-
摘要:
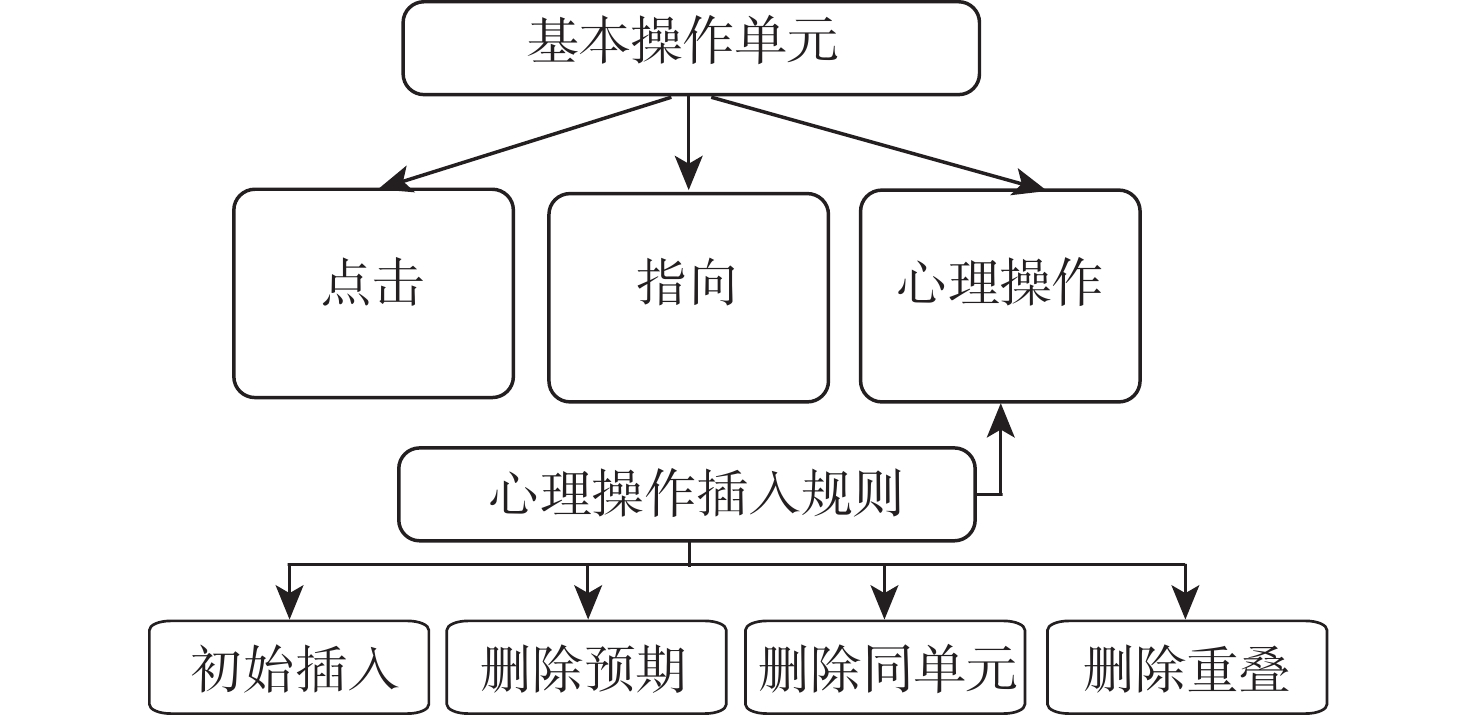
传统的击键水平模型(KLM)专注于键盘和鼠标的操作分析,适用于简单软件界面任务完成时间的快速定量评估,但将其迁移到包含复杂信息特征的指控系统软件界面评估时,却会产生较大误差。为此,基于KLM,结合用户视觉特性,面向指挥控制系统典型任务,提出基于用户视觉搜索处理时间的物理操作时间单元指标,并通过实验获取用户视觉搜索处理时间典型参数,建立更精确的指控系统任务操作分析模型—击键和视觉搜索模型(KLSM),即考虑视觉搜索特性因素的影响。选取5类典型指控任务,进行对比实验验证,KLSM对任务完成时间的预测评估更为准确。
Abstract:The traditional keystroke level model (KLM) focuses on the operation analysis of the keyboard and mouse, which is well-suited for efficiently quantifying job completion time in straightforward software interfaces. However, a significant error occurs when the software interface of the command and control system is transferred to evaluate complicated information characteristics. This paper introduces a physical operation time unit index for the command and control system, based on the visual search processing time of users. The index is derived from experiments that determine the typical parameters of user visual search processing time. Additionally, a more precise task operation analysis model called keystroke level and visual search model (KLSM) is established, which takes into account the impact of visual search characteristic factors. The comparative test examines the accuracy of the KLSM model in forecasting and evaluating the task completion time by using 5 typical command and control tasks as examples.
-
表 1 KLM基本操作时间
Table 1. Basic operation time of KLM
操作 典型值/s 含义 K 0.2 敲击键盘中一个键所用的时间 P 1.1 用户指向显示器某个位置所用的时间 M 1.35 用户进入下一步所需心理准备时间 表 2 不同任务中被试者平均注视时长
Table 2. Average gaze duration of subjects in different tasks
任务 平均注视时长/ms 标准差/ms 最大值/ms 最小值/ms 任务1 608.50 127.06 774.00 470.00 任务2 713.50 254.59 1132.00 393.00 任务3 646.17 210.35 885.00 377.00 任务4 707.67 173.02 948.00 446.00 任务5 724.33 377.64 1151.00 214.00 表 3 不同被试者的平均注视时长
Table 3. Average gaze duration of different subjects
被试者 平均注视时长/ms 标准差/ms 最大值/ms 最小值/ms 1 720.80 210.48 1003.00 477.00 2 851.60 187.30 1151.00 660.00 3 672.20 106.30 806.00 555.00 4 400.00 61.22 470.00 314.00 5 692.00 173.31 858.00 434.00 6 743.60 347.42 1132.00 214.00 表 4 各被试者多重比较
Table 4. Multiple comparisons for each subject
被试者 比较被试者 注视时长平均
值差值/msP值 95% 置信区间 下限 上限 1 2 −130.800 0.316 −394.66 133.06 3 48.600 0.707 −215.26 312.46 4 320.800* 0.019 56.94 584.66 5 28.800 0.824 −235.06 292.66 6 −22.800 0.860 −286.66 241.06 2 1 130.800 0.316 −133.06 394.66 3 179.400 0.173 −84.46 443.26 4 451.600* 0.002 187.74 715.46 5 159.600 0.224 −104.26 423.46 6 108.000 0.407 −155.86 371.86 3 1 −48.600 0.707 −312.46 215.26 2 −179.400 0.173 −443.26 84.46 4 272.200* 0.044 8.34 536.06 5 −19.800 0.878 −283.66 244.06 6 −71.400 0.582 −335.26 192.46 4 1 −320.800* 0.019 −584.66 −56.94 2 −451.600* 0.002 −715.46 −187.74 3 −272.200* 0.044 −536.06 −8.34 5 −292.000* 0.032 −555.86 −28.14 6 −343.600* 0.013 −607.46 −79.74 5 1 −28.800 0.824 −292.66 235.06 2 −159.600 0.224 −423.46 104.26 3 19.800 0.878 −244.06 283.66 4 292.000* 0.032 28.14 555.86 6 −51.600 0.690 −315.46 212.26 6 1 22.800 0.860 −241.06 286.66 2 −108.000 0.407 −371.86 155.86 3 71.400 0.582 −192.46 335.26 4 343.600* 0.013 79.74 607.46 5 51.600 0.690 −212.26 315.46 注:*表示平均值差值的显著性水平为0.05。 表 5 平均注视时长总体描述统计结果
Table 5. Overall descriptive statistical results for mean gaze duration
平均值/
ms标准差/
ms最小值/
ms最大值/
ms百分位数下的平均注视时长/ms 第25个 第50个 第75个 680.03 231.148 214 1151 475.25 668.50 840.00 表 6 KLSM基本参数
Table 6. Basic parameters of KLSM
操作 典型值/s 含义 K 0.2 敲击键盘中一个键所用的时间 P 1.1 用户指向显示器某个位置所用的时间 S 0.67 用户查看一个信息点所用的时间 M 1.35 用户进入下一步所需心理准备时间 表 7 2类模型的任务步骤分解
Table 7. Decomposition of task steps for two types of models
任务流程 具体操作步骤 KLM单
元分解KLSM单
元分解开启界面 ①双击系统图标,点击下拉框,选择相应席位,点击
“登录”2P+5K+1M 2P+5K+1M+3S ②点击“集群”“任务管理”,弹出任务界面 1P+2K 1P+2K+2S 规划任务 ③在任务列表中选择一个任务,点击“任务规划”,弹出窗口 1M+1P+2K 1M+1P+2K+2S ④点击“任务规划调整”
进行2位成员的分组修改, 点击“提交修改”2P+4K+1M 2P+4K+1M+4S 修改信息 ⑤选择通道,点击“成员信息”“信道调整”,弹出对话框,选中成员,拖动信道调整 1M+2P+3K 1M+2P+3K+6S ⑥点击“提交”,弹出“保存成功”提示框,点击确定 1P+2K 1P+2K+3S 绑定站点 ⑦点击“集群”“规划”
弹出对话框。选中信息,点击“绑定”1M+1P+4K 1M+1P+4K+4S 集群申请 ⑧在信息框中选择可用站点,点击“申请” 1M+1P+2K 1M+1P+2K+2S ⑨弹出确认弹窗,先点击对应标识,再点击“确定”,完成申请 1P+2K 1P+2K+2S 表 8 任务操作总时长
Table 8. Total task operation time
被试者 操作总时长/s 1 52.508 2 45.031 3 76.704 4 59.386 5 115.252 6 42.060 表 9 5类任务操作单元分解对比
Table 9. Comparison of task decomposition under five types of tasks
任务 KLM模型 KLSM模型 任务1 6M+12P+26K 6M+12P+26K+29S 任务2 8M+13P+28K 8M+13P+28K+30S 任务3 4M+10P+22K 4M+10P+22K+19S 任务4 15M+17P+40K 15M+17P+40K+10S 任务5 5M+11P+23K 5M+11P+23K+22S 表 10 5类任务下模型预测时长对比
Table 10. Comparison of model prediction duration under five types of tasks
任务 KLM预测
时长/sKLSM预测
时长/s视觉搜索
处理时间/s实际任务
时长/s任务1 26.50 45.93 19.43 55.138 任务2 30.70 50.80 20.10 60.365 任务3 20.80 33.53 12.73 40.267 任务4 46.95 53.65 6.70 58.602 任务5 23.45 38.19 14.74 44.820 -
[1] 王璐, 霍其恩, 李青山, 等. 基于并行搜索优化的指控系统自适应决策方法[J]. 软件学报, 2022, 33(5): 1774-1799.WANG L, HUO Q E, LI Q S, et al. Self-adaptation decision-making based on parallel search optimization for command and control information system[J]. Journal of Software, 2022, 33(5): 1774-1799(in Chinese). [2] 周海瑞, 李皓昱, 介冲. 美军联合作战指挥体制及其指挥控制系统[J]. 指挥信息系统与技术, 2016, 7(5): 10-18.ZHOU H R, LI H Y, JIE C. Military joint operation command system and its C2 systems[J]. Command Information System and Technology, 2016, 7(5): 10-18(in Chinese). [3] 王颖, 牟苏斌. 基于GOMS模型的机载指控系统人机界面优化研究[J]. 计算机与数字工程, 2016, 44(7): 1378-1382. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9722.2016.07.041WANG Y, MOU S B. Human computer interface optimization based on GOMS model for airborne command and control system[J]. Computer & Digital Engineering, 2016, 44(7): 1378-1382(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9722.2016.07.041 [4] 陈建明, 金传洋, 魏琨. 装甲指控软件的可用性问题研究[J]. 计算机测量与控制, 2013, 21(8): 2278-2281. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4598.2013.08.077CHEN J M, JIN C Y, WEI K. Study on usability problem of command and control software for armored vehicle[J]. Computer Measurement& Control, 2013, 21(8): 2278-2281(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4598.2013.08.077 [5] REN F J, BAO Y W. A review on human-computer interaction and intelligent robots[J]. International Journal of Information Technology & Decision Making, 2020, 19(1): 5-47. [6] CARD K S. The psychology of human-computer interaction[M]. New York: CRC Press, 2018: 12-48. [7] SCHREPP M. GOMS analysis as a tool to investigate the usability of web units for disabled users[J]. Universal Access in the Information Society, 2010, 9(1): 77-86. doi: 10.1007/s10209-009-0155-2 [8] JUNG K, JANG J. Development of a two-step touch method for website navigation on smartphones[J]. Applied Ergonomics, 2015, 48: 148-153. doi: 10.1016/j.apergo.2014.11.006 [9] HUANG P H, CHIU M C. Integrating user centered design, universal design and goal, operation, method and selection rules to improve the usability of DAISY player for persons with visual impairments[J]. Applied Ergonomics, 2016, 52: 29-42. doi: 10.1016/j.apergo.2015.06.008 [10] RAMKUMAR A, STAPPERS P J, NIESSEN W J, et al. Using GOMS and NASA-TLX to evaluate human–computer interaction process in interactive segmentation[J]. International Journal of Human-Computer Interaction, 2017, 33(2): 123-134. doi: 10.1080/10447318.2016.1220729 [11] ROSE J A, BEARMAN C. Making effective use of task analysis to identify human factors issues in new rail technology[J]. Applied Ergonomics, 2012, 43(3): 614-624. doi: 10.1016/j.apergo.2011.09.005 [12] CHRISTOU G, RITTER F E, JACOB R J K. Codein—A new notation for GOMS to handle evaluations of reality-based interaction style interfaces[J]. International Journal of Human-Computer Interaction, 2012, 28(3): 189-201. doi: 10.1080/10447318.2011.581893 [13] CARD S K, MORAN T P, NEWELL A. The psychology of human-computer interaction[M]. Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Inc, 1983: 12-33. [14] FINDLATER L, FROEHLICH J E, FATTAL K, et al. Age-related differences in performance with touchscreens compared to traditional mouse input[C]//Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. New York: ACM, 2013: 343-346. [15] 赵欣, 陈凯翔, 谷贺瑾, 等. 基于触屏移动操作界面的KLM模型改良[J]. 包装工程, 2018, 39(16): 31-35.ZHAO X, CHEN K X, GU H J, et al. Evolving KLM for touchscreen based mobile interface[J]. Packaging Engineering, 2018, 39(16): 31-35(in Chinese). [16] 张楠, 苏玉婷, 廖斌. 时间压力视角下人格特征与视觉搜索策略及绩效的关系[J]. 人类工效学, 2023, 29(3): 25-29.ZHANG N, SU Y T, LIAO B. A study on the relationship between personality trait and visual search strategy and performance in a time pressure perspective[J]. Chinese Journal of Ergonomics, 2023, 29(3): 25-29(in Chinese). [17] 田晨智, 宋敏, 田继伟, 等. 基于眼动追踪的指挥控制系统人机交互效能评估方法[J]. 航空兵器, 2023, 30(4): 57-66.TIAN C Z, SONG M, TIAN J W, et al. Evaluation method of human-computer interaction effectiveness of command and control system based on eye tracking[J]. Aero Weaponry, 2023, 30(4): 57-66(in Chinese). [18] GOLDBERG J H, KOTVAL X P. Computer interface evaluation using eye movements: Methods and constructs[J]. International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, 1999, 24(6): 631-645. doi: 10.1016/S0169-8141(98)00068-7 [19] POOLE A, BALL L J. Eye tracking in HCI and usability research[J]. Medicine, 2005, 1: 211-219. -







 下载:
下载:





