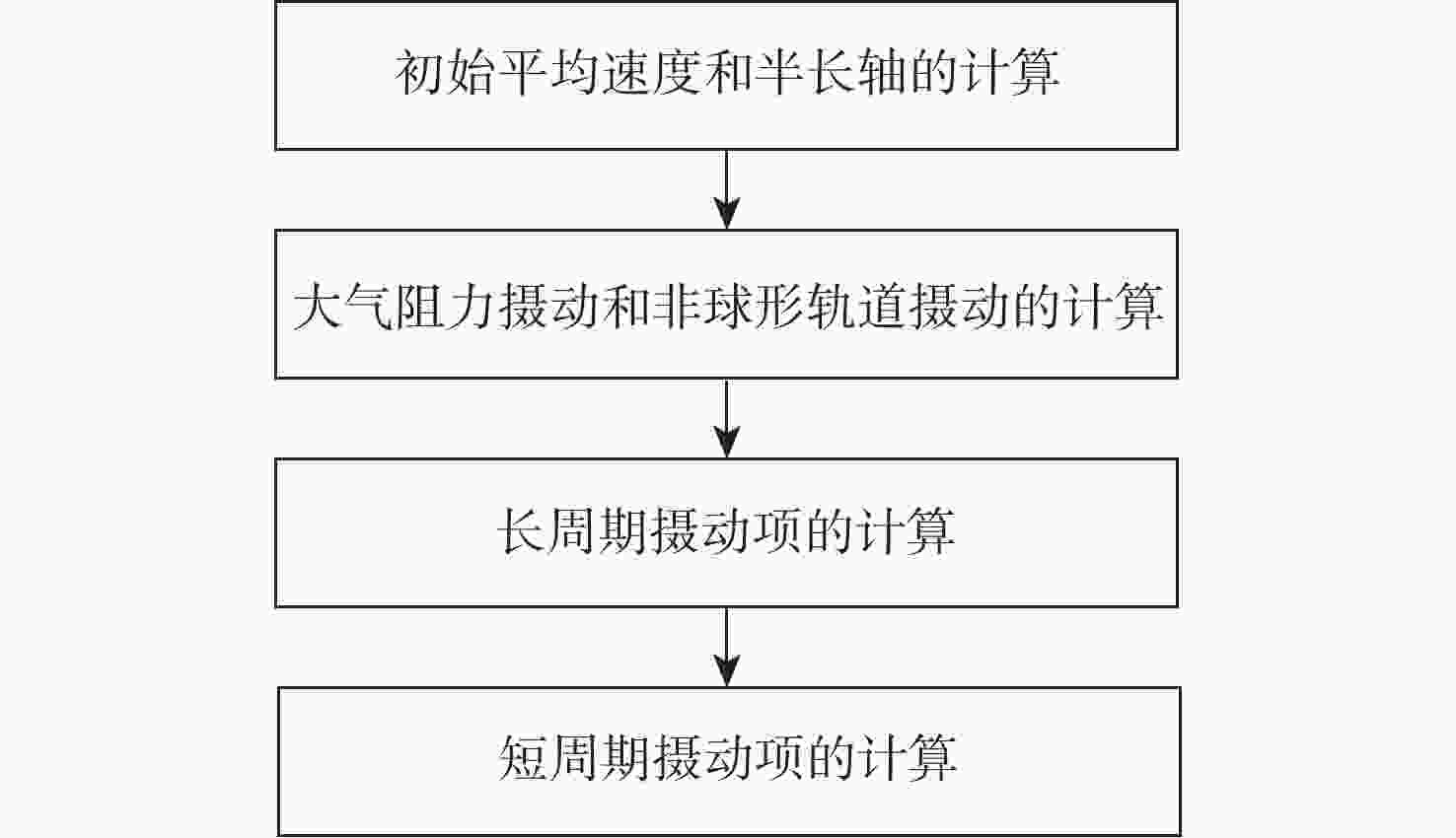
Single-station TLE estimation of NC-LEO satellite for space-based opportunistic positioning
-
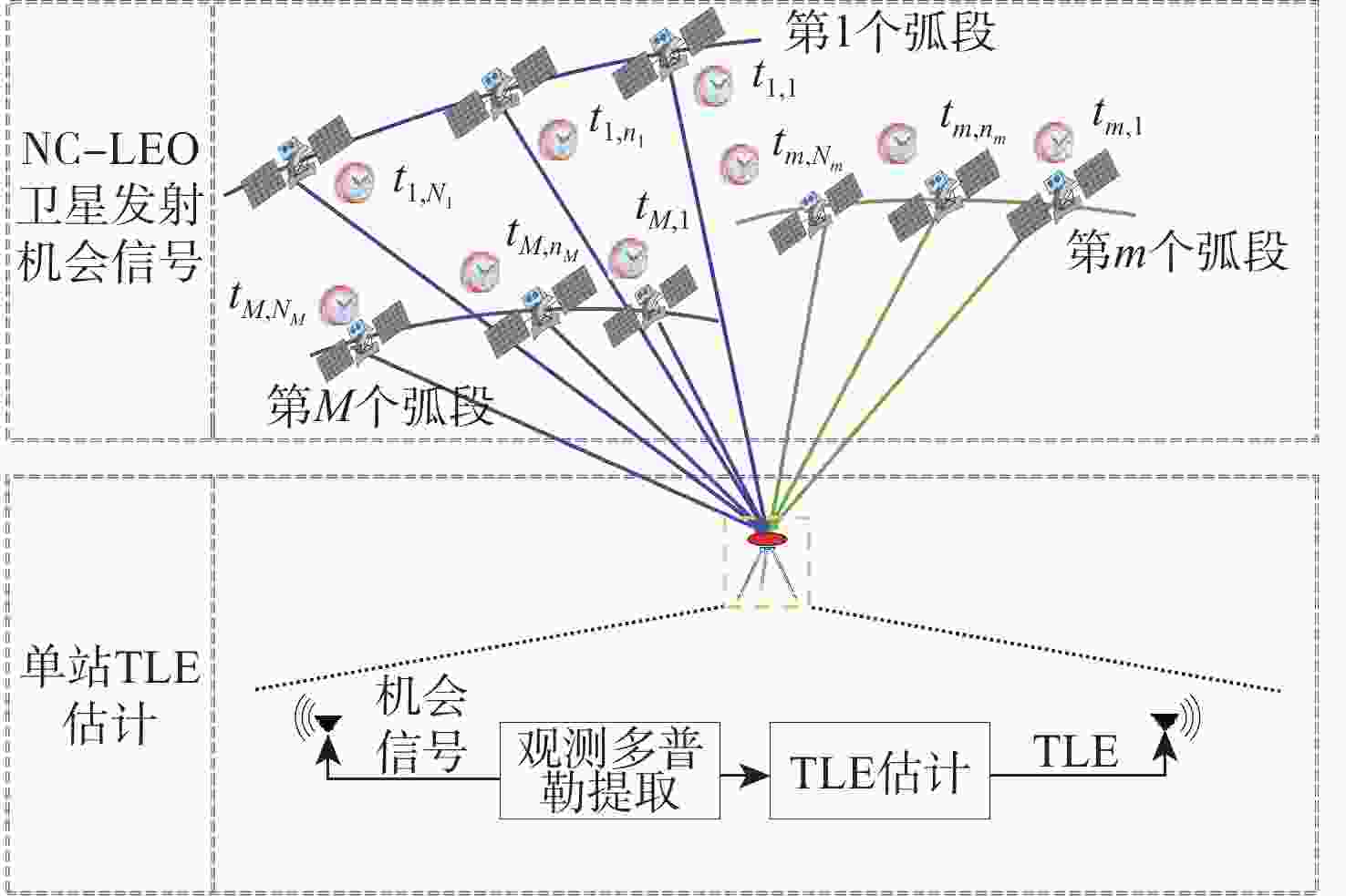
摘要:
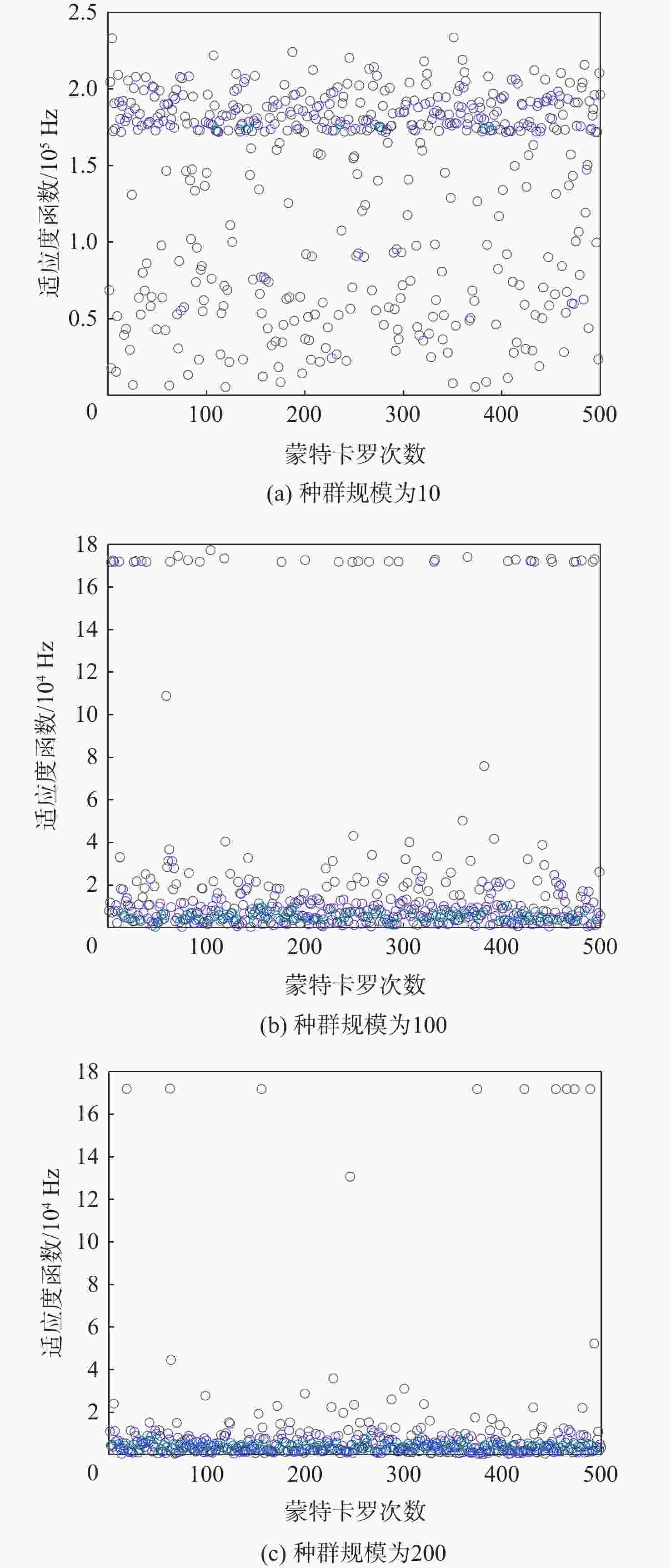
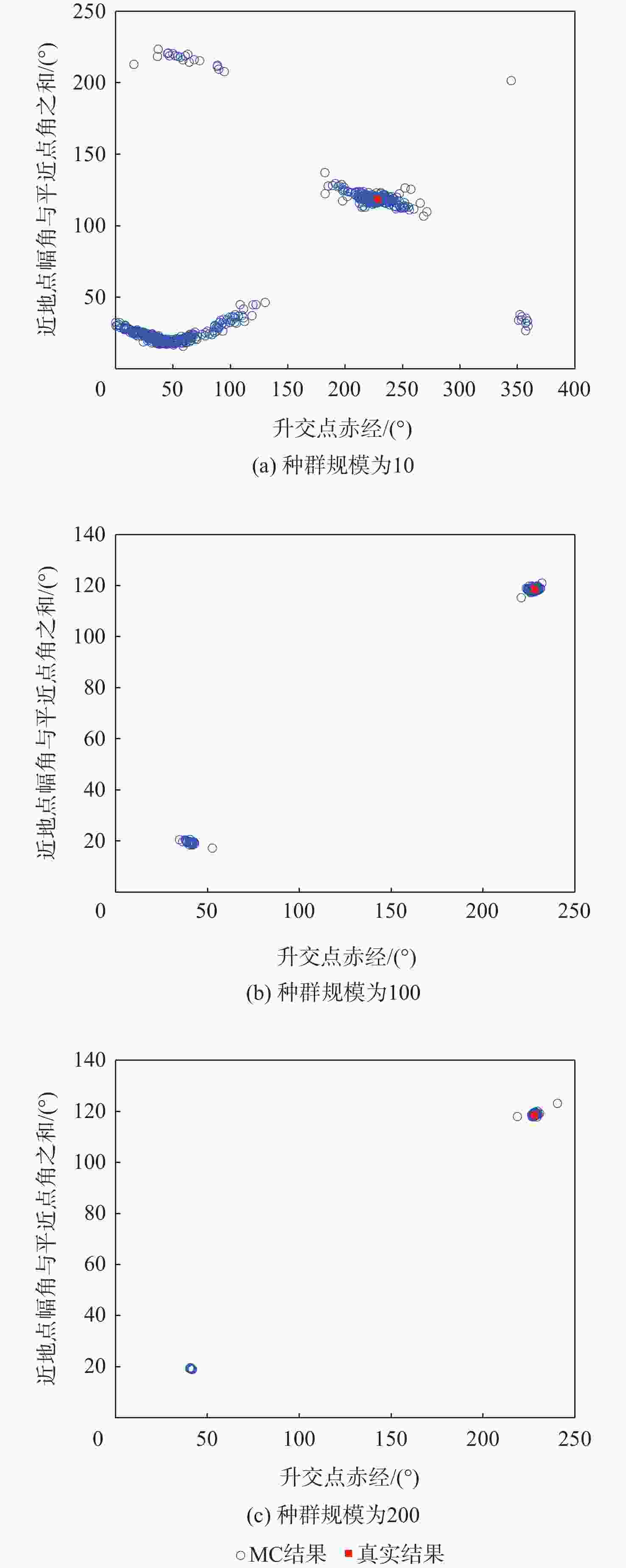
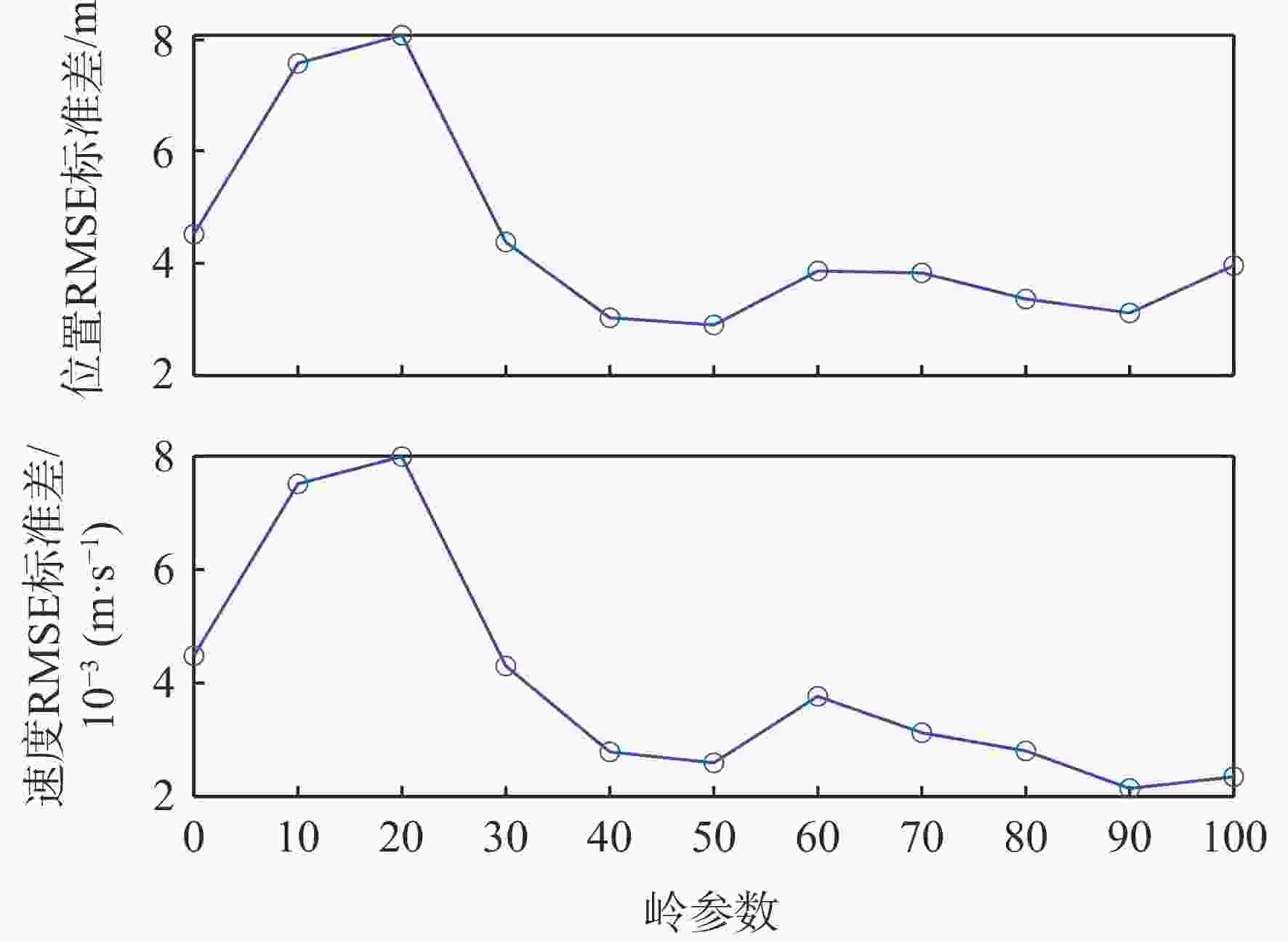
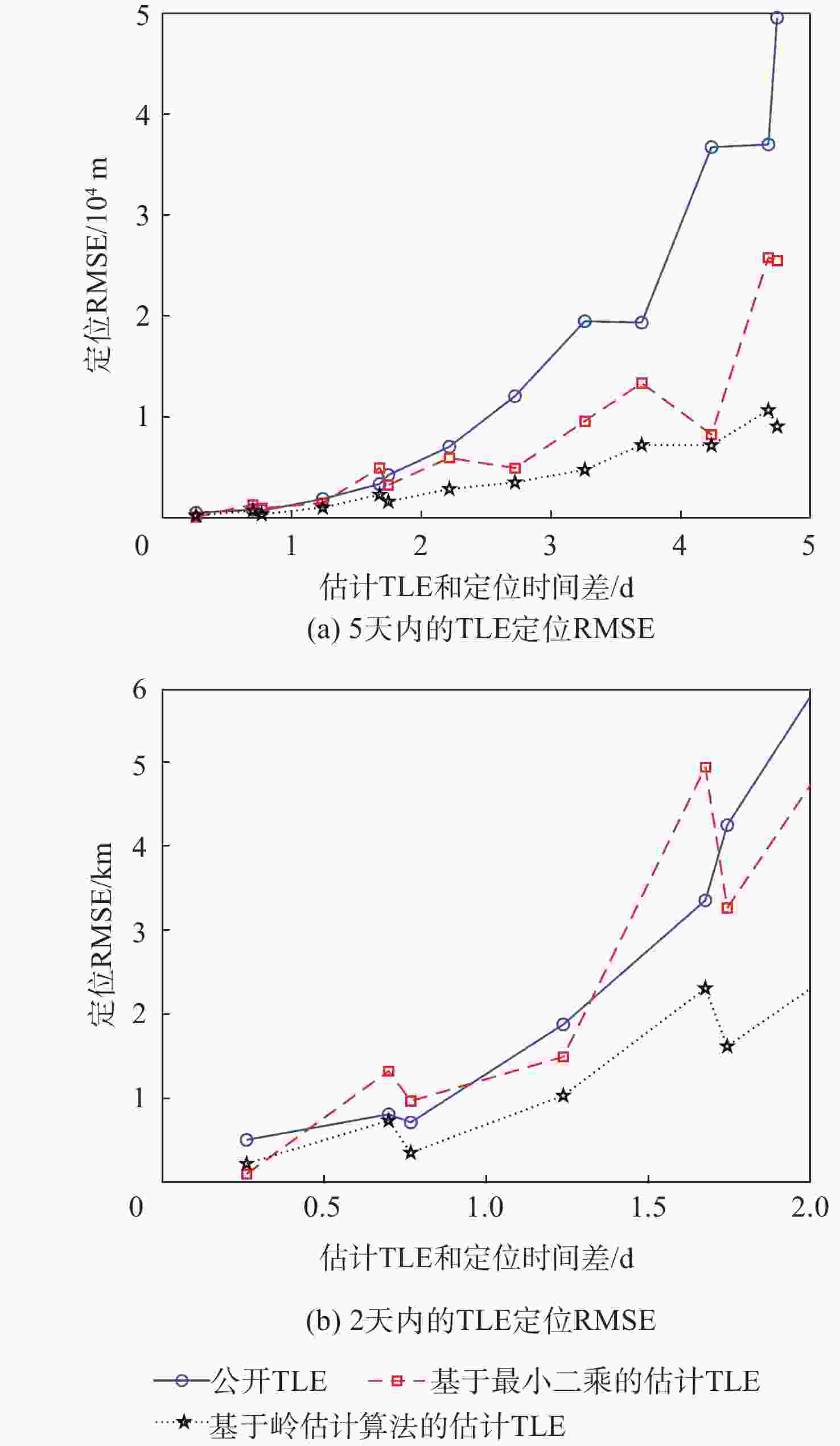
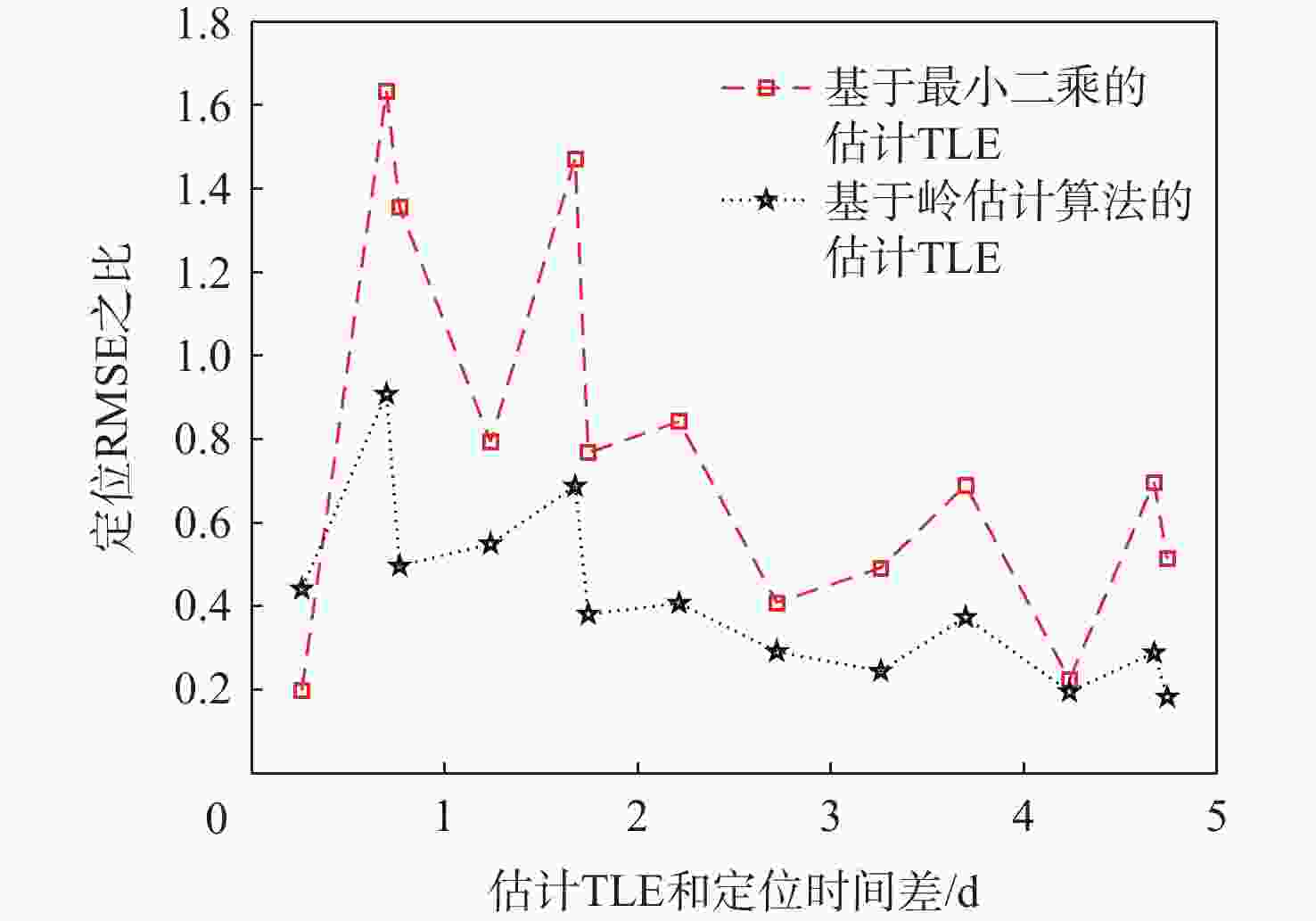
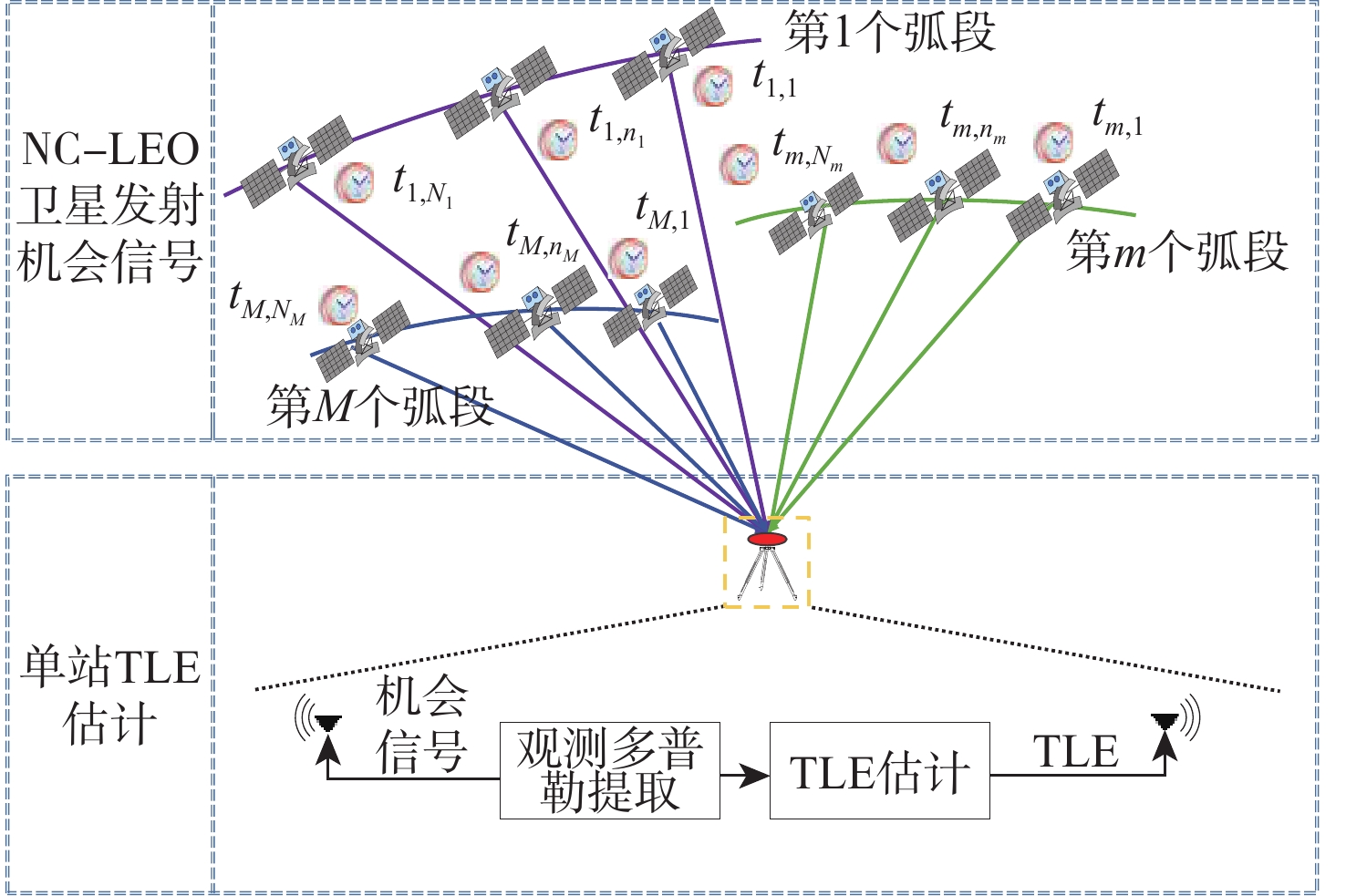
天基机会信号定位是弹性定位、导航与授时(PNT)体系的重要部分,当前大部分定位终端所用的非合作低轨(NC-LEO)卫星轨道可靠性和精度差。为解决该问题,提出NC-LEO卫星单站两行轨道根数(TLE)估计的体系结构,通过单站提取的多普勒观测量和星座设计轨道参数获取精密TLE。同时,提出基于多初始化策略的遗传算法-岭估计的TLE估计算法,实现在先验轨道不完备和法方程病态的情况下获取精密TLE。实际试验证明:相比基于NORAD公开的TLE定位,基于所提方法获取的TLE定位精度更高。
Abstract:The space-based opportunistic positioning is an integral part of the resilient positioning, navigation, and timing (PNT) system. At the moment, most space-based opportunistic positioning terminals depend on the non-cooperative low Earth orbit (NC-LEO) satellite’s unreliable and imprecise orbit. To address this problem, this paper presents a framework for single-station two line element (TLE) estimation of non-cooperative low Earth orbit satellites. The precise TLE is obtained using Doppler observations from a single-station and the orbital parameters for constellation design. Additionally, a TLE estimation algorithm is proposed based on a genetic algorithm-ridge estimation approach with multiple initialization strategies. This method facilitates the acquisition of accurate TLE even in situations where prior orbit information is incomplete, and when the problem is ill-conditioned. Finally, real-world tests confirm that using TLEs computed using the suggested method leads to improved accuracy when compared to placement based on NORAD’s publicly available TLEs.
-
表 1 2颗目标卫星的轨道参数
Table 1. Orbital parameters of two target satellites
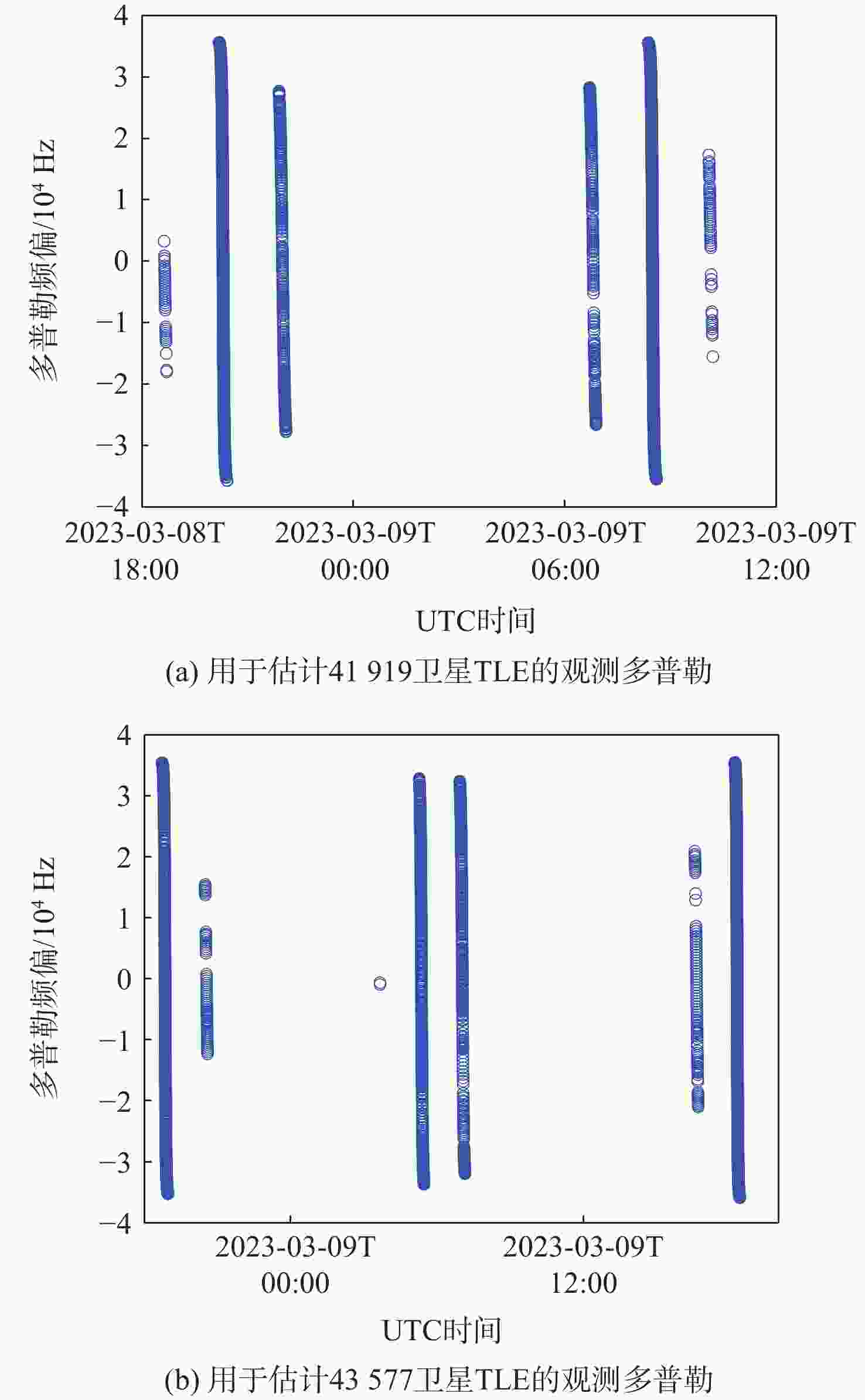
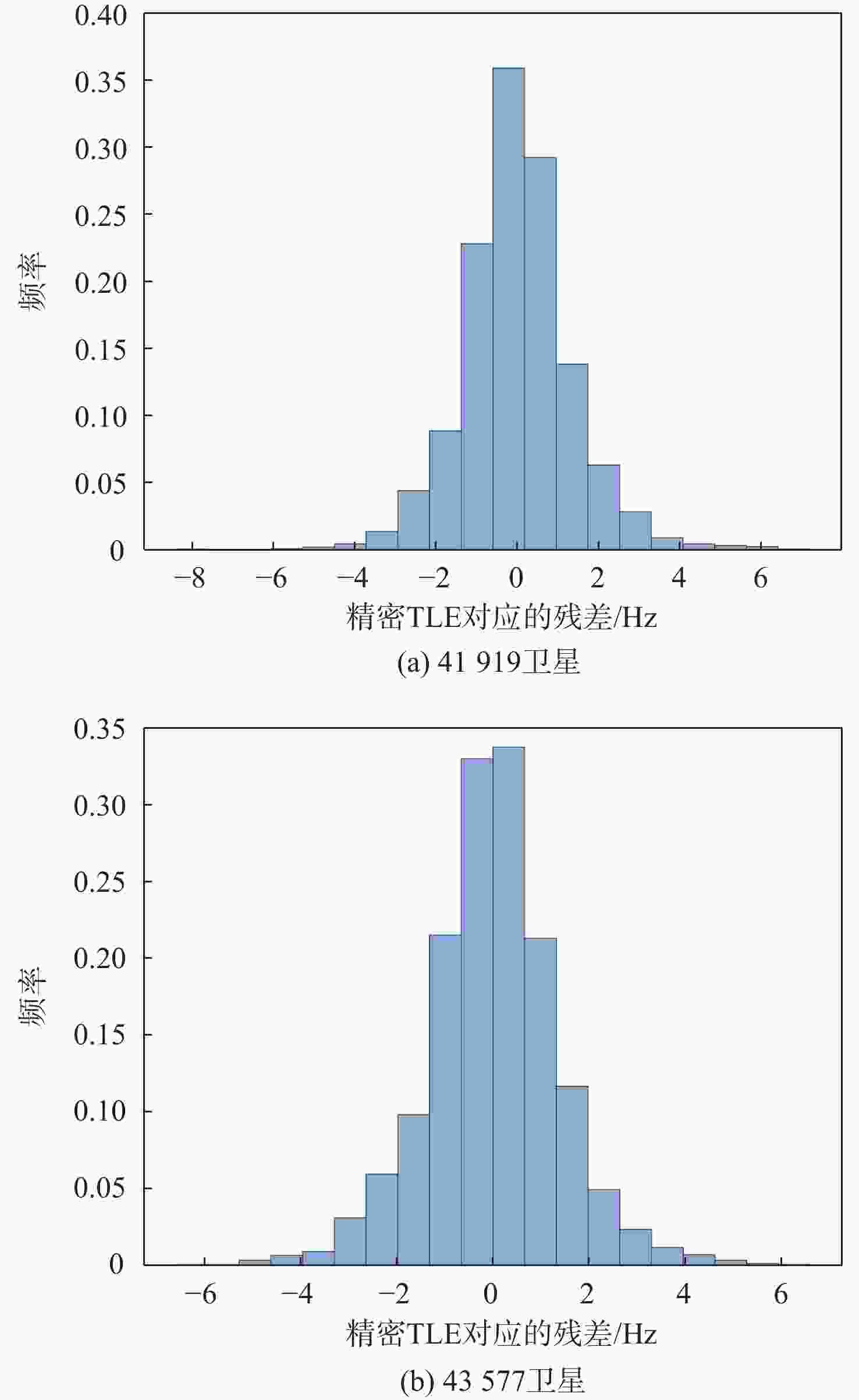
卫星编号 一天绕地球圈数 轨道倾角/(°) 偏心率 升交点赤经/(°) 近地点幅角/(°) 平近点角/(°) 弹道系数 41919 卫星14.34220991 86.3975 0.0002160 228.0428 91.9051 26.7190 − 0.00179080 43577 卫星14.34217309 86.4037 0.0002372 196.3858 100.9897 346.6261 0.00089653 -
[1] MORTON Y J, VAN DIGGELEN F, SPILKER J J, et al. Position, navigation, and timing technologies in the 21st Century: integrated satellite navigation, sensor systems, and civil applications, volume 1[M]. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, 2021: 3-4. [2] IANNUCCI P A, HUMPHREYS T E. Fused low-Earth-orbit GNSS[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2024, 60(4): 3730-3749. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2022.3180000 [3] PROL F S, FERRE R M, SALEEM Z, et al. Position, navigation, and timing (PNT) through low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites: a survey on current status, challenges, and opportunities[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 83971-84002. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3194050 [4] 秦红磊, 李志强, 赵超. Iridium/ORBCOMM机会信号融合定位 技术[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2022, 48(10): 1845-1853.QIN H L, LI Z Q, ZHAO C. Fusion positioning based on Iridium/ORBCOMM signals of opportunity[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2022, 48(10): 1845-1853(in Chinese). [5] 秦红磊, 武宁, 赵超. 基于视向矢量修正的 Iridium 机会信号多普勒差分定位技术[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2024, 50(3): 748-756.QIN H L, WU N, ZHAO C. Differential positioning with Doppler measurements from Iridium based on lines of sight correction[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2024, 50(3): 748-756(in Chinese). [6] NEINAVAIE M, KHALIFE J, KASSAS Z M. Acquisition, Doppler tracking, and positioning with starlink LEO satellites: first results[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58(3): 2606-2610. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3127488 [7] LEE B S. NORAD TLE conversion from osculating orbital element[J]. Journal of Astronomy and Space Sciences, 2002, 19(4): 395-402. doi: 10.5140/JASS.2002.19.4.395 [8] KRAG H, KLINKRAD H, ALARCÓN-RODRIGUEZ J R. Assessment of orbit uncertainties for collision risk predictions at ESA[C]//Proceedings of the 2nd IAASS Conference “Space Safety in a Global World”. [S. l. ]: International Association for the Advancement of Space Safety, 2007: 14-16. [9] VALLADO D A, CRAWFORD P. SGP4 orbit determination: AIAA 2008-6770[R]. Reston: AIAA, 2008. [10] WANG R, LIU J, ZHANG Q M. Propagation errors analysis of TLE data[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2009, 43(7): 1065-1069. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2008.11.017 [11] SPERETTA S, SUNDARAMOORTHY P P, GILL E K A. Long-term performance analysis of NORAD two-line elements for CubeSats and PocketQubes[C]//Proceedings of the Small Satellites for Earth Observation. Berlin: DLR, 2017. [12] KAHR E, MONTENBRUCK O, O’KEEFE K P G. Estimation and analysis of two-line elements for small satellites[J]. Journal of Spacecraft and Rockets, 2013, 50(2): 433-439. doi: 10.2514/1.A32352 [13] MONTENBRUCK O. An epoch state filter for use with analytical orbit models of low Earth satellites[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2000, 4(4): 277-287. doi: 10.1016/S1270-9638(00)00133-4 [14] 张耀, 刘静. 基于角度转化的空间碎片测角数据精密定轨方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2023, 49(7): 1600-1605.ZHANG Y, LIU J. Precise orbit determination method for angle-only observation data of space debris based on angle conversion theory[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2023, 49(7): 1600-1605(in Chinese). [15] 李庆扬, 莫孜中, 祁力群. 非线性方程组的数值解法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1987.LI Q Y, MO Z Z, QI L Q. Numerical solution of nonlinear equations[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1987(in Chinese). [16] MORALES-FERRE R, LOHAN E S, FALCO G, et al. GDOP-based analysis of suitability of LEO constellations for future satellite-based positioning[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Wireless for Space and Extreme Environments. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 147-152. [17] 耿涛, 刘经南, 赵齐乐, 等. 星地监测网下的北斗导航卫星轨道确定[J]. 测绘学报, 2011, 40(S1): 46-51.GENG T, LIU J N, ZHAO Q L, et al. Compass precise orbit determination based on space-ground monitoring network[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2011, 40(S1): 46-51(in Chinese). [18] 李斐, 郝卫峰, 王文睿, 等. 非线性病态问题解算的扰动分析[J]. 测绘学报, 2011, 40(1): 5-9.LI F, HAO W F, WANG W R, et al. The perturbation analysis of nonlinear ill conditioned solution[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2011, 40(1): 5-9(in Chinese). [19] 李文华, 袁建平. 单站多普勒跟踪定轨的优化算法[J]. 宇航学报, 2001, 22(3): 69-73. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1328.2001.03.011LI W H, YUAN J P. Optimal algorithm of orbit tracking and determination by single station Dopper radar[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2001, 22(3): 69-73(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1328.2001.03.011 [20] LOVELL T A. Application of genetic algorithms to state estimation of tethered systems[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2003, 192(15): 1799-1819. doi: 10.1016/S0045-7825(03)00202-0 [21] BAJPAI P, KUMAR M. Genetic algorithm: an approach to solve global optimization problems[J]. Indian Journal of Computer Science and Engineering, 2010, 1(3): 199-206. [22] HOERL A E, KENNARD R W. Ridge regression: biased estimation for nonorthogonal problems[J]. Technometrics, 1970, 12(1): 55-67. doi: 10.1080/00401706.1970.10488634 [23] JANG D H, ANDERSON-COOK C M. Visualization approaches for evaluating ridge regression estimators in mixture and mixture-process experiments[J]. Quality and Reliability Engineering International, 2015, 31(8): 1483-1494. doi: 10.1002/qre.1683 [24] OU J K, DING W W, LIU J H, et al. An improved algorithm for autonomous orbit determination of navigation satellite constellation[J]. Survey Review, 2011, 43(322): 361-369. doi: 10.1179/003962611X13055561708669 [25] 胡敏, 曾国强. 平均轨道根数与密切轨道根数的互换[J]. 飞行器测控学报, 2012, 31(2): 77-81.HU M, ZENG G Q. Transformation between mean and osculating orbital elements[J]. Journal of Spacecraft TT& C Technology, 2012, 31(2): 77-81(in Chinese). [26] 刘一帆. 基于 SGP4 模型的低轨道航天器轨道预报方法研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2009: 27-33.LIU Y F. Research on low Earth orbit spacecraft orbit prediction strategy based on SGP4 model[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2009: 27-33(in Chinese). [27] PRATT J, AXELRAD P, LARSON K M, et al. Satellite clock bias estimation for iGPS[J]. GPS Solutions, 2013, 17(3): 381-389. doi: 10.1007/s10291-012-0286-4 [28] MORALES J J, KHALIFE J, SANTA CRUZ U, et al. Orbit modeling for simultaneous tracking and navigation using LEO satellite signals[C]//Proceedings of the International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation. Manassas: ION, 2019: 2090-2099. [29] 曲国庆, 孙振, 苏晓庆, 等. 非线性参数估计的自适应松弛正则化算法[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2019, 44(10): 1491-1497.QU G Q, SUN Z, SU X Q, et al. Adaptive relaxation regularization algorithm for nonlinear parameter estimation[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2019, 44(10): 1491-1497 (in Chinese). [30] 梁亚澜, 聂长海. 覆盖表生成的遗传算法配置参数优化[J]. 计算机学报, 2012, 35(7): 1522-1538. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1016.2012.01522LIANG Y L, NIE C H. The optimization of configurable genetic algorithm for covering arrays generation[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2012, 35(7): 1522-1538(in Chinese). doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1016.2012.01522 [31] ANSALONE L, CURTI F. A genetic algorithm for initial orbit determination from a too short arc optical observation[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2013, 52(3): 477-489. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2013.04.004 [32] HANSEN P C, O’LEARY D P. The use of the L-curve in the regularization of discrete ill-posed problems[J]. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 1993, 14(6): 1487-1503. doi: 10.1137/0914086 [33] MORTLOCK T, KASSAS Z M. Assessing machine learning for LEO satellite orbit determination in simultaneous tracking and navigation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Aerospace Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 1-8. -






 下载:
下载: