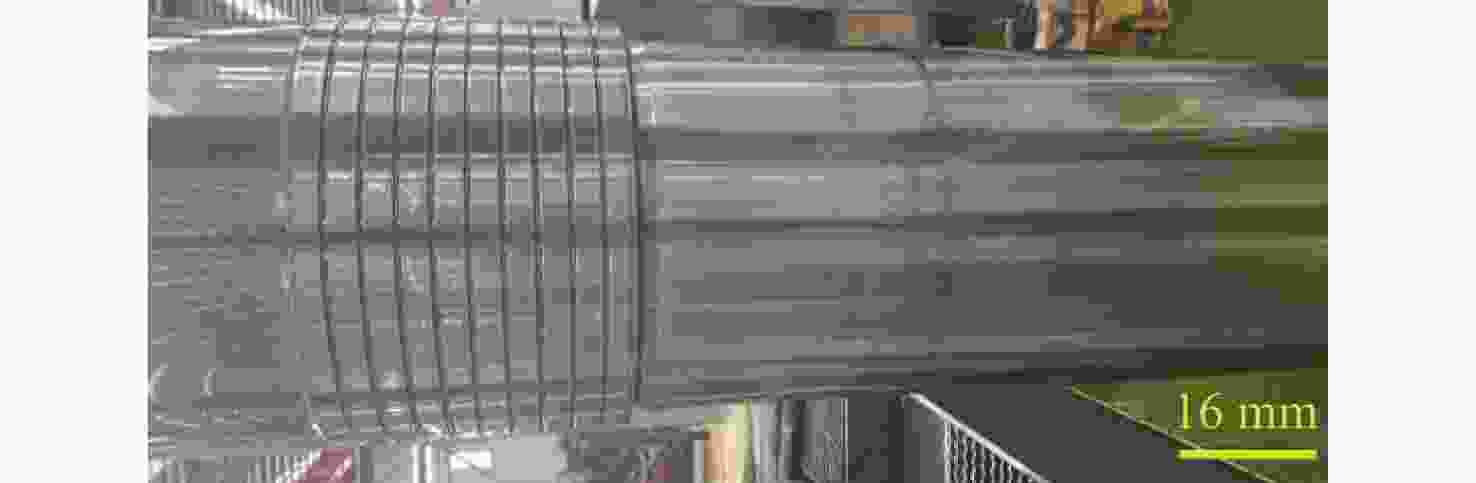
Mechanism analysis and process optimization of transverse cracking of hydraulic crushing hammer piston
-
摘要:
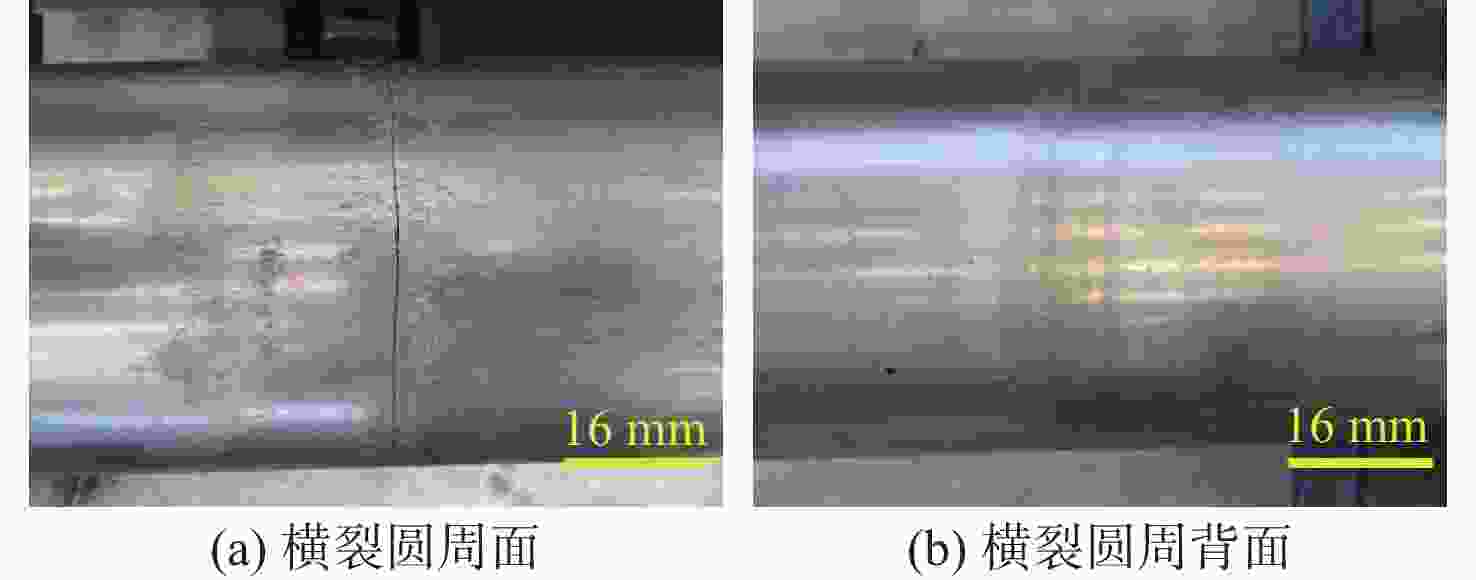
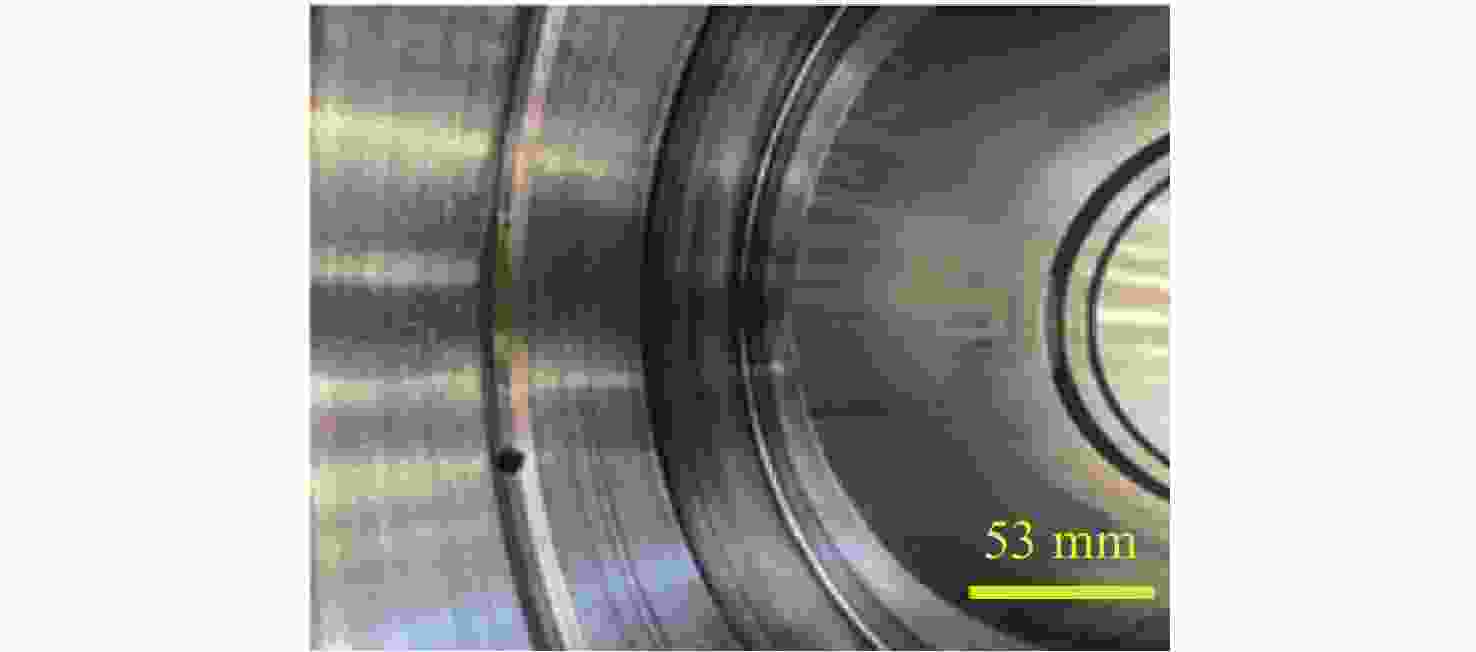
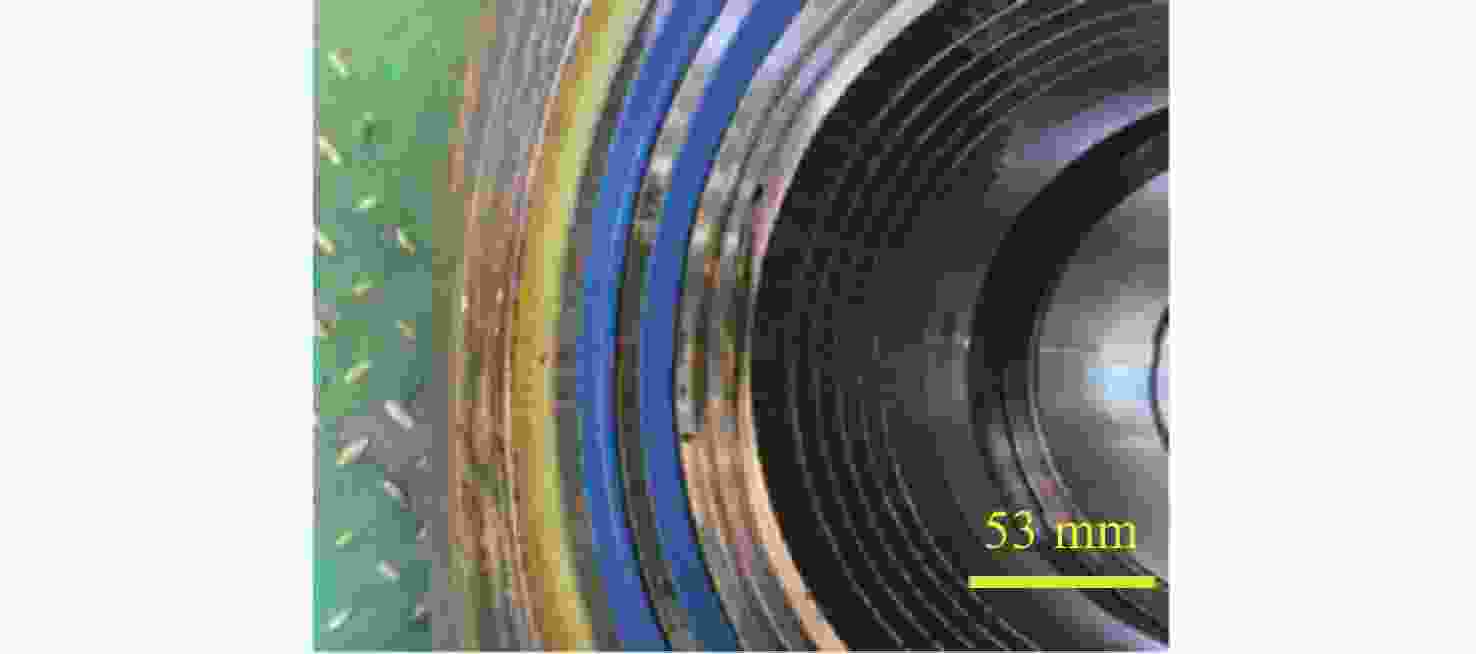
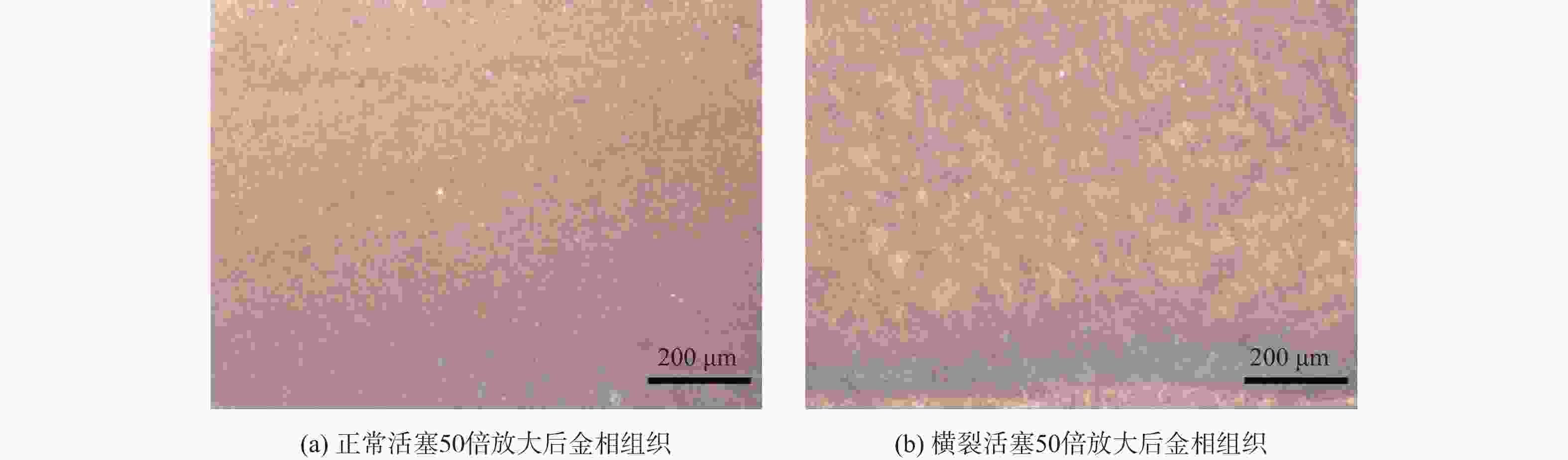
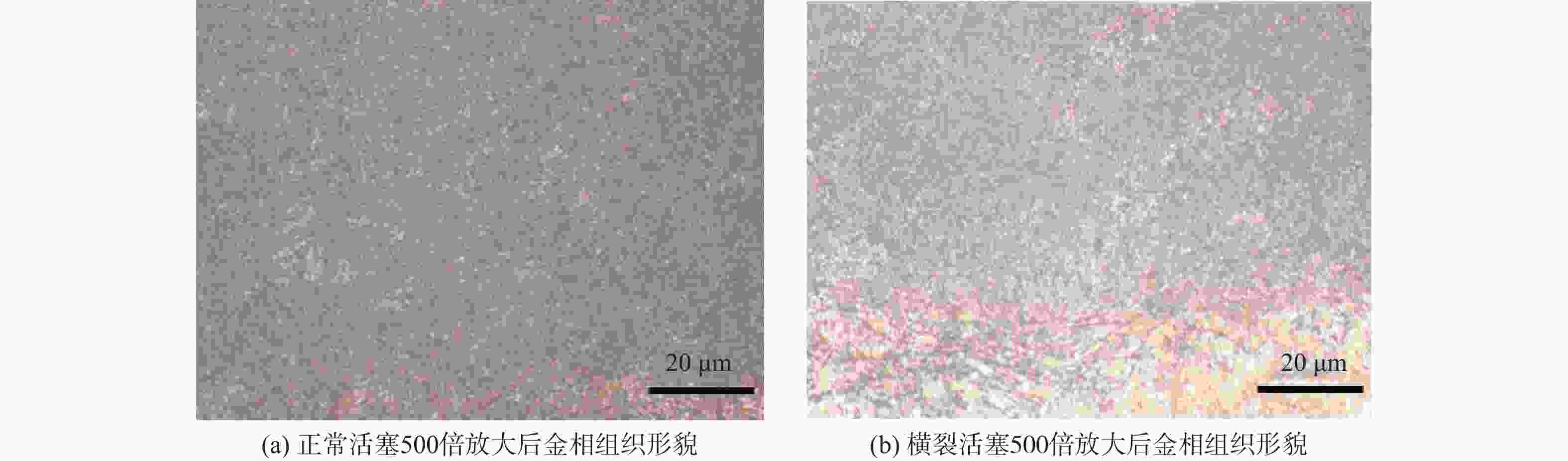
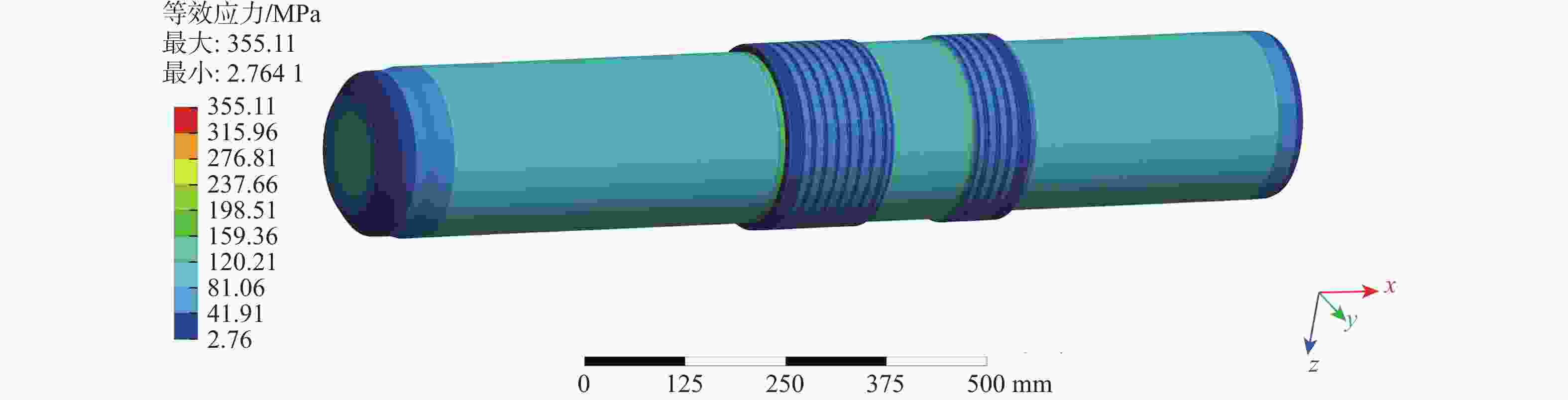
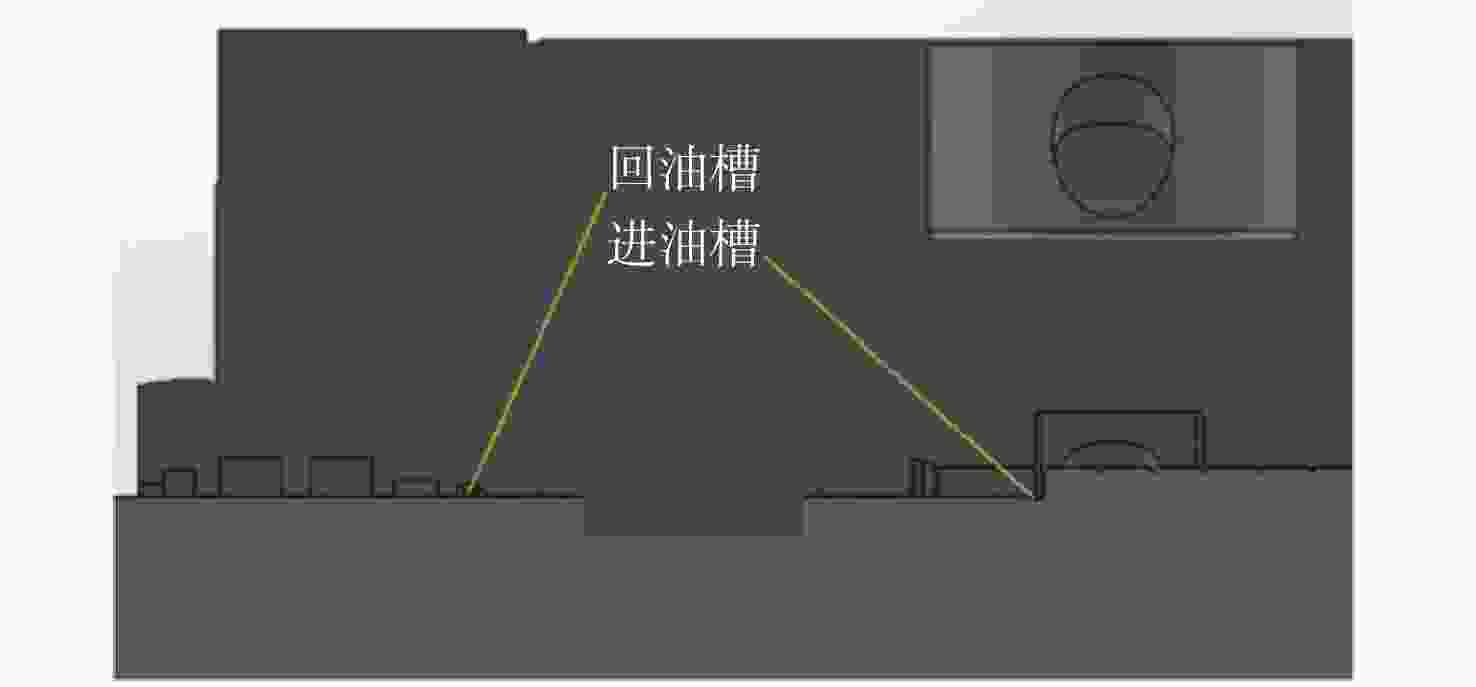
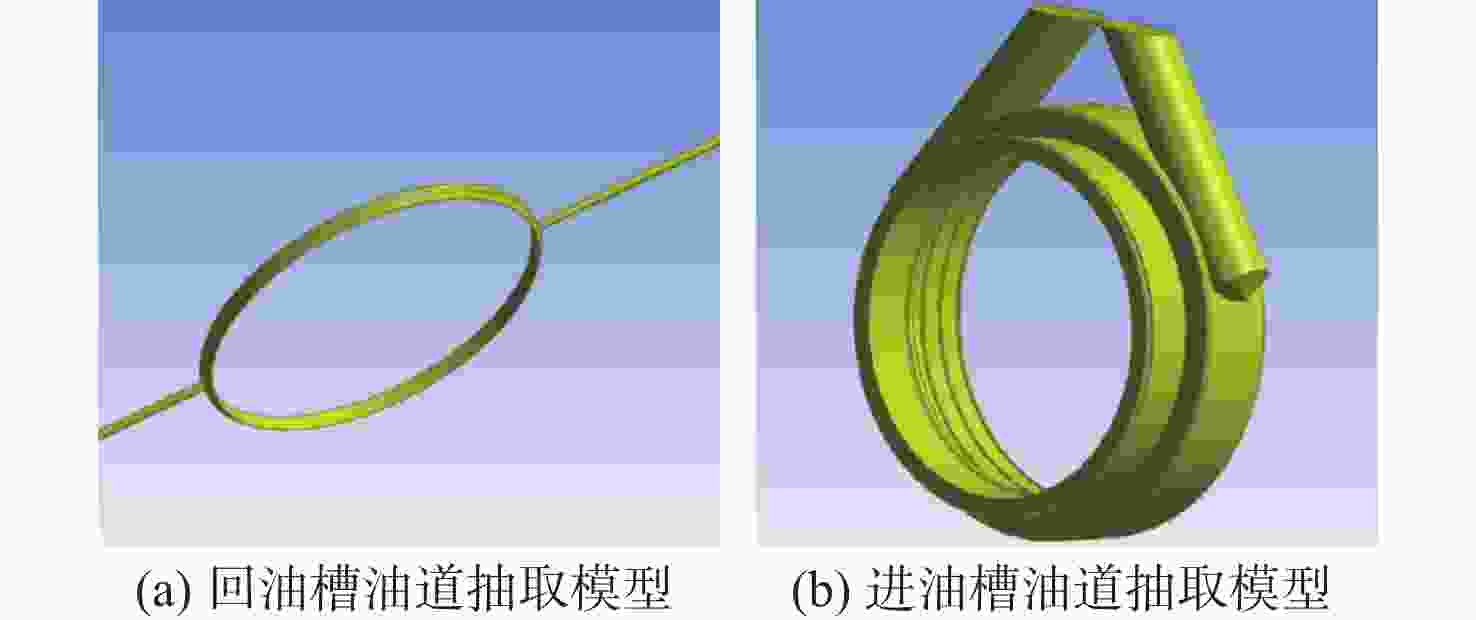
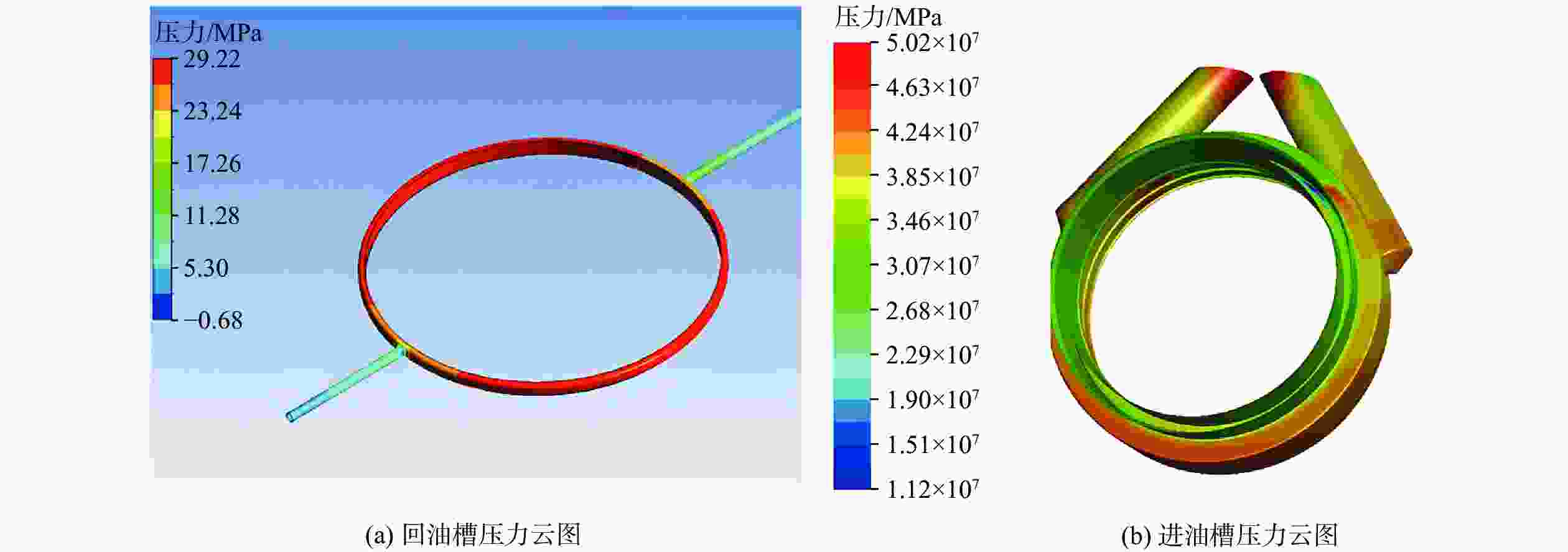
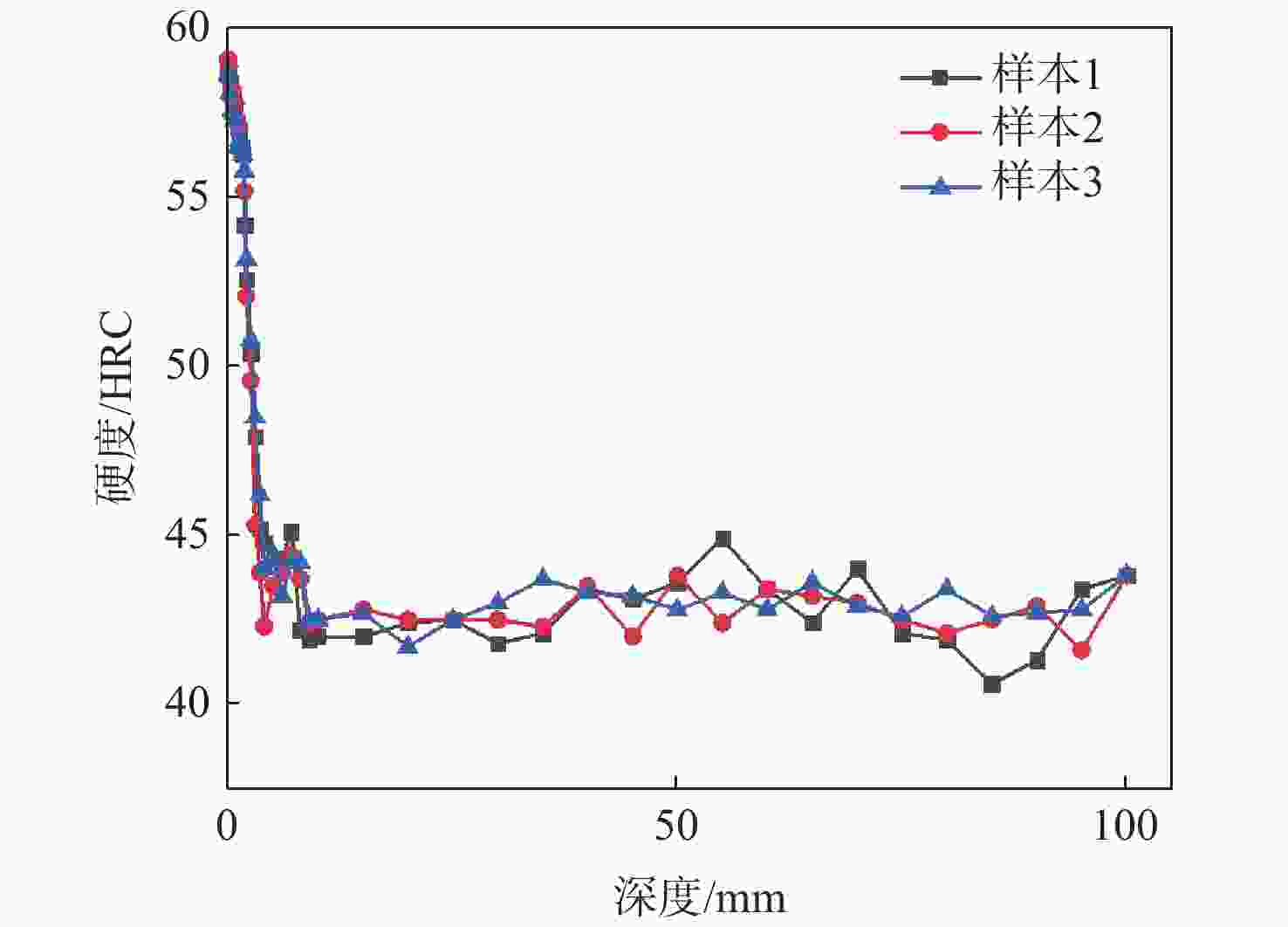
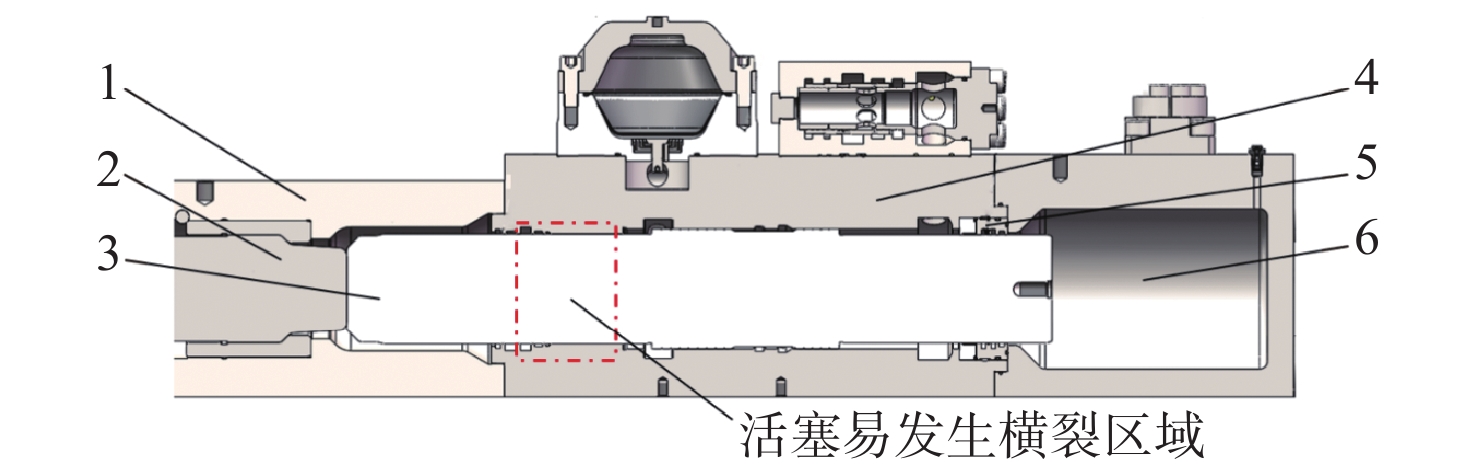
针对破碎锤中的活塞横裂现象,分析了活塞产生横裂的机理,并提出了一种新的活塞热处理制造工艺。采用硬度计和金相组织显微镜对活塞材料进行分析,得出发生活塞横裂故障部位的材料成分和金相组织符合设计要求,而硬度和硬化层深度低于设计要求。利用ANSYS求解活塞 “卡死”情况下的最大应力为1 229.8 MPa,超出材料的屈服极限850 MPa,最大应力的位置在活塞横裂处;利用Fluent求解活塞所受的径向不平衡力,在活塞的回油槽中受到的最大径向力为3 408 N,最小径向力为10 N,在活塞的进油槽中,最大径向力为15 675 N,最小径向力为73 N。结果表明,活塞在径向不平衡力作用下形成的“卡死”现象是活塞发生横裂的主要原因。提出延长活塞的渗碳时间、增加活塞在热处理过程中的校直次数等热处理新工艺,经耐久实验验证,所提工艺可以有效解决活塞横裂问题。
Abstract:In view of the phenomenon of piston transverse crack in crushing hammer, the paper analyzes the transverse crack of piston, and puts forward a new heat treatment process of piston. The piston material was analyzed by using a hardness tester and a metallographic microscope. It is found that the material composition and metallographic structure at the location of the piston transverse crack failure are in line with the design requirements, while the hardness and hardened layer depth are lower than the design. Using Ansys, the maximum stress of the piston is
1229.8 MPa, which exceeds the yield limit of the material by 850 MPa, and the maximum stress is located at the transverse crack of the piston. Fluent was used to solve the radial unbalance force on the piston. The maximum radial force and the minimum radial force in the oil return groove of the piston were3408 N and 10 N. In the oil inlet groove of the piston, the maximum radial force is15675 N and the minimum radial force is 73 N. The results show that the "stuck" phenomenon formed by the radial unbalanced force is the main reason for the transverse crack of the piston. A new heat treatment process such as extending the carburizing time of piston and increasing the number of times of piston straightening during heat treatment is proposed. The durability test shows that the proposed process can effectively solve the problem of piston transverse cracking.-
Key words:
- hydraulic crushing hammer /
- pistons /
- transverse cracking /
- jamming /
- radial unbalance force
-
表 1 活塞合格金属材质元素质量分数范围
Table 1. Piston qualified metal material element mass fraction range
元素 质量分数 Ni 0.028~0.033 Si 0.0015 ~0.003Mn 0.008~0.012 P ≤ 0.00015 S ≤ 0.0001 Cr 0.014~0.018 Mo 0.004~0.006 表 2 活塞正常区域金属材质光谱分析
Table 2. Spectral Analysis of metal material spectrum in the normal area of piston
元素 质量分数 Ni 0.0324 Si 0.0019 Mn 0.0116 P 0.00007 S 0.00006 Cr 0.0173 Mo 0.00587 表 3 活塞横裂区域金属材质光谱分析
Table 3. Piston cross-crack area metal material spectrum analysis
元素 质量分数 Ni 0.0318 Si 0.0021 Mn 0.0108 P 0.00009 S 0.00008 Cr 0.0175 Mo 0.00584 表 4 破碎锤参数
Table 4. Crushing hammer parameters
参数 数值 活塞上端直径D2/mm 185 活塞中部直径D/mm 208 活塞下端直径D1/mm 190 钎杆尾部直径D3/mm 125 破碎锤工作压力P1/MPa 28 氮气室的初始容积V/L 24 氮气室的初始压力P/MPa 3.0 活塞质量Mp/kg 284 活塞材料弹性模量E/(N·m2) 2.12×1011 活塞材料密度$ \rho $/(kg·m−3) 7850 活塞打击头直径D4/mm 146 表 5 网格无关性验证结果
Table 5. Grid independence verification results
网格单元数量 应力值/MPa 2 893 229 457.62 3 170 064 514.68 3 674 387 510.92 4 460 354 356.35 4 699 218 364.33 4 976 105 355.11 -
[1] 连萌. 液压挖掘机破碎锤钎杆的冲击特性分析[J]. 黄河水利职业技术学院学报, 2017, 29(1): 46-50.LIAN M. The impact characteristics analysis of hydraulic excavator broken hammer drill rod[J]. Journal of Yellow River Conservancy Technical Institute, 2017, 29(1): 46-50(in Chinese). [2] 周广星. 液压破碎锤回油孔处结构对卡紧力影响研究[J]. 液压气动与密封, 2021, 41(5): 68-70.ZHOU G X. Study on the effect of hydraulic crushing hammer on clamping force[J]. Hydraulics Pneumatics & Seals, 2021, 41(5): 68-70(in Chinese). [3] 曹傲. 液压凿岩机的参数优化研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2020.CAO A. Research on parameter optimization of hydraulic rock drill[D]. Xi’an: Changan University, 2020(in Chinese). [4] 罗亮光. 内回转气动凿岩机活塞运动设计计算的新理念与实践[J]. 凿岩机械气动工具, 2021, 47(1): 6-15.LUO L G. New concepts and practices on design computation for movements of pistons in interanlly rotary pneumatic rock drills[J]. Rock Drilling Machinery & Pneumatic Tools, 2021, 47(1): 6-15(in Chinese). [5] 高波, 徐雪锋, 夏剑辉. 液压凿岩机活塞应力分析[J]. 凿岩机械气动工具, 2020, 46(4): 15-20.GAO B, XU X F, XIA J H. Stress analysis of piston of hydraulic rock drill[J]. Rock Drilling Machinery & Pneumatic Tools, 2020, 46(4): 15-20(in Chinese). [6] SOKOLSKI M, SOKOLSKI P. Problems of strength estimation of the vulnerable zones in the tools of hydraulic hammers for mining[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Aided Engineering. Berlin: Springer, 2019: 696-704. [7] SOKOLSKI M, SOKOLSKI P. Strength estimation of the impact zone–A critical area of the tools of the hydraulic hammers[J]. Archives of Civil and Mechanical Engineering, 2016, 16(4): 767-776. doi: 10.1016/j.acme.2016.04.007 [8] BAKHSHANDI R K, TKACHUK A, SADEK M, et al. Failure analysis of two cylindrical impact pistons subjected to high velocity impacts in drilling applications[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2022, 140: 106623. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2022.106623 [9] ANDERSSON H, HOLMBERG L J, SIMONSSON K, et al. Simulation of leakage flow through dynamic sealing gaps in hydraulic percussion units using a co-simulation approach[J]. Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory, 2021, 111: 102351. doi: 10.1016/j.simpat.2021.102351 [10] WANG J L, HAN B, WANG C, et al. Failure analysis of the piston used in a pneumatic down the hole impactor[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2021, 127: 105561. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2021.105561 [11] 张涛. 某高功率柴油机活塞失效分析及解决方案[J]. 内燃机与配件, 2021(1): 23-25.ZHANG T. Analysis and solution on fracture failure of the piston used in a high power diesel engine[J]. Internal Combustion Engine & Parts, 2021(1): 23-25(in Chinese). [12] 王中伟. 基于Workbench的液压碎石车工作装置有限元分析[J]. 凿岩机械气动工具, 2015(2): 18-24.WANG Z W. Finite element analysis of hydraulic rock breaker working device based on workbench[J]. Rock Drilling Machinery & Pneumatic Tools, 2015(2): 18-24(in Chinese). [13] HAO S R, SHEN Y X, CHENG J B. Phase field formulation for the fracture of a metal under impact with a fluid formulation[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2022, 261: 108142. doi: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2021.108142 [14] LANG L, ZHU Z M, DENG S, et al. Study on the arresting mechanism of two arrest-holes on moving crack in brittle material under impacts[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2020, 229: 106936. doi: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2020.106936 [15] HÜTTER G, ZYBELL L, KUNA M. Micromechanisms of fracture in nodular cast iron: From experimental findings towards modeling strategies–A review[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2015, 144: 118-141. doi: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2015.06.042 [16] 陈富强, 陈晓伟. 球墨铸铁曲轴断裂失效分析[J]. 金属热处理, 2011, 36(12): 124-126.CHEN F Q, CHEN X W. Fracture failure investigation on nodular cast iron crankshaft[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2011, 36(12): 124-126(in Chinese). [17] 闫佳兵. 船用柴油机活塞损坏原因分析[J]. 内燃机与配件, 2020(7): 163-164.YAN J B. Cause analysis of piston damage of marine diesel engine[J]. Internal Combustion Engine & Parts, 2020(7): 163-164(in Chinese). [18] 王宏伟, 李君, 张峥, 等. 压缩机活塞杆断裂原因分析[J]. 材料工程, 2009, 37(12): 5-9.WANG H W, LI J, ZHANG Z, et al. Failure analysis on fracture of compressor piston rod[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2009, 37(12): 5-9(in Chinese). [19] XU L Q, YU X K, HOU Z G. Analysis of the causes of driving gear shaft fractures in gear pumps[J]. Journal of Failure Analysis and Prevention, 2020, 20(1): 242-248. doi: 10.1007/s11668-020-00825-w [20] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 钢件渗碳淬火回火金相检验: GB/T 25744—2010[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2011.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Metallographic examination for carburizing quenching and tempering of steel parts: GB/T 25744—2010[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2011(in Chinese). [21] 张明松, 苏志成, 王宏. 液压破碎锤动态特性的研究[J]. 南方农机, 2021, 52(3): 106-107.ZHANG M S, SU Z C, WANG H. Research on dynamic characteristics of hydraulic breaker[J]. China Southern Agricultural Machinery, 2021, 52(3): 106-107(in Chinese). [22] 杨文军, 陈新元, 邓江洪. 间隙密封液压缸的活塞卡紧力分析[J]. 液压与气动, 2012(9): 107-109.YANG W J, CHEN X Y, DENG J H. Clamping force analysis of hydraulic cylinder with piston sealing[J]. Chinese Hydraulics & Pneumatics, 2012(9): 107-109(in Chinese). [23] 朱德, 刘杰, 肖欣谕, 等. 基于Fluent的液压密封流体膜压力精确化研究[J]. 机床与液压, 2021, 49(10): 122-129.ZHU D, LIU J, XIAO X Y, et al. Precise study on fluid film pressure of hydraulic seal based on fluent[J]. Machine Tool & Hydraulics, 2021, 49(10): 122-129(in Chinese). -






 下载:
下载: