-
摘要:
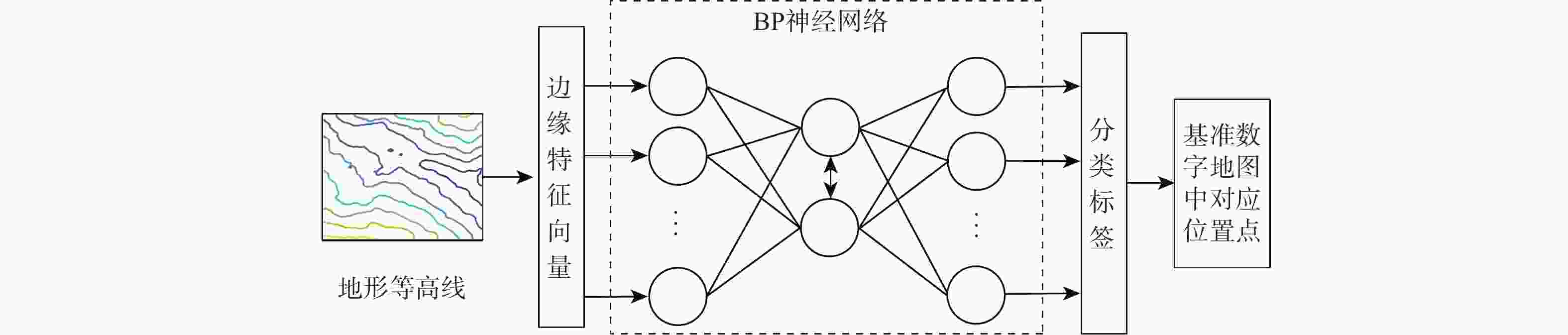
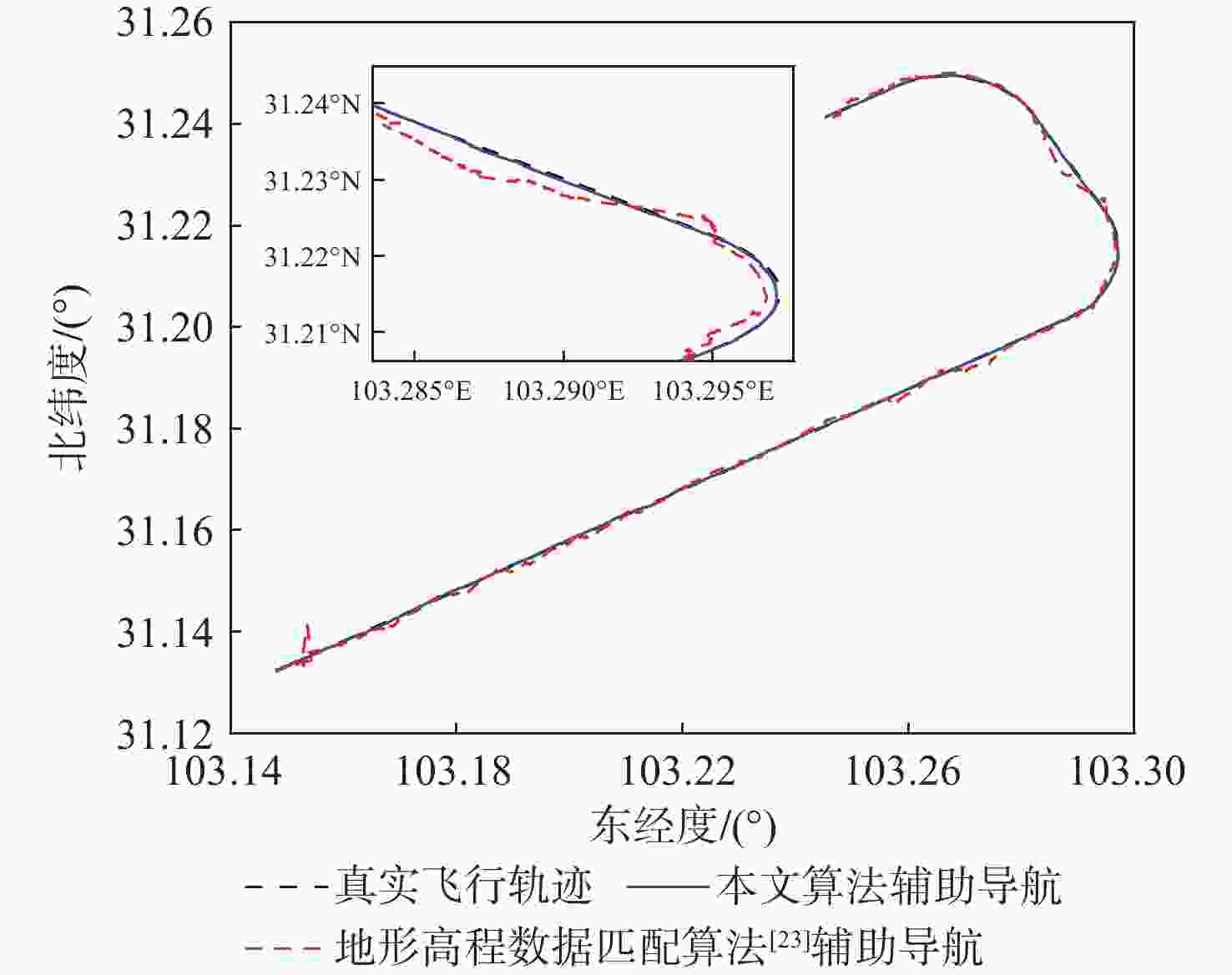
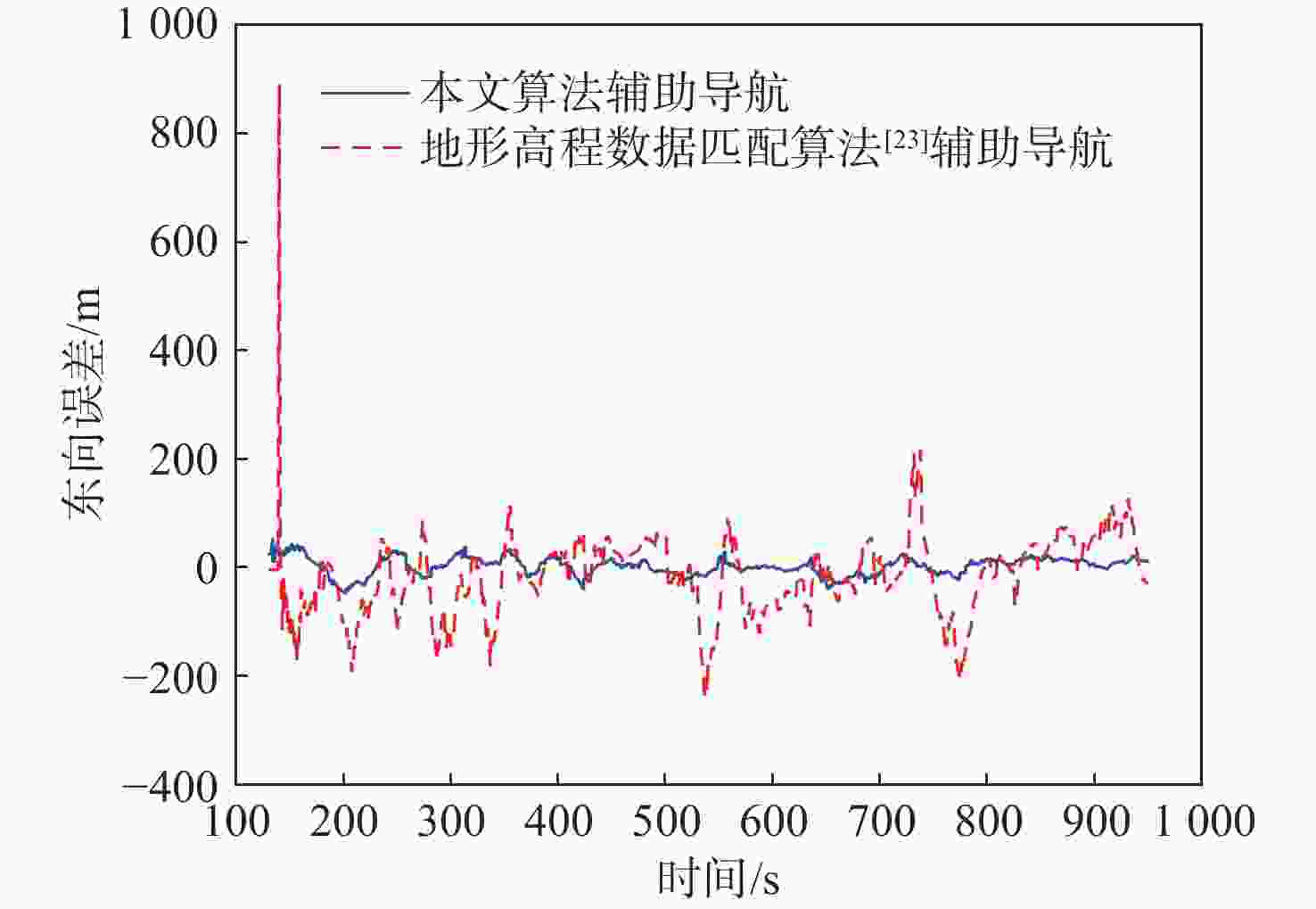
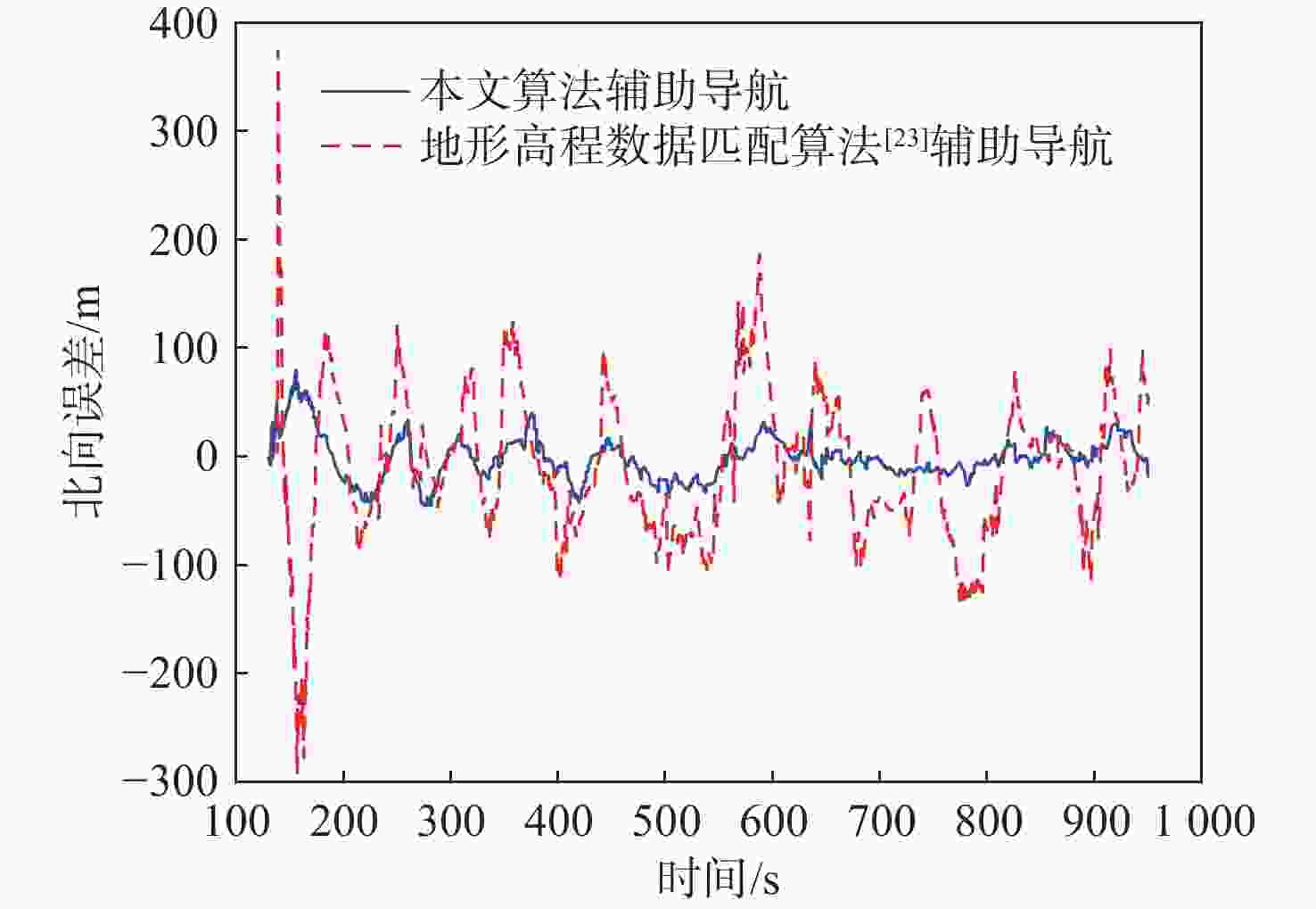
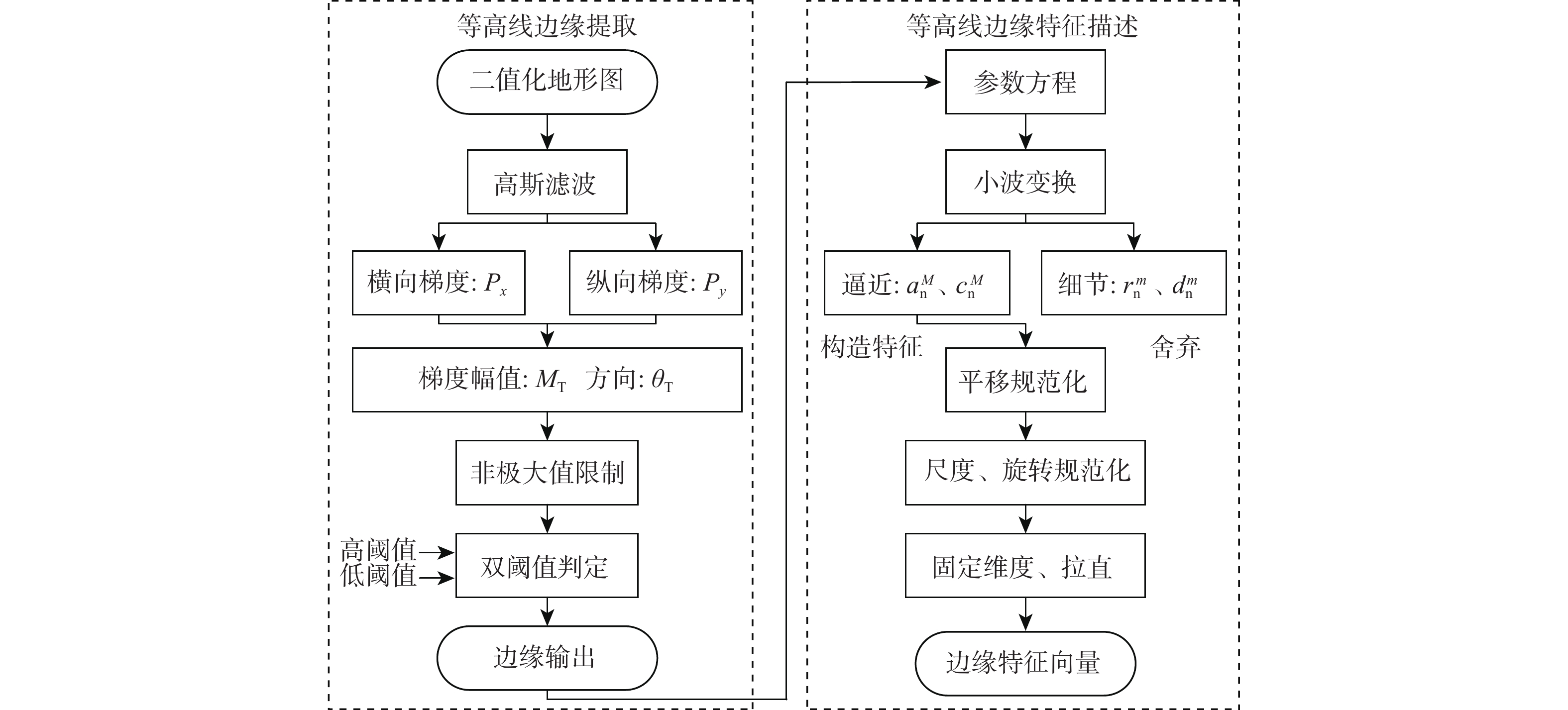
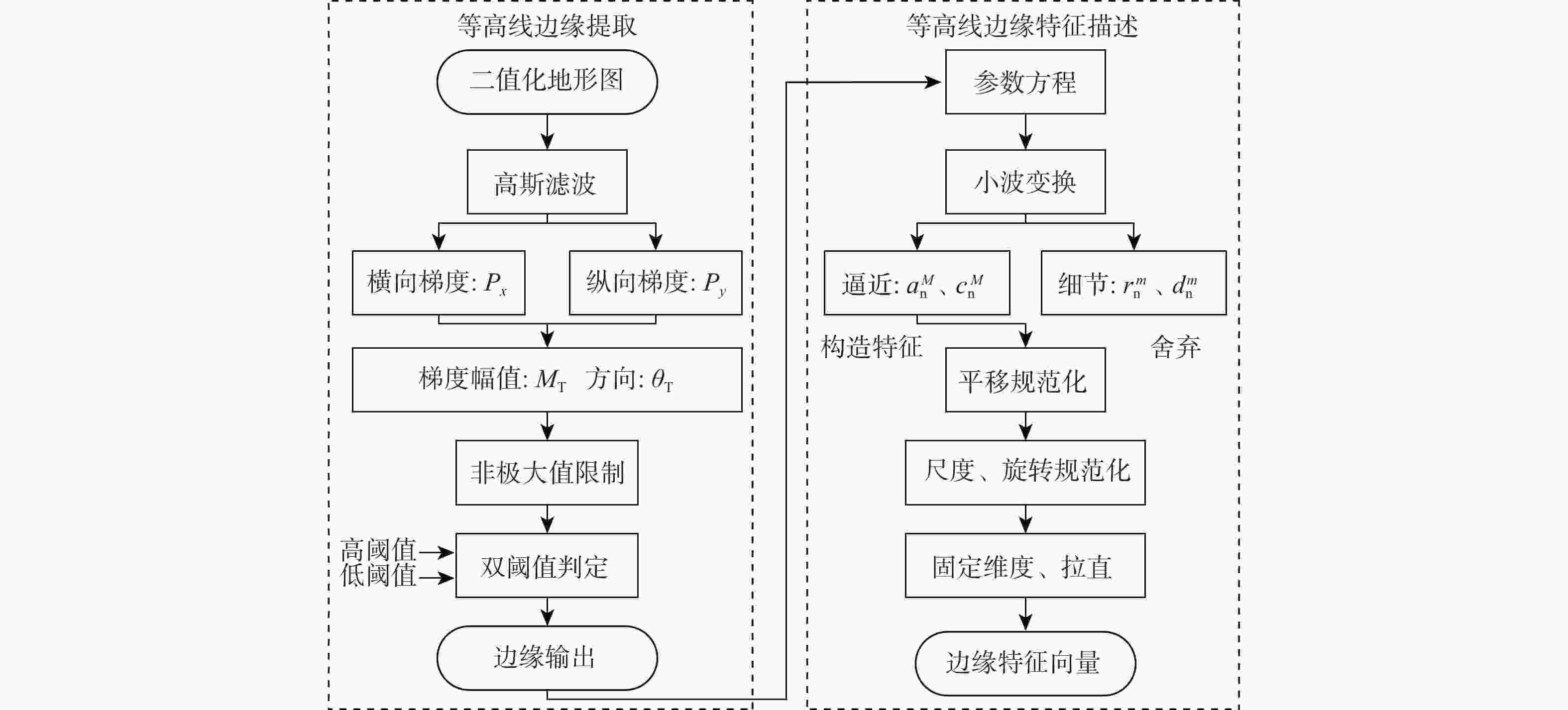
针对地形高程匹配定位精度低及遍历搜索方式实时性差的问题,提出一种基于神经网络的地形等高线辅助导航方法。研究二维等高线特征匹配以提高匹配算法在高程噪声下的鲁棒能力,考虑小波变换具备旋转、平移不变性特点,利用小波变换子提取等高线边缘特征;同时提出基于神经网络的等高线边缘特征匹配算法,利用多个子网进行分类识别代替传统遍历搜索匹配过程,显著提高算法实时性及匹配准确度。仿真实验表明:所提算法与地形高程匹配相比匹配成功率提高30%以上,较基于遍历搜索的地形等高线匹配算法匹配时长缩短97%以上。
Abstract:Addressing the issues of low accuracy in terrain elevation matching and poor real-time performance in iterative search methods, we propose a neural network-based method for terrain contour-aided navigation. This study focuses on two-dimensional contour feature matching to enhance the robustness of matching algorithms under elevation noise. Considering the rotational and translational invariance characteristics of wavelet transforms, we extract contour edge features using wavelet transform sub-bands. Furthermore, we present a contour edge feature matching algorithm based on neural networks that replaces the conventional iterative search matching process by using multiple sub-networks for classification recognition, greatly enhancing the algorithm's matching accuracy and real-time performance. In comparison to terrain elevation matching, simulation results show that the suggested approach improves the matching success rate by more than 30% and reduces the matching time by more than 97% when compared to iterative search-based terrain contour matching techniques.
-
表 1 仿真主要参数设置
Table 1. Setting of main simulation parameters
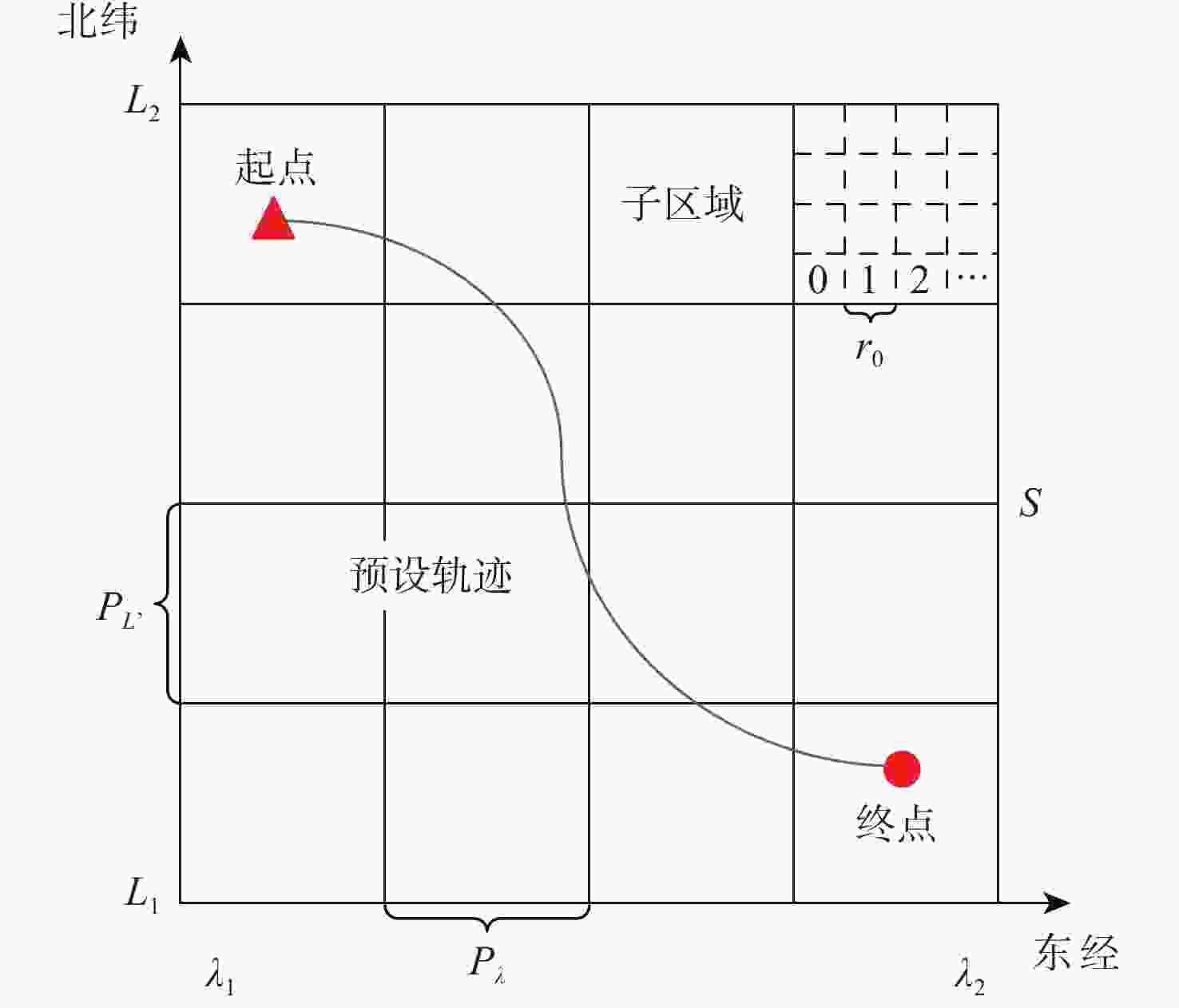
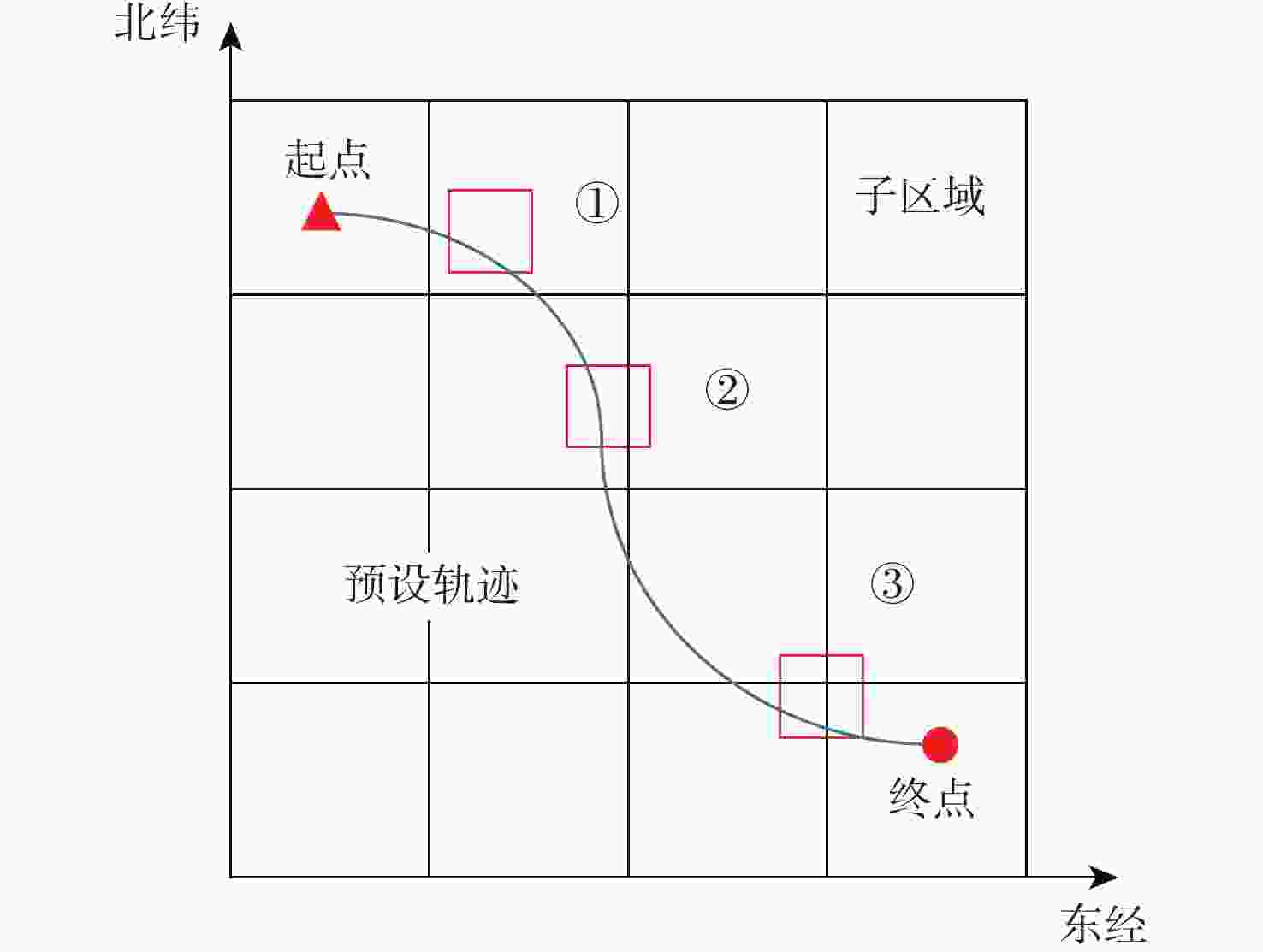
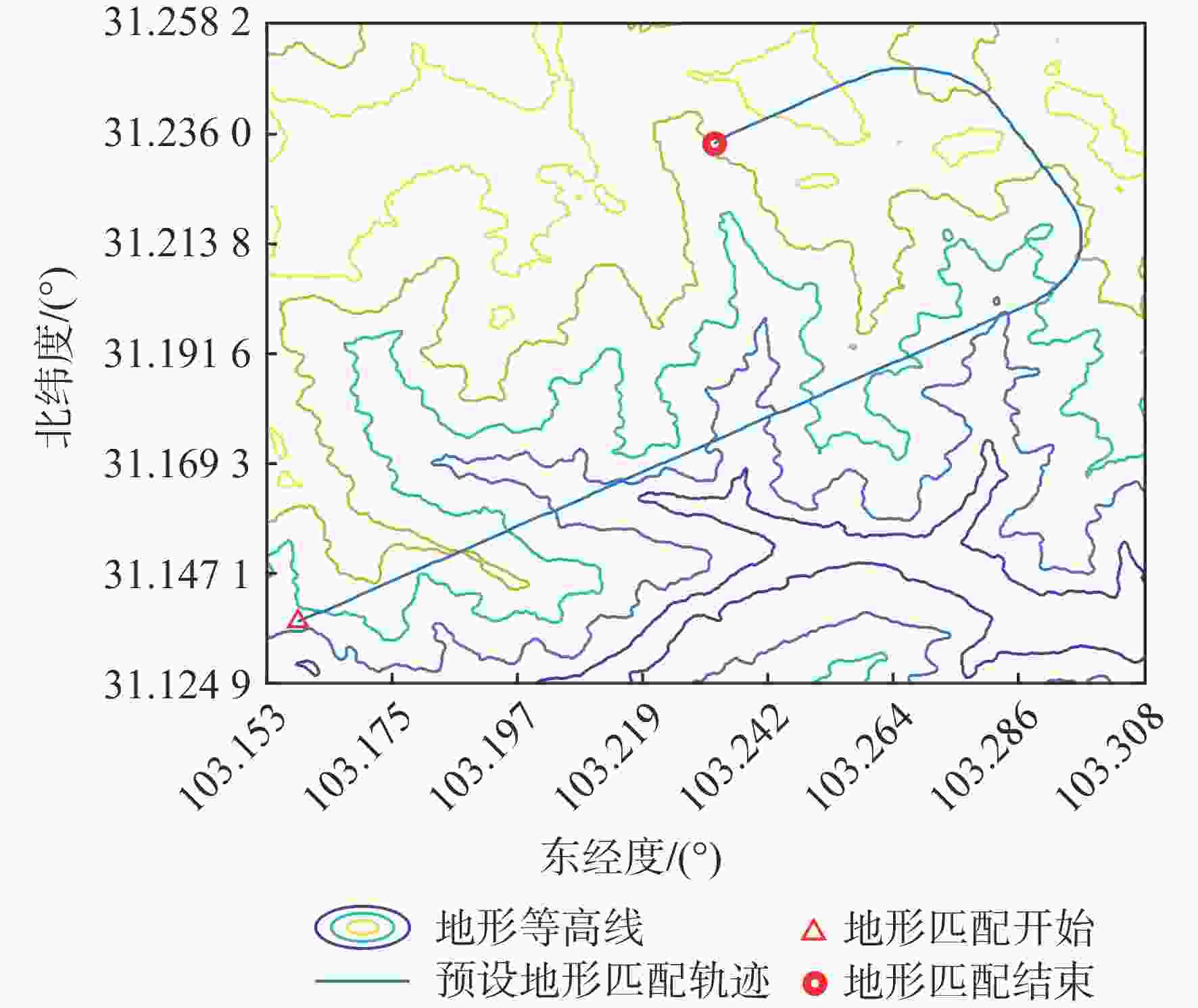
参数 数值 数字地图分辨率/m 30$\subseteq $30 子区域大小/(″) $80 \times 80$ 子区域内位置点数量 6400 测量地形高程图大小/m 630×630(21×21) 高度量测误差/m 5 (1倍标准差) 表 2 惯导仿真参数设置
Table 2. SINS parameters setting
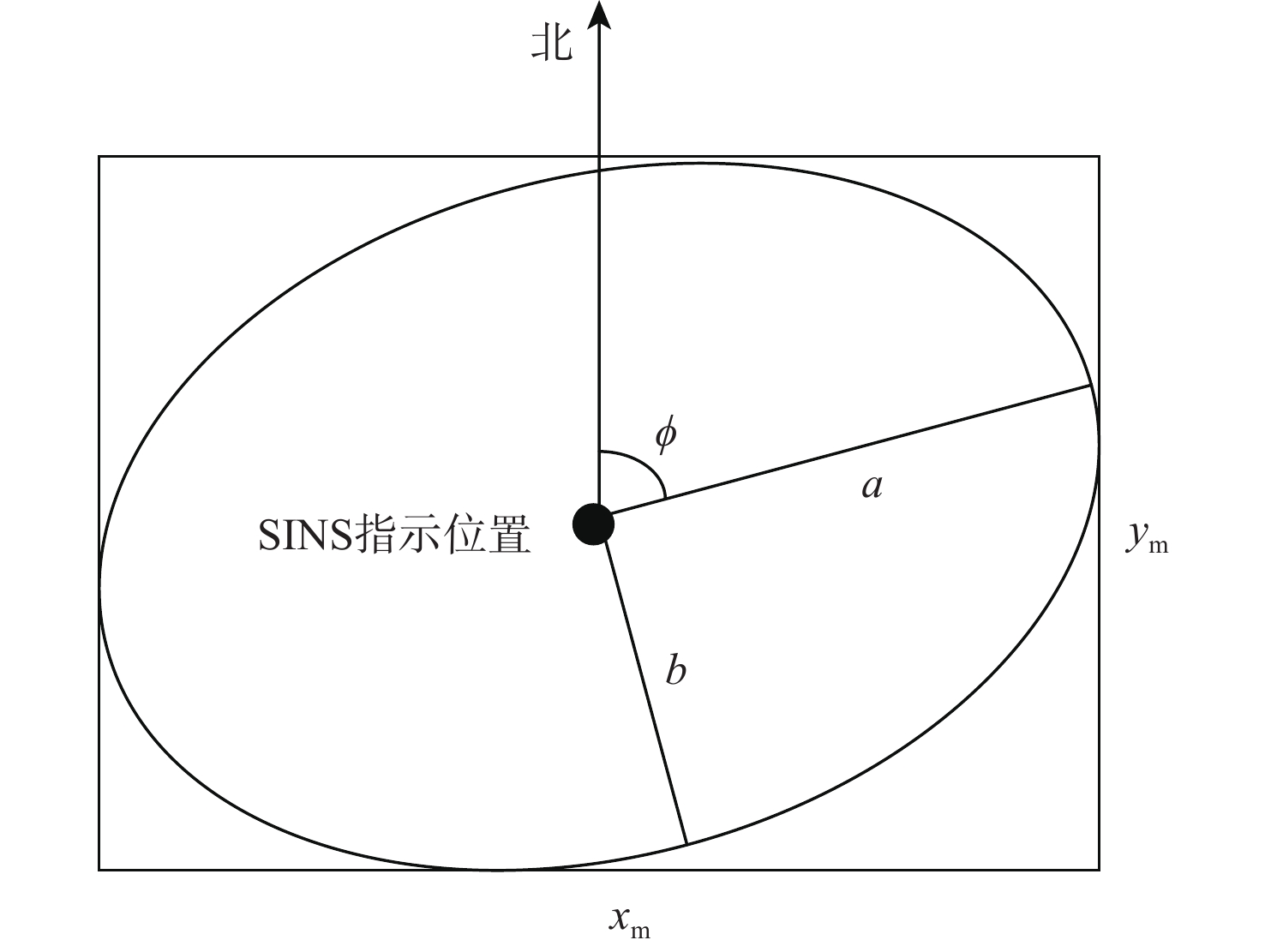
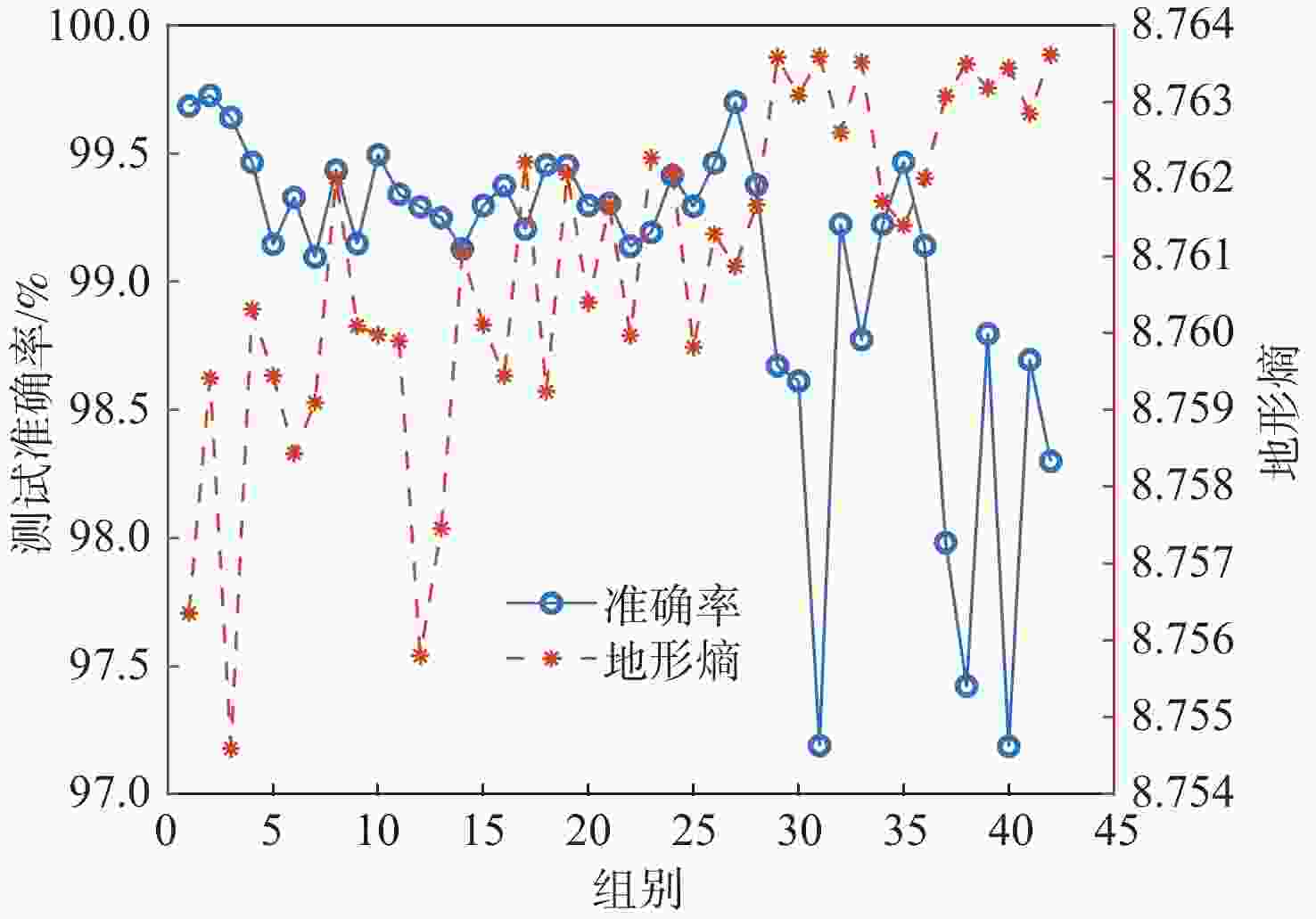
参数 数值 SINS解算周期/s 0.01 陀螺常值漂移/((°)·h−1) $ [0.01,0.015,0.02] $ 陀螺角度随机游走/((°)·h−1/2) 0.001 加速度计常值零偏/μg $[80,90,100]\;$ 加速度计速度随机游走/(μg·Hz−1/2) 0.5 表 3 2 m高度量测误差时匹配成功率统计
Table 3. Statistics of matching success rate with a height measurement error of 2 m
表 4 5 m高度量测误差时匹配成功率统计
Table 4. Statistics of matching success rate with a height measurement error of 5 m
-
[1] MA T, DING S S, LI Y, et al. A review of terrain aided navigation for underwater vehicles[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2023, 281: 114779. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2023.114779 [2] DING P, CHENG X H. A new contour-based combined matching algorithm for underwater terrain-aided strapdown inertial navigation system[J]. Measurement, 2022, 202: 111870. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2022.111870 [3] ZHAO W L, QI S J, LIU R T, et al. A review of underwater multi-source positioning and navigation technology[M]//Advances in Guidance, Navigation and Control. Berlin: Springer, 2023: 5466-5479. [4] 田阳, 李国庆, 宋新. 一种三维地形特征提取和匹配方法[J]. 宇航学报, 2018, 39(6): 690-696.TIAN Y, LI G Q, SONG X. A novel 3D terrain feature detecting and matching method[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2018, 39(6): 690-696(in Chinese). [5] 鲜勇, 任乐亮, 杨子成, 等. 高超声速滑翔飞行器地形匹配辅助导航方法研究[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2020, 46(4): 691-702.XIAN Y, REN L L, YANG Z C, et al. Terrain match aided navigation method of hypersonic glide vehicle[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(4): 691-702(in Chinese). [6] 王丹, 刘利强, 奔粤阳, 等. 基于改进TERCOM的地形辅助导航算法[J]. 中国惯性技术学报, 2023, 31(2): 165-170.WANG D, LIU L Q, BEN Y Y, et al. Terrain aided navigation algorithm based on improved TERCOM[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2023, 31(2): 165-170(in Chinese). [7] RUI J, WANG C, ZHANG H, et al. Matching multi-source DEMs in mountainous terrains[J]. Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 7(6): 571-580. doi: 10.1080/2150704X.2016.1168944 [8] WANG K D, ZHU T Q, GAO Y F, et al. Efficient terrain matching with 3-D Zernike moments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018, 55(1): 226-235. [9] LI Y, WANG R P, CHEN P Y, et al. Terrain matching positioning method based on node multi-information fusion[J]. Journal of Navigation, 2017, 70(1): 82-100. doi: 10.1017/S0373463316000369 [10] LI Z W, ZHENG W, WU F. Geodesic-based method for improving matching efficiency of underwater terrain matching navigation[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(12): 2709. doi: 10.3390/s19122709 [11] CHEN P Y, LIU Y, CHEN X L, et al. Underwater terrain positioning method based on Markov random field for unmanned underwater vehicles[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 2023, 10: 1201716. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2023.1201716 [12] LI Y, MA T, CHEN P Y, et al. Autonomous underwater vehicle optimal path planning method for seabed terrain matching navigation[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2017, 133: 107-115. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2017.01.026 [13] 何艳萍, 刘新学, 蔡艳平, 等. 基于粒子群优化的飞行器地形匹配新算法[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2016, 45(S1): 122-127.HE Y P, LIU X X, CAI Y P, et al. A new algorithm for aircraft terrain matching based on particle swarm optimization[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2016, 45(S1): 122-127(in Chinese). [14] WANG D, LIU L Q, BEN Y Y, et al. Seabed terrain-aided navigation algorithm based on combining artificial bee colony and particle swarm optimization[J]. Applied Sciences, 2023, 13(2): 1166. doi: 10.3390/app13021166 [15] ZHANG F, BIAN H Y, GE W, et al. Exploiting deep matching and underwater terrain images to improve underwater localization accuracy[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2023, 20: 7501305. [16] 袁慧, 谭章禄, 王福浩. 一种高效的相似性度量方法及其分类效果研究[J]. 中国科学: 技术科学, 2022, 52(7): 1096-1110. doi: 10.1360/SST-2022-0049YUAN H, TAN Z L, WANG F H. An efficient similarity measurement method and its classification effect[J]. Scientia Sinica (Technologica), 2022, 52(7): 1096-1110(in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/SST-2022-0049 [17] 陈俊风, 王玉浩, 张学武, 等. 基于小波变换与差分变异BSO-BP算法的大坝变形预测[J]. 控制与决策, 2021, 36(7): 1611-1618.CHEN J F, WANG Y H, ZHANG X W, et al. Dam deformation prediction based on wavelet transform and differential mutation BSO-BP algorithm[J]. Control and Decision, 2021, 36(7): 1611-1618(in Chinese). [18] MA J Y, JIANG X Y, FAN A X, et al. Image matching from handcrafted to deep features: a survey[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2021, 129(1): 23-79. doi: 10.1007/s11263-020-01359-2 [19] 张睿, 李万睿, 肖勇, 等. 基于航迹规划的无人机地形辅助导航[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2024, 45(3): 459-465.ZHANG R, LI W R, XIAO Y, et al. Path planning-based terrain contour matching navigation of unmanned aerial vehicles[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2024, 45(3): 459-465(in Chinese). [20] 龙远, 邓小龙, 杨希祥, 等. 基于PSO-BP神经网络的平流层风场短期快速预测[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2022, 48(10): 1970-1978.LONG Y, DENG X L, YANG X X, et al. Short-term rapid prediction of stratospheric wind field based on PSO-BP neural network[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2022, 48(10): 1970-1978(in Chinese). [21] 崔西明, 邱志鹏, 魏嘉, 等. 基于数据驱动的结构钢表面应力磁巴克豪森噪声表征方法[J]. 航空学报, 2023, 44(8): 427237.CUI X M, QIU Z P, WEI J, et al. Data-driven method for characterization of structural steel surface stress of magnetic Barkhausen noise[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2023, 44(8): 427237(in Chinese). [22] 张硕俨, 陆洋. 基于地形匹配的直升机低空飞行前视告警方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2019, 45(2): 340-346.ZHANG S Y, LU Y. Helicopter forward looking alert method for low-altitude flight based on terrain matching[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2019, 45(2): 340-346(in Chinese). [23] 赵龙, 颜廷君. 不同传感器精度下的地形辅助导航系统性能评估[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2013, 39(8): 1016-1019.ZHAO L, YAN T J. Performance evaluation of a terrain-aided navigation system under different accuracy of sensor[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2013, 39(8): 1016-1019(in Chinese). [24] 马丹山, 王明海, 聂锋, 等. 基于等高线和Hausdorff距离的地形匹配方法[J]. 弹箭与制导学报, 2009, 29(6): 81-84.MA D S, WANG M H, NIE F, et al. Terrain matching algorithm based on contour line and Hausdorff distance[J]. Journal of Projectiles, Rockets, Missiles and Guidance, 2009, 29(6): 81-84(in Chinese). -






 下载:
下载: