High-speed target drone somersault maneuver control based on neural network incremental dynamic inversion
-
摘要:
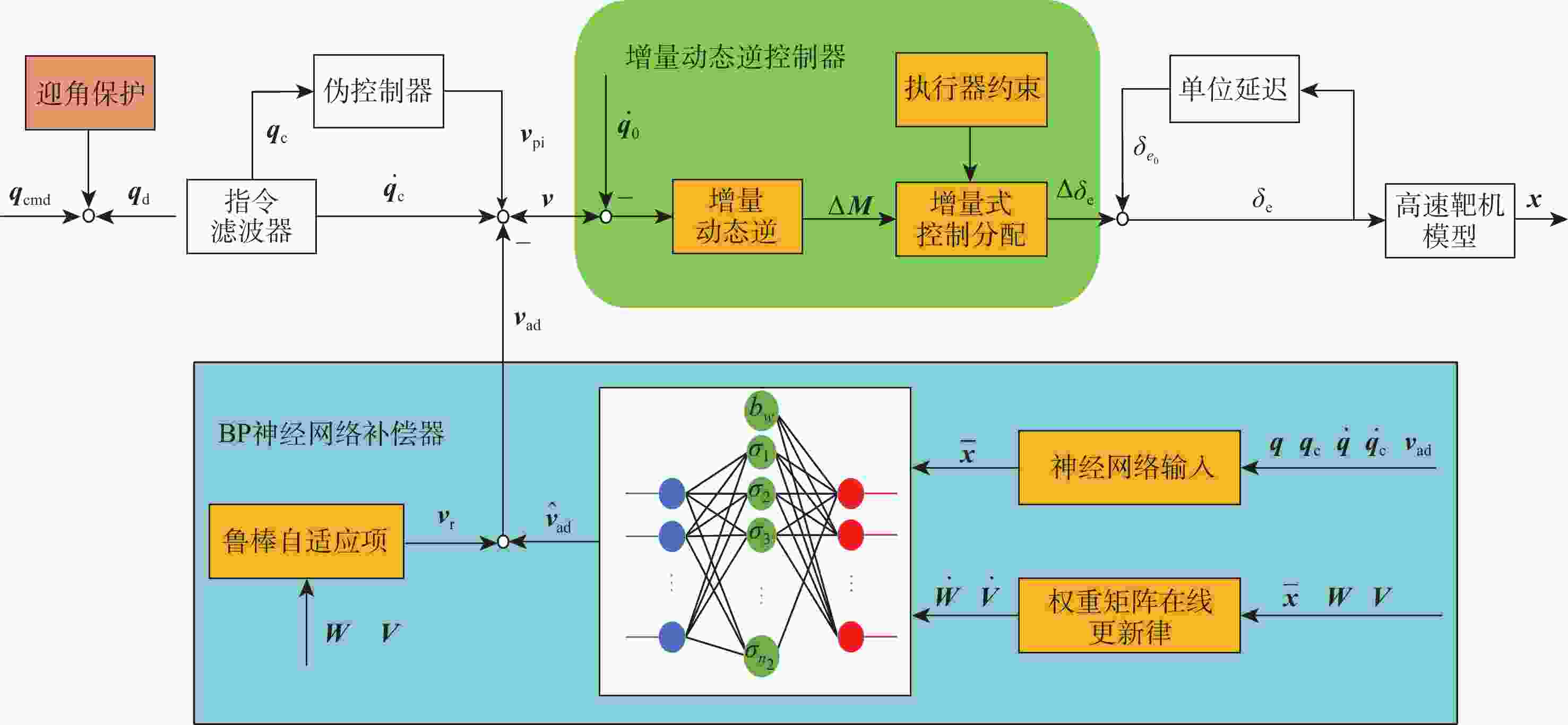
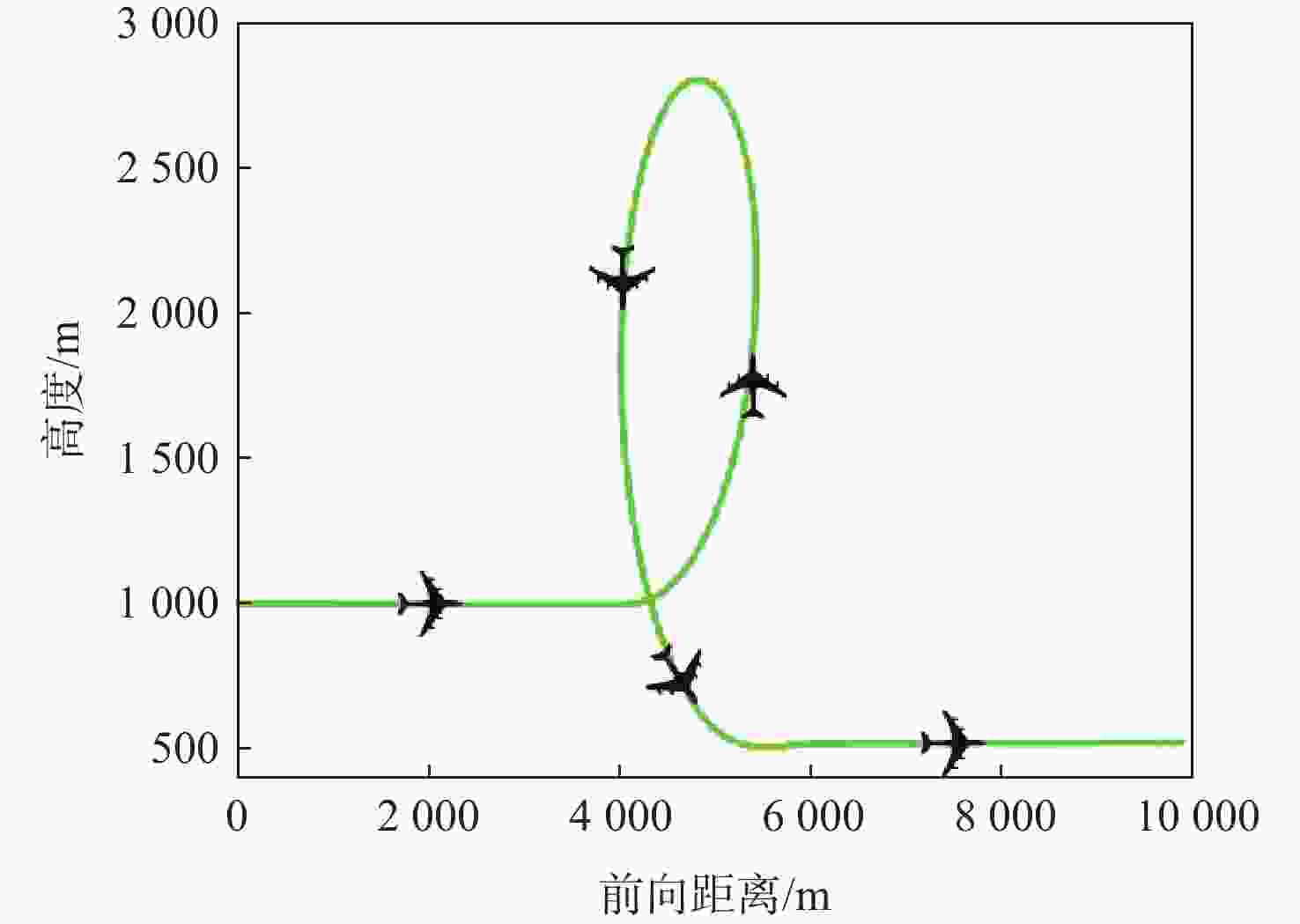
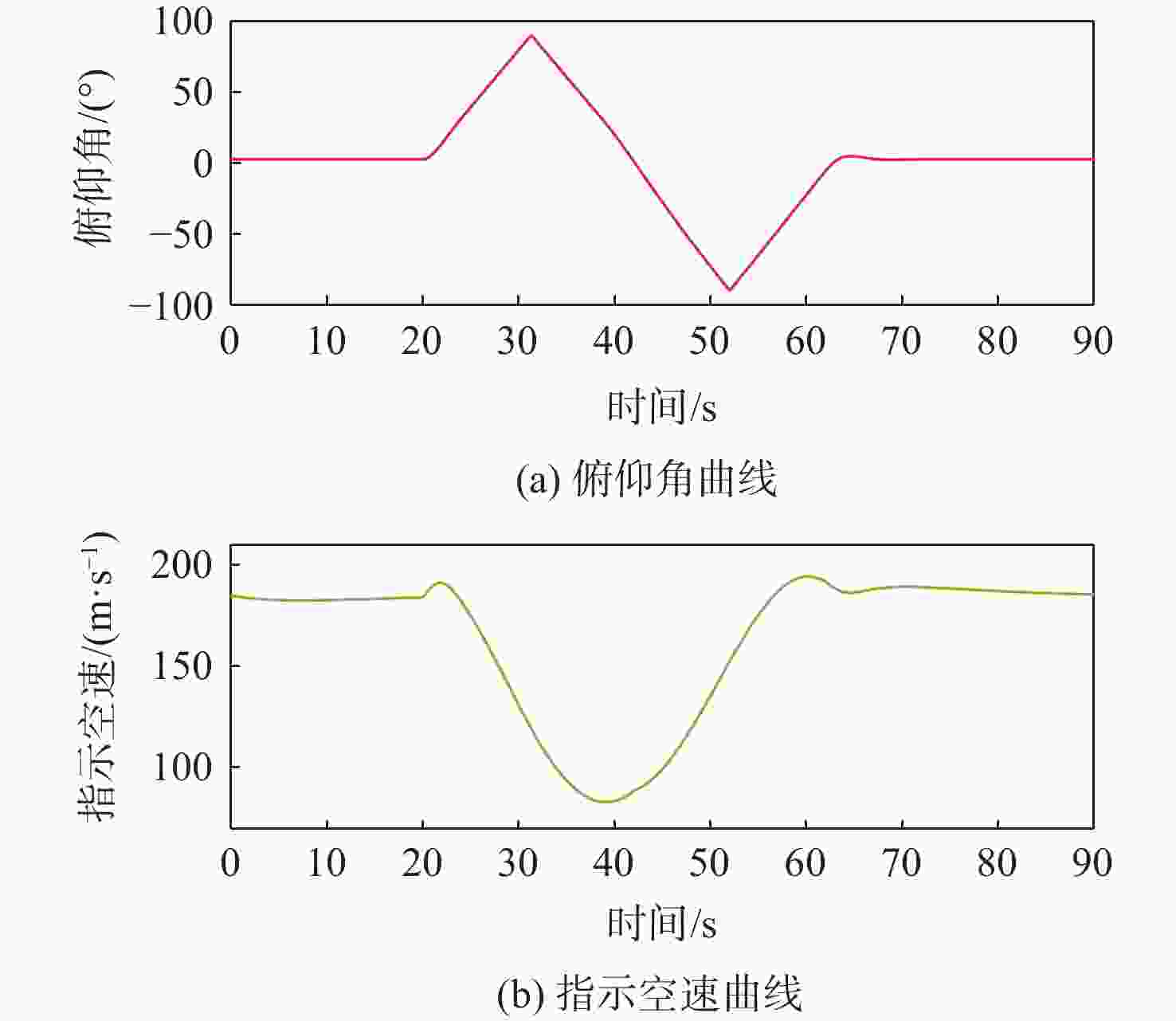
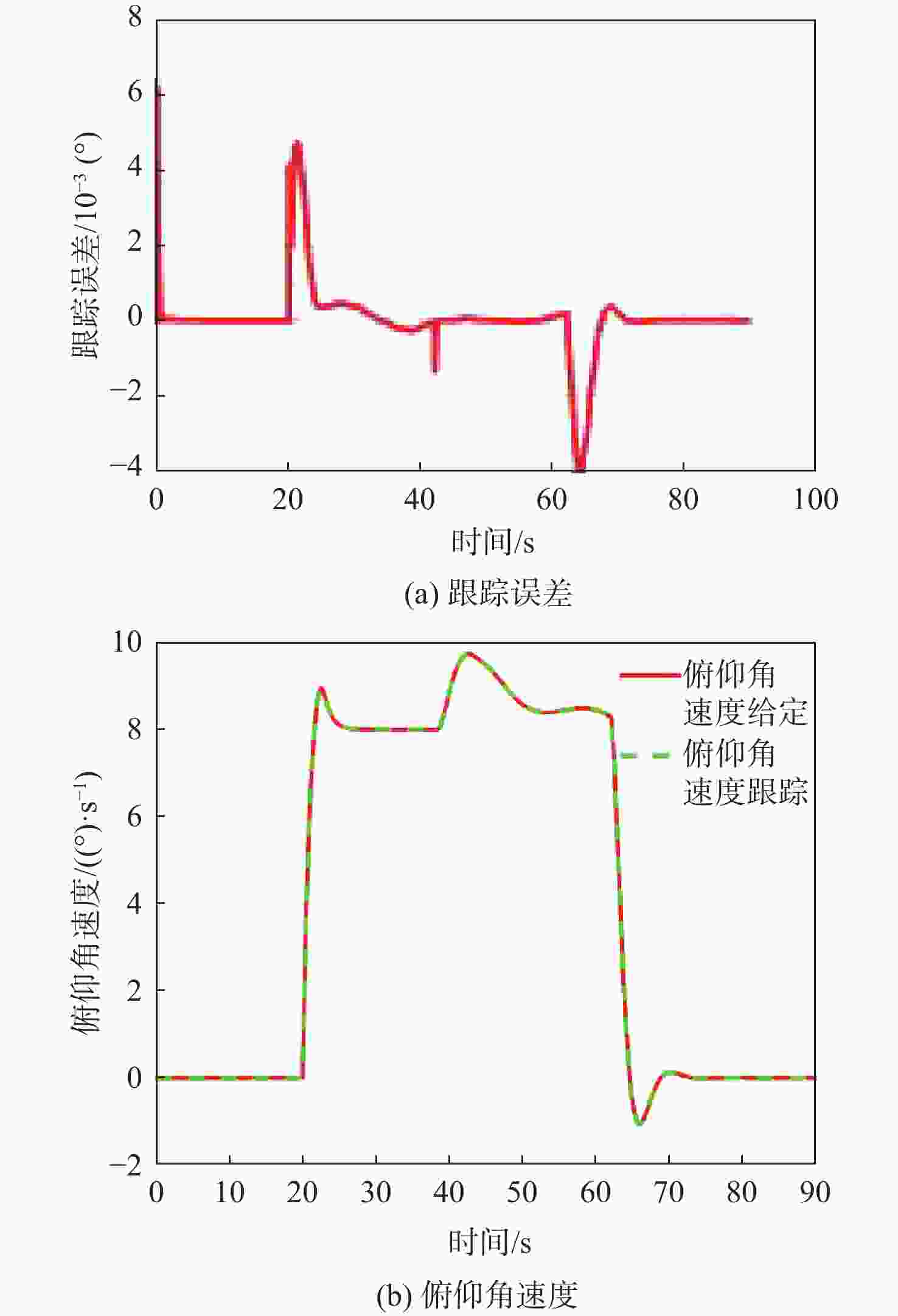
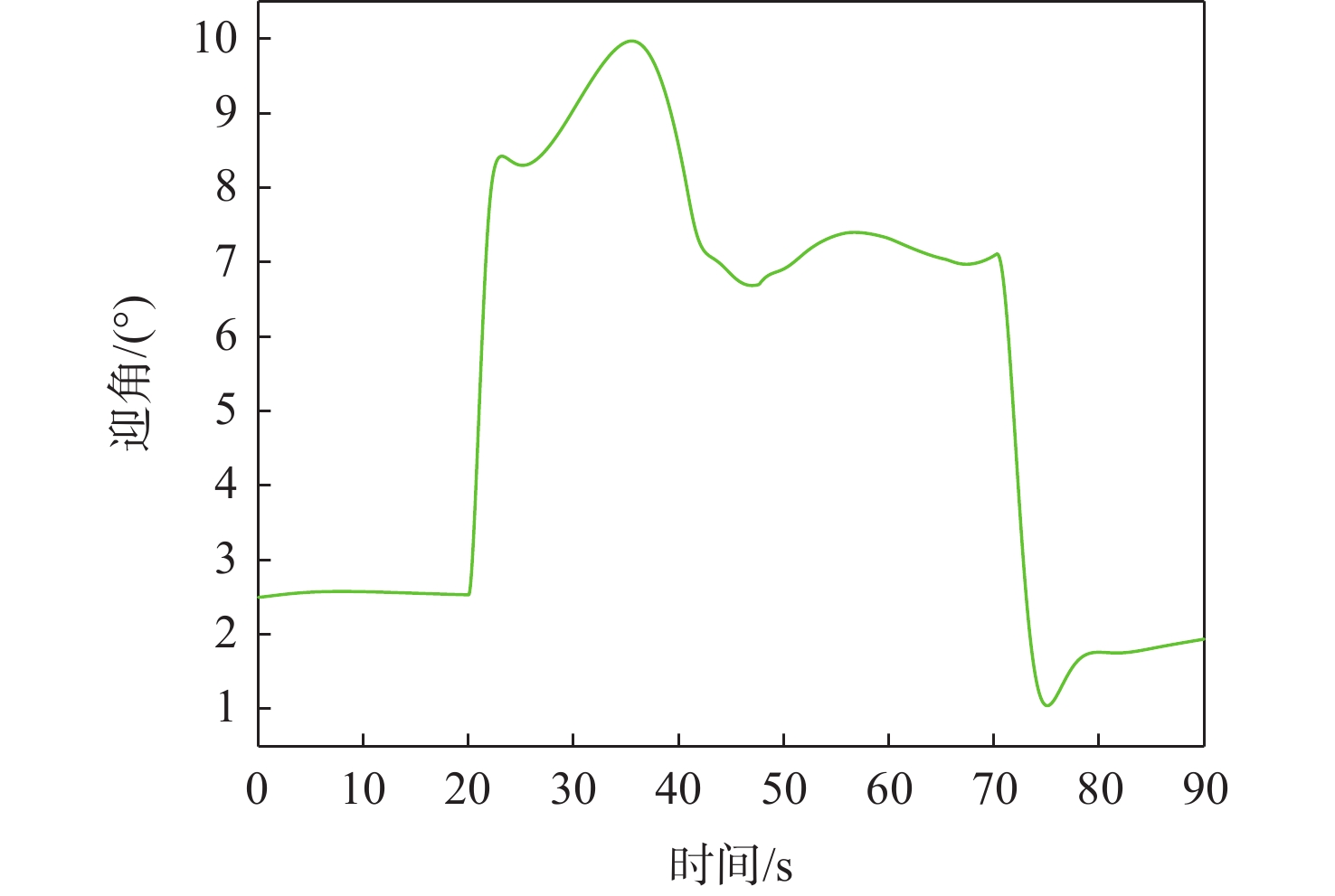
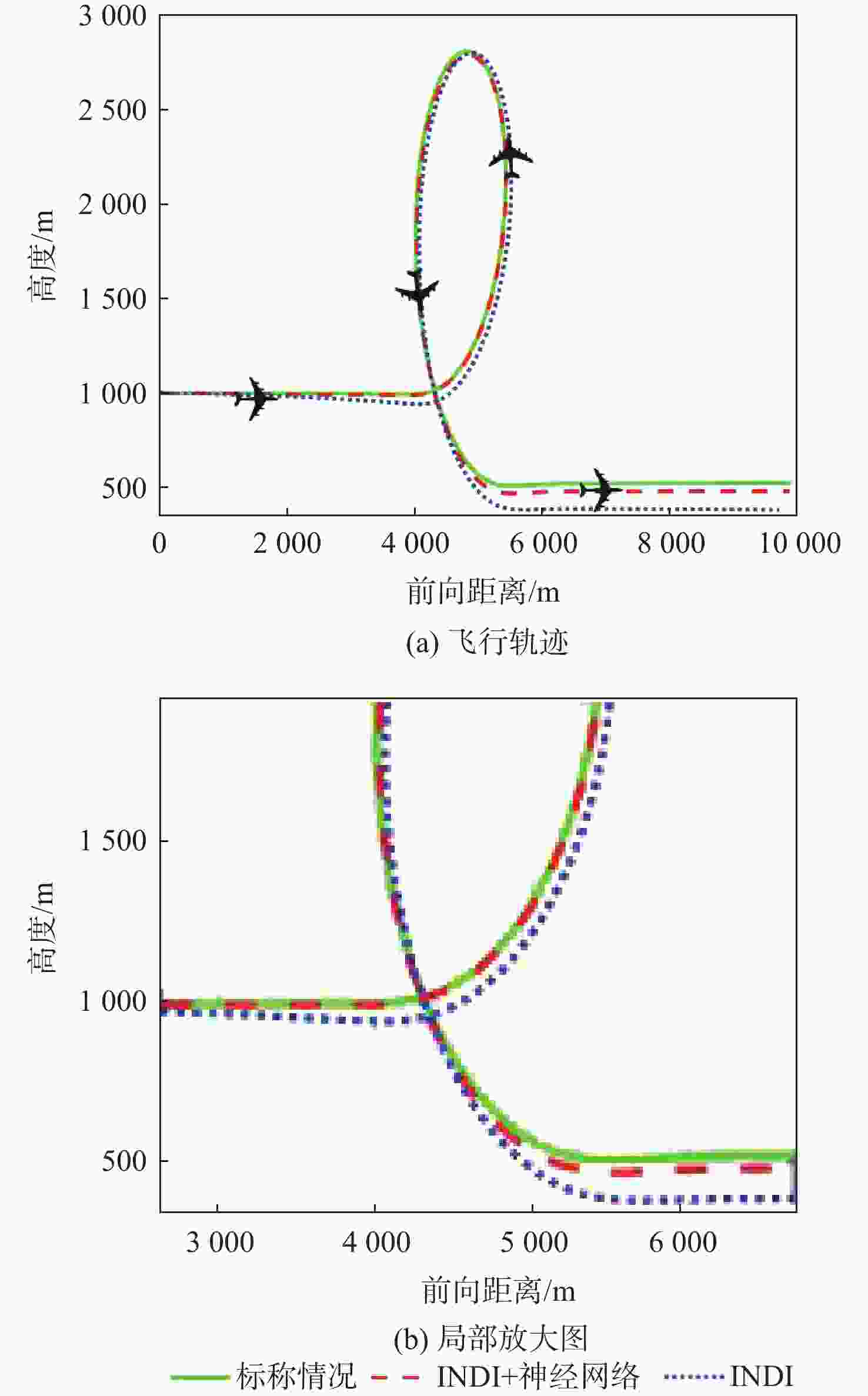
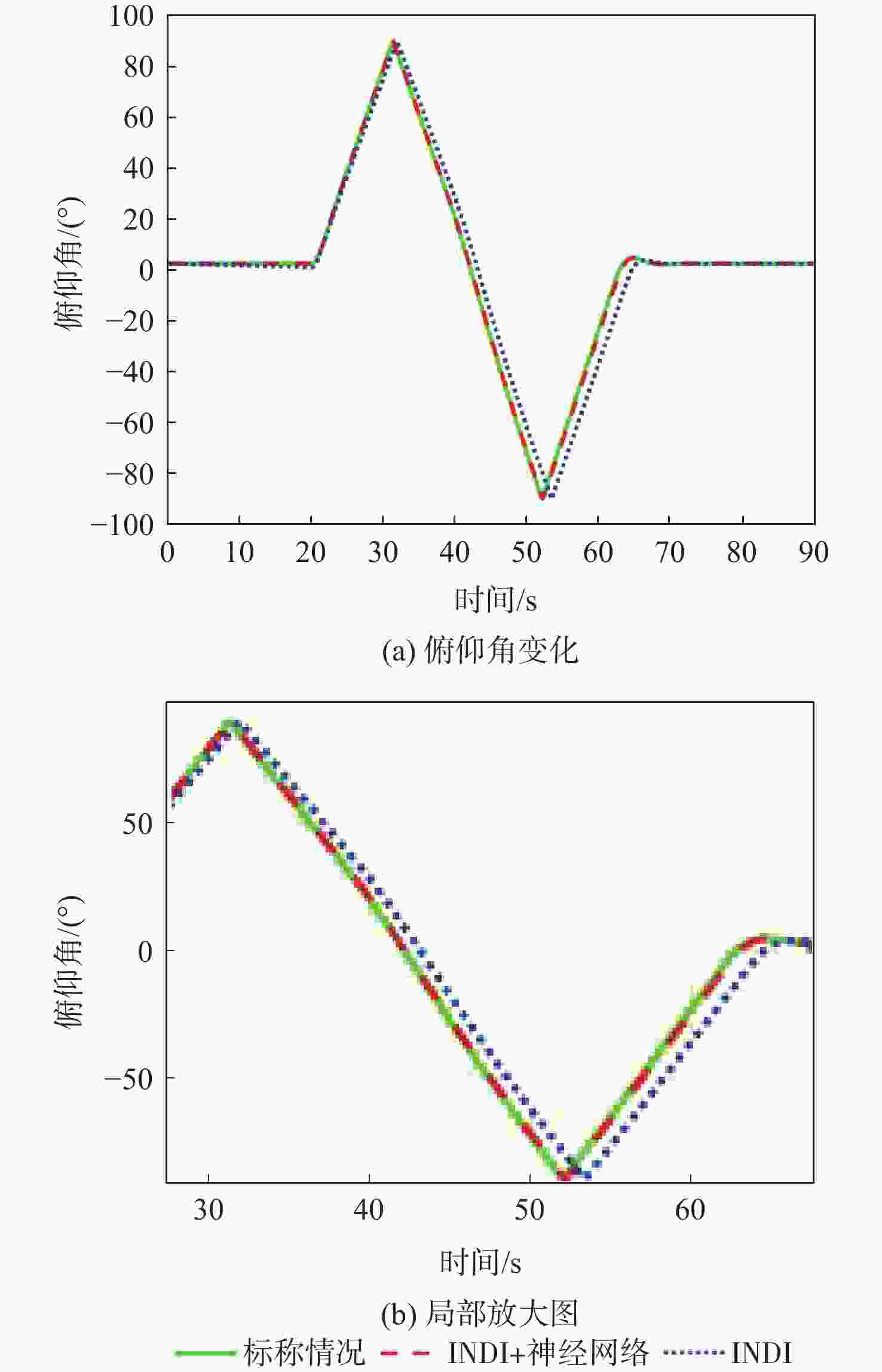
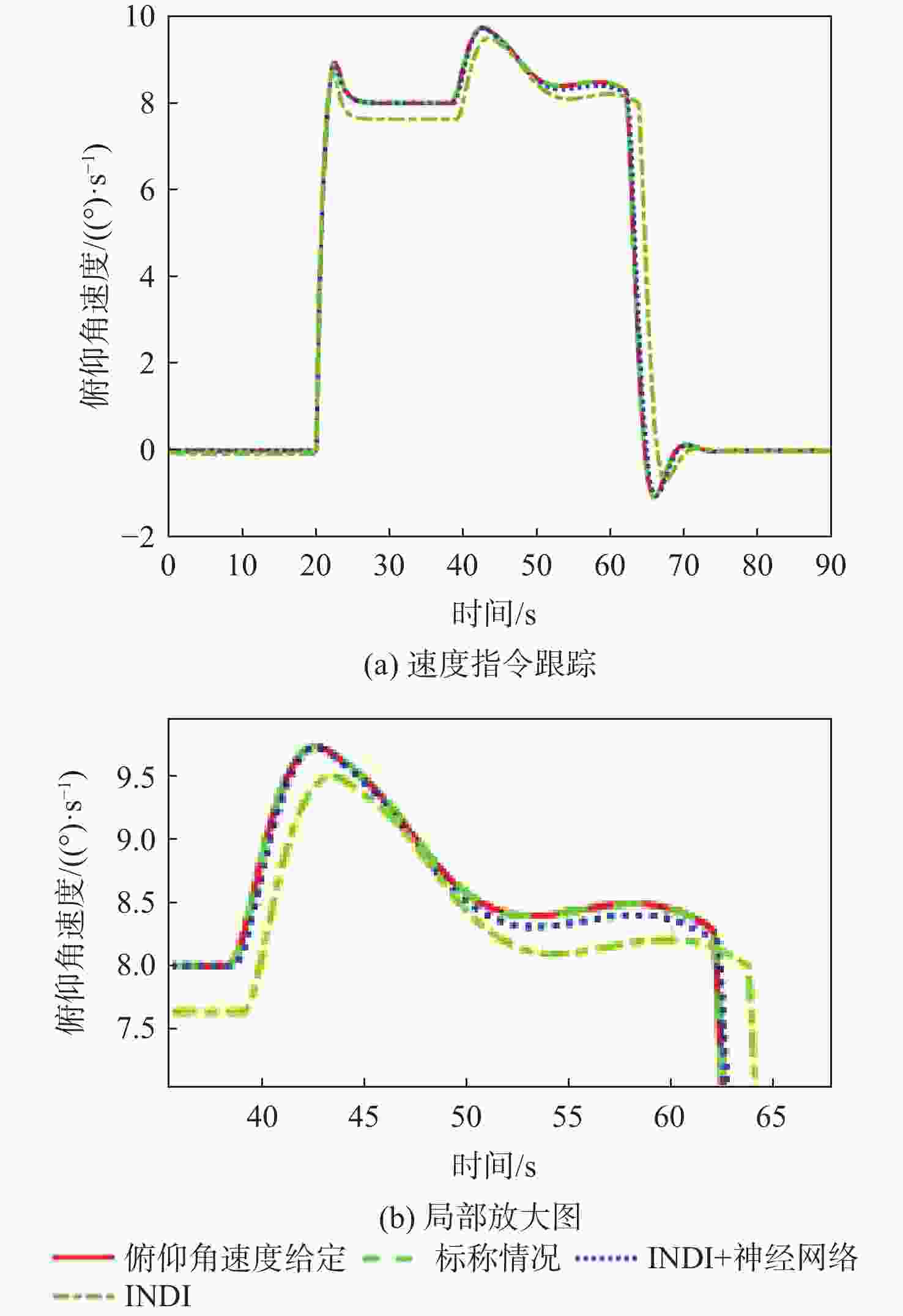
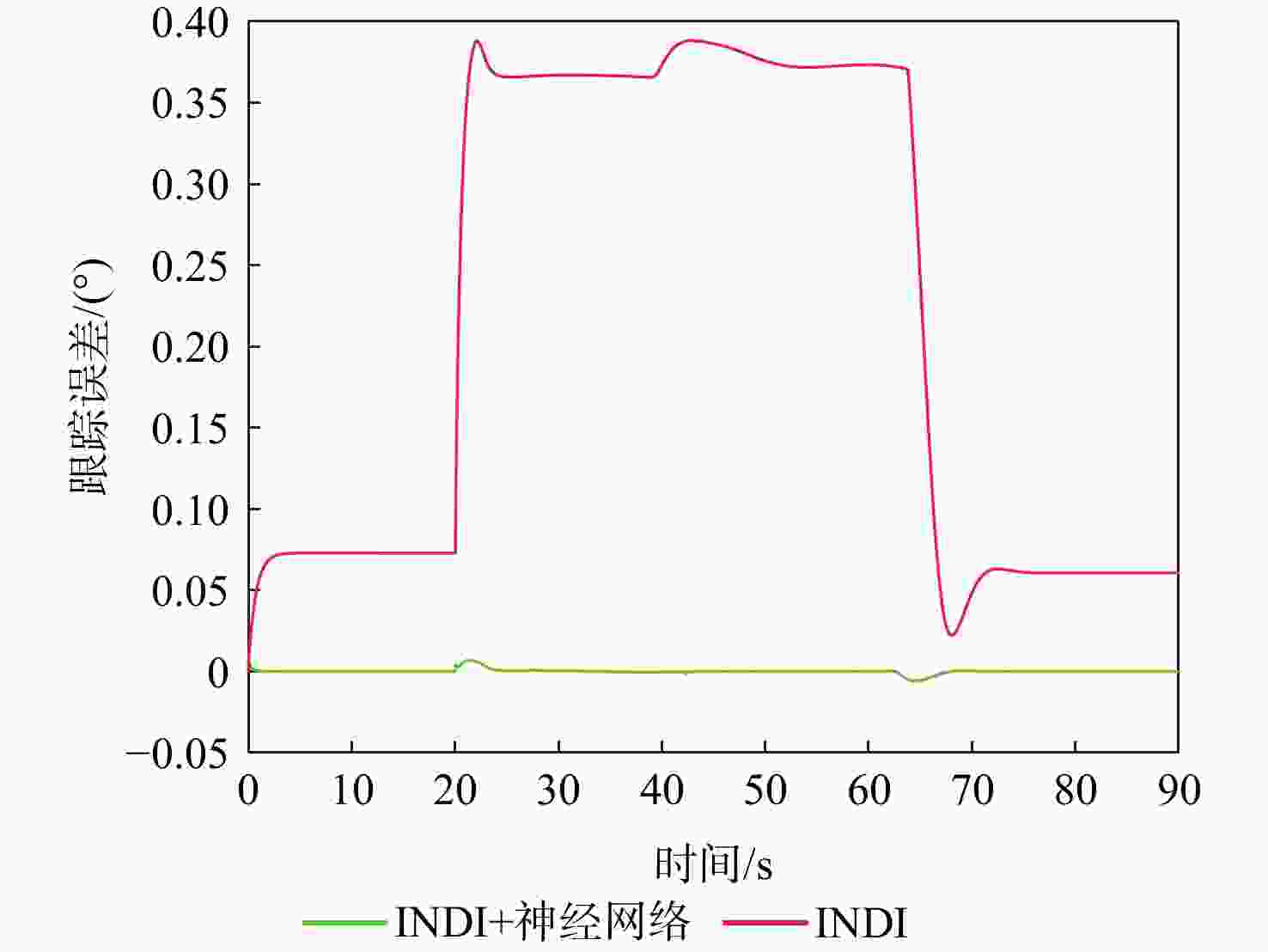
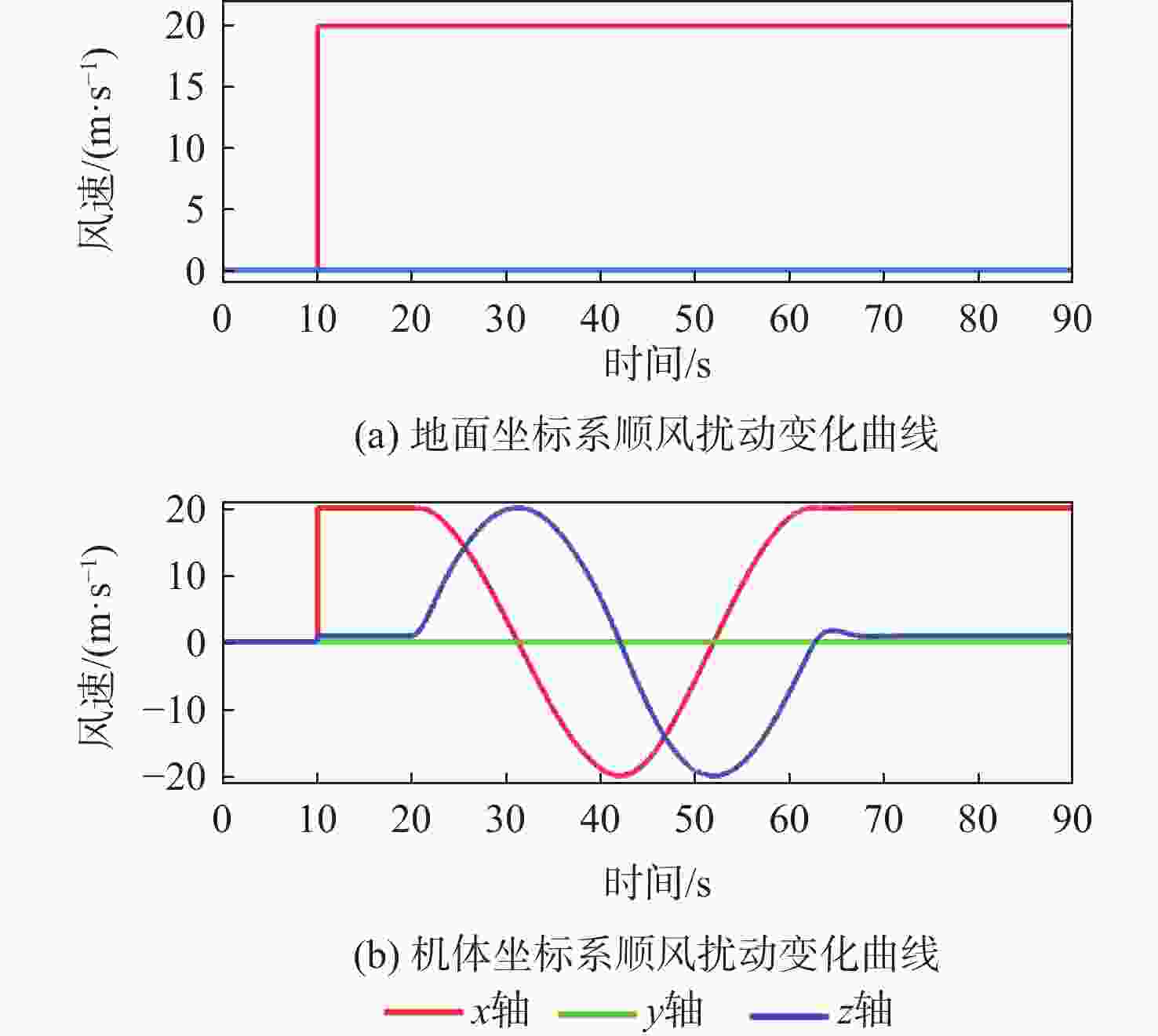
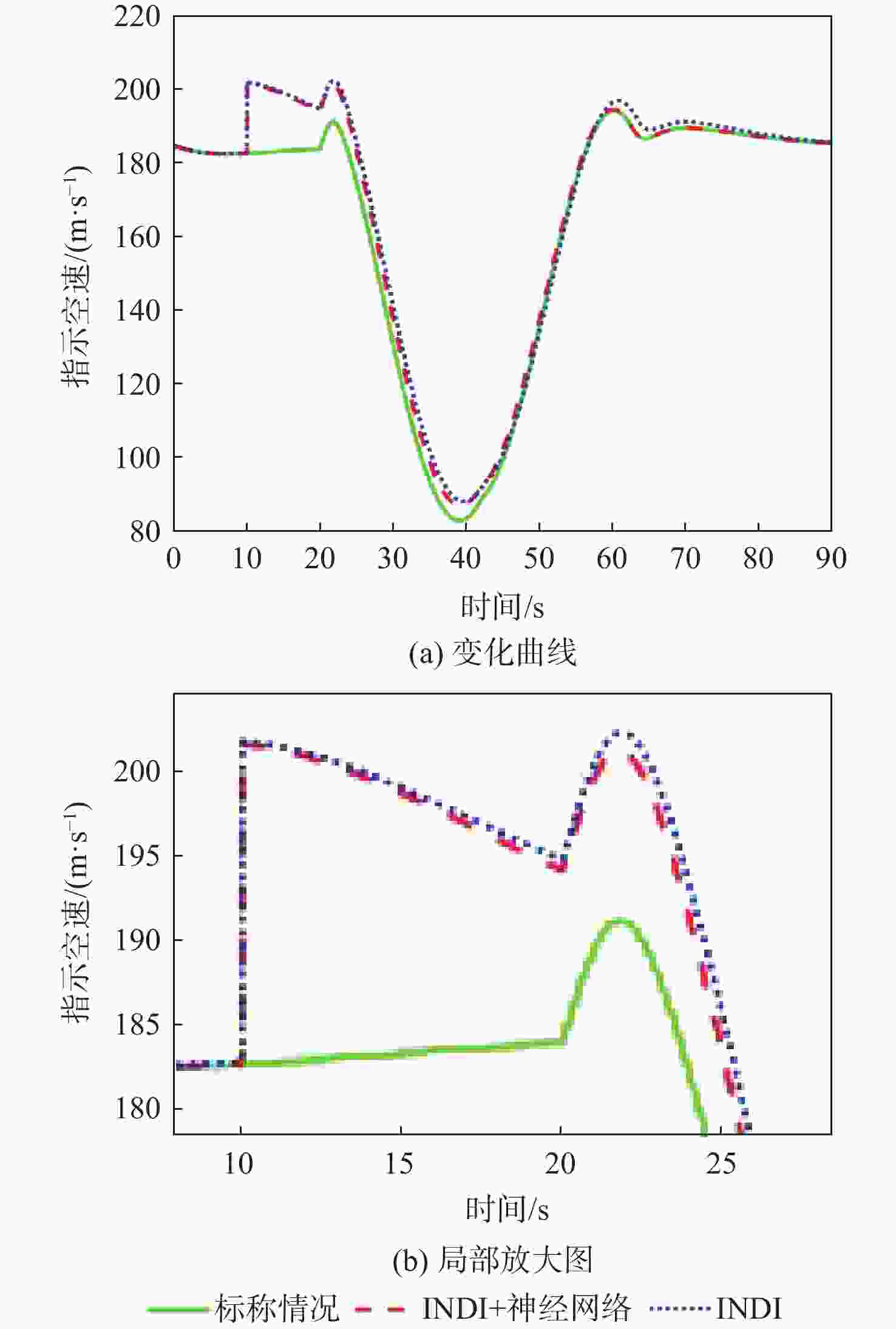
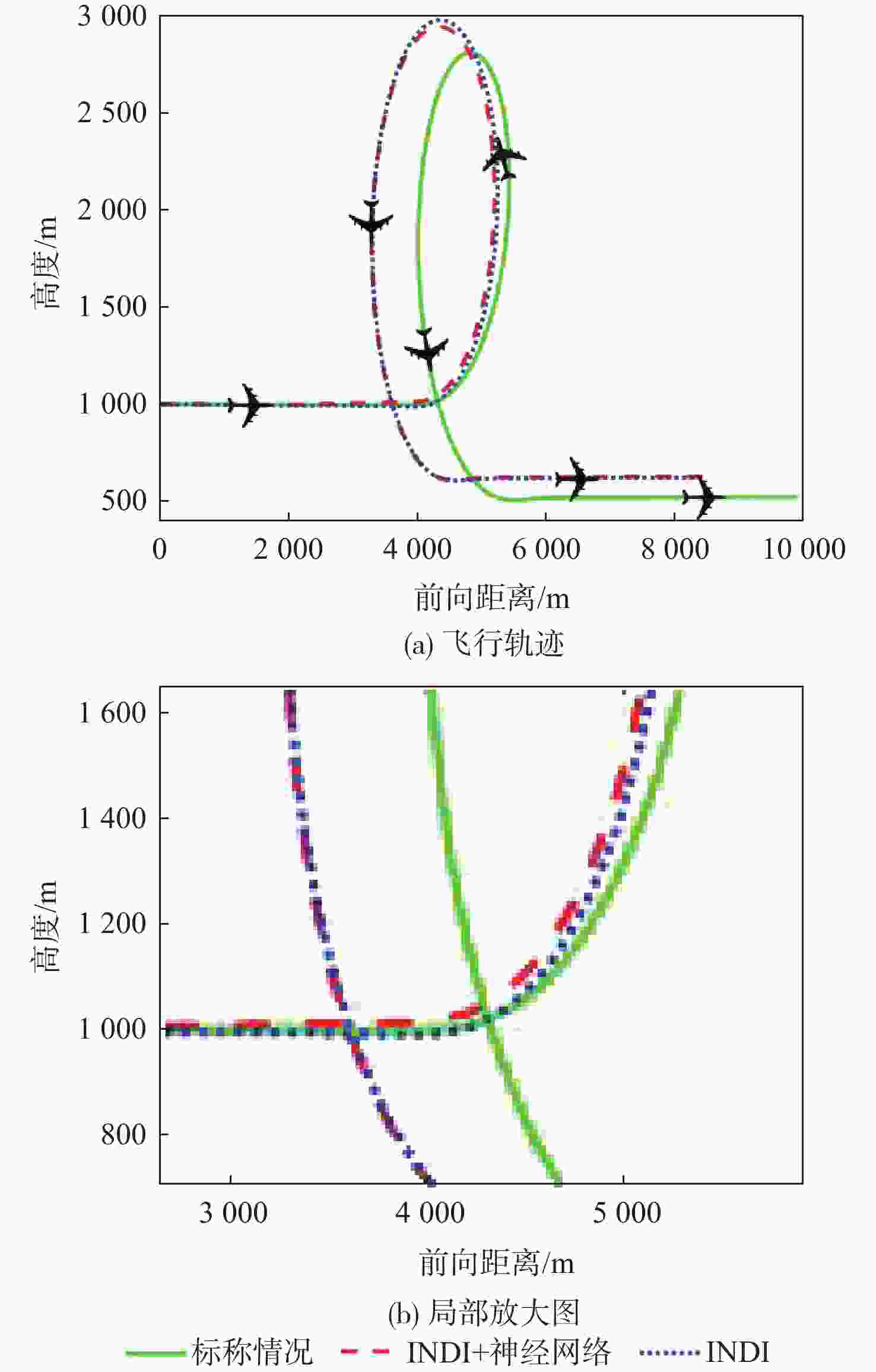
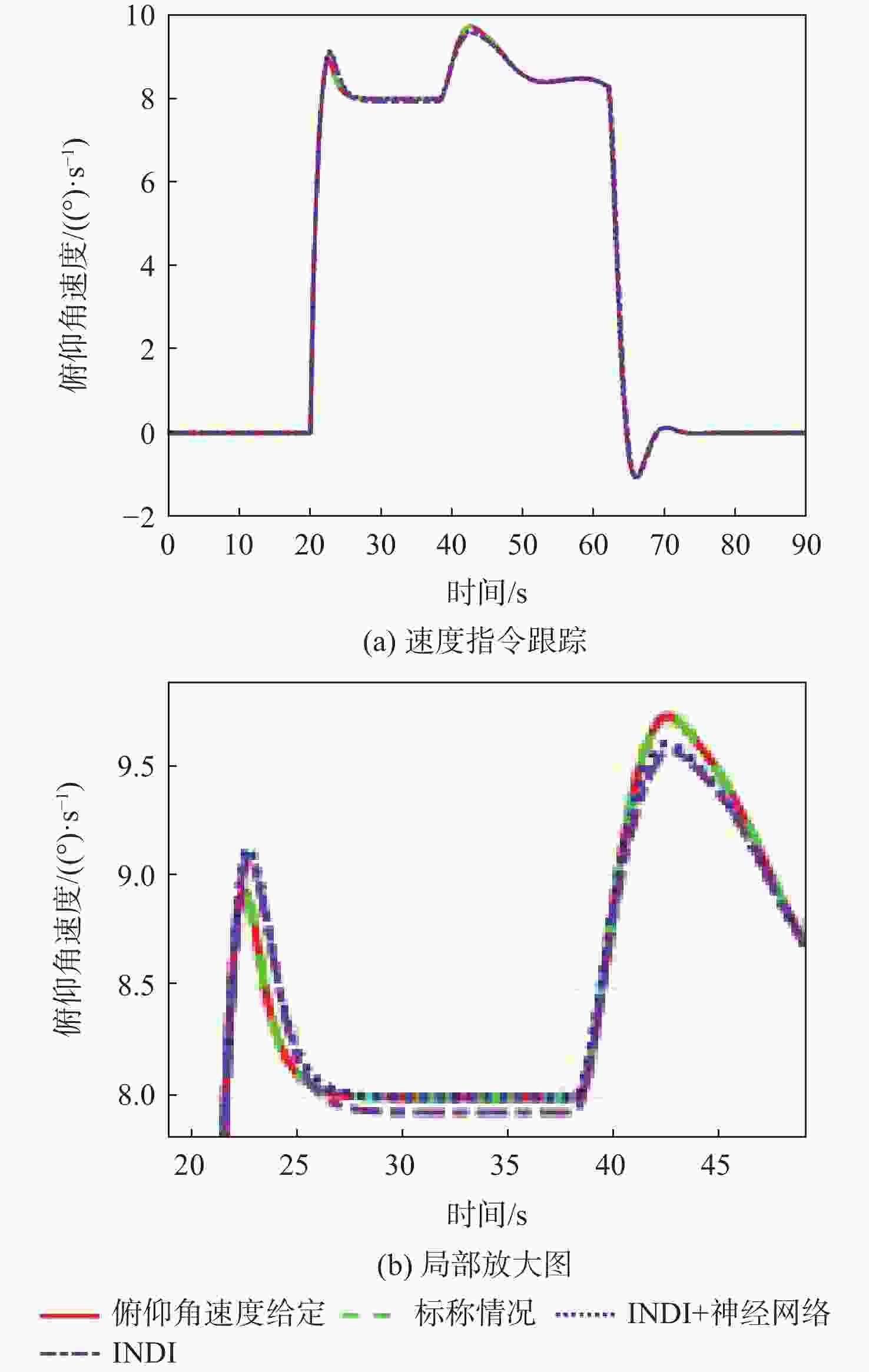
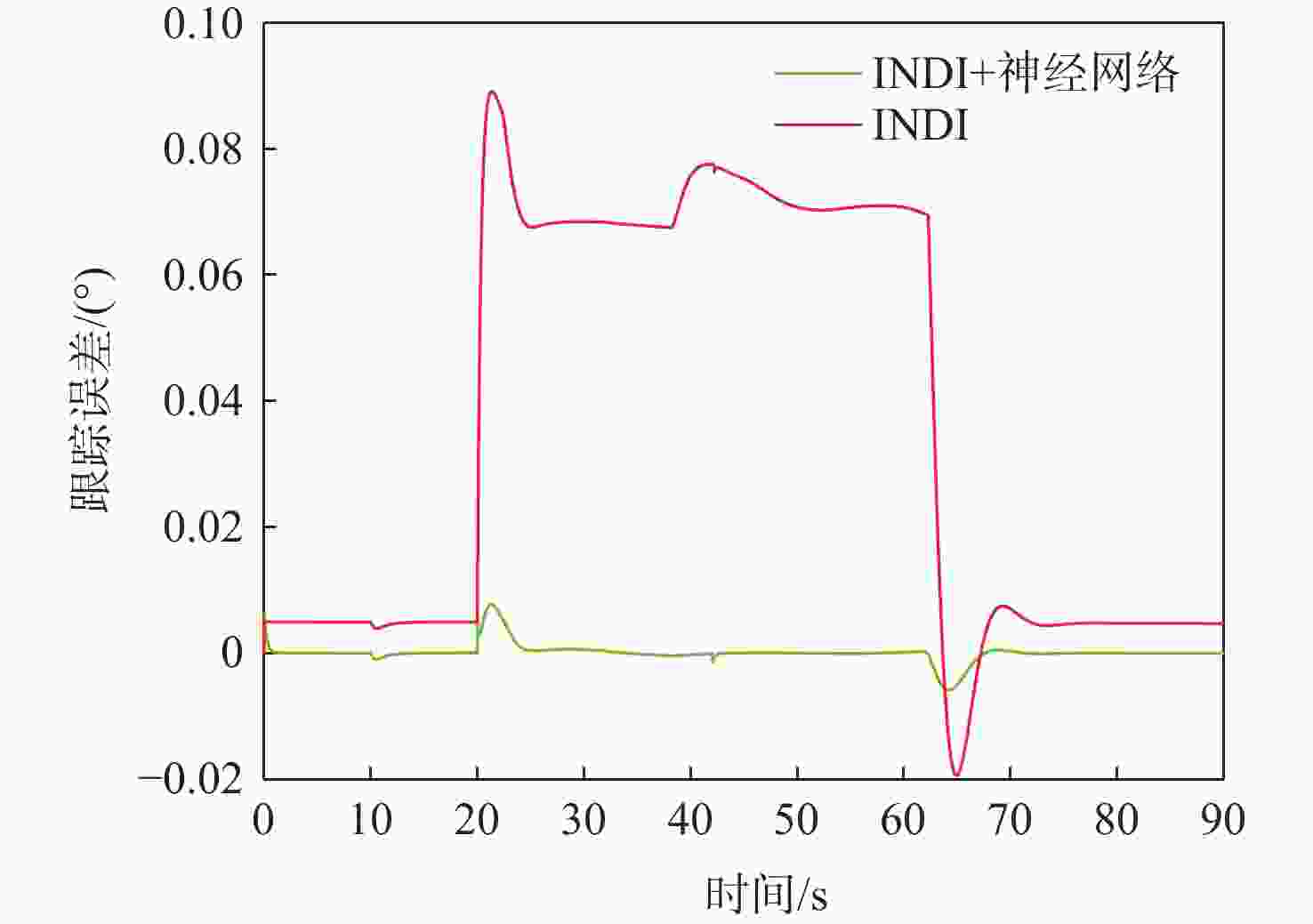
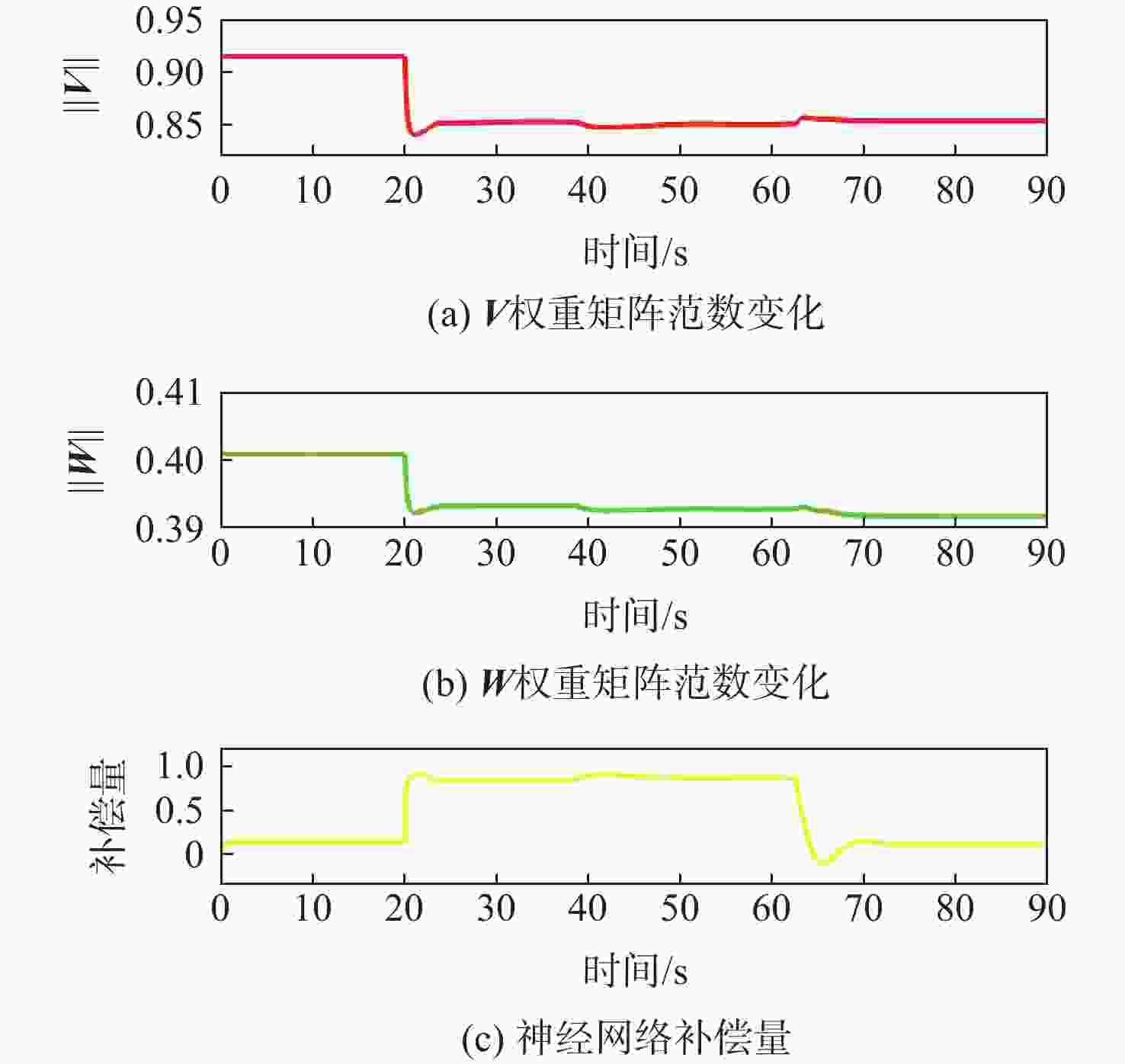
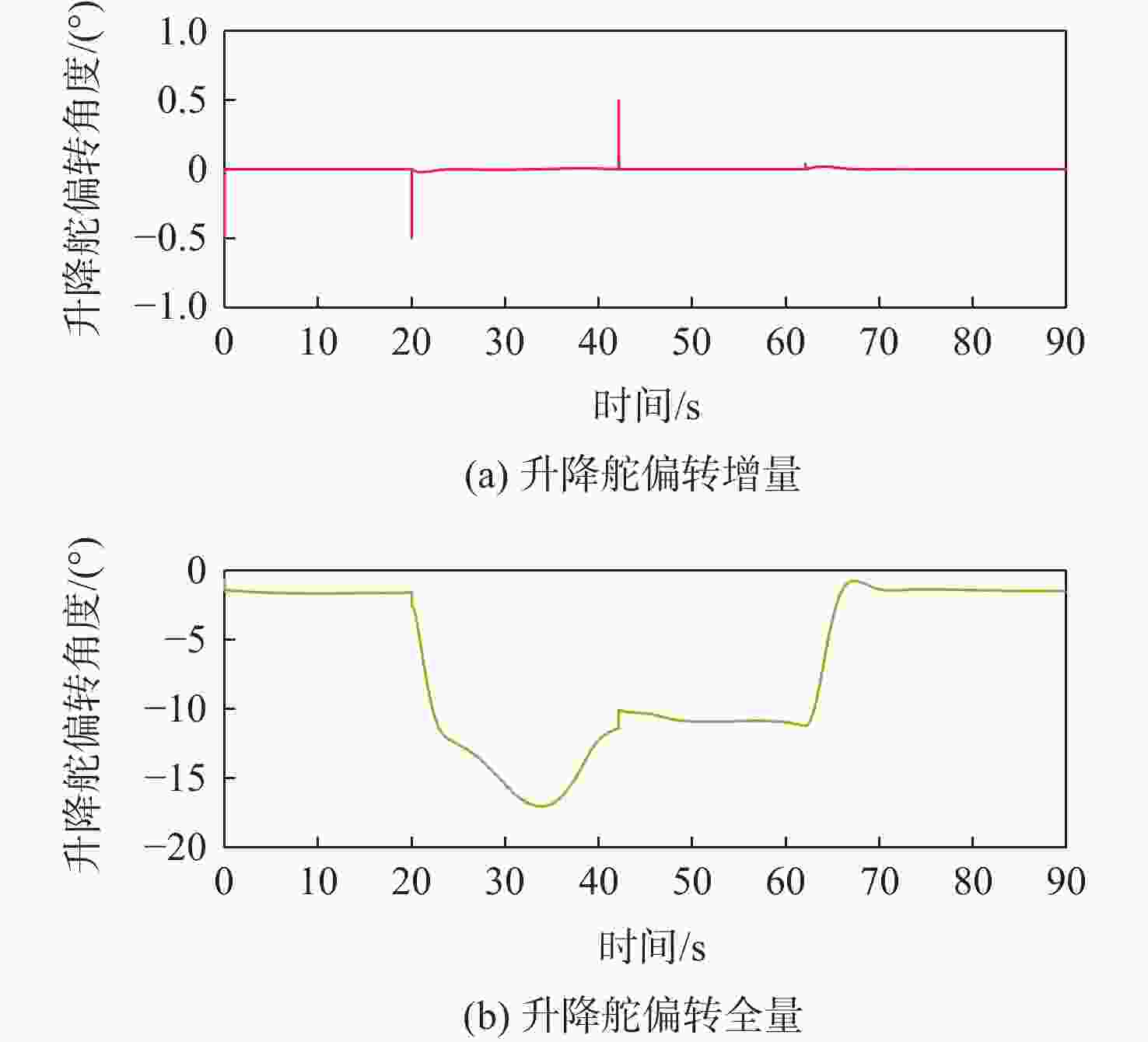
针对受外界未知气流扰动下的高速靶机在筋斗机动过程中易激发出强烈且时变的非线性气动特性问题,提出一种考虑执行器输入约束的神经网络增量非线性动态逆(INDI)控制器,通过反向传播(BP)神经网络在线补偿无人机筋斗机动飞行过程中的各种不确定扰动因素。建立基于INDI的无人机筋斗机动飞行控制框架;考虑INDI控制律抗扰动能力的不足,在该控制框架下引入神经网络在线补偿模型误差,并根据李雅普诺夫定理对系统稳定性进行分析,保证系统半全局一致且最终有界跟踪;提出一种增量式控制分配方法,以跟踪误差最小原则设计目标函数,求解满足执行器输入速率及饱和约束的舵面偏转角增量。仿真结果表明:所设计的神经网络INDI控制器可保证高速靶机在模型失配及外界扰动情况下仍快速准确地完成筋斗机动指令。
Abstract:A neural network incremental nonlinear dynamic inversion (INDI) controller accounting for the actuator input constraint is proposed to address the issue of the high-speed target drone’s propensity to produce strong and time-varying nonlinear aerodynamic characteristics during the somersault maneuver. This controller employs a back propagation (BP) neural network to compensate for a variety of uncertain disturbance factors during the UAV’s somersault maneuver flight. Firstly, the flight control framework of the UAV somersault maneuver based on INDI is established. Secondly, considering that the INDI control law has insufficient anti-disturbance ability, a neural network is introduced to compensate for the model error under the control framework, and the system stability is analyzed according to Lyapunov’s theorem to ensure the semi-global consistent final bounded tracking of the system. Then, an incremental control allocation method is proposed to design the objective function based on the principle of minimum tracking error to solve the rudder deflection angle increment satisfying the actuator input rate and saturation constraints. Lastly, the simulation results demonstrate that even in the event of model mismatch and external disturbance, the neural network incremental dynamic inversion controller can guarantee that the high-speed target drone can still execute the somersault maneuver command precisely and swiftly.
-
表 1 迎角安全边界
Table 1. Angle of attack safety boundary
$ \alpha _{\min }^0 $/(°) $ \alpha _{\min }^1 $/(°) $ \alpha _{\max }^0 $/(°) $ \alpha _{\max }^1 $/(°) 0 2 8 10 表 2 神经网络参数设计
Table 2. Neural network parameter design
参数 数值 输入层偏置$ {b_v} $ 0.1 隐藏层偏置$ {b_w} $ 0.1 鲁棒调整项增益$ {K_{\text{r}}} $ 1 权重矩阵最值$ {\bar {{Z}}} $ 1 自适应速率因子$ {\gamma _w} $ 200 自适应速率因子$ {\gamma _v} $ 90 阻尼因子$ \lambda $ 0.5 -
[1] 方斌, 许瑞, 高翔, 等. 靶机装备现状与发展需求[J]. 科技导报, 2020, 38(20): 50-56.FANG B, XU R, GAO X, et al. The current state and the development requirement of target drones[J]. Science & Technology Review, 2020, 38(20): 50-56(in Chinese). [2] 李雪兵, 李春涛, 坤娅. 鲁棒自适应控制的靶机蛇形机动控制律设计[J]. 电光与控制, 2018, 25(5): 56-63.LI X B, LI C T, KUN Y. Design of S maneuver control law for target drones based on robust adaptive control[J]. Electronics Optics & Control, 2018, 25(5): 56-63(in Chinese). [3] 依蔓, 宋磊. 藏在飞行表演中的“机动” 奥秘[J]. 知识就是力量, 2023(1): 44-45.YI M, SONG L. The mystery of “maneuver” hidden in air show[J]. Knowledge is Power, 2023(1): 44-45(in Chinese). [4] LOPEZ-SANCHEZ I, MORENO-VALENZUELA J. PID control of quadrotor UAVs: a survey[J]. Annual Reviews in Control, 2023, 56: 100900. doi: 10.1016/j.arcontrol.2023.100900 [5] KIMATHI S, LANTOS B. Modelling and attitude control of an agile fixed wing UAV based on nonlinear dynamic inversion[J]. Periodica Polytechnica Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, 2022, 66(3): 227-235. doi: 10.3311/PPee.20287 [6] XIAO L, ZHAO Z H, CAO D, et al. Composite nonlinear dynamic inversion control for quadrotor UAV with multi-source disturbances and actuator faults[C]//Proceedings of the 2022 41st Chinese Control Conference (CCC). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2022: 386-391. [7] PFEIFLE O, FICHTER W. Cascaded incremental nonlinear dynamic inversion for three-dimensional spline-tracking with wind compensation[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2021, 44(8): 1559-1571. doi: 10.2514/1.G005785 [8] LI Y, LIU X X, LU P, et al. Angular acceleration estimation-based incremental nonlinear dynamic inversion for robust flight control[J]. Control Engineering Practice, 2021, 117: 104938. doi: 10.1016/j.conengprac.2021.104938 [9] LU P, VAN KAMPEN E J, DE VISSER C, et al. Aircraft fault-tolerant trajectory control using incremental nonlinear dynamic inversion[J]. Control Engineering Practice, 2016, 57: 126-141. doi: 10.1016/j.conengprac.2016.09.010 [10] LOMBAERTS T, KANESHIGE J, SCHUET S, et al. Dynamic inversion based full envelope flight control for an eVTOL vehicle using a unified framework[C]//Proceedings of the AIAA Scitech 2020 Forum. Reston: AIAA, 2020: 1619. [11] YANG Z B, CHENG B, LV C X, et al. Fuzzy neural network dynamic inverse control strategy for quadrotor UAV based on atmospheric turbulence[J]. Applied Sciences, 2022, 12(23): 12232. [12] RAZMI H, AFSHINFAR S. Neural network-based adaptive sliding mode control design for position and attitude control of a quadrotor UAV[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2019, 91: 12-27. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2019.04.055 [13] ZHENG F Y, XIONG B W, ZHANG J Y, et al. Improved neural network adaptive control for compound helicopter with uncertain cross-coupling in multimodal maneuver[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2022, 108(4): 3505-3528. doi: 10.1007/s11071-022-07382-x [14] VAN OVEREEM S, WANG X R, VAN KAMPEN E J. Handling quality improvements for the flying-V aircraft using incremental nonlinear dynamic inversion[C]//Proceedings of the AIAA Scitech 2023 Forum. Reston: AIAA, 2023: 0105. [15] 张翾, 吴梅, 王宇航. 基于BP神经网络动态逆的纵列式直升机控制[J]. 飞行力学, 2021, 39(6): 36-41.ZHANG X, WU M, WANG Y H. Tandem helicopter control based on BP neural network dynamic inversion[J]. Flight Dynamics, 2021, 39(6): 36-41(in Chinese). [16] JOHNSON E, KANNAN S. Adaptive flight control for an autonomous unmanned helicopter[C]//Proceedings of the AIAA Guidance, Navigation, and Control Conference and Exhibit. Reston: AIAA, 2002: 4439. [17] 王嵘冰, 徐红艳, 李波, 等. BP神经网络隐含层节点数确定方法研究[J]. 计算机技术与发展, 2018, 28(4): 31-35.WANG R B, XU H Y, LI B, et al. Research on method of determining hidden layer nodes in BP neural network[J]. Computer Technology and Development, 2018, 28(4): 31-35(in Chinese). [18] CAO S, YU H C. An adaptive control framework for the autonomous aerobatic maneuvers of fixed-wing unmanned aerial vehicle[J]. Drones, 2022, 6(11): 316. doi: 10.3390/drones6110316 [19] RYSDYK R, CALISE A J. Robust nonlinear adaptive flight control for consistent handling qualities[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2005, 13(6): 896-910. doi: 10.1109/TCST.2005.854345 [20] MATAMOROS I, DE VISSER C C. Incremental nonlinear control allocation for a tailless aircraft with innovative control effectors[C]//Proceedings of the 2018 AIAA Guidance, Navigation, and Control Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2018: 1116. [21] YANG C, WANG M Y, WANG W D, et al. An efficient vehicle-following predictive energy management strategy for PHEV based on improved sequential quadratic programming algorithm[J]. Energy, 2021, 219: 119595. -







 下载:
下载: