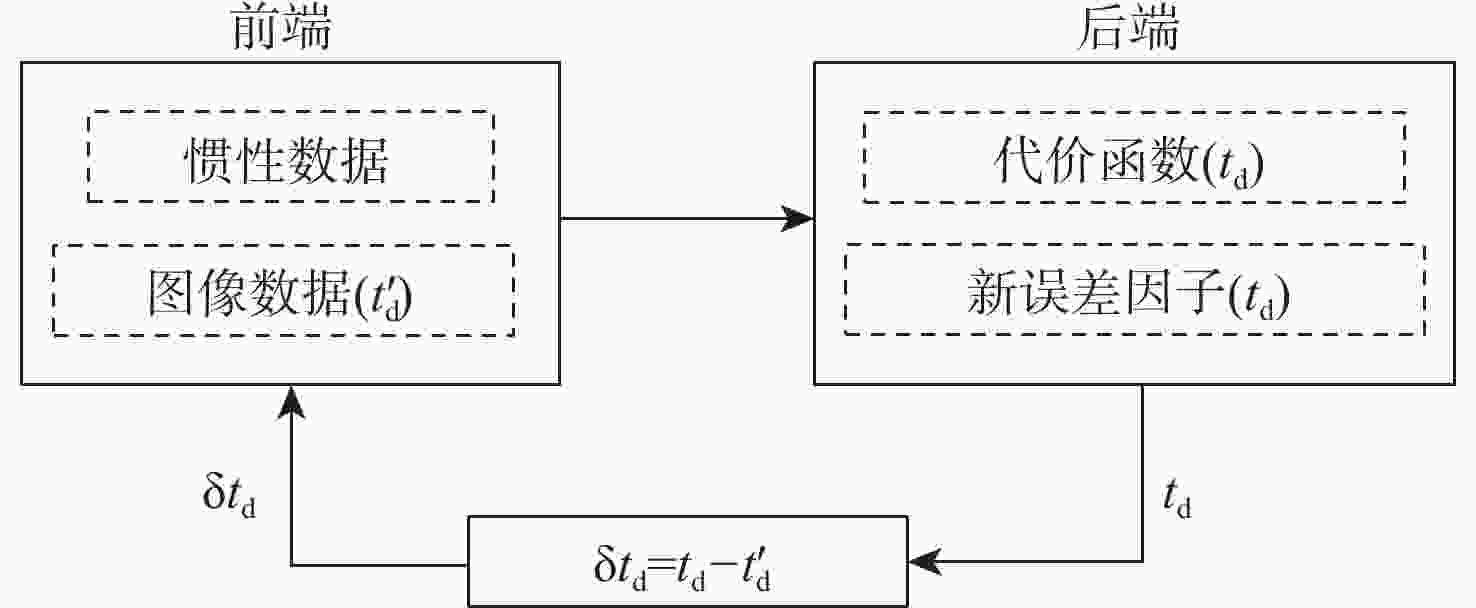
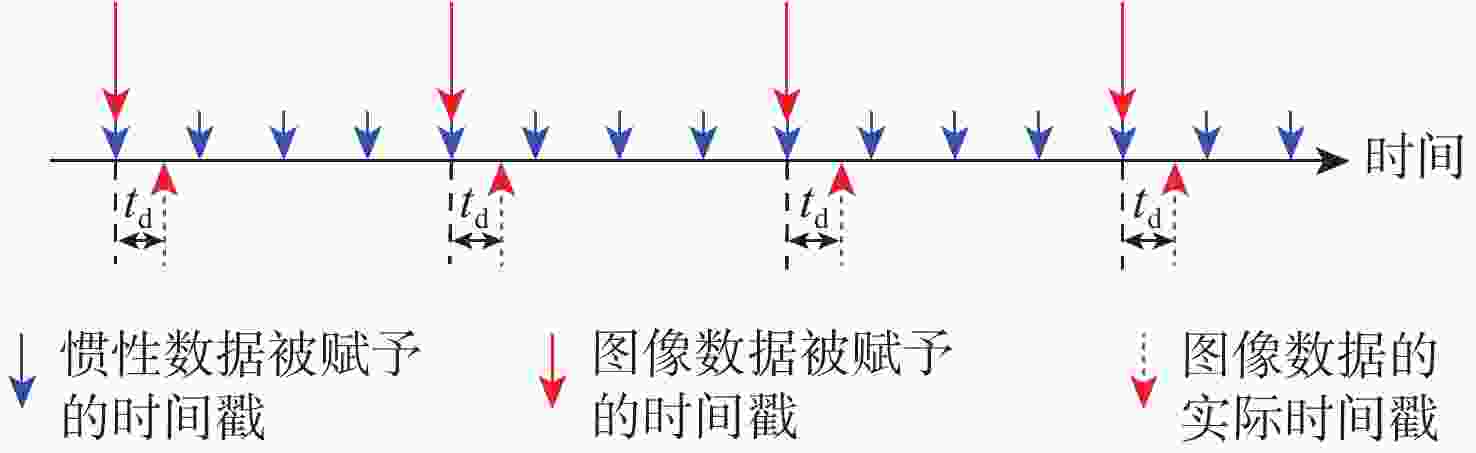
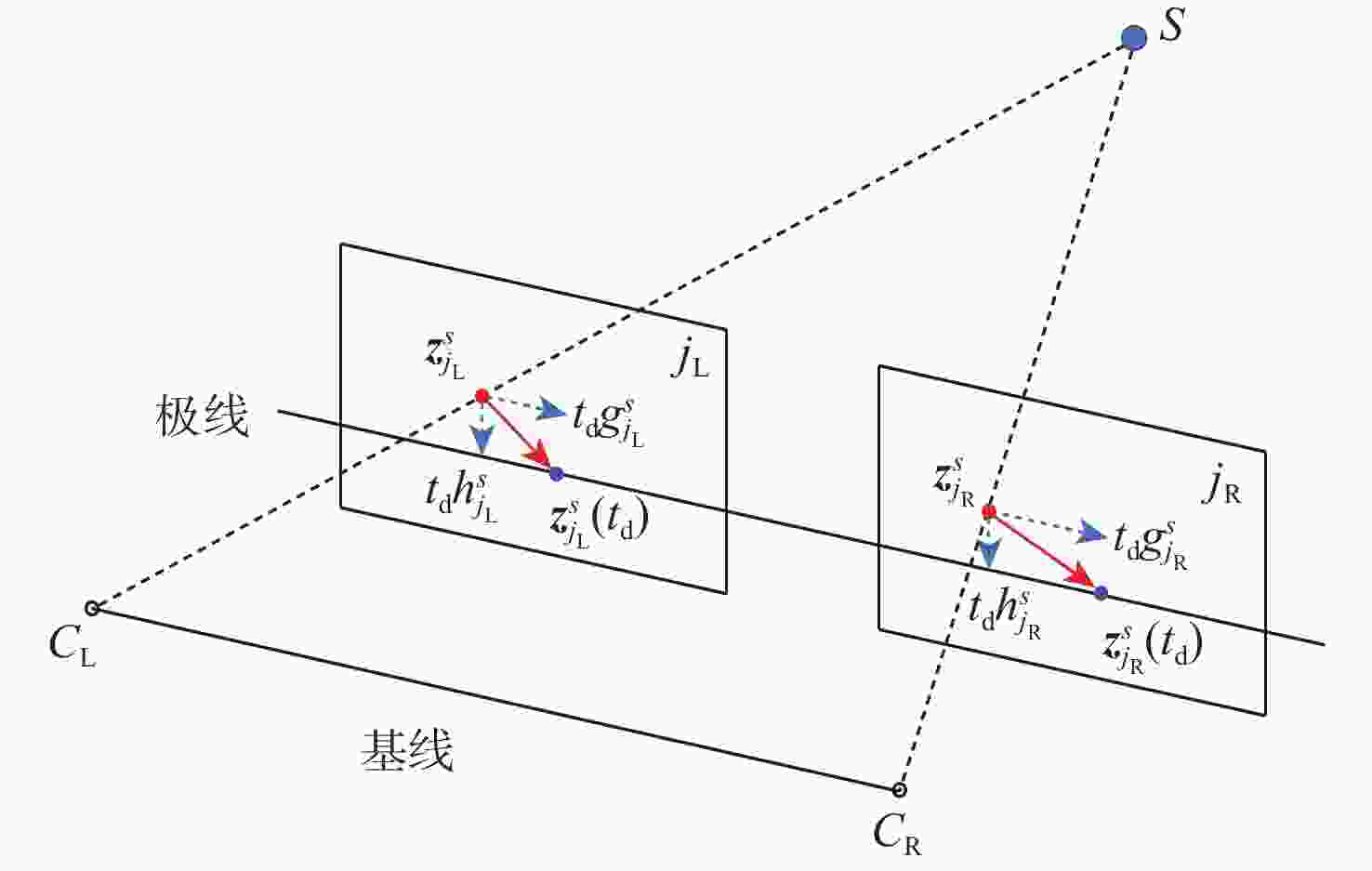
Nonlinear optimization-based online temporal calibration method of stereo camera and inertial measurement unit in stereo VIO
-
摘要:
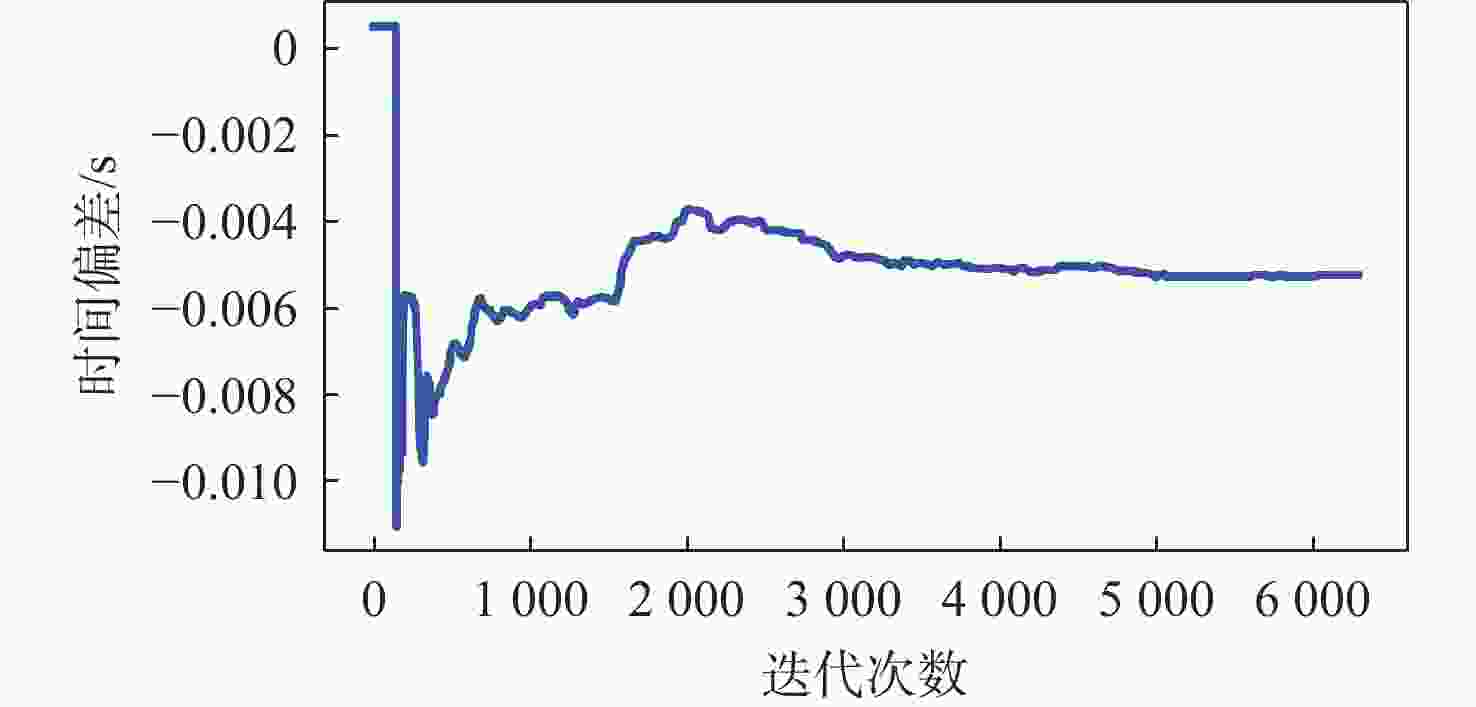
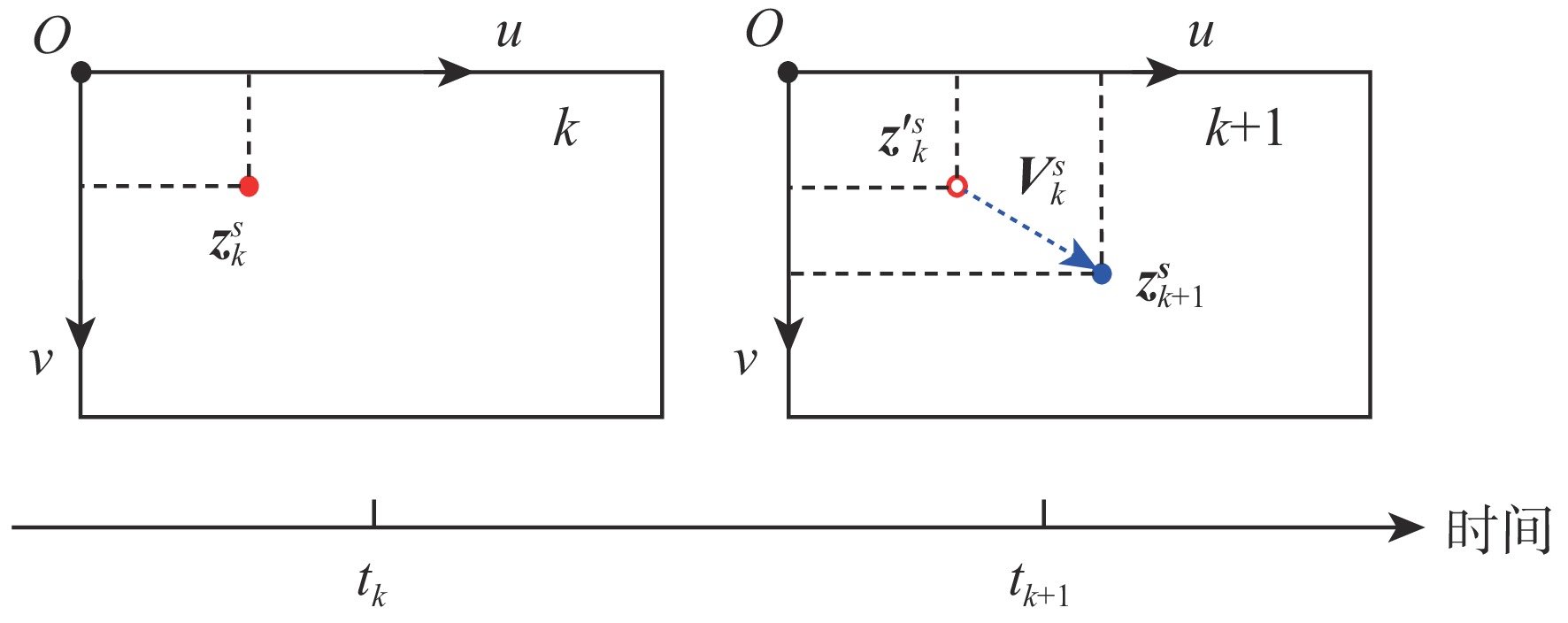
基于非线性优化的双目视觉惯性里程计(VIO)系统在低纹理等环境下长时间运行误差累积问题严重。因此,针对基于非线性优化的双目VIO系统,提出在线时间偏差标定方法。所提方法充分发挥双目相机的优势,利用双目相机中的极线约束构建误差因子,减少特征点误匹配对时间偏差标定的负面影响,提高系统鲁棒性和状态估计的准确度,适用于低成本,自组装系统。在公开数据集上的实验表明:所提方法准确度更高,收敛速度更快,能够提高系统状态估计的准确度和鲁棒性。真实场景下的实验也验证了所提方法的有效性。
Abstract:The error accumulation problem in srereo visual-inertial odometry (VIO) systems based on nonlinear optimization is serious when operating for extended periods in low-texture environments. Therefore, we propose an online temporal calibration method for the stereo VIO system based on nonlinear optimization. This approach makes full use of the benefits of stereo cameras by constructing error factors using epipolar constraints, which enhances system robustness and state estimation accuracy while lessening the detrimental effect of feature point mismatches on time offset calibration. It is suitable for low-cost, self-assembled systems. Experiments on public datasets show that the proposed calibration method has higher accuracy and faster convergence speed than current advanced calibration methods, thereby improving the accuracy and robustness of system state estimation. Experiments in real-world scenarios also validate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
-
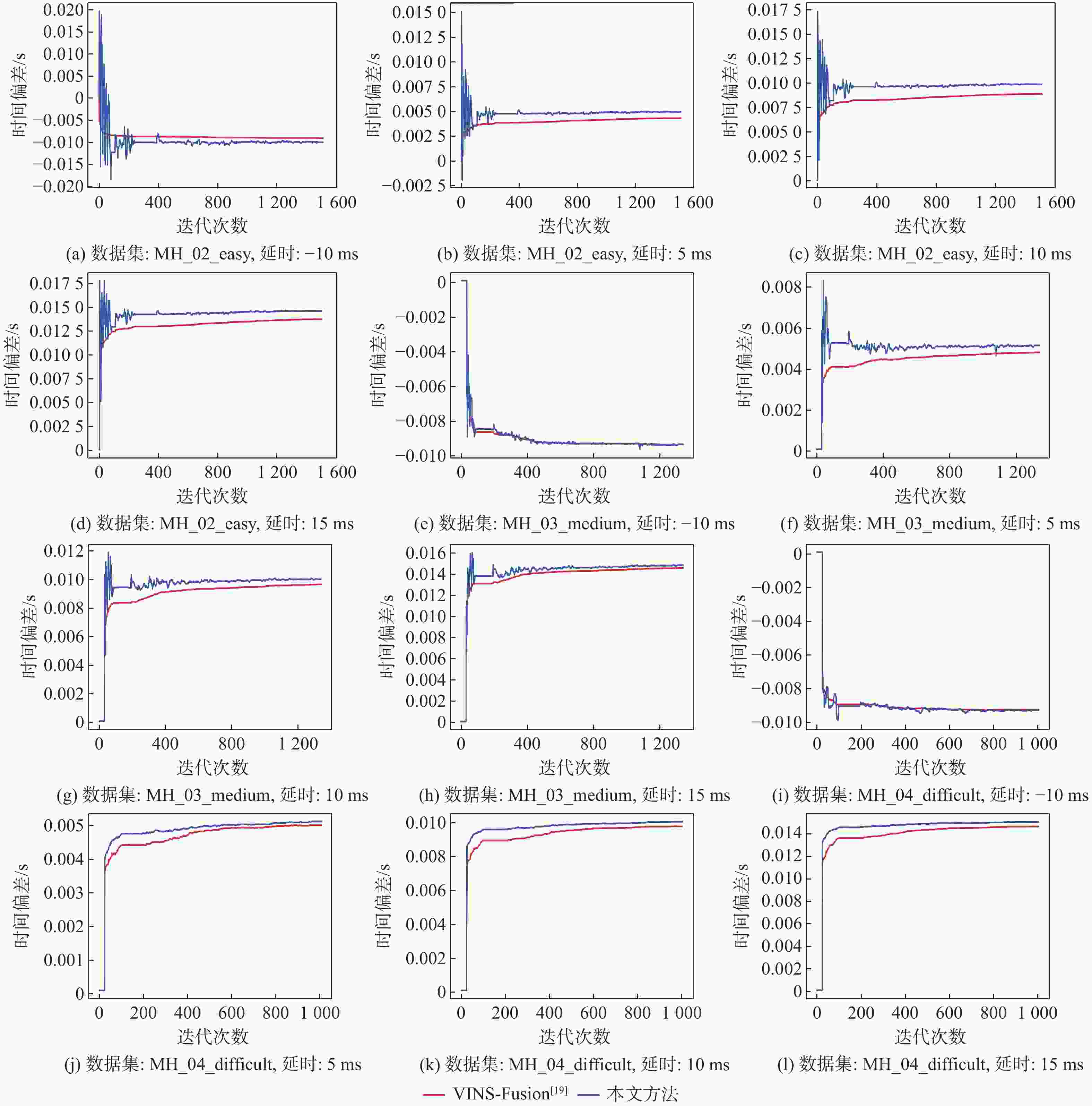
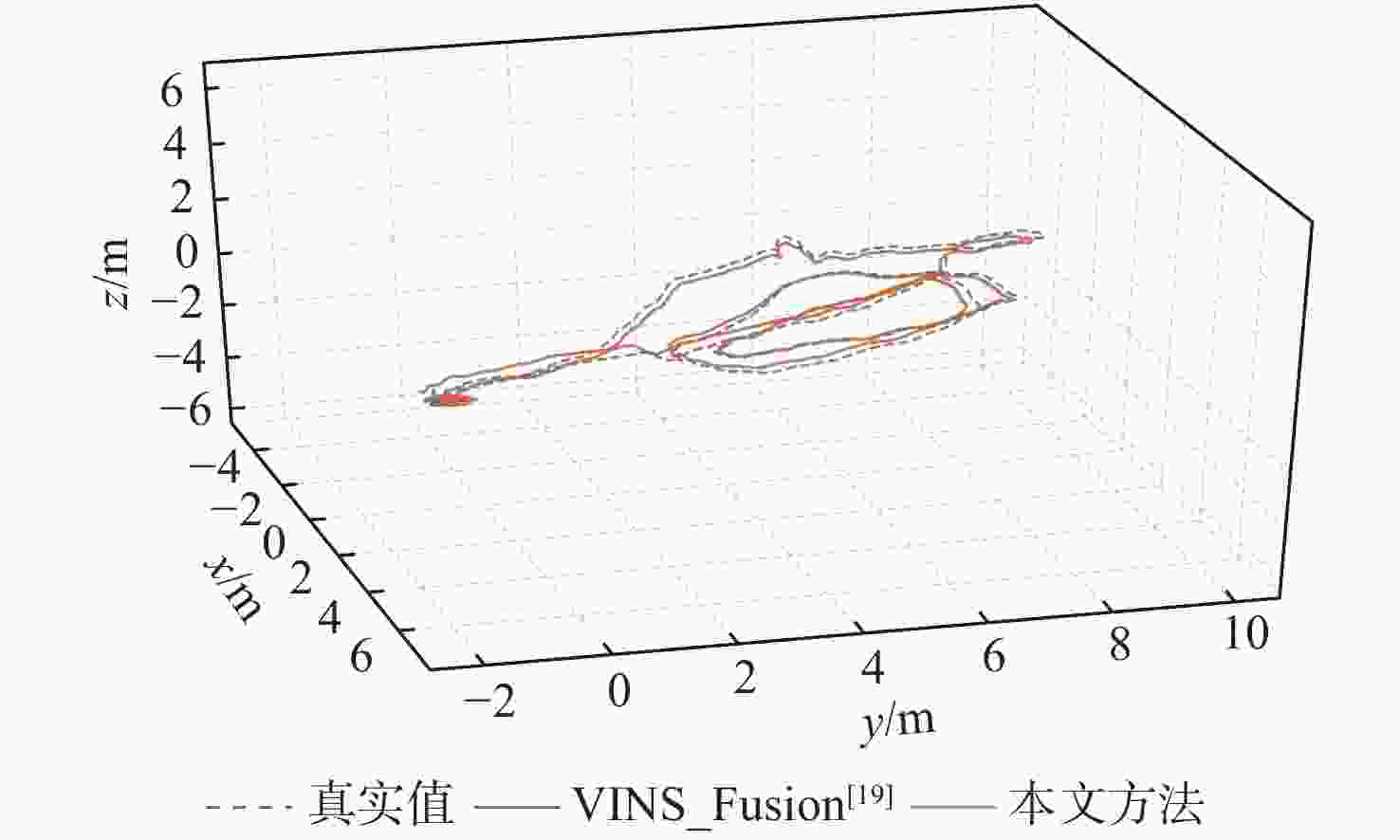
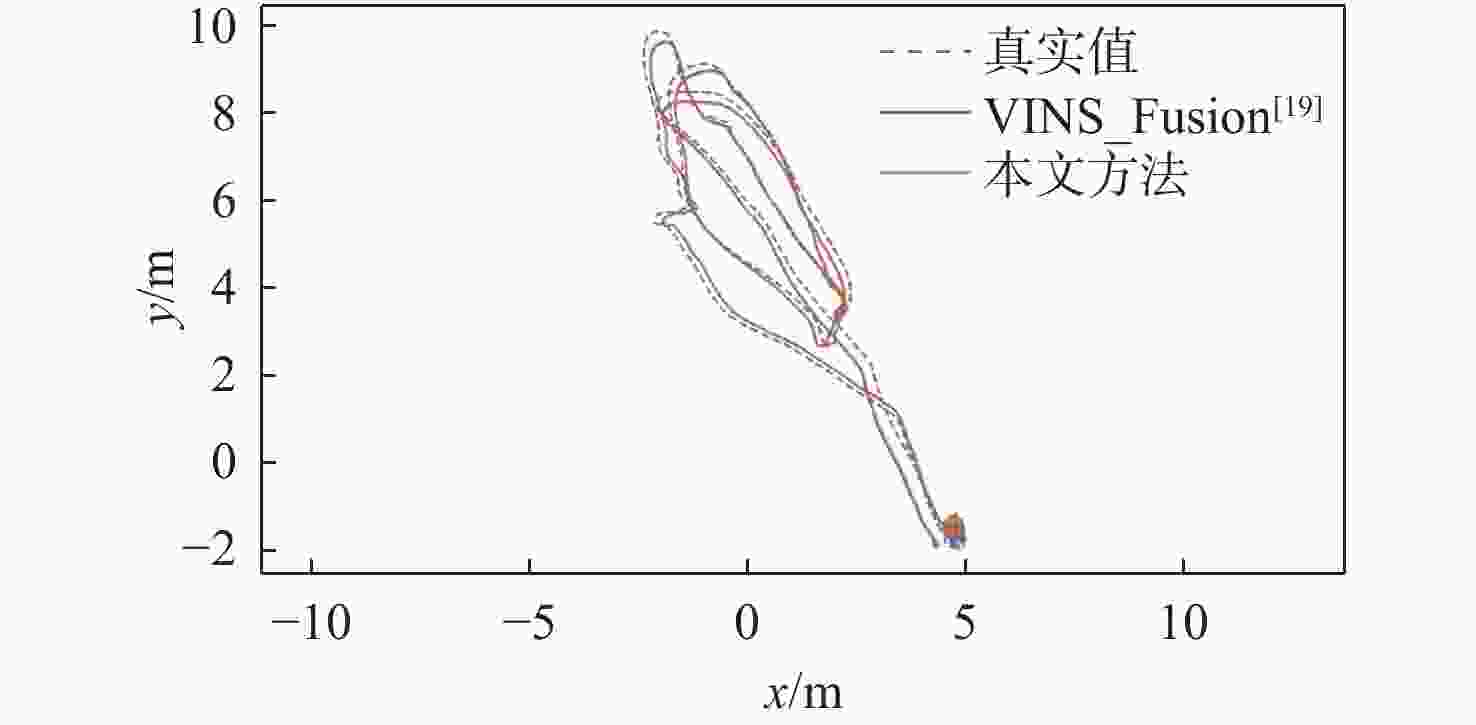
表 1 仿真实验中的标定结果
Table 1. Simulation experiment of calibration results
数据集 延时设定值/ms 延时估计值/ms 本文方法 VINS-Fusion[19] MH_02_easy −10 −9.98 −9.00 5 4.97 4.35 10 9.87 8.91 15 14.61 13.73 MH_03_midium −10 −9.37 −9.37 5 5.17 4.86 10 10.01 9.64 15 14.83 14.57 MH_04_difficult −10 −9.31 −9.28 5 5.12 5.01 10 10.05 9.77 15 15.06 14.65 表 2 仿真实验中的RMSE结果
Table 2. Simulation experiment of RMSE results
数据集 延时设定值/ms RMSE/m 本文方法 VINS-Fusion[19] MH_02_easy −10 0.2692 0.2742 5 0.2609 0.2615 10 0.2690 0.2686 15 0.2768 0.2702 MH_03_medium −10 0.4480 0.4785 5 0.4529 0.4540 10 0.4526 0.4548 15 0.4523 0.4497 MH_04_difficult −10 0.5297 0.5258 5 0.5299 0.5358 10 0.5308 0.5346 15 0.5298 0.5298 -
[1] 王朋, 郝伟龙, 倪翠, 等. 视觉SLAM方法综述[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2024, 50(2): 359-367.WANG P, HAO W L, NI C, et al. An overview of visual SLAM methods[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2024, 50(2): 359-367(in Chinese). [2] 左晋, 张皓, 远子涵, 等. 移动机器人SLAM发展现状综述[J]. 北京印刷学院学报, 2023, 31(6): 30-32.ZUO J, ZHANG H, YUAN Z H, et al. A review on the development status of mobile robot and SLAM[J]. Journal of Beijing Institute of Graphic Communication, 2023, 31(6): 30-32(in Chinese). [3] 曾庆化, 罗怡雪, 孙克诚, 等. 视觉及其融合惯性的SLAM技术发展综述[J]. 南京航空航天大学学报, 2022, 54(6): 1007-1020.ZENG Q H, LUO Y X, SUN K C, et al. Review on SLAM technology development for vision and its fusion of inertial information[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics, 2022, 54(6): 1007-1020(in Chinese). [4] CADENA C, CARLONE L, CARRILLO H, et al. Past, present, and future of simultaneous localization and mapping: toward the robust-perception age[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2016, 32(6): 1309-1332. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2016.2624754 [5] FUENTES-PACHECO J, RUIZ-ASCENCIO J, RENDÓN-MANCHA J M. Visual simultaneous localization and mapping: a survey[J]. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2015, 43(1): 55-81. doi: 10.1007/s10462-012-9365-8 [6] KLEIN G, MURRAY D. Parallel tracking and mapping for small AR workspaces[C]//Proceedings of the 6th IEEE and ACM International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2007: 225-234. [7] BRESSON G, ALSAYED Z, YU L, et al. Simultaneous localization and mapping: a survey of current trends in autonomous driving[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2017, 2(3): 194-220. doi: 10.1109/TIV.2017.2749181 [8] CORKE P, LOBO J, DIAS J. An introduction to inertial and visual sensing[J]. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2007, 26(6): 519-535. [9] VAN BRUMMELEN J, O’BRIEN M, GRUYER D, et al. Autonomous vehicle perception: the technology of today and tomorrow[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2018, 89: 384-406. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2018.02.012 [10] CHEN C, ZHU H, LI M G, et al. A review of visual-inertial simultaneous localization and mapping from filtering-based and optimization-based perspectives[J]. Robotics, 2018, 7(3): 45. doi: 10.3390/robotics7030045 [11] ZOU D P, WU Y X, PEI L, et al. StructVIO: visual-inertial odometry with structural regularity of man-made environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2019, 35(4): 999-1013. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2019.2915140 [12] QIN T, LI P L, SHEN S J. VINS-mono: a robust and versatile monocular visual-inertial state estimator[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2018, 34(4): 1004-1020. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2018.2853729 [13] CAMPOS C, ELVIRA R, RODRÍGUEZ J J G, et al. ORB-SLAM3: an accurate open-source library for visual, visual–inertial, and multimap SLAM[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2021, 37(6): 1874-1890. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2021.3075644 [14] WEN S H, TAO S, LIU X, et al. CD-SLAM: a real-time stereo visual–inertial SLAM for complex dynamic environments with semantic and geometric information[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2024, 73: 2517808. [15] ZHANG T, XU J Y, SHEN H, et al. RMSC-VIO: robust multi-stereoscopic visual-inertial odometry for local visually challenging scenarios[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2024, 9(5): 4130-4137. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2024.3377008 [16] MUR-ARTAL R, TARDÓS J D. Visual-inertial monocular SLAM with map reuse[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2017, 2(2): 796-803. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2017.2653359 [17] MOURIKIS A I, ROUMELIOTIS S I. A multi-state constraint Kalman filter for vision-aided inertial navigation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2007: 3565-3572. [18] LEUTENEGGER S, LYNEN S, BOSSE M, et al. Keyframe-based visual-inertial odometry using nonlinear optimization[J]. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2015, 34(3): 314-334. doi: 10.1177/0278364914554813 [19] QIN T, SHEN S J. Online temporal calibration for monocular visual-inertial systems[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 3662-3669. [20] KELLY J, SUKHATME G S. A general framework for temporal calibration of multiple proprioceptive and exteroceptive sensors[C]//Proceedings of the Experimental Robotics. Berlin: Springer, 2014: 195-209. [21] FURGALE P, REHDER J, SIEGWART R. Unified temporal and spatial calibration for multi-sensor systems[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2013: 1280-1286. [22] LI M Y, MOURIKIS A I. 3-D motion estimation and online temporal calibration for camera-IMU systems[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2013: 5709-5716. [23] STURM J, ENGELHARD N, ENDRES F, et al. A benchmark for the evaluation of RGB-D SLAM systems[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2012: 573-580. [24] BURRI M, NIKOLIC J, GOHL P, et al. The EuRoC micro aerial vehicle datasets[J]. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2016, 35(10): 1157-1163. doi: 10.1177/0278364915620033 -






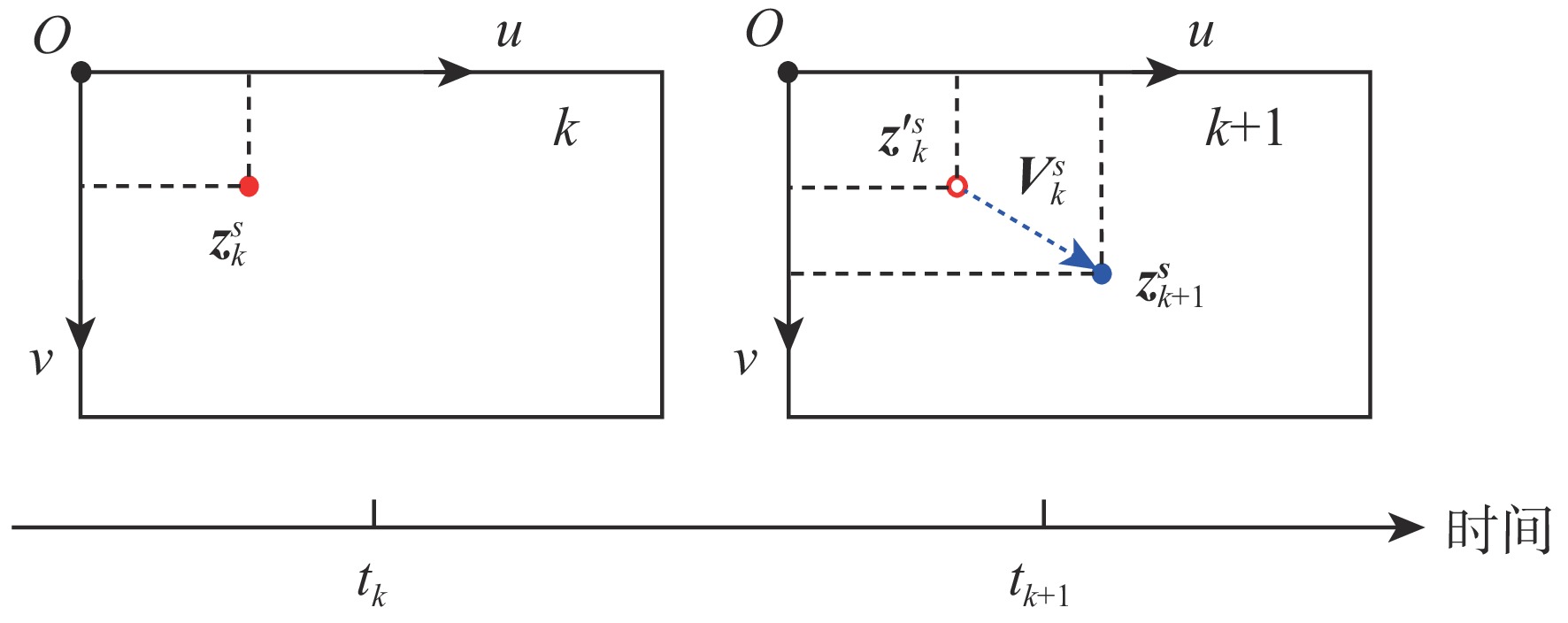
 下载:
下载: