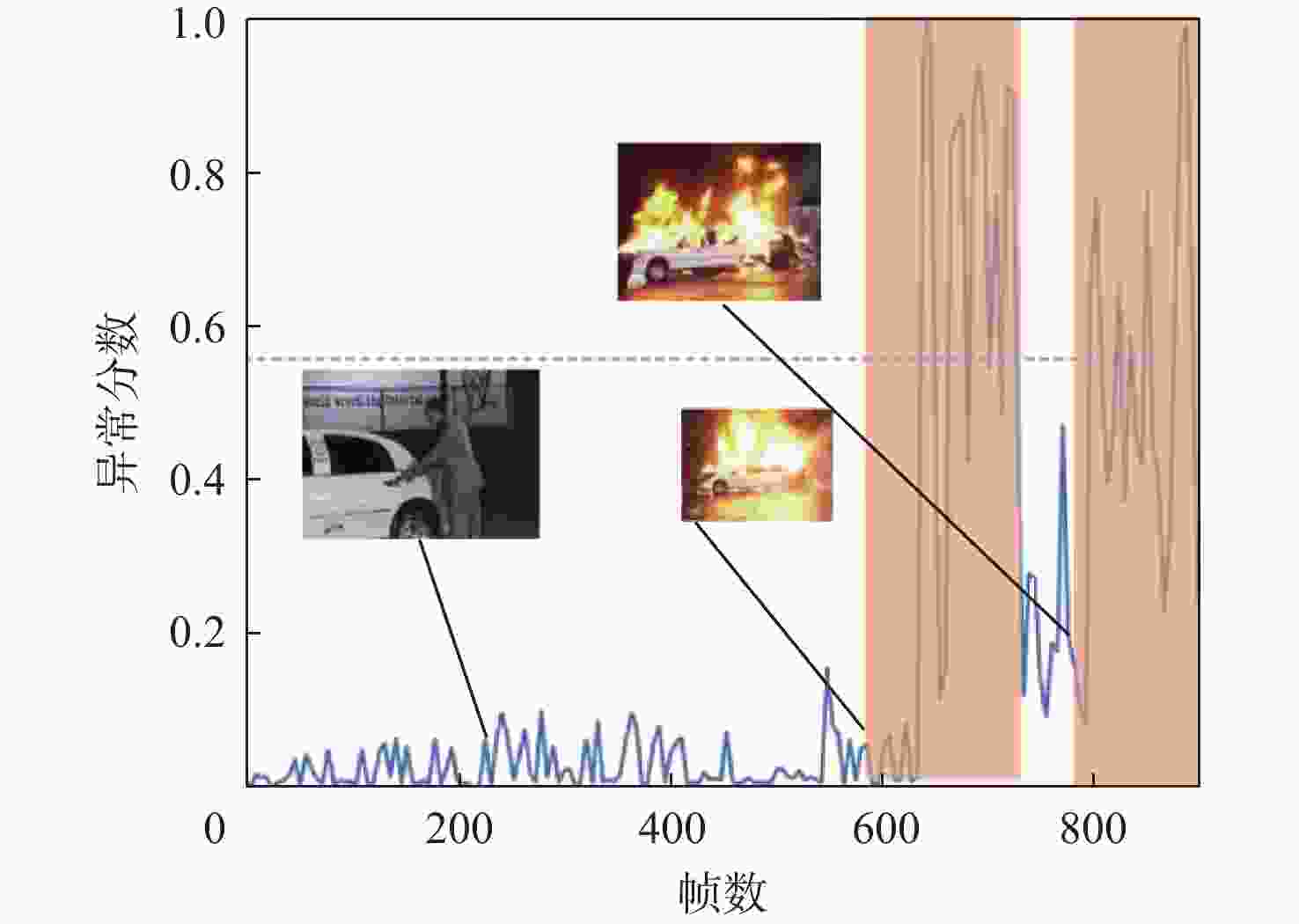
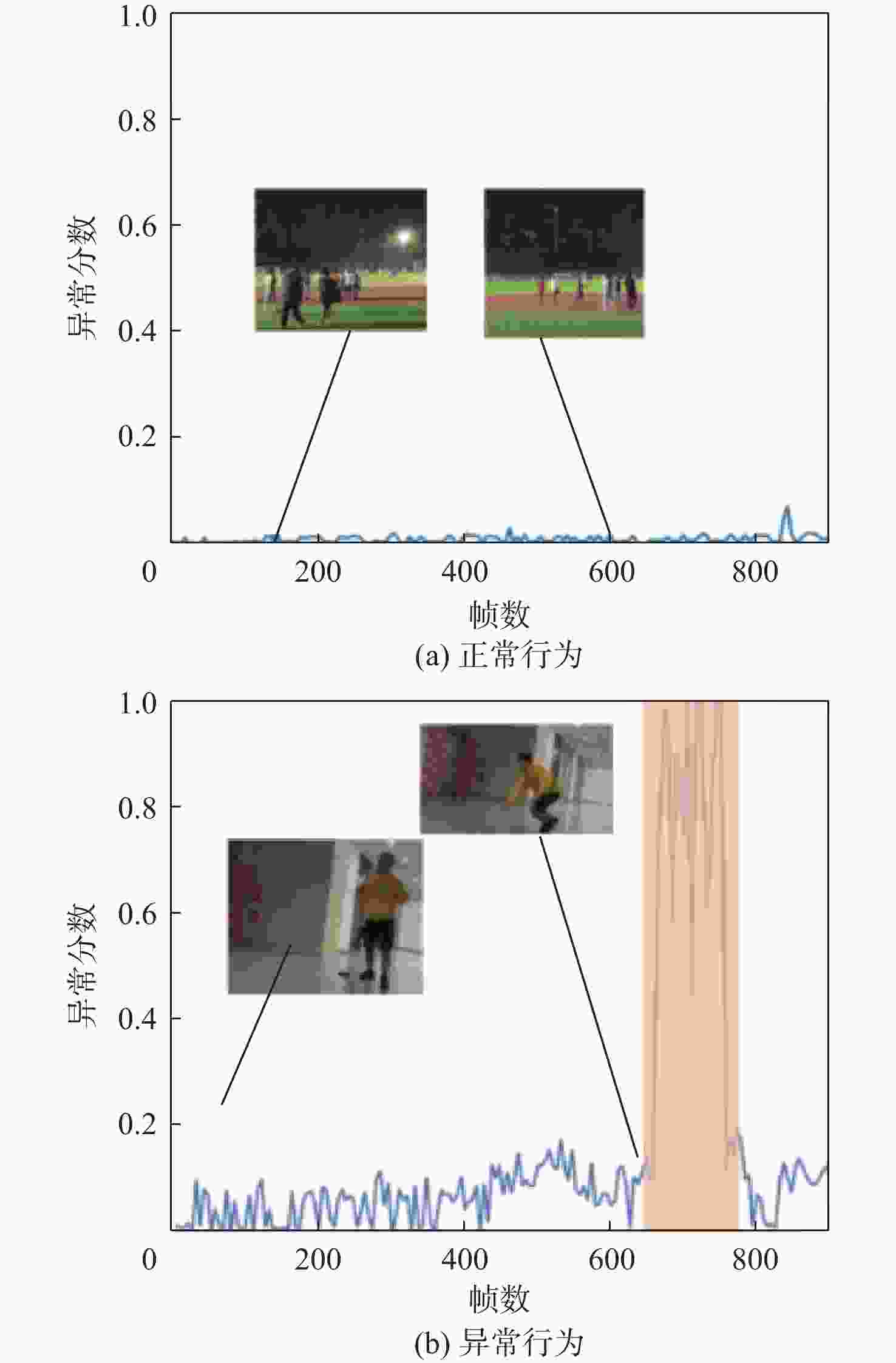
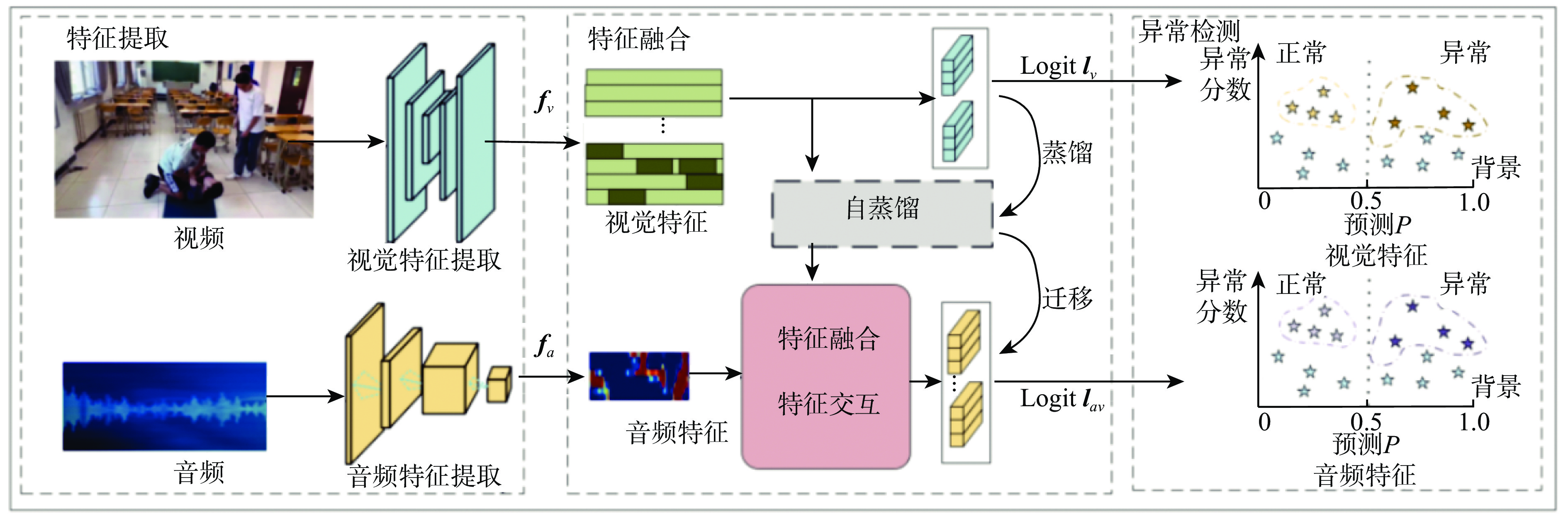
-
摘要:
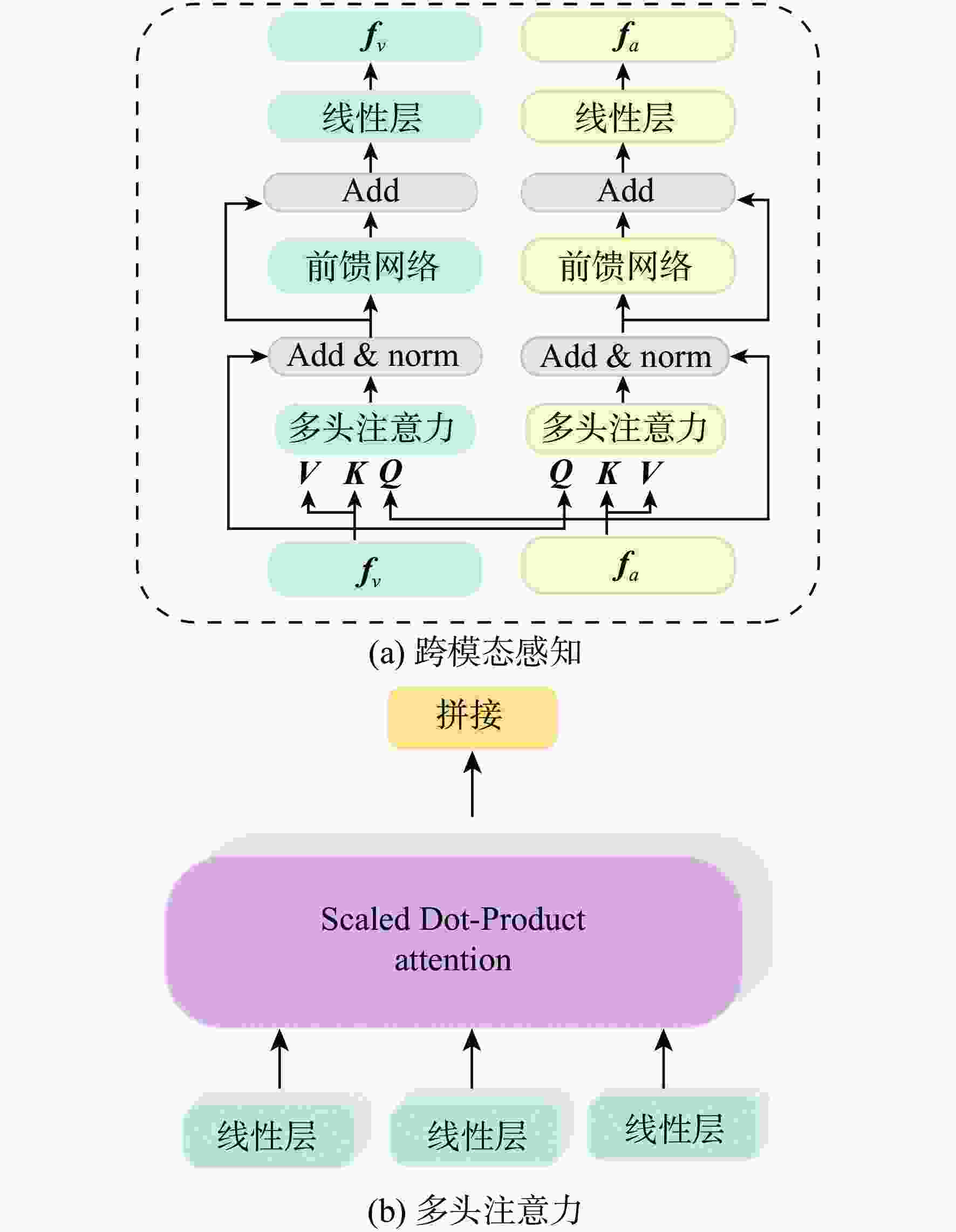
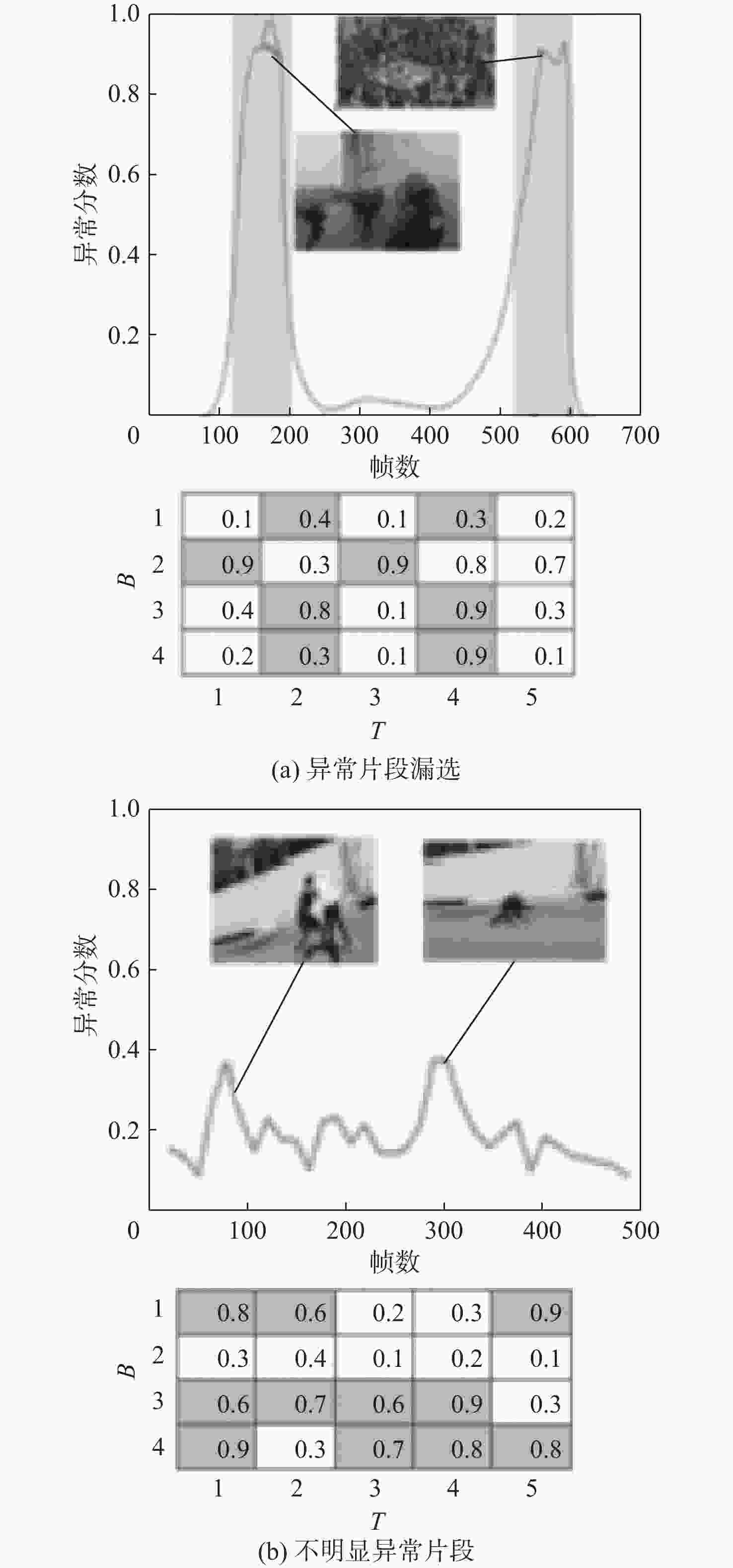
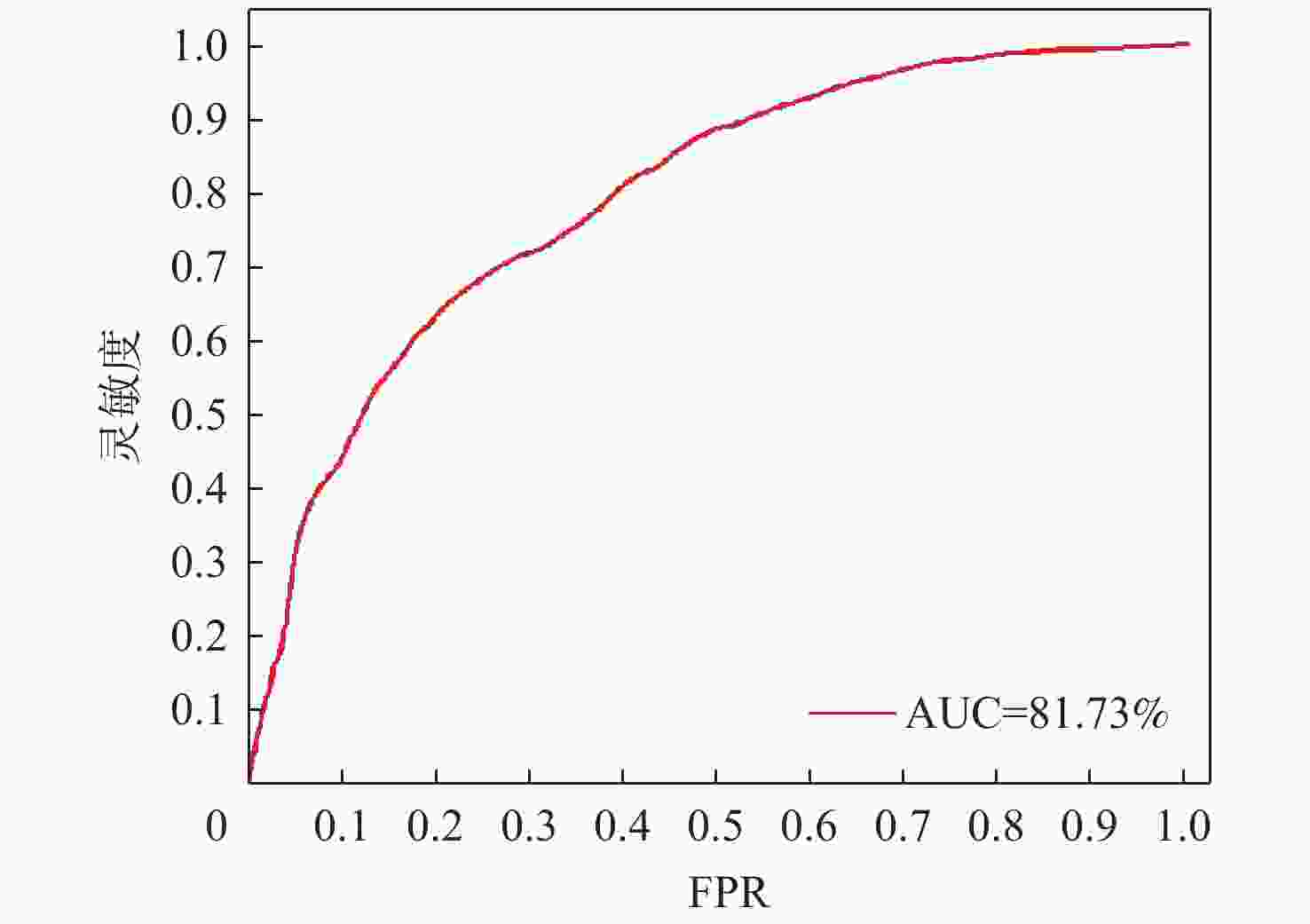
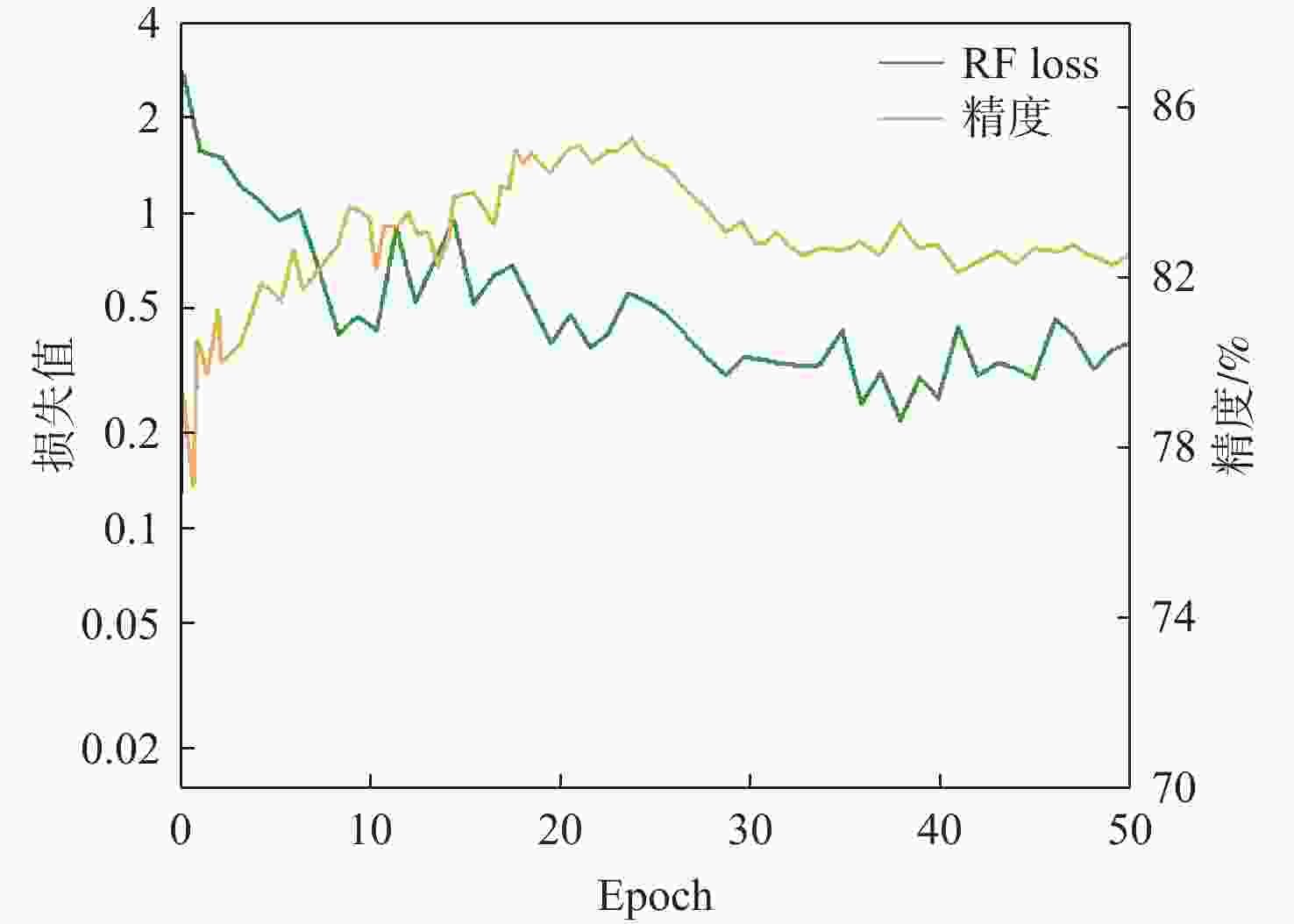
针对视频中的异常行为检测易发生误检、漏检以及正负样本数量不平衡的问题,提出了一种多模态特征融合的异常行为检测方法。设计了跨模态感知模块,利用交叉注意力机制进行特征融合,提高跨模态数据特征的表达能力,并通过共享参数策略减少网络参数量。采用改进的二元交叉熵损失函数训练网络,在训练过程中针对较易区分样本实现动态降低权重,并将较大的权重聚焦在较难区分的样本上,提高了不均衡、难分类数据的处理能力,提高异常行为检测准确率。通过样本批次选择的策略,利用统计分析方法过滤出更多异常片段,有效解决异常片段漏选问题。在XD-Violence、Shanghai-Tech公开数据集及自制数据集上进行测试,在XD-Violence数据集上的AP值达到85.32%,在Shanghai-Tech数据集及自制数据集上的AUC检测值分别为96.84%和81.73%,实验结果充分证明了所提方法的有效性及泛化能力。
Abstract:Aiming at the problems of false detection, missing detection and imbalance of positive and negative samples in video abnormal behavior detection, a multi-modal feature fusion method for abnormal behavior detection is proposed. Firstly, a cross-modal sensing module is designed, which uses the cross-attention mechanism for feature fusion to improve the expression ability of cross-modal data features, and reduces the number of network parameters by sharing parameter strategies. Then, the improved binary cross entropy loss function is used to train the network. In the training process, the weight is reduced dynamically for the easily distinguishable samples, and the larger weight is focused on the difficult to distinguish samples, which improves the processing ability of unbalanced and difficult to classify data and improves the detection accuracy of abnormal behavior. Finally, through the strategy of sample batch selection, more abnormal fragments are filtered out by statistical analysis method to effectively solve the problem of missing abnormal fragments selection. Tests were conducted on XD-Violence, Shanghai-Tech open data set and self-made data set. The AP value of XD-Violence data set reached 85.32%, and the AUC value of Shanghai-Tech data set and self-made data set were 96.84% and 81.73%, respectively. Experimental results fully prove the effectiveness and generalization ability of this method.
-
表 1 实验平台配置
Table 1. Experimental platform configuration
名称 配置 操作系统 Ubuntu 20.04 GPU A 100 CPU 32核CPU,16 G内存 深度学习框架 Pytorch + Tensorflow 编程语言 Python 3.8 GPU加速平台 CUDA 11.0 表 2 XD-Violence数据集上的实验结果对比
Table 2. Comparison of experimental results on the XD-Violence dataset
表 3 在Shanghai-Tech数据集上的实验结果对比
Table 3. Comparison of experimental results on the Shanghai-Tech dataset
表 4 消融实验结果
Table 4. Ablation study results
模块 Cross-Attention RF Loss SBS AP/% baseline 83.40 0 √ 83.57 1 √ 84.75 2 √ 84.23 3 √ √ 84.82 4 √ √ 84.73 5 √ √ 83.89 6 √ √ √ 85.32 -
[1] XU H T. Research on abnormal behavior detection in video based on deep learning[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2022, 31(2): 1-7. [2] BERMEJO NIEVAS E, DENIZ SUAREZ O, BUENO GARCÍA G, et al. Violence detection in video using computer vision techniques[C]//Proceedings of the Computer Analysis of Images and Patterns. Berlin: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2011: 332-339. [3] DENIZ O, SERRANO I, BUENO G, et al. Fast violence detection in video[C]//Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications. Lisbon: SCITEPRESS-Science and Technology Publications, 2014 : 478-485. [4] LI A. Research on the key techniques of group abnormal behavior detection in surveillance video [D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2021, 31(2): 1-4. [5] MA S, ZENG Z, Mcduff D, et al. Active contrastive learning of audio-visual video representations[EB/OL]. (2020-08-31)[2024-05-10]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2009.09805. [6] FANG Z, WANG J, WANG L, et al. Seed: self-supervised distillation for visual representation[J]. (2021-01-12)[2024-05-11]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2101.04731. [7] FENG J C, HONG F T, ZHENG W S. MIST: multiple instance self-training framework for video anomaly detection[C]//Proceedings of the 2021 the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 14004-14013. [8] PANG W F, HE Q H, HU Y J, et al. Violence detection in videos based on fusing visual and audio information[C]//Proceedings of the ICASSP 2021-2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 2260-2264. [9] PEIXOTO B, LAVI B, BESTAGINI P, et al. Multimodal violence detection in videos[C]//Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020-2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 2957-2961. [10] CHEN L Q, WANG D, GAN Z, et al. Wasserstein contrastive representation distillation[C]//Proceedings of the 2021 the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 16291-16300. [11] CHEN T, KORNBLITH S, NOROUZI M, et al. A simple framework for contrastive learning of visual representations[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning. New York: PMLR, 2020: 1597-1607. [12] LI S, LIU F, JIAO L C. Self-training multi-sequence learning with transformer for weakly supervised video anomaly detection[J]. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2022, 36(2): 1395-1403. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v36i2.20028 [13] HAN K, XIAO A, WU E, et al. Transformer in transformer[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2021, 34: 15908-15919. [14] WU P, LIU J, SHI Y J, et al. Not only look, but also listen: learning multimodal violence detection under weak supervision[C]//Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2020. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2020: 322-339. [15] YU J S, LIU J Y, CHENG Y, et al. Modality-aware contrastive instance learning with self-distillation for weakly-supervised audio-visual violence detection[C]//Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. New York: ACM, 2022: 6278-6287. [16] ZHOU Y X, QU Y, XU X, et al. BatchNorm-based weakly supervised video anomaly detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2024, 34: 13642-13654. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2024.3450734 [17] CHEN H L, XIE W D, VEDALDI A, et al. Vggsound: A large-scale audio-visual dataset[C]//Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020-2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 721-725. [18] LIU J Y, CHENG Y, ZHANG Y J, et al. Self-supervised video representation learning with motion-contrastive Perception[C]//2022 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2022: 1-6. [19] SCHÖLKOPF B, WILLIAMSON R C, SMOLA A, et al. Support vector method for novelty detection[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 1999, 12: 582-588. [20] IOFFE S, SZEGEDY C. Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning. New York: PMLR, 2015: 448-456. [21] FAN Y D, YU Y X, LU W H, et al. Weakly-supervised video anomaly detection with snippet anomalous attention[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2024, 34(7): 5480-5492. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2024.3350084 [22] TIAN Y, PANG G S, CHEN Y H, et al. Weakly-supervised video anomaly detection with robust temporal feature magnitude learning[C]//Proceedings of the 2021 Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 4955-4966. [23] ZHOU H, YU J Q, YANG W. Dual memory units with uncertainty regulation for weakly supervised video anomaly detection[J]. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2023, 37(3): 3769-3777. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v37i3.25489 [24] GONG D, LIU L Q, LE V, et al. Memorizing normality to detect anomaly: memory-augmented deep autoencoder for unsupervised anomaly detection[C]//Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 1705-1714. [25] LIU Y, LIU J, YANG K, et al. AMP-net: appearance-motion prototype network assisted automatic video anomaly detection system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2024, 20(2): 2843-2855. doi: 10.1109/TII.2023.3298476 [26] WAN B Y, FANG Y M, XIA X, et al. Weakly supervised video anomaly detection via center-guided discriminative learning[C]//Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 1-6. [27] LV H, YUE Z Q, SUN Q R, et al. Unbiased multiple instance learning for weakly supervised video anomaly detection[C]//Proceedings of the 2023 Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2023: 8022-8031. -






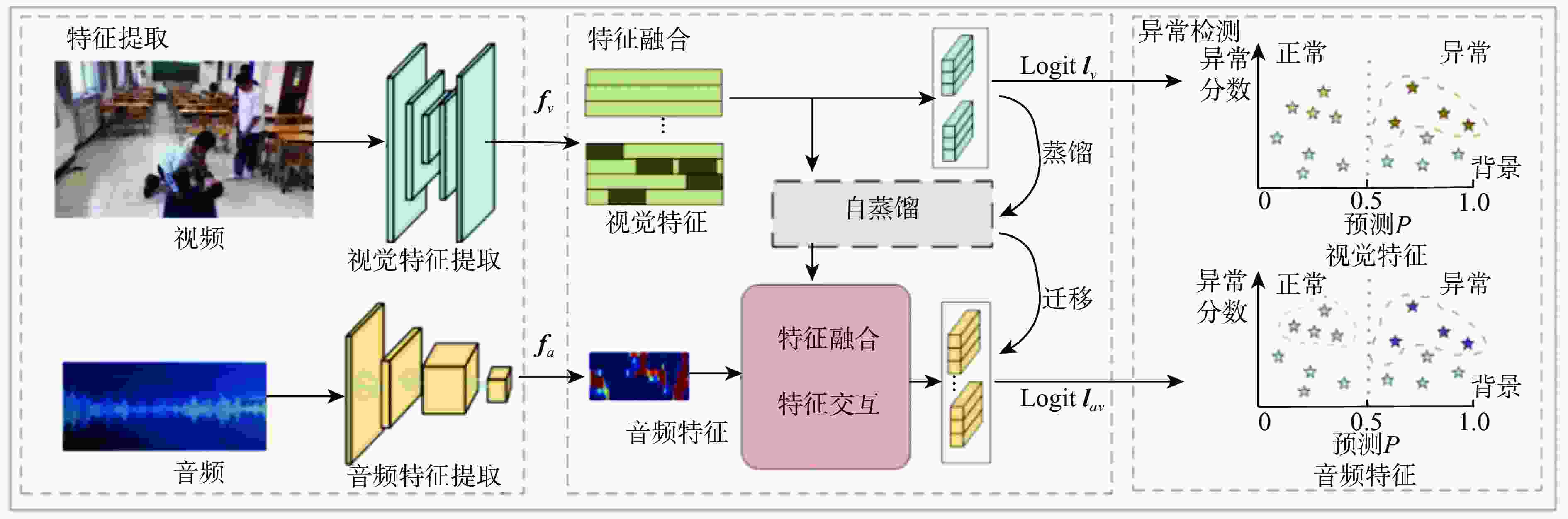
 下载:
下载: