-
摘要:
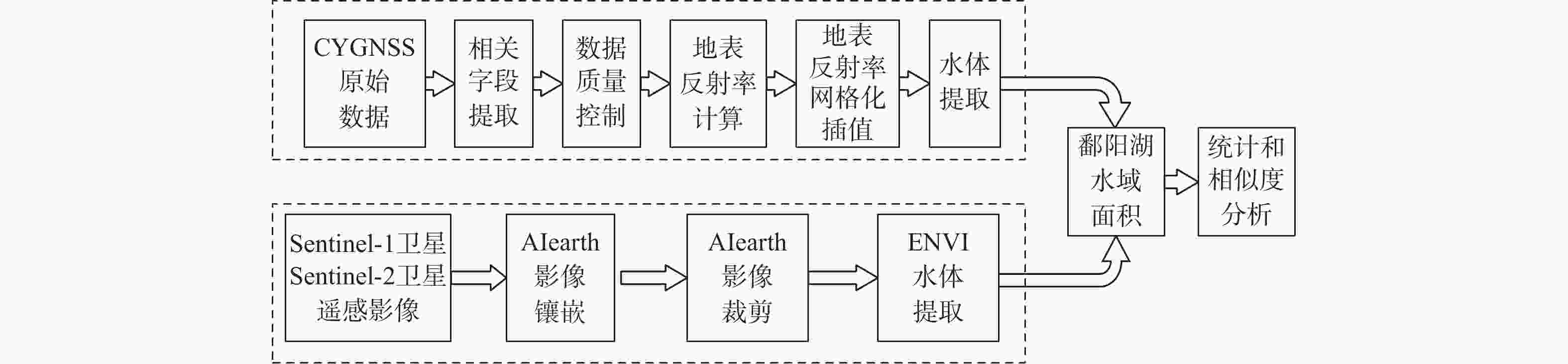
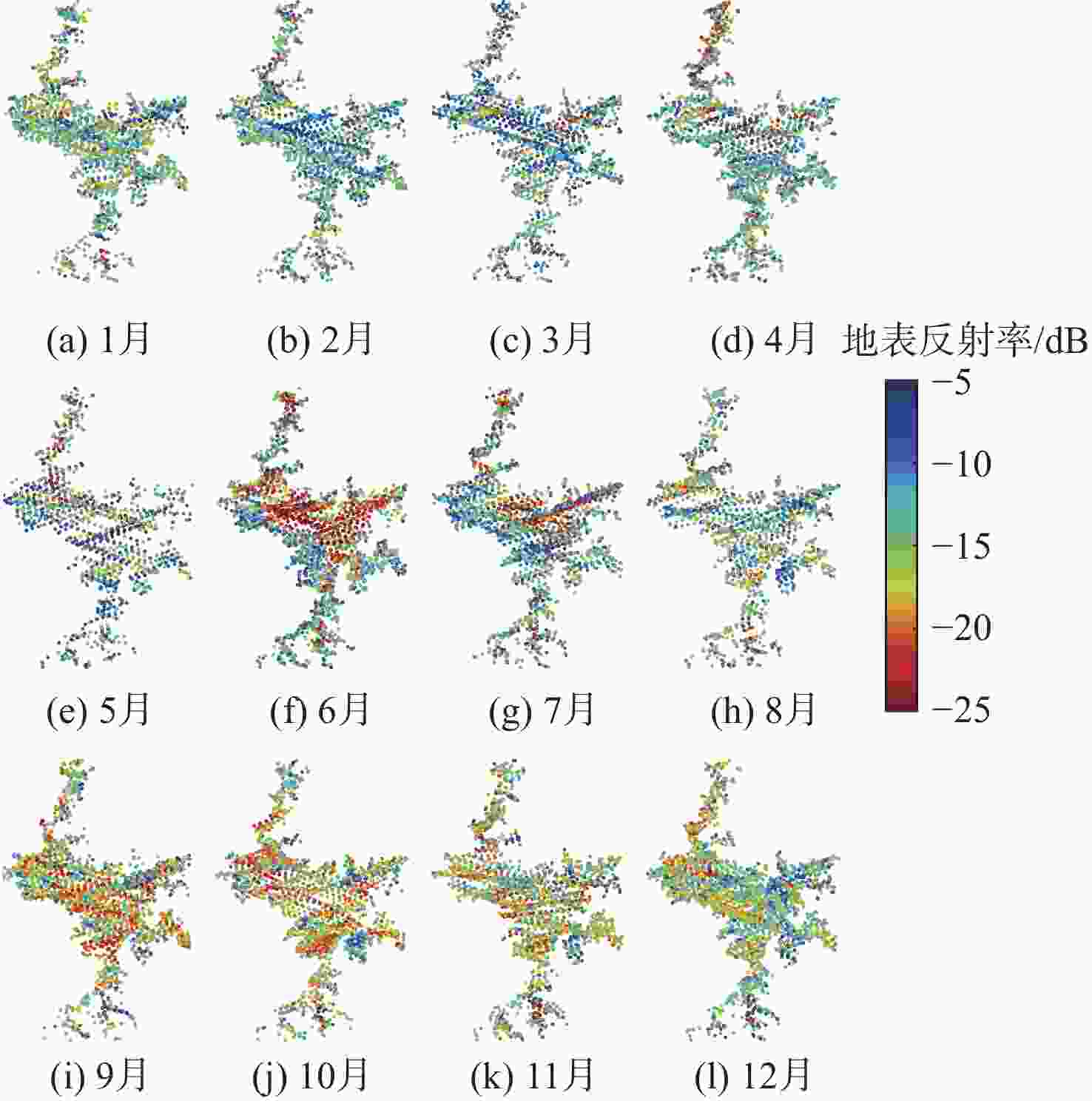
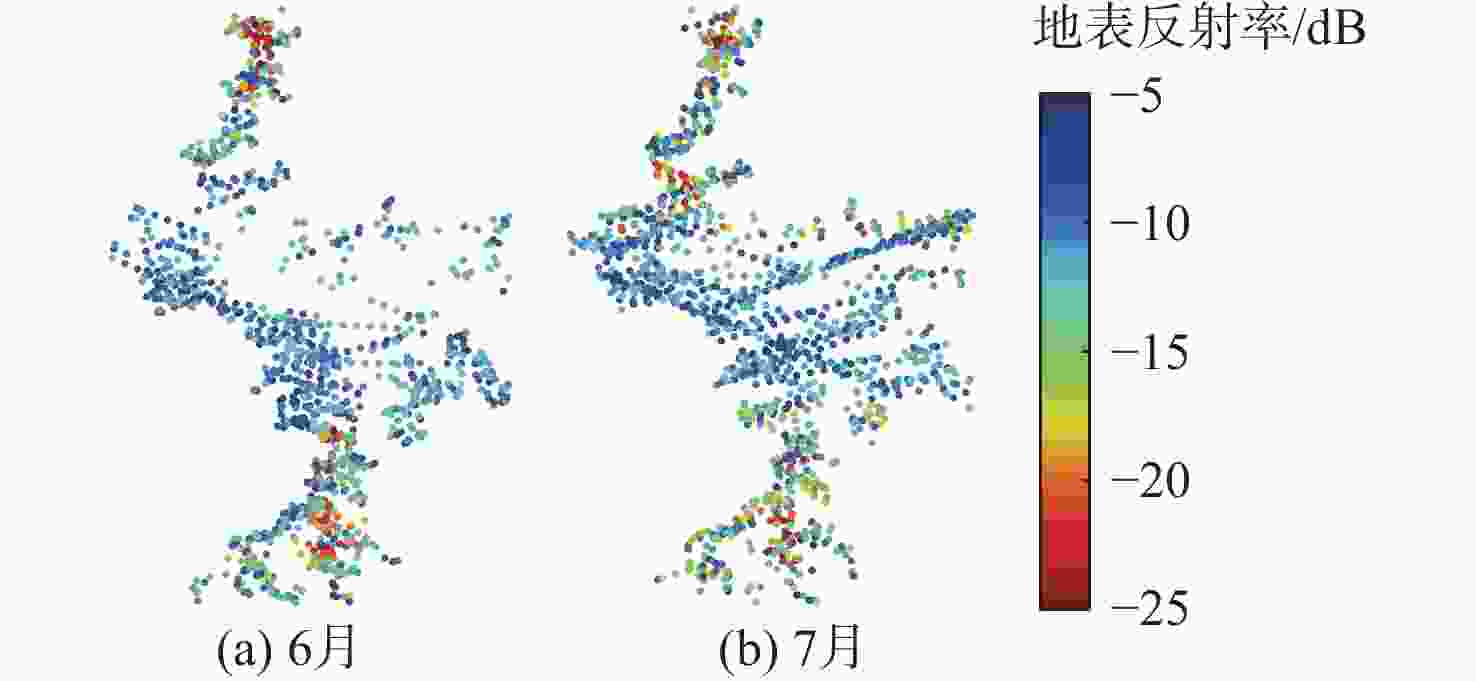
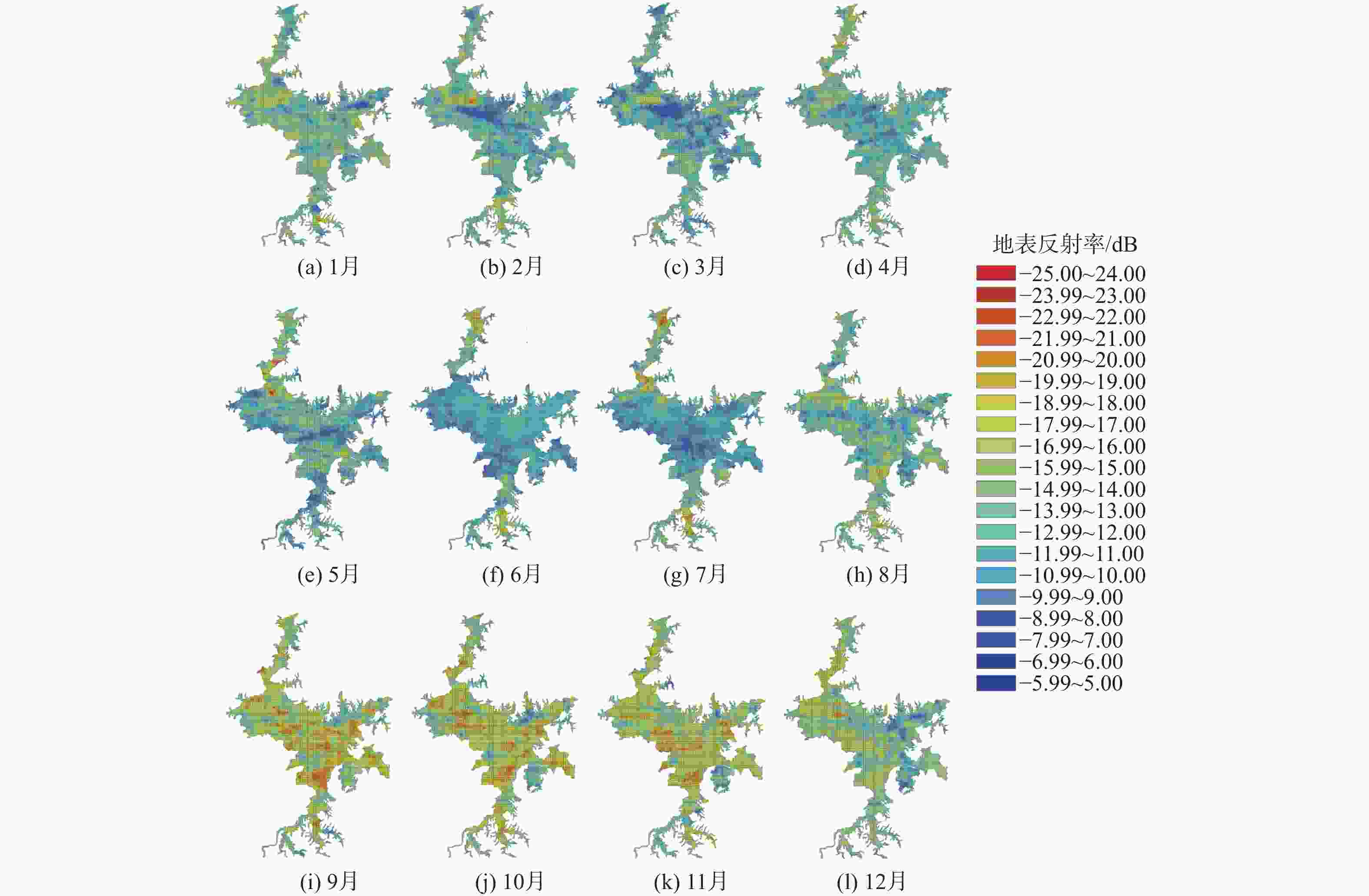
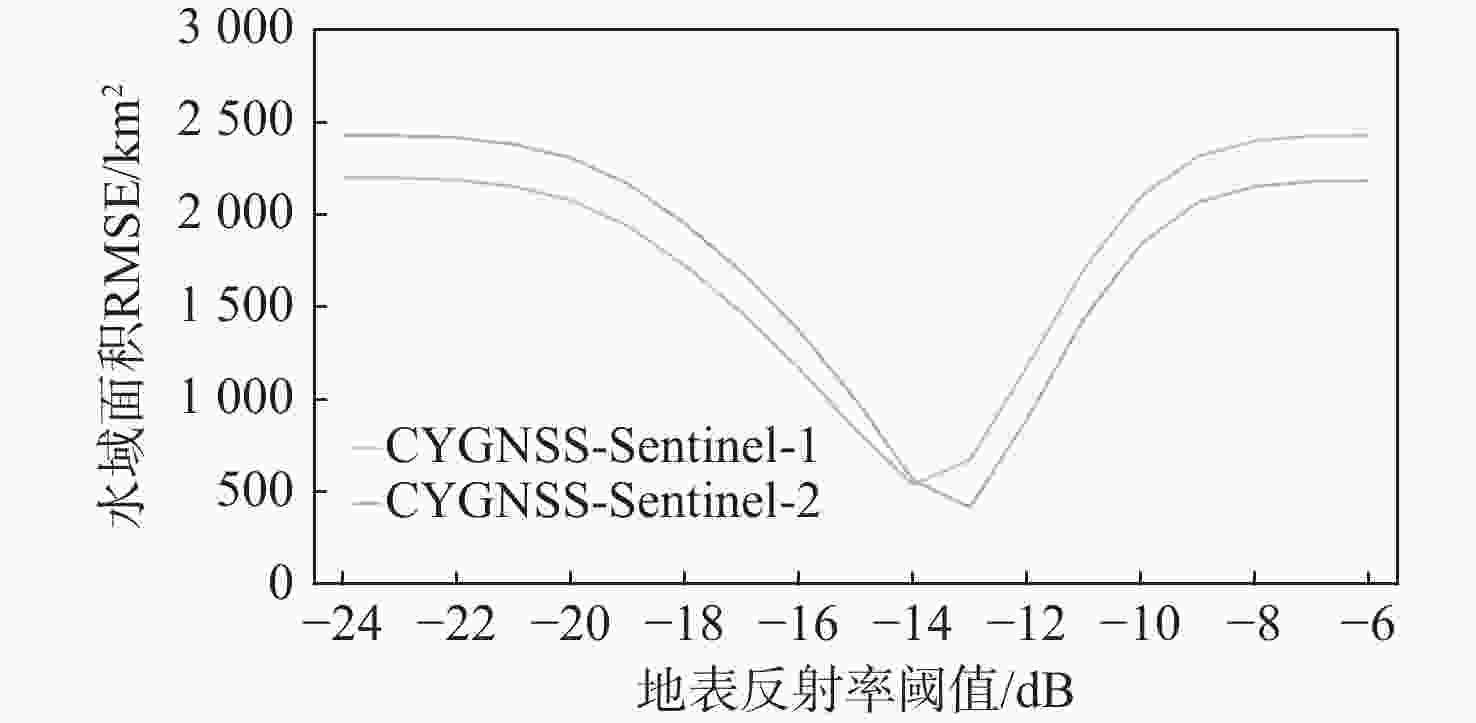
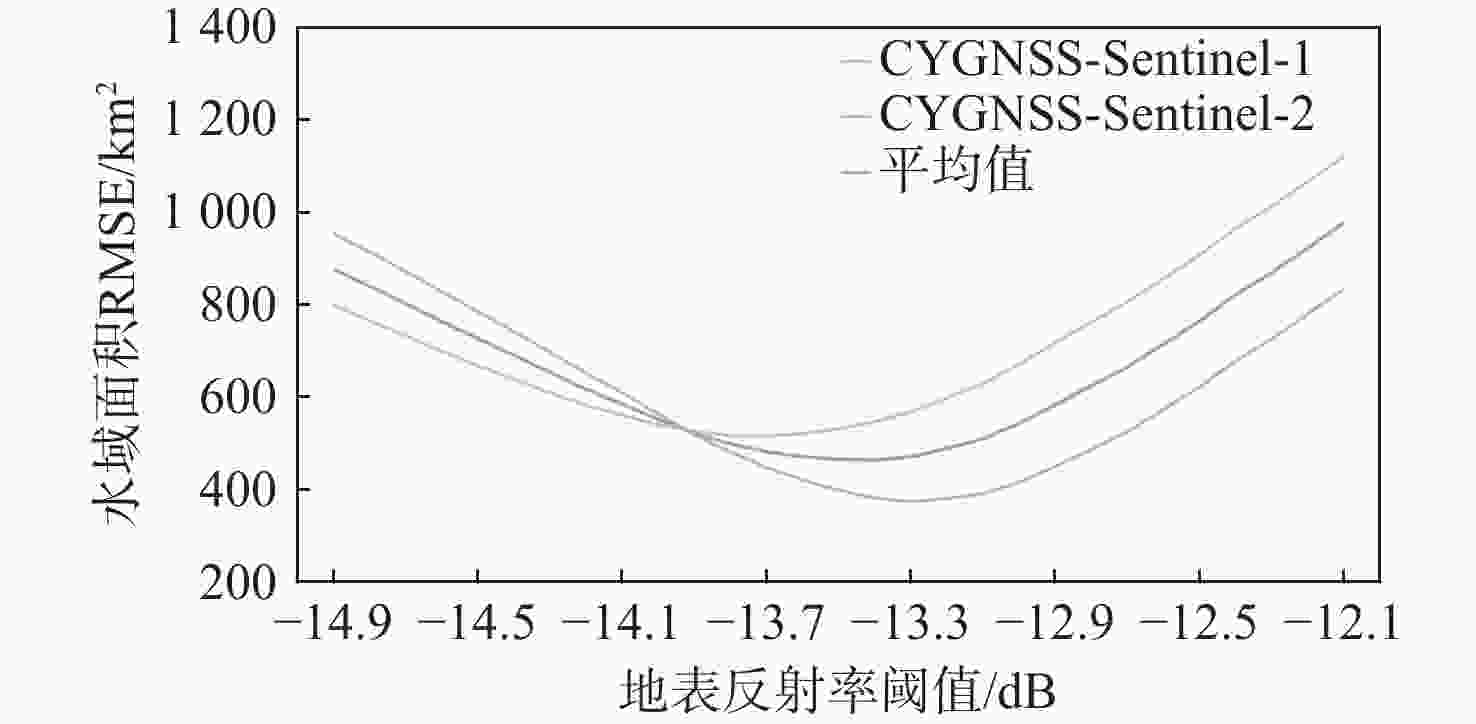
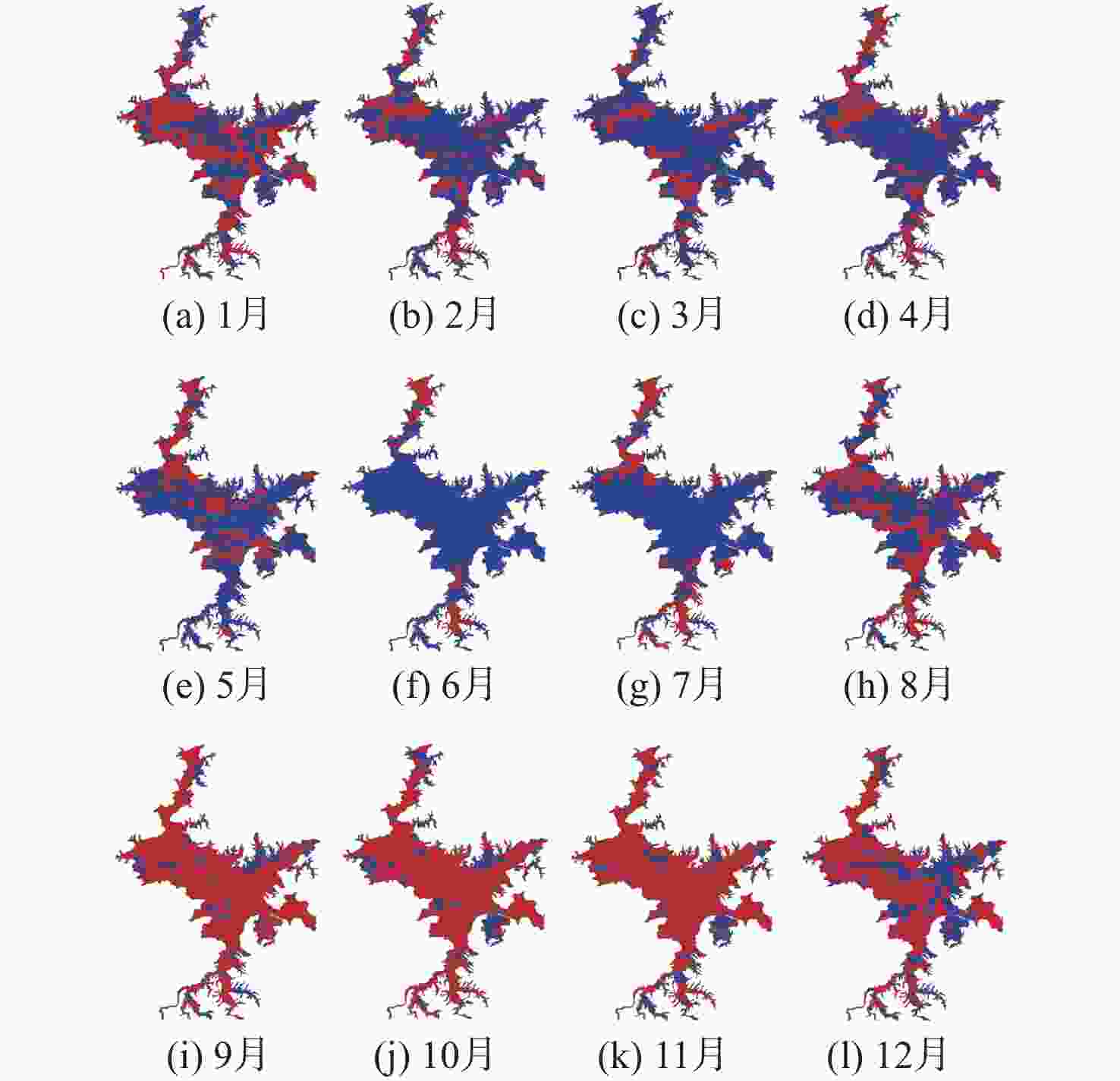
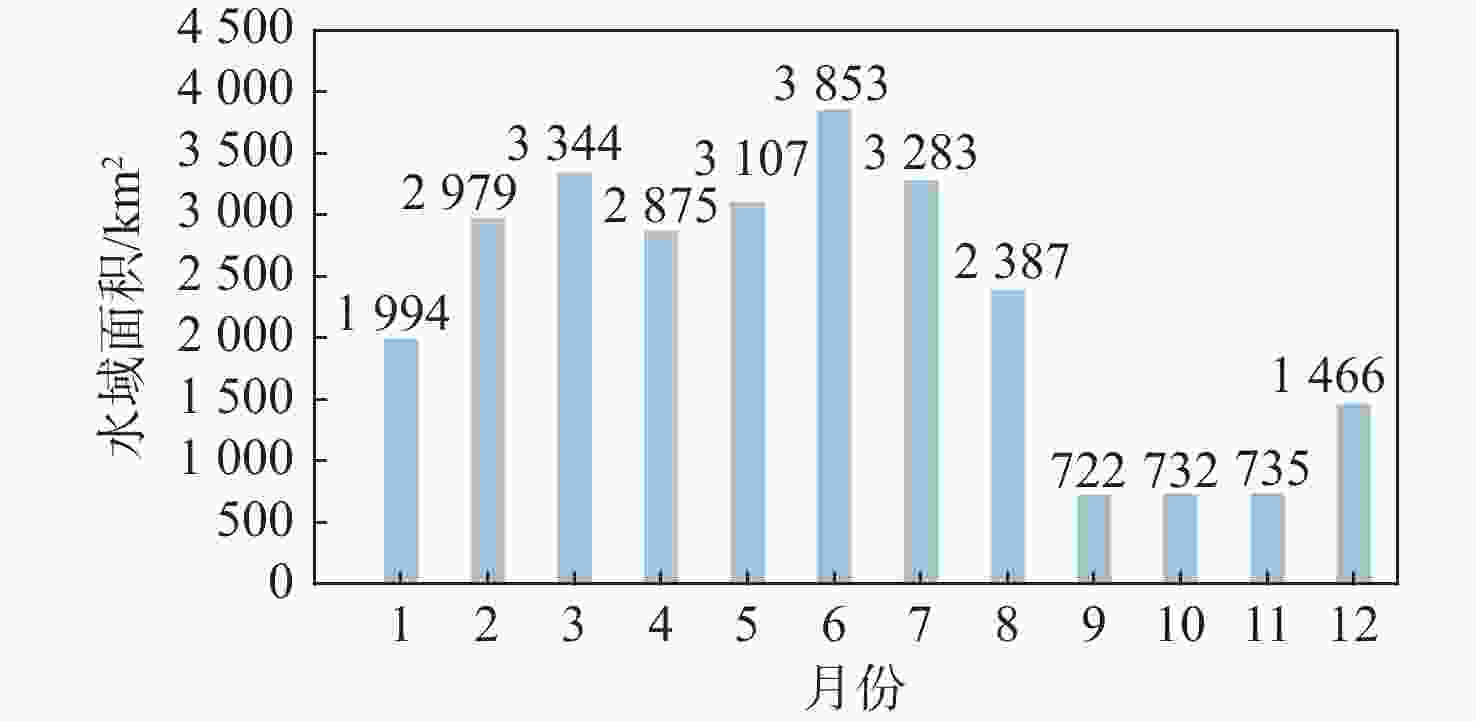
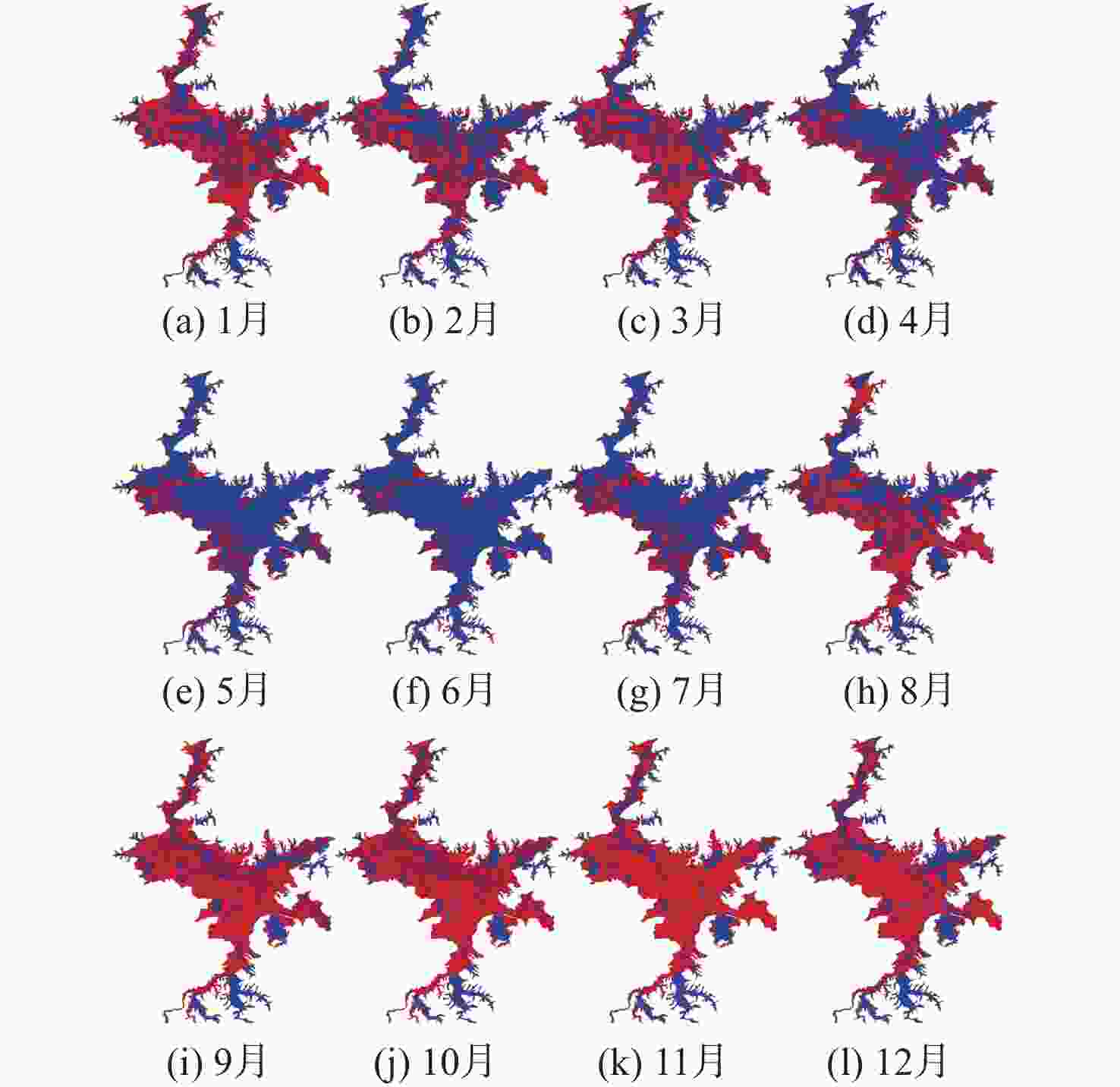
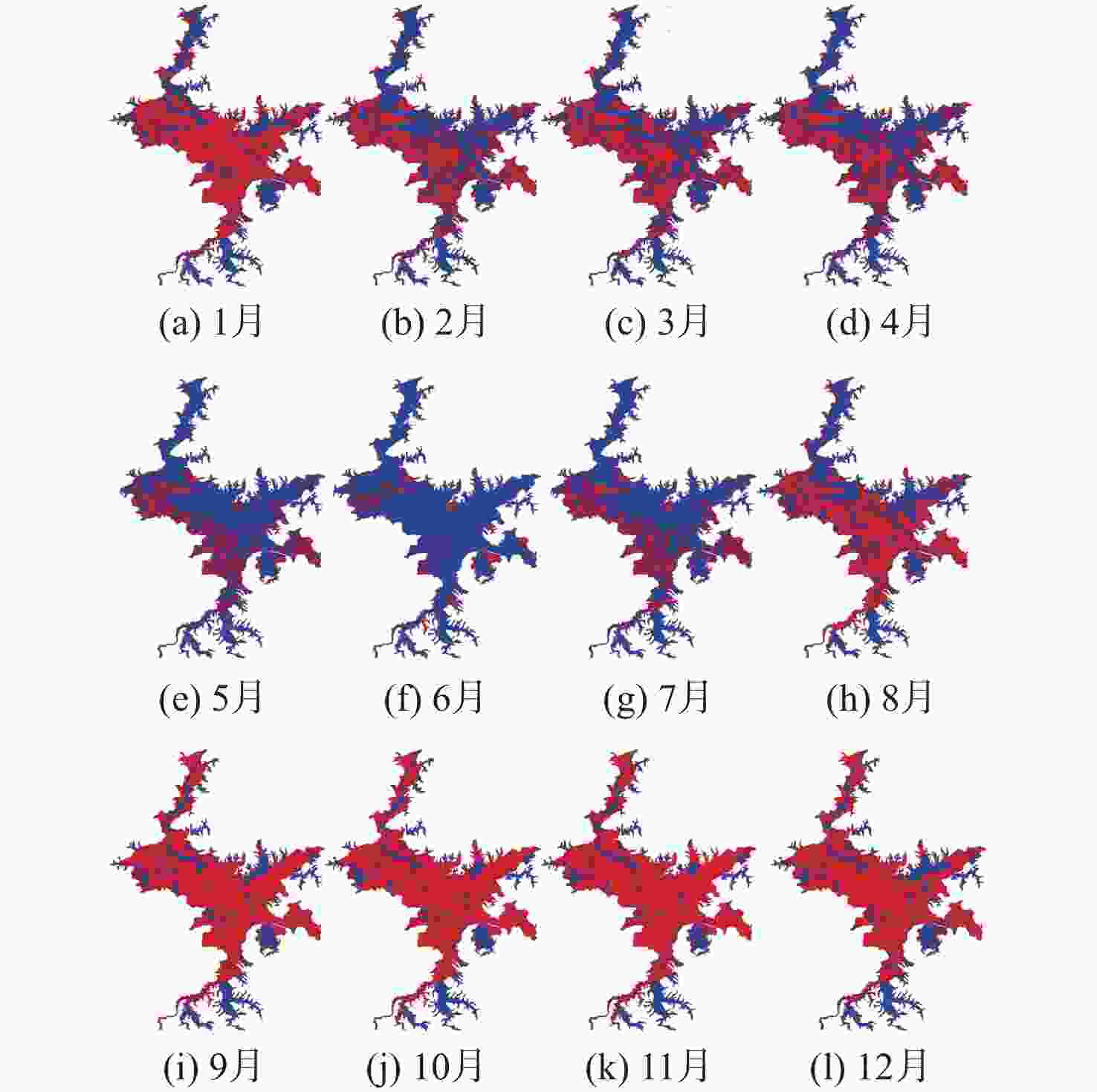
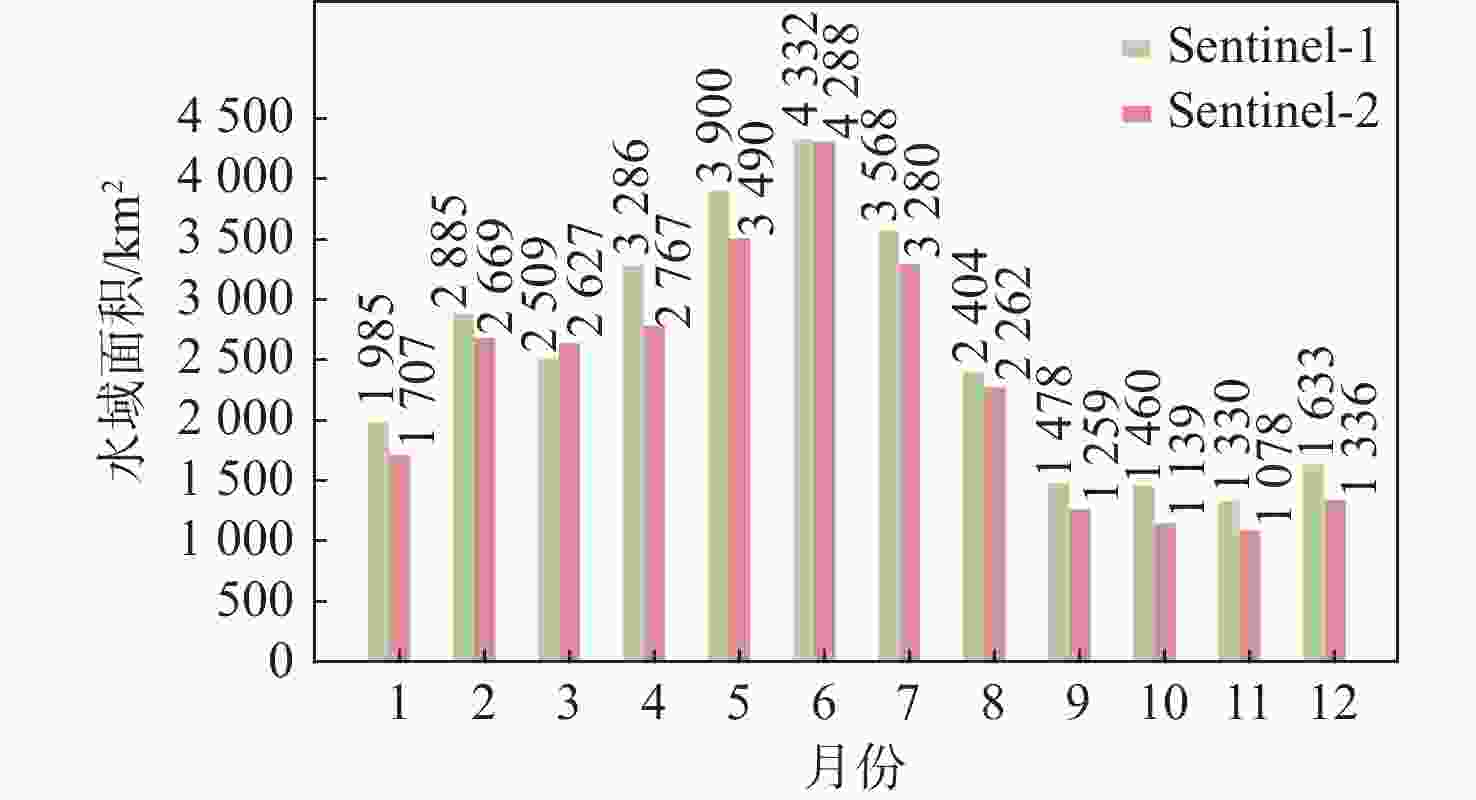
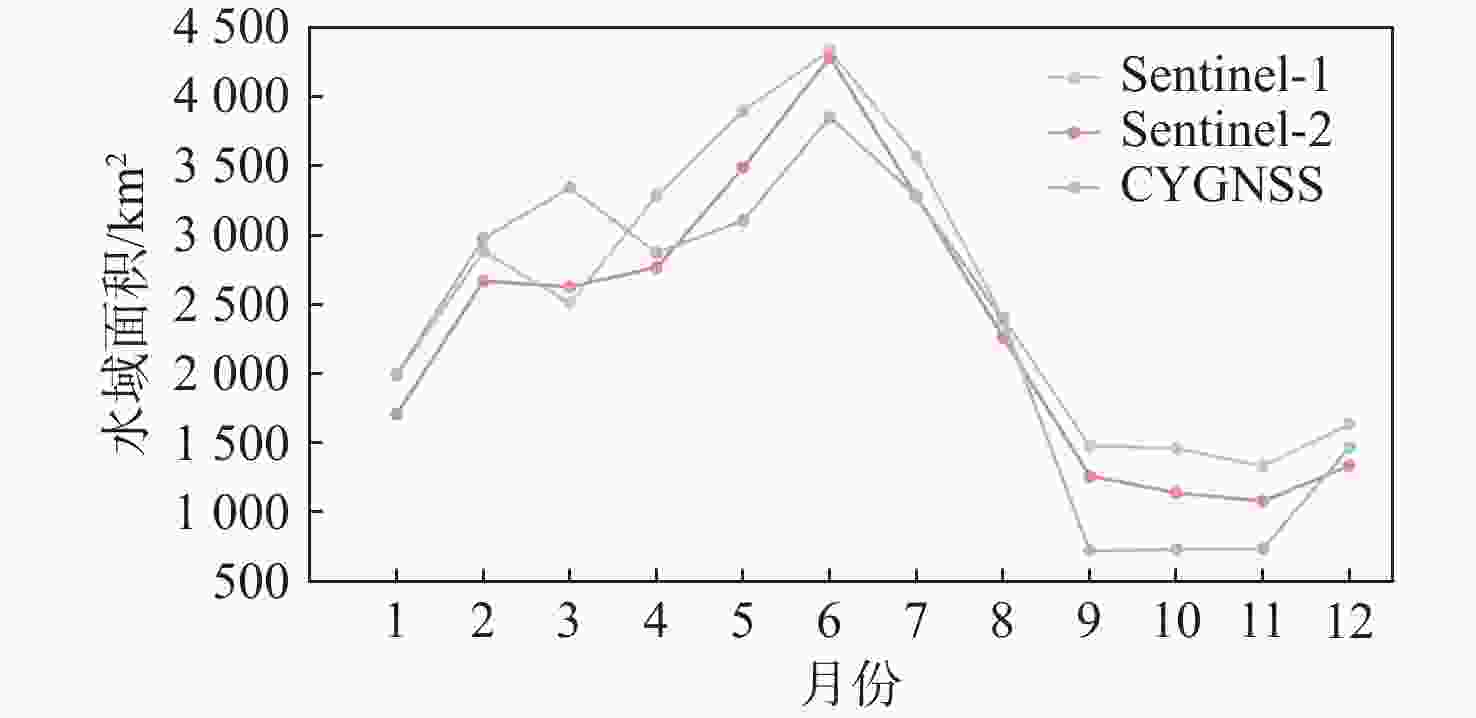
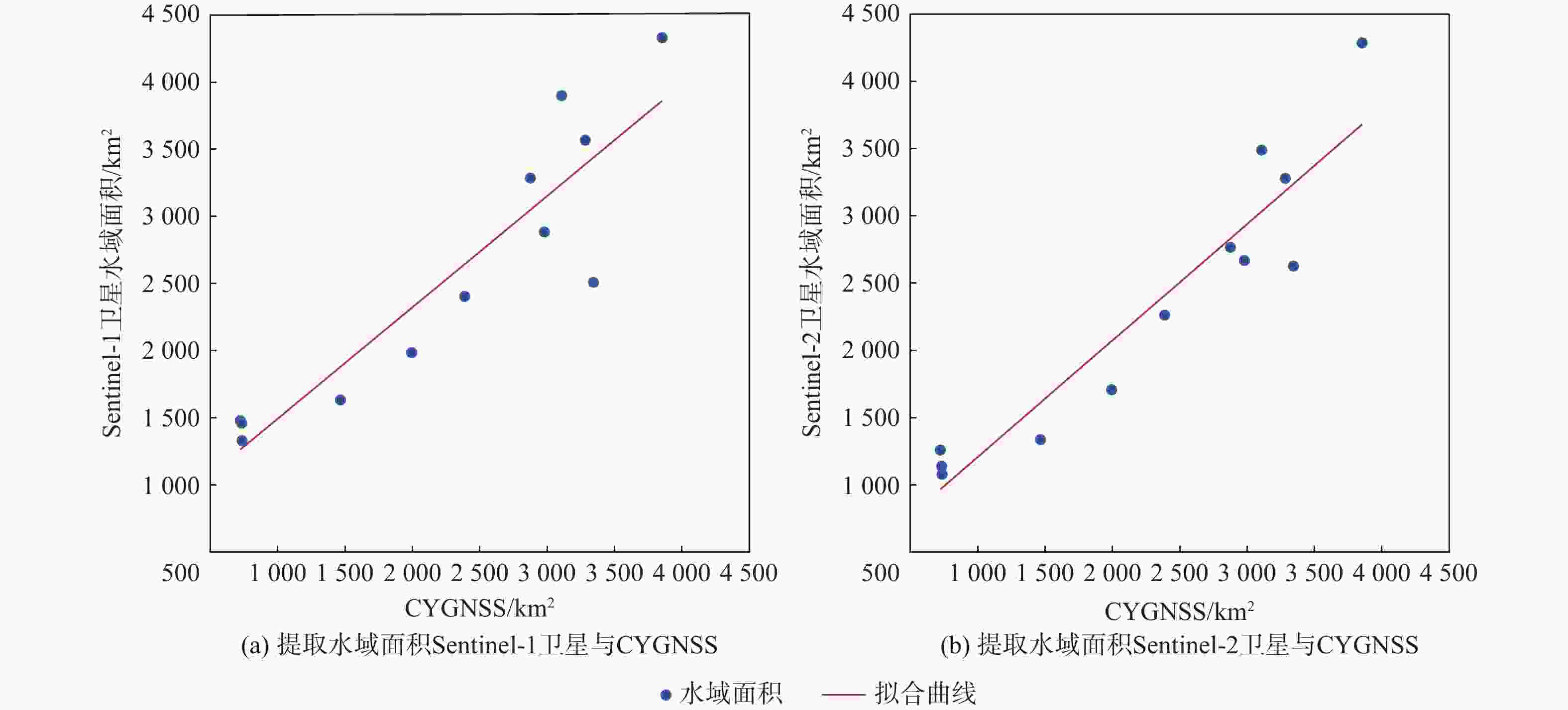
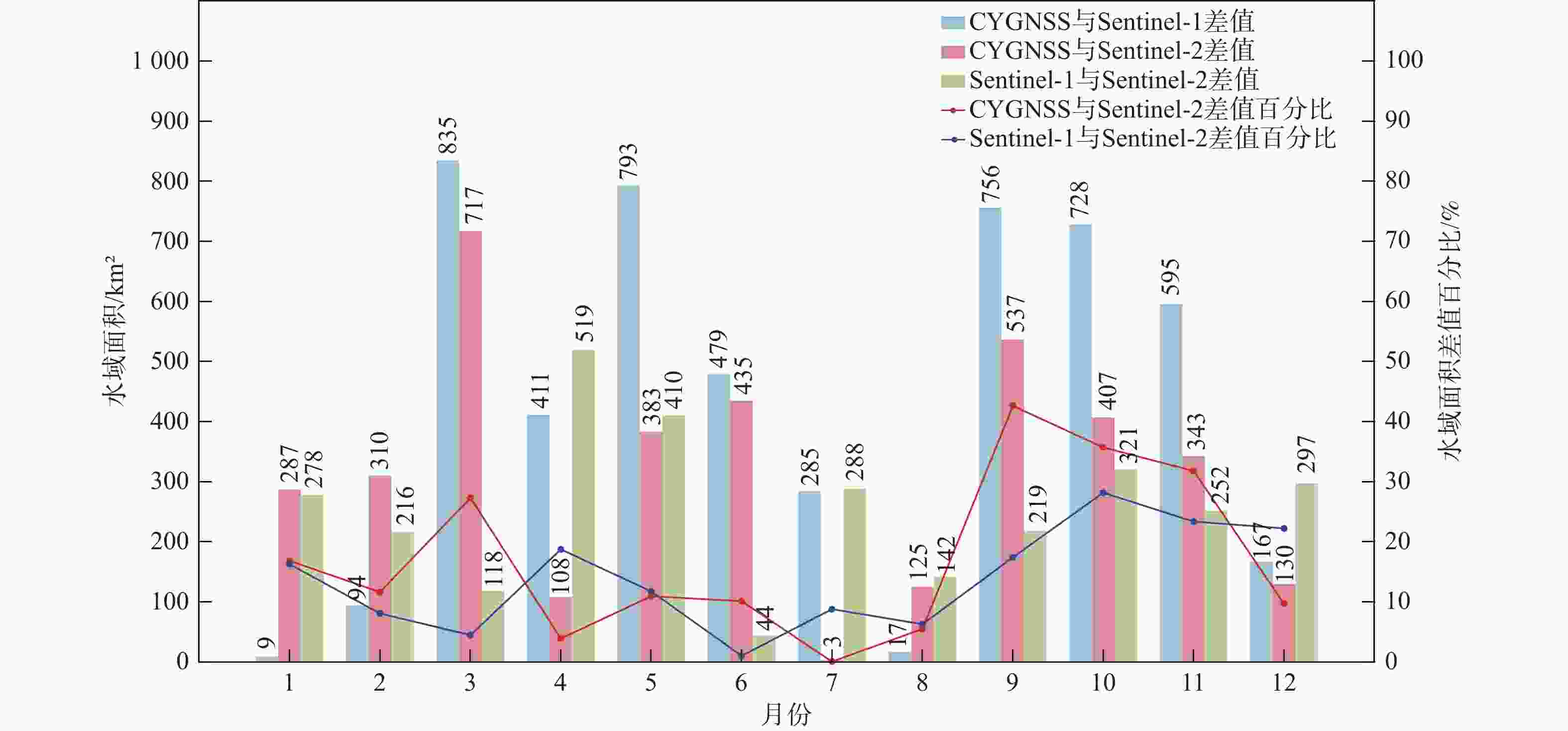
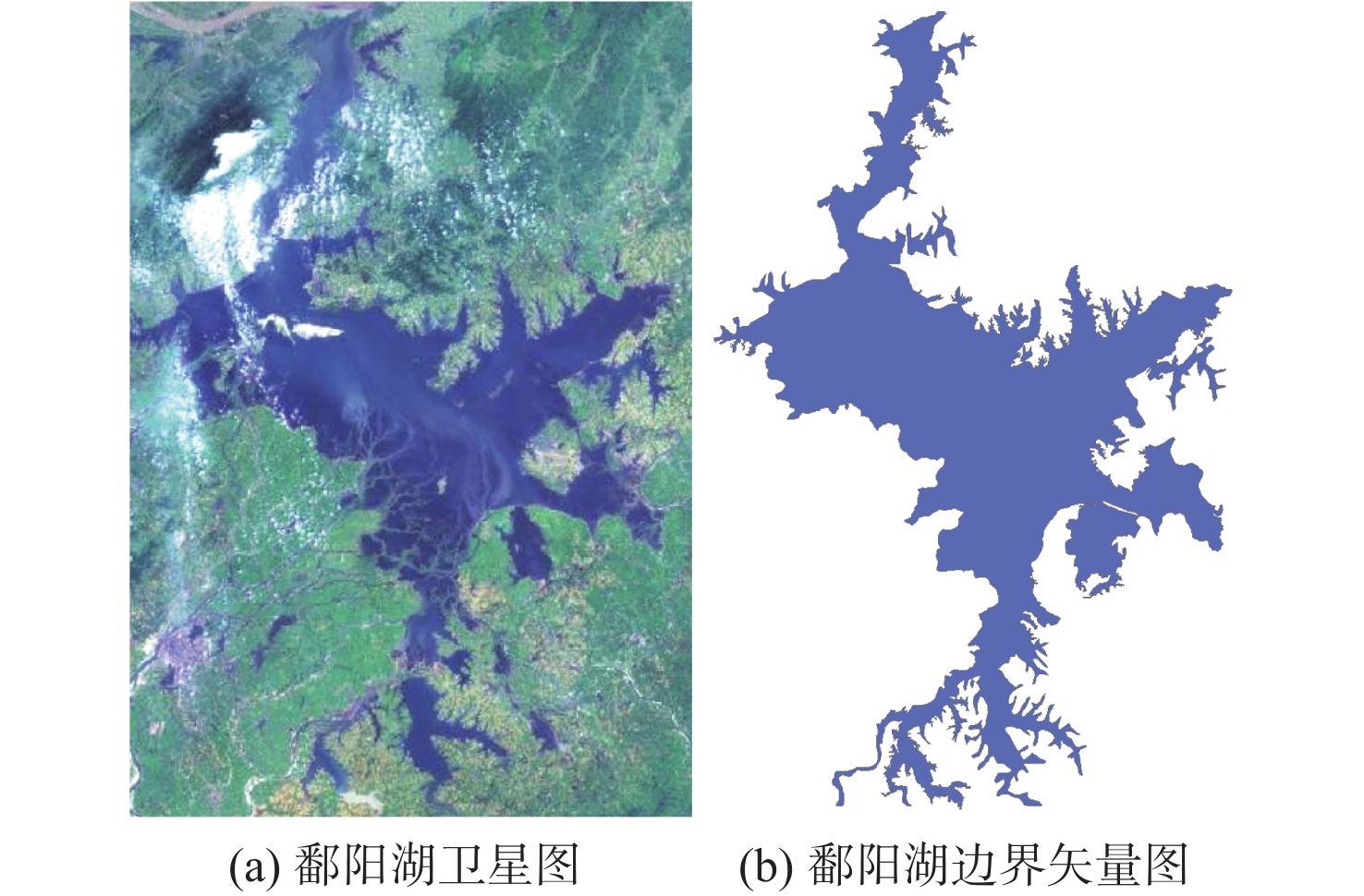
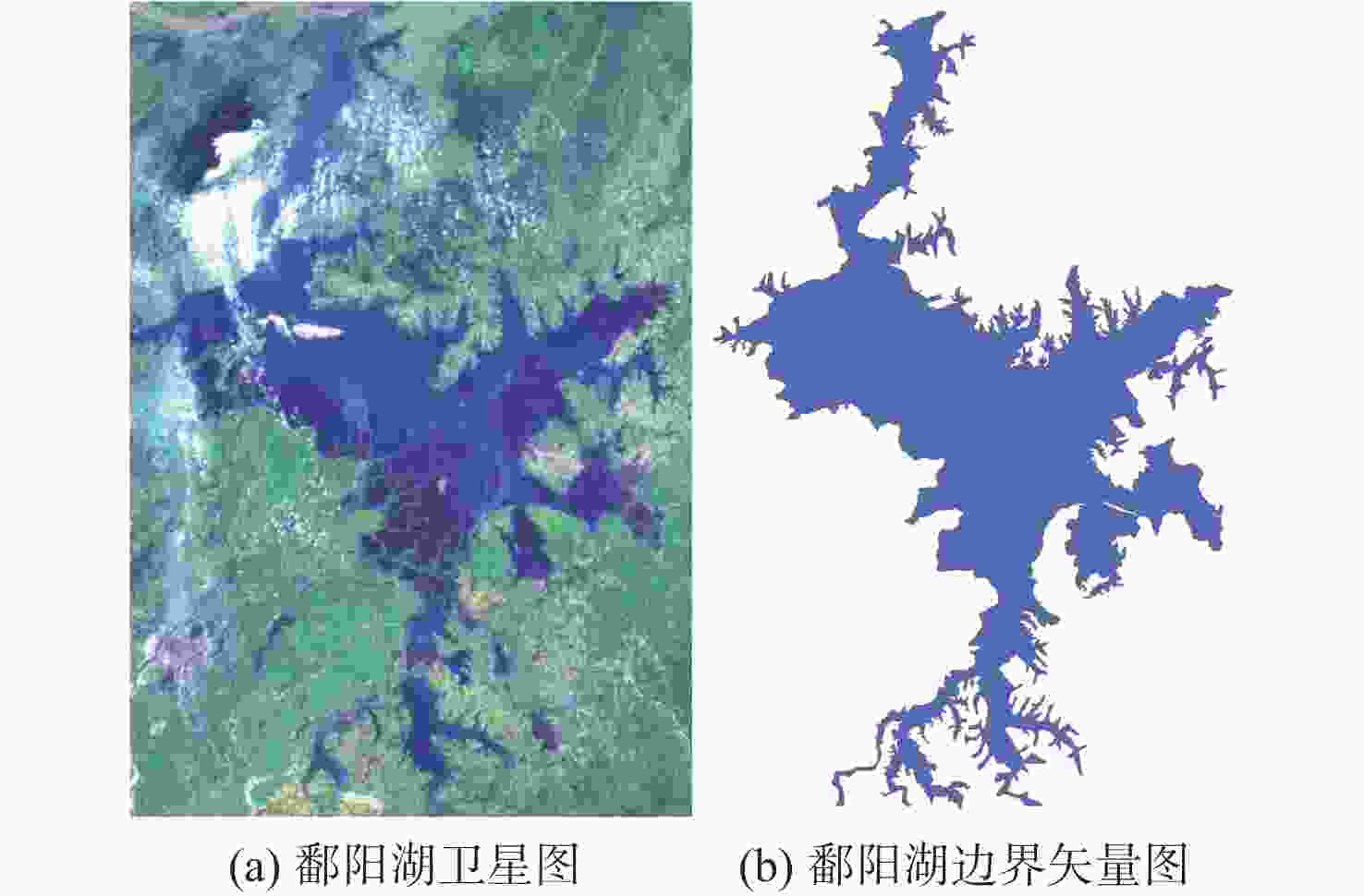
鄱阳湖是中国第一大淡水湖,其水域面积变化对水资源管理、灾害防控和社会经济发展等多个方面具有重要的影响。利用星载全球导航卫星系统反射(GNSS-R)技术对湖泊水域面积进行估算。基于星载GNSS-R地表反射模型和GNSS-R卫星旋风卫星导航系统(CYGNSS)的观测数据,计算得到鄱阳湖区域的地表反射率;利用网格化插值并通过阈值法进行水域范围的识别;根据水体的格网数量及其空间分辨率进行水域面积计算。研究表明:基于星载GNSS-R技术提取的鄱阳湖水域面积与Sentinel-1卫星和Sentinel-2卫星图像处理得到的鄱阳湖水域面积之间存在显著的相似度,皮尔逊相关系数分别为0.91和0.94。以Sentinel-2卫星的结果为参考,基于CYGNSS和Sentinel-1卫星获取的鄱阳湖水域面积月平均偏差值分别为315.42 km2和271.45 km2,对应的月平均偏差百分比分别为17.2%和13.1%。进一步验证了星载GNSS-R技术在高时空分辨率的湖泊水域面积监测中的可靠性和应用前景,可为水资源管理和灾害防控等提供数据支持。
-
关键词:
- 星载GNSS-R技术 /
- CYGNSS /
- Sentinel-1 /
- Sentinel-2 /
- 湖泊水域面积监测 /
- 阈值法
Abstract:Poyang Lake is the largest freshwater lake in China, and its changes in water area have a significant impact on water resource management, disaster prevention and control, and socio-economic development. This study focuses on the application of the spaceborne global navigation satellite system-reflectometry (GNSS-R) technology in monitoring the area changes of the lake. Using the cyclone global navigation satellite system (CYGNSS) satellite's observation data, the surface reflectance is computed as a characteristic parameter based on the GNSS-R scattering model. Additionally, the water area is identified and computed. The specific steps are as follows: based on the satellite GNSS-R surface reflectance calculation model, the surface reflectance of the Poyang Lake area is first calculated. Then, the location of the water is identified by using the grid interpolation and threshold method. Finally, the water area is estimated based on the number of grids passing through water bodies and their spatial resolution. The results of the water area computation method suggested in this study are also evaluated using Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 remote sensing pictures to confirm its efficacy. This study shows that there is a significant similarity between the water area of Poyang Lake extracted from spaceborne GNSS-R technology and the water area of Poyang Lake obtained from Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2. The Pearson correlation coefficients between them are 0.91 and 0.94, respectively. Based on the results of Sentinel-2, the monthly average deviation of the water area of Poyang Lake based on CYGNSS and Sentinel-1 was 315.42 km2 and 271.45 km2, respectively, and the corresponding monthly average deviation percentages were 17.2% and 13.1%, respectively. This study furtherly verifies the reliability and the application prospects of spaceborne GNSS-R technology in monitoring lake water areas with high spatiotemporal resolution, providing data support for water resource management and disaster prevention.
-
Key words:
- spaceborne GNSS-R technology /
- CYGNSS /
- Sentinel-1 /
- Sentinel-2 /
- monitoring of lake water area /
- threshold method
-
-
[1] 宋利娟, 景海涛, 徐嘉慧, 等. 联合哨兵卫星系列雷达与光学影像的洞庭湖水域面积变化高时空分辨率监测[J]. 遥感学报, 2023, 27(11): 2516-2529. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20221562SONG L J, JING H T, XU J H, et al. High spatial and temporal resolution monitoring of water area changes of Dongting Lake by joint Sentinel satellite series of radar and optical images[J]. National Remote Sensing Bulletin, 2023, 27(11): 2516-2529(in Chinese). doi: 10.11834/jrs.20221562 [2] 杨东凯, 张其善. GNSS反射信号处理基础与实践[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2012.YANG D K, ZHANG Q S. GNSS reflected signal processing: fundamentals and applications[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2012(in Chinese). [3] MARTIN-NEIRA M. A passive reflectometry and interferometry system (PARIS): application to ocean altimetry[J]. ESA Journal, 1993, 17(4): 331-355. [4] JING C, NIU X L, DUAN C D, et al. Sea surface wind speed retrieval from the first Chinese GNSS-R mission: technique and preliminary results[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(24): 3013. doi: 10.3390/rs11243013 [5] 布金伟, 余科根, 韩帅. 星载GNSS-R海浪有效波高反演模型构建[J]. 测绘学报, 2022, 51(9): 1920-1930. doi: 10.11947/j.issn.1001-1595.2022.9.chxb202209009BU J W, YU K G, HAN S. Construction of spaceborne GNSS-R ocean waves significant wave height retrieval model[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2022, 51(9): 1920-1930(in Chinese). doi: 10.11947/j.issn.1001-1595.2022.9.chxb202209009 [6] WANG X L, HE X F, ZHANG Q, et al. Angle dependence analysis method to determine SNR arc applied to GNSS-MR sea level retrieval[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2021, 4(2): 14-26. [7] 李婷, 张显云, 邓小东, 等. 顾及多径环境差异和粗差的GNSS-MR土壤湿度反演[J]. 遥感学报, 2021, 25(6): 1324-1337. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20219098LI T, ZHANG X Y, DENG X D, et al. GNSS-MR soil moisture retrieval considering the multipath environments differences and gross error[J]. National Remote Sensing Bulletin, 2021, 25(6): 1324-1337(in Chinese). doi: 10.11834/jrs.20219098 [8] 陶庭叶, 李江洋, 朱勇超, 等. 阶段模型修正的星载GNSS-R土壤湿度反演方法[J]. 测绘学报, 2022, 51(9): 1942-1950. doi: 10.11947/j.issn.1001-1595.2022.9.chxb202209011TAO T Y, LI J Y, ZHU Y C, et al. Spaceborne GNSS-R for retrieving soil moisture based on the correction of stage model[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2022, 51(9): 1942-1950(in Chinese). doi: 10.11947/j.issn.1001-1595.2022.9.chxb202209011 [9] 朱勇超. 星载GNSS-R海冰检测与海冰密集度反演方法研究[J]. 测绘学报, 2020, 49(12): 1643.ZHU Y C. Study of spaceborne GNSS-R for sea ice detection and sea ice concentration retrieval methods[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2020, 49(12): 1643(in Chinese). [10] 陈国庆, 何秀凤, 王笑蕾, 等. 基于信号强度的多模多频GNSS-MR雪深反演研究[J]. 遥感学报, 2024, 28(09): 2240-2251.CHEN G Q, HE X F, WANG X L, et al. Multi-mode and multi-frequency GNSS-MR snow depth inversion based on signal strength[J]. National Remote Sensing Bulletin, 2024, 28(09): 2240-2251(in Chinese). [11] 管栋良, 梁子亮, 王勇. 地基GNSS-R在复杂地形条件下的积雪探测[J]. 地球物理学报, 2022, 65(11): 4236-4248. doi: 10.6038/cjg2022P0716GUAN D L, LIANG Z L, WANG Y. Snow detection under the complicated terrain conditions using the ground-based GNSS-R technique[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2022, 65(11): 4236-4248(in Chinese). doi: 10.6038/cjg2022P0716 [12] YU K G, LI Y W, CHANG X. Snow depth estimation based on combination of pseudorange and carrier phase of GNSS dual-frequency signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(3): 1817-1828. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2869284 [13] ZHANG S C, ZHOU M L, WANG Y J, et al. Ground-based GPS used in the snow depth survey of Greenland[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2021, 4(2): 47-55. [14] GERLEIN-SAFDI C, RUF C S. A CYGNSS-based algorithm for the detection of inland waterbodies[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2019, 46(21): 12065-12072. doi: 10.1029/2019GL085134 [15] GHASEMIGOUDARZI P, HUANG W M, DE SILVA O, et al. Flash flood detection from CYGNSS data using the RUSBoost algorithm[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 171864-171881. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3025302 [16] AL-KHALDI M M, JOHNSON J T, GLEASON S, et al. Inland water body mapping using CYGNSS coherence detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(9): 7385-7394. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3047075 [17] WAN W, LIU B J, ZENG Z Y, et al. Using CYGNSS data to monitor China’s flood inundation during typhoon and extreme precipitation events in 2017[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(7): 854. doi: 10.3390/rs11070854 [18] YANG W T, GAO F, XU T H, et al. Daily flood monitoring based on spaceborne GNSS-R data: a case study on Henan, China[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(22): 4561. doi: 10.3390/rs13224561 [19] ZHANG S C, MA Z M, LI Z H, et al. Using CYGNSS data to map flood inundation during the 2021 extreme precipitation in Henan Province, China[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(24): 5181. [20] YAN Q Y, HUANG W M, JIN S G, et al. Pan-tropical soil moisture mapping based on a three-layer model from CYGNSS GNSS-R data[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2020, 247: 111944. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2020.111944 [21] DE ROO R D, ULABY F T. Bistatic specular scattering from rough dielectric surfaces[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1994, 42(2): 220-231. doi: 10.1109/8.277216 [22] KURUM M, DESHPANDE M, JOSEPH A T, et al. SCoBi-Veg: a generalized bistatic scattering model of reflectometry from vegetation for signals of opportunity applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(2): 1049-1068. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2864631 [23] VORONOVICH A G, ZAVOROTNY V U. Bistatic radar equation for signals of opportunity revisited[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(4): 1959-1968. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2771253 [24] ZAVOROTNY V U, GLEASON S, CARDELLACH E, et al. Tutorial on remote sensing using GNSS bistatic radar of opportunity[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2014, 2(4): 8-45. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2014.2374220 [25] BARTIER P M, KELLER C P. Multivariate interpolation to incorporate thematic surface data using inverse distance weighting (IDW)[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 1996, 22(7): 795-799. [26] RUF C. CYGNSS handbook[M]. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press, 2022. [27] 张云, 王雨, 周绍辉, 等. 星载GNSS-R检测太湖水华可行性分析[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2024, 50(3): 695-705.ZHANG Y, WANG Y, ZHOU S H, et al. Analysis on feasibility of detecting water blooms in Taihu Lake with spaceborne GNSS-R[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2024, 50(3): 695-705(in Chinese). [28] LIU M J, WANG J, ZHONG S L, et al. Quantitative evaluation of sea-ice disaster in Bohai sea based on GOCI and Sentinel-1[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2021, 4(1): 49-55. [29] 张艳梅, 王萍, 罗想, 等. 利用Sentinel-1数据和SBAS-InSAR技术监测西安地表沉降[J]. 测绘通报, 2017(4): 93-97.ZHANG Y M, WANG P, LUO X, et al. Sentinel-1 data and SBAS-InSAR technology were used to monitor surface subsidence in Xi'an[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2017(4): 93-97(in Chinese). [30] WANG Q M, SHI W Z, LI Z B, et al. Fusion of sentinel-2 images[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2016, 187: 241-252. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2016.10.030 [31] ROHIL M K, MATHUR S. CYGNSS-derived soil moisture: status, challenges and future[J]. Ecological Informatics, 2022, 69: 101621. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoinf.2022.101621 [32] 杨文涛, 徐天河, 王娜子, 等. 星载GNSS-R土壤湿度反演中开放水域的影响[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2023, 49(7): 1779-1786.YANG W T, XU T H, WANG N Z, et al. Influence of open water in retrieval of soil moisture by spaceborne GNSS-R[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2023, 49(7): 1779-1786(in Chinese). [33] CHEW C, REAGER J T, SMALL E. CYGNSS data map flood inundation during the 2017 Atlantic hurricane season[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 9336. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-27673-x [34] MORRIS M, CHEW C, REAGER J T, et al. A novel approach to monitoring wetland dynamics using CYGNSS: everglades case study[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2019, 233: 111417. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2019.111417 -






 下载:
下载: