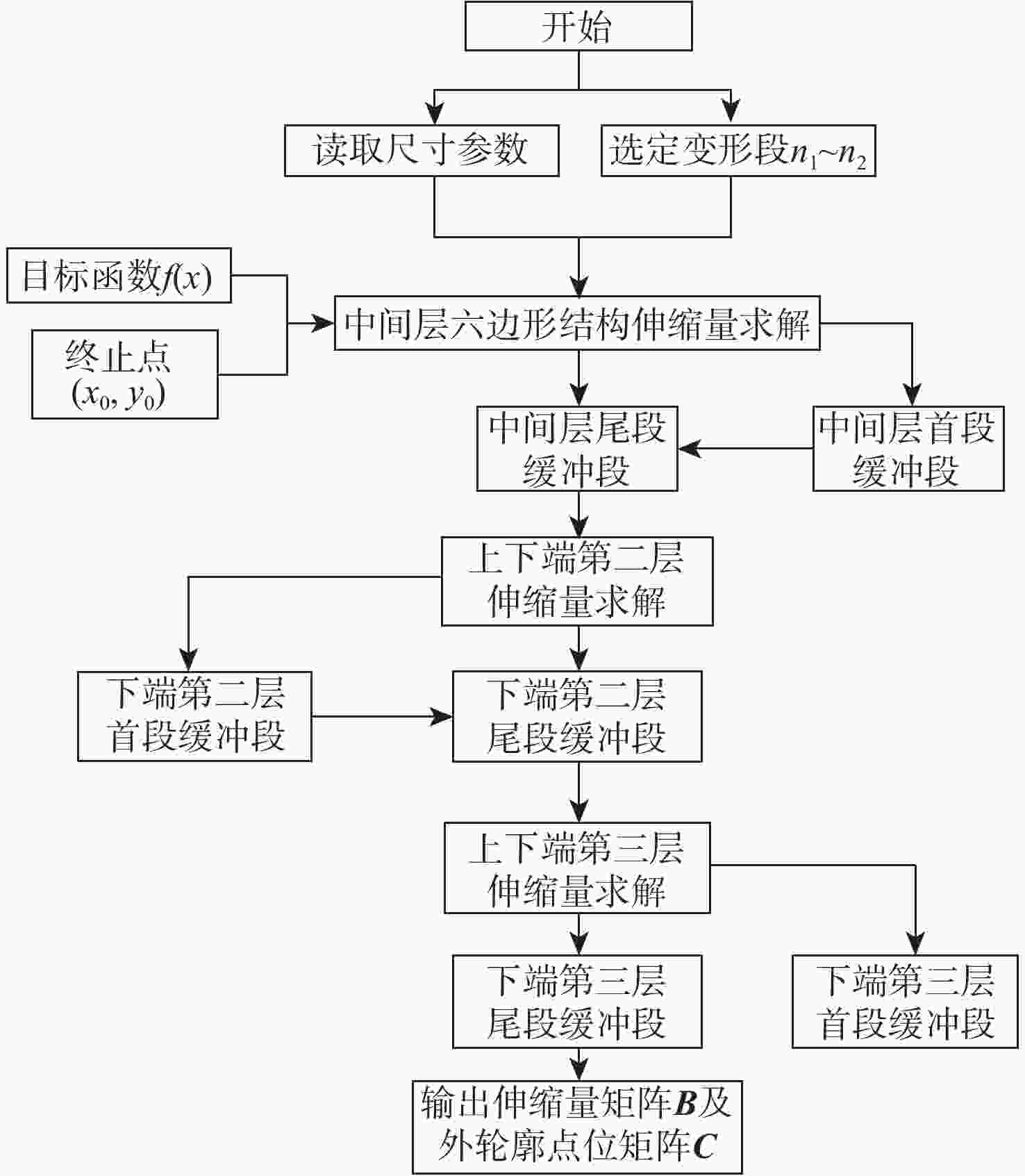
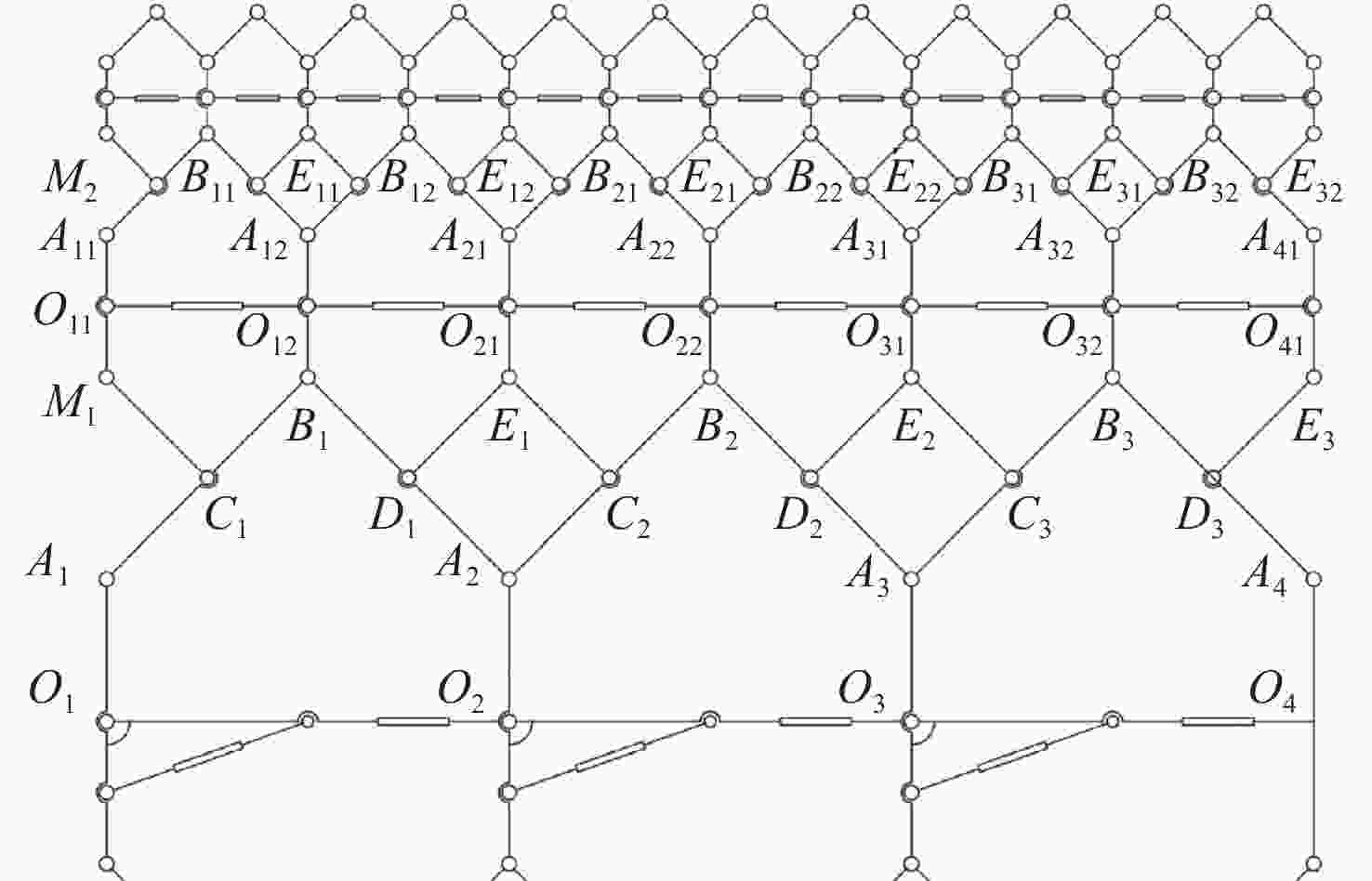
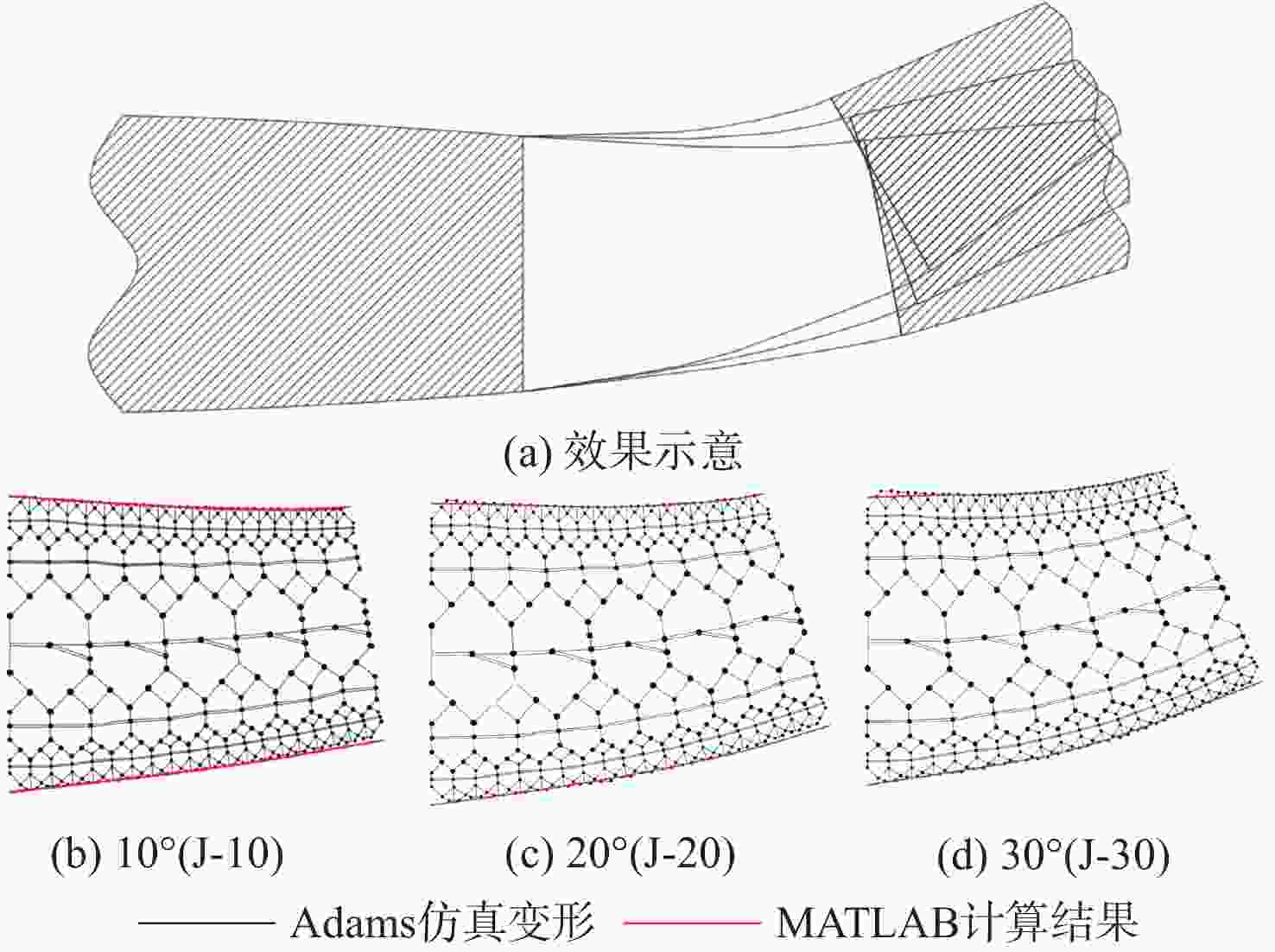
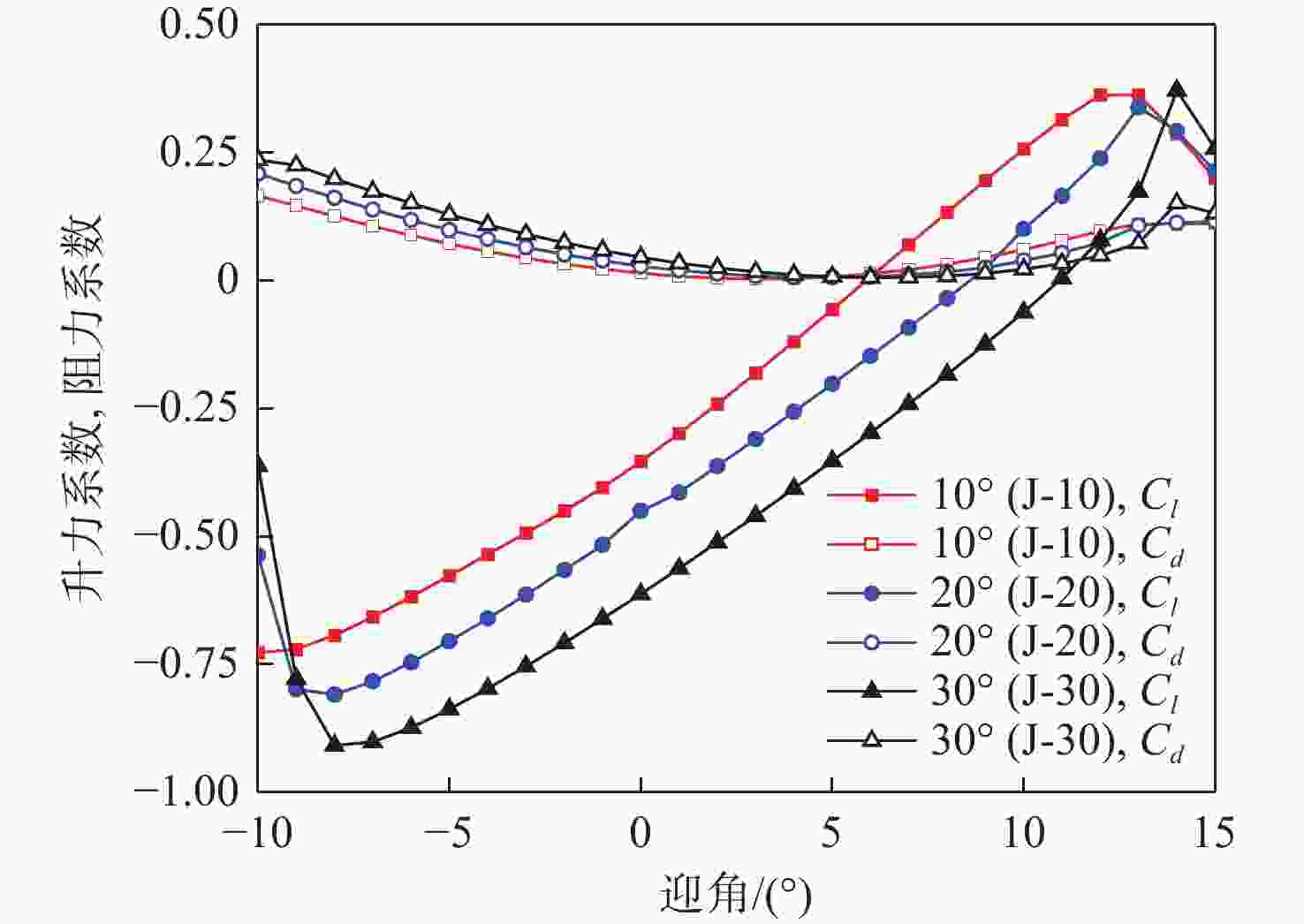
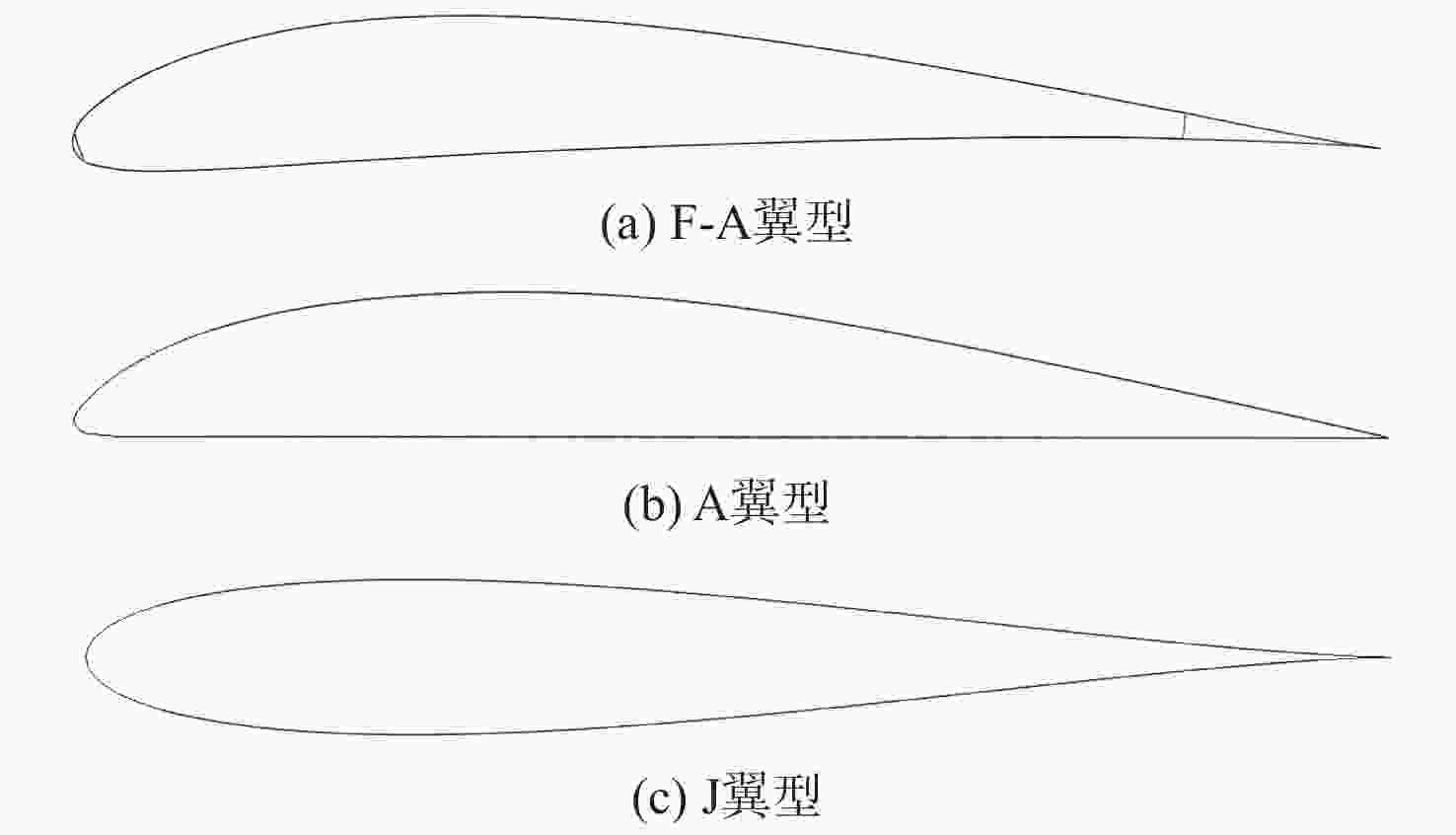
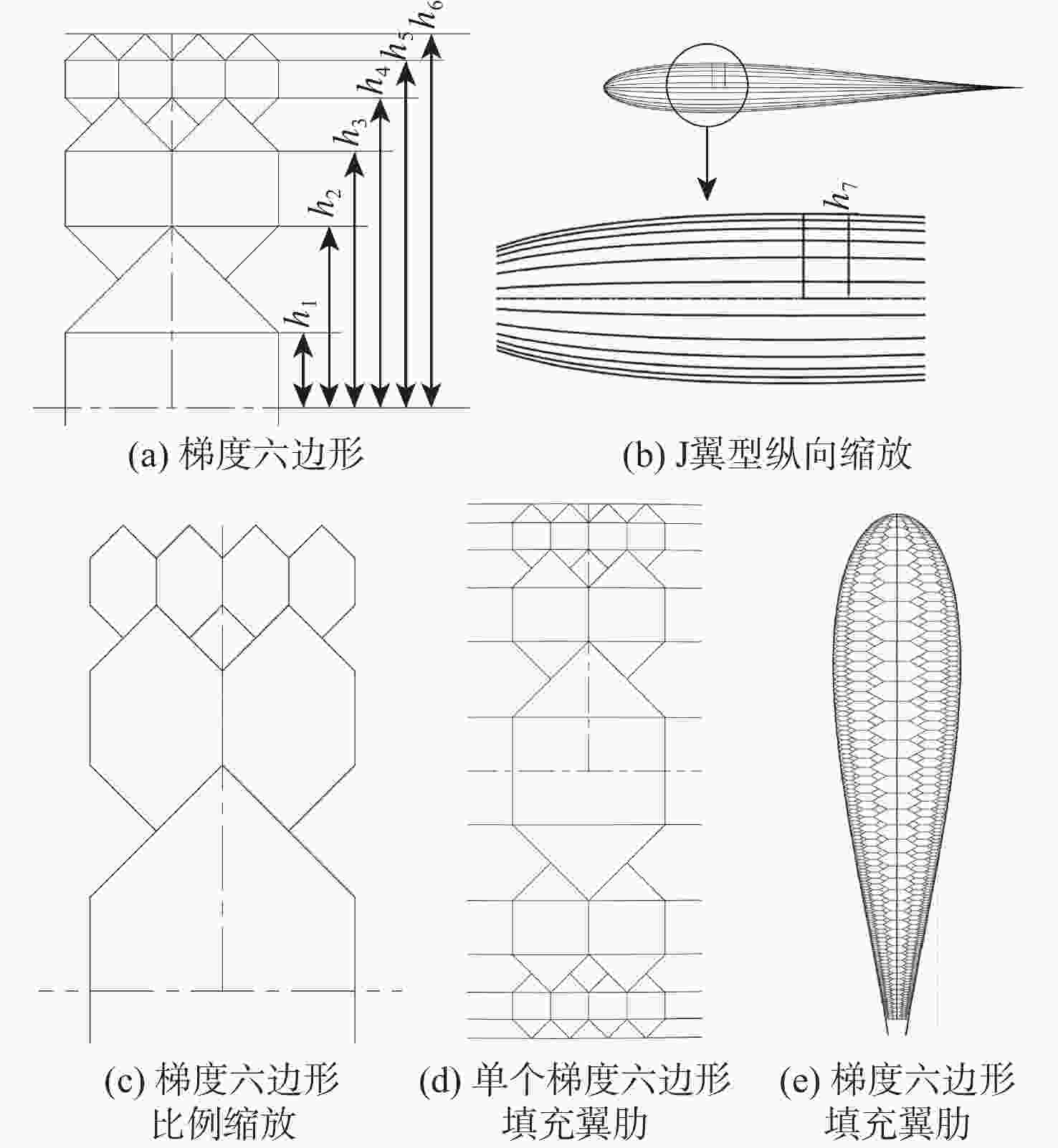
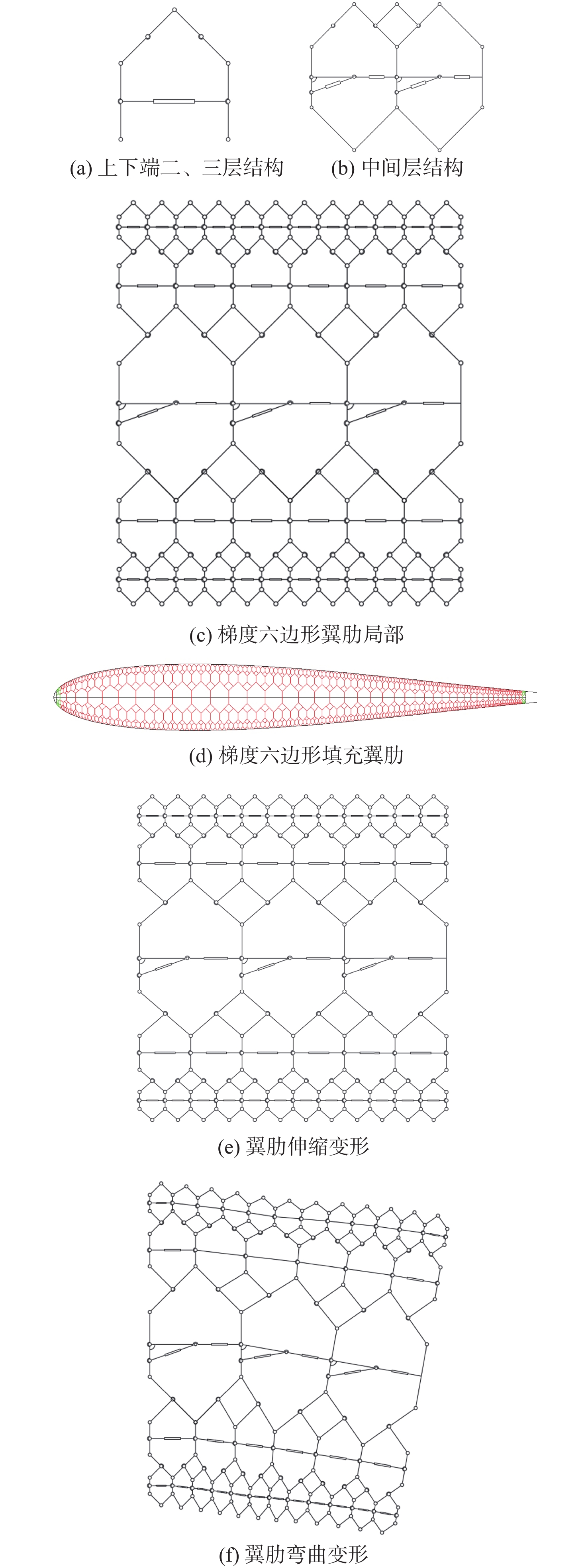
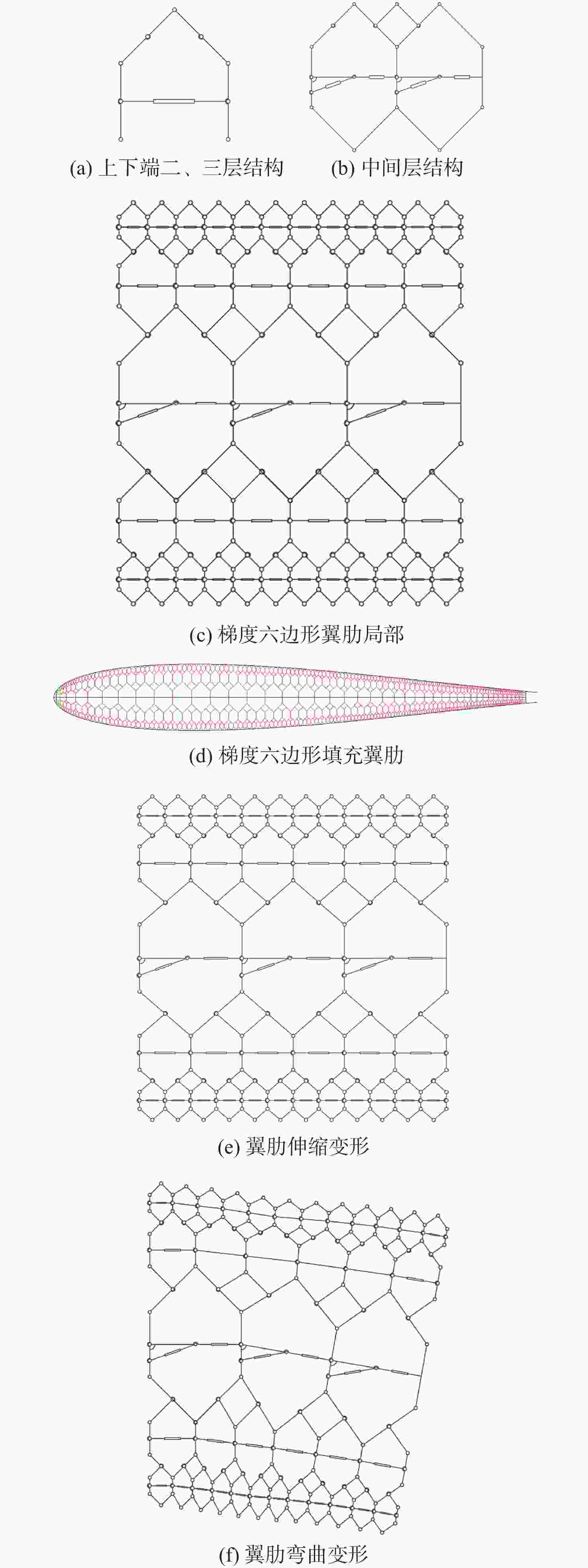
由于可变形机翼可满足不同工况下飞机气动性能需求,已被广泛应用于各类飞行器中。针对现有可变形机翼存在不能实现连续变形、变形幅度小、变形外轮廓不圆滑等问题,设计了一种梯度六边形结构填充的机翼结构及内部驱动装置,并给出了对应控制算法,分析了该可变形机翼可实现的2种典型变形模式:机翼尾缘弯曲变形和翼型仿制变形,具体分析了2种变形模式下翼型的气动性能,并与已有翼型气动性能进行比较,充分说明了所设计机翼的优势。
Abstract:The ability of deformable wings to satisfy the aerodynamic performance needs of aircraft under diverse operating situations has led to their widespread application in a variety of aircraft. In response to the current problems of deformable wings, such as inability to achieve continuous deformation, small deformation amplitude, and non-smooth outer contour, this paper designs a gradient hexagonal structure filled wing structure and internal driving device, and provides corresponding control algorithms. Subsequently, it analyzes the two typical deformation modes that the deformable wing can achieve-tail bending deformation and airfoil imitation deformation. This article thoroughly illustrates the benefits of the developed wing over the current airfoil aerodynamic performance by analyzing the aerodynamic performance of the airfoil under two deformation modes.
-
Key words:
- deformable wings /
- gradient hexagonal /
- control algorithm /
- variable curvature /
- high lift
-
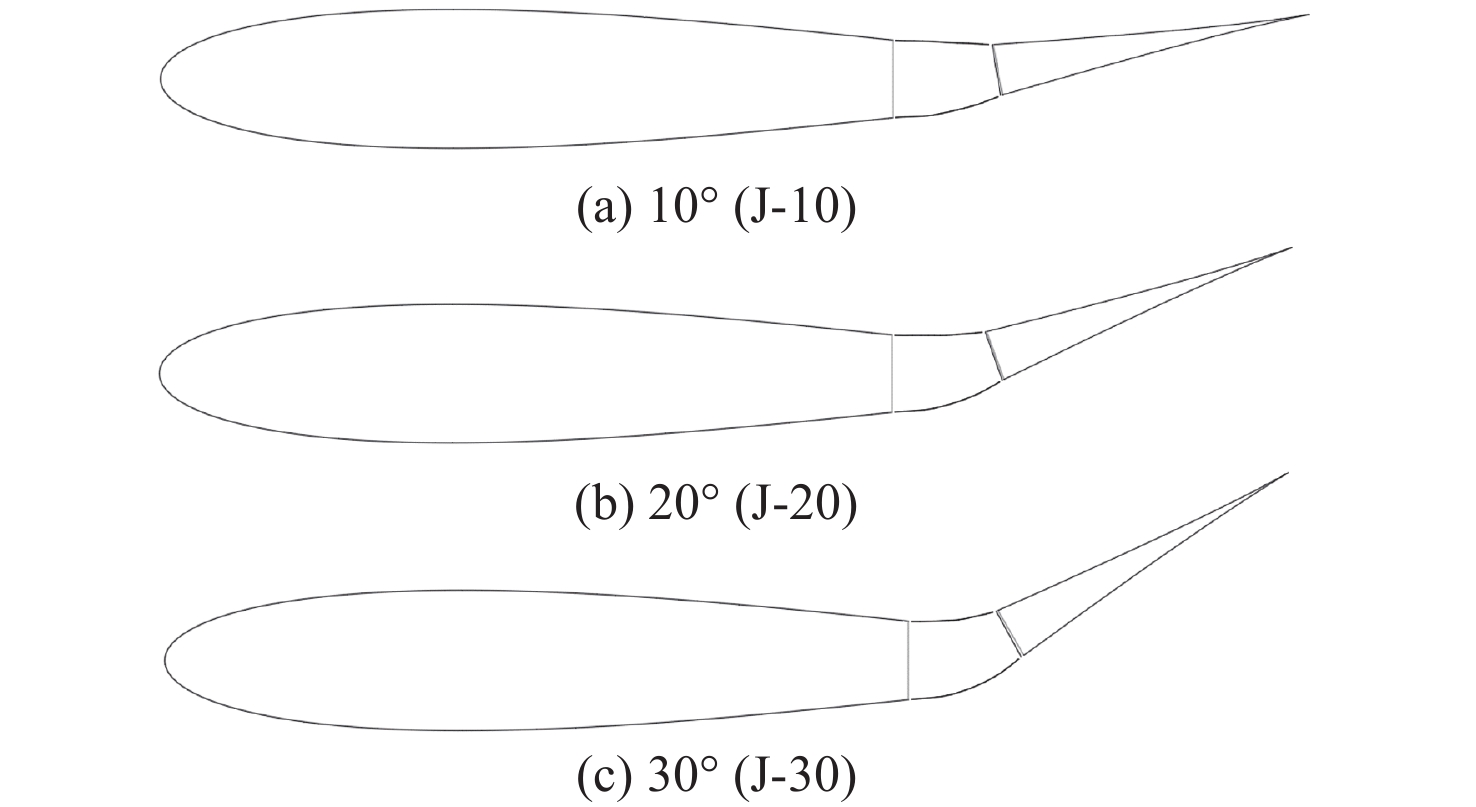
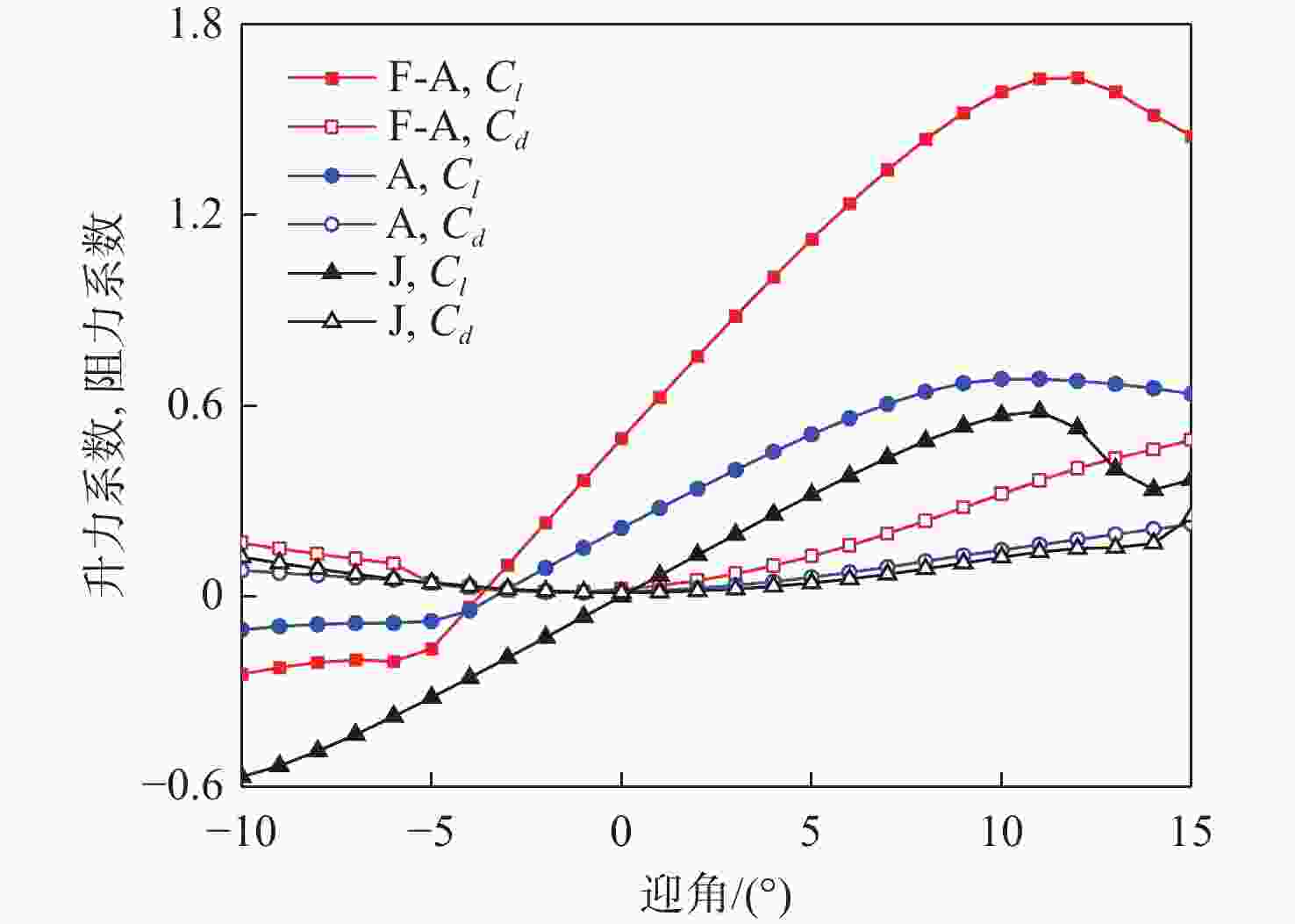
表 1 机翼尾缘弯曲参数
Table 1. Parameters of wing tail edge bending
机翼尾缘弯曲 起始
段n1终止
段n2切分
段数n3目标
函数f(x)终止点
(x0,y0)10°(J-10) 26 30 100 y=0.008x2 (11,0.968) 20°(J-20) 26 60 100 y= 0.0165 x2(11, 1.9965 )30°(J-30) 26 30 100 y= 0.0262 x2(11, 3.1702 )表 2 仿制翼型参数
Table 2. Parameters of imitation airfoil
起始段n1 终止段n2 切分段数n3 目标函数f(x) 终止点(x0,y0) 2 43 100 y=−3.906×10−8x4+2.015×10−5x3− 0.0043 ×10−8x2+0.0169 x+0.0829 (11, 3.1702 ) -
[1] 孙杨, 昌敏, 白俊强. 变形机翼飞行器发展综述[J]. 无人系统技术, 2021, 4(3): 65-77.SUN Y, CHANG M, BAI J Q. Review of morphing wing aircraft[J]. Unmanned Systems Technology, 2021, 4(3): 65-77(in Chinese). [2] 祝连庆, 孙广开, 李红, 等. 智能柔性变形机翼技术的应用与发展[J]. 机械工程学报, 2018, 54(14): 28-42.ZHU L Q, SUN G K, LI H, et al. Intelligent and flexible morphing wing technology: a review[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2018, 54(14): 28-42(in Chinese). [3] 白鹏, 陈钱, 徐国武, 等. 智能可变形飞行器关键技术发展现状及展望[J]. 空气动力学学报, 2019, 37(3): 426-443.BAI P, CHEN Q, XU G W, et al. Development status and prospects of key technologies for intelligent deformable aircraft[J]. Journal of Aerodynamics, 2019, 37(3): 426-443(in Chinese). [4] WEISSHAAR T A. Morphing aircraft technology-new shapes for aircraft design: RTO-MP-AVT-141[R]. Brussels: NATO, 2006. [5] BARBARINO S, BILGEN O, AJAJ R M, et al. A review of morphing aircraft[J]. Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 2011, 22(9): 823-877. doi: 10.1177/1045389X11414084 [6] 冉茂鹏, 王成才, 刘华华, 等. 变体飞行器控制技术发展现状与展望[J]. 航空学报, 2022, 43(10): 527449. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2022.27449RAN M P, WANG C C, LIU H H, et al. Research status and future development of morphing aircraft control technology[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2022, 43(10): 527449(in Chinese). doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2022.27449 [7] PHAN H V, PARK H C. Design and evaluation of a deformable wing configuration for economical hovering flight of an insect-like tailless flying robot[J]. Bioinspiration & Biomimetics, 2018, 13(3): 036009. [8] WALKER S M, THOMAS A L R, TAYLOR G K. Deformable wing kinematics in free-flying hoverflies[J]. Journal of the Royal Society, Interface, 2010, 7(42): 131-142. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2009.0120 [9] 王军, 张震, 李富强, 等. 仿生扑翼无人系统研究综述[J]. 智能系统学报, 2023, 18(3): 410-439.WANG J, ZHANG Z, LI F Q, et al. A review of the research on bionic flapping-wing unmanned systems[J]. CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems, 2023, 18(3): 410-439(in Chinese). [10] PHAN H V, PARK H C. Insect-inspired, tailless, hover-capable flapping-wing robots: recent progress, challenges, and future directions[J]. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 2019, 111: 100573. [11] XIAO S J, HU K, HUANG B X, et al. A review of research on the mechanical design of hoverable flapping wing micro-air vehicles[J]. Journal of Bionic Engineering, 2021, 18(6): 1235-1254. [12] PHAN H V, PARK H C. Mechanisms of collision recovery in flying beetles and flapping-wing robots[J]. Science, 2020, 370(6521): 1214-1219. doi: 10.1126/science.abd3285 [13] 张弘志, 宋笔锋, 孙中超, 等. 扑翼飞行器驱动机构回顾与展望[J]. 航空学报, 2021, 42(2): 024024.ZHANG H Z, SONG B F, SUN Z C, et al. Driving mechanism of flapping wing aircraft: review and prospect[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2021, 42(2): 024024(in Chinese). [14] 年鹏, 宋笔锋, 宣建林, 等. 扑翼飞行器动力系统建模方法[J]. 航空学报, 2021, 42(9): 224646.NIAN P, SONG B F, XUAN J L, et al. Modeling method for propulsion system of flapping wing vehicles[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2021, 42(9): 224646(in Chinese). [15] SEIGLER T M, NEAL D A, BAE J S, et al. Modeling and flight control of large-scale morphing aircraft[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 2007, 44(4): 1077-1087. [16] WOODS B K S, FINCHAM J H S, FRISWELL M I. Aerodynamic modelling of the fish bone active camber morphing concept[C]// Proceedings of the Royal Aeronautical Society Conference on Advanced Aero Concepts, Designs and Operations. [S. l: s. n. ], 2014. [17] WOODS B K S, DAYYANI I, FRISWELL M I. Fluid/structure-interaction analysis of the fish-bone-active-camber morphing concept[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 2014, 52(1): 307-319. [18] 杨智春, 解江. 柔性后缘自适应机翼的概念设计[J]. 航空学报, 2009, 30(6): 1028-1034.YANG Z C, XIE J. Concept design of adaptive wing with flexible trailing edge[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2009, 30(6): 1028-1034(in Chinese). [19] 冯文正, 于菲, 姜涛, 等. 变后掠角与变翼型厚度机翼的气动特性分析[J]. 飞行力学, 2023, 41(1): 9-13.FENG W Z, YU F, JIANG T, et al. Analysis of aerodynamic characteristics of wings with variable sweep angle and variable airfoil thickness[J]. Flight Mechanics, 2023, 41(1): 9-13(in Chinese). [20] 辛涛, 李斌. 一种刚柔混合弦向变弯度机翼后缘设计[J]. 兵工学报, 2023, 44(8): 2465-2476.XIN T, LI B. A design of the trailing edge of a rigid flexible mixed chord variable curvature wing[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2023, 44(8): 2465-2476(in Chinese). [21] 张桢锴, 贾思嘉, 宋晨, 等. 柔性变弯度后缘机翼的风洞试验模型优化设计[J]. 航空学报, 2022, 43(3): 226071.ZHANG Z K, JIA S J, SONG C, et al. Optimum design of wind tunnel test model for compliant morphing trailing edge[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2022, 43(3): 226071(in Chinese). [22] 张立启, 岳承宇, 赵永辉. 变后掠翼的参变气动弹性建模与分析[J]. 力学学报, 2021, 53(11): 3134-3146. doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-21-275ZHANG L Q, YUE C Y, ZHAO Y H. Parameter-varying aeroelastic modeling and analysis for a variable-sweep wing[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2021, 53(11): 3134-3146 (in Chinese). doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-21-275 [23] DAI P, YAN B B, HUANG W, et al. Design and aerodynamic performance analysis of a variable-sweep-wing morphing waverider[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2020, 98: 105703. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2020.105703 [24] MA T R, FAN Y D, CHANG N, et al. Design of a variable-sweep wing structure with flexible shear skin[J]. Aerospace Systems, 2022, 5(1): 37-46. doi: 10.1007/s42401-021-00123-9 [25] SUN J, GUAN Q H, LIU Y J, et al. Morphing aircraft based on smart materials and structures: a state-of-the-art review[J]. Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 2016, 27(17): 2289-2312. doi: 10.1177/1045389X16629569 [26] 姜松成, 杨慧, 王岩, 等. 变形翼可调泊松比柔性蒙皮力学特性分析[J]. 航空学报, 2023, 44(13): 227748.JIANG S C, YANG H, WANG Y, et al. Analysis of mechanical characteristics of flexible skin with tunable Poisson’s ratio for morphing wing[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2023, 44(13): 227748(in Chinese). [27] 王元锋, 祝连庆, 何彦霖, 等. 变构型飞行器柔性蒙皮形状光纤重构方法[J]. 中国机械工程, 2023, 34(15): 1873-1880. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2023.15.012WANG Y F, ZHU L Q, HE Y L, et al. Fiber optic reconstruction method for flexible skin shape of deformable aircraft[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2023, 34(15): 1873-1880(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2023.15.012 [28] POPOV A V, GRIGORIE L T, BOTEZ R, et al. Closed-loop control validation of a morphing wing using wind tunnel tests[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 2010, 47(4): 1309-1317. doi: 10.2514/1.47281 [29] POPOV A V, GRIGORIE T L, BOTEZ R M, et al. Modeling and testing of a morphing wing in open-loop architecture[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 2010, 47(3): 917-923. doi: 10.2514/1.46480 [30] BUBERT E, WOODS B K S, KOTHERA C, et al. Design and fabrication of a passive 1-d morphing aircraft skin[J]. Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 2010, 21(17): 1699-1717. doi: 10.1177/1045389X10378777 [31] JHA A K, KUDVA J N. Morphing aircraft concepts, classifications, and challenges[C]//Proceedings of the Smart Structures and Materials 2004. Bellingham: SPIE, 2004: 213-224. [32] CRAMER N B, CELLUCCI D W, FORMOSO O B, et al. Elastic shape morphing of ultralight structures by programmable assembly[J]. Smart Materials & Structures, 2019, 28(5): 055006. -






 下载:
下载: