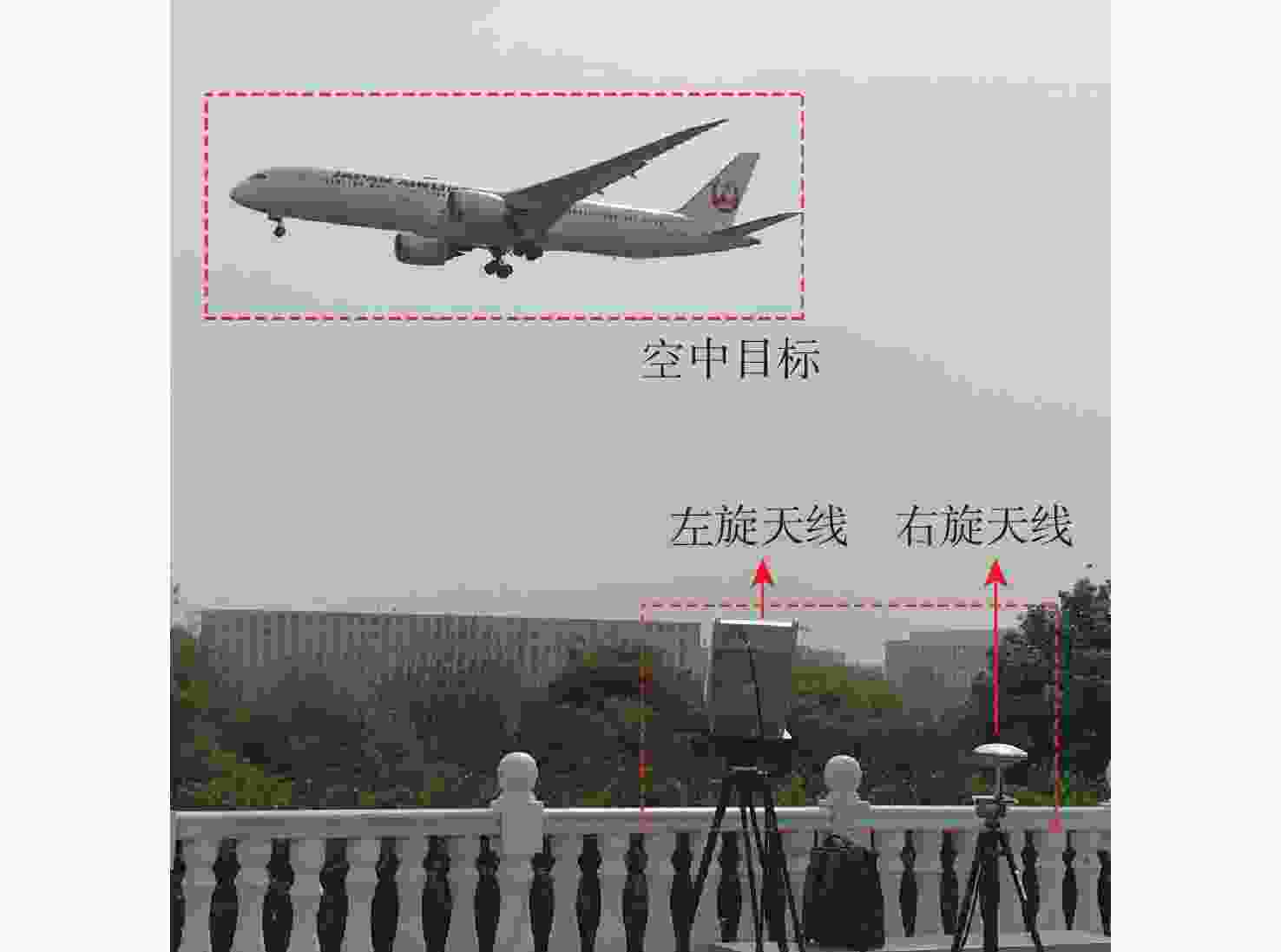
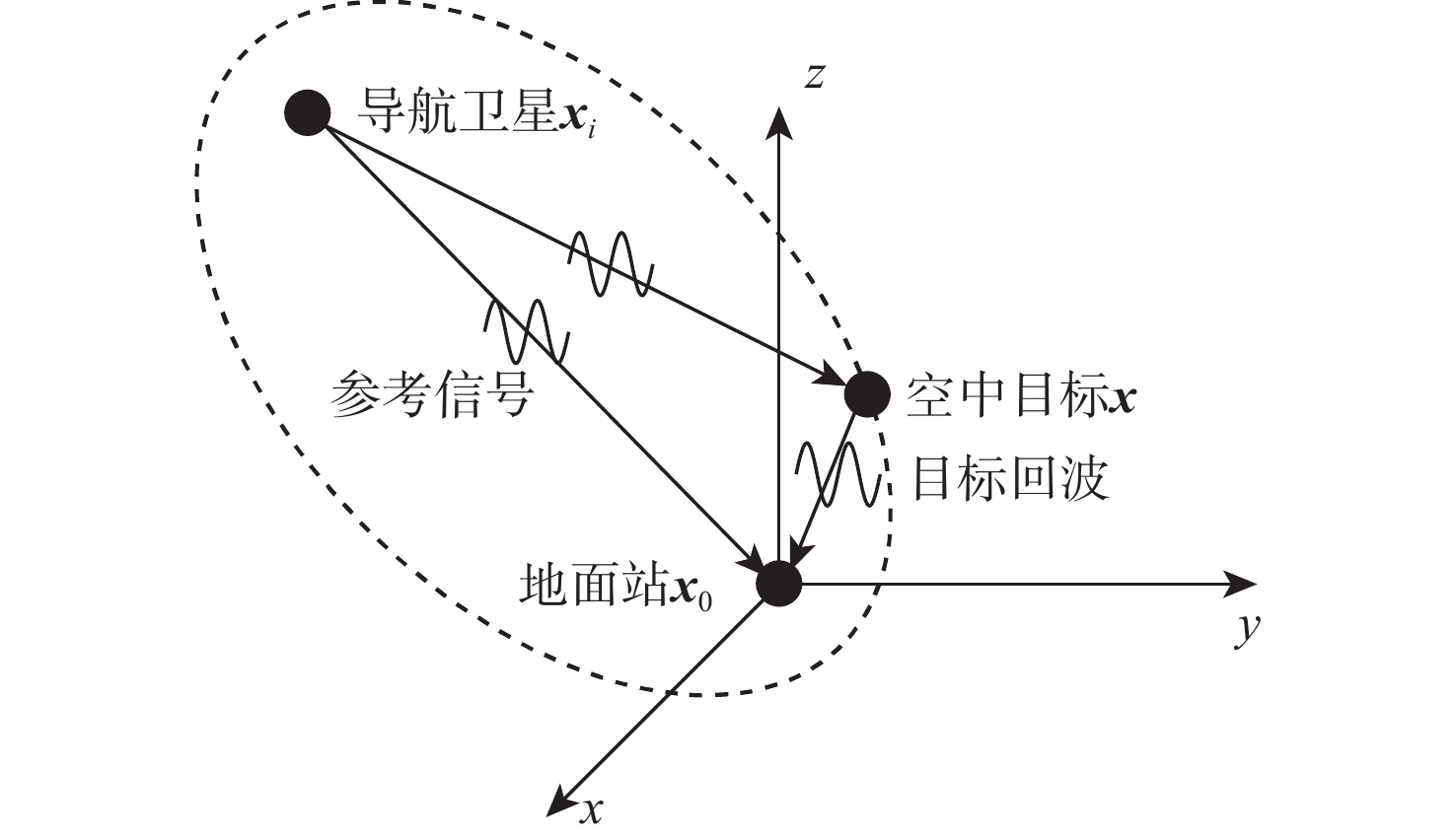
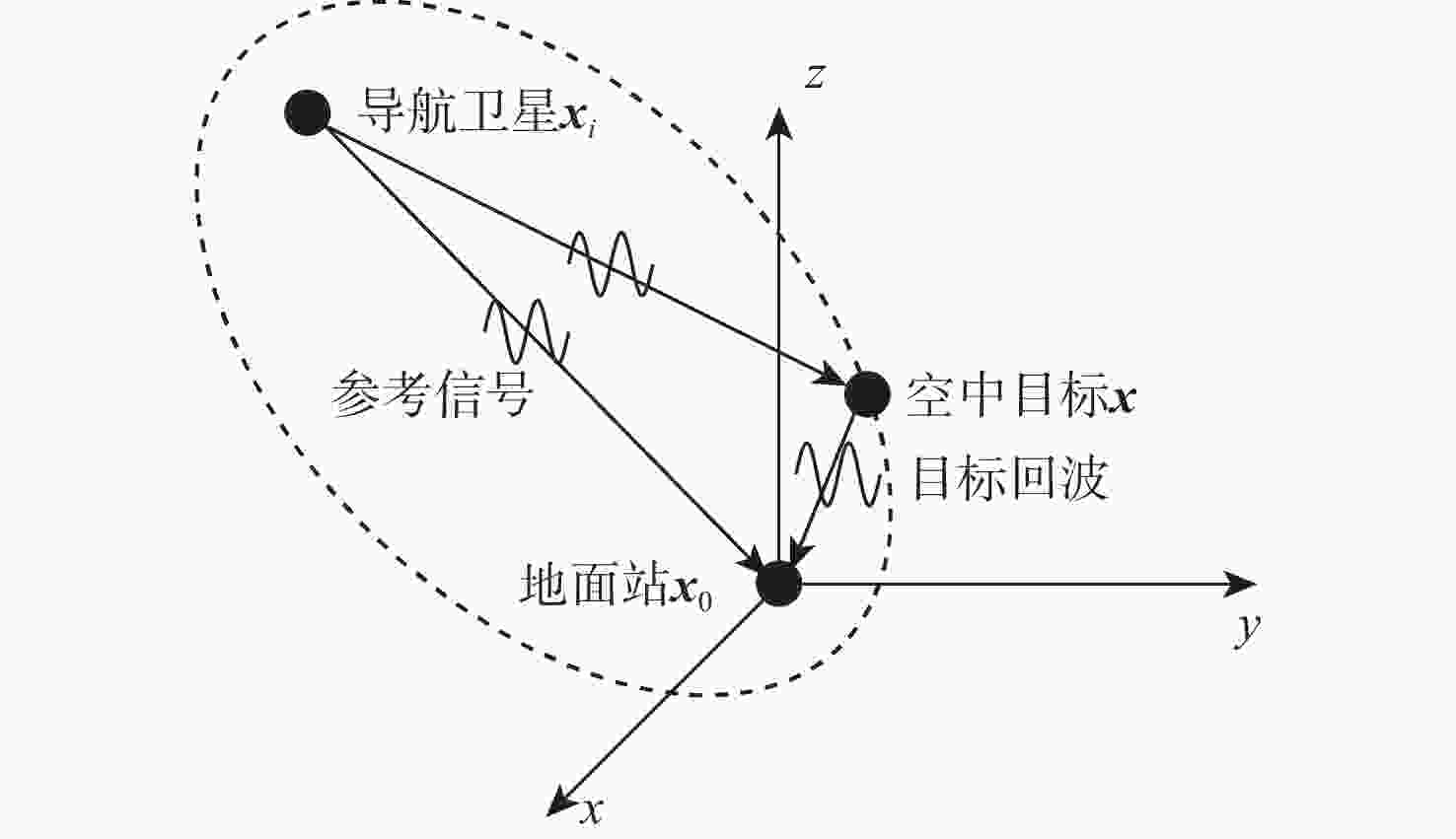
Evaluation of TDOA based air target localization algorithm using GNSS-based passive radar
-
摘要:
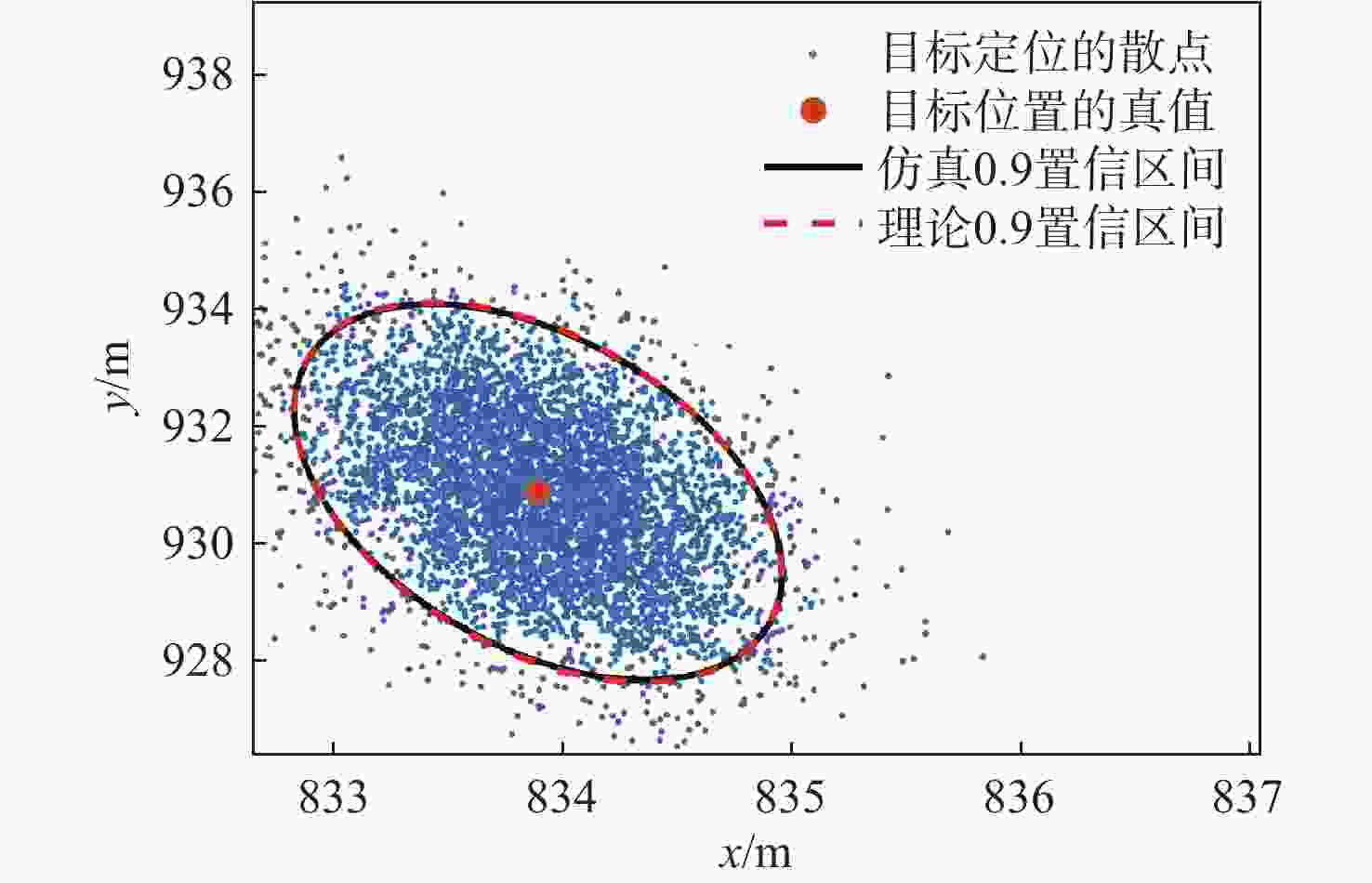
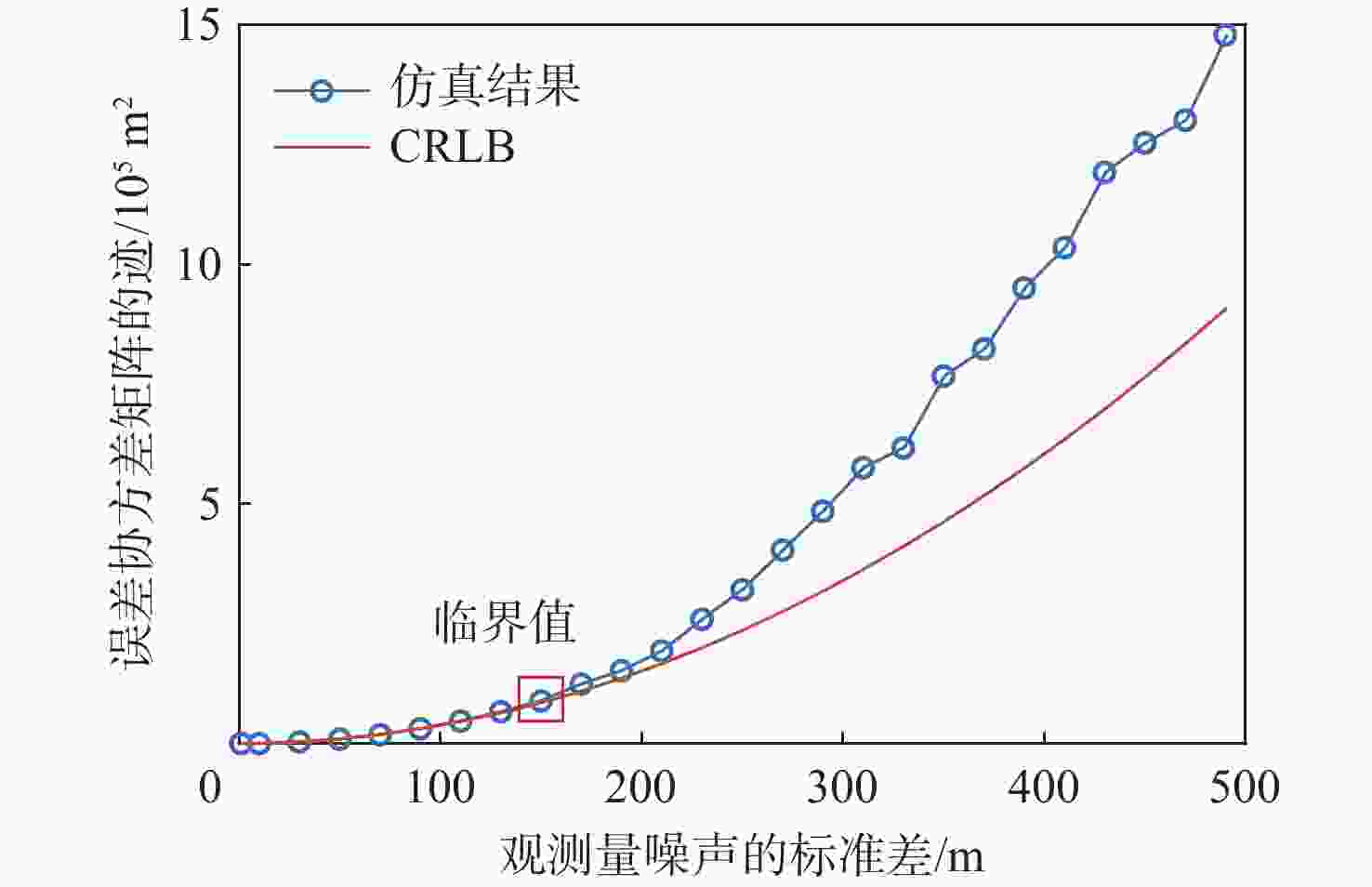
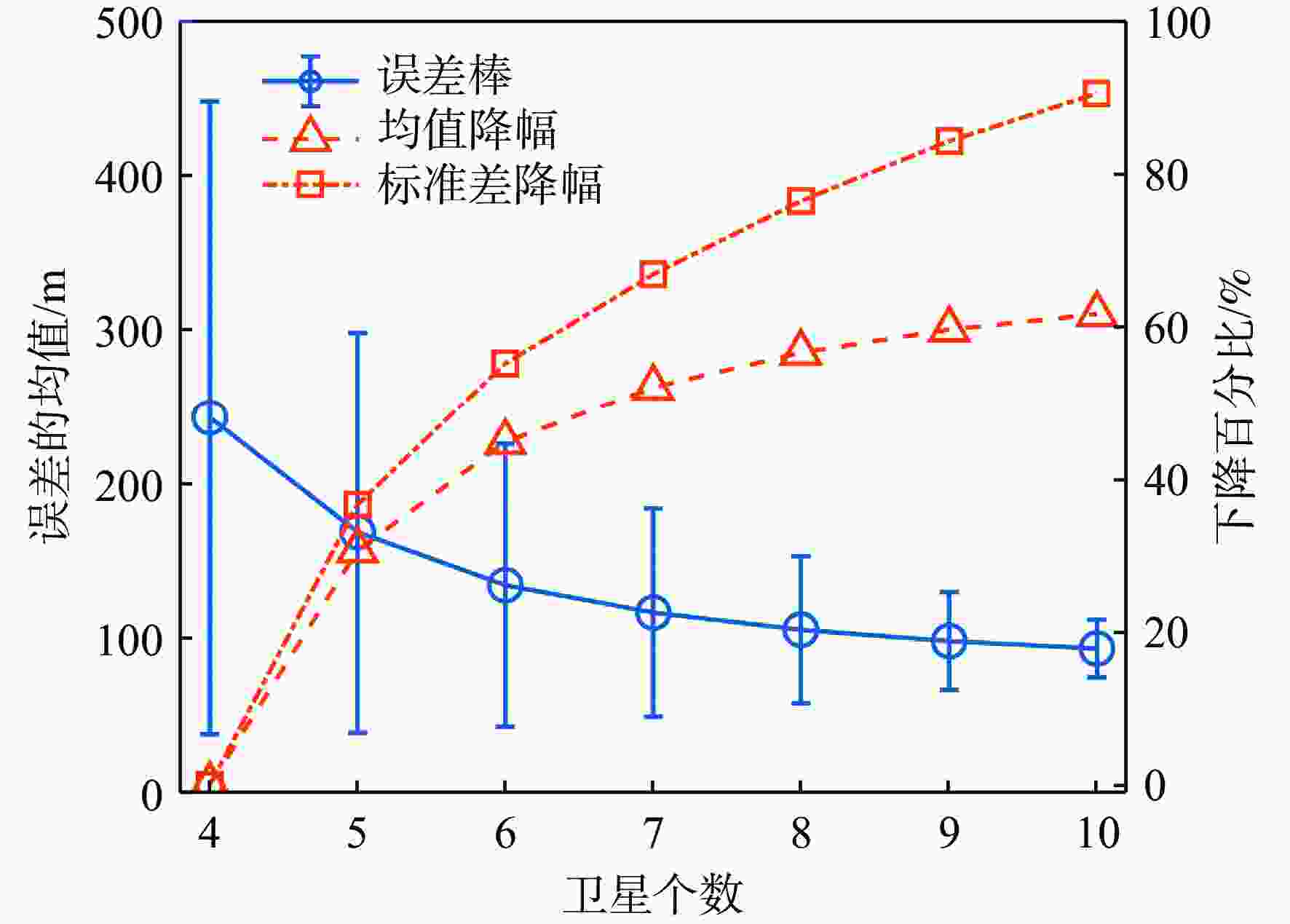
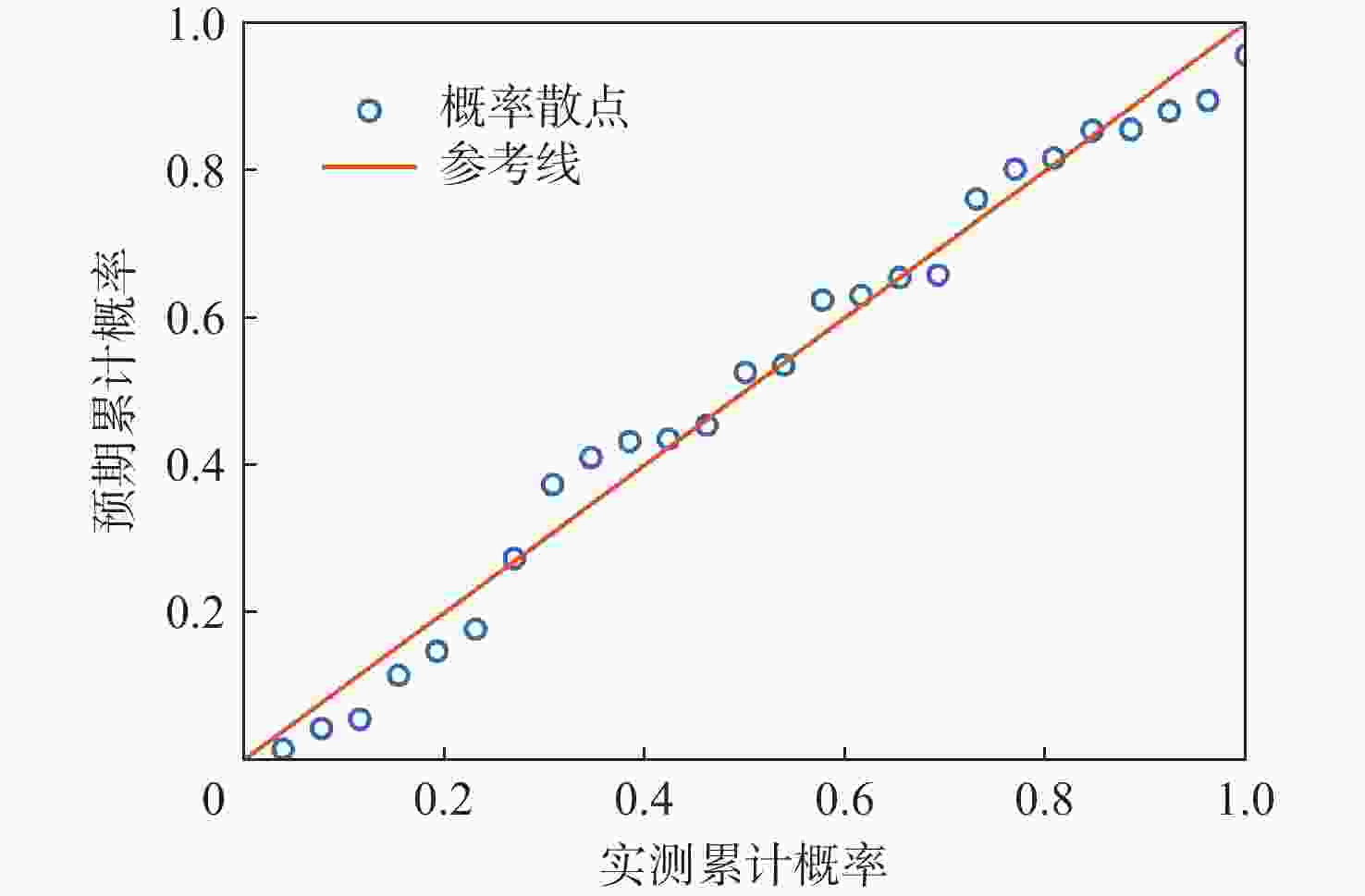
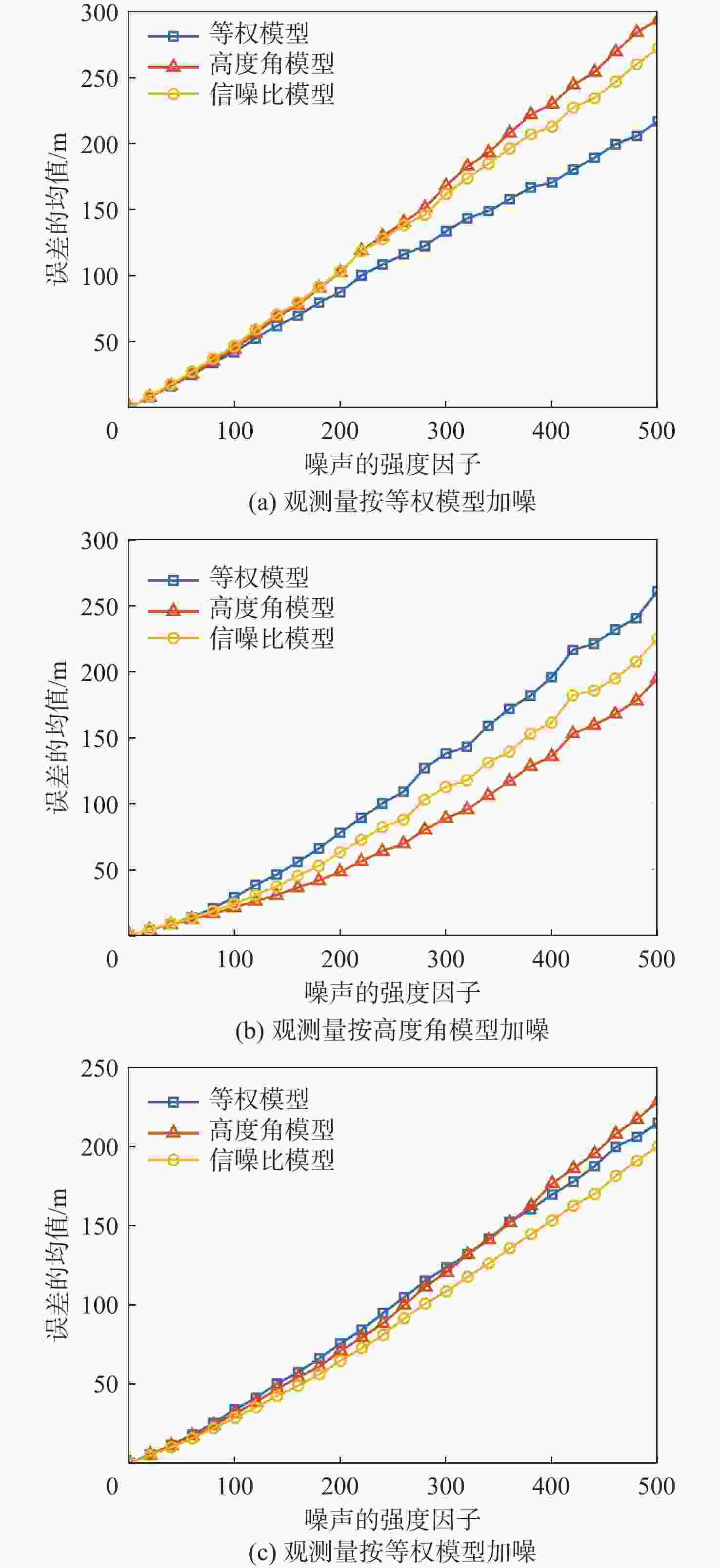
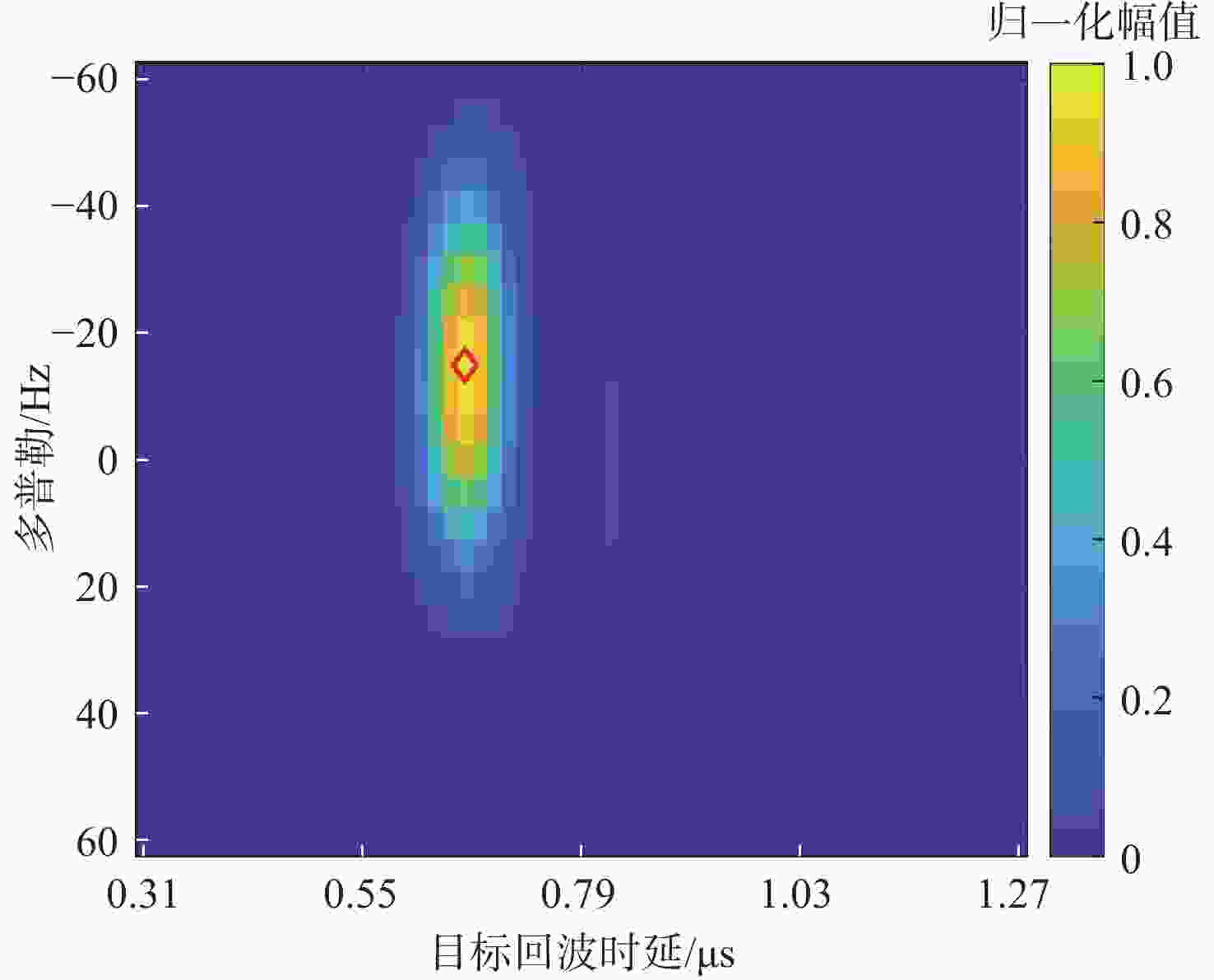
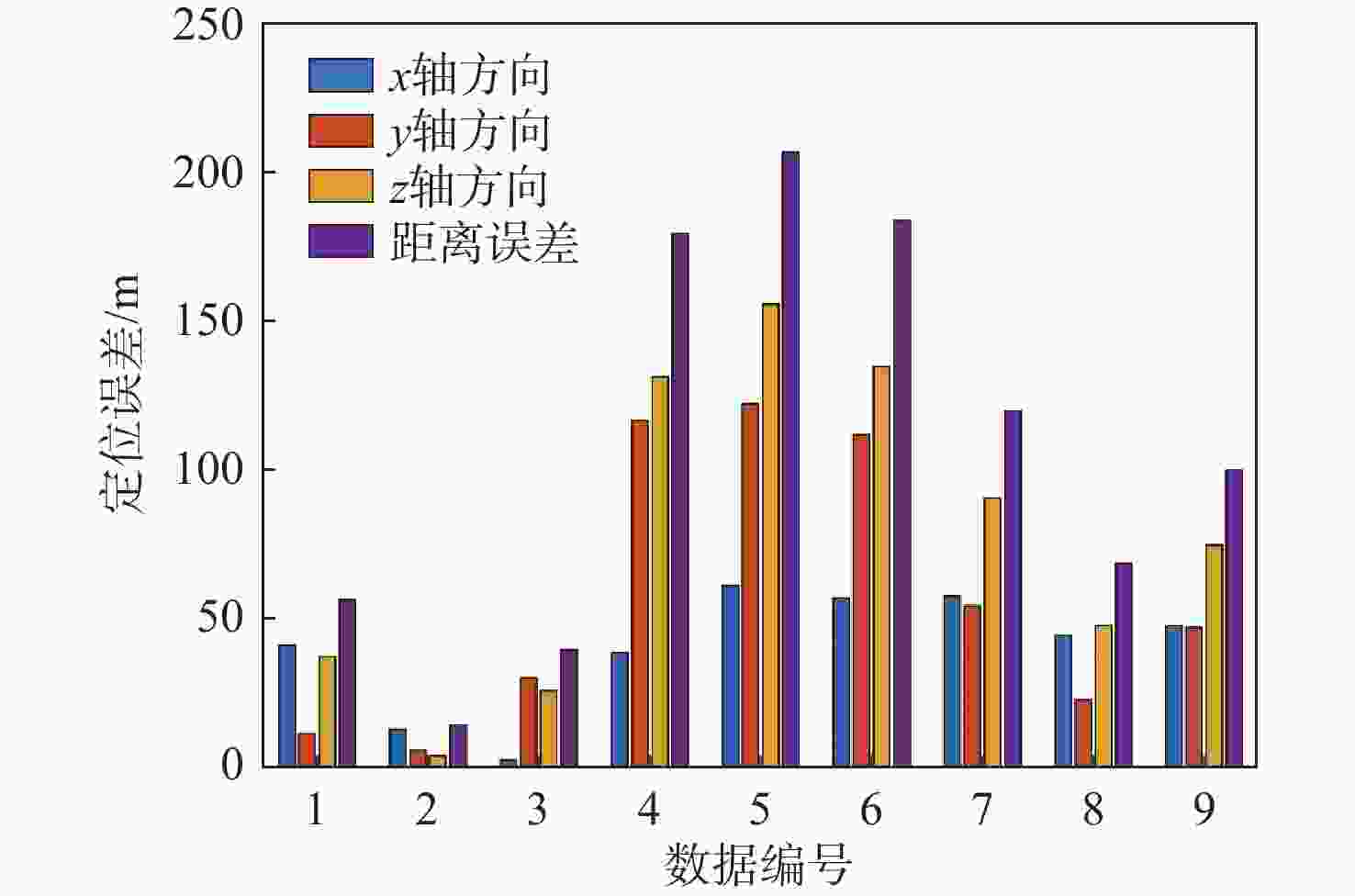
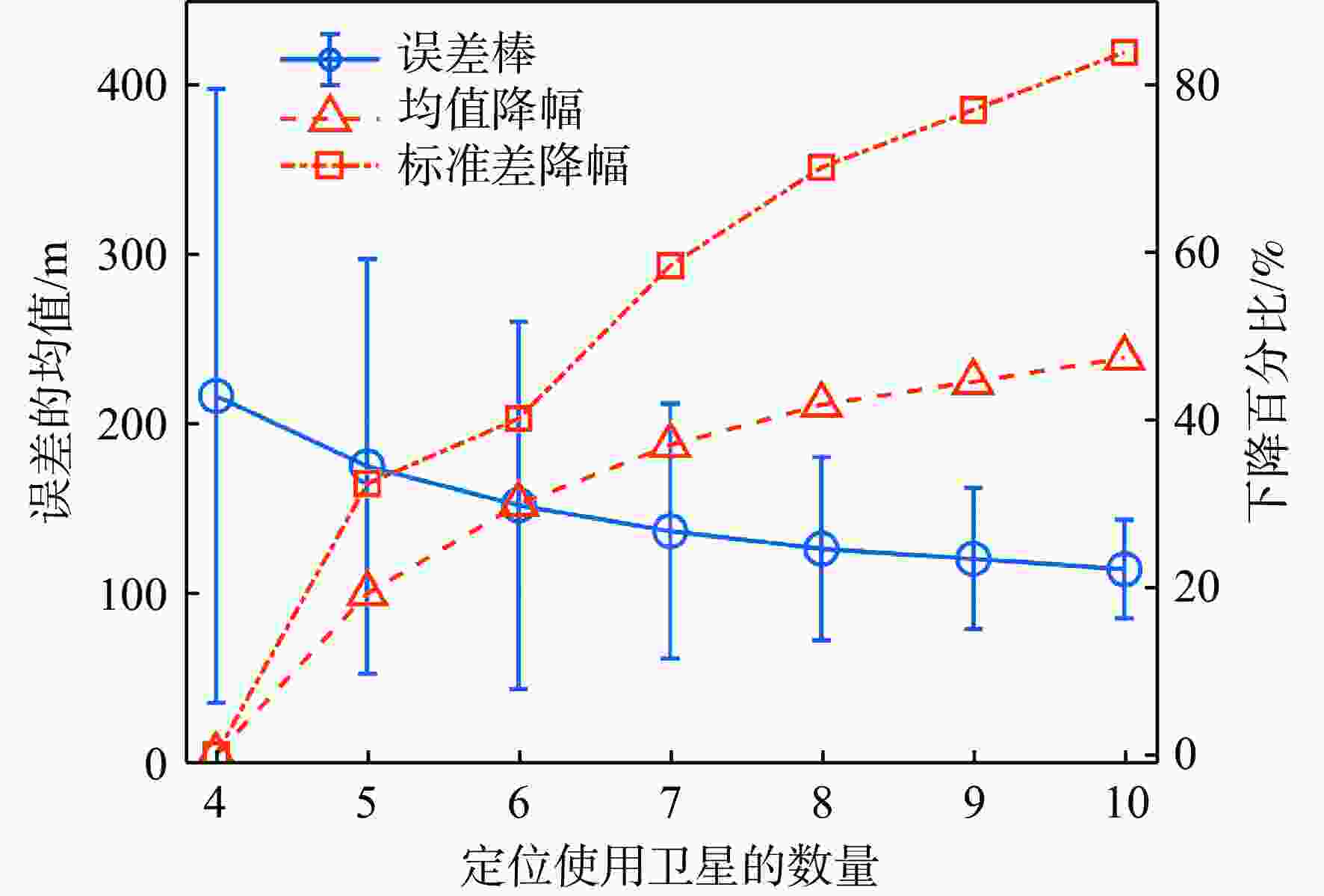
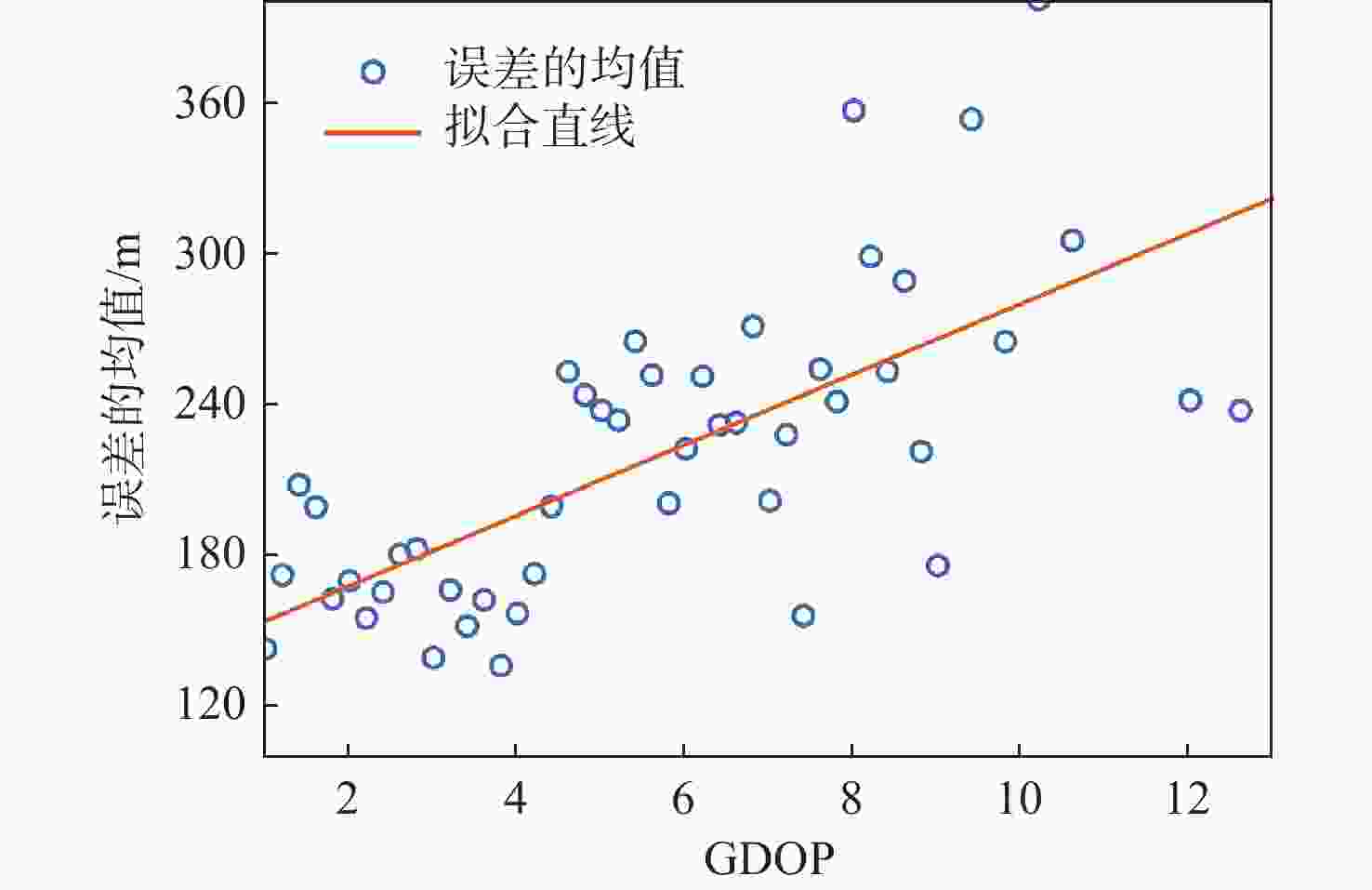
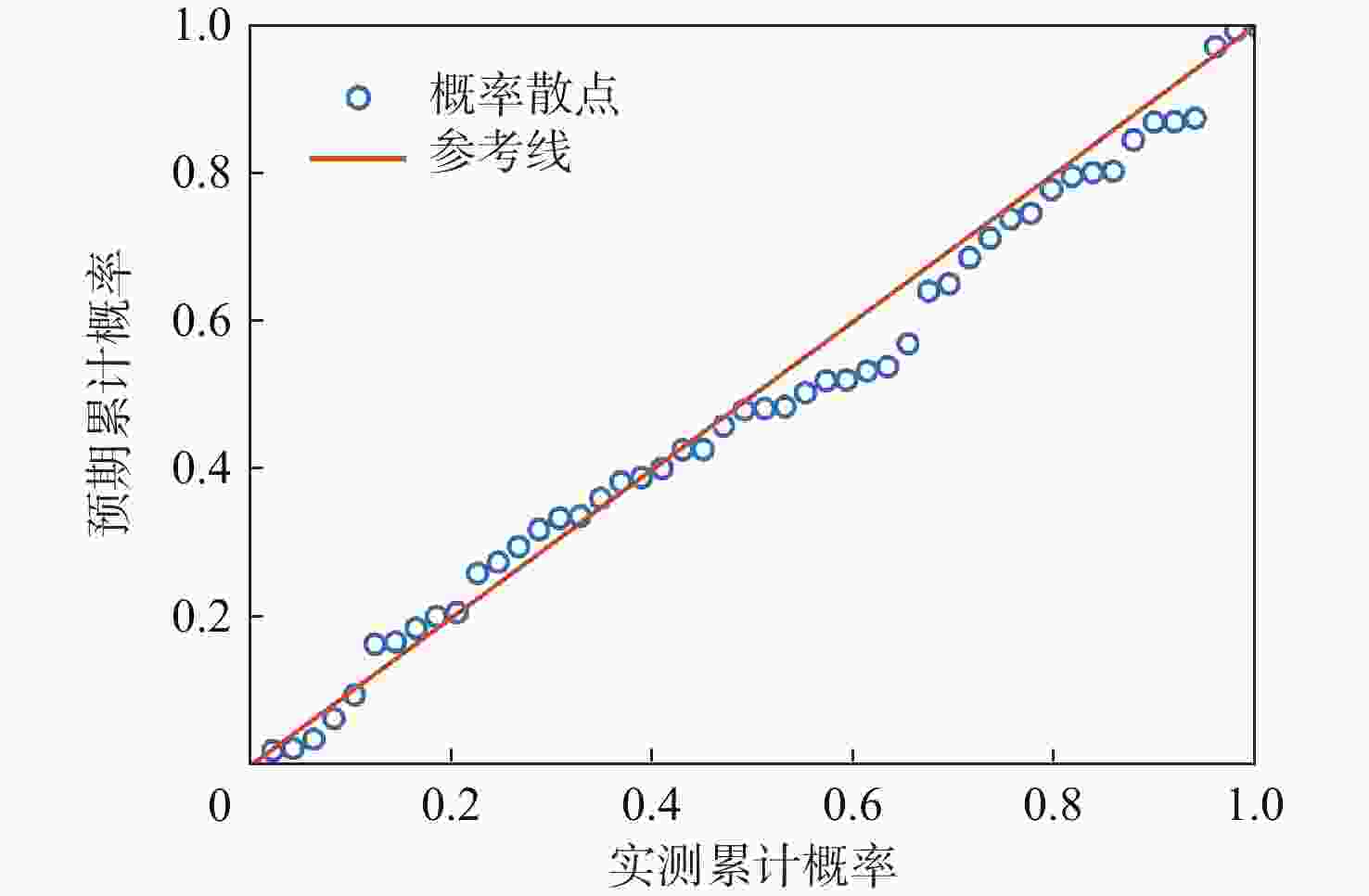
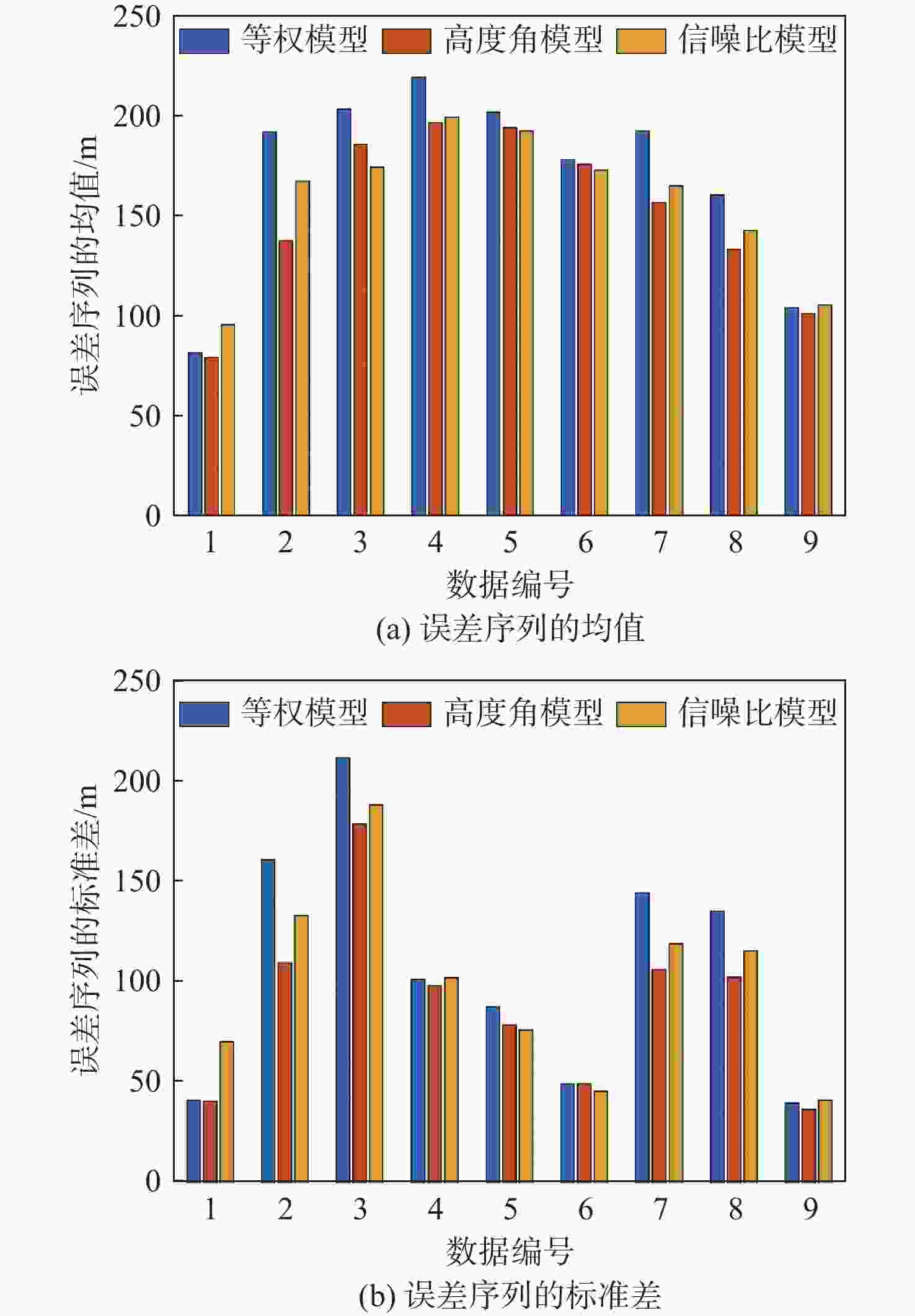
对全球导航卫星系统(GNSS)外辐射源雷达空中目标到达时间差(TDOA)定位算法的性能进行评估,推导TDOA定位方程及方程的加权最小二乘解,引入高度角权重模型和信噪比(SNR)权重模型2种定权方案,分析权重模型、卫星数量、几何精度因子对定位误差的影响。进行仿真试验和外场试验,结果表明:与等权模型相比,高度角权重模型、信噪比权重模型均能有效降低TDOA算法的定位误差,高度角权重模型的降低效果略优于信噪比权重模型;对卫星数量的分析表明,定位中使用的卫星数量小于7颗时定位性能随卫星数量的增加而快速提升,但超过7颗后定位性能的提升速度放缓;对几何精度因子的分析表明,几何精度因子与定位误差的均值呈线性正相关。外场试验中对民航客机的最大定位误差为206.30 m、最小定位误差为13.85 m。
Abstract:The effectiveness of the air target localization method based on time difference of arrival (TDOA) is assessed using passive radar based on the global navigation satellite system (GNSS). The equations of localization and their weighted least squares solution are derived. To determine the weight matrix, an elevation-dependent model and a signal to noise ratio(SNR)-dependent model are introduced. Simulation and outdoor experiment results show that the elevation-dependent model and SNR-dependent model can effectively reduce the position error of the TDOA based air target localization algorithm compared with the unweighted model. When the number of satellites used for localization is fewer than seven, the position performance improves quickly as the number of satellites used increases. However, the improvement trend slows down if more than seven satellites are employed. The evaluation of geometric dilution of precision shows that there is a positive linear correlation between the geometric dilution of precision and position error. In outdoor experiment, the maximum position error of airliners is 206.30 m, and the minimum position error is 13.85 m.
-
表 1 仿真条件
Table 1. Simulation conditions
编号 $ x/ $m $ y $/m $ {\textit{z}} $/m 地面站 0 0 0 空中目标 833.88 930.84 1067.10 卫星1 2874701.46 18323941.72 12163715.47 卫星2 − 17796907.72 15098203.19 27454679.68 卫星3 − 10832994.37 20313279.47 − 3114663.86 卫星4 − 1480434.16 15176177.60 15471755.24 卫星5 − 12042034.11 21659654.86 25834343.54 卫星6 − 18396103.15 32511284.53 − 3687283.66 卫星7 − 14087596.33 − 1462340.29 18377118.55 卫星8 − 12585913.97 35077823.98 − 4628896.76 卫星9 − 2339303.01 22727493.15 28099180.15 卫星10 − 32147874.59 20112733.37 − 4036209.35 卫星11 14019148.46 20442049.95 692344.88 表 2 试验所用设备及其性能
Table 2. Equipment used for the test and its performance
设备名称 设备性能 右旋天线 圆极化天线
全向天线
最大增益为5.5 dBi左旋天线 圆极化天线
波束范围为±10°;
最大增益为10 dBi采集器 中频为15.48 MHz
采样率为64 MHz
量化位数为8 bit计算机 Intel i5-7500 CPU
16 GB RAM表 3 每组数据的可见卫星和选星方案数量
Table 3. Number of visible satellites and satellite selection programmes per data set
数据编号 可见卫星数量 选星方案总数 1 6 22 2 7 64 3 11 1816 4 9 382 5 6 22 6 10 848 7 9 382 8 10 848 9 7 64 -
[1] GRIFFITHS H D. From a different perspective: principles, practice and potential of bistatic radar[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Radar. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2004: 1-7. [2] 万显荣, 易建新, 占伟杰, 等. 基于多照射源的被动雷达研究进展与发展趋势[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(6): 939-958. doi: 10.12000/JR20143WAN X R, YI J X, ZHAN W J, et al. Research progress and development trend of the multi-illuminator-based passive radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(6): 939-958. doi: 10.12000/JR20143 [3] MOCCIA A. Bistatic radar: emerging technology[M]. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, 2008. [4] SLAVOV A, SANDENBERGH S, O’HAGAN D, et al. Multiple FM-based passive bistatic pairs for robust target detection with improved position accuracy[C]//Proceedings of the 23rd International Radar Symposium. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2022: 332-337. [5] MAKSYMIUK R, PŁOTKA M, ABRATKIEWICZ K, et al. 5G network-based passive radar for drone detection[C]//Proceedings of the 24th International Radar Symposium. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2023: 1-10. [6] MARTELLI T, CABRERA O, COLONE F, et al. Exploitation of long coherent integration times to improve drone detection in DVB-S based passive radar[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Radar Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 1-6. [7] 杨东凯, 谭传瑞, 王峰, 等. 基于高度角随机模型的GNSS外辐射源雷达定位算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(4): 1373-1381. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230462YANG D K, TAN C R, WANG F, et al. Elevation-dependent stochastic localization algorithm for GNSS-based passive radar[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(4): 1373-1381 (in Chinese). doi: 10.11999/JEIT230462 [8] 杨进佩. 基于GPS的无源雷达技术研究[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2006.YANG J P. Research on passive radar technology based on GPS[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2006 (in Chinese). [9] KOCH V, WESTPHAL R. New approach to a multistatic passive radar sensor for air/space defense[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 1995, 10(11): 24-32. doi: 10.1109/62.473409 [10] BEHAR V, KABAKCHIEV C. Detectability of air targets using bistatic radar based on GPS L5 signals[C]//Proceedings of the 12th International Radar Symposium (IRS). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2011: 212-217. [11] 苗铎, 杨东凯, 许志超, 等. GNSS外辐射源雷达低慢小目标探测概率[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2023, 49(3): 657-664.MIAO D, YANG D K, XU Z C, et al. Low-altitude, slow speed and small target detection probability of passive radar based on GNSS signals[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2023, 49(3): 657-664 (in Chinese). [12] ZHOU X K, WANG P B, CHEN J, et al. A modified radon Fourier transform for GNSS-based bistatic radar target detection[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 19: 3501805. [13] MAHMUD M S, QAISAR S U, LAMBERT A, et al. Demonstration of LEO object detection using GNSS passive radar: a proof of concept[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium (PLANS). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 1556-1562. [14] WANG P B, ZHOU X K, FANG Y, et al. GNSS-based passive inverse SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2022, 16: 508-521. [15] SANTI F, BUCCIARELLI M, PASTINA D, et al. Spatial resolution improvement in GNSS-based SAR using multistatic acquisitions and feature extraction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(10): 6217-6231. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2583784 [16] SANTI F, ANTONIOU M, PASTINA D. Point spread function analysis for GNSS-based multistatic SAR[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(2): 304-308. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2337054 [17] FAN X Z, LIU F F, ZHANG T, et al. Passive SAR with GNSS transmitters: latest results and research progress[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1043-1046. [18] ZHANG L Z, LIU F F, WANG Z Z, et al. Passive GNSS-based SAR data acquisition and real-time preprocessing system[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Signal, Information and Data Processing (ICSIDP). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 1-4. [19] ANTONIOU M, CHERNIAKOV M, MA H. Space-surface bistatic synthetic aperture radar with navigation satellite transmissions: a review[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2015, 58(6): 1-20. [20] MA H, ANTONIOU M, STOVE A G, et al. Maritime moving target localization using passive GNSS-based multistatic radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(8): 4808-4819. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2838682 [21] GOMEZ-DEL-HOYO P, JARABO-AMORES M P, MATA-MOYA D, et al. 2D ground target location using GPS based passive radar[C]//Proceedings of the Signal Processing Symposium (SPSympo). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 202181-86. [22] 左燕, 周夏磊, 蒋陶然. 传感器位置误差下外辐射源雷达三维定位代数解算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(3): 555-562. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190292ZUO Y, ZHOU X L, JIANG T R. Algebraic solution for 3D localization of multistatic passive radar in the presence of sensor position errors[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2020, 42(3): 555-562 (in Chinese). doi: 10.11999/JEIT190292 [23] NOROOZI A, ALI SEBT M. Target localization in multistatic passive radar using SVD approach for eliminating the nuisance parameters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2017, 53(4): 1660-1671. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2669558 [24] 王鼎, 尹洁昕, 吴志东, 等. 一种基于多普勒频率的恒模信号直接定位方法[J]. 航空学报, 2017, 38(9): 321084.WANG D, YIN J X, WU Z D, et al. Direct localization method for constant modulus source based on Doppler frequency shifts[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2017, 38(9): 321084 (in Chinese). [25] WAX M, KAILATH T. Decentralized processing in sensor arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1985, 33(5): 1123-1129. doi: 10.1109/TASSP.1985.1164706 [26] WEISS A J. Direct position determination of narrowband radio frequency transmitters[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2004, 11(5): 513-516. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2004.826501 [27] HACK D E, PATTON L K, HIMED B, et al. Detection in passive MIMO radar networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(11): 2999-3012. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2014.2319776 [28] SANTI F, PIERALICE F, PASTINA D. Multistatic GNSS-based passive radar for maritime surveillance with long integration times: Experimental results[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf18). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 1260-1265. [29] 卢铭迪. 以卫星信号为外辐射源的直接定位方法研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2019.LU M D. Research on direct positioning method with satellite signal as external radiation source[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2019 (in Chinese). [30] 宋媛媛. 运动单站直接定位技术[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2020.SONG Y Y. Direct positioning technology of moving single station[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2020 (in Chinese). [31] 薛文丽. 无源定位中的直接定位技术研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2020.XUE W L. Research on direct positioning technology in passive positioning[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2020 (in Chinese). [32] 夏楠, 高丹阳, 邢宝辉, 等. 基于外辐射源的空中目标直接定位算法[J]. 通信学报, 2023, 44(6): 117-124. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2023120XIA N, GAO D Y, XING B H, et al. Direct localization algorithm of the aerial target based on external radiation source[J]. Journal on Communications, 2023, 44(6): 117-124 (in Chinese). doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2023120 [33] 闫攀, 栗强强, 闫会峰. 基于北斗卫星外辐射源的目标直接定位算法[J]. 无线电工程, 2023, 53(2): 410-416. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3106.2023.02.019YAN P, LI Q Q, YAN H F. Direct position determination of moving target using BeiDou satellite external illuminators[J]. Radio Engineering, 2023, 53(2): 410-416 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3106.2023.02.019 [34] 边少锋, 刘一, 纪兵, 等. 北斗三号卫星观测信息高度角相关随机模型统计特性分析[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2022, 47(10): 1615-1624.BIAN S F, LIU Y, JI B, et al. Analysis of statistic testing of elevation-dependent stochastic models of BDS-3 satellite observation[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2022, 47(10): 1615-1624 (in Chinese). [35] 刘琳. GNSS观测值精度估计及随机模型精化方法研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2019.LIU L. Research on accuracy estimation of GNSS observations and refinement method of stochastic model[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2019 (in Chinese). [36] OLIVE D J. Linear regression[M]. New York : Springer International Publishing, 2017: 29-36. [37] 飞友科技有限公司. 全球航班飞行轨迹实时跟踪雷达[DB/OL]. (2023-12-03)[2023-12-03]. https://flightadsb.variflight.com.Feiyou Technology Co. , Ltd. Real time tracking radar for global flight trajectories[DB/OL]. (2023-12-03)[2023-12-03]. https://flightadsb.variflight.com. -






 下载:
下载: