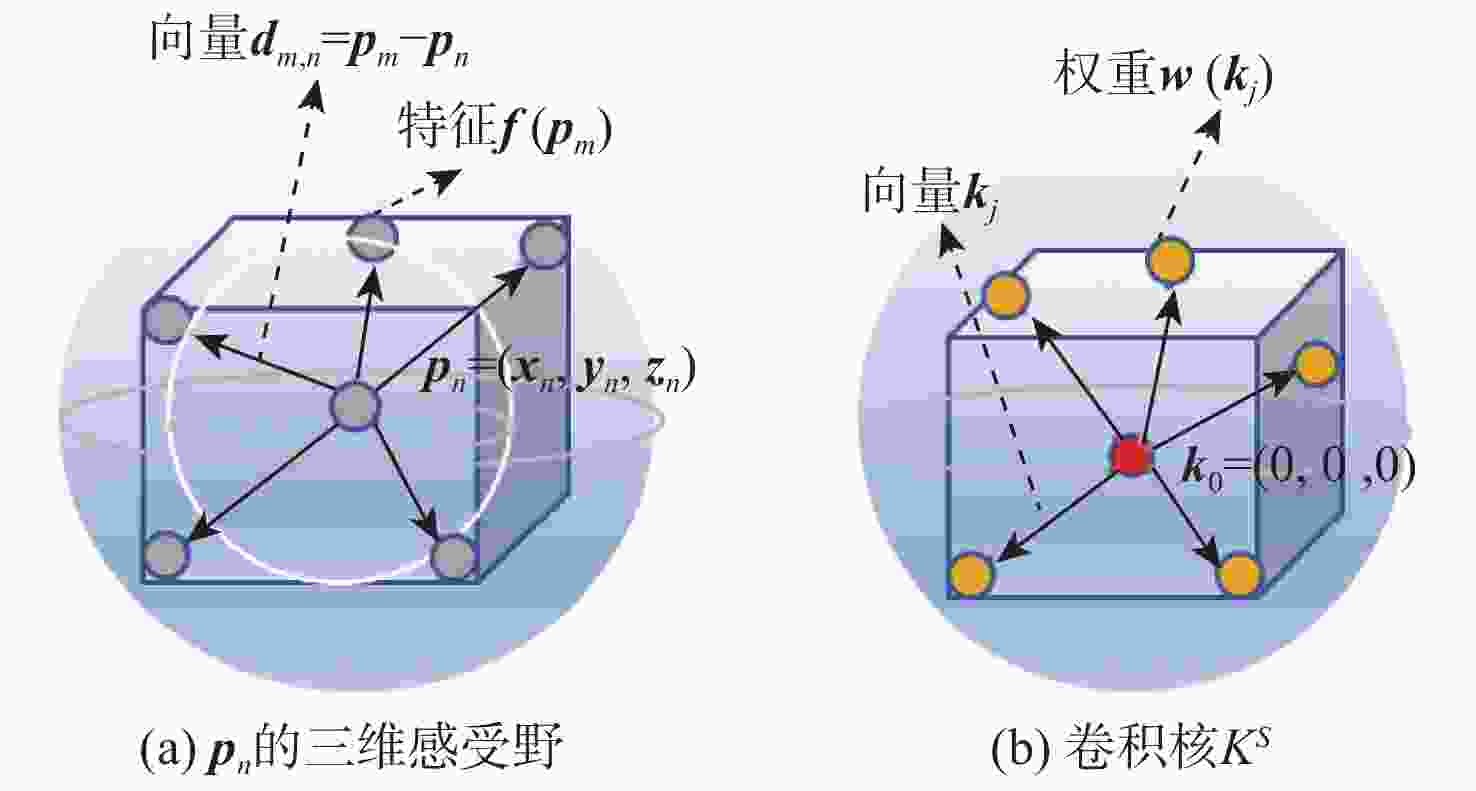
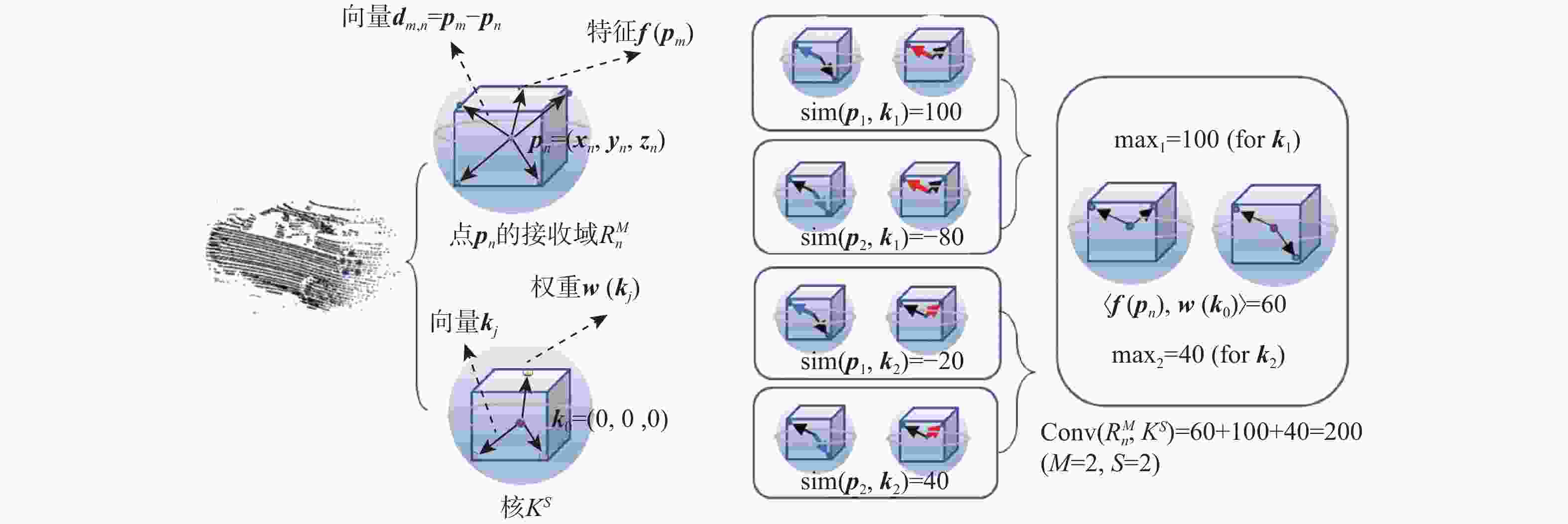
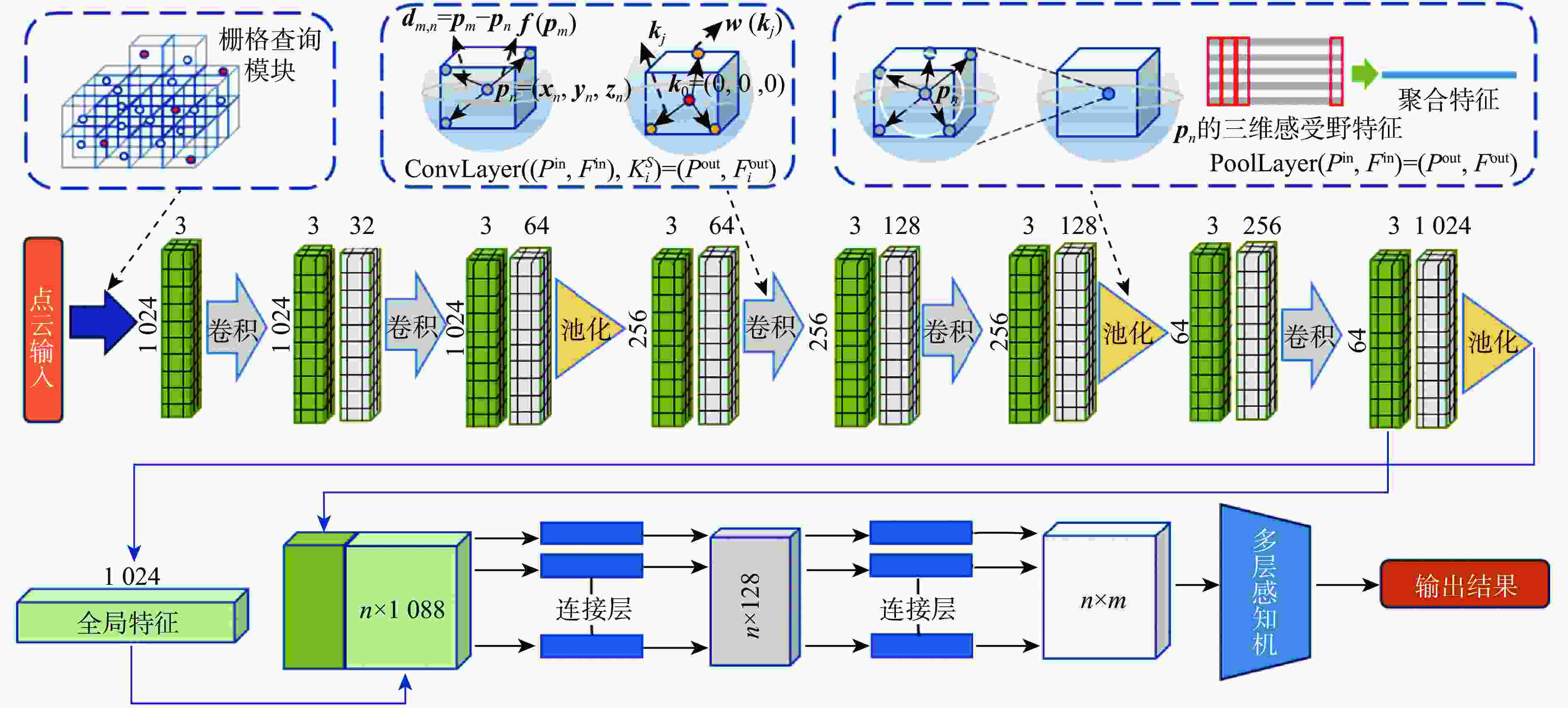
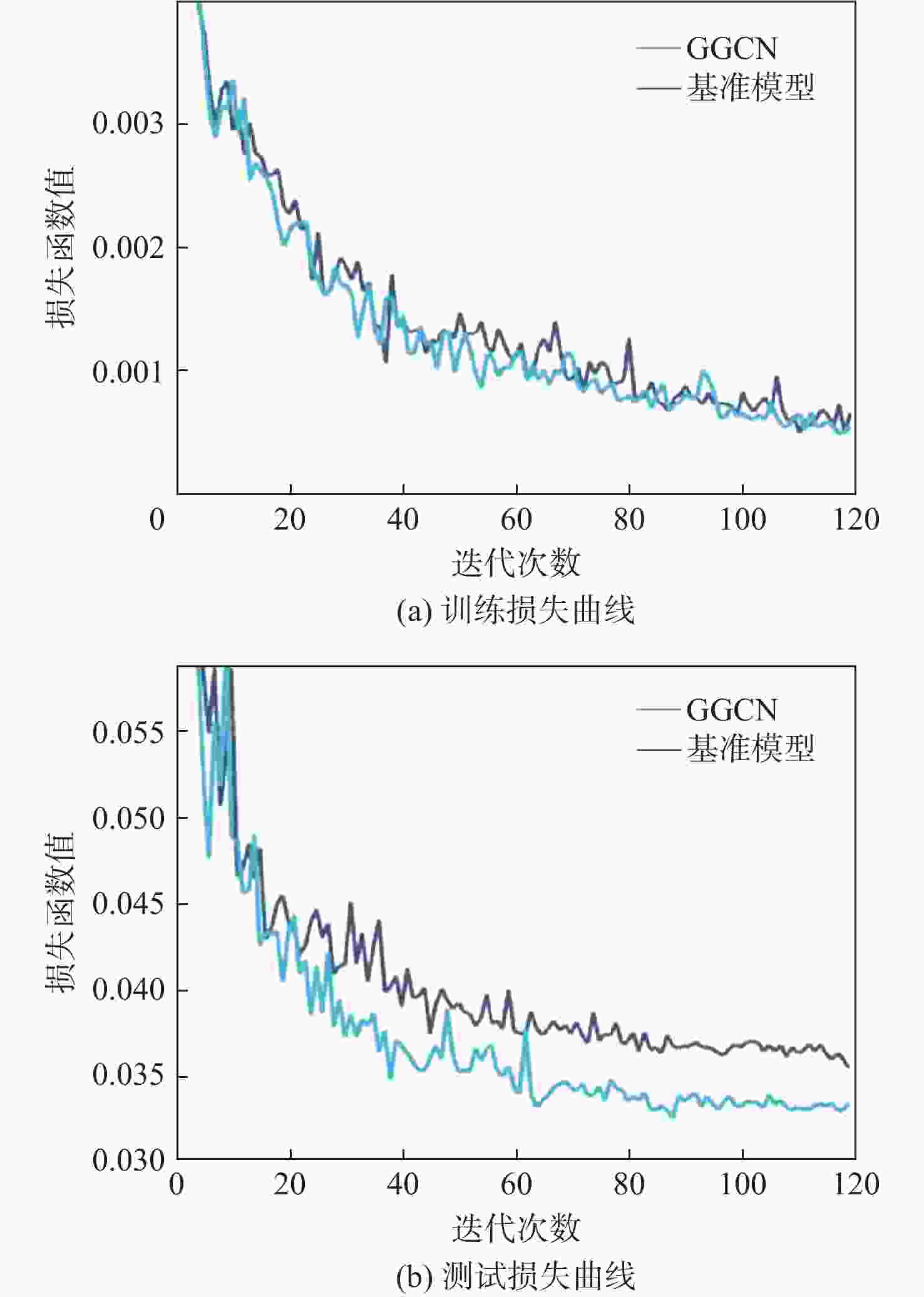
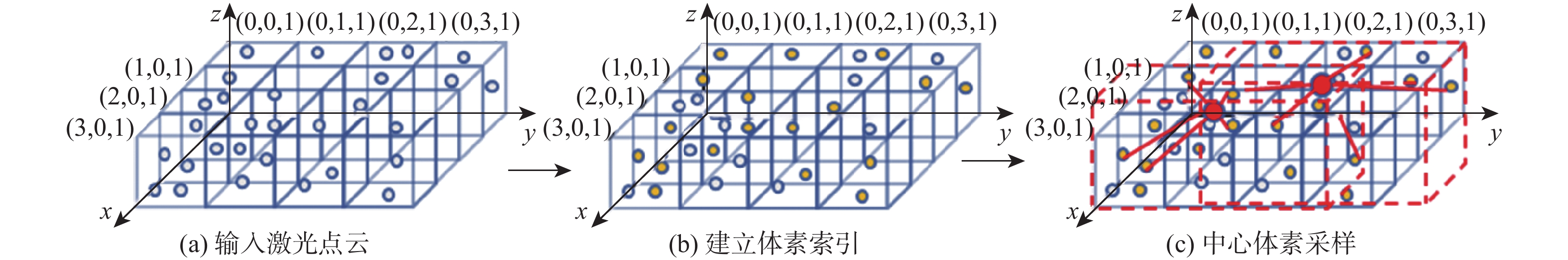
Learnable graph convolution-based semantic segmentation method for 3D LiDAR point clouds in road scenes
-
摘要:
针对现有自动驾驶系统中三维激光点云语义分割普遍存在的局部特征提取能力不足和难以捕捉全局上下文信息等问题,提出一种基于可学习图卷积的道路场景三维激光点云语义分割网络。通过将激光点云体素化后进行节点选取,设计的栅格查询模块可以为学习过程提供更完整的激光点云覆盖,同时,设计可学习卷积核,其形状和权值在训练阶段是可学习的,能更好地处理激光点云中的形变问题;在基准网络结构的每一层后加入改进图卷积层,能够通过动态图计算获得点的局部邻域信息,并在全连接层叠加局部信息获取全局属性。利用数据集Semantickitti对改进前后模型进行对比分析,实验结果表明:改进网络模型的平均交并比(mIoU)值达到59.7%,相比基准模型提高了3.9%,比动态图卷积神经网络(DGCNN)和Lattice Net也分别提高了3.6%和0.9%。研究成果证实了所提的改进网络模型能有效提高自动驾驶道路环境下激光点云语义分割精度,有助于提升激光雷达在自动驾驶中的应用效果。
Abstract:Aiming at the problems of insufficient local feature extraction ability and difficulty in capturing global context information in the semantic segmentation of 3D LiDAR point clouds in the existing autonomous driving system, an intelligent semantic segmentation network of 3D LiDAR point cloud road scenes based on improved graph convolution is proposed. First, the proposed grid query module may offer more comprehensive point cloud coverage for the learning process by rasterizing the point cloud and choosing the nodes. At the same time, a learnable convolution kernel is designed, and its shape and weight are learnable in the training phase, which can better deal with the deformation problem in the point cloud. Secondly, an improved graph convolution layer is added after each layer of the base network structure. The improved graph convolution layer can obtain the local neighborhood information of the point through the dynamic graph calculation, and superimpose the local information in the fully connected layer to obtain the global attribute. Finally, the data set Semantickitti is used to compare and analyze the models before and after improvement. The experimental results show that the mean intersection-over-union (mIoU) value of the improved network reaches 59.7%, which is 3.9% higher than the benchmark model, 3.6% and 0.9% higher than dynamic graph convolutional neural network (DGCNN) and Lattice Net, respectively. The findings of the study demonstrate that the suggested enhanced model can successfully raise the point cloud semantic segmentation accuracy in the autonomous driving road environment, which helps to enhance the LiDAR application effect in autonomous driving.
-
表 1 Semantickitti数据集各类别分割结果比较
Table 1. Comparison of segmentation results for various categories in Semantickitti dataset
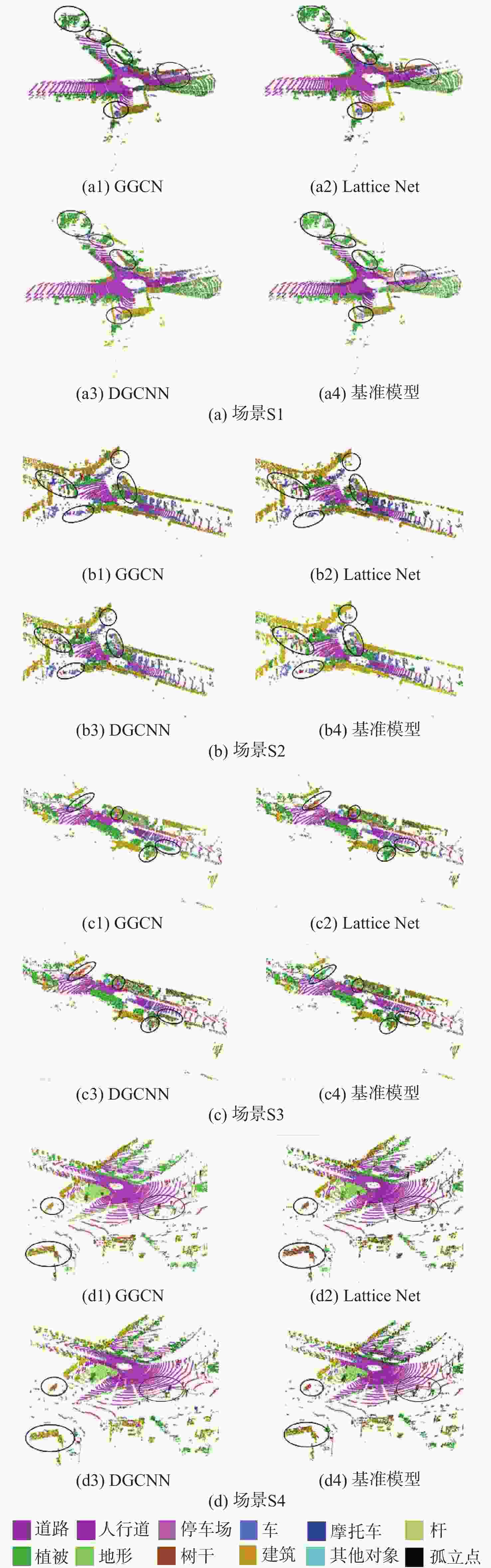
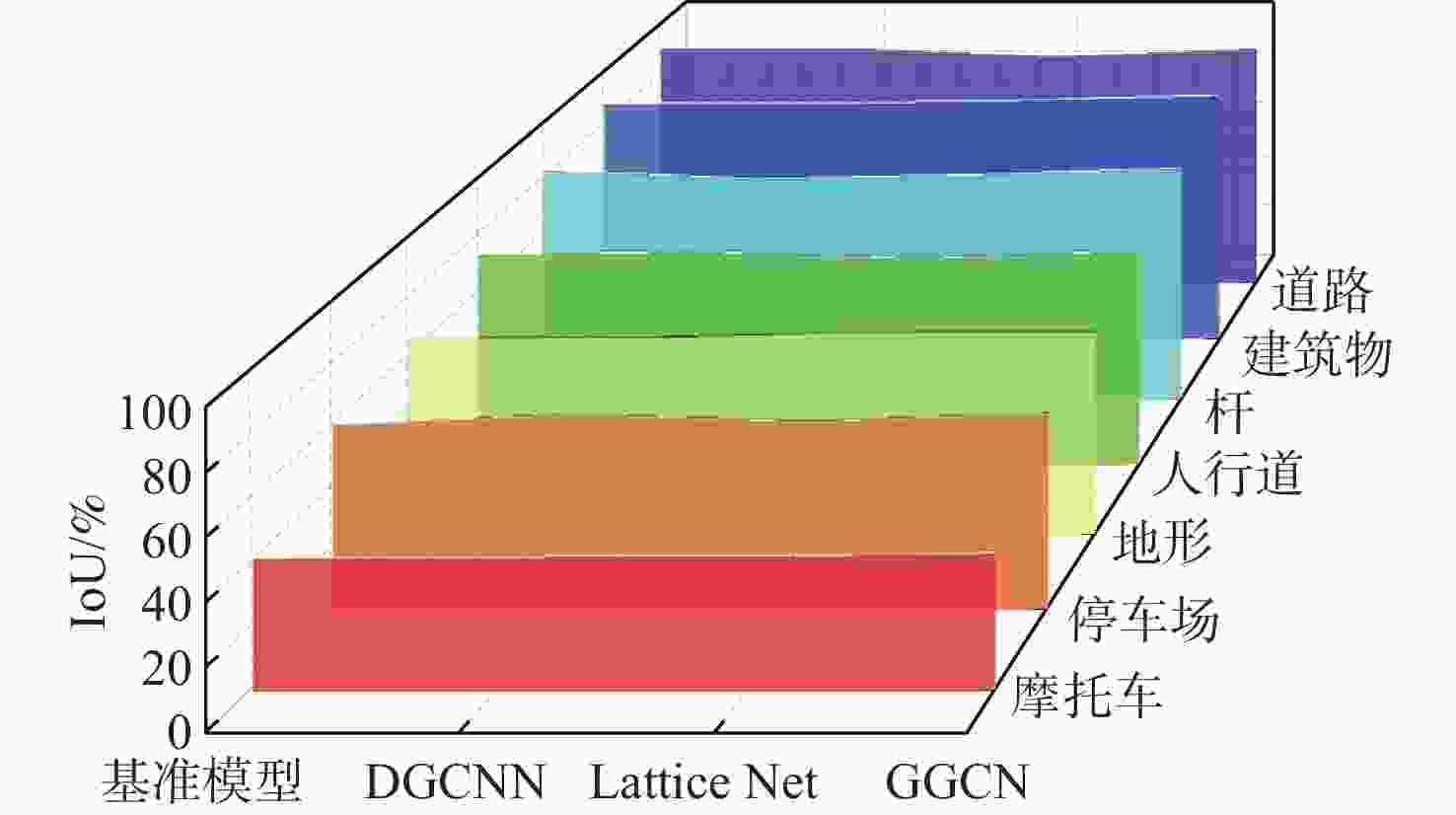
% 模型 IoU 道路 人行道 停车场 车 摩托车 杆 植被 地形 树干 建筑物 基准模型 91.6 73.6 60.2 90.5 42.1 83.4 81.4 66.7 61.4 89.4 DGCNN 91.8 74.9 63.6 91.6 42.4 80.1 81.1 66.5 61.8 89.2 Lattice Net 88.8 72.1 61.3 96.0 42.5 81.6 84.6 68.5 69.2 90.5 GGCN 91.8 75.3 64.0 95.6 43.6 84.0 81.0 68.7 65.3 92.3 表 2 Semantickitti数据集评价指标对比
Table 2. Comparison of evaluation indicators of Semantickitti dataset
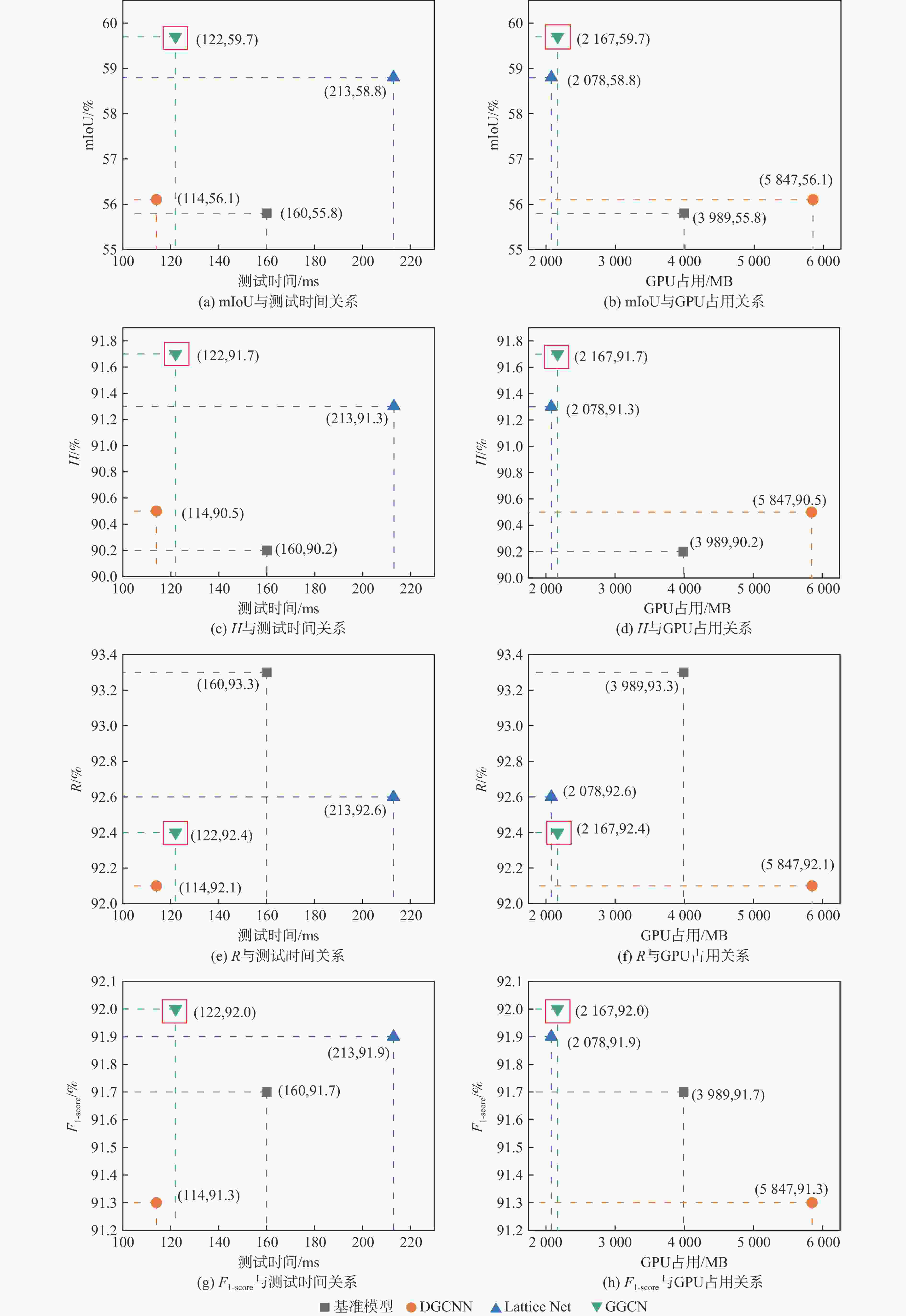
% 模型 mIoU H R F1-score 基准模型 55.8 90.2 93.3 91.7 DGCNN 56.1 90.5 92.1 91.3 Lattice Net 58.8 91.3 92.6 91.9 GGCN 59.7 91.7 92.4 92.0 表 3 不同网络模块消融结果
Table 3. Ablation results of different network modules
基准模型 栅格查询模块 可学习卷积核 损失函数模块 mIoU/% √ 55.8 √ √ 56.6 √ √ √ 58.6 √ √ √ √ 59.7 表 4 评价指标误差分析
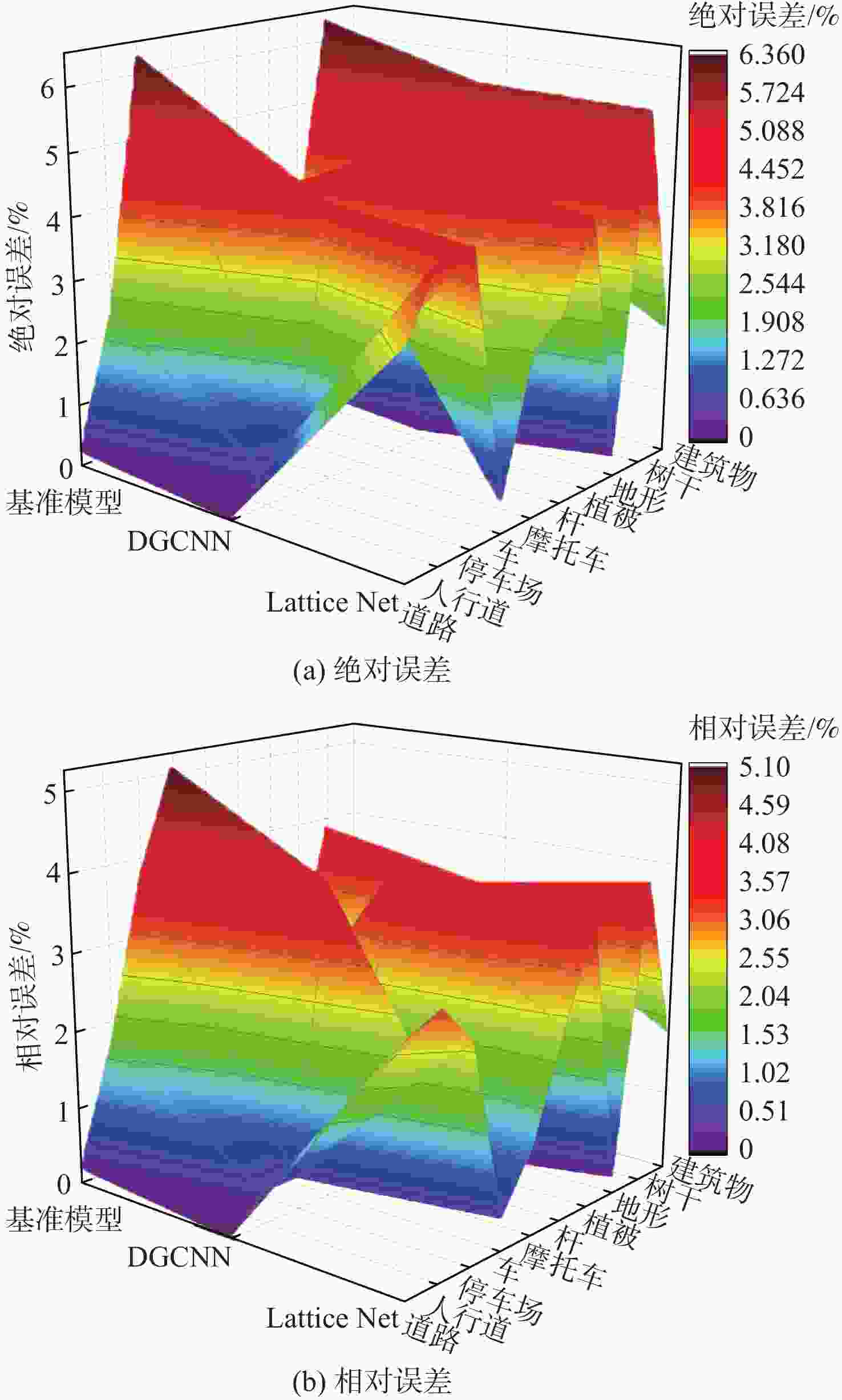
Table 4. Error analysis table of evaluation indicators
% 模型 EAI EAH EAR EAF ERI ERH ERR ERF 基准模型 3.9 1.5 0.9 0.3 7.0 1.7 1.0 0.4 DGCNN 3.6 1.2 0.3 0.8 6.4 1.3 0.3 0.8 Lattice Net 0.9 0.4 0.2 0.1 1.5 0.4 0.2 0.1 -
[1] LI Y, IBANEZ-GUZMAN J. Lidar for autonomous driving: the principles, challenges, and trends for automotive lidar and perception systems[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2020, 37(4): 50-61. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2020.2973615 [2] KURANI A, DOSHI P, VAKHARIA A, et al. A comprehensive comparative study of artificial neural network (ANN) and support vector machines (SVM) on stock forecasting[J]. Annals of Data Science, 2023, 10(1): 183-208. doi: 10.1007/s40745-021-00344-x [3] 陈科, 管海燕, 雷相达, 等. 基于特征增强核点卷积网络的多光谱LiDAR点云分类方法[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2023, 25(5): 1075-1087.CHEN K, GUAN H Y, LEI X D, et al. Multispectral LiDAR point cloud classification method based on feature-enhanced kernel point convolutional network[J]. Journal of Geo-Information Science, 2023, 25(5): 1075-1087(in Chinese). [4] WANG P S, LIU Y, GUO Y X, et al. O-CNN: Octree-based convolutional neural networks for 3D shape analysis[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2017, 36(4): 1-11. [5] LIANG P, FANG Z J, HUANG B, et al. PointFusionNet: point feature fusion network for 3D point clouds analysis[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2021, 51(4): 2063-2076. doi: 10.1007/s10489-020-02004-8 [6] 张硕, 叶勤, 史婧, 等. 改进RangeNet++损失函数的车载点云小目标语义分割方法[J]. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2021, 33(5): 704-711.ZHANG S, YE Q, SHI J, et al. Semantic segmentation method for vehicle-mounted point cloud small target improved RangeNet++ loss function[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design & Computer Graphics, 2021, 33(5): 704-711(in Chinese). [7] 谭光鸿, 侯进, 韩雁鹏, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的低参数量实时图像分割算法[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2019, 56(9): 100-108.TAN G H, HOU J, HAN Y P, et al. Low-parameter real-time image segmentation algorithm based on convolutional neural network[J]. Progress in Laser & Optoelectronics, 2019, 56(9): 100-108(in Chinese). [8] 程鑫, 王宏飞, 周经美, 等. 基于体素柱形的激光雷达点云车辆目标检测算法[J]. 中国公路学报, 2023, 36(3): 247-260.CHENG X, WANG H F, ZHOU J M, et al. Vehicle target detection algorithm in Lidar point cloud based on voxel column[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transportation, 2023, 36(3): 247-260(in Chinese). [9] SHI S S, JIANG L, DENG J J, et al. PV-RCNN++: point-voxel feature set abstraction with local vector representation for 3D object detection[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2023, 131(2): 531-551. doi: 10.1007/s11263-022-01710-9 [10] 吴泽群, 曹猛, 韩世超, 等. 基于高密度激光点云和深度学习的高速公路标线识别[J]. 公路, 2022, 67(6): 247-253.WU Z Q, CAO M, HAN S C, et al. Highway marking recognition based on high-density laser point cloud and deep learning[J]. Highway, 2022, 67(6): 247-253(in Chinese). [11] 黄郑, 顾徐, 王红星, 等. 基于改进PointNet++的输电杆塔点云语义分割模型[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56(3): 77-85.HUANG Z, GU X, WANG H X, et al. Semantic segmentation model of transmission tower point cloud based on improved PointNet++[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56(3): 77-85(in Chinese). [12] 吴军, 崔玥, 赵雪梅, 等. SSA-PointNet++: 空间自注意力机制下的3D点云语义分割网络[J]. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2022, 34(3): 437-448.WU J, CUI Y, ZHAO X M, et al. SSA-PointNet++: 3D point cloud semantic segmentation network based on spatial self-attention mechanism[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design & Computer Graphics, 2022, 34(3): 437-448(in Chinese). [13] 马庆禄, 黄筱潇, 孔国英. 基于通道注意力和图卷积的激光三维目标检测[J]. 计算机工程与设计, 2023, 44(9): 2740-2746.MA Q L, HUANG X X, KONG G Y. Laser 3D object detection based on channel attention and graph convolution[J]. Computer Engineering and Design, 2023, 44(9): 2740-2746(in Chinese). [14] 杨军, 党吉圣. 基于上下文注意力CNN的三维点云语义分割[J]. 通信学报, 2020, 41(7): 195-203.YANG J, DANG J S. Semantic segmentation of three-dimensional point cloud based on contextual attention CNN[J]. Journal on Communications, 2020, 41(7): 195-203(in Chinese). [15] 张坤, 朱亚薇, 王晓红, 等. 基于空间图卷积的三维点云语义分割[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2023, 60(2): 387-395.ZHANG K, ZHU Y W, WANG X H, et al. Three-dimensional point cloud semantic segmentation based on spatial graph convolution[J]. Progress in Laser and Optoelectronics, 2023, 60(2): 387-395(in Chinese). [16] WANG Y, SUN Y B, LIU Z W, et al. Dynamic graph CNN for learning on point clouds[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2019, 38(5): 1-12. [17] WEN S H, WANG T, TAO S. Hybrid CNN-LSTM architecture for LiDAR point clouds semantic segmentation[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2022, 7(3): 5811-5818. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2022.3153899 [18] 杨军, 李博赞. 基于自注意力特征融合组卷积神经网络的三维点云语义分割[J]. 光学精密工程, 2022, 30(7): 840-853.YANG J, LI B Z. Three-dimensional point cloud semantic segmentation based on convolutional neural network of self-attention feature fusion group[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2022, 30(7): 840-853(in Chinese). [19] 兰红, 陈浩, 张蒲芬. 集图卷积和三维方向卷积的点云分类分割模型[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2023, 59(8): 182-191.LAN H, CHEN H, ZHANG P F. Point cloud classification segmentation model for set map convolution and three-dimensional directional convolution[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2023, 59(8): 182-191(in Chinese). -






 下载:
下载: