Lightweight multi-target detection and tracking method for small unmanned aerial vehicles
-
摘要:
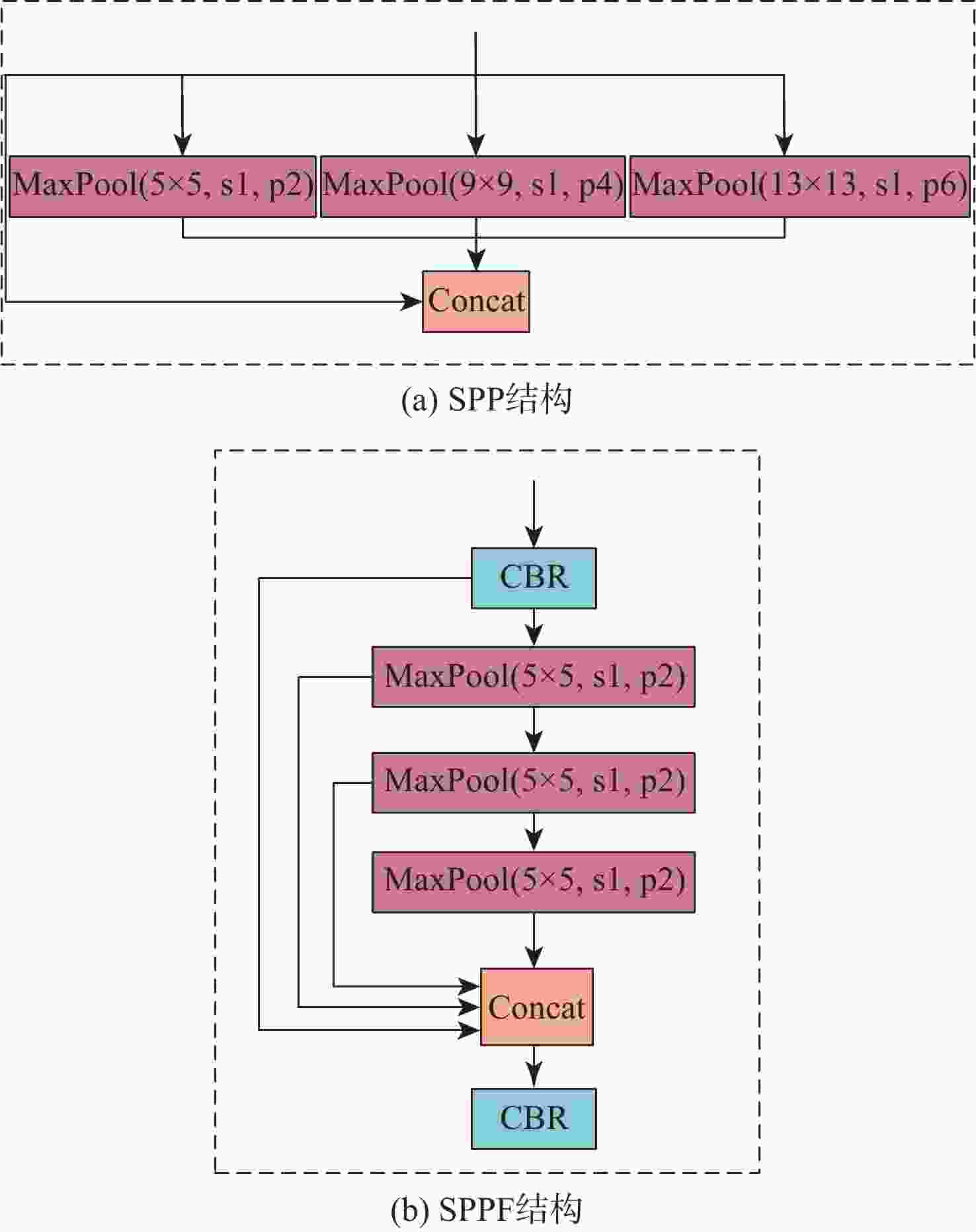
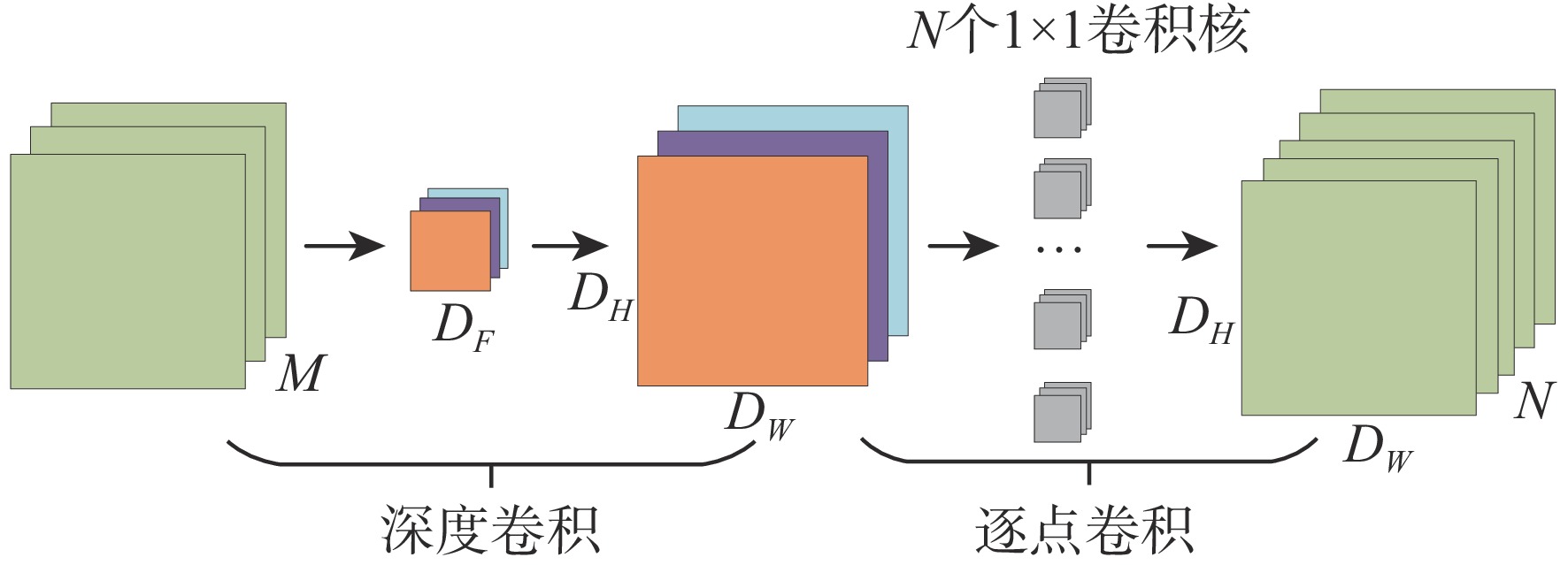
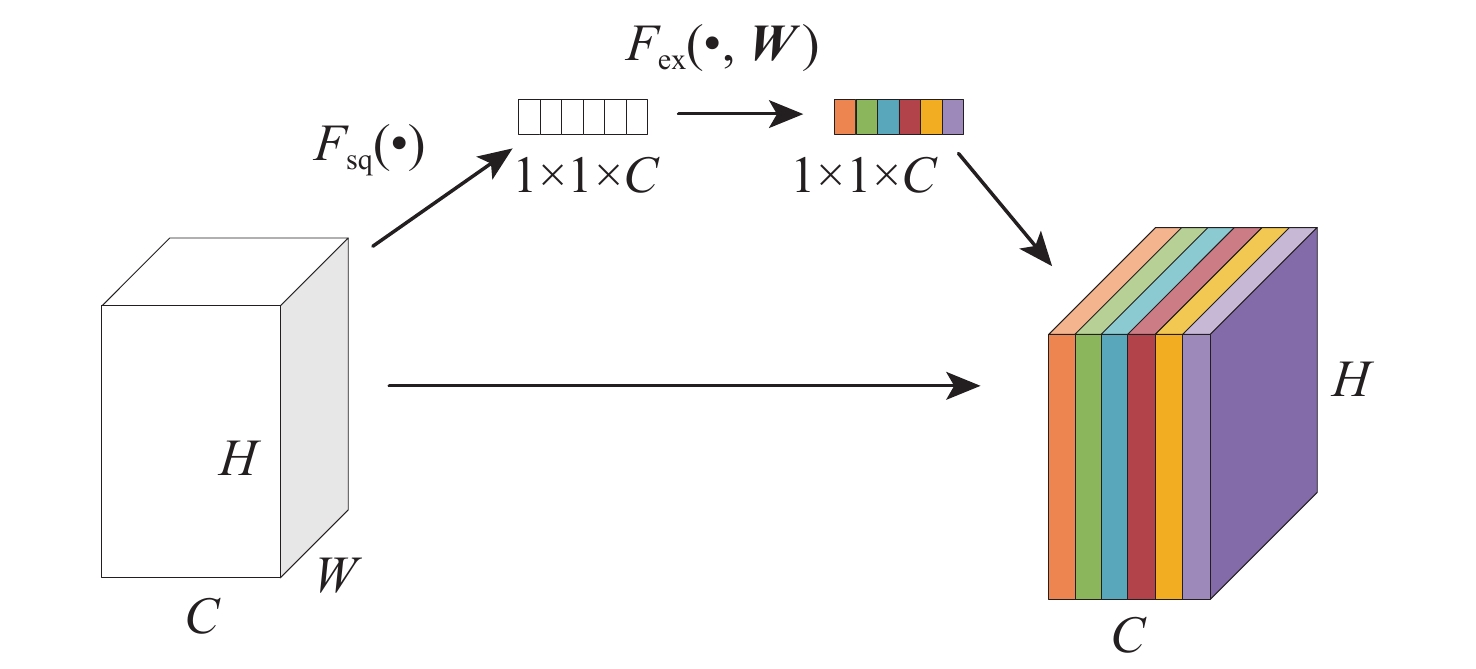
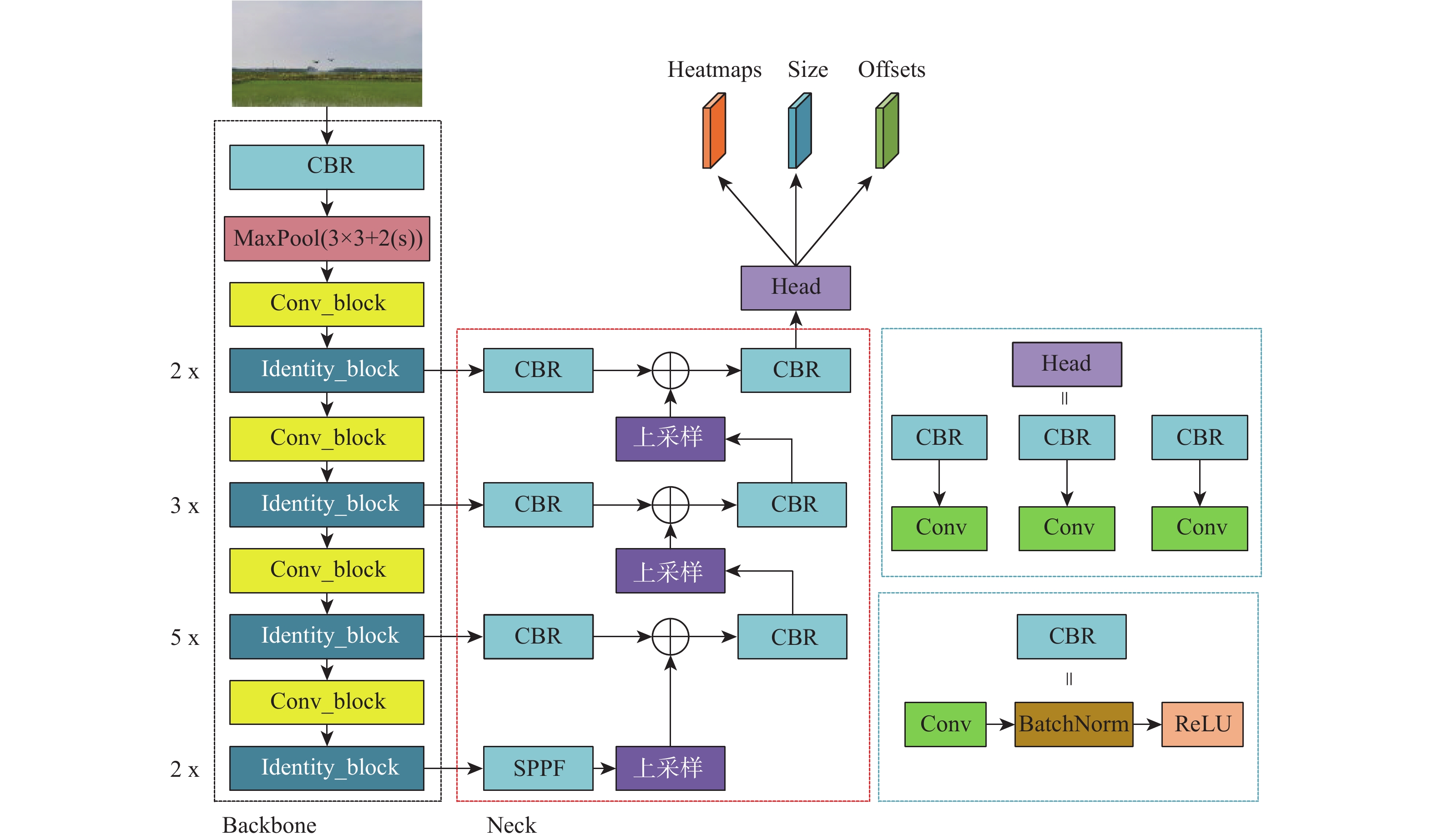
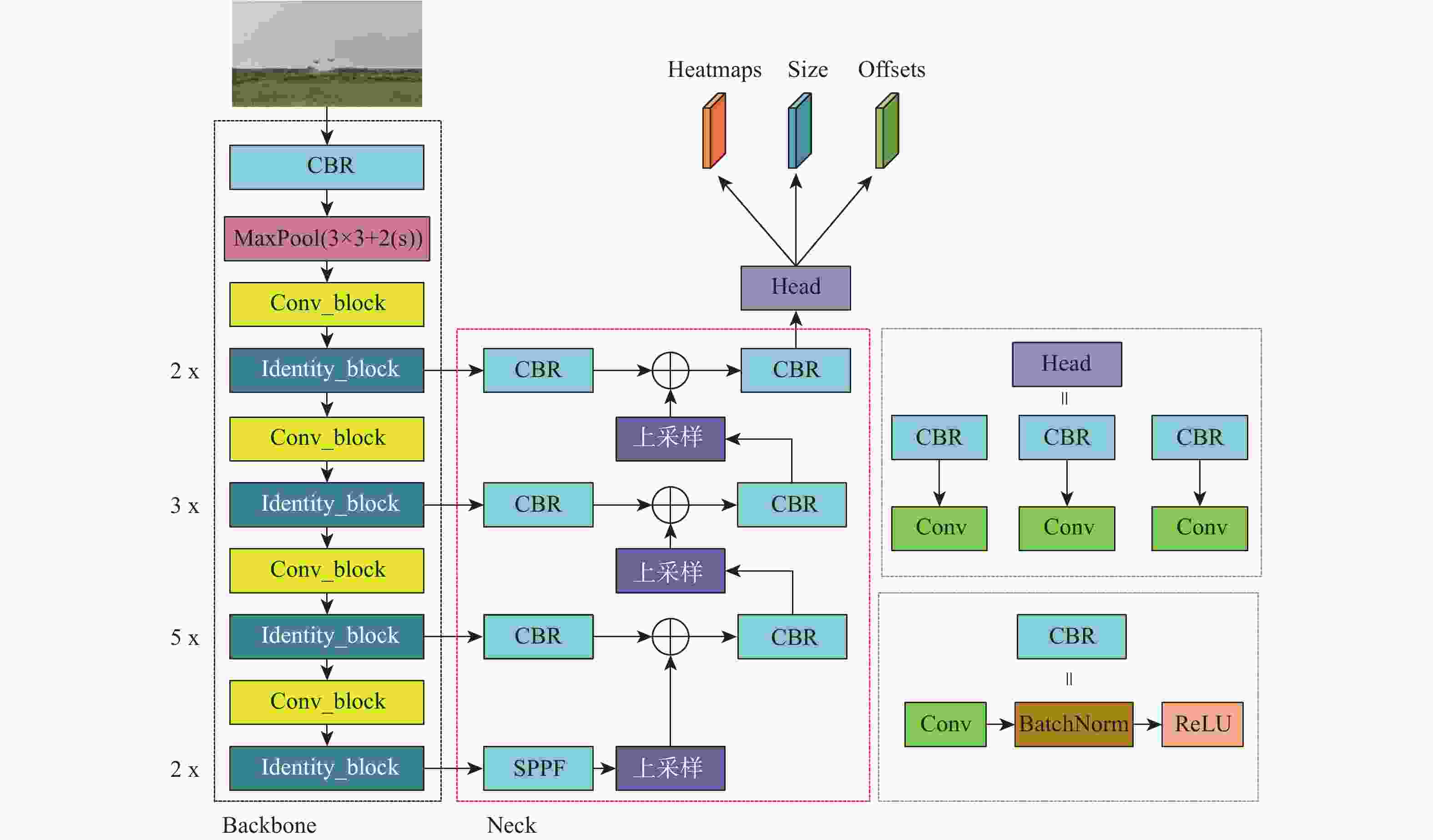
为有效地探测城镇、厂区等复杂环境中的低慢小无人机(UAV)目标,提出一种轻量化多无人机目标视觉检测及跟踪方法。该方法以CenterNet目标检测算法为基础,通过引入多层次特征融合和快速空间金字塔池化(SPPF)结构,并采用MobileNet轻量化主干网络,实现对小型无人机目标的准确检测。为解决长焦相机跟踪无人机目标过程中的不稳定问题,提出一种基于优化DeepSORT的无人机多目标跟踪方法。采用自适应噪声卡Kalman波器进行目标轨迹预测,同时引入相机运动补偿模块和BYTE目标关联算法,以实现对多个无人机目标的准确跟踪。构建小型无人机目标检测及跟踪数据集,对算法进行训练和测试,并在嵌入式设备Jetson NX上进行部署验证。实验结果显示,所提算法平均模型参数量减少了56.9%,mAP提高了1.18%,平均计算量减少了66.5%。在Jetson NX上,单帧图像平均处理时间为36.4 ms,平均模型大小为14.5 MB。该算法具有较好的检测准确性和运行实时性,适用于算力较小的边缘设备部署。
Abstract:A lightweight method for detecting and tracking small unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) targets in complex environments, such as urban and industrial areas, is proposed. Leveraging the CenterNet target detection algorithm as its foundation, this method integrates multi-level feature fusion and a rapid spatial pyramid pooling (SPPF) structure while employing the MobileNet lightweight backbone network to ensure precise detection of small UAV targets. An enhanced DeepSORT-based multi-target tracking technique is presented to overcome the inherent instability in monitoring UAV targets with telescopic cameras. This method utilizes an adaptive noise Kalman filter (NSA Kalman Filter) for target trajectory prediction and incorporates a camera motion compensation module and BYTE target association algorithm to achieve accurate tracking of multiple UAV targets. Furthermore, a dataset for detecting and tracking small UAV targets is constructed, and the proposed algorithm is trained, tested, and validated on the embedded Jetson NX device. Experimental results demonstrate a reduction of 56.9% in average model parameter count, a 1.18% increase in mAP, and a 66.5% reduction in average computational load. With an average model size of 14.5 MB and an average processing time per frame of 36.4 ms on the Jetson NX platform, the algorithm's efficacy in accomplishing accurate identification, real-time operation, and appropriateness for deployment on edge devices with constrained computational resources is confirmed.
-
Key words:
- small UAVs /
- lightweight /
- target detection /
- multi-object tracking /
- deep learning
-
表 1 关键硬件参数
Table 1. Key hardware parameters
硬件 配置 GPU NVIDIA RTX 3090(单卡) CPU 13th Gen Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-13400 硬盘 SAMSUNG 980 SSD 1TB 内存 8 GB*2 表 2 DroneBirds数据集测试结果
Table 2. DroneBirds dataset test results
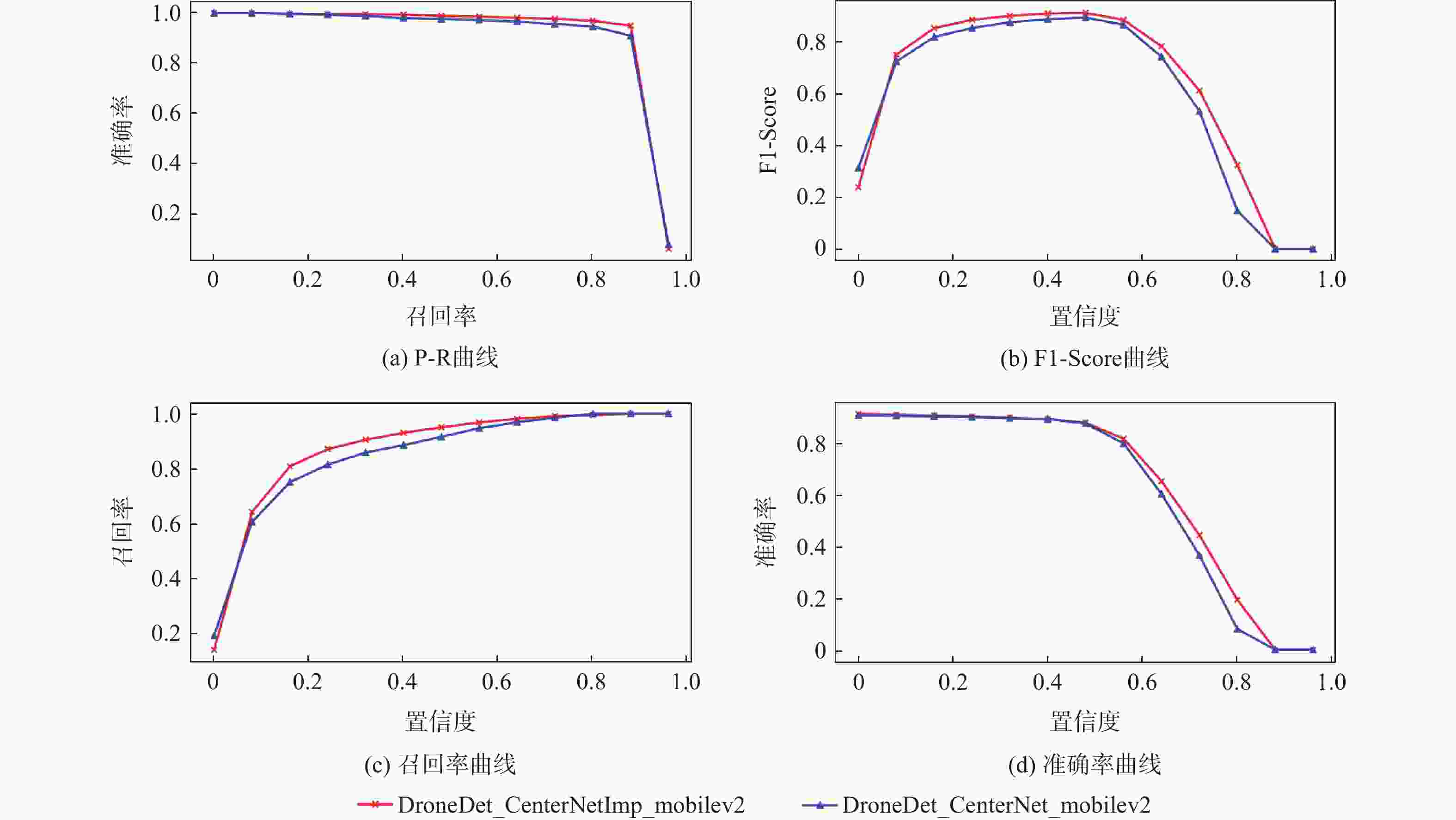
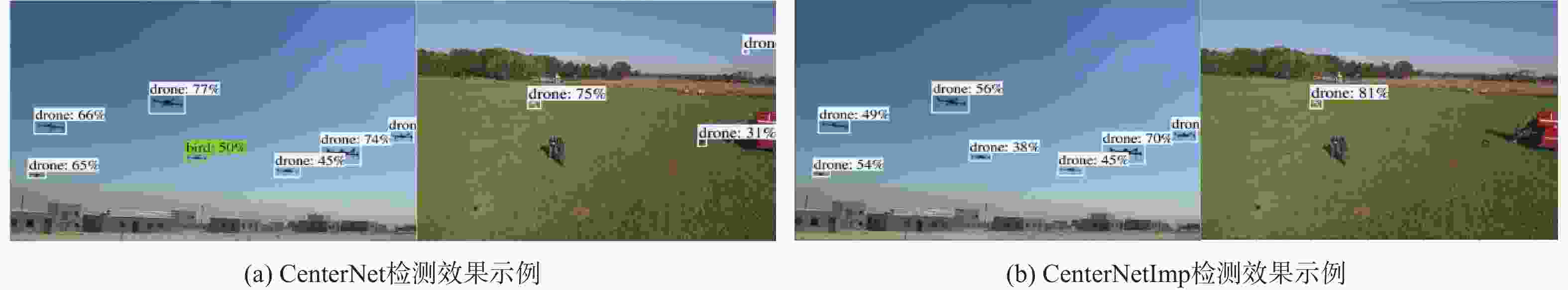
模型 主干网络 mAP50 模型参数/百万 计算量/(109 s−1) CenterNet[25] ResNet-18 92.8 20.2 41.44 ResNet-50 93.7 45.12 66.38 MobileNetV2 92.3 17.54 40.06 MobileNetV3 91.6 15.67 36.87 CenterNetImp
(基于CenterNet改进)ResNet-18 94.4 12.21 17.02 ResNet-50 94.8 27.08 30.40 MobileNetV2 93.5 4.11 9.28 MobileNetV3 92.4 4.41 8.67 表 3 本文算法与主流多目标跟踪算法对比
Table 3. Comparison of proposed algorithm with mainstream multi-target tracking algorithms
表 4 不同运动补偿算法效果对比
Table 4. Comparison of the effects of different motion compensation algorithms
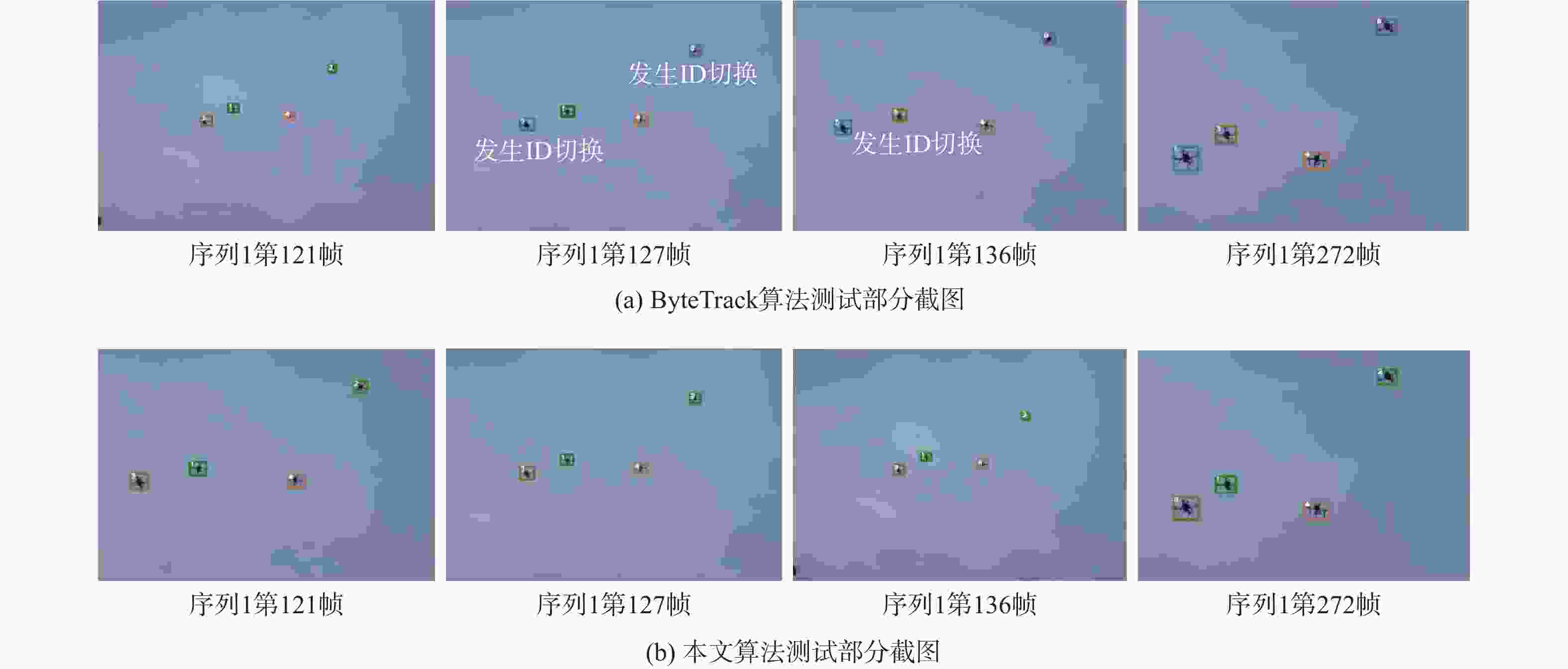
相机运动补偿方法 IDF1↑ MOTA↑ MOTP↓ IDs↓ FP↓ FN↓ FPS↑ 光流法 94.00 97.28 0.1567 9 176 260 54.92 ORB特征点配准 93.00 96.79 0.1622 62 189 375 70.73 SIFT特征点配准 89.54 96.86 0.1616 37 197 332 23.38 无相机运动补偿 83.07 96.29 0.1721 29 203 320 79.93 表 5 表观特征模型消融实验
Table 5. Ablation experiment of appearance feature model
表观特征模型 IDF1↑ MOTA↑ MOTP↓ IDs↓ FP↓ FN↓ FPS↑ 否 94.00 97.28 0.1567 9 176 260 54.92 是 92.40 96.32 0.1534 17 196 242 47.34 表 6 本文算法在Jetson NX上部署后的运行时间
Table 6. The running time of the algorithm after deployment on Jetson NX
模型 主干网络/加速精度 检测时间/ms 跟踪时间/ms 总时间/ms 帧率 CenterNet[25] ResNet-18/FP16 42.379 12.347 54.726 18.27 ResNet-18/FP32 62.429 12.886 75.315 13.27 MobileNetV2/FP16 40.401 11.853 52.254 19.13 MobileNetV2/FP32 65.656 12.382 78.038 12.81 MobileNetV3/FP16 41.829 11.946 53.775 18.59 MobileNetV3/FP32 59.025 12.203 71.228 14.03 CenterNetImp ResNet-18/FP16 24.856 11.632 36.488 27.40 ResNet-18/FP32 34.727 11.371 46.098 21.69 MobileNetV2/FP16 25.934 11.498 37.432 26.71 MobileNetV2/FP32 28.804 11.347 40.151 24.90 MobileNetV3/FP16 23.855 11.436 35.291 28.33 MobileNetV3/FP32 28.93 11.267 40.197 24.87 表 7 本文算法模型大小与改进前对比
Table 7. Comparison of the algorithm in this paper with that before improvement
模型 主干网络 ONNX模型/MB FP32优化模型/MB FP16优化模型/MB CenterNet[25] ResNet-18 78 106 39 MobileNetV2 67 68 34 MobileNetV3 60 62 32 CenterNetImp ResNet-18 47 77 24 MobileNetV2 16 18 8.6 MobileNetV3 17 21 11 -
[1] HE K M, GKIOXARI G, DOLLÁR P, et al. Mask R-CNN[C]// Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 2980-2988. [2] REDMON J, DIVVALA S, GIRSHICK R, et al. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection[C]// Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 779-788. [3] REDMON J, FARHADI A. YOLO9000: better, faster, stronger[C]// Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 6517-6525. [4] REDMON J, FARHADI A. Yolov3: an incremental improvement[EB/OL]. (2018-04-08) [2024-06-01]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1804.02767. [5] BOCHKOVSKIY A, WANG C Y, LIAO H Y M. Yolov4: optimal speed and accuracy of object detection[EB/OL]. (2020-04-23)[2024-6-5]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2004.10934. [6] WANG C Y, BOCHKOVSKIY A, LIAO H Y M. YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors[C]// Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2023: 7464-7475. [7] LIU W, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: single shot multibox detector[C]// European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 21-37. [8] HOWARD A G, ZHU M, CHEN B, et al. MobileNets: efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications[EB/OL]. (2017-04-17)[2024-06-05]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.04861. [9] SANDLER M, HOWARD A, ZHU M L, et al. MobileNetV2: inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks[C]// Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 4510-4520. [10] HOWARD A, SANDLER M, CHEN B, et al. Searching for mobileNetV3[C]// Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 1314-1324. [11] ZHANG X Y, ZHOU X Y, LIN M X, et al. ShuffleNet: An extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices[C]// Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 6848-6856. [12] MA N N, ZHANG X Y, ZHENG H T, et al. ShuffleNet V2: practical guidelines for efficient CNN architecture design[C]// European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 122-138. [13] WU B C, KEUTZER K, DAI X L, et al. FBNet: hardware-aware efficient ConvNet design via differentiable neural architecture search[C]// Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 10726-10734. [14] DAI X, WAN A, ZHANG P, et al. FBNetV3: joint architecture-recipe search using neural acquisition function[EB/OL]. (2021-03-30)[2024-06-05]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2006.02049. [15] JIANG N, WANG K R, PENG X K, et al. Anti-UAV: a large-scale benchmark for vision-based UAV tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2021, 25: 486-500. [16] COLUCCIA A, FASCISTA A, SCHUMANN A, et al. Drone-Vs-Bird detection challenge at IEEE AVSS2021[C]// Proceedings of the 2021 17th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 1-8. [17] ZHAO J, ZHANG J S, LI D D, et al. Vision-based anti-UAV detection and tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(12): 25323-25334. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2022.3177627 [18] YU Q J, MA Y C, HE J F, et al. A unified Transformer-based tracker for anti-UAV tracking[C]// Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2023: 3036-3046. [19] 谢学立, 席建祥, 卢瑞涛, 等. 动态区域聚焦的反无人机红外长时跟踪算法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2025, 51(9): 3039-3051.XIE X L, XI J X, LU R T, et al. Long-term infrared object tracking algorithm based on dynamic region focusing for anti-UAV[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2025, 51(9): 3039-3051(in Chinese). [20] 陈家俊, 李响, 宋延嵩, 等. 双置信度下多特征自适应融合的红外弱小目标实时跟踪 [J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2024, 50 (2): 433-442.Chen J J, Li X, Song Y S, et al. Real - time Tracking of Infrared Dim and Small Targets Based on Adaptive Fusion of Multi-features Under Dual Confidence Levels[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2024, 50(2): 433-442(in Chinese). [21] 刘芳, 杨雨妍, 王鑫. 基于特征融合和分块注意力的无人机跟踪算法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2025, 51(5): 1566-1578.LIU F, YANG Y Y, WANG X. UAV tracking algorithm based on feature fusion and block attention[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2025, 51(5): 1566-1578 (in Chinese). [22] MEINHARDT T, KIRILLOV A, LEAL-TAIXÉ L, et al. TrackFormer: multi-object tracking with transformers[C]// Proceedings of 2022 the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2023. [23] LI S Y, FISCHER T, KE L, et al. Ovtrack: open-vocabulary multiple object tracking[C]// Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2023: 5567-5577. [24] QIN Z, ZHOU S P, WANG L, et al. Motiontrack: learning robust short-term and long-term motions for multi-object tracking[C]// Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2023: 17939-17948. [25] DUAN K W, BAI S, XIE L X, et al. Centernet: keypoint triplets for object detection[C]// Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 6568-6577. [26] PUJARA A, BHAMARE M. DeepSORT: real time & multi-object detection and tracking with YOLO and TensorFlow[C]// Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Augmented Intelligence and Sustainable Systems. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2022: 456-460. [27] DU Y H, WAN J F, ZHAO Y Y, et al. GIAOTracker: a comprehensive framework for MCMOT with global information and optimizing strategies in VisDrone 2021[C]// Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 2809-2819. [28] AHARON N, ORFAIG R, BOBROVSKY B Z. BoT-SORT: robust associations multi-pedestrian tracking[EB/OL]. (2022-07-07)[2024-06-03]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2206.14651. -






 下载:
下载: