Cooperative path planning for multiple unmanned aerial vehicles system in a game-theoretic environment
-
摘要:
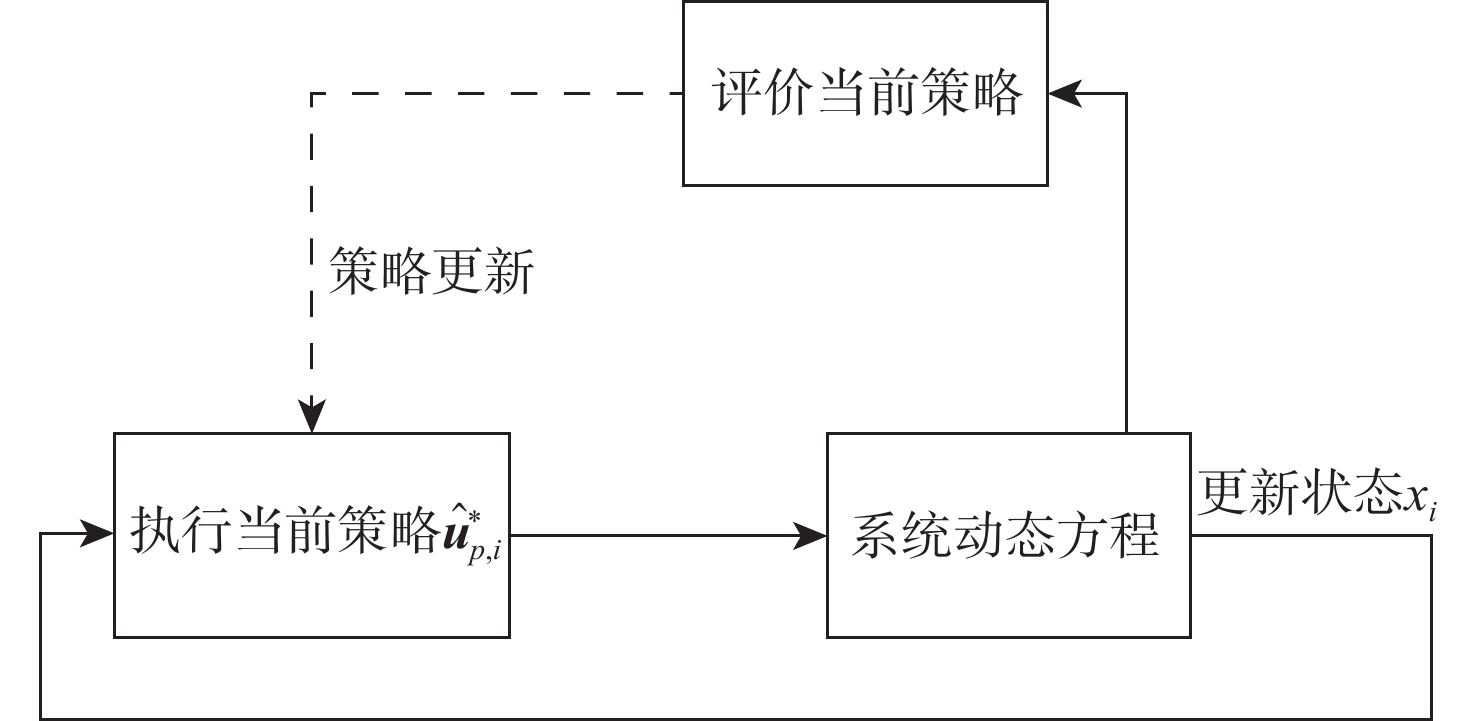
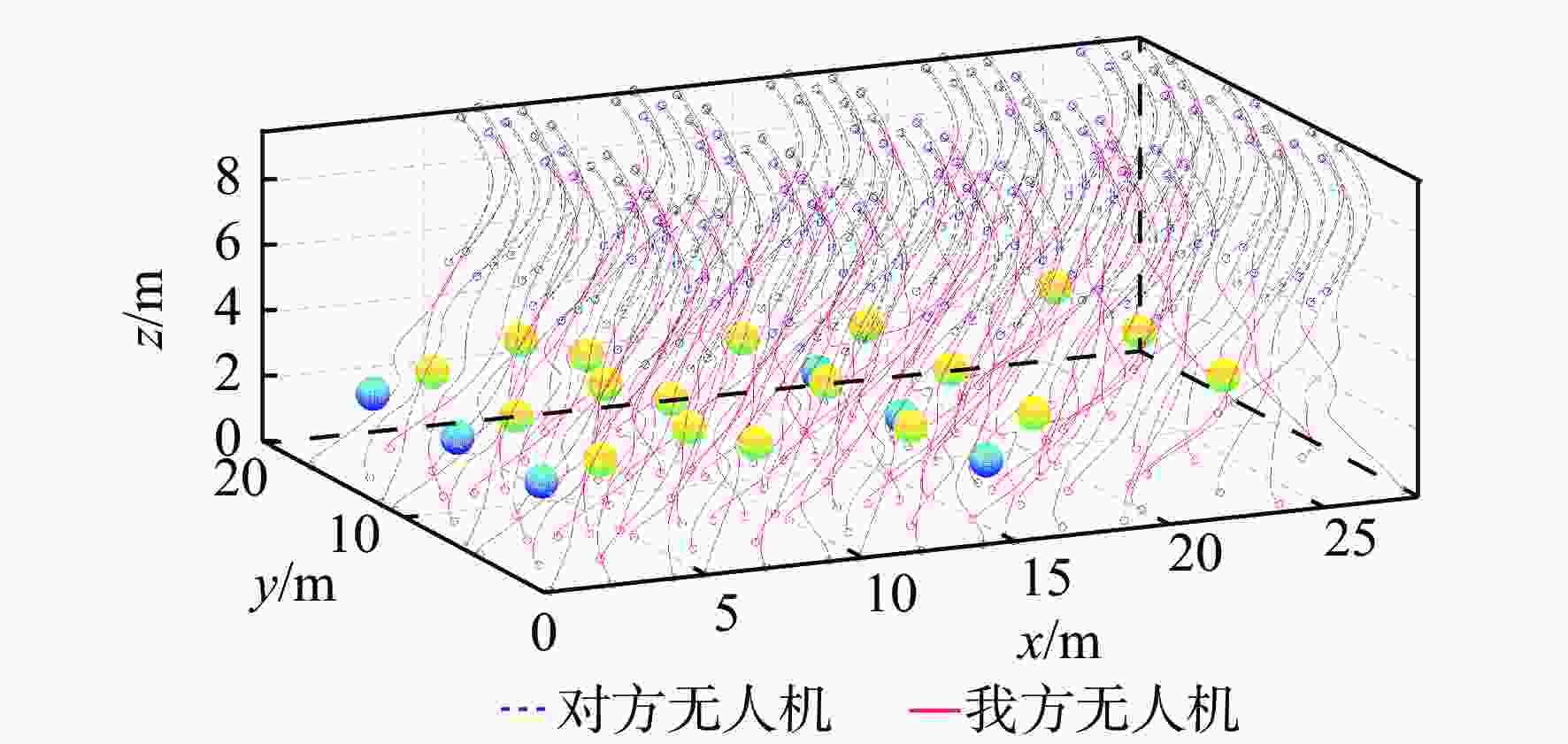
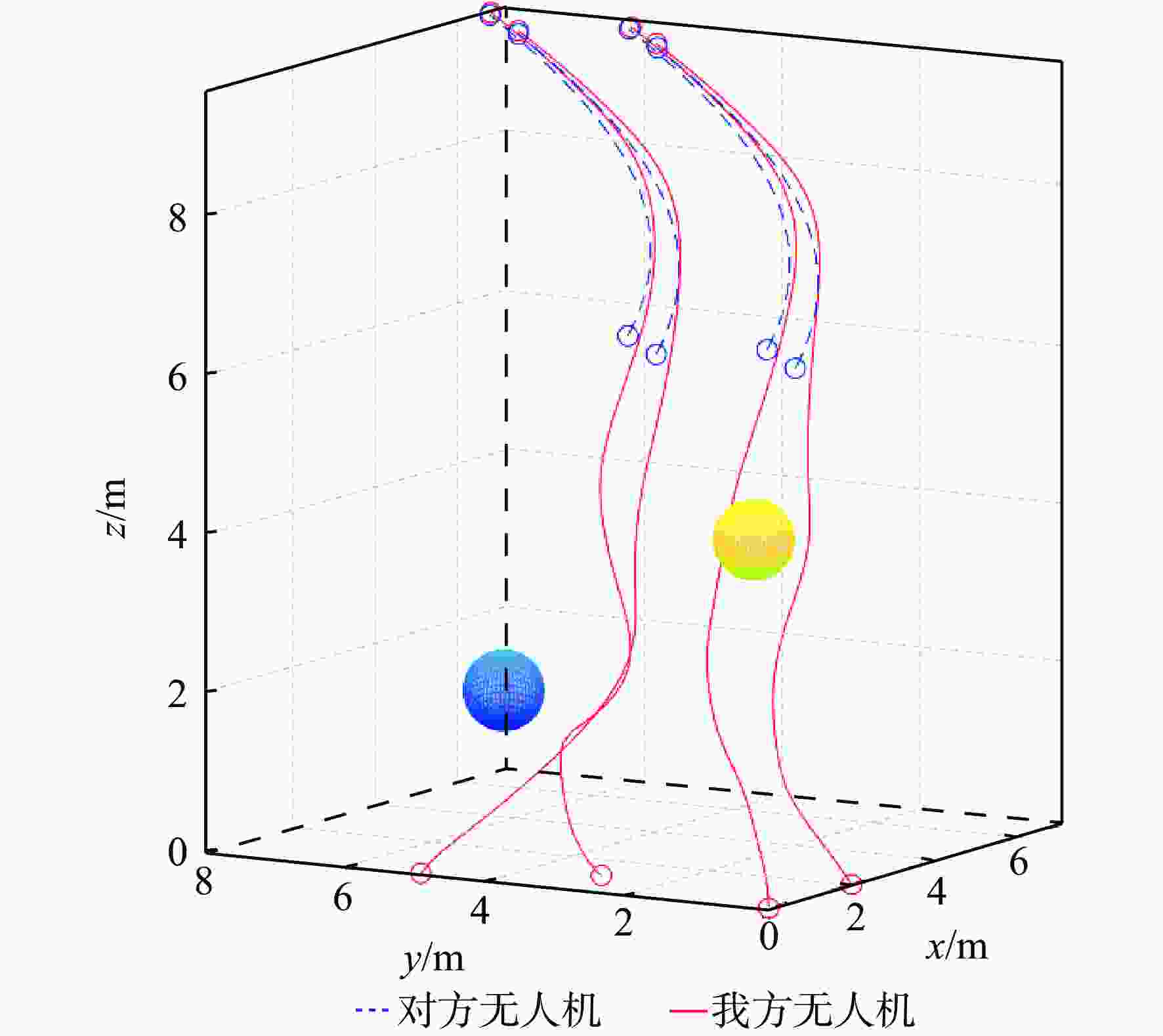
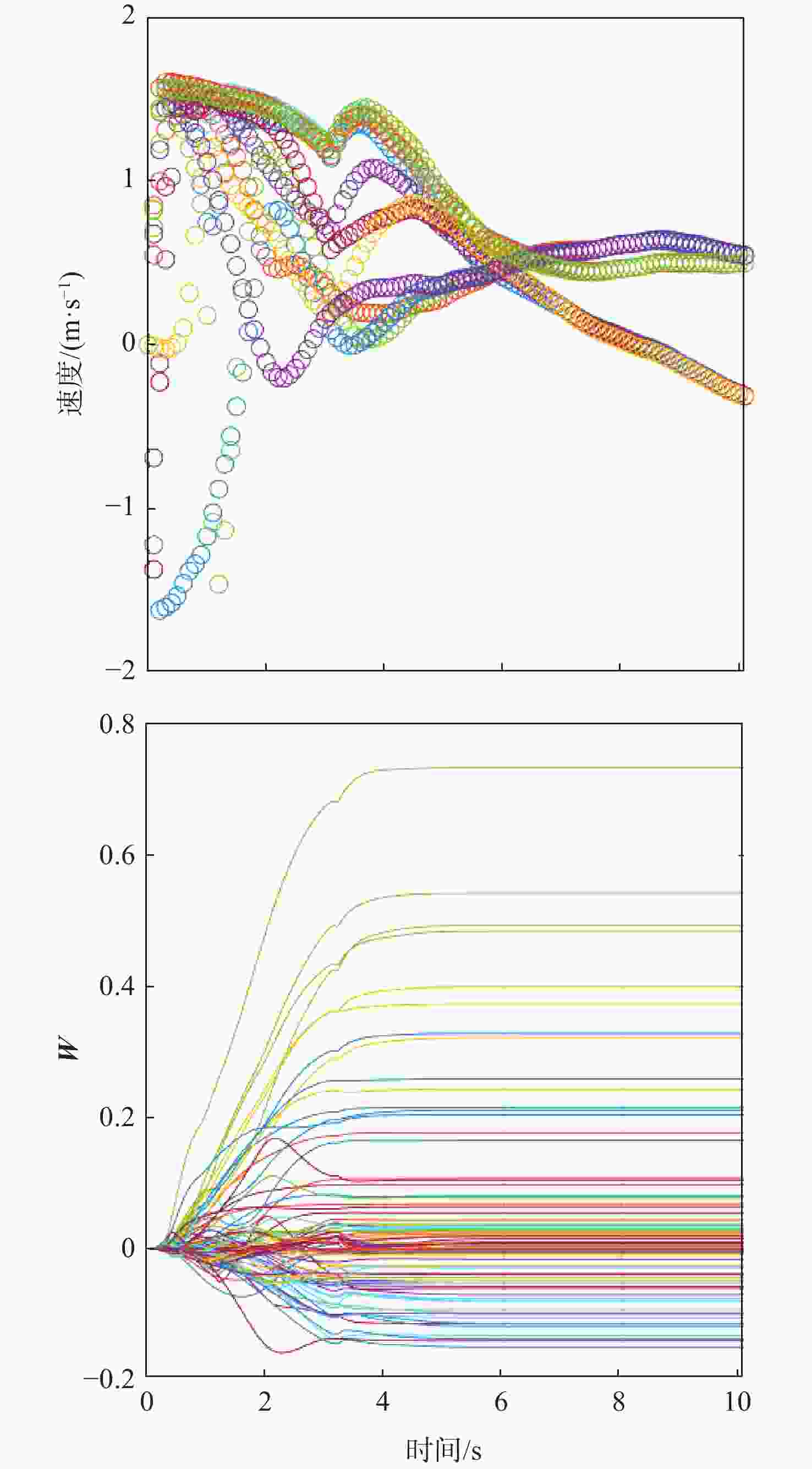
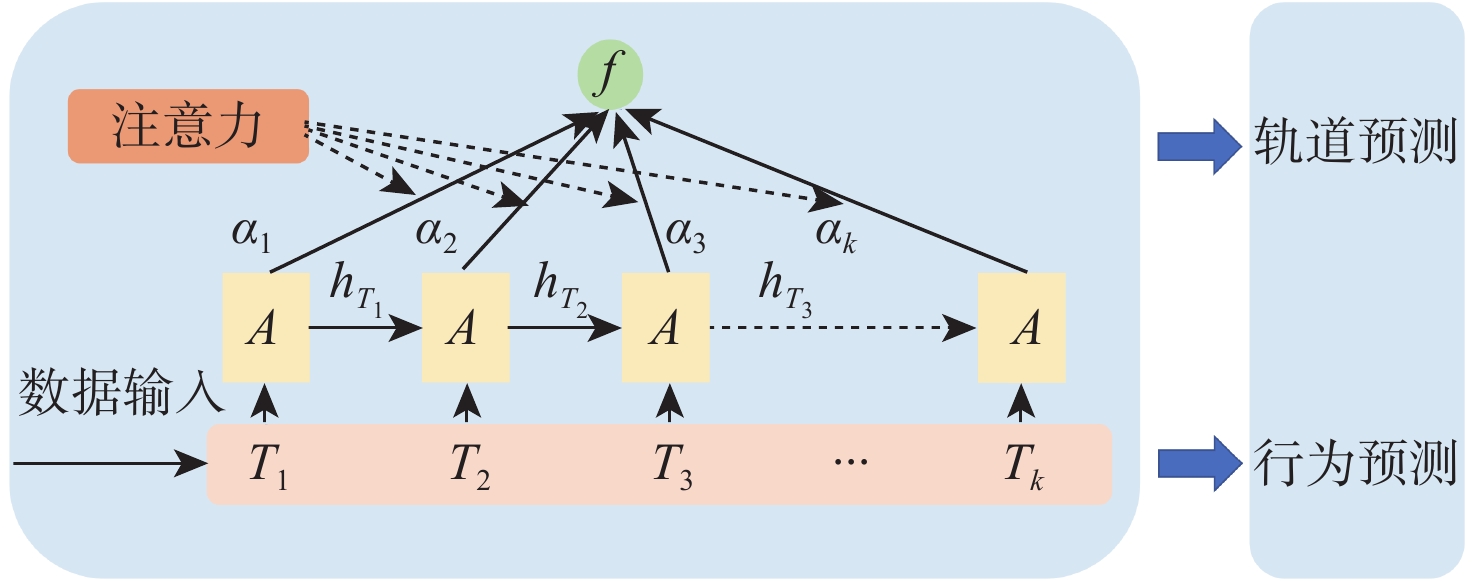
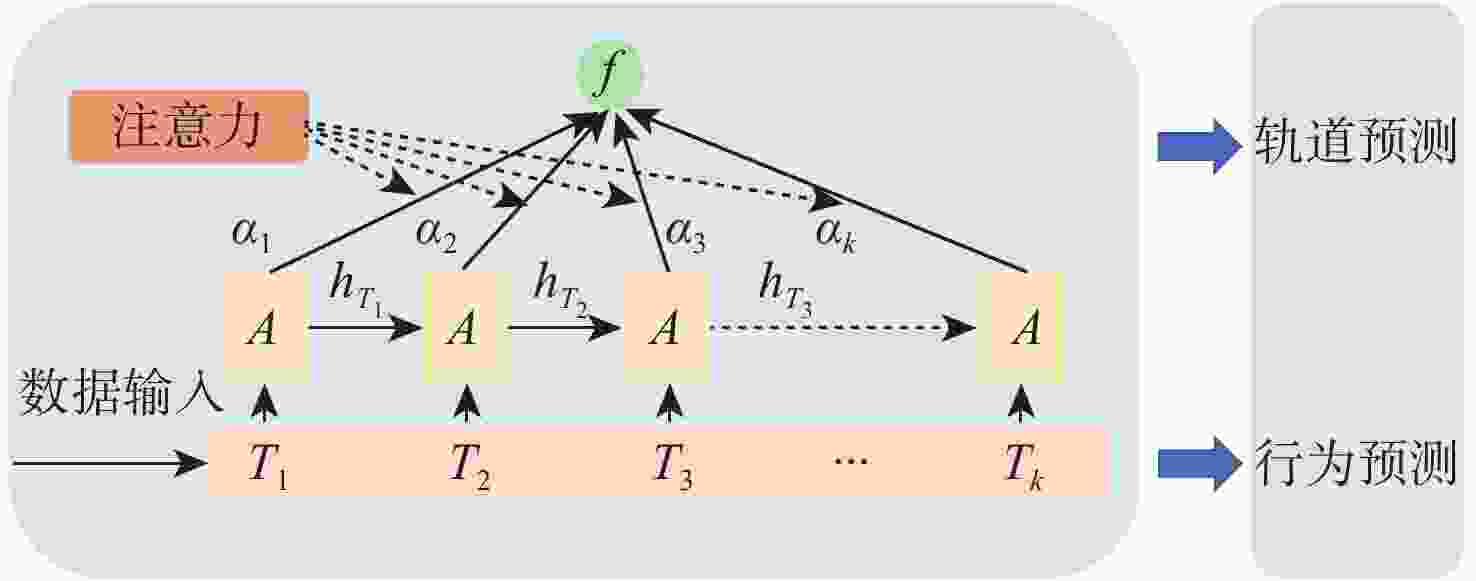
研究了博弈环境下多无人机系统在模型动力学不确定和输入受限条件下的协同路径规划问题。在博弈环境中,我方无人机需要通过协同路径规划捕获对方无人机,并考虑避开禁区和避碰。首先,提出一种基于注意力机制的长短期记忆(LSTM)模型来预测对方无人机的轨迹,帮助我方无人机进行后续的协同路径规划。然后,通过构造性能函数,将协同路径规划问题转化为输入受限条件下的最优控制问题。提出一种基于历史数据的不依赖于模型参数的积分强化学习方法,实现了输入受限条件下的最优控制。仿真结果验证了所提方法的有效性。
Abstract:In this paper, the cooperative path planning problem in games for the unmanned aerial vehicles system is addressed under conditions of unknown dynamics and input constraints. By planning their routes and avoiding collisions and prohibited areas, friendly and enemy unmanned aerial vehicles must catch up to each other in the game. The trajectory of the opposing unmanned aerial vehicles is predicted to assist path planning by a long short term memory (LSTM) model with an attention mechanism. By creating the value function, the cooperative path planning issue is transformed into an optimum control problem with input restrictions. A method based on integral reinforcement learning is designed to achieve optimal control using the historical data, without the knowledge of inertial parameters. The results of the simulation confirm the efficacy of the proposed method.
-
Key words:
- multi-agent system /
- path planning /
- nonlinear system /
- reinforcement learning /
- unmanned aerial vehicle
-
[1] CAMPION M, RANGANATHAN P, FARUQUE S. Notice of removal: a review and future directions of UAV swarm communication architectures[C]//Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Electro/Information Technology. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 903-908. [2] LIU J J, WANG W P, WANG T, et al. A motif-based rescue mission planning method for UAV swarms using an improved PICEA[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 40778-40791. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2857503 [3] 吴傲, 杨任农, 梁晓龙, 等. 基于信息素决策的无人机集群协同搜索算法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2021, 47(4): 814-827.WU A, YANG R N, LIANG X L, et al. Cooperative search algorithm based on pheromone decision for UAV swarm[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2021, 47(4): 814-827(in Chinese). [4] NIU X, YUAN X D, ZHOU Y W, et al. UAV track planning based on evolution algorithm in embedded system[J]. Microprocessors and Microsystems, 2020, 75: 103068. doi: 10.1016/j.micpro.2020.103068 [5] 吴学礼, 王超, 赵俊棋, 等. 改进麻雀算法的无人机三维路径规划[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2024, 24(15): 6534-6542.WU X L, WANG C, ZHAO J Q, et al. Improved sparrow algorithm for UAV 3D path planning[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2024, 24(15): 6534-6542(in Chinese). [6] RAHEEM F A, IBRAHIM U I. Path planning algorithm using D* heuristic method based on PSO in dynamic environment[J]. American Scientific Research Journal for Engineering, Technology, and Sciences, 2006, 49: 257-271. [7] ZHANG Z, WU J, DAI J Y, et al. Optimal path planning with modified A-Star algorithm for stealth unmanned aerial vehicles in 3D network radar environment[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part G: Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 2022, 236(1): 72-81. doi: 10.1177/09544100211007381 [8] CHEN Y B, YU J Q, SU X L, et al. Path planning for multi-UAV formation[J]. Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, 2015, 77(1): 229-246. [9] NOREEN I, KHAN A, HABIB Z. Optimal path planning using RRT* based approaches: a survey and future directions[J]. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications, 2016, 7(11): 97-107. [10] ZHU D Q, LIU Y, SUN B. Task assignment and path planning of a multi-AUV system based on a glasius bio-inspired self-organising map algorithm[J]. The Journal of Navigation, 2018, 71(2): 482-496. doi: 10.1017/S0373463317000728 [11] LUIS C E, SCHOELLIG A P. Trajectory generation for multiagent point-to-point transitions via distributed model predictive control[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2019, 4(2): 375-382. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2018.2890572 [12] LUIS C E, VUKOSAVLJEV M, SCHOELLIG A P. Online trajectory generation with distributed model predictive control for multi-robot motion planning[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2020, 5(2): 604-611. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2020.2964159 [13] LU Y, GUO Y H, ZHAO G X, et al. Distributed safe reinforcement learning for multi-robot motion planning[C]//Proceedings of the 2021 29th Mediterranean Conference on Control and Automation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 1209-1214. [14] HE C Y, WAN Y, GU Y X, et al. Integral reinforcement learning-based approximate minimum time-energy path planning in an unknown environment[J]. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2021, 31(6): 1905-1922. doi: 10.1002/rnc.5122 [15] HE C Y, WAN Y, GU Y X, et al. Integral reinforcement learning-based multi-robot minimum time-energy path planning subject to collision avoidance and unknown environmental disturbances[J]. IEEE Control Systems Letters, 2021, 5(3): 983-988. doi: 10.1109/LCSYS.2020.3007663 [16] ROUSSEAS P, BECHLIOULIS C P, KYRIAKOPOULOS K J. Optimal robot motion planning in constrained workspaces using reinforcement learning[C]//Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 6917-6922. [17] ROUSSEAS P, BECHLIOULIS C P, KYRIAKOPOULOS K J. Optimal motion planning in unknown workspaces using integral reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2022, 7(3): 6926-6933. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2022.3178788 [18] LI X H, ZHAO Y, ZHANG J, et al. A hybrid PSO algorithm based flight path optimization for multiple agricultural UAVS[C]//Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 28th International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 691-697. [19] QIE H, SHI D X, SHEN T L, et al. Joint optimization of multi-UAV target assignment and path planning based on multi-agent reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 146264-146272. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2943253 [20] GUO Y H, CHEN G. Robust near-optimal coordination in uncertain multiagent networks with motion constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2023, 53(5): 2841-2851. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2021.3125318 [21] JENSEN-NAU K R, HERMANS T, LEANG K K. Near-optimal area-coverage path planning of energy-constrained aerial robots with application in autonomous environmental monitoring[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2020, 18(3): 1453-1468. [22] DUAN H B, YUAN Y, ZENG Z G. Distributed cooperative control of multiple UAVs in the presence of actuator faults and input constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2022, 69(11): 4463-4467. [23] SHI Z Y, XU M, PAN Q. 4-D flight trajectory prediction with constrained LSTM network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2020, 22(11): 7242-7255. [24] KANT R, SAINI P, KUMARI J. Long short-term memory auto-encoder-based position prediction model for fixed-wing UAV during communication failure[J]. IEEE Transactions on Artificial Intelligence, 2022, 4(1): 173-181. [25] LIU H, MA T, LEWIS F L, et al. Robust formation control for multiple quadrotors with nonlinearities and disturbances[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, 50(4): 1362-1371. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2018.2875559 [26] LIU H, TIAN Y, LEWIS F L, et al. Robust formation tracking control for multiple quadrotors under aggressive maneuvers[J]. Automatica, 2019, 105: 179-185. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2019.03.024 [27] BHASIN S, KAMALAPURKAR R, JOHNSON M, et al. A novel actor–critic–identifier architecture for approximate optimal control of uncertain nonlinear systems[J]. Automatica, 2013, 49(1): 82-92. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2012.09.019 [28] DEPTULA P, BELL Z I, DOUCETTE E A, et al. Data-based reinforcement learning approximate optimal control for an uncertain nonlinear system with control effectiveness faults[J]. Automatica, 2020, 116: 108922. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2020.108922 -






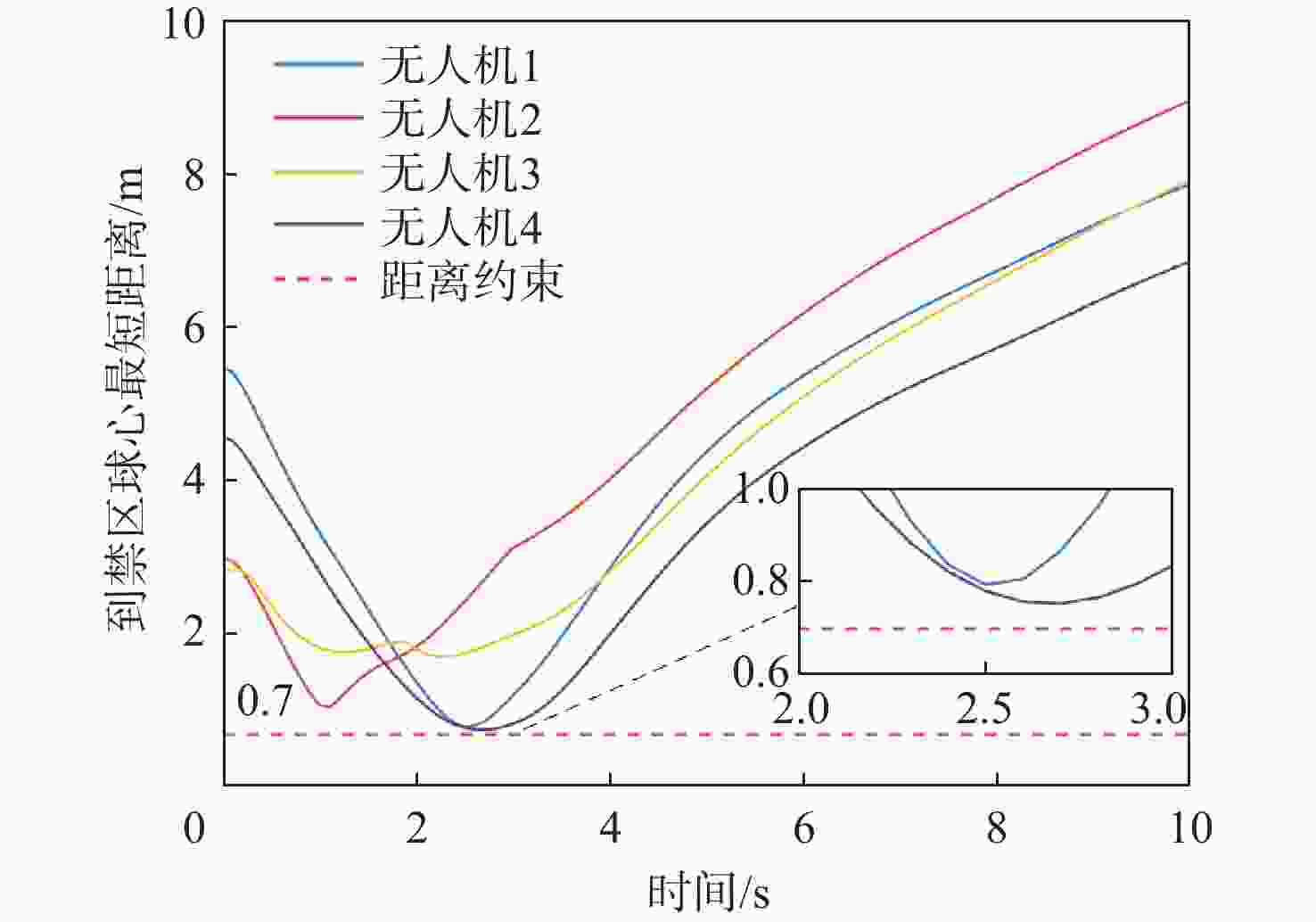
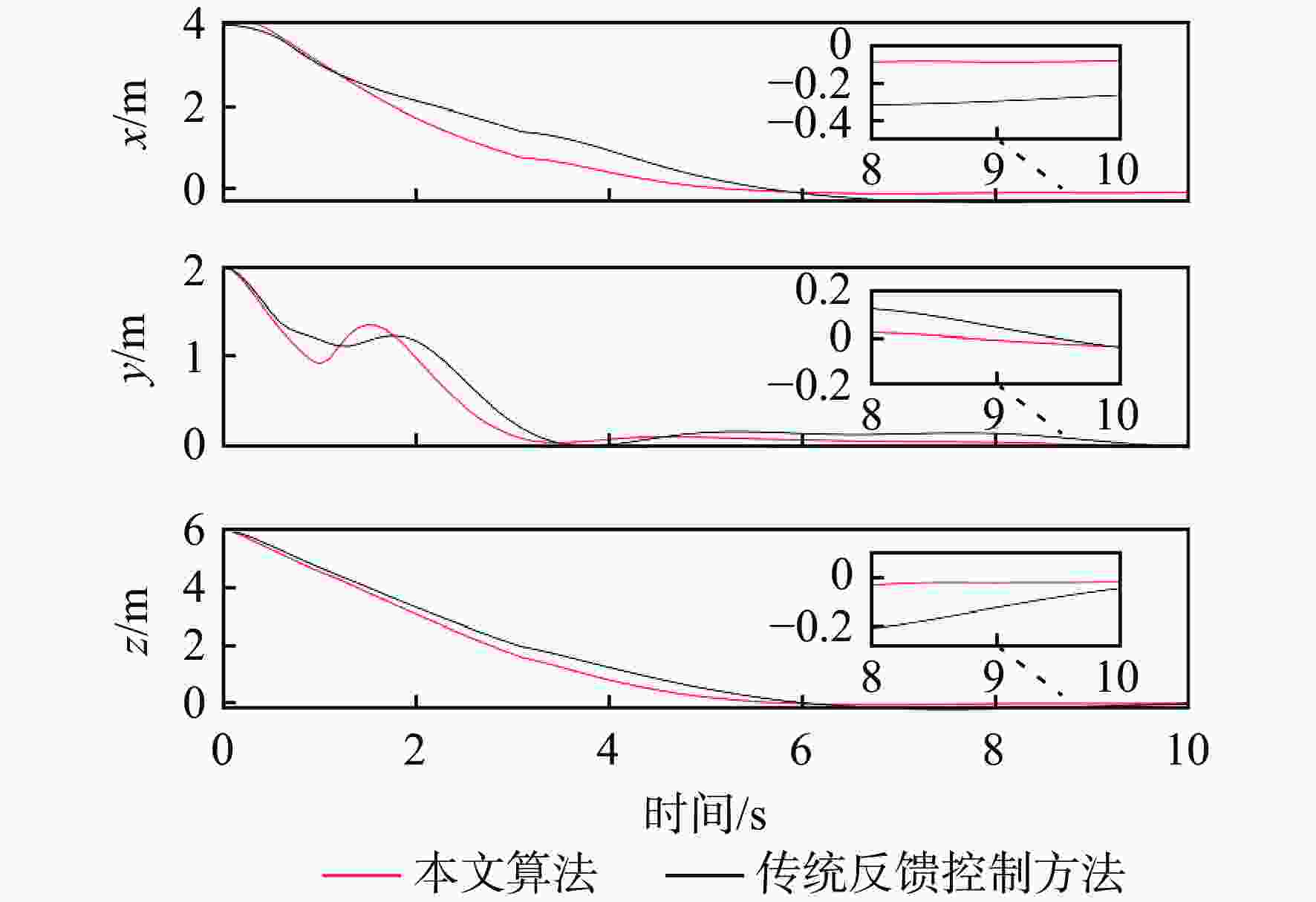
 下载:
下载: