A referring image segmentation method based on bidirectional vision-language interaction module
-
摘要:
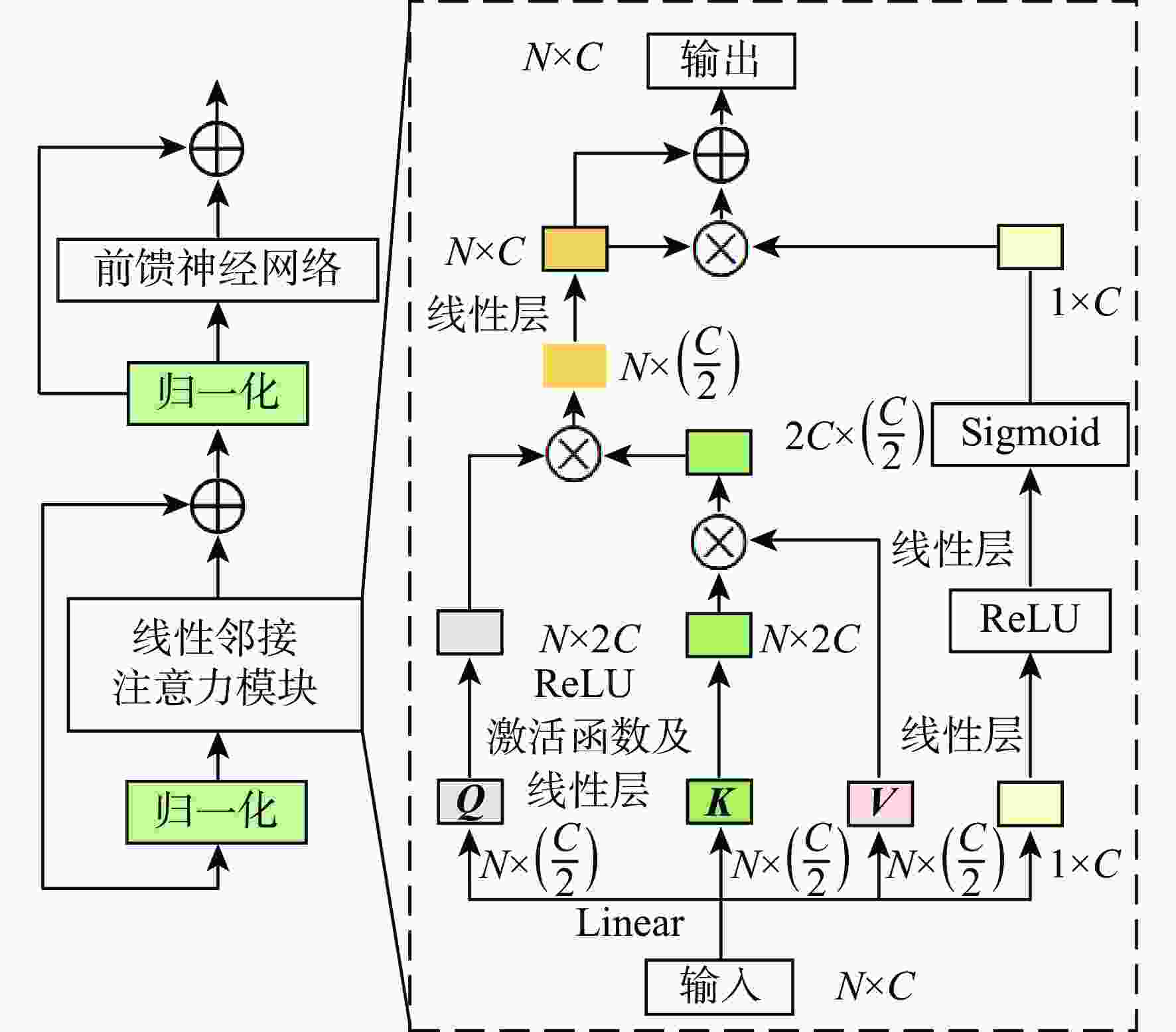
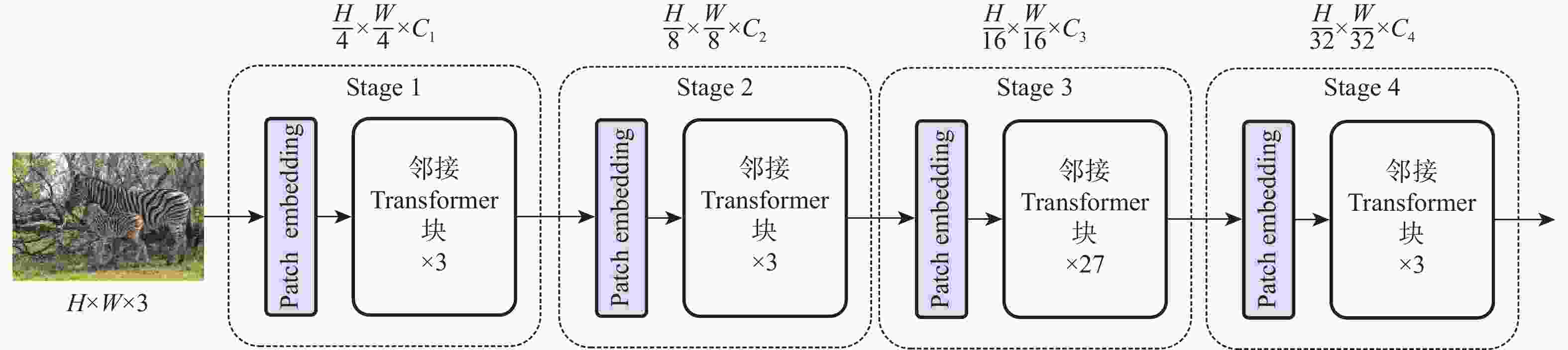
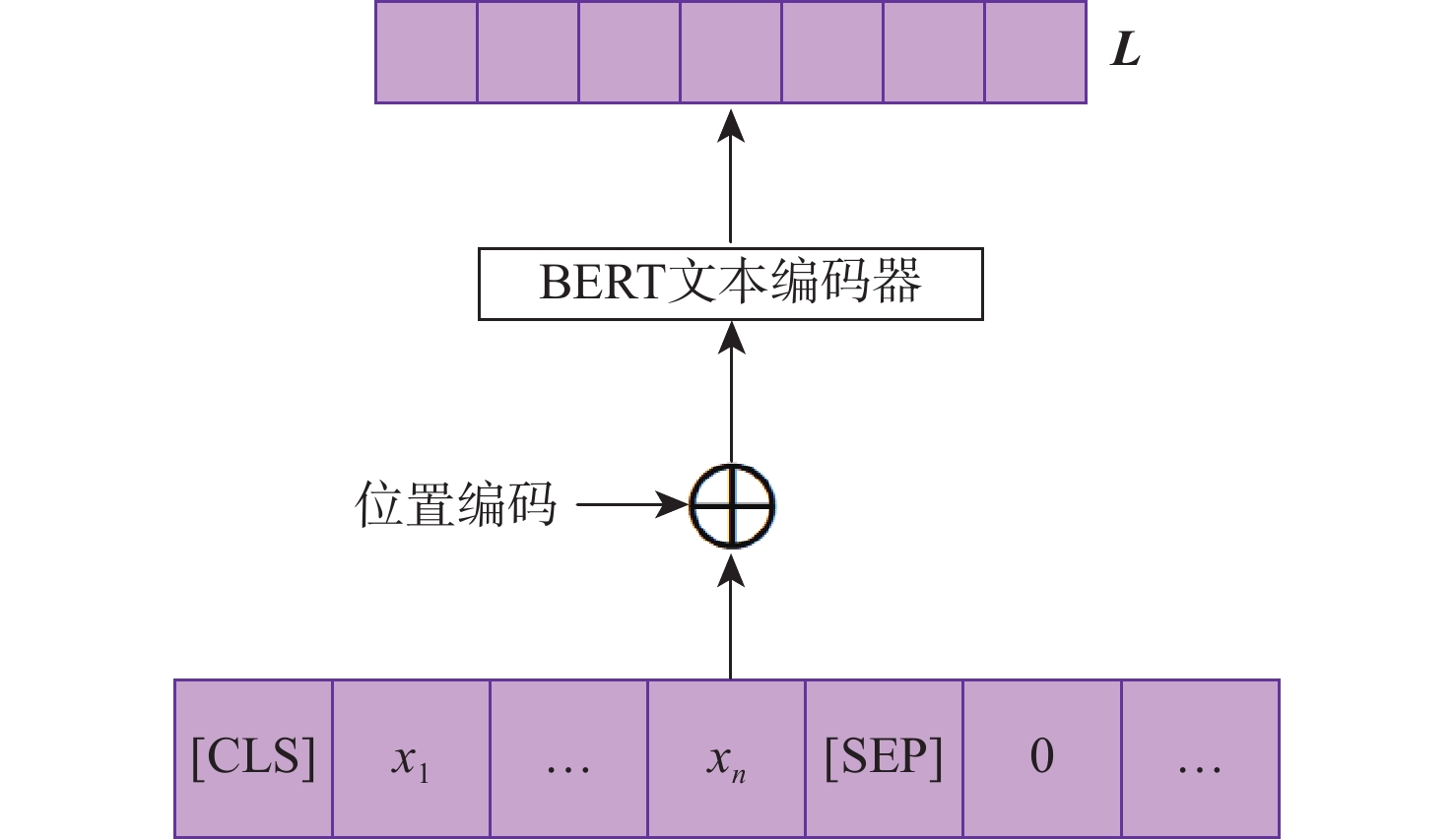
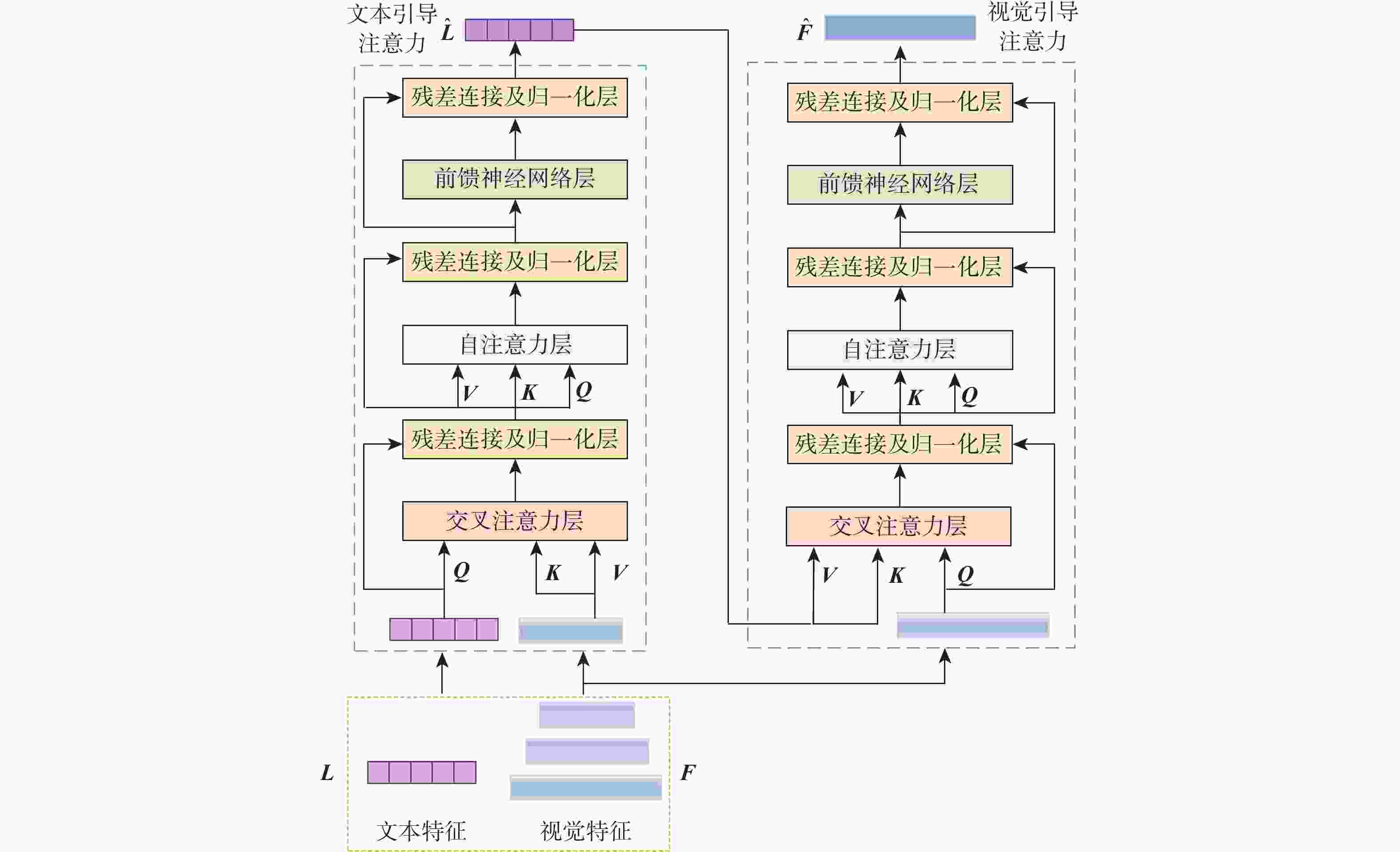
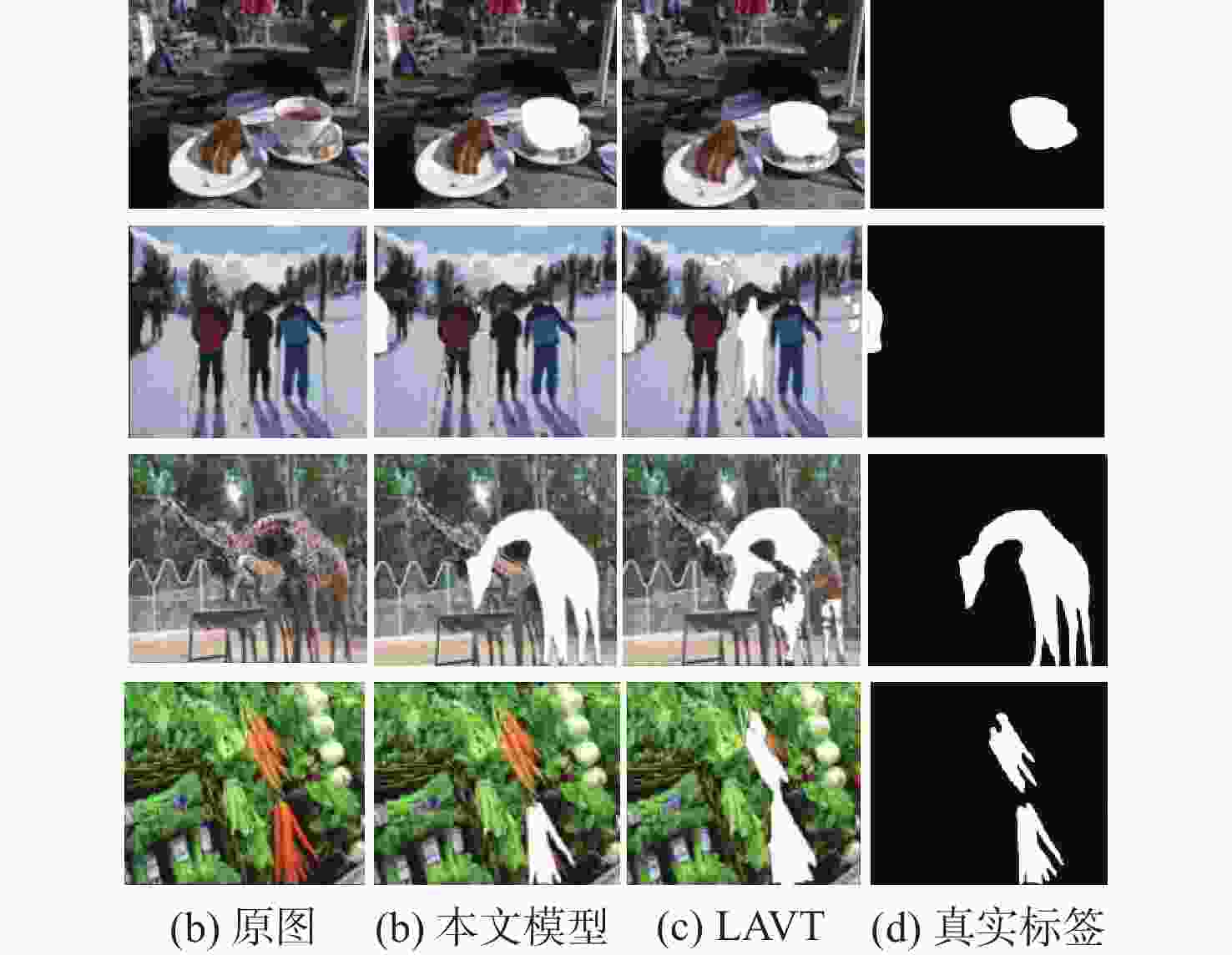
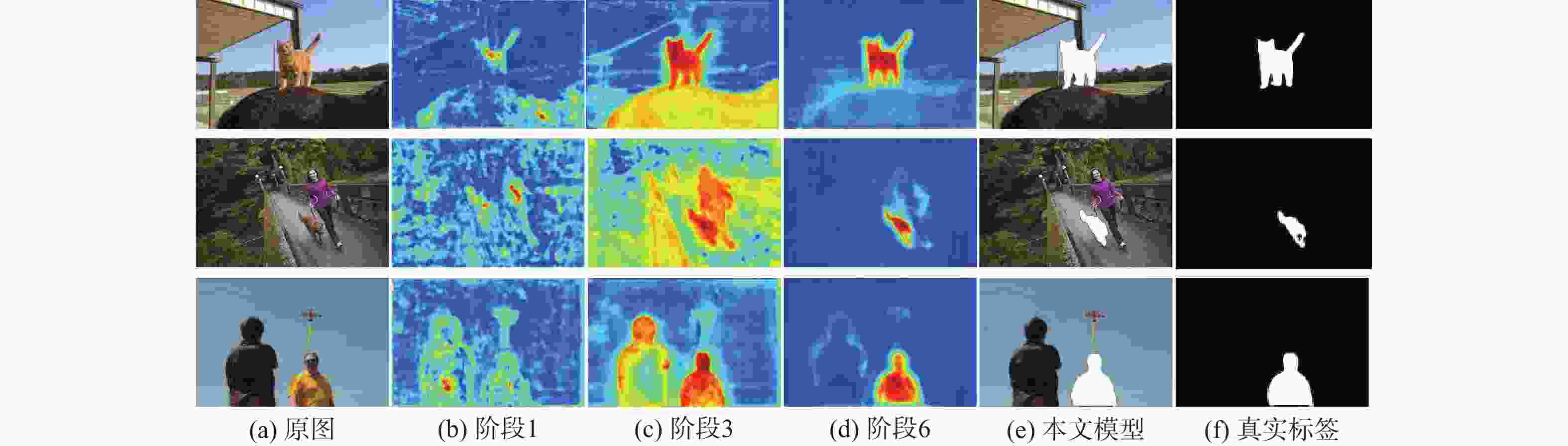
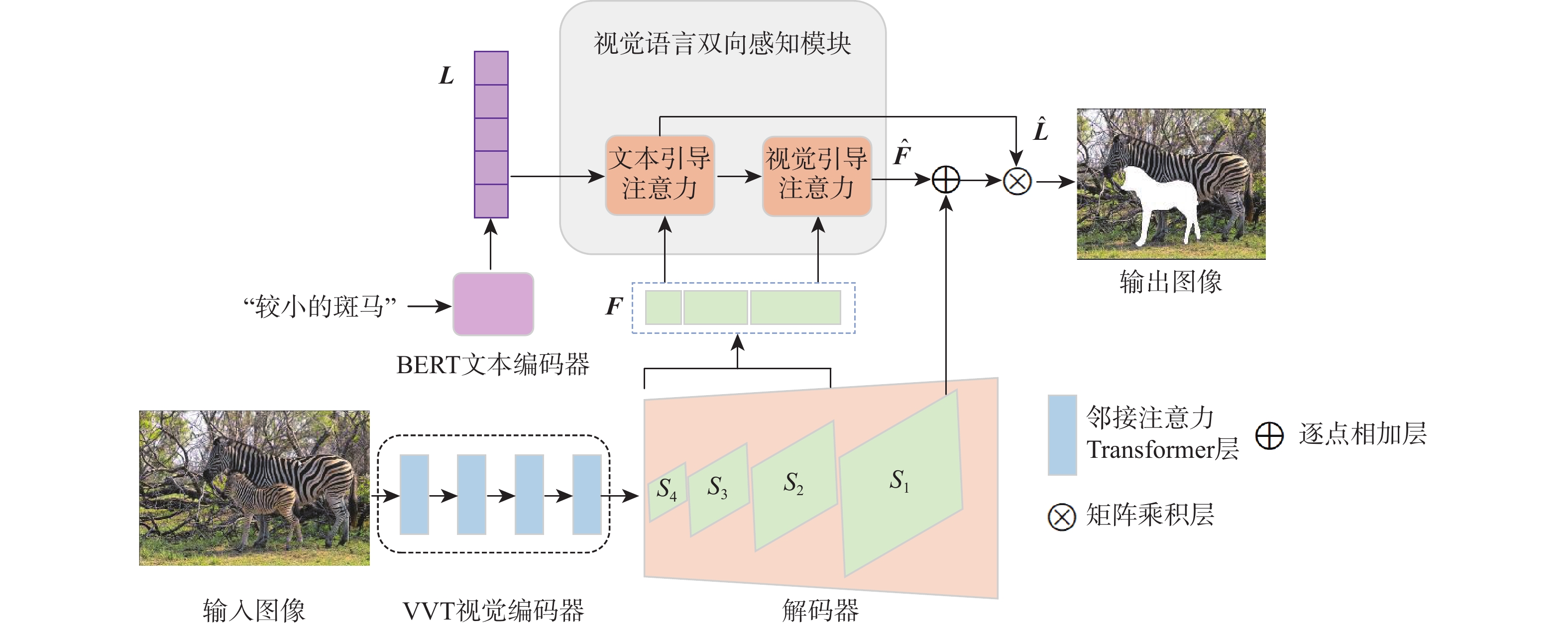
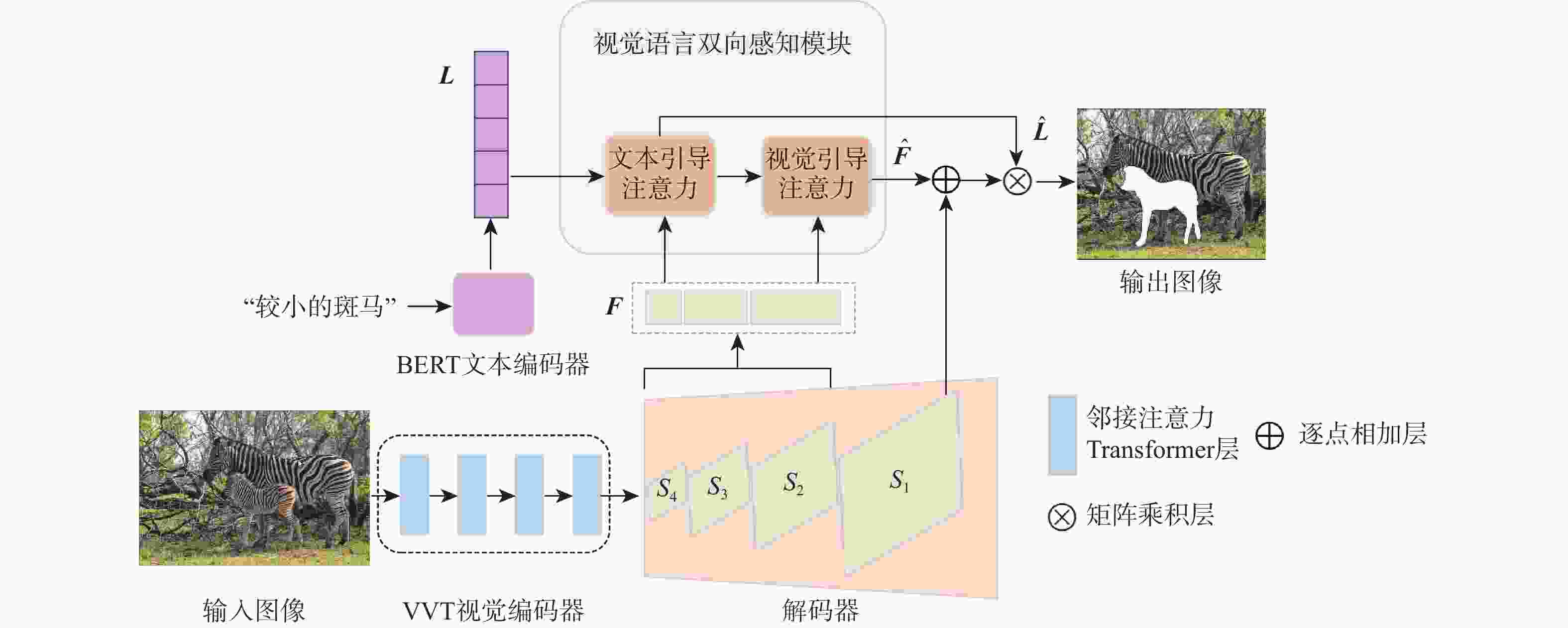
图像指代分割旨在根据自然语言描述从图像中分割出相应的目标区域。针对当前方法中跨模态特征融合不充分,导致目标区域和背景判别不准确的问题,提出一种基于视觉语言双向感知的图像指代分割方法。利用多层视觉特征编码网络提取多尺度视觉特征,增强每个像素对周围信息的感知能力,丰富其语义信息;将多尺度视觉特征输入双向视觉语言注意力解码模块中,通过跨模态注意力机制进行跨模态对齐,增强跨模态特征的上下文感知能力;通过双线性插值上采样得到逐像素分割掩码。在RefCOCO、RefCOCO+和G-Ref数据集上与主流方法进行对比实验,所提方法的总体IoU值分别达到74.85%、66.18%和64.95%,相较于LAVT算法分别提升2.12%、4.04%和3.71%,证明所提方法能够有效提升图像指代分割的性能。
-
关键词:
- 图像指代分割 /
- 跨模态 /
- 注意力机制 /
- 特征融合 /
- Transformer
Abstract:Referring image segmentation aims to segment corresponding target regions in an image described by a natural language description. In response to the problem that insufficient fusion of cross-modal features still exists in current methods, leading to inaccurate discrimination of target regions and backgrounds. This paper proposes a referring image segmentation method based on a bidirectional vision-language interaction module. Firstly, multi-scale visual features are extracted using a multi-level visual feature encoding network, which enhances each pixel's semantic content and fortifies its perception of surrounding information. Secondly, the bidirectional vision-language attention decoding module receives multi-scale visual features as input. A cross-modal attention mechanism is then used to achieve cross-modal alignment, which improves the cross-modal features' contextual awareness. Finally, the pixel-by-pixel segmentation mask is obtained by upsampling with bilinear interpolation. Comparative experiments were carried out on the RefCOCO, RefCOCO+, and G-Ref datasets with mainstream methods. The overall IoU of our method reached 74.85%, 66.18%, and 64.95%, respectively, which were 2.12%, 4.04%, and 3.71% higher than the LAVT algorithm. The results demonstrate that the proposed method can effectively improve the performance of image representation segmentation.
-
Key words:
- referring image segmentation /
- cross-modal /
- attention mechanism /
- feature fusion /
- Transformer
-
表 1 不同方法在3个数据集上的实验对比结果
Table 1. Comparation of results with different methods in terms of OIoU on three dataset
% 对比方法 主干网络 RefCOCO RefCOCO+ G-Ref 验证集 测试集A 测试集B 验证集 测试集A 测试集B 验证集U 测试集U 验证集G MCN[2] Darknet-53 62.44 64.20 59.71 50.62 54.99 44.69 49.22 49.40 BRINet[21] ResNet-101 60.98 62.99 59.21 48.17 52.32 42.11 63.46 EFN[22] ResNet-101 62.76 65.69 59.67 51.50 55.24 43.01 66.70 LTS[23] Darknet-53 65.43 67.76 63.08 54.21 58.32 48.02 54.40 54.24 VLT[12] Darknet-53 65.65 68.29 62.73 55.50 59.20 49.36 52.99 56.65 ReSTR[7] ViT-B-16 67.22 69.30 64.45 55.78 60.44 48.27 54.48 70.18 CRIS[24] ResNet-101 70.47 73.18 66.10 62.27 68.08 53.68 59.87 60.36 DMMI[25] Swin-B 74.13 77.13 70.16 63.98 69.73 57.03 63.46 64.19 61.98 SADLR[14] Swin-B 74.24 76.25 70.06 64.28 69.09 55.19 63.60 63.56 61.16 LAVT[20] Swin-B 72.73 75.82 68.79 62.14 68.38 55.10 61.24 62.09 本文 VVT 74.83 77.86 71.70 66.18 72.41 58.24 64.95 64.25 63.76 表 2 视觉主干网络对比实验结果
Table 2. Comparative experimental results of visual backbone network
% 视觉主干网络 P@0.5 P@0.7 P@0.9 mIoU OIoU ResNet50 84.97 75.71 36.83 74.52 71.87 SwinTransformer 86.51 78.66 38.29 76.02 73.62 VVT 86.95 80.57 39.89 77.53 74.83 表 3 跨模态融合方式对比实验结果
Table 3. Comparative experimental results of cross-modal fusion methods
% 融合方式 P@0.5 P@0.7 P@0.9 mIoU OIoU Mul 79.36 72.17 31.72 72.31 68.46 PWAM 82.84 79.28 38.72 76.58 73.31 Attention-Guided 86.95 80.57 39.89 77.53 74.83 -
[1] HU R H, ROHRBACH M, DARRELL T. Segmentation from natural language expressions[C]//Proceedings of the Computer Vision – ECCV 2016. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2016: 108-124. [2] LUO G, ZHOU Y Y, SUN X S, et al. Multi-task collaborative network for joint referring expression comprehension and segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 10031-10040. [3] LIU C X, LIN Z, SHEN X H, et al. Recurrent multimodal interaction for referring image segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1280-1289. [4] HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 770-778. [5] BELLVER M, VENTURA C, SILBERER C, et al. A closer look at referring expressions for video object segmentation[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2023, 82(3): 4419-4438. doi: 10.1007/s11042-022-13413-x [6] CHEN L C, PAPANDREOU G, SCHROFF F, et al. Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation[EB/OL]. (2017-06-17)[2022-05-20]. https://doi.ory/10.48550/arXiv.1706.05587. [7] KIM N, KIM D, KWAK S, et al. ReSTR: convolution-free referring image segmentation using transformers[C]//Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2022: 18124-18133. [8] MARGFFOY-TUAY E, PÉREZ J C, BOTERO E, et al. Dynamic multimodal instance segmentation guided by natural language queries[C]//Proceedings of the Computer Vision – ECCV 2018. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2018: 656-672. [9] LIU S, HUI T R, HUANG S F, et al. Cross-modal progressive comprehension for referring segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(9): 4761-4775. [10] YE L W, ROCHAN M, LIU Z, et al. Cross-modal self-attention network for referring image segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 10494-10503. [11] LI W, GAO C, NIU G, et al. Unimo: towards unified-modal understanding and generation via cross-modal contrastive learning[EB/OL]. (2020-12-31)[2022-05-21]. http://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2012.15409. [12] DING H H, LIU C, WANG S C, et al. Vision-language transformer and query generation for referring segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 16301-16310. [13] LI J, LI D, SAVARESE S, et al. Blip-2: bootstrapping language-image pre-training with frozen image encoders and large language models[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning. Honolulu: PMLR, 2023: 19730-19742. [14] YANG Z, WANG J Q, TANG Y S, et al. Semantics-aware dynamic localization and refinement for referring image segmentation[J]. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2023, 37(3): 3222-3230. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v37i3.25428 [15] SUN W X, QIN Z, DENG H, et al. Vicinity vision transformer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, 45(10): 12635-12649. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2023.3285569 [16] DEVLIN J, CHANG M W, LEE K, et al. Bert: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding[C]//Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Minneapolis: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2019: 4171–4186. [17] YU L C, POIRSON P, YANG S, et al. Modeling context in referring expressions[C]// Computer Vision – ECCV 2016. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2016: 69-85. [18] MAO J H, HUANG J, TOSHEV A, et al. Generation and comprehension of unambiguous object descriptions[C]//Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 11-20. [19] LIN T Y, MAIRE M, BELONGIE S, et al. Microsoft COCO: common objects in context[C]//Proceedings of the Computer Vision – ECCV 2014. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2014: 740-755. [20] YANG Z, WANG J Q, TANG Y S, et al. LAVT: Language-aware vision transformer for referring image segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2022: 18134-18144. [21] FENG G, HU Z W, ZHANG L H, et al. Bidirectional relationship inferring network for referring image localization and segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(5): 2246-2258. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3106153 [22] FENG G, HU Z W, ZHANG L H, et al. Encoder fusion network with co-attention embedding for referring image segmentation[C]// Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 15501-15510. [23] JING Y, KONG T, WANG W, et al. Locate then segment: A strong pipeline for referring image segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 9853-9862. [24] WANG Z Q, LU Y, LI Q, et al. CRIS: CLIP-driven referring image segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2022: 11676-11685. [25] HU Y T, WANG Q X, SHAO W Q, et al. Beyond one-to-one: Rethinking the referring image segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2023: 4044-4054. -






 下载:
下载: