Intelligent scheduling method for space-based optical sensors based on heterogeneous graph
-
摘要:
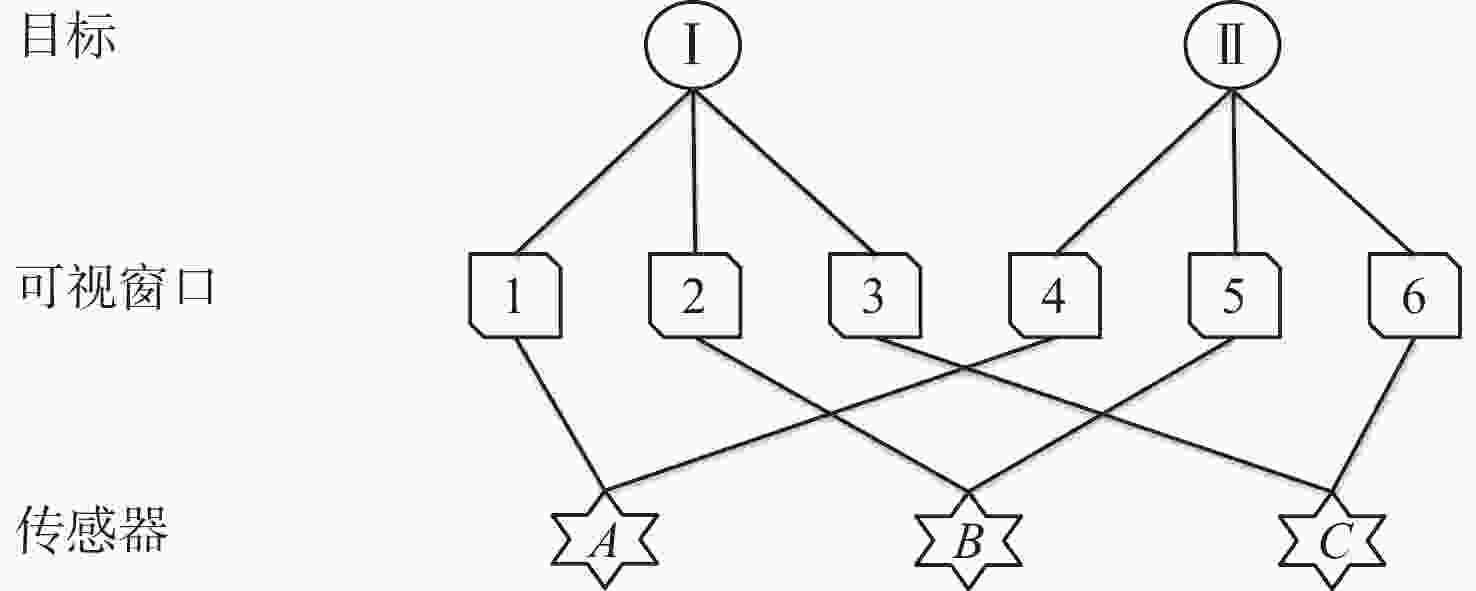
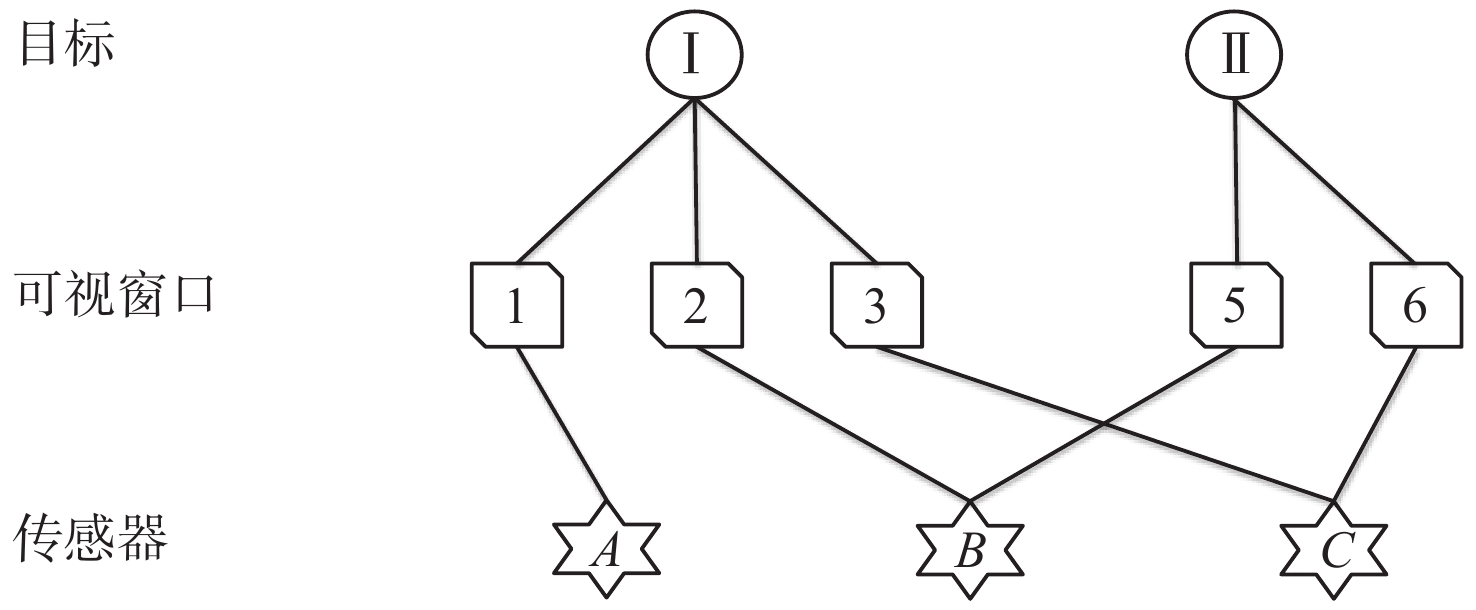
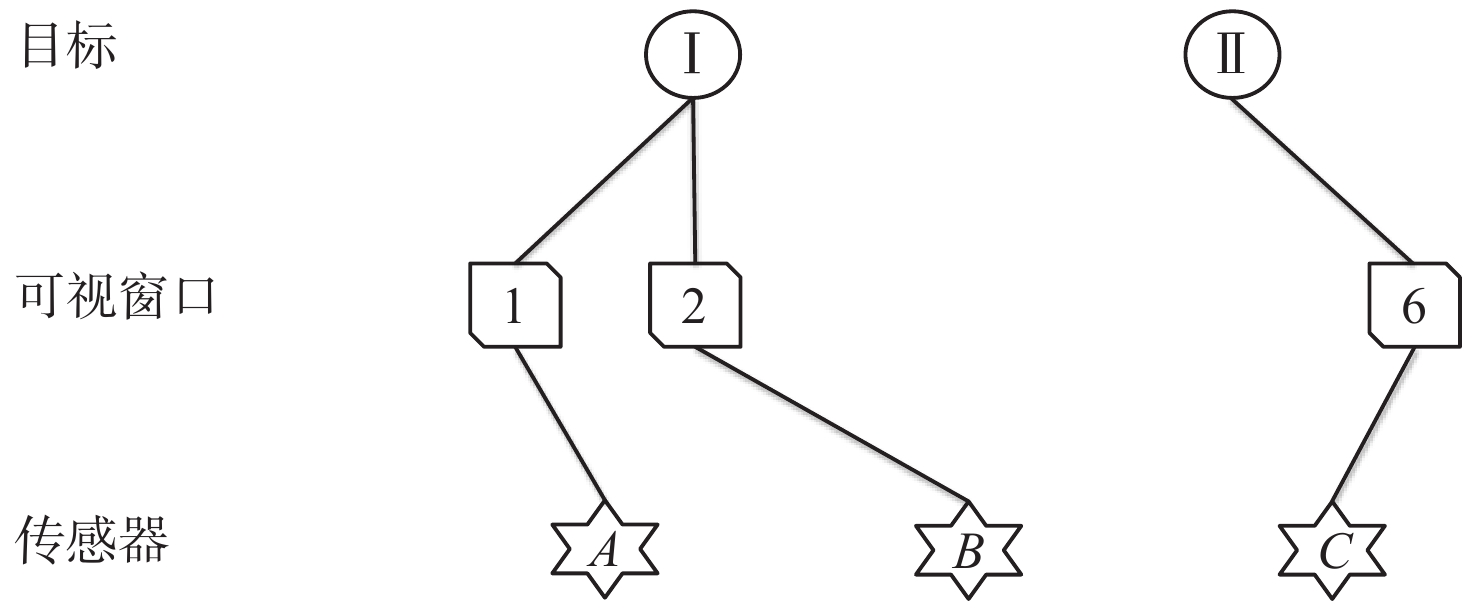
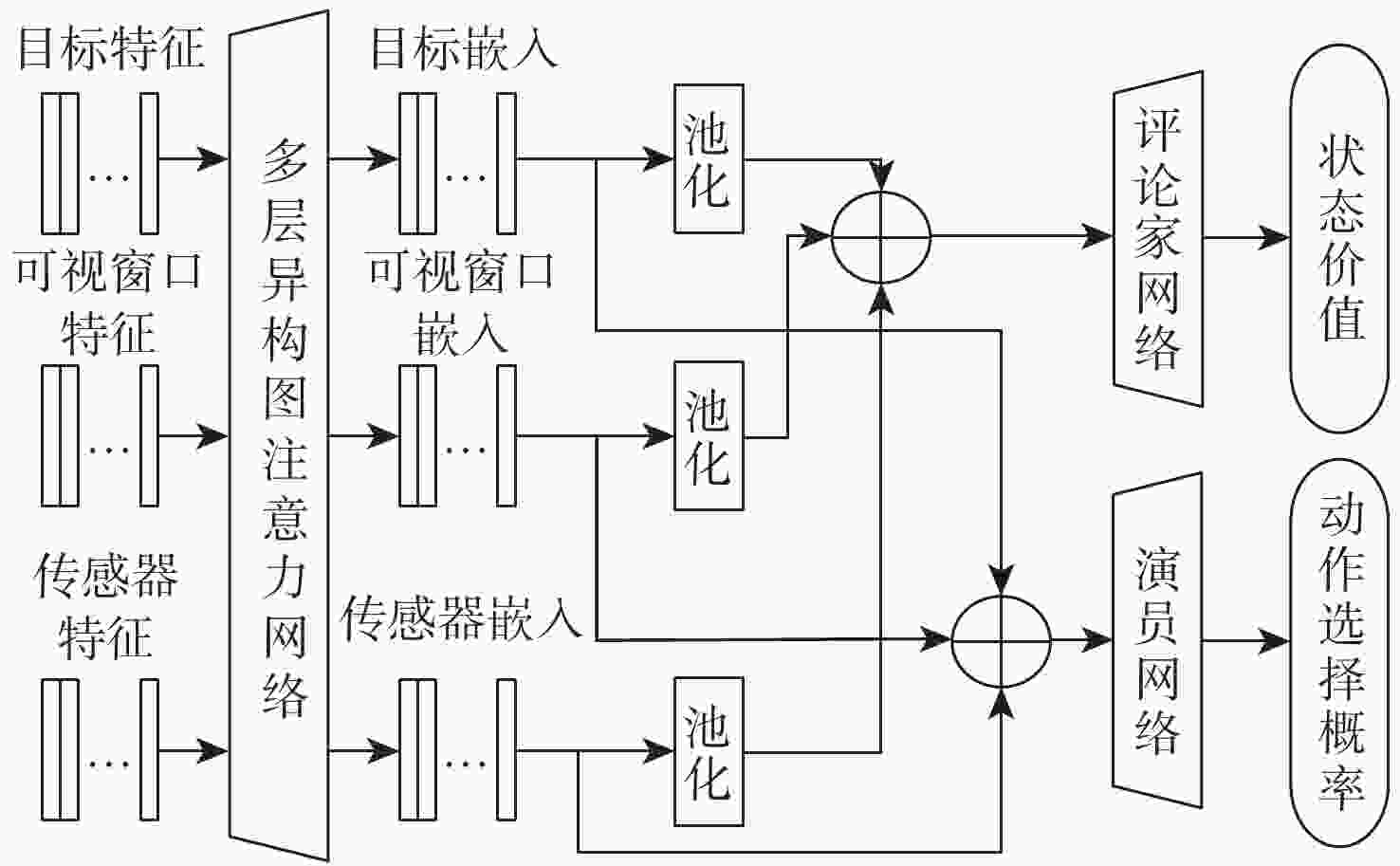
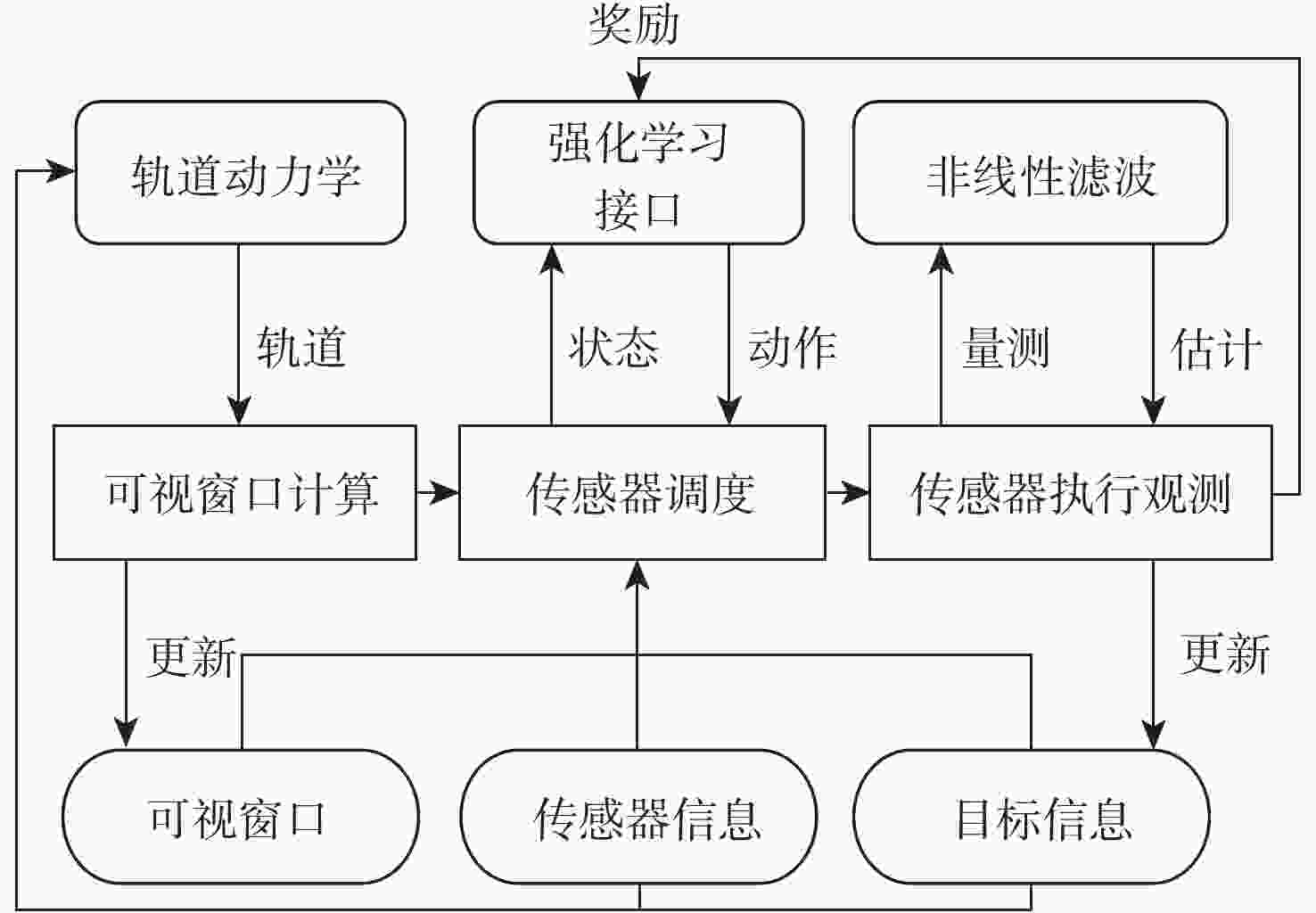
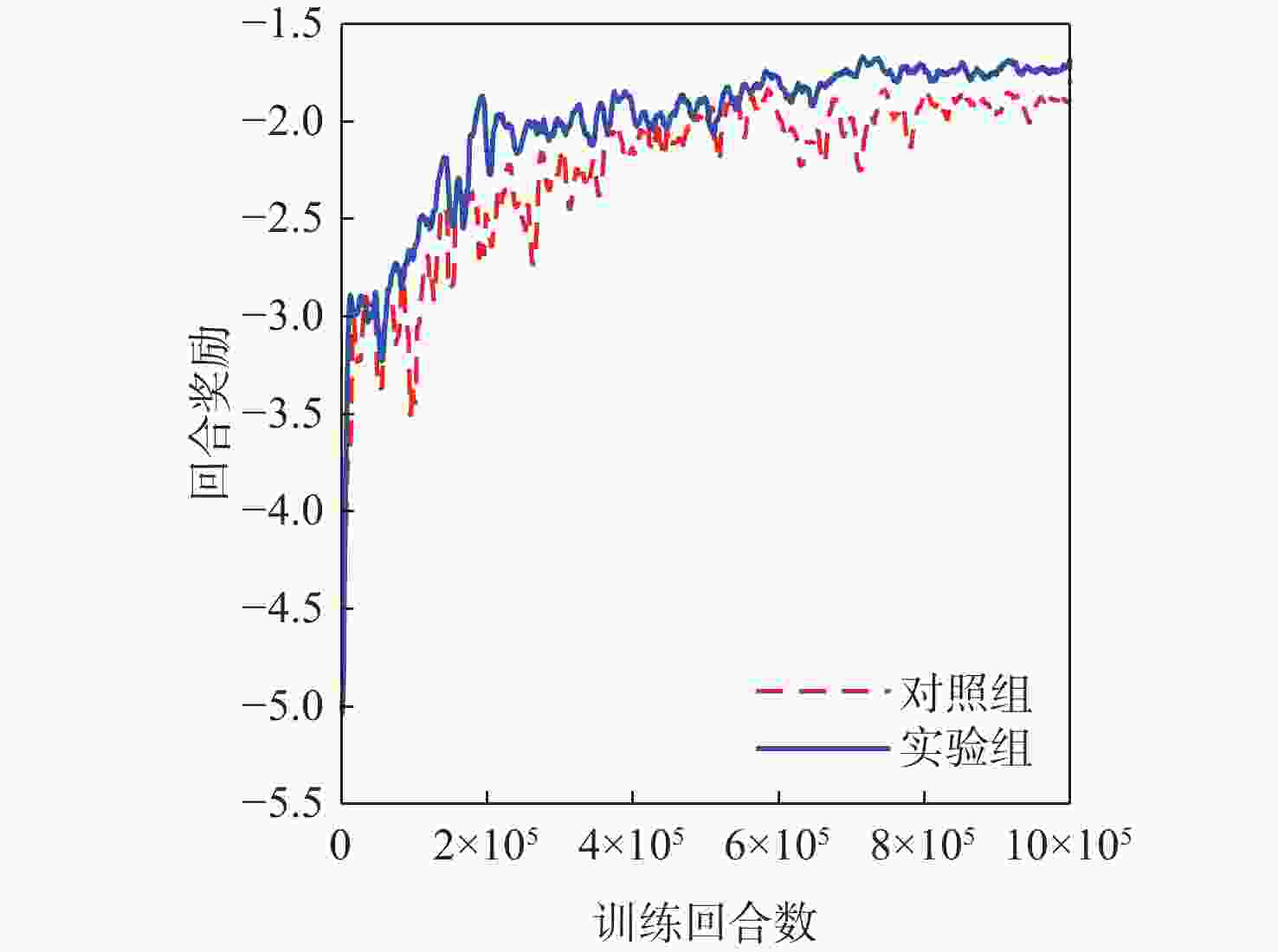
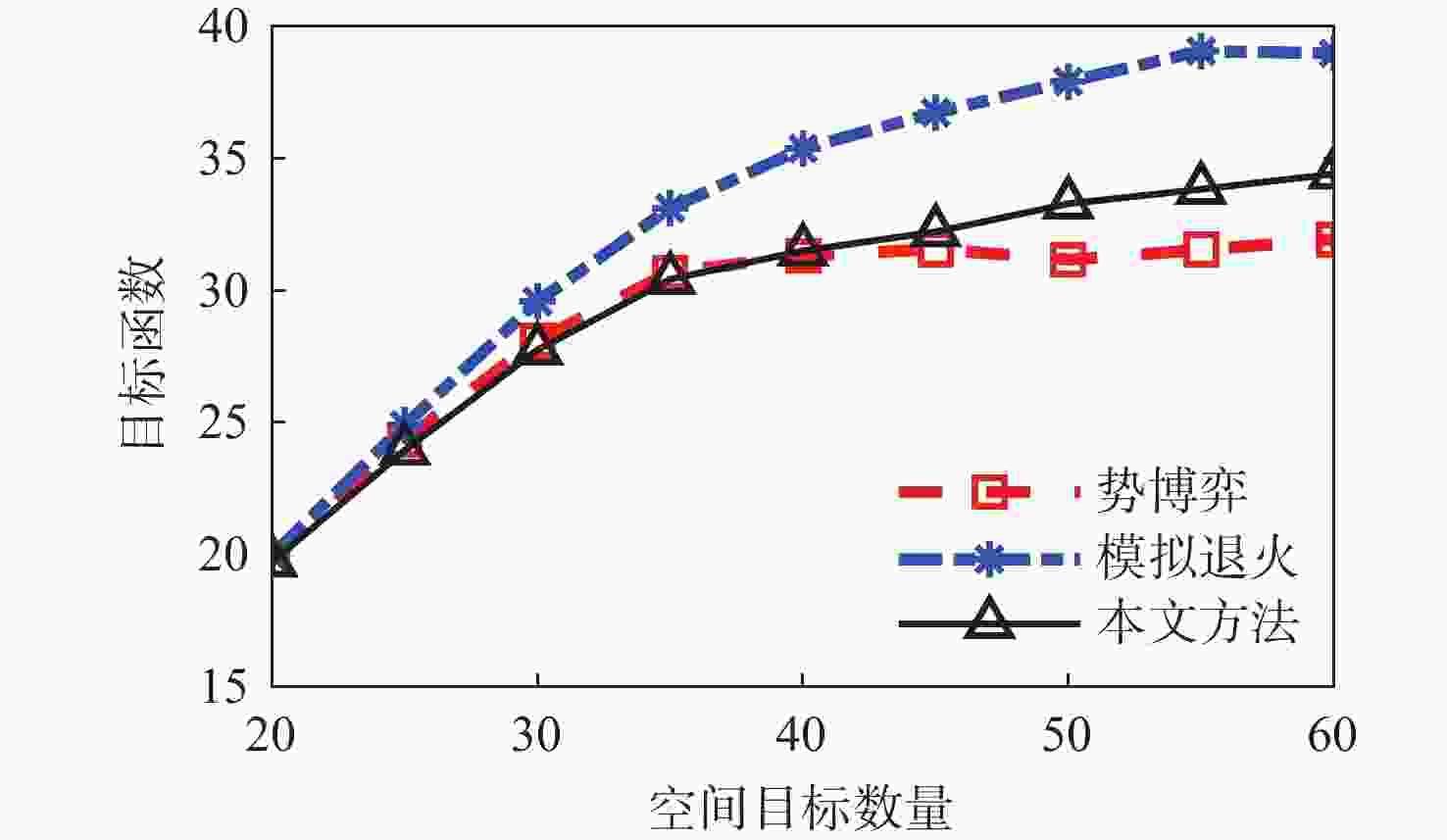
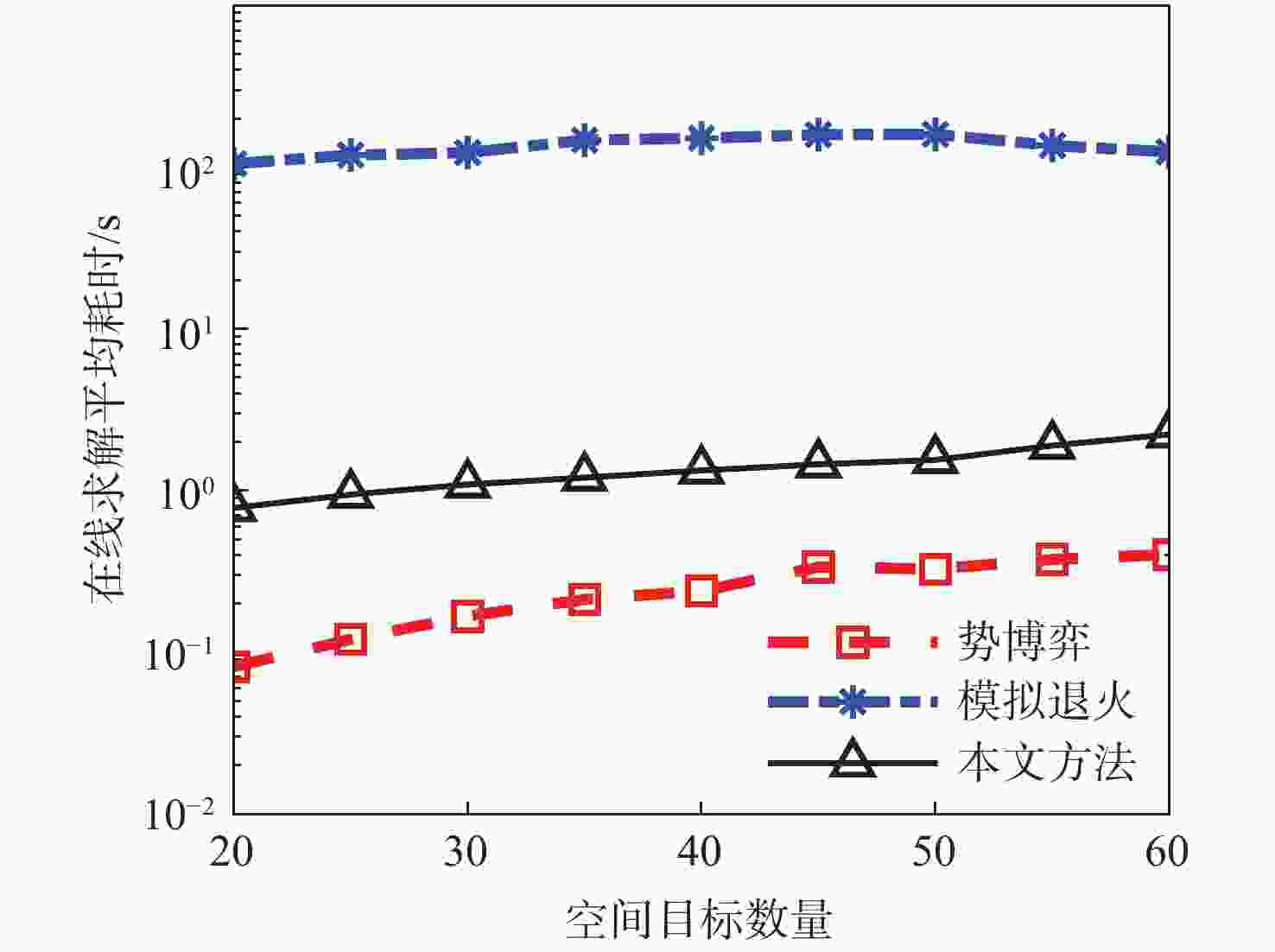
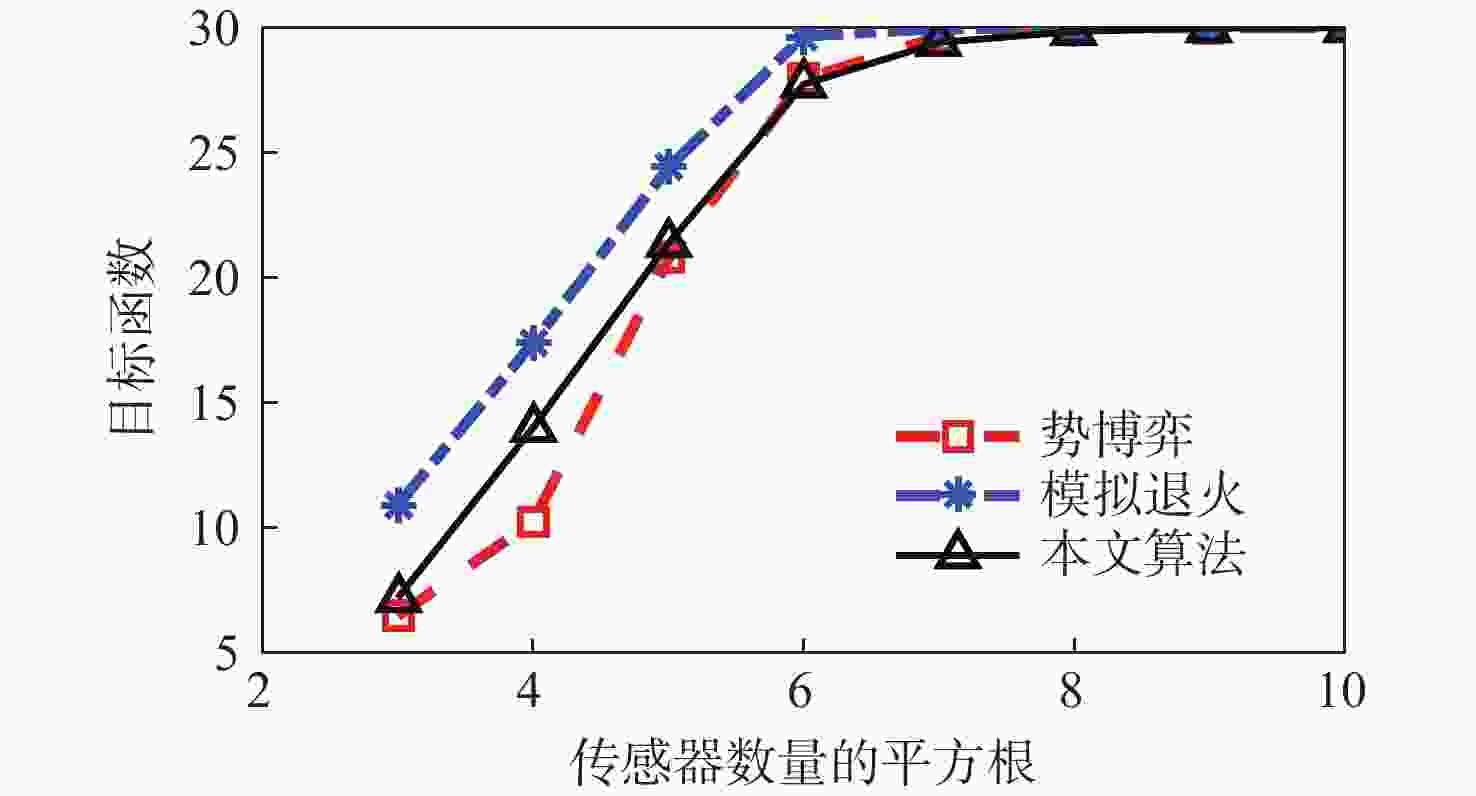
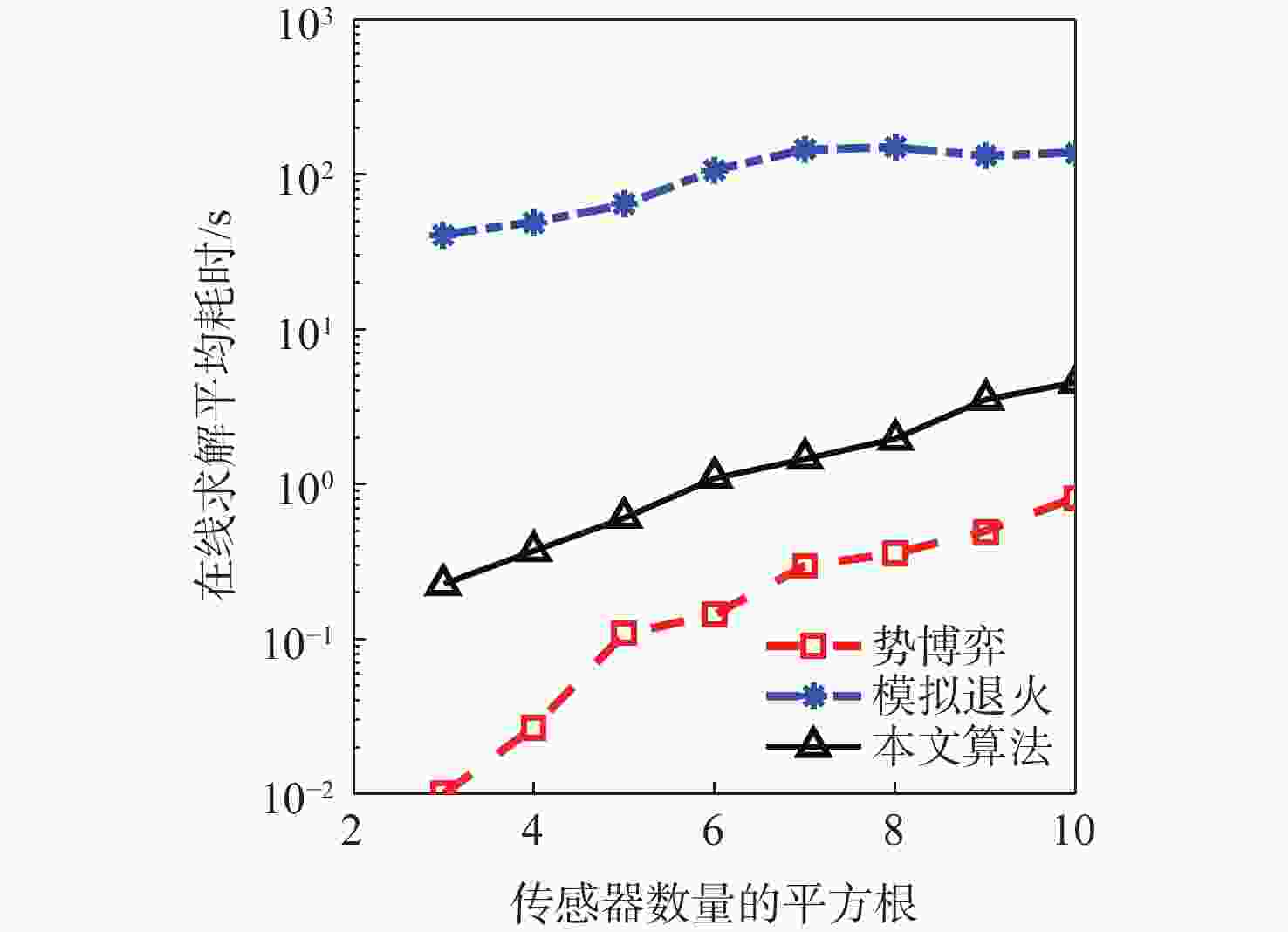
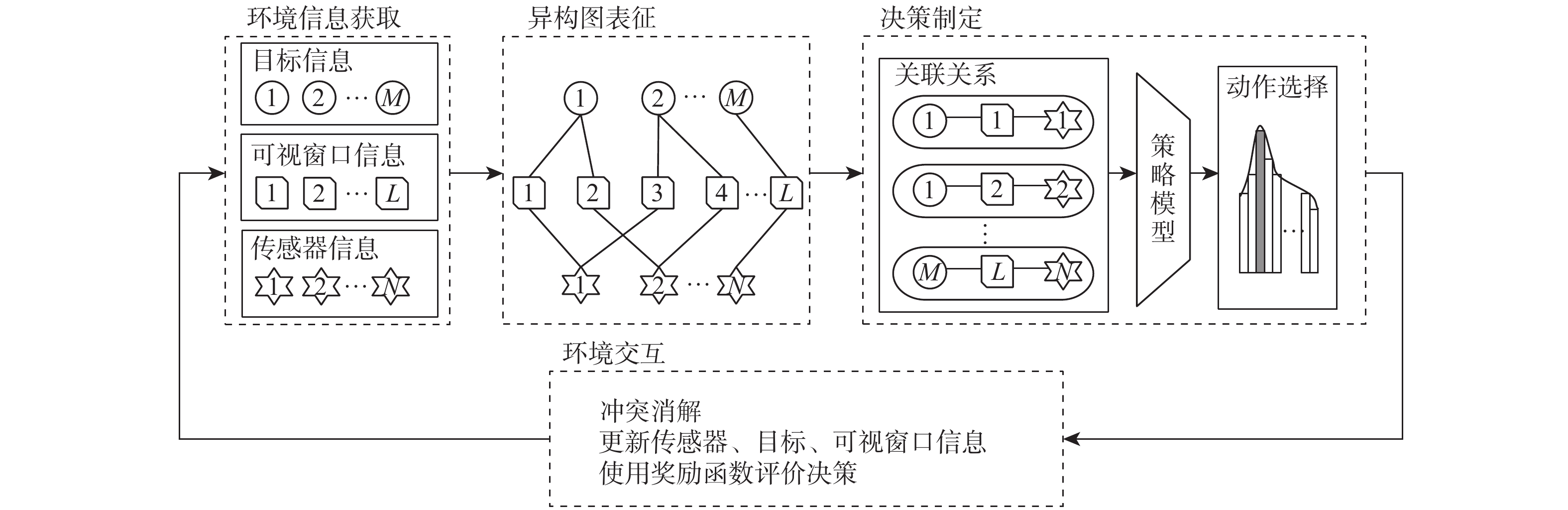
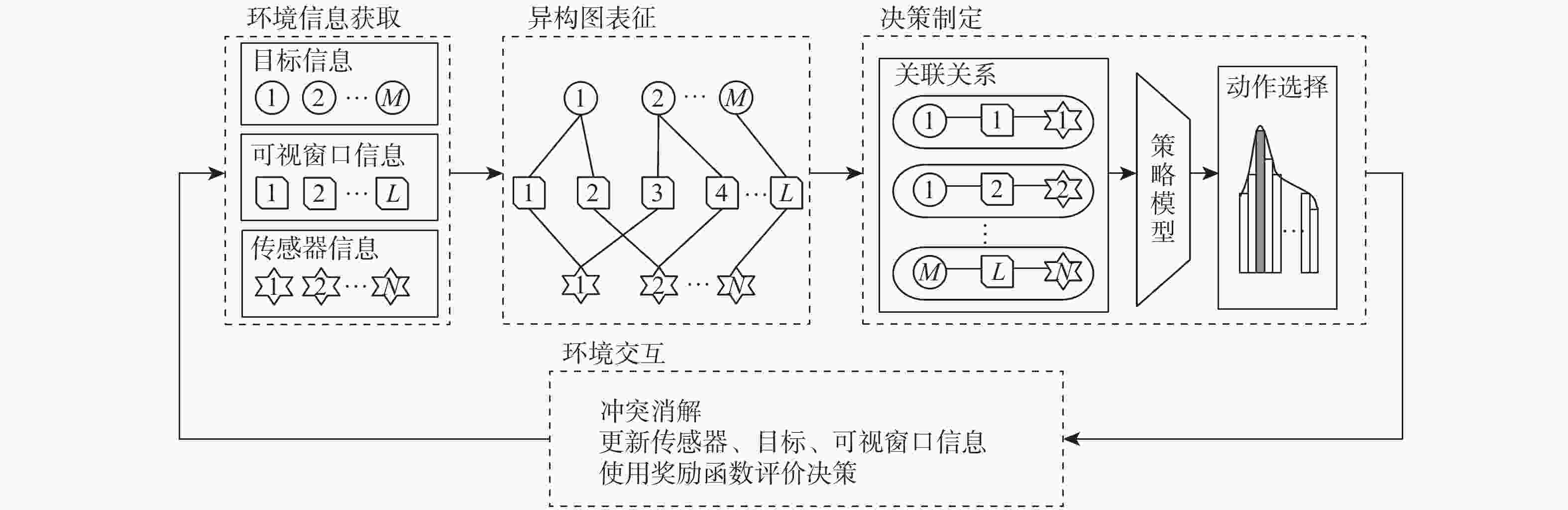
随着空间环境日益复杂,如何在线调度有限的天基光学传感器资源以观测更多的空间目标成为紧迫的问题。基于此,提出一种基于异构图的传感器智能调度方法。该方法将传感器调度方案的求解过程建模为马尔可夫决策过程(MDP),并将传感器调度方案表征为由目标、传感器和可视窗口3类节点构成的异构图结构,采用异构图神经网络对异构图结构进行编码,通过强化学习对传感器调度智能体开展训练。消融实验表明:提出的异构图神经网络编码方案比多层感知机编码方案的策略收益高7.5%。在不同目标数量和传感器数量的仿真场景中对比了所提方法与模拟退火方法和势博弈方法,结果表明:相较于2种对比方法,所提方法更好地兼顾了在线求解速度和目标容量2个方面。
Abstract:With the increasingly complex orbital environment, how to schedule the limited space-based optical sensor resources to observe more space targets has become an urgent problem. To solve this problem, an intelligent sensor scheduling method based on heterogeneous graphs is proposed. In this method, the solution process of the sensor scheduling scheme is modeled as a Markov decision process (MDP), and the sensor scheduling scheme is characterized as a heterogeneous graph structure composed of three kinds of nodes: targets, sensors and visible time windows. The sensor scheduling agent is taught via reinforcement learning, while the heterogeneous graph neural network encodes the heterogeneous graph topology. According to the ablation study, the multi-layer perceptron encoder has a 7.5% lower return than the suggested heterogeneous graph neural network encoder. The proposed method is compared with the simulated annealing method and potential game method in test scenarios with different numbers of targets and sensors. The results show that compared with the two methods, the proposed algorithm has a more balanced performance in terms of online solving speed and target capacity.
-
表 1 参数设置
Table 1. Parameter settings
参数 数值 学习率 0.0001 折扣因子 1 参考精度/km 10 节点嵌入维数 64 编码器网络层数 2 评论家网络层数 2 演员网络层数 2 多层感知机单层尺寸 192 -
[1] BOROWITZ M. Examining the growth of the global space situational awareness sector: a network analysis approach[J]. Space Policy, 2022, 59: 101444. doi: 10.1016/j.spacepol.2021.101444 [2] DU J L, CHEN J Y, LI B, et al. Tentative design of SBSS constellations for LEO debris catalog maintenance[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2019, 155: 379-388. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2018.06.054 [3] NEEMA K, SUBRAMANIAN S V, DELAURENTIS D. Dual phase consensus algorithm for distributed sensor management[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2016, 52(4): 1893-1907. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2016.150196 [4] THARMARASA R, KIRUBARAJAN T, SINHA A, et al. Decentralized sensor selection for large-scale multisensor-multitarget tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2011, 47(2): 1307-1324. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2011.5751260 [5] KALANDROS M. Covariance control for multisensor systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2002, 38(4): 1138-1157. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2002.1145739 [6] XIONG K, ZHANG T X, CUI G L, et al. Coalition game of radar network for multitarget tracking via model-based multiagent reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(3): 2123-2140. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2022.3208865 [7] YU V F, SUSANTO H, JODIAWAN P, et al. A simulated annealing algorithm for the vehicle routing problem with parcel lockers[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 20764-20782. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3152062 [8] ALI I M, SALLAM K M, MOUSTAFA N, et al. An automated task scheduling model using non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm II for fog-cloud systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cloud Computing, 2022, 10(4): 2294-2308. doi: 10.1109/TCC.2020.3032386 [9] PENG H W, LI J D, TIAN J F, et al. A game theoretic self-organization for satellite-based optical sensor allocation[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2023, 133: 108149. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2023.108149 [10] 李国梁, 李峭, 徐亚军, 等. 基于DDQN的片上网络混合关键性消息调度方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2022, 48(7): 1233-1241.LI G L, LI Q, XU Y J, et a1. A DDQN-based mixed-criticality messages scheduling method for network-on-chip[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2022, 48(7): 1233-1241(in Chinese). [11] SONG W, CHEN X Y, LI Q Q, et al. Flexible job-shop scheduling via graph neural network and deep reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2023, 19(2): 1600-1610. doi: 10.1109/TII.2022.3189725 [12] 吴兰, 吴元明, 孔凡士, 等. 基于深度强化学习与扩展卡尔曼滤波相结合的交通信号灯配时方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2022, 48(8): 1353-1363.WU L, WU Y M, KONG F S, et al. Traffic signal timing method based on deep reinforcement learning and extended Kalman filter[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2022, 48(8): 1353-1363(in Chinese). [13] 张晟宇, 朱振才, 胡海鹰. 红外低轨星座突发任务多重策略调度方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2022, 48(12): 2405-2414. ZHANG S Y, ZHU Z C, HU H Y. Burst tasks scheduling method for infrared LEO constellation based on multi-strategies[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2022, 48(12): 2405-2414(in Chinese). [14] LI S E. Reinforcement learning for sequential decision and optimal control[M]. Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore, 2023: 93-94. [15] 刘建业, 王华, 周晚萌. 基于GA-SA的低轨星座传感器资源调度算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2018, 40(11): 2476-2481.LIU J Y, WANG H, ZHOU W M. LEO constellation sensor resources scheduling algorithm based on genetic and simulated annealing[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(11): 2476-2481(in Chinese). [16] VELIČKOVIĆ P, CUCURULL G, CASANOVA A, et al. Graph attention networks[EB/OL]. (2018-02-04)[2023-10-18]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1710.10903. [17] HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[EB/OL]. (2015-12-10)[2023-10-18]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.03385. [18] SCHULMAN J, WOLSKI F, DHARIWAL P, et al. Proximal policy optimization algorithms[EB/OL]. (2017-08-28)[2023-10-18]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1707.06347. [19] SCHULMAN J, MORITZ P, LEVINE S, et al. High-dimensional continuous control using generalized advantage estimation[EB/OL]. (2015-06-08)[2023-10-18]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1506.02438. -






 下载:
下载: