Optimization design method of winged aircraft formation configuration and communication topology for cooperative penetration
-
摘要:
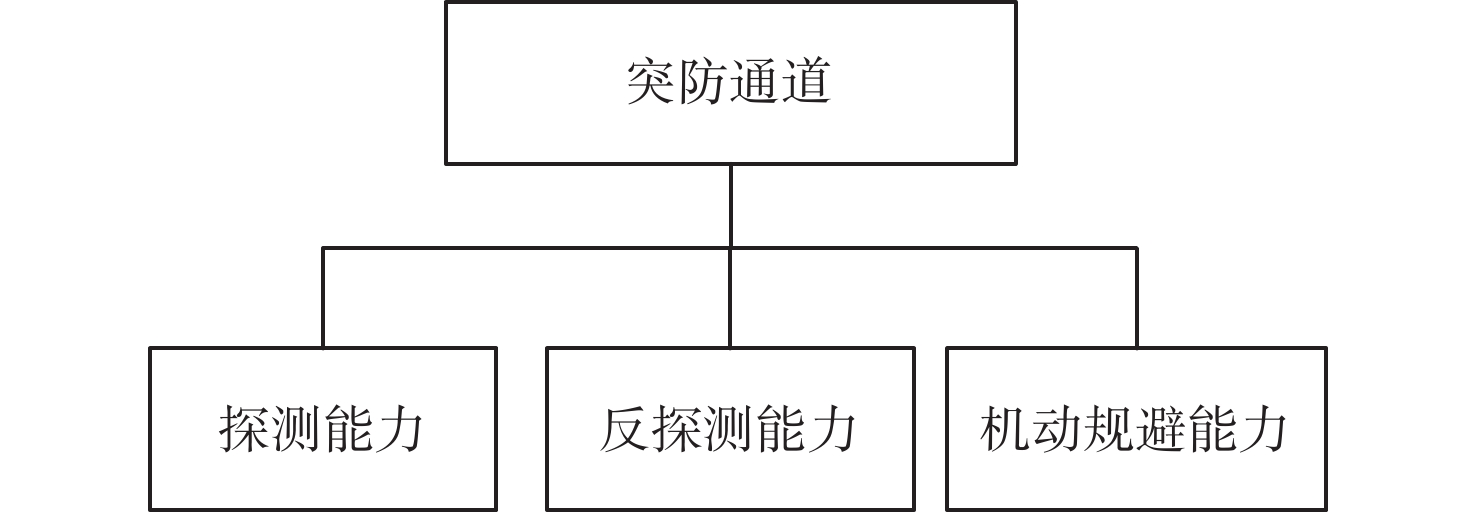
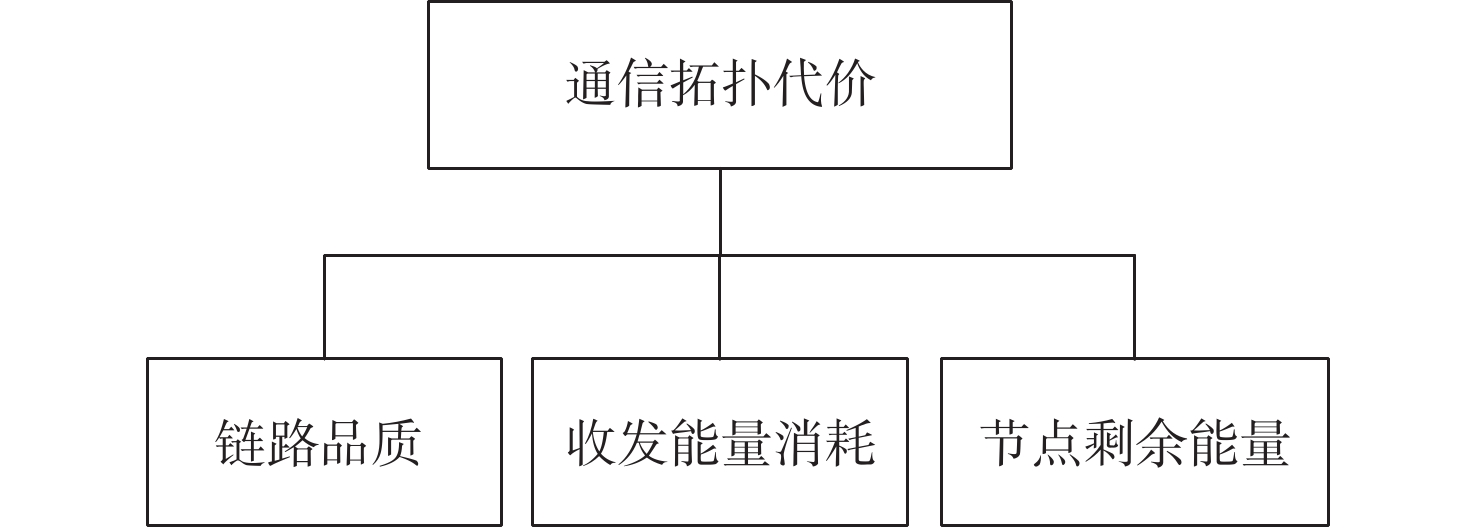
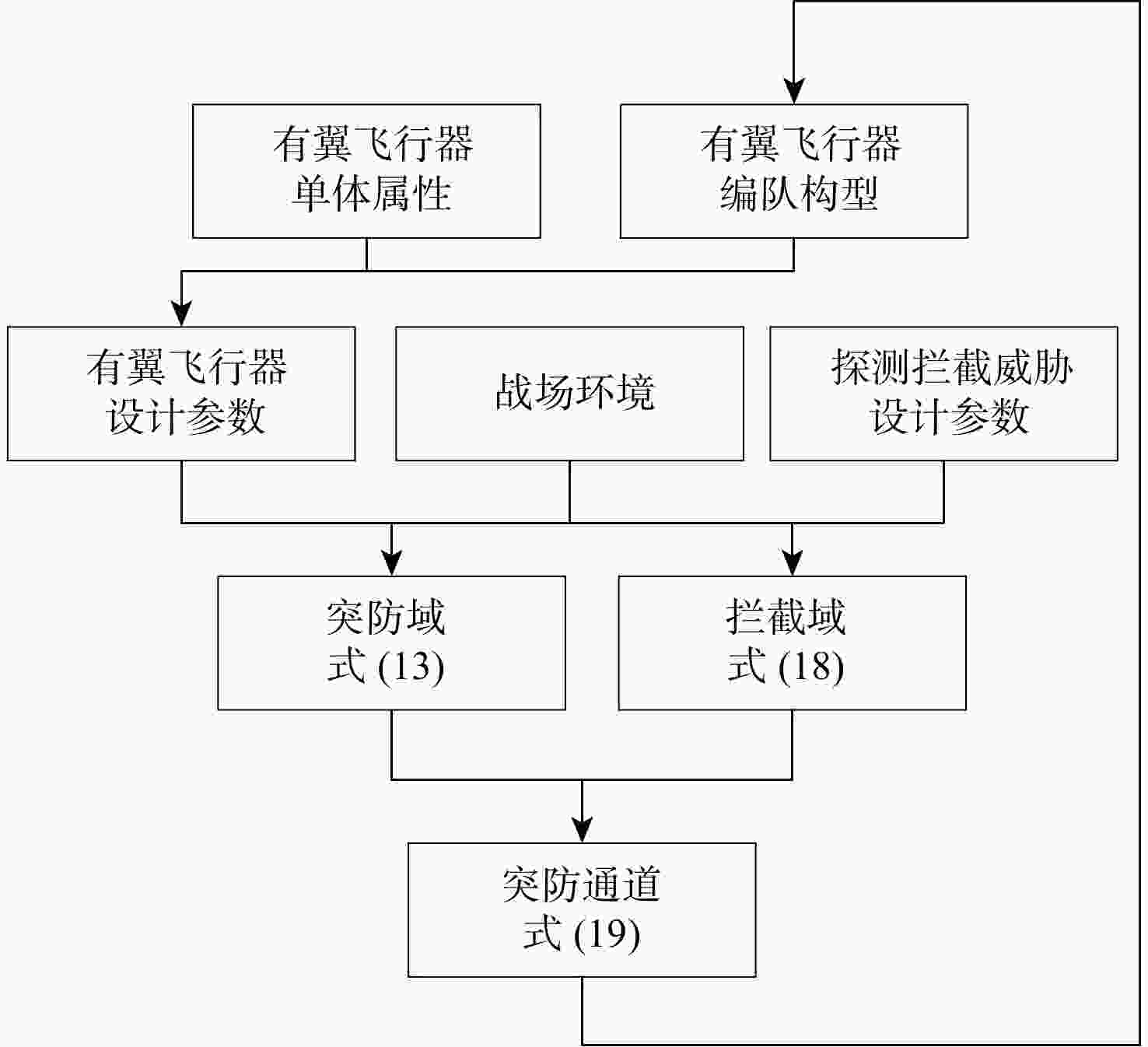
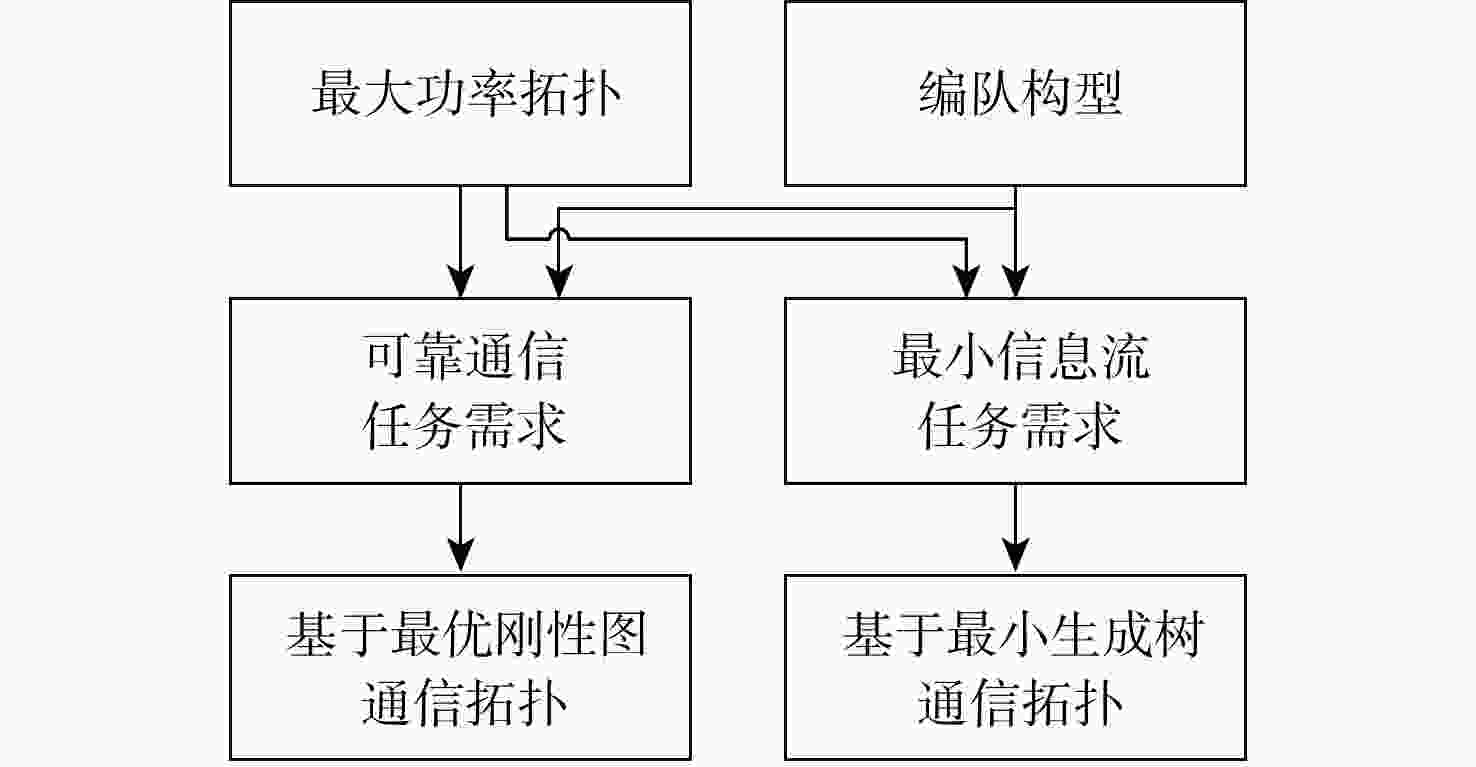
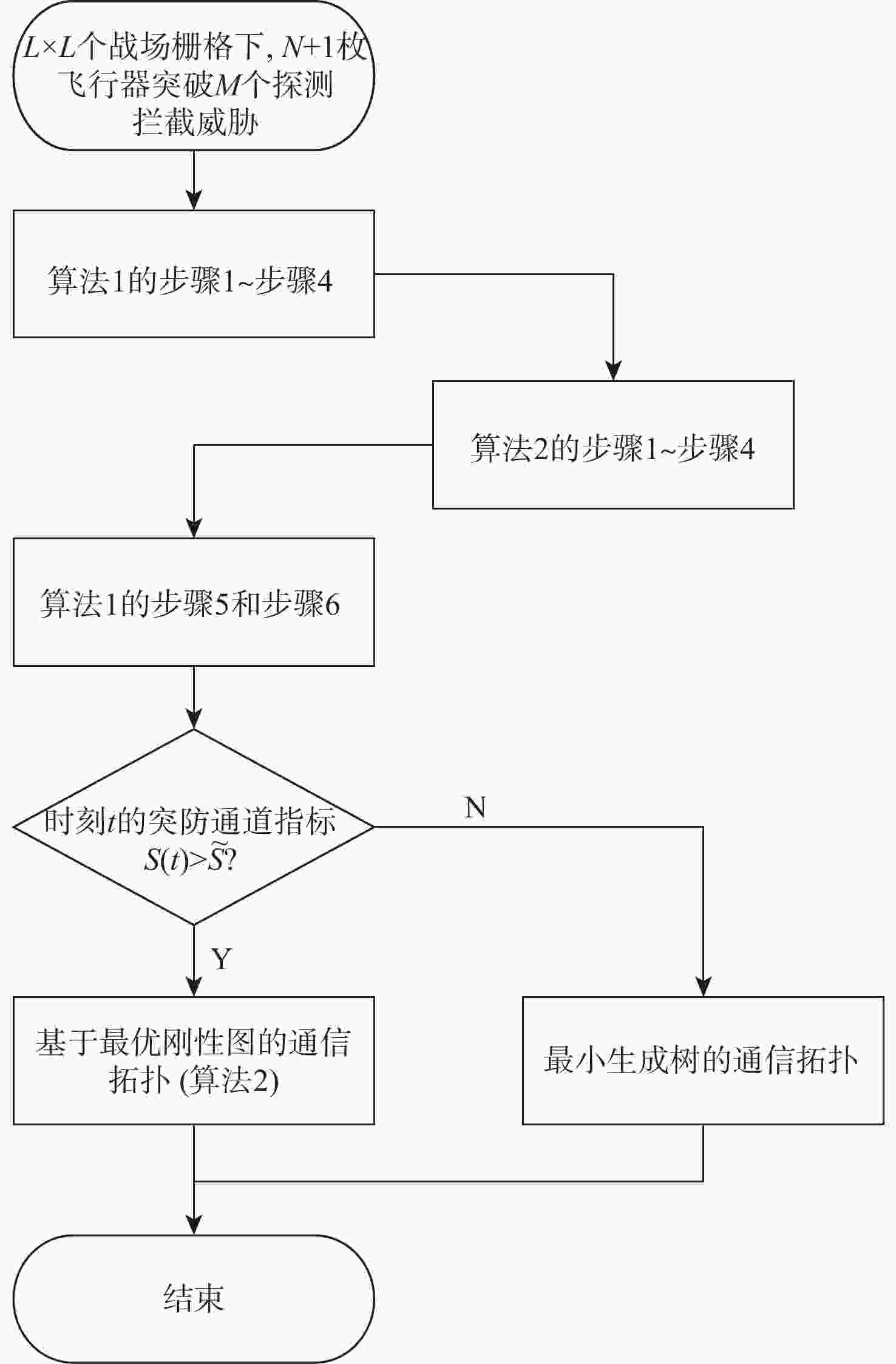
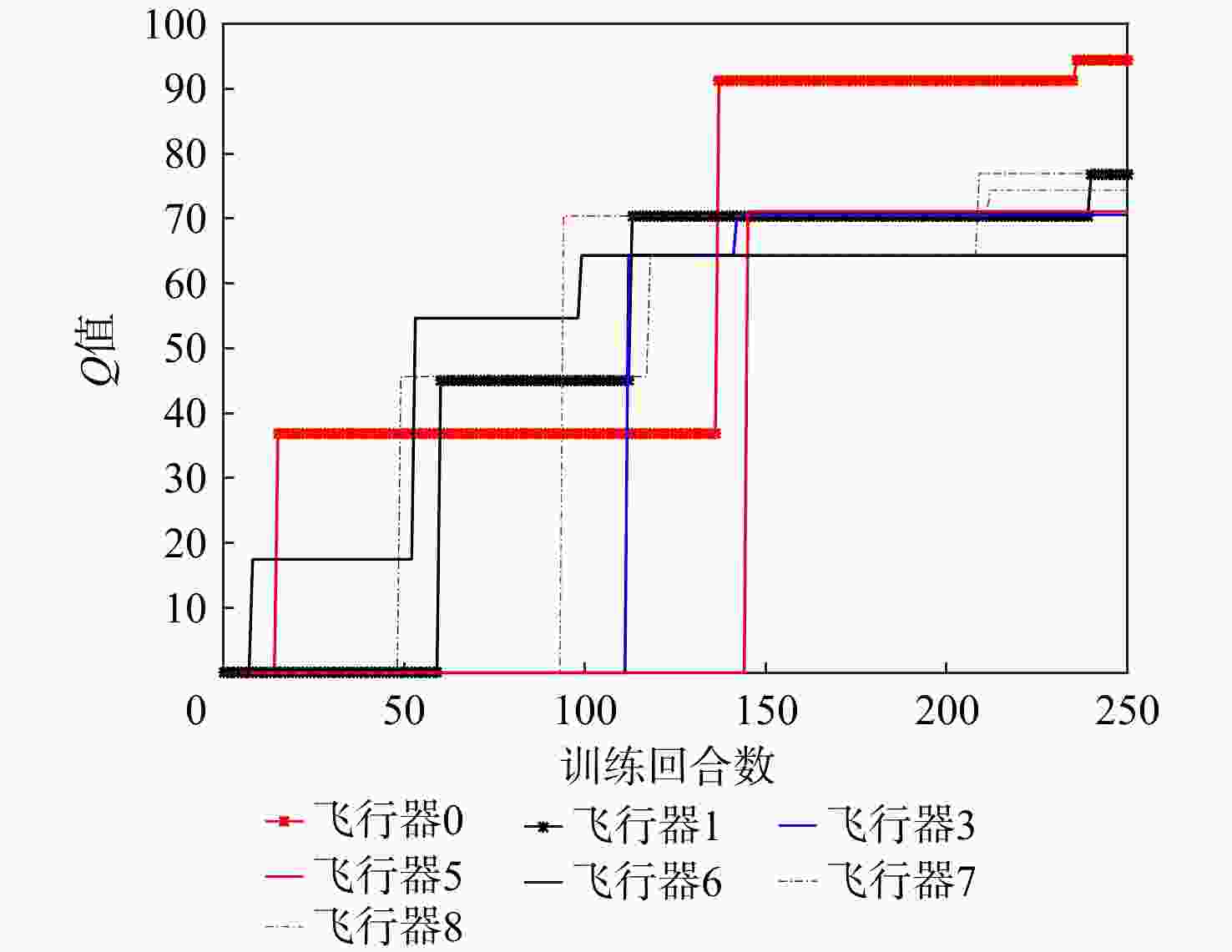
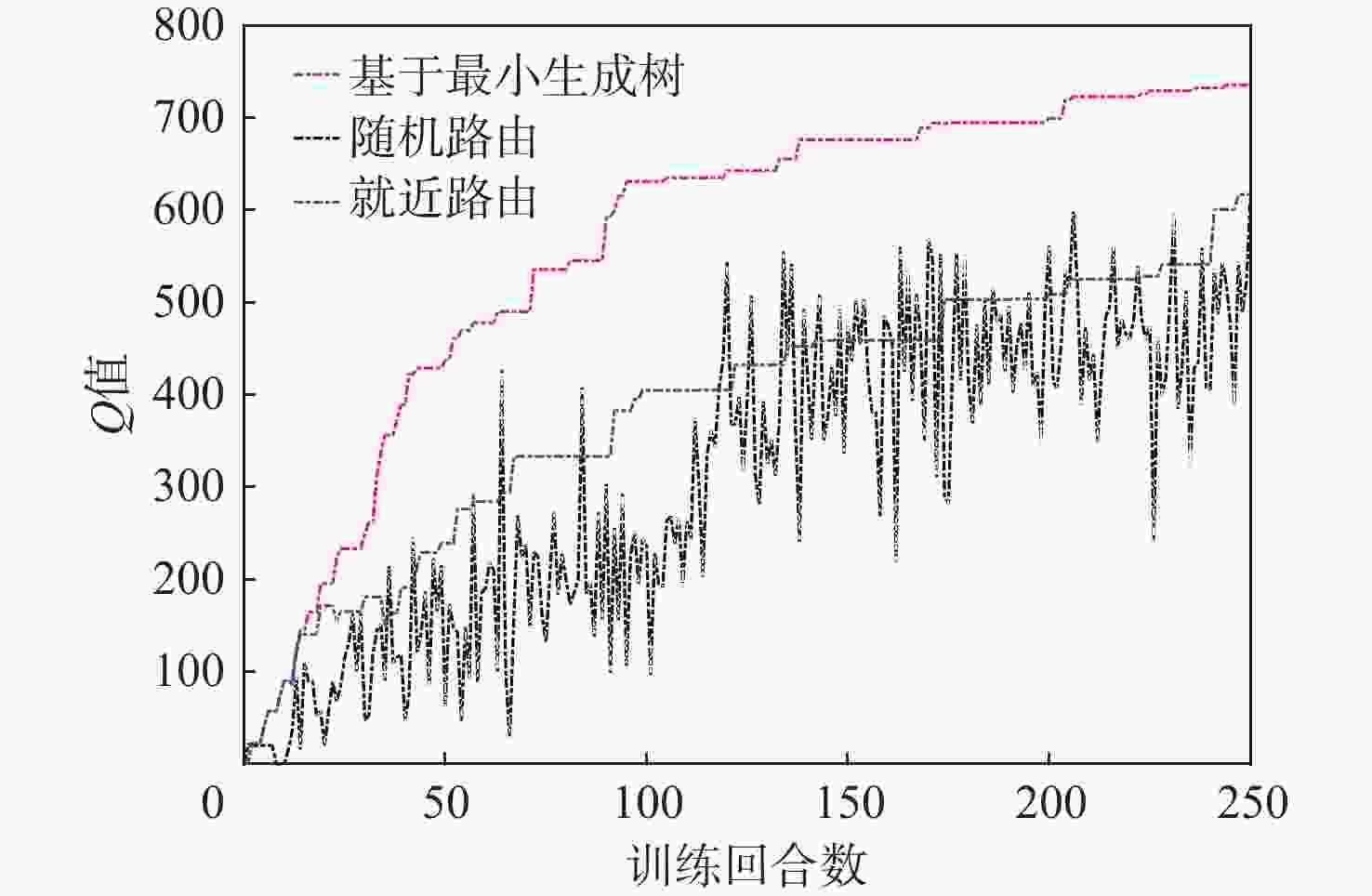
有翼飞行器编队构型和通信拓扑优化在编队协同突防应用场景下有着迫切需求。针对编队构型优化中的参考基准选择和飞行器/拦截力量/战场之间关系的建模问题,提出一种基于突防通道的编队构型优化设计方法。通过通信拓扑优化获得领导者飞行器角色,先使用各组长的几何中心、后使用领导者飞行器作为编队构型的参考基准,设计时变编队构型的显式表达式,摆脱了对事先获取领导者飞行器先验信息的依赖;建立有翼飞行器突防通道模型,保证有翼飞行器在各战场栅格处的探测、反探测、机动规避能力优势;针对通信拓扑优化需要兼顾信息共享和均衡网络负载的问题,在编队构型约束下构建通信拓扑,提出基于最小生成树和最优刚性图的通信拓扑优化设计方法,给出基于战场威胁态势的拓扑切换策略,实现了编队构型和通信拓扑的优化。以有翼飞行器编队协同突防探测拦截威胁为例,验证了所提方法的有效性。
Abstract:In the cooperative penetration application scenario, there is an immediate need to optimize the communication topology and wing aircraft formation structure. A formation configuration optimization design method based on penetration thoroughfares is proposed to address the issues of reference benchmark selection and modeling of aircraft/interception force/battlefield relationships in formation configuration optimization. The leader aircraft’s role is obtained by the optimization of the communication topology. The formation configuration is referenced by the geometric centers of the leader aircraft and each team leader in turn. Explicit expressions for the formation configuration are designed to eliminate the dependence on obtaining prior information about the leader aircraft. A penetration thoroughfares model is established for winged aircraft to ensure their advantages in detection, anti-detection, and maneuver avoidance capabilities at various battlefield grids. To address the issue of balancing information sharing and network load on communication topology optimization, a communication topology is constructed under the constraints of formation configuration. In order to optimize both formation configuration and communication topology, a topology switching strategy depending on battlefield conditions is suggested after a communication topology optimization approach based on minimal spanning tree and optimal rigid graph is presented. Finally, the effectiveness of the designed optimization method is verified by taking the cooperative penetration against military threats for winged aircraft as an example.
-
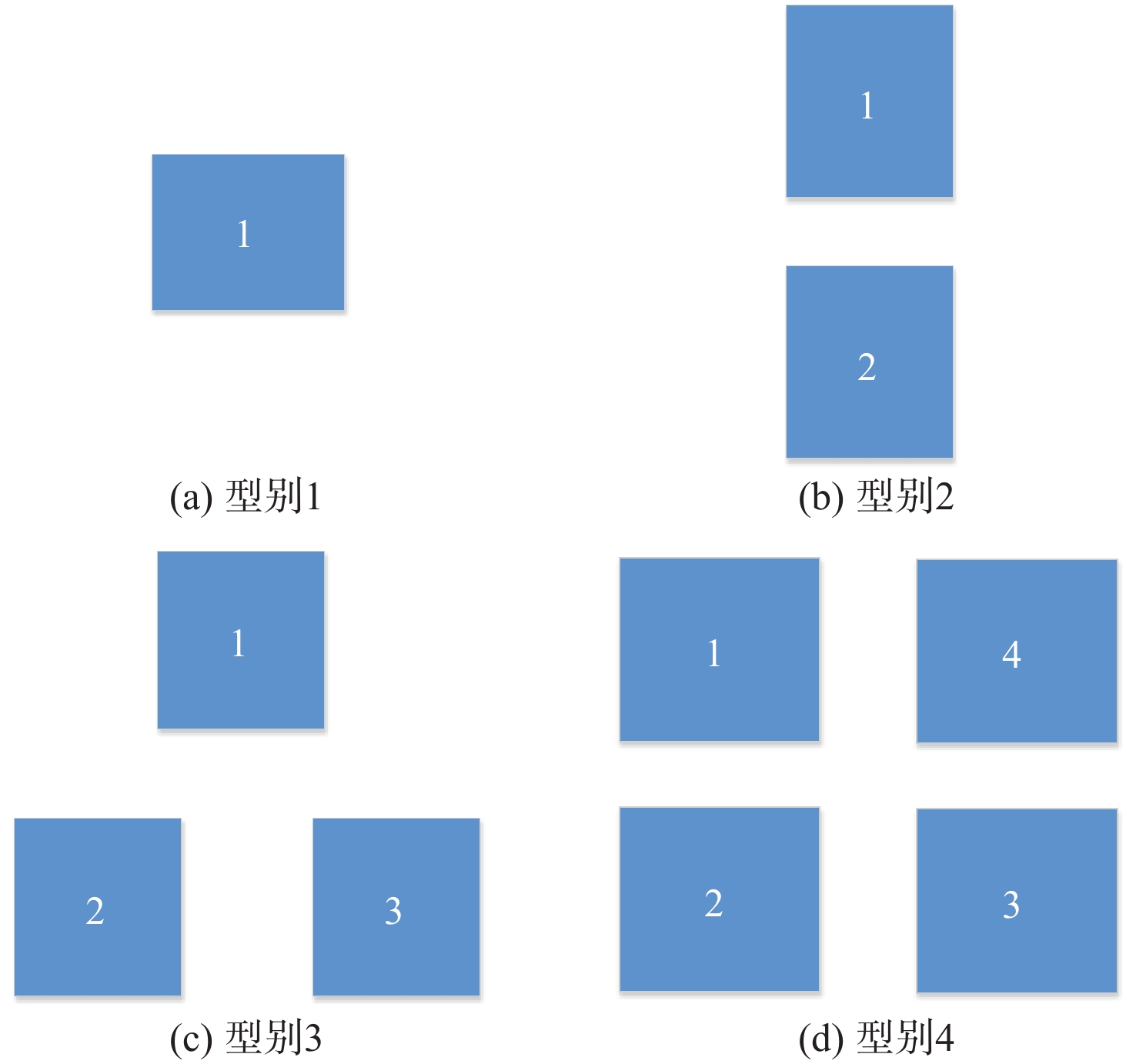
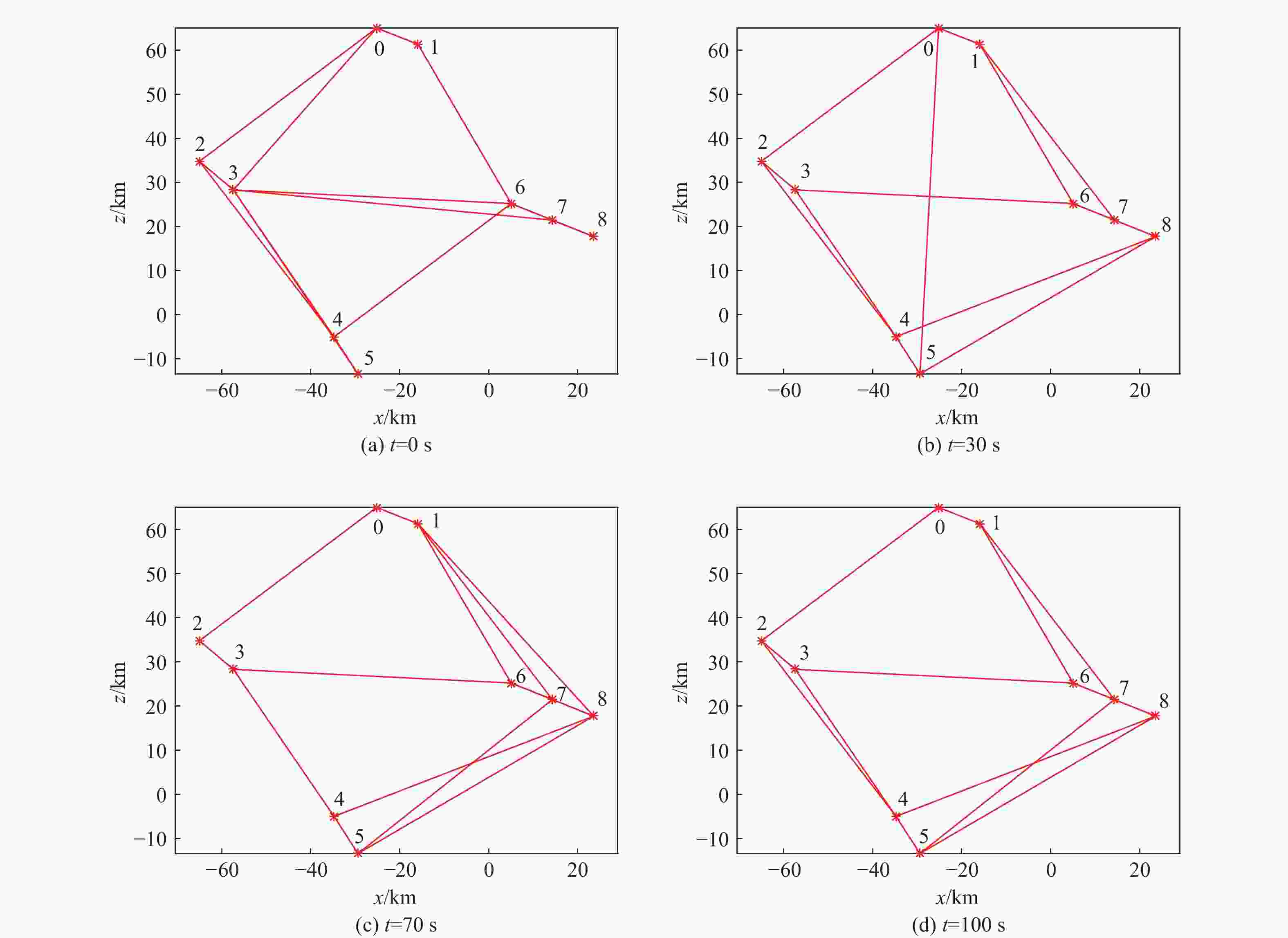
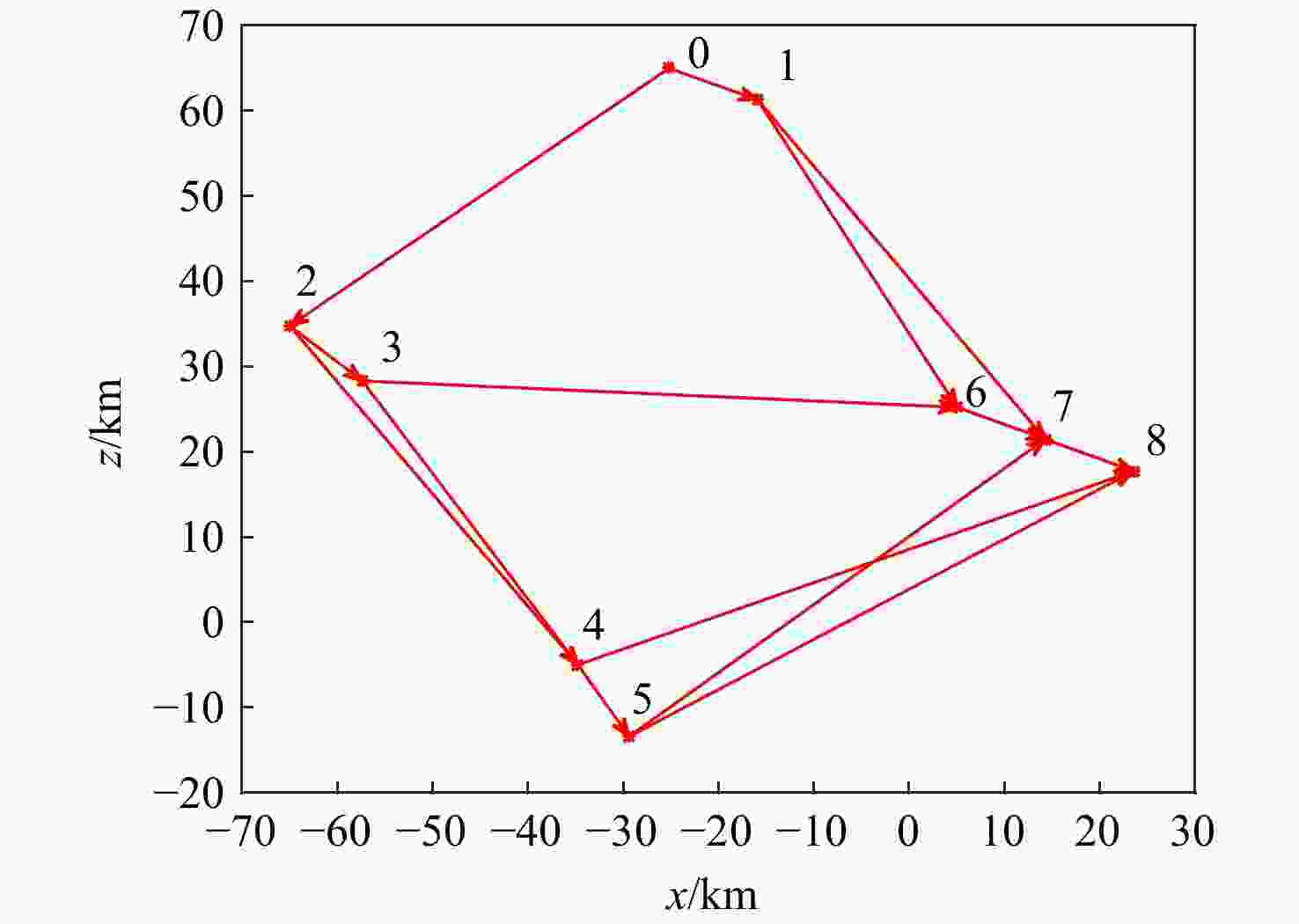
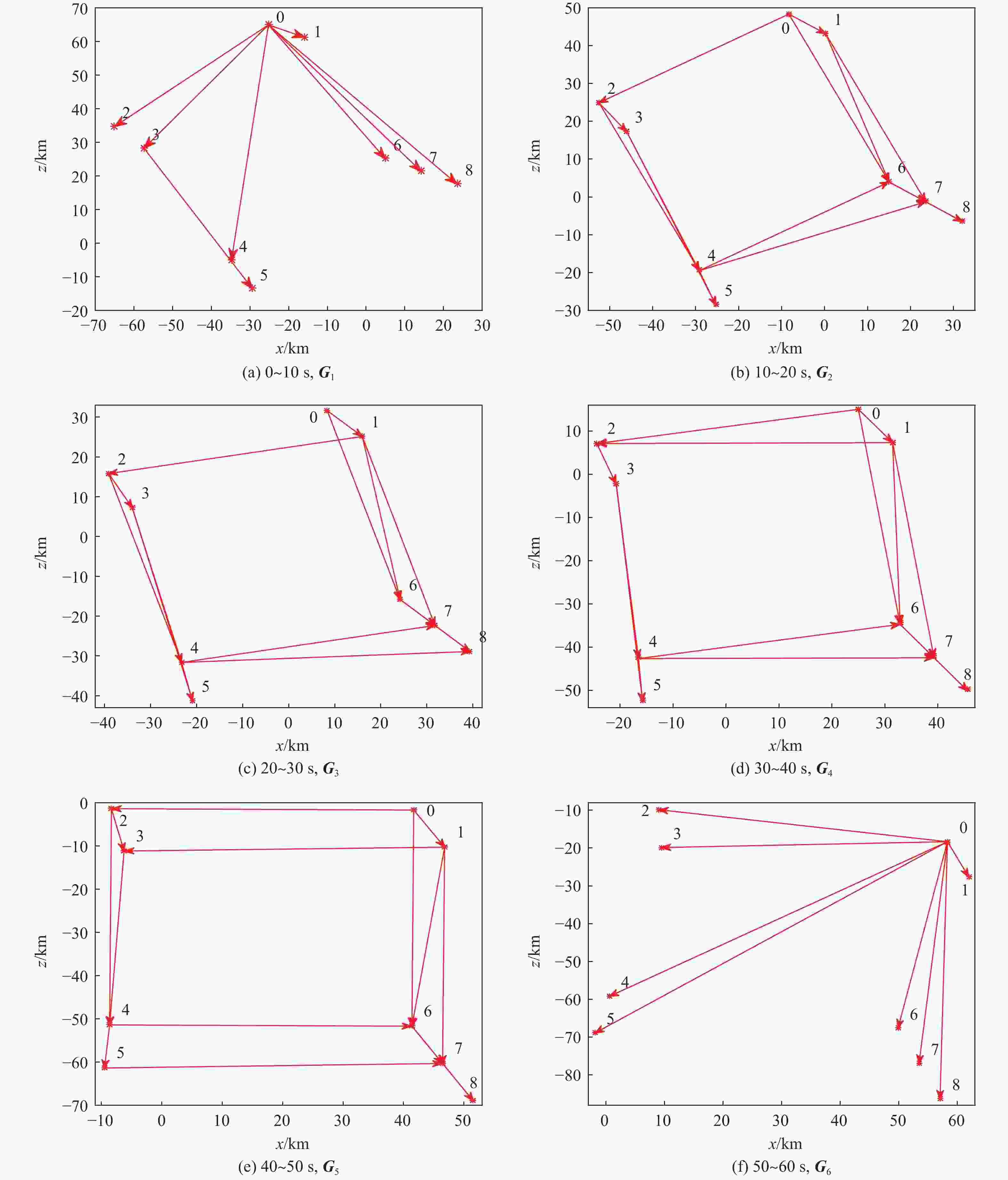
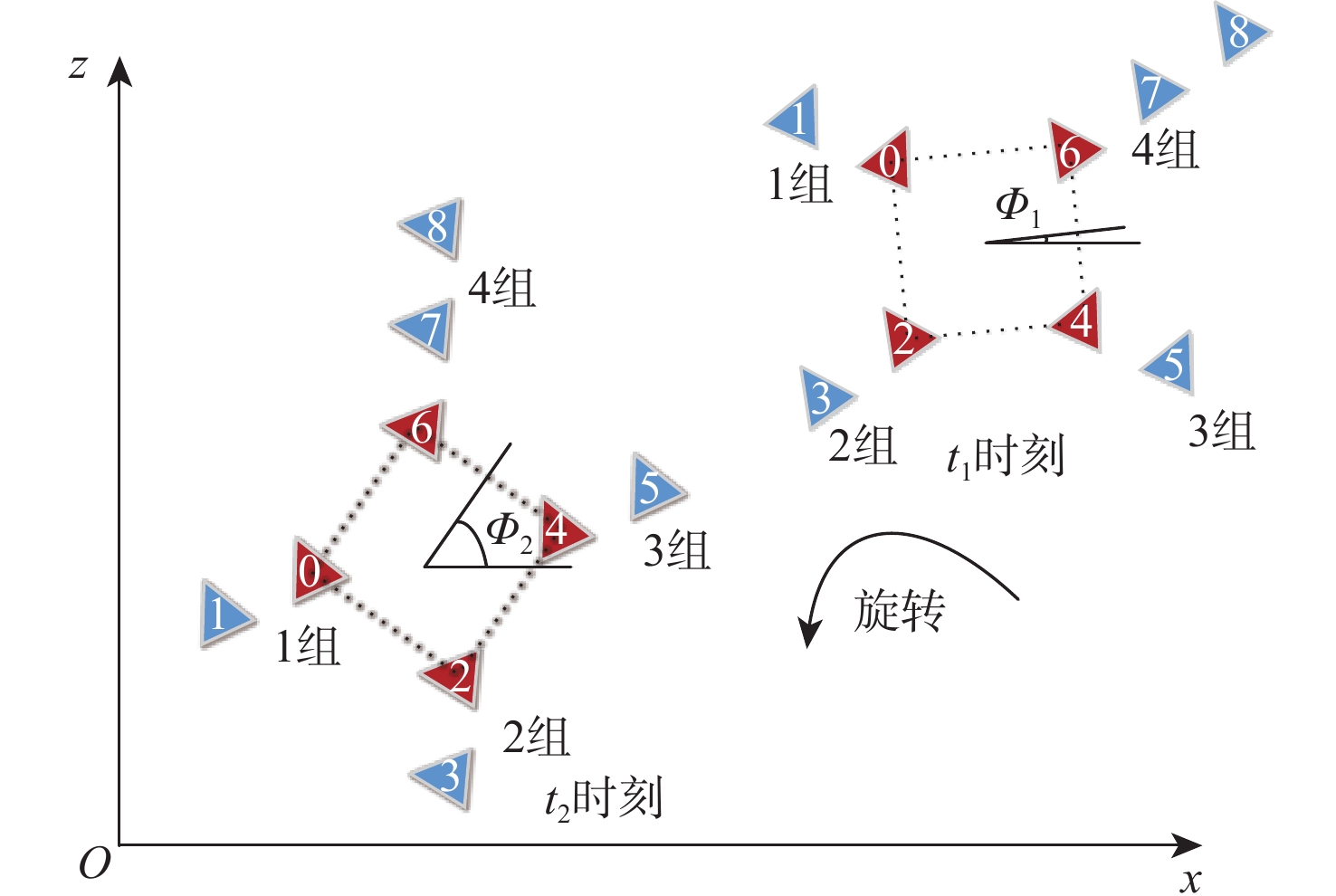
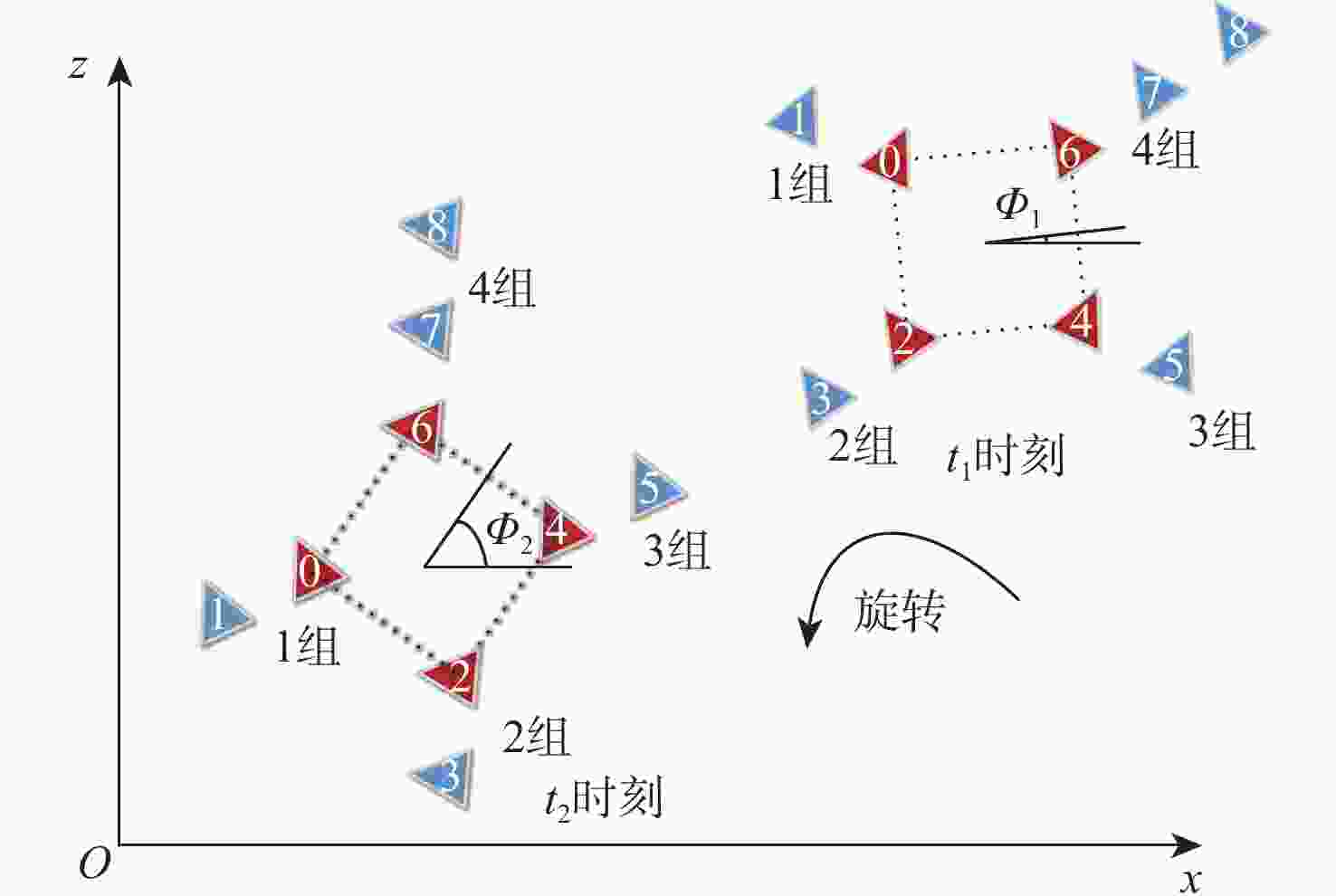
表 1 基本队形描述
Table 1. Basic formation description
基本队形 形状 尺寸变量 2 

2相对1顺时针
旋转角度$\theta $3 


2和3相对1顺时针
旋转角度$\theta $注:红色三角形代表组长。 表 2 阵位设置情况
Table 2. Formation setting
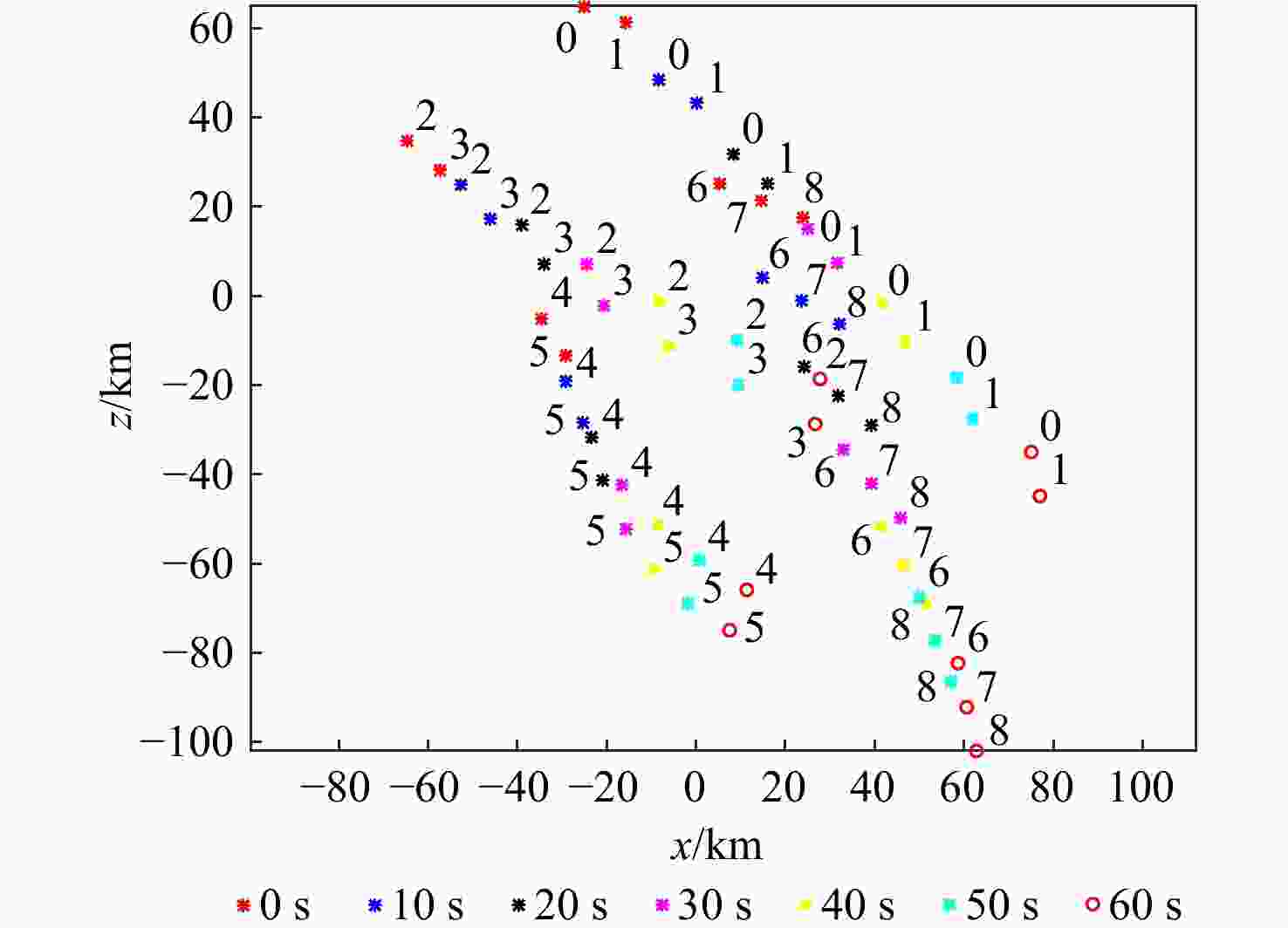
作战单元 x/km z/km 几何中心 −30 30 威胁1 40 −60 威胁2 40 −70 威胁3 30 −50 威胁4 50 −50 威胁5 60 −30 威胁6 70 −40 威胁7 80 −40 威胁8 60 −40 威胁9 60 −50 威胁10 60 −60 威胁11 70 −50 威胁12 70 −60 威胁13 70 −70 威胁14 80 −50 威胁15 80 −60 表 3 有翼飞行器性能指标
Table 3. Performance index of winged aircraft
${R_{\rm{DE}}}$/km ${\vartheta _{\mathrm{R}}}$/(°) ${P_{\rm{DE}}}$ ${K_{\rm{DE}}}$ ${m_{\rm{DE}}}$ $W$/m 180 65 0.95 1.6 3 0.8 ${\lambda^{\text{L}}}$/m ${A_{{\mathrm{RCS}}}}$/m2 ${m_{{\mathrm{des}}}}$ ${R_{{\mathrm{bat}}}}$/km $V$/(m·s−1) ${a_{\max }}$/(m·s−2) 5 0.3 0.5 300 2000 60 表 4 探测拦截威胁性能指标
Table 4. Performance indicators of detection and interception threat
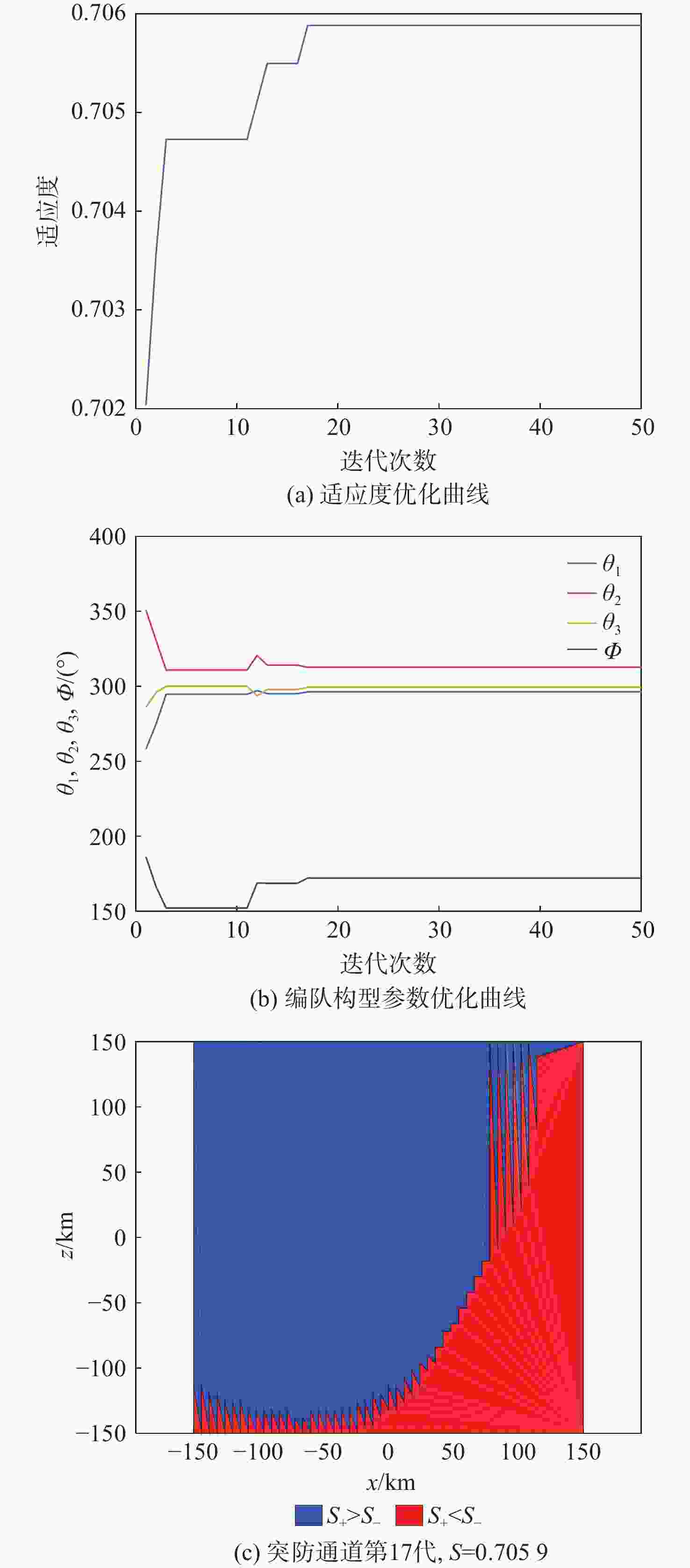
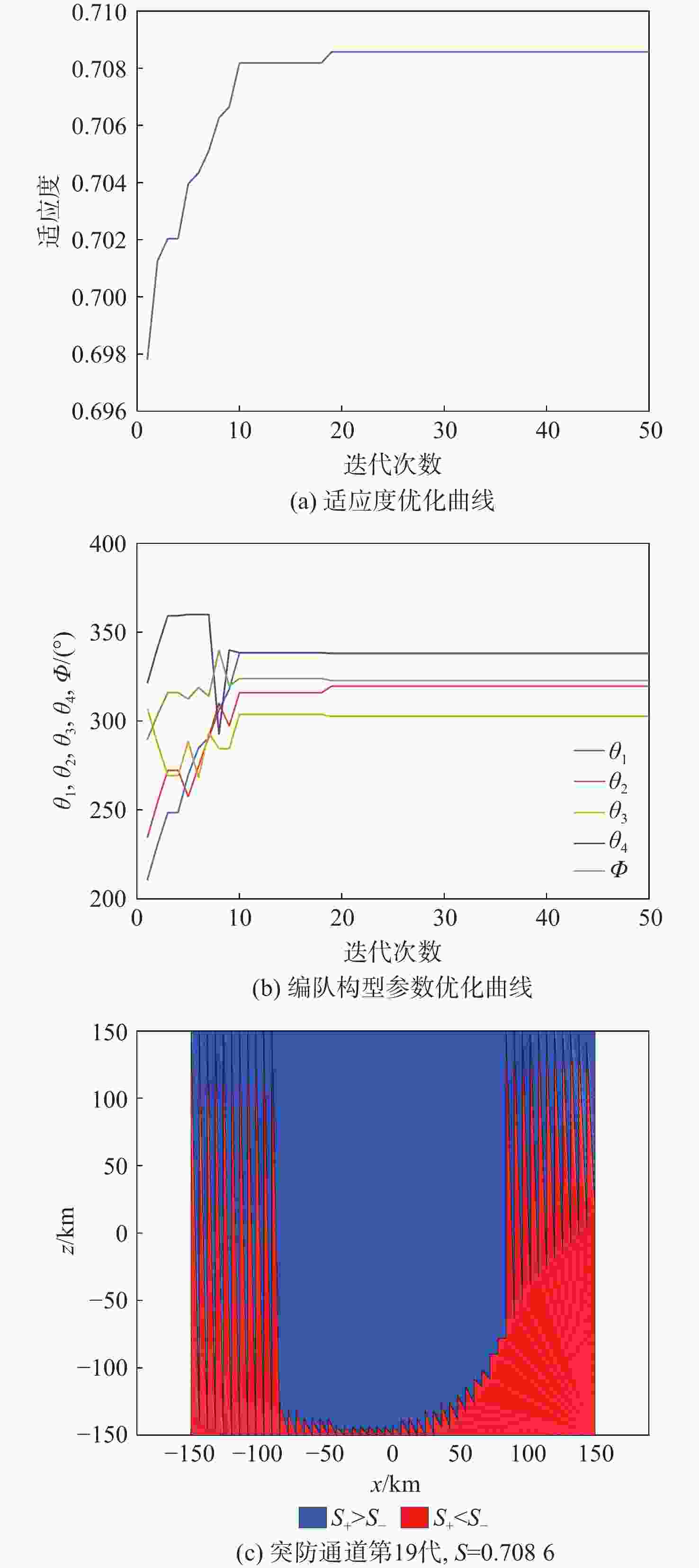
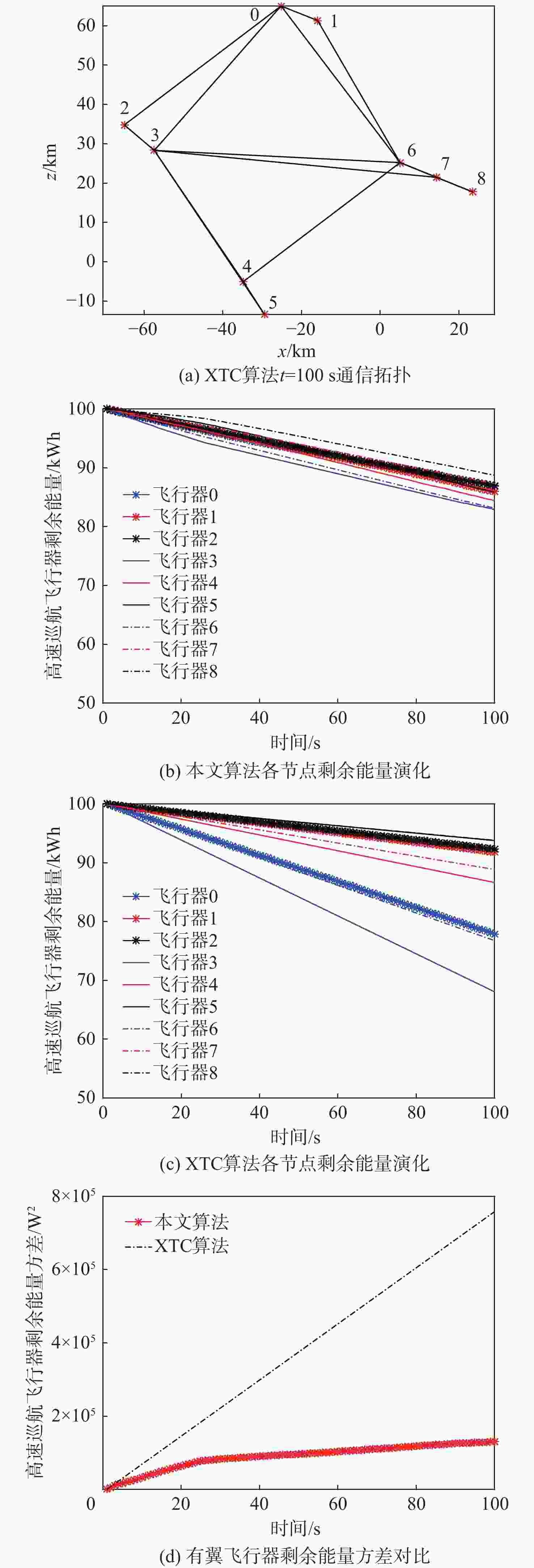
${R_{\rm{DE}}}$/km ${\vartheta _{\mathrm{R}}}$/(°) ${P_{\rm{DE}}}$ ${K_{\rm{DE}}}$ ${m_{\rm{DE}}}$ $W$/m 150 45 0.9 2 2 1 λL/m ${A_{{\mathrm{RCS}}}}$/m2 ${m_{{\mathrm{des}}}}$ ${R_{{\mathrm{bat}}}}$/km $V$/(m·s−1) ${a_{\max }}$/(m·s−2) 7 0.9 0.3 300 1000 120 表 5 编队构型优化参数对比
Table 5. Comparison of formation configuration optimization parameters
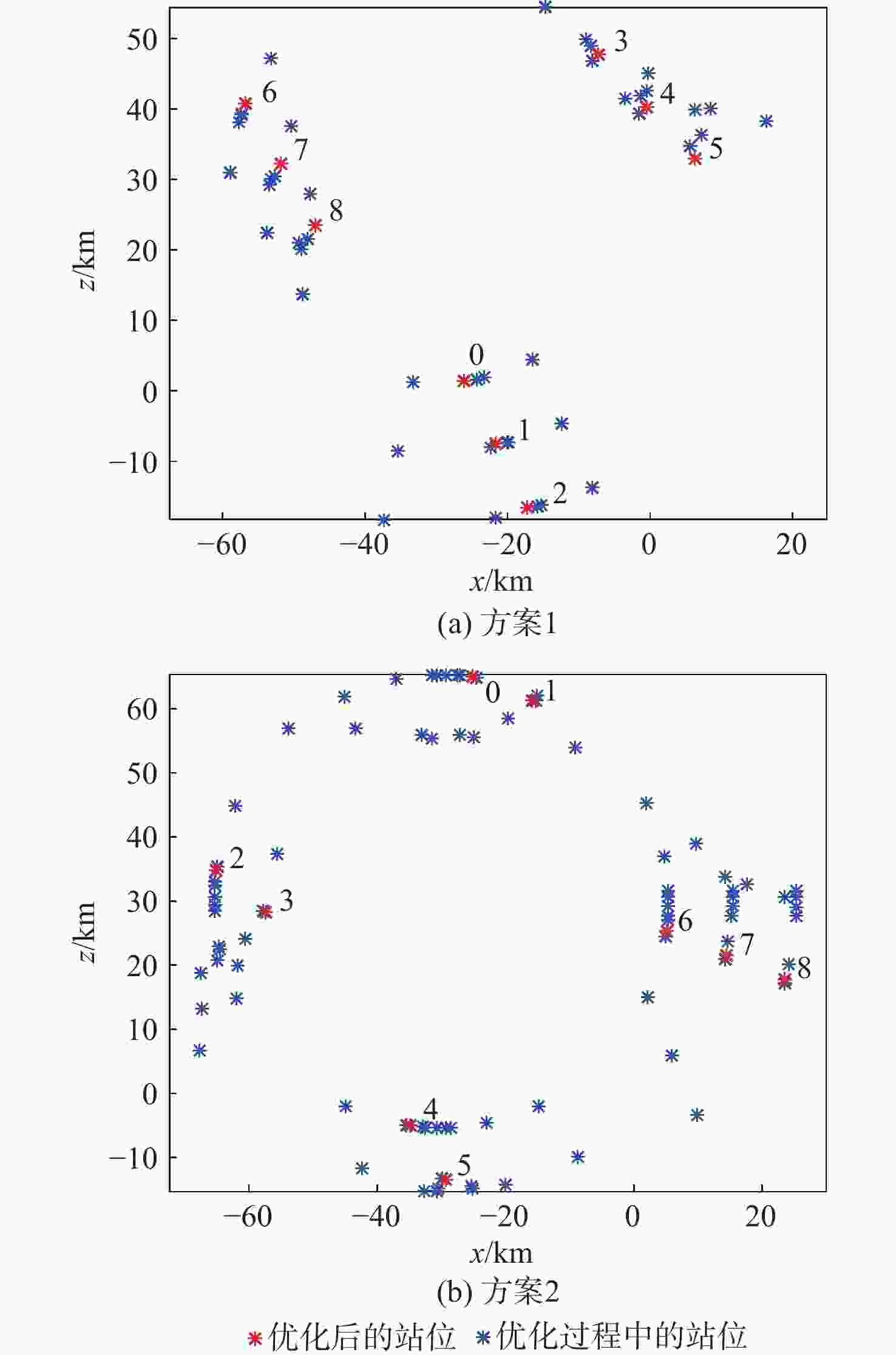
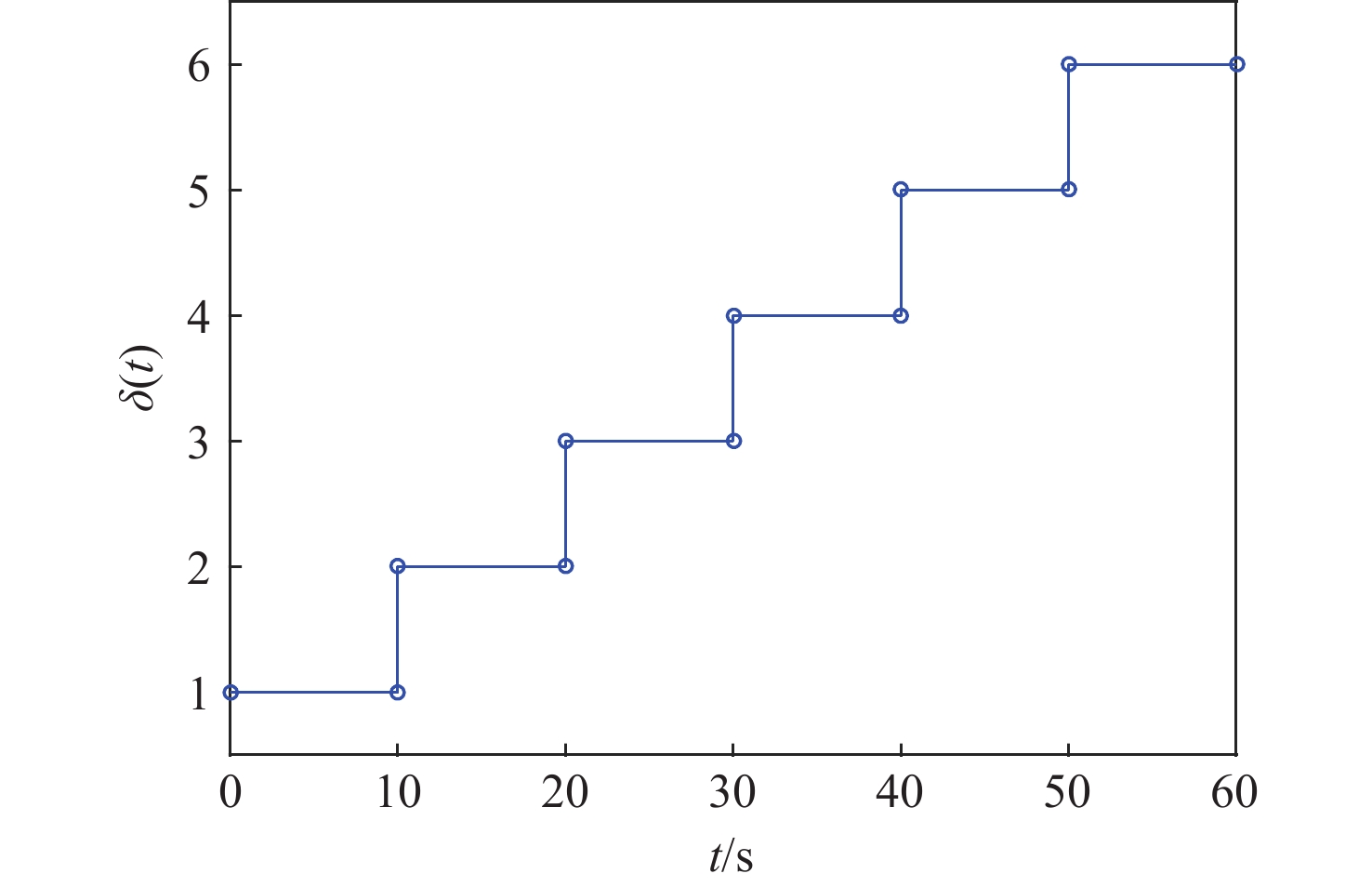
编组
方案最大
适应度迭代
次数组员绕组长的
旋转角度/(°)各组长绕型
别初始位置的
旋转角度/(°)方案1 0.7059 17 296.4,312.8,
299.5172.2 方案2 0.7086 19 338.3,319.6,
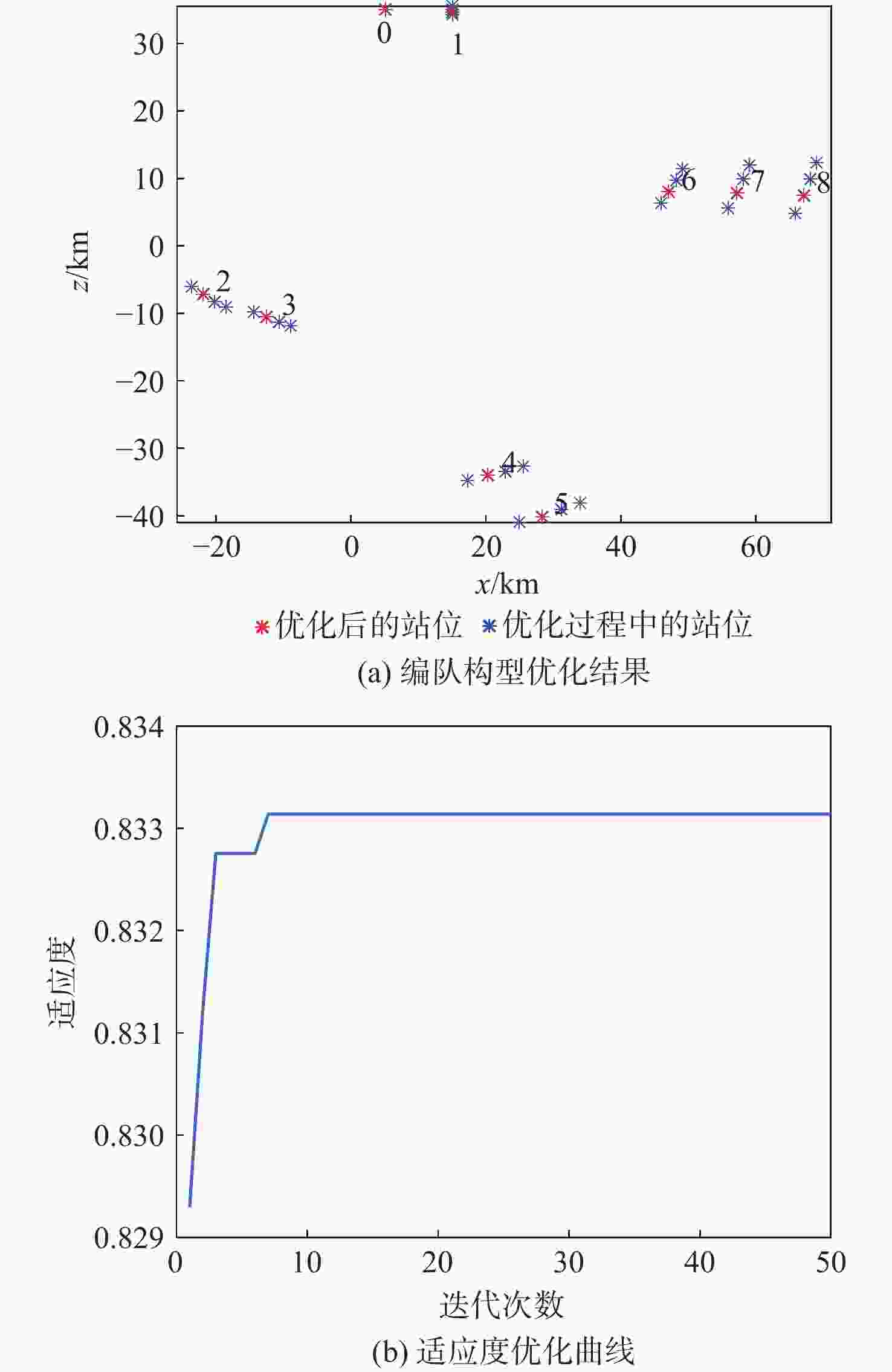
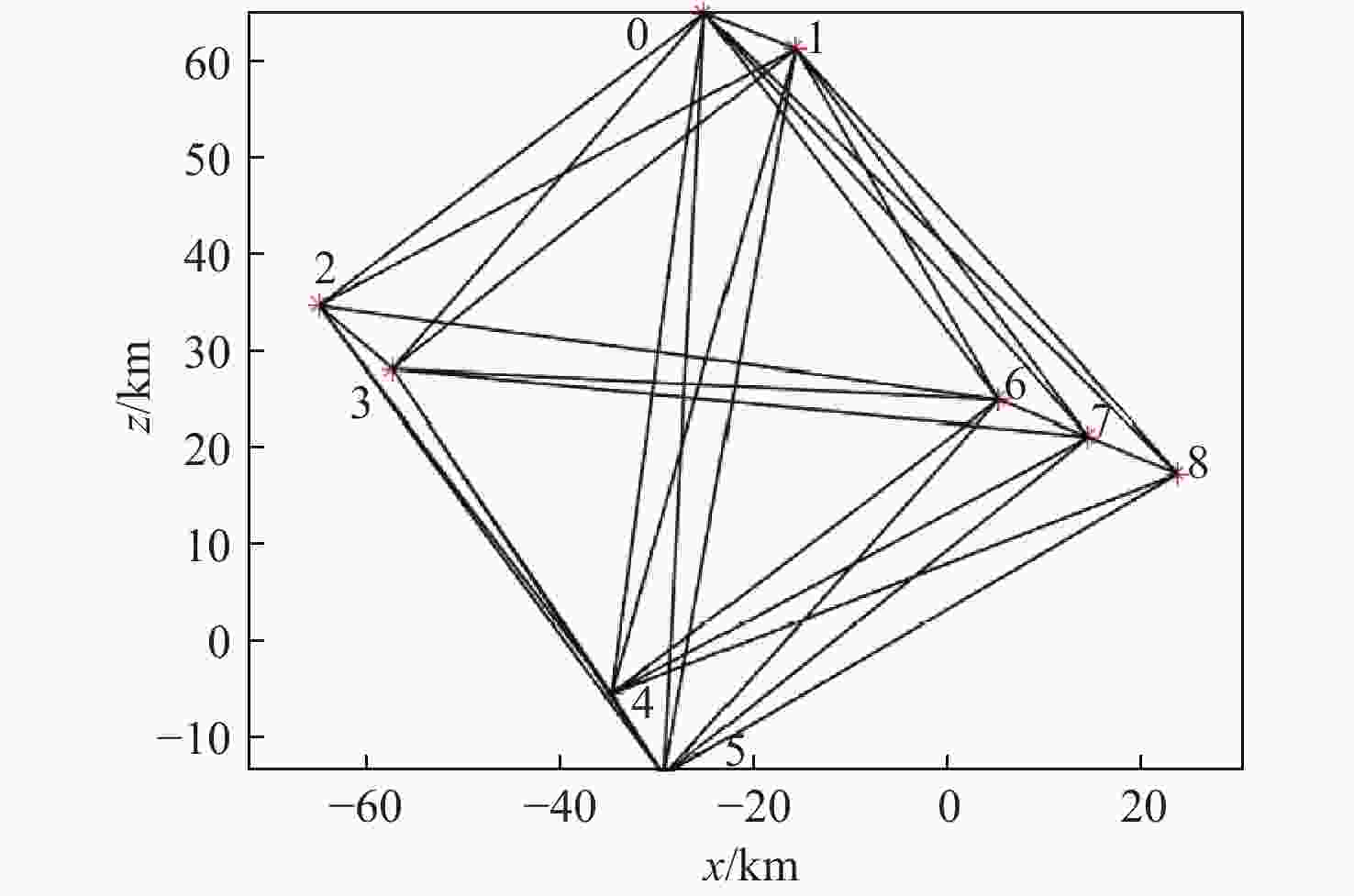
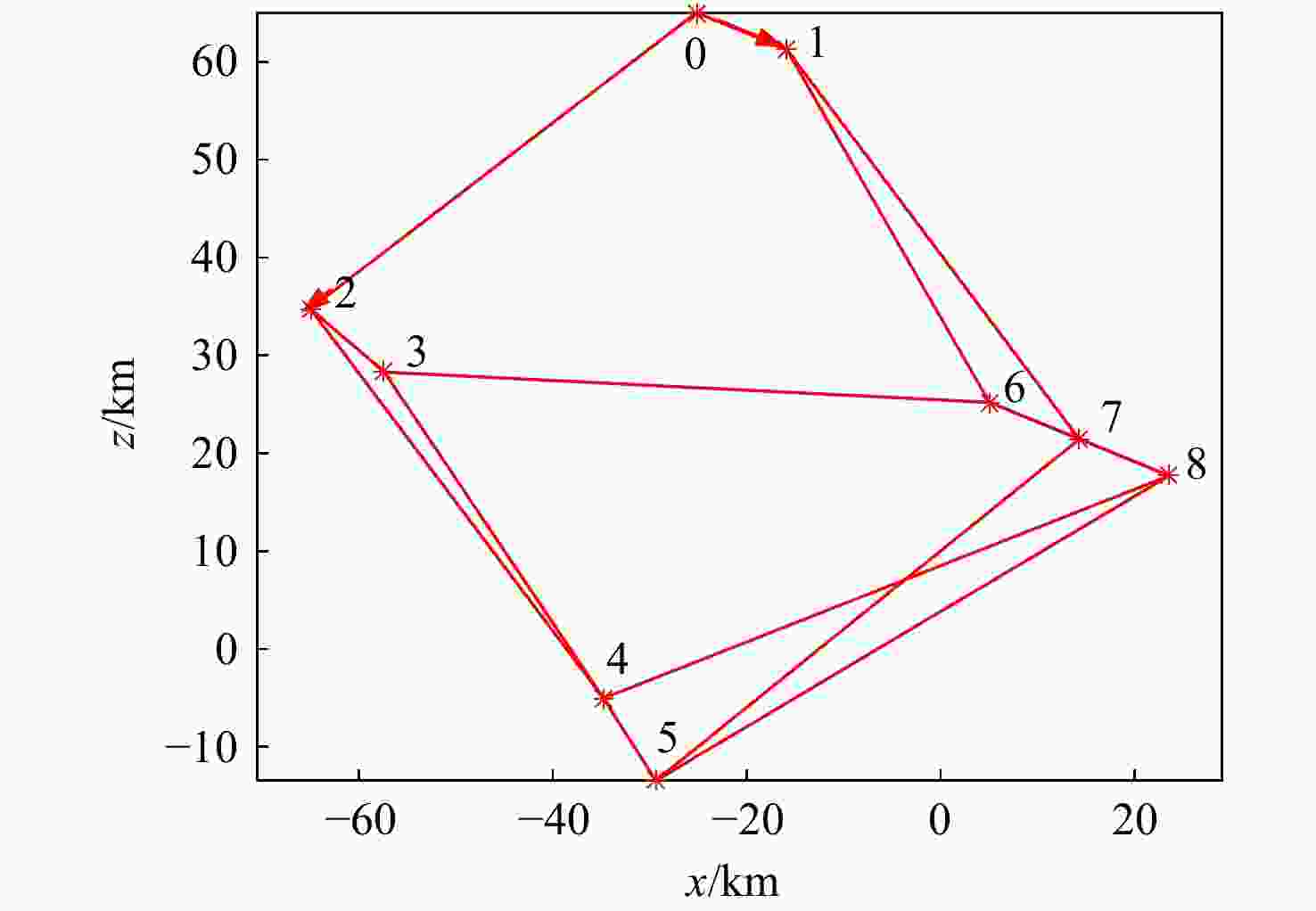
302.7,338322.8 表 6 时变编队构型参数设计结果
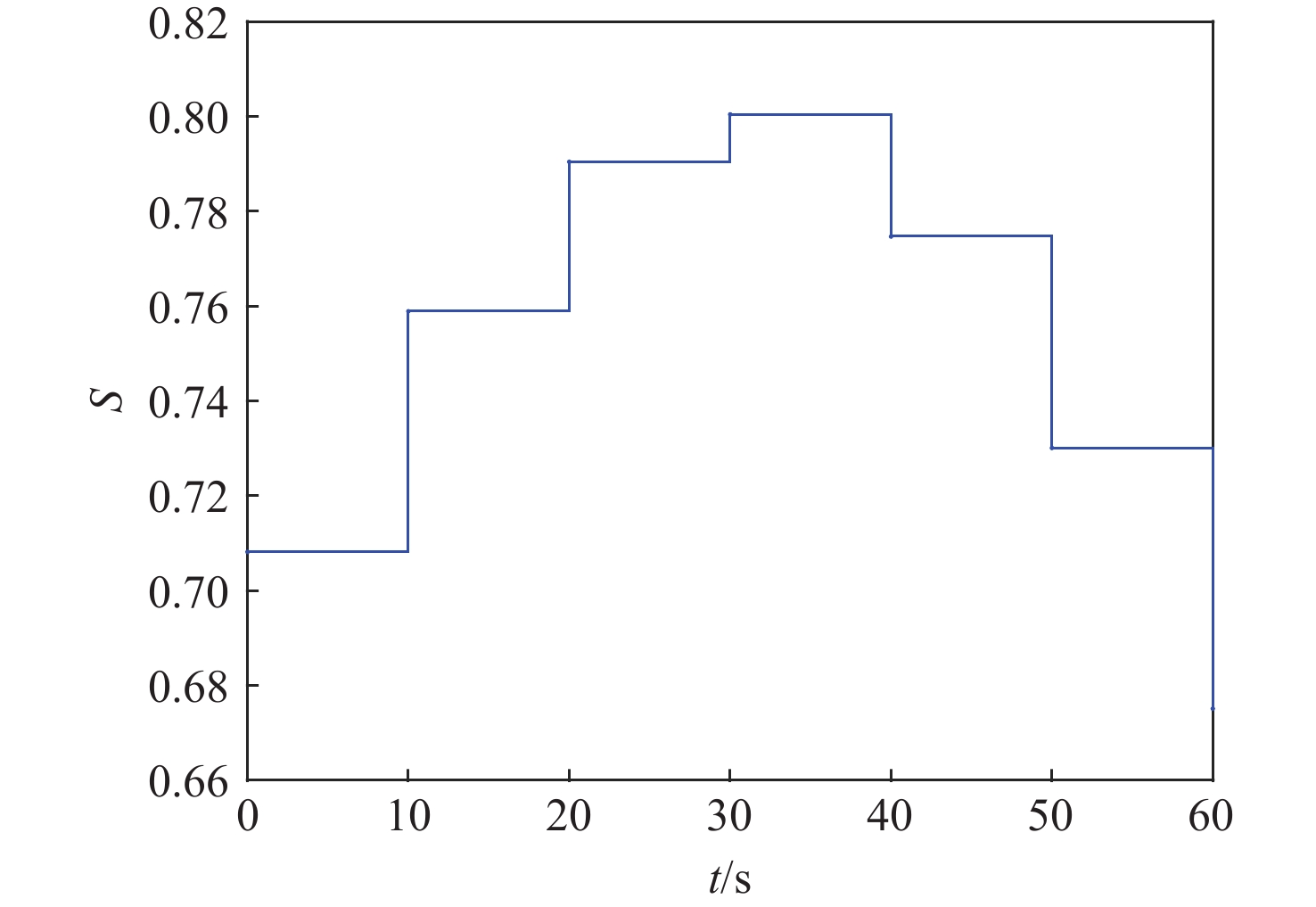
Table 6. Design results of time-varying formation vector parameters
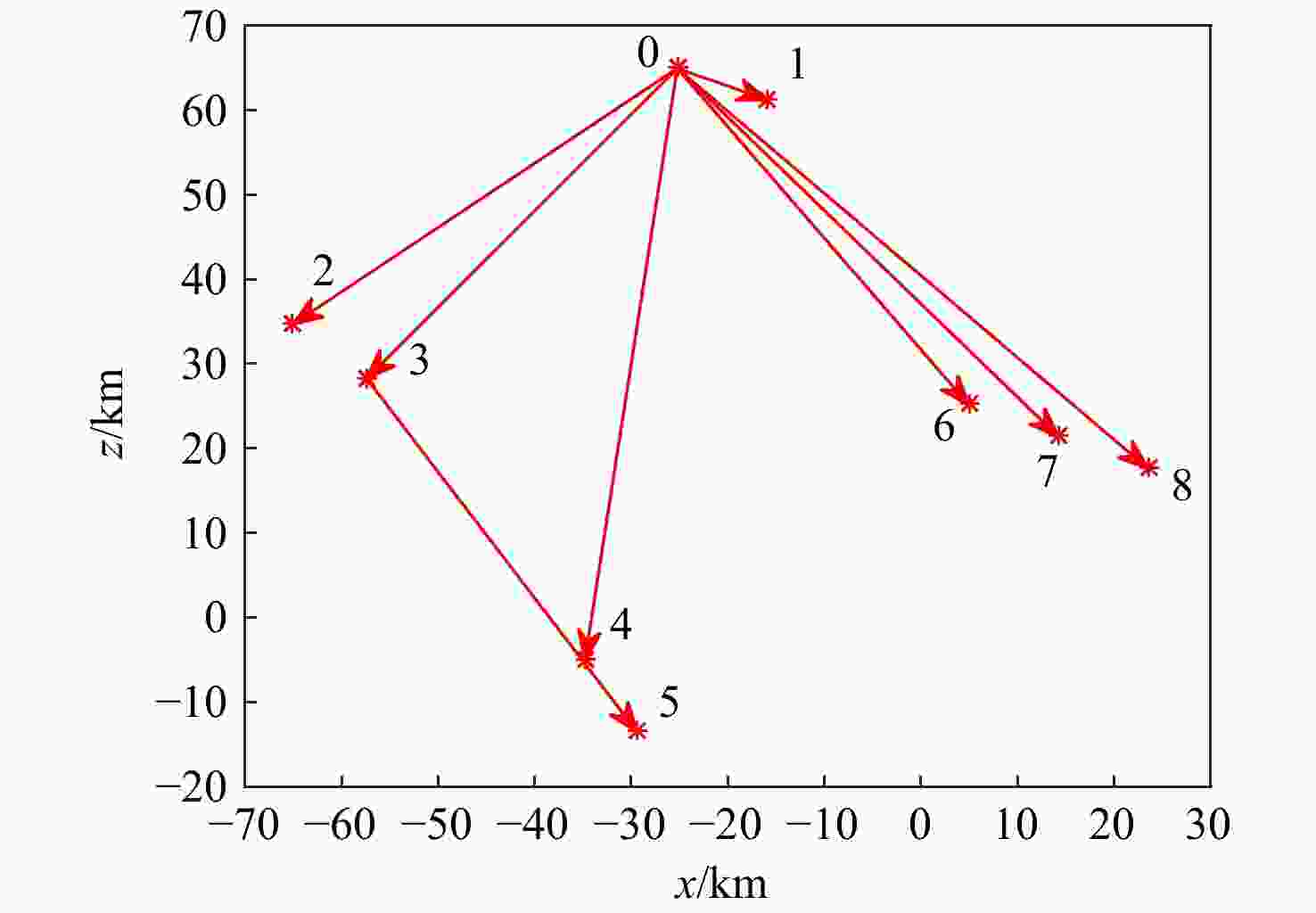
飞行器 相对距离${A_i}$/km 相对相位${\varphi _i}$/(°) 飞行器1 10 −21.71 飞行器2 50 −142.78 飞行器3 48.84 −131.25 飞行器4 70.71 −97.78 飞行器5 78.59 −93.05 飞行器6 50 −52.78 飞行器7 58.82 −47.8 飞行器8 67.96 −44.12 -
[1] 段海滨, 邱华鑫. 基于群体智能的无人机集群自主控制[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2018.DUAN H B, QIU H X. Unmanned aerial vehicle swarm autonomous control based on swarm intelligence[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2018(in Chinese). [2] 董文奇, 何锋. 大规模UAV编队信息交互拓扑的分级分布式生成[J]. 航空学报, 2021, 42(6): 324380.DONG W Q, HE F. Hierarchical and distributed generation of information interaction topology for large scale UAV formation[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2021, 42(6): 324380(in Chinese). [3] 冉华明, 熊蓉玲. 空战中机群编队分层优化算法[J]. 航空学报, 2020, 41(增刊2): 724257.RAN H M, XIONG R L. Hierarchical optimization algorithm for fleet formation in air combat[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2020, 41(Sup 2): 724257(in Chinese). [4] DUAN H B, ZHAO J X, DENG Y M, et al. Dynamic discrete pigeon-inspired optimization for multi-UAV cooperative search-attack mission planning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(1): 706-720. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2020.3029624 [5] 杨之元, 段海滨, 范彦铭. 基于莱维飞行鸽群优化的仿雁群无人机编队控制器设计[J]. 中国科学: 技术科学, 2018, 48(2): 161-169. doi: 10.1360/N092017-00127YANG Z Y, DUAN H B, FAN Y M. Unmanned aerial vehicle formation controller design via the behavior mechanism in wild geese based on Levy flight pigeon-inspired optimization[J]. Scientia Sinica (Technologica), 2018, 48(2): 161-169(in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/N092017-00127 [6] GUO J G, HU G J, GUO Z Y, et al. Evaluation model, intelligent assignment, and cooperative interception in multimissile and multitarget engagement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58(4): 3104-3115. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2022.3144111 [7] 于江龙, 董希旺, 李清东, 等. 拦截机动目标的分布式协同围捕制导方法[J]. 航空学报, 2022, 43(9): 325817.YU J L, DONG X W, LI Q D, et al. Distributed cooperative encirclement hunting guidance method for intercepting maneuvering target[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2022, 43(9): 325817(in Chinese). [8] WU J, LUO C B, LUO Y, et al. Distributed UAV swarm formation and collision avoidance strategies over fixed and switching topologies[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022, 52(10): 10969-10979. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2021.3132587 [9] SHIN H S, ANTONIADIS A F, TSOURDOS A. Parametric study on formation flying effectiveness for a blended-wing UAV[J]. Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, 2019, 93(1): 179-191. [10] ZHAO Q L, DONG X W, SONG X, et al. Time-varying formation pursuit based cooperative guidance for multiple missiles to intercept a maneuvering target[C]//Proceedings of the 37th Chinese Control Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 4779-4784. [11] 杨秀霞, 罗超, 张毅, 等. 导弹编队队形参数优化设计[J]. 飞行力学, 2018, 36(6): 54-58.YANG X X, LUO C, ZHANG Y, et al. Optimization for multi-missile formation parameters[J]. Flight Dynamics, 2018, 36(6): 54-58(in Chinese). [12] SUN Z Y, YANG J Y. Multi-missile interception for multi-targets: dynamic situation assessment, target allocation and cooperative interception in groups[J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2022, 359(12): 5991-6022. [13] DONG X W, ZHOU Y, REN Z, et al. Time-varying formation tracking for second-order multi-agent systems subjected to switching topologies with application to quadrotor formation flying[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64(6): 5014-5024. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2016.2593656 [14] WANG Y Z, SHAN M, WANG D W. Motion capability analysis for multiple fixed-wing UAV formations with speed and heading rate constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2020, 7(2): 977-989. doi: 10.1109/TCNS.2019.2929658 [15] 徐星光, 王晓峰, 姚璐, 等. 固定翼无人机编队构型与通信拓扑优化[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2022, 44(9): 2936-2946.XU X G, WANG X F, YAO L, et al. Formation configuration and communication topology optimization for fixed-wing UAVs[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(9): 2936-2946(in Chinese). [16] CUI G Z, XU H, CHEN X K, et al. Fixed-time distributed adaptive formation control for multiple QUAVs with full-state constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(4): 4192-4206. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2023.3237784 [17] DE LIMA FILHO G M, KUROSWISKI A R, MEDEIROS F L L, et al. Optimization of unmanned air vehicle tactical formation in war games[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 21727-21741. [18] YANG Y, LIU Q D, TAN H R, et al. Collision-free and connectivity-preserving formation control of nonlinear multi-agent systems with external disturbances[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 72(8): 9956-9968. [19] HU W J, YU Y, LIU S M, et al. Multi-UAV coverage path planning: a distributed online cooperation method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 72(9): 11727-11740. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2023.3266817 [20] WU Y, LIANG T J, GOU J Z, et al. Heterogeneous mission planning for multiple UAV formations via metaheuristic algorithms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(4): 3924-3940. [21] 王芳. 导弹编队协同突防—攻击一体化队形优化设计及最优控制研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2016.WANG F. Research on optimal design and optimal control of missile formation cooperative penetration-attack integrated formation[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2016(in Chinese). [22] GONG X, GONG L Q, HUANG T W, et al. Resilient path planning of UAV formation flight against covert attacks on ultra-wideband sensors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Cyber-Physical Systems, 2023, 1: 101-112. [23] GONG X, BASIN M V, FENG Z G, et al. Resilient time-varying formation-tracking of multi-UAV systems against composite attacks: a two-layered framework[J]. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2023, 10(4): 969-984. doi: 10.1109/JAS.2023.123339 [24] YIN T T, GU Z, XIE X P. Observer-based event-triggered sliding mode control for secure formation tracking of multi-UAV systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2023, 10(2): 887-898. doi: 10.1109/TNSE.2022.3223978 [25] ZHANG Z Y, DUAN H B, CHEN W. Leader-follower formation control via fixed-time distributed observer over directed topology: theories and applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2025, 72(9): 5033-5045. [26] XU L W, JIN X J, WANG Y, et al. Stochastic stable control of vehicular platoon time-delay system subject to random switching topologies and disturbances[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2022, 71(6): 5755-5769. [27] 王国强. 面向队形保持的无人机编队信息交互拓扑优化问题的研究[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2016.WANG G Q. Research on information exchange topology optimization problem of UAV formation during formation keeping[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2016(in Chinese). [28] ZHANG Y F, WU Z G, SHI P. Resilient event-/self-triggering leader-following consensus control of multiagent systems against DoS attacks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2023, 19(4): 5925-5934. doi: 10.1109/TII.2022.3187747 [29] JIANG X L, XIA G H. Nonfragile formation control of leaderless unmanned surface vehicles with memory sampling data and packet loss[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2023, 17(2): 3026-3035. [30] YANG J, SUN K X, HE H S, et al. Dynamic virtual topology aided networking and routing for aeronautical ad-hoc networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2022, 70(7): 4702-4716. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2022.3177599 [31] 冯志高, 关成启, 张红文. 高超声速飞行器概论[M]. 北京: 北京理工大学出版社, 2016.FENG Z G, GUAN C Q, ZHANG H W. An introduction to hypersonic aircraft[M]. Beijing: Beijing Insititute of Technology Press, 2016(in Chinese). [32] KOUSHIK A M, HU F, KUMAR S. Deep Q-learning-based node positioning for throughput-optimal communications in dynamic UAV swarm network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2019, 5(3): 554-566. [33] LUO X Y, ZHONG W J, LI X L, et al. Rigid graph-based three-dimension localization algorithm for wireless sensor networks[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 29(5): 927-936. doi: 10.21629/JSEE.2018.05.05 [34] LUO X, LIU D, GUAN X, et al. Flocking in target pursuit for multi-agent systems with partial informed agents[J]. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2012, 6(4): 560-569. [35] 罗小元, 邵士凯, 关新平, 等. 多智能体最优持久编队动态生成与控制[J]. 自动化学报, 2013, 39(9): 1431-1438.LUO X Y, SHAO S K, GUAN X P, et al. Dynamic generation and control of optimally persistent formation for multi-agent systems[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(9): 1431-1438(in Chinese). [36] BERADY A, JAUME M, TONG V V T, et al. From TTP to IoC: advanced persistent graphs for threat hunting[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 2021, 18(2): 1321-1333. [37] 罗贺, 李晓多, 王国强. 能耗均衡的三维最优持久编队通信拓扑生成[J]. 航空学报, 2022, 43(1): 324922.LUO H, LI X D, WANG G Q. Energy-balanced communication topology generation of three-dimensional optimally persistent formation[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2022, 43(1): 324922(in Chinese). [38] 徐星光, 廖志刚, 任章, 等. 战术导弹分层混合贝叶斯网络测试性建模和评价方法[J]. 战术导弹技术, 2019(6): 1-8.XU X G, LIAO Z G, REN Z, et al. Hierarchical hybrid testability modeling and evaluation based on Bayesian network for tactical missiles[J]. Tactical Missile Technology, 2019(6): 1-8(in Chinese). [39] KUHN F, WATTENHOFER R, ZOLLINGER A. An algorithmic approach to geographic routing in ad hoc and sensor networks[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2008, 16(1): 51-62. -






 下载:
下载: