Finite time robust control of morphing aircraft based on time-varying gain observer
-
摘要:
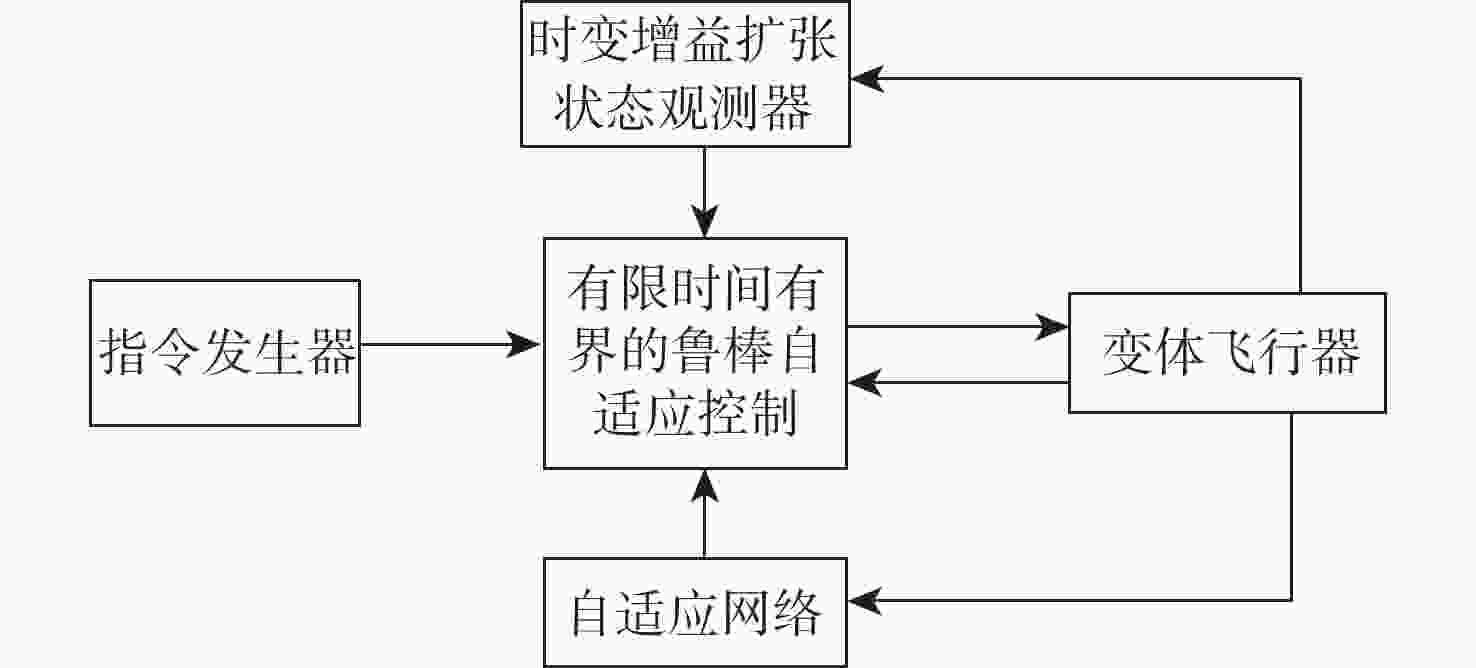
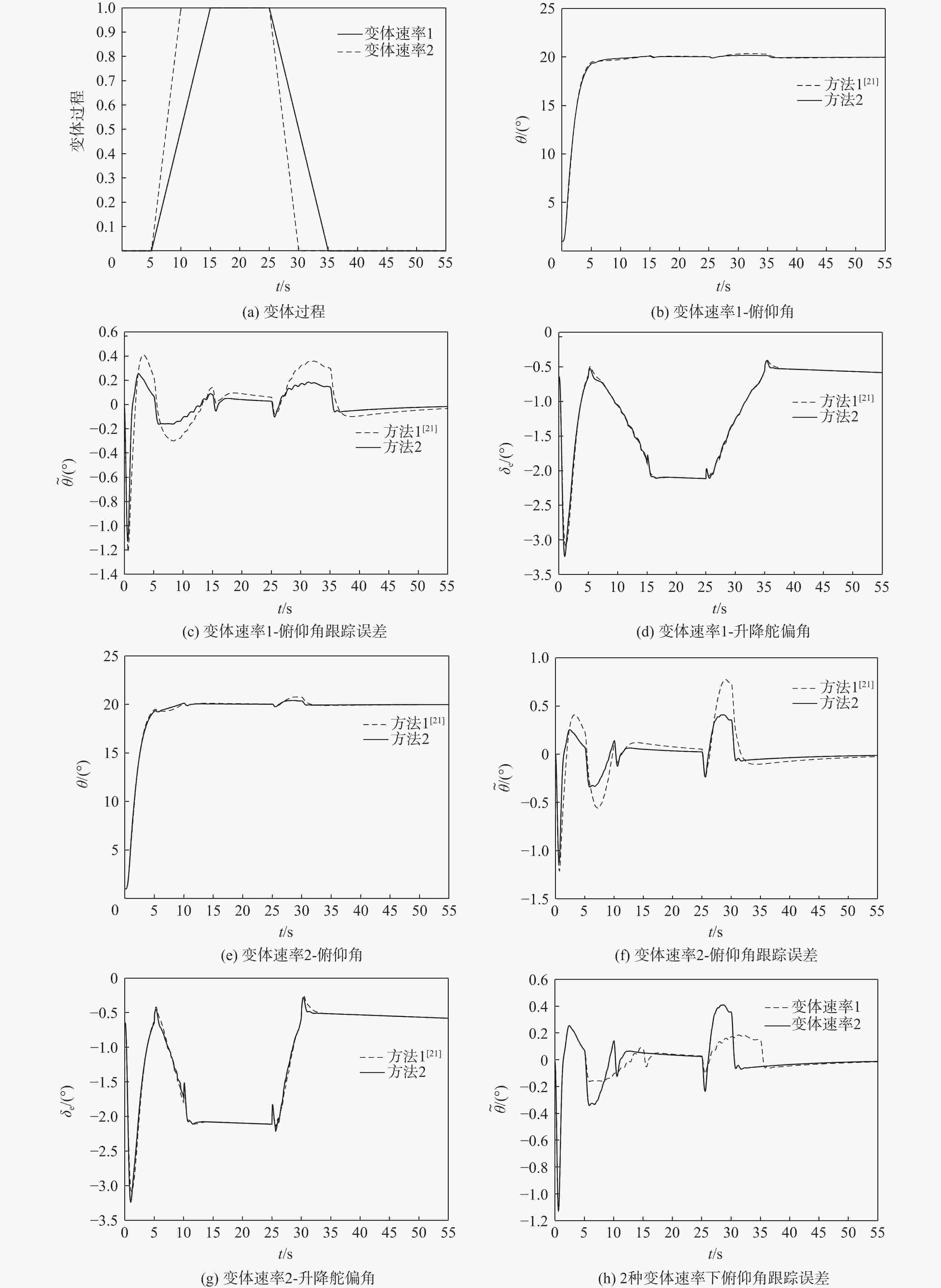
变体飞行器在变体过程中具有强非线性、强耦合和强时变等特性,给其飞行控制系统设计带来了较大挑战。针对该问题,提出一种时变增益扩张状态观测器,对系统耦合项进行精确逼近。结合自适应反步控制技术、有限时间控制理论,设计了一种有限时间有界的鲁棒自适应控制器,通过设计障碍Lyapunov函数,逐级递推得到实际控制律和自适应网络更新律,保证了系统指令跟踪误差在有限时间内能够收敛到预先给定的范围内。通过姿态控制仿真对所设计控制系统的有效性进行验证,仿真结果表明:变体飞行器在变体过程中能够很好地跟踪指令信号,基本不受变体速率的影响。
Abstract:The morphing aircraft has the characteristics of strong nonlinearity, strong coupling, and strong time variation characteristics in the morphing process, which brings great challenges to the design of the flight control system. To solve this problem, a time-varying gain extended state observer was proposed to accurately approximate the system coupling term. A finite time constrained robust adaptive controller was created by combining finite time control theory with adaptive backstepping control technology. By designing an obstacle Lyapunov function, the actual control law and adaptive network update law were recursively obtained step by step, ensuring that the system command tracking error can converge to a predetermined range in finite time. Finally, the effectiveness of the designed control system was verified through attitude control simulation. According to the simulation results, the morphing aircraft is essentially unaffected by the morphing rate and is capable of tracking command messages during the morphing process.
-
Key words:
- morphing aircraft /
- time varying gain /
- extended state observer /
- finite time bounded /
- robust control
-
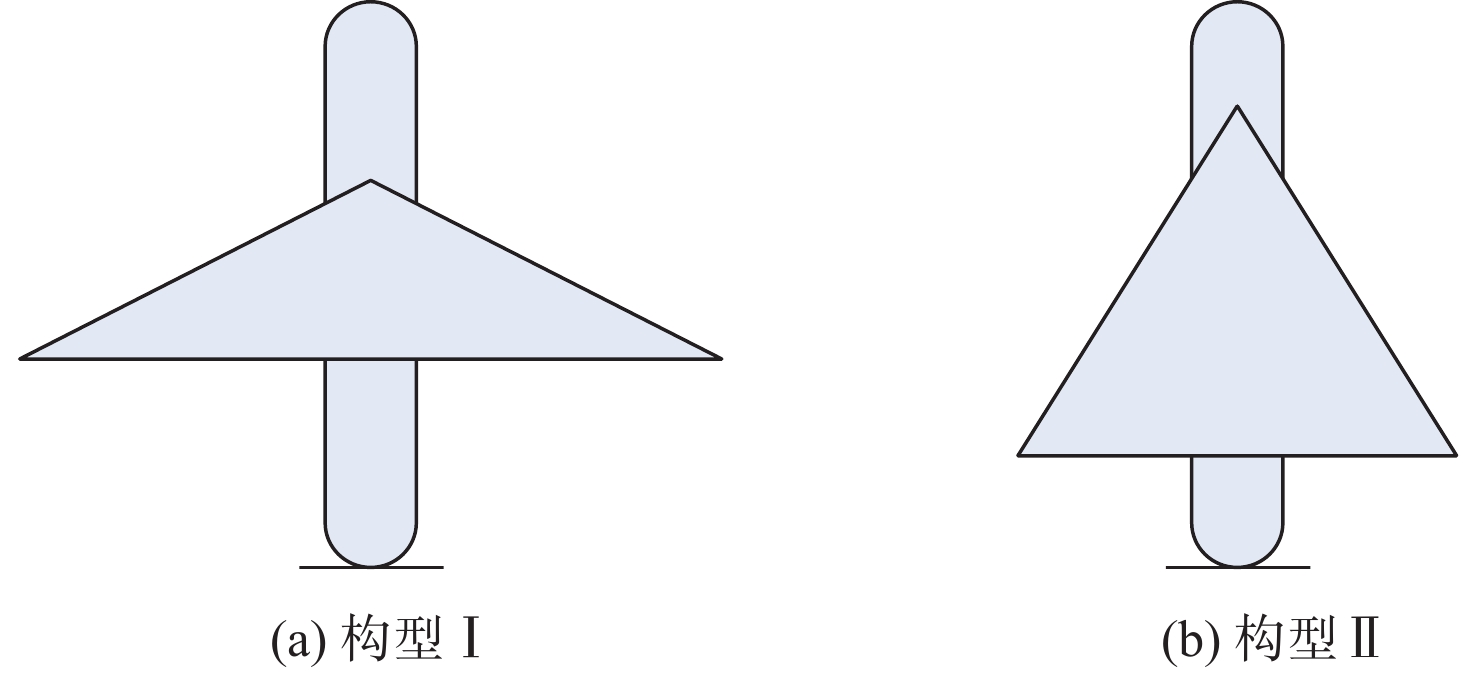
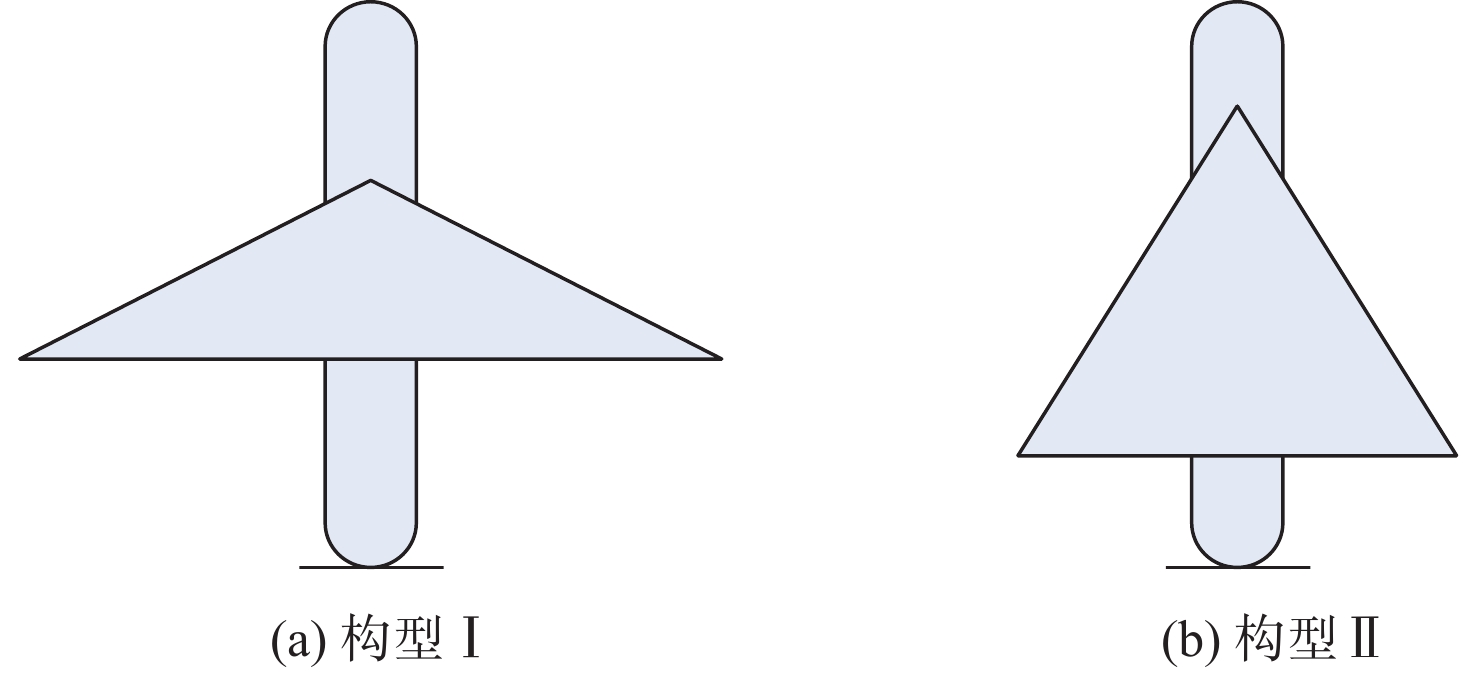
表 1 变体飞行器几何参数
Table 1. Geometric parameters of morphing aircraft
构型 展长/m 弦长/m 机翼面积/m2 构型Ⅰ 3 0.4 1.3 构型Ⅱ 2 0.8 1.5 -
[1] YUE T, WANG L X, AI J Q. Gain self-scheduled H∞ control for morphing aircraft in the wing transition process based on an LPV model[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2013, 26(4): 909-917. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2013.06.004 [2] CHAKRAVARTHY A, GRANT D T, LIND R. Time-varying dynamics of a micro air vehicle with variable-sweep morphing[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2012, 35(3): 890-903. doi: 10.2514/1.55078 [3] WU Z H, LU J C, ZHOU Q, et al. Modified adaptive neural dynamic surface control for morphing aircraft with input and output constraints[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2017, 87(4): 2367-2383. doi: 10.1007/s11071-016-3196-0 [4] YUE T, WANG L X, AI J Q. Longitudinal linear parameter varying modeling and simulation of morphing aircraft[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 2013, 50(6): 1673-1681. doi: 10.2514/1.C031316 [5] 邢伯阳, 潘峰, 王位, 等. 基于复合地标导航的动平台四旋翼飞行器自主优化降落技术[J]. 航空学报, 2019, 40(6): 322601.XING B Y, PAN F, WANG W, et al. Moving platform self-optimization landing technology for quadrotor based on hybrid landmark[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2019, 40(6): 322601(in Chinese). [6] SALIH A L, MOGHAVVEMI M, MOHAMED H A F, et al. Modelling and PID controller design for a quadrotor unmanned air vehicle[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Automation, Quality and Testing, Robotics. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2010: 1-5. [7] BESNARD L, SHTESSEL Y B, LANDRUM B. Quadrotor vehicle control via sliding mode controller driven by sliding mode disturbance observer[J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2012, 349(2): 658-684. doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2011.06.031 [8] 王慧东, 周来宏. 四旋翼无人机反步积分自适应控制器设计[J]. 兵工学报, 2021, 42(6): 1283-1289.WANG H D, ZHOU L H. Design of A backstepping integral adaptive controller for quadrotor UAV[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2021, 42(6): 1283-1289(in Chinese). [9] SHIRZADEH M, ASL H J, AMIRKHANI A, et al. Vision-based control of a quadrotor utilizing artificial neural networks for tracking of moving targets[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2017, 58: 34-48. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2016.10.016 [10] 卢凯文, 杨忠, 张秋雁, 等. 推力矢量可倾转四旋翼自抗扰飞行控制方法[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2020, 37(6): 1377-1387.LU K W, YANG Z, ZHANG Q Y, et al. Active disturbance rejection flight control method for thrust-vectored quadrotor with tiltable rotors[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2020, 37(6): 1377-1387(in Chinese). [11] 张泽鹏, 院老虎, 杜白雨, 等. 变体飞行器LPV建模与内外环鲁棒控制[J]. 战术导弹技术, 2023(1): 105-114.ZHANG Z P, YUAN L H, DU B Y, et al. LPV modeling and robust control of inner and outer loops for morphing aircraft[J]. Tactical Missile Technology, 2023(1): 105-114(in Chinese). [12] 梁帅, 杨林, 杨朝旭, 等. 基于Kalman滤波的变体飞行器T-S模糊控制[J]. 航空学报, 2020, 41(S2): 724274.LIANG S, YANG L, YANG Z X, et al. Kalman filter based T-S fuzzy control for morphing aircraft[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2020, 41(S2): 724274(in Chinese). [13] SEIGLER T M, NEAL D A. Analysis of transition stability for morphing aircraft[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2009, 32(6): 1947-1954. doi: 10.2514/1.44108 [14] SEIGLER T M, NEAL D A, BAE J S, et al. Modeling and flight control of large-scale morphing aircraft[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 2007, 44(4): 1077-1087. doi: 10.2514/1.21439 [15] 夏川, 董朝阳, 程昊宇, 等. 变体飞行器有限时间切H∞跟踪控制[J]. 兵工学报, 2018, 39(3): 485-493.XIA C, DONG C Y, CHENG H Y, et al. Finite-time H∞ tracking control for switched morphing aircraft[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2018, 39(3): 485-493(in Chinese). [16] 李新凯, 张宏立, 范文慧. 基于时变障碍李雅普诺夫函数的变体无人机有限时间控制[J]. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(8): 2062-2074.LI X K, ZHANG H L, FAN W H. Finite-time control for morphing aerospace vehicle based on time-varying barrier Lyapunov function[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(8): 2062-2074(in Chinese). [17] 滕青芳, 佐俊, 潘浩, 等. 基于时变增益扩张状态观测器的逆变器系统自适应super-twisting电压鲁棒控制[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2020, 37(9): 1880-1894.TENG Q F, ZUO J, PAN H, et al. Robust voltage control for inverter system using time-varying gain extended state observer-based adaptive super-twisting algorithm[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2020, 37(9): 1880-1894(in Chinese). [18] 陈伟, 冯高鹏. 变体飞机建模及自适应动态面控制[J]. 测控技术, 2016, 35(2): 91-95.CHEN W, FENG G P. Modeling and adaptive dynamic surface control of morphing aircraft[J]. Measurement & Control Technology, 2016, 35(2): 91-95(in Chinese). [19] 陈伟, 卢京潮, 王晓光, 等. 基于backstepping/RHO的变体飞机控制器设计[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2014, 40(8): 1060-1065.CHEN W, LU J C, WANG X G, et al. Design of a controller for morphing aircraft based on backstepping/RHO[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2014, 40(8): 1060-1065(in Chinese). [20] WANG H H, CHEN B, LIN C, et al. Adaptive finite-time control for a class of uncertain high-order non-linear systems based on fuzzy approximation[J]. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2017, 11(5): 677-684. [21] EHAB S, AHMED M K. Generic UAV autopilot prototype based on adaptive modified incremental backstepping[C]//Proceedings of the AIAA SciTech Forum and Exposition. Reston: AIAA, 2021. -






 下载:
下载: