Chaos ephemeran algorithm combining polynomial difference learning and dimensional variation
-
摘要:
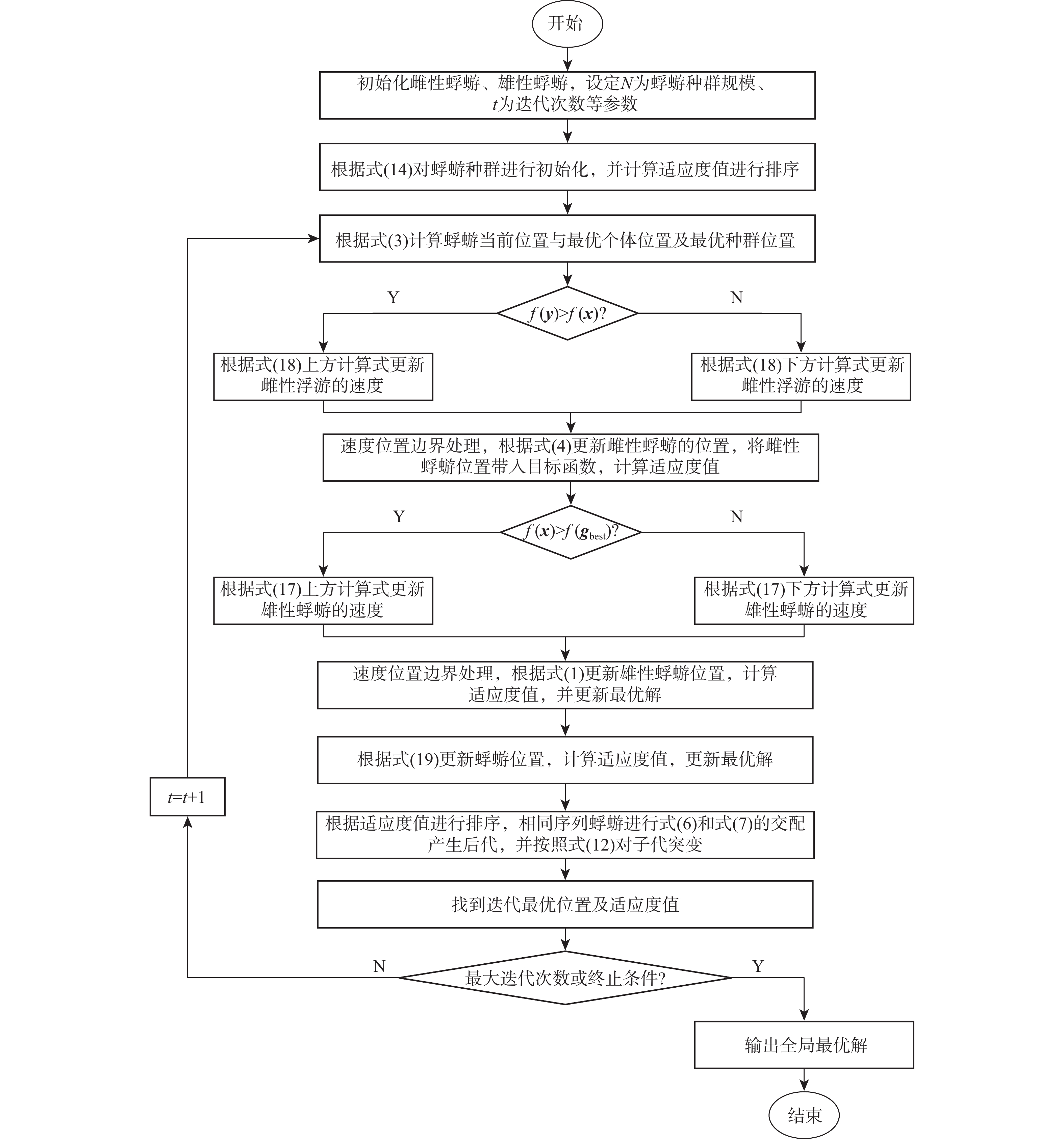
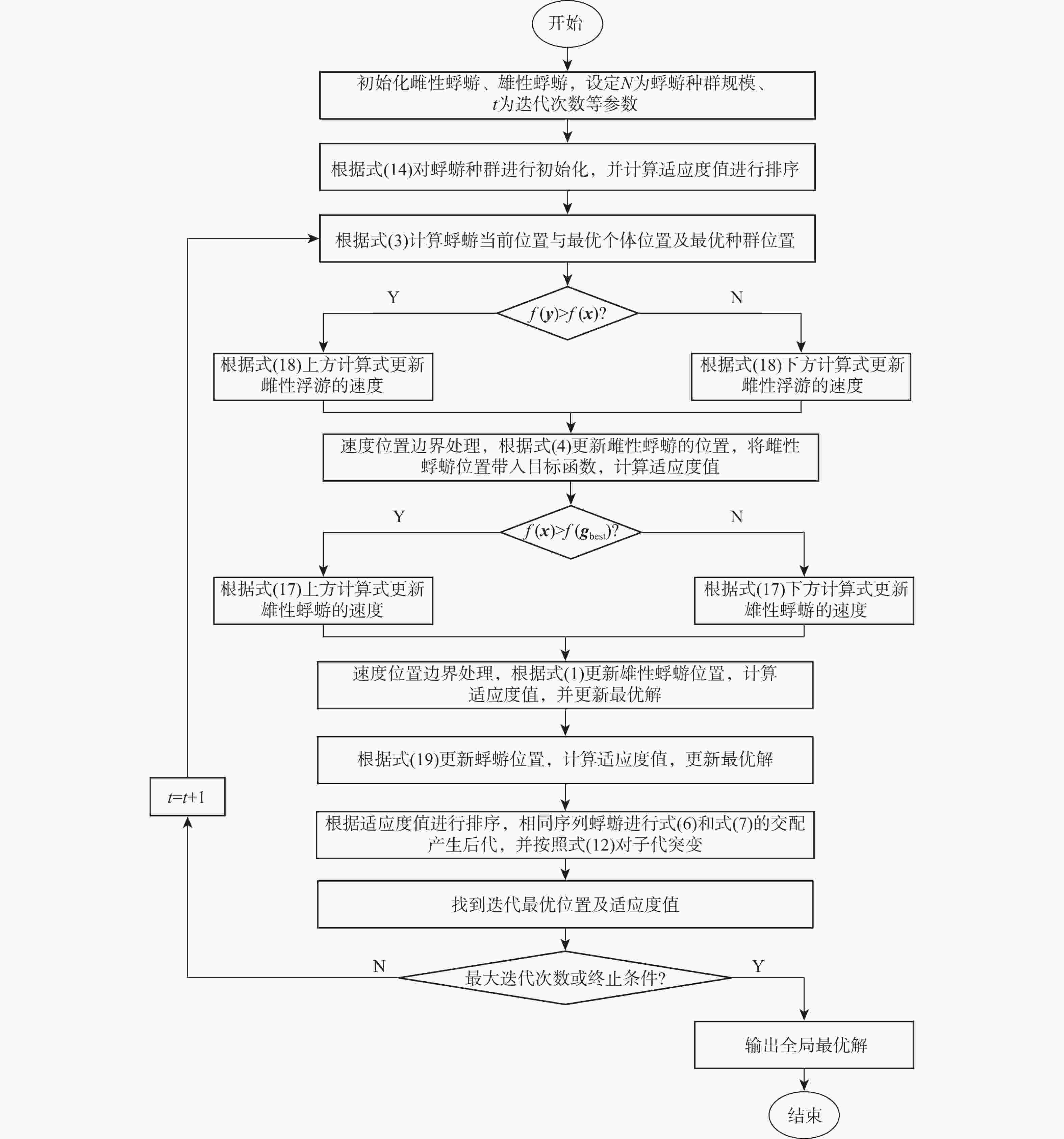
由于蜉蝣算法(MA)前期收敛速度缓慢,后期收敛精度也不高。基于此,将多项式差分学习和逐维变异相结合,构造一种融合多项式差分学习和逐维变异策略的混沌蜉蝣算法(LOPMA)。该算法提出改进Logistic混沌使初始解均匀分布,避免算法出现早熟现象;采用逐维变异策略,防止算法受不同维度之间影响陷入局部最优;采用多项式差分策略对蜉蝣算法进行改进,通过改善种群间信息交流来提升算法的寻优精度。并将3种改进策略分别引入仿真,进行消融实验对比分析,证明每种改进策略的有效性。在12个可变维度的基准测试函数上对LOPMA进行仿真对比分析,在CEC2017测试函数上将其他6种智能优化算法与较为新颖的其他策略改进的蜉蝣算法与LOPMA进行对比实验。结果表明:将多项式差分学习和逐维变异相结合,使LOPMA具有更好的稳定性、更快的收敛速度和更高的精度。
-
关键词:
- 蜉蝣算法 /
- 改进型Logistic混沌 /
- 逐维变异 /
- 多项式差分学习 /
- CEC2017测试函数
Abstract:Due to the slow convergence speed in the early stages and low convergence accuracy in the later stages of the Mayfly Algorithm (MA), a chaotic mayfly algorithm incorporating polynomial differential learning and dimension-wise mutation, named LOPMA, is proposed. This algorithm introduces an improved Logistic chaotic mapping to ensure uniform distribution of initial solutions, thereby avoiding premature convergence. A dimension-wise mutation strategy is adopted to prevent the algorithm from being trapped in local optima due to inter-dimensional interference. Furthermore, a polynomial differential learning strategy is integrated to enhance the information exchange among individuals, thereby improving the optimization precision. Each of the three improvement strategies was individually implemented and evaluated through ablation experiments to demonstrate their respective effectiveness. Comparative simulations of LOPMA were conducted on 12 benchmark functions with variable dimensions. On the CEC2017 test functions, LOPMA was compared with six other intelligent optimization algorithms as well as other recently proposed variants of mayfly algorithms. The results show that the combination of polynomial differential learning and dimension-wise mutation enables LOPMA to achieve better stability, faster convergence speed, and higher accuracy.
-
表 1 标准测试函数
Table 1. Standard test functions
函数 名称 取值范围 最优解 f1 Sphere [−100,100] 0 f2 Schwefel’s 2.22 [−10,10] 0 f3 Schwefel’s 1.2 [−100,100] 0 f4 Schwefel’s 2.21 [−100,100] 0 f5 Rosenbrock’s [−30,30] 0 f6 Step [−100,100] 0 f7 Quartic [−1.28,1.28] 0 f8 Rastrigin’s [−5.12,5.12] 0 f9 Ackely ’s [−32,32] 0 f10 Griewank’s [−600,600] 0 f11 P enalized 1 [−50,50] 0 f12 Penalized 2 [−50,50] 0 表 2 部分CEC2017测试函数
Table 2. Part of CEC2017 test functions
函数 特征 取值范围 最优解 CEC03 UN [−100,100] 300 CEC06 MN [−100,100] 600 CEC09 MN [−100,100] 900 CEC12 HF [−100,100] 1200 CEC15 HF [−100,100] 1500 CEC18 HF [−100,100] 1800 CEC21 CF [−100,100] 2100 CEC24 CF [−100,100] 2400 CEC27 CF [−100,100] 2700 表 3 消融实验在基准函数下的对比分析
Table 3. Comparative analysis of ablation experiments under reference function
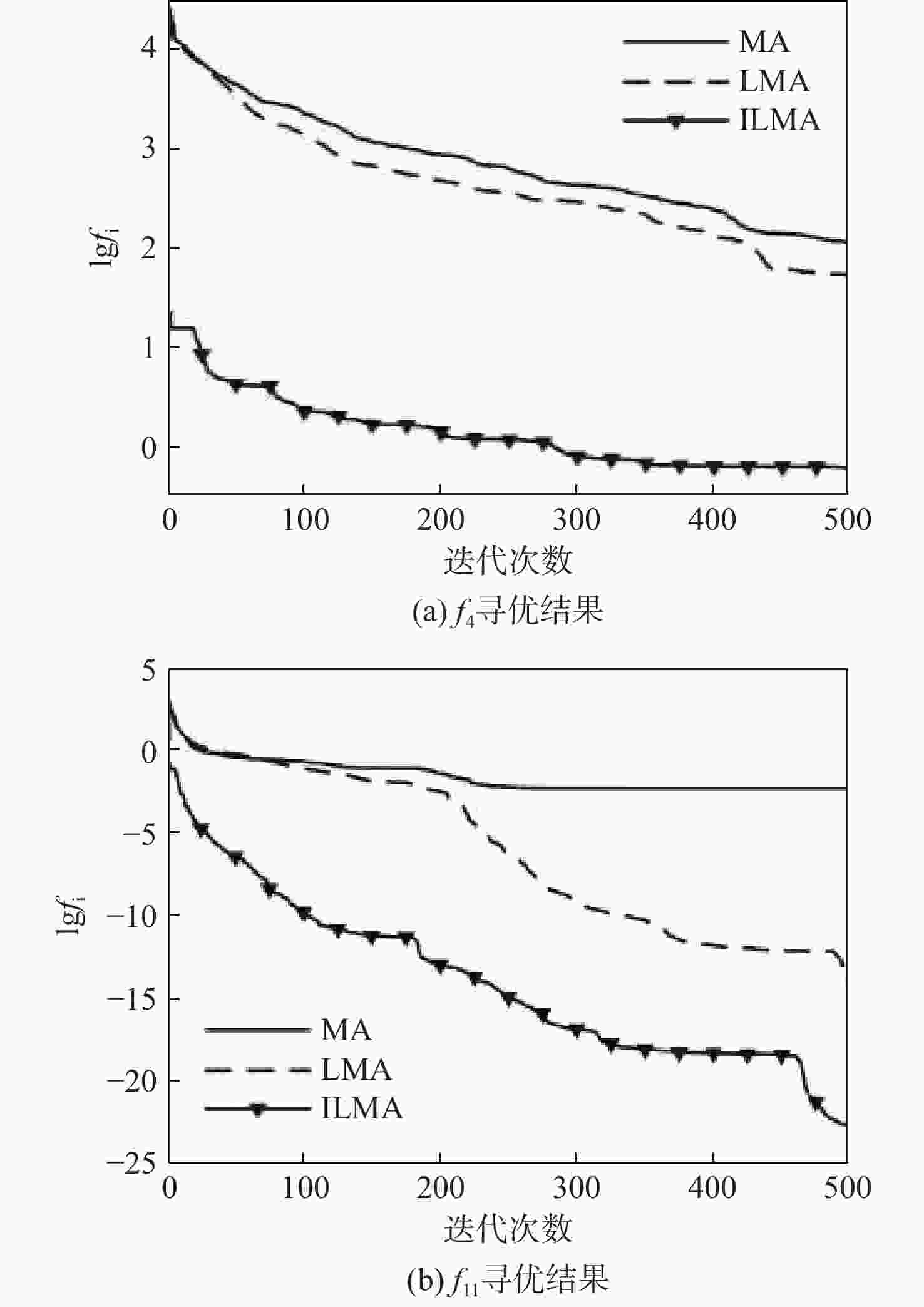
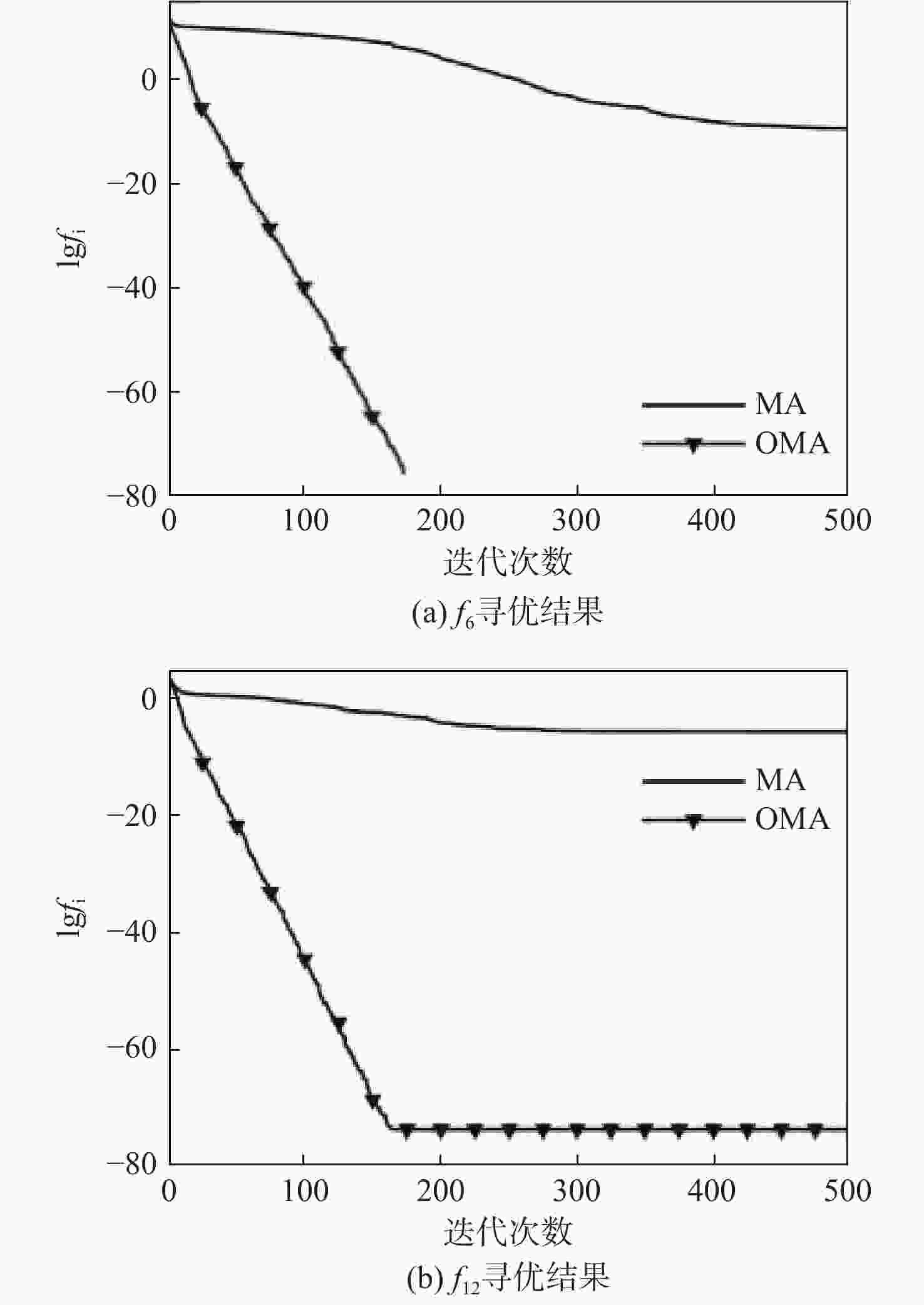
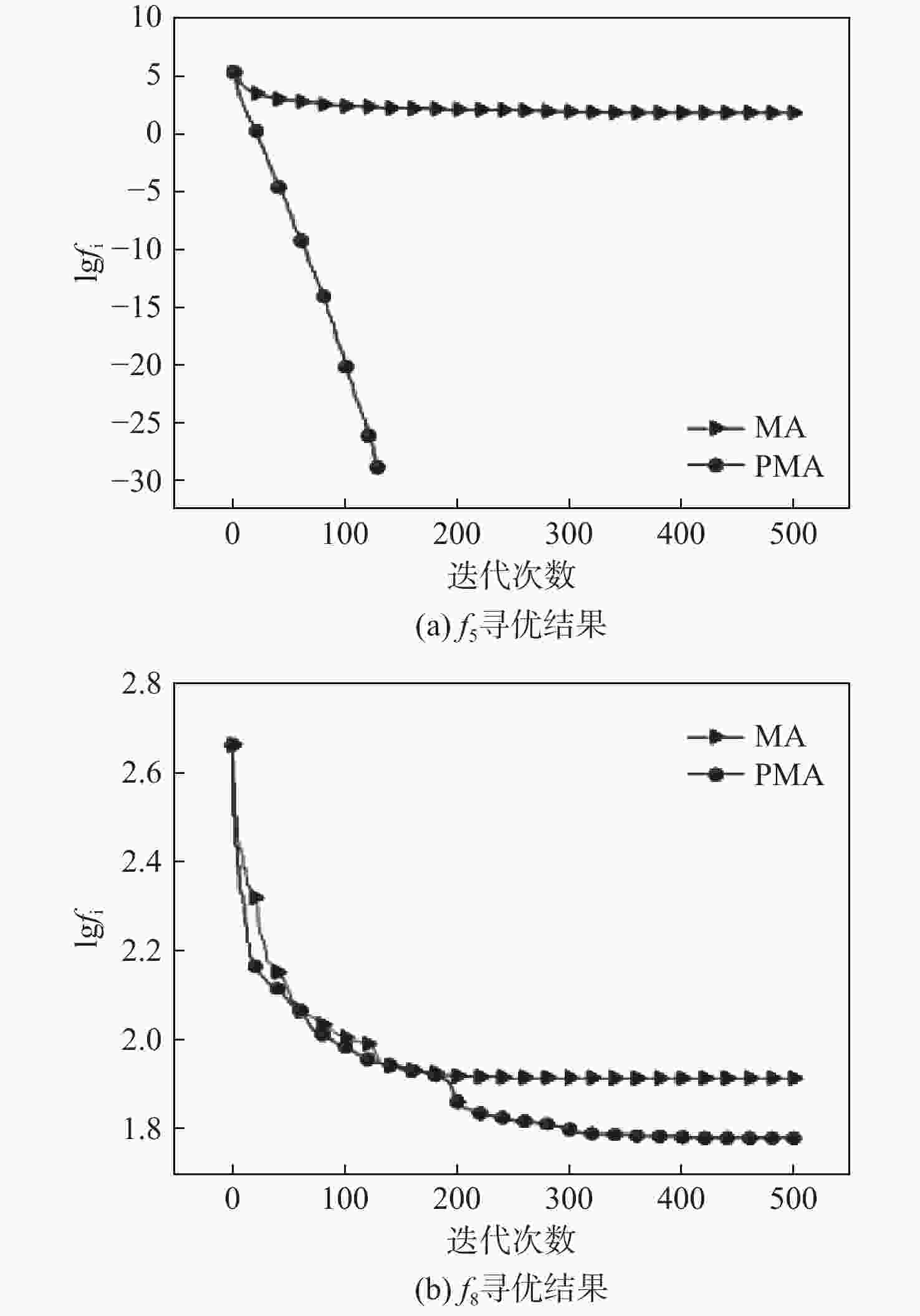
函数 算法 平均值 标准差 d'=10 d'=50 d'=100 d'=10 d'=50 d'=100 f1 MA 2.58×10−35 2.58×10−35 1.38×102 1.12×10−32 1.12×10−34 1.53×102 ILMA 1.08×10−36 1.07×10−66 8.42×10−50 4.65×10−35 2.46×10−66 1.95×10−49 OMA 6.55×10−74 6.55×10−74 4.43×10−50 3.57×10−73 3.57×10−73 5.59×10−50 PMA 1.61×10−140 1.37×10−127 3.26×10−127 6.30×10−140 6.80×10−127 1.49×10−126 LOPMA 3.99×10−141 9.76×10−128 2.28×10−127 1.31×10−140 1.88×10−127 6.27×10−127 f3 MA 4.38×10−13 4.38×10−13 2.51×104 9.97×10−13 9097×10−13 8.20×103 ILMA 7.36×10−14 1.08×10−61 2.64×10−44 3.78×10−14 2.74×10−61 1.41×10−43 OMA 1.12×10−62 3.84×10−26 2.44×10−45 4.05×10−62 1.19×10−25 4.72×10−45 PMA 9.47×10−142 4.86×10−131 3.25×10−130 4.71×10−141 1.53×10−130 1.28×10−129 LOPMA 1.25×10−140 3.43×10−131 3.74×10−131 4.78×10−140 1.13×10−130 1.95×10−130 f4 MA 3.50×10−4 1.79×101 2.98×101 5.91×10−4 4.75 3.96 ILMA 1.00×10−6 3.81×10−26 7.29×10−26 1.20×10−6 8.89×10−26 1.07×10−25 OMA 9.32×10−33 3.84×10−26 5.81×10−26 3.96×10−32 1.19×10−25 9.53×10−26 PMA 1.17×10−71 9.35×10−67 3.20×10−65 2.50×10−71 1.76×10−66 1.27×10−64 LOPMA 9.03×10−74 4.85×10−68 6.82×10−66 3.47×10−73 1.25×10−67 1.64×10−65 f6 MA 1.66×10−30 2.79×10−2 1.36×102 6.85×10−30 5.17×10−2 4.54×102 ILMA 1.08×10−31 1.03×10−34 2.05×10−34 4.65×10−32 5.63×10−34 7.81×10−34 OMA 0 3.08×10−34 1.03×10−34 0 9.40×10−34 5.63×10−34 PMA 0 0 0 0 0 0 LOPMA 0 0 0 0 0 0 f8 MA 3.16 6.32×101 1.54×102 2.83 1.65×101 3.71×101 ILMA 4.90×10−1 5.17×101 1.10×102 1.80 1.64×101 2.83×101 OMA 7.31×10−1 1.03×101 5.61×101 1.01 4.25 1.38×101 PMA 5.42 5.06×101 9.51×101 2.08 1.78×101 2.45×101 LOPMA 6.63×10−1 8.71 4.63×101 1.12×10−1 3.17 8.60 f11 MA 2.07×10−2 5.92×10−2 1.92×10−1 7.89×10−2 1.01×10−1 1.71×10−1 ILMA 1.04×10−2 4.20×10−3 1.00×10−3 5.68×10−2 1.58×10−2 5.70×10−3 OMA 5.45×10−16 4.10×10−3 4.71×10−33 2.98×10−15 1.58×10−2 7.38×10−36 PMA 2.07×10−2 2.10×10−3 4.71×10−33 7.89×10−2 1.14×10−2 1.39×10−48 LOPMA 1.04×10−2 1.70×10−3 3.67×10−33 5.68×10−2 1.17×10−3 1.25×10−49 表 4 算法参数设置
Table 4. Algorithm parameter settings
算法 参数设置 LOPMA $ \begin{aligned}& a_1=1, a_2=1.5, \beta=2, f_{\rm{l}}=1 \\& d_{\text{damp}}=0.8, f_{\text{damp}}^{{\rm{l}}}=0.99, d'=5\end{aligned} $ WOA $ a_{\max }=2, a_{\min }=0 $ GA $ p_{1}=0.9, p_{2}=0.1 $ GWO $ a_{\max }=2, a_{\min }=0, r_{1}, r_{2} \in[0,1] $ PSO $ \omega=0.9, c_{1}=c_{2}=1.5 $ 表 5 标准测试函数寻优结果
Table 5. Optimization results of standard test functions
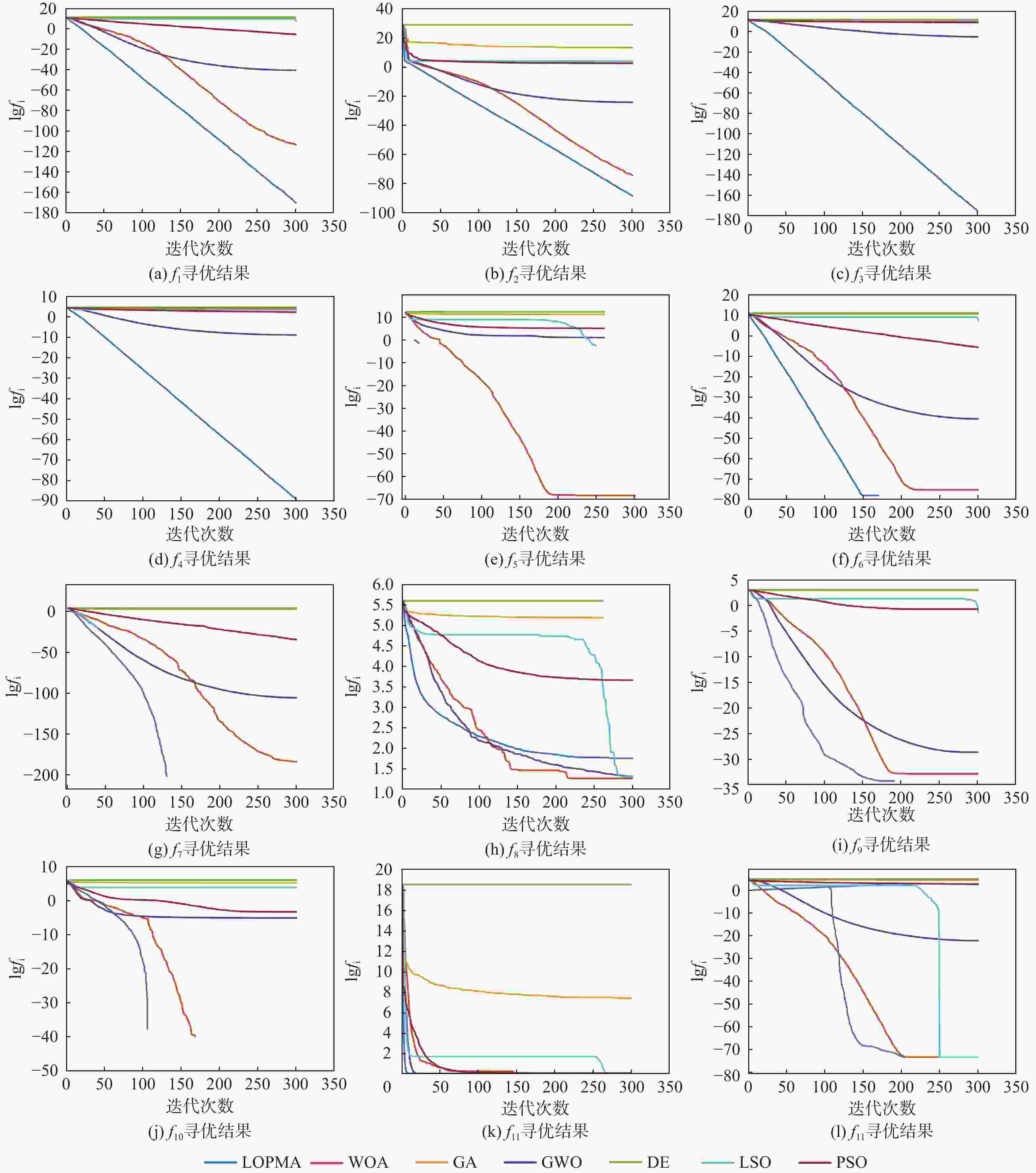
函数 算法 最优值 平均值 标准差 函数 算法 最优值 平均值 标准差 f1 LOPMA 2.80×10−205 2.33×10−169 0 f7 LOPMA 0 0 0 WOA 7.50×10−78 3.19×10−69 1.51×10−68 WOA 2.20×10−123 9.30×10−97 5.09×10−96 GA 4.36×104 3.88×104 4.75×103 GA 4.86×101 4.20×101 8.36 GWO 2.90×10−25 1.99×10−25 2.72×10−25 GWO 2.63×10−46 4.43×10−47 1.28×10−46 DE 7.07×104 6.31×104 7.54×103 DE 4.51×101 4.04×101 8.96 LSO 2.27×103 9.34×102 1.10×103 LSO 0 7.58×10−16 2.21×10−15 PSO 1.43×10−3 4.59×10−4 8.16×10−4 PSO 2.68 2.06 3.50 f2 LOPMA 6.86×10−96 6.75×10−88 3.68×10−87 f8 LOPMA 0 0 0 WOA 9.12×10−52 4.41×10−49 2..04×10−48 WOA 0 7.49 4.10×101 GA 4.01×105 5.21×106 1.24×107 GA 3.56×102 3.31×10−2 2.34×101 GWO 7.20×10−16 1.14×10−15 7.02×10−16 GWO 2.84×10−13 3.42 5.18 DE 6.59×1012 1.69×1012 3.63×1012 DE 2.90×102 2.70×102 1.62×101 LSO 4.28×101 2.86×101 1.95×101 LSO 2.85 3.69 2.02×101 PSO 1.99×101 9.66 8.71 PSO 7.77×101 9.97×101 3.07×101 f3 LOPMA 2.49×10−198 1.17×10−130 6.39×10−130 f9 LOPMA 8.88×10−16 8.88×10−16 0 WOA 6.12×104 5.04×104 1.22×104 WOA 4.44×10−15 4.80×10−15 2.16×10−15 GA 5.48×104 4.82×104 6.79×103 GA 1.98×101 1.96×101 2.96×10−1 GWO 1.50×10−5 4.60×10−5 9.57×10−5 GWO 2.42×10−13 2.08×10−13 5.72×10−14 DE 1.46×105 1.18×105 3.10×104 DE 2.00 2.00 4.17×10−2 LSO 3.73×103 2.02×103 2.88×103 LSO 8.88×10−16 2.16×10−1 1.18 PSO 1.63×104 6.70×103 5.68×103 PSO 1.65 4.00 2.44 f4 LOPMA 5.52×10−119 7.06×10−85 3.81×10−84 f10 LOPMA 0 0 0 WOA 0.89×102 0.49×102 0.28×102 WOA 0 6.90×10−3 3.78×10−2 GA 0.72×102 0.72×102 4.02 GA 3.94×102 3.50×102 4.28×101 GWO 1.15×10−6 3.50×10−6 3.29×10−6 GWO 0 3.90×10−3 1.04×10−2 DE 8.75×101 8.59×101 3.34 DE 3.88×102 3.48×102 4.11×101 LSO 2.33×101 1.78×101 5.98 LSO 3.26 4.08 1.32×101 PSO 0.12×102 9.90 3.53 PSO 7.90×10−2 8.09×10−2 1.36×10−1 f5 LOPMA 0 0 0 f11 LOPMA 1.57×10−32 1.57×10−32 5.57×10−48 WOA 0 4.12×10−31 1.57×10−30 WOA 1.57×10−32 1.57×10−32 5.57×10−48 GA 9.55×104 7.64×104 1.71×104 GA 9.29 1.20×101 2.23 GWO 1.03×10−15 0.39×10−2 2.16×10−2 GWO 1.82×10−29 3.15×10−29 3.34×10−29 DE 2.46×105 2.05×105 4.78×104 DE 1.31×101 1.84×101 3.07 LSO 2.60 1.38×101 3.15 LSO 2.36×10−32 2.36×10−32 8.35×10−48 PSO 0.27×102 1.39×102 3.04×102 PSO 2.86×10−9 1.59×10−1 3.02×101 f6 LOPMA 0 0 0 f12 LOPMA 1.35×10−32 1.35×10−32 5.57×10−48 WOA 0 2.05×10−34 7.82×10−34 WOA 1.35×10−32 1.35×10−32 5.57×10−48 GA 4.36×104 3.88×104 4.75×103 GA 1.49×101 1.52×101 2.75 GWO 3.00×10−25 1.99×10−25 2.72×10−25 GWO 2.13×10−29 1.38×10−28 2.22×10−28 DE 70.7×104 6.31×104 7.54×103 DE 1.45×102 1.34×102 1.71×101 LSO 2.27×103 9.34×102 1.01×103 LSO 1.35×10−32 1.35×10−32 5.57×10−48 PSO 0.14×10−2 4.60×10−4 8.16×10−4 PSO 3.50×10−6 1.82×10−2 4.18×10−2 表 6 LOPMA与其他算法的显著性差异检验结果
Table 6. Significance difference test results between LOPMA and other algorithms
函数 p LOPMA和WOA LOPMA和GA LOPMA和GWO LOPMA和MA LOPMA和DE LOPMA和LSO LOPMA和PSO f1 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 1.90×10−3 3.02×10−11 f2 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 6.61×10−1 3.02×10−11 f3 3.01×10−11 3.01×10−11 3.01×10−11 3.01×10−11 3.02×10−11 1.90×10−3 3.01×10−11 f4 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 f5 6.54×10−1 2.16×10−8 2.16×10−8 2.16×10−8 3.26×10−11 1.61×10−11 2.16×10−8 f6 1.67×10−1 1.21×10−12 1.21×10−12 1.21×10−12 1.21×10−12 1.70×10−8 1.21×10−12 f7 5.31×10−10 5.31×10−10 5.31×10−10 5.31×10−10 9.10×10−9 1.18×10−12 5.31×10−10 f8 2.17×10−10 3.02×10−11 9.49×10−7 3.02×10−11 3.02×10−11 1.55×10−10 3.02×10−11 f9 6.42×10−8 9.16×10−1 9.16×10−1 9.16×10−1 9.19×10−7 7.68×10−13 9.16×10−1 f10 1.17×10−13 4.57×10−12 4.91×10−13 4.57×10−12 7.72×10−5 7.72×10−5 4.57×10−12 f11 1.61×10−1 2.37×10−12 1.24×10−9 4.40×10−11 2.372×10−12 1.61×10−1 2.07×10−10 f12 1.35×10−8 3.31×10−11 3.31×10−11 3.31×10−11 3.37×10−11 5.55×10−11 3.31×10−11 表 7 与其他改进蜉蝣算法性能对比
Table 7. Compared with other improved in the performance of the ephemera algorithms
函数 平均值 标准差 对照组1 对照组2 对照组1 对照组2 LOPMA MIWMA[26] LOPMA MIMA[27] LOPMA MIMA[26] LOPMA MIMA[27] f1 3.65×10−124 1.40×10−135 2.89×10−262 1.49×10−192 2.01×10−125 6.50×10−134 0 0 f2 9.02×10−65 2.05×10−60 9.59×10−133 7.61×10−98 2.23×10−64 9.61×10−60 5.54×10−132 1.16×10−97 f3 3.73×10−129 2.55×10−113 6.81×10−268 9.82×10−64 1.37×10−128 1.70×10−112 0 4.28×10−63 f4 4.81×10−65 1.88×10−60 1.32×10−134 4.93×10−34 1.64×10−64 1.17×10−59 3.90×10−134 2.42×10−33 f7 1.65×10−5 5.62×10−5 3.59×10−3 1.25×10−4 2.44×10−6 4.08×10−5 2.64×104 1.32×10−4 f8 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 f9 8.88×10−16 8.88×10−16 8.88×10−16 8.88×10−16 0 0 0 0 f10 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 f11 6.23×10−14 6.43×10−13 1.24×10−32 2.38×10−32 4.40×10−13 6.72×10−13 4.26×10−33 5.83×10−34 表 8 CEC2017寻优结果
Table 8. CEC2017 optimization results
函数 平均值 标准差 AFSMA[28] I-GWO[29] WOA LSO MA LOPMA AFSMA[28] I-GWO[29] WOA LSO MA LOPMA CEC03 4.80×104 1.84×104 2.67×105 1.30×105 1.35×105 6.64×104 1.44×104 3.46×103 7.62×104 3.94×104 6.39×104 2.78×103 CEC06 6.24×102 7.02×102 6.83×102 6.77×102 6.67×102 6.41×102 1.02×101 1.11×102 1.36×101 1.15×101 9.50×100 8.61×100 CEC09 5.05×103 1.14×103 1.15×104 1.04×104 6.03×103 3.42×103 1.56×103 3.32×103 3.83×103 1.97×103 1.25×103 1.29×103 CEC12 3.37×106 4.86×106 4.28×108 4.82×109 1.43×107 2.78×106 3.13×106 4.14×106 2.55×108 1.63×109 1.55×107 3.06×106 CEC15 1.33×104 6.04×104 1.08×107 4.55×108 2.23×104 5.41×103 1.33×104 4.06×104 1.89×107 5.20×108 1.82×104 5.94×103 CEC18 2.45×106 4.56×105 1.16×107 3.98×107 2.02×105 1.62×105 2.72×106 2.91×105 1.22×107 2.02×105 1.96×105 1.68×105 CEC21 2.45×103 3.21×103 2.66×103 2.67×103 2.73×103 2.45×103 3.67×101 1.31×102 6.48×101 3.35×101 5.01×101 3.14×101 CEC24 2.98×103 2.74×103 3.27×103 3.43×103 3.73×103 2.52×103 4.81×101 6.83×102 1.14×102 1.35×101 1.75×102 4.44×101 CEC27 3.25×103 3.21×103 3.45×103 3.72×103 4.55×103 3.21×103 2.09×101 7.02×102 1.37×102 2.25×102 7.31×102 1.64×101 -
[1] KHISHE M, MOSAVI M R. Chimp optimization algorithm[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2020, 149: 113338. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2020.113338 [2] ALSATTAR H A, ZAIDAN A A, ZAIDAN B B. Novel meta-heuristic bald eagle search optimisation algorithm[J]. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2020, 53(3): 2237-2264. doi: 10.1007/s10462-019-09732-5 [3] MIRJALILI S, GANDOMI A H, MIRJALILI S Z, et al. Salp swarm algorithm: a bio-inspired optimizer for engineering design problems[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 2017, 114: 163-191. doi: 10.1016/j.advengsoft.2017.07.002 [4] SALGOTRA R, SINGH U, SINGH G, et al. A self-adaptive hybridized differential evolution naked mole-rat algorithm for engineering optimization problems[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2021, 383: 113916. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2021.113916 [5] BRAIK M S. Chameleon swarm algorithm: a bio-inspired optimizer for solving engineering design problems[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2021, 174: 114685. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2021.114685 [6] ZERVOUDAKIS K, TSAFARAKIS S. A mayfly optimization algorithm[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2020, 145: 106559. [7] KENNEDY J, EBERHART R. Particle swarm optimization[C]//Proceedings of the ICNN'95−International Conference on Neural Networks. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 1995: 1942-1948. [8] GOLDBERG D. Genetic algorithms in search, optimization and machine learning[M]. Boston: Addison-Wesley Longman Publishing Co. , Inc. , 1989. [9] YANG X S. Nature-inspired metaheuristic algorithms[M]. United Kingdom: Luniver Press, 2010: 79-90. [10] HOU S, YU J Q, SU Y C, et al. Flow distribution optimization of parallel pumps based on improved mayfly algorithm[J]. Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems, 2023, 44(2): 2065-2083. [11] FARKI A, SALEKSHAHREZAEE Z, TOFIGH A M, et al. COVID-19 diagnosis using capsule network and fuzzy C-means and mayfly optimization algorithm[J]. BioMed Research International, 2021, 2021: 2295920. doi: 10.1155/2021/2295920 [12] ZHANG S J, HOU T T, QU Q, et al. An improved mayfly method to solve distributed flexible job shop scheduling problem under dual resource constraints[J]. Sustainability, 2022, 14(19): 12120. doi: 10.3390/su141912120 [13] XIAO Y Q, WU Y J. Robust visual tracking based on modified mayfly optimization algorithm[J]. Image and Vision Computing, 2023, 135: 104691. doi: 10.1016/j.imavis.2023.104691 [14] GUO L, XU C, YU T H, et al. An improved mayfly optimization algorithm based on Median position and its application in the optimization of PID parameters of hydro-turbine governor[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 36335-36349. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3160714 [15] 席万强, 常保帅, 林思伟, 等. 多策略改进蜉蝣算法的无人机航迹规划[J]. 电光与控制, 2023, 30(11): 80-84.XI W Q, CHANG B S, LIN S W, et al. A multi-strategy improved mayfly algorithm for UAV path planning[J]. Electronics Optics & Control, 2023, 30(11): 80-84(in Chinese). [16] 李林丰, 刘卫东, 李乐. 基于改进蜉蝣算法的水下磁场测量误差补偿[J]. 西北工业大学学报, 2022, 40(5): 1004-1011. doi: 10.1051/jnwpu/20224051004LI L F, LIU W D, LI L. Underwater magnetic field measurement error compensation based on improved mayfly algorithm[J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2022, 40(5): 1004-1011(in Chinese). doi: 10.1051/jnwpu/20224051004 [17] 毛清华, 王迎港. 融合改进Logistics混沌和正弦余弦算子的自适应t分布海鸥算法[J]. 小型微型计算机系统, 2022, 43(11): 2271-2277.MAO Q H, WANG Y G. Adaptive t-distribution seagull optimization algorithm combining improved logistics chaos and sine-cosine operator[J]. Journal of Chinese Computer Systems, 2022, 43(11): 2271-2277(in Chinese). [18] 宁杰琼, 何庆. 混合策略改进的蝴蝶优化算法[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2021, 38(6): 1718-1723.NING J Q, HE Q. Mixed strategy to improve butterfly optimization algorithm[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2021, 38(6): 1718-1723(in Chinese). [19] 邬贵昌, 韦文山, 李尚平, 等. 基于混沌的多策略优化麻雀算法及应用[J]. 微电子学与计算机, 2022, 39(12): 21-30.WU G C, WEI W S, LI S P, et al. Multi-strategy optimization sparrow search algorithm based on chaos and its application[J]. Microelectronics & Computer, 2022, 39(12): 21-30(in Chinese). [20] 张伟康, 刘升, 任春慧. 混合策略改进的麻雀搜索算法[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2021, 57(24): 74-82.ZHANG W K, LIU S, REN C H. Mixed strategy improved sparrow search algorithm[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2021, 57(24): 74-82(in Chinese). [21] 张超. 基于t-分布精英保留机制的花朵授粉算法[J]. 安徽理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 38(3): 50-58.ZHANG C. Flower pollination algorithm based on t-distribution elitist retention mechanism[J]. Journal of Anhui University of Science and Technology (Natural Science), 2018, 38(3): 50-58(in Chinese). [22] 毛清华, 赵冰, 王迎港. 融合T-分布小波变异的混沌鲸鱼优化算法[J]. 小型微型计算机系统, 2024, 45(10): 2362-2369.MAO Q H, ZHAO B, WANG Y G. Chaotic whale optimization algorithm with T-distributed wavelet variation[J]. Journal of Chinese Computer Systems, 2024, 45(10): 2362-2369(in Chinese). [23] 杜永兆, 范宇凌, 柳培忠, 等. 多种群协方差学习差分进化算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(6): 1488-1495.DU Y Z, FAN Y L, LIU P Z, et al. Multi-populations covariance learning differential evolution algorithm[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2019, 41(6): 1488-1495(in Chinese). [24] 刘小龙, 许岩, 徐维军. 基于统计引导和多项式差分学习的樽海鞘优化算法[J]. 运筹与管理, 2021, 30(1): 43-49.LIU X L, XU Y, XU W J. Salp swarm algorithm based on statistical guidance and polynomial difference learning[J]. Operations Research and Management Science, 2021, 30(1): 43-49(in Chinese). [25] 毛清华, 王迎港, 牛晓辉. 基于反吸引速度更新机制的改进蜉蝣算法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2024, 50(6): 1770-1783.MAO Q H, WANG Y G, NIU X H. Improved mayfly optimization algorithm based on anti-attraction velocity update mechanism[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2024, 50(6): 1770-1783(in Chinese). [26] 王义, 张达敏, 邹诚诚. 增强全局搜索和自适应蜉蝣算法[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2022, 54(11): 137-150.WANG Y, ZHANG D M, ZOU C C. Enhance global search and adaptive mayfly algorithm[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2022, 54(11): 137-150(in Chinese). [27] 蒋宇飞, 许贤泽, 徐逢秋, 等. 多策略融合改进的自适应蜉蝣算法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2024, 50(4): 1416-1426.JIANG Y F, XU X Z, XU F Q, et al. Multi-strategy fusion improved adaptive mayfly algorithm[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2024, 50(4): 1416-1426(in Chinese). [28] 肖子雅, 刘升. 精英反向黄金正弦鲸鱼算法及其工程优化研究[J]. 电子学报, 2019, 47(10): 2177-2186.XIAO Z Y, LIU S. Study on elite opposition-based golden-sine whale optimization algorithm and its application of project optimization[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2019, 47(10): 2177-2186(in Chinese). [29] NADIMI-SHAHRAKI M H, TAGHIAN S, MIRJALILI S. An improved grey wolf optimizer for solving engineering problems[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2021, 166: 113917. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2020.113917 -






 下载:
下载: