Flight schedule optimization considering passengers’ transit duration and transit service selection preference
-
摘要:
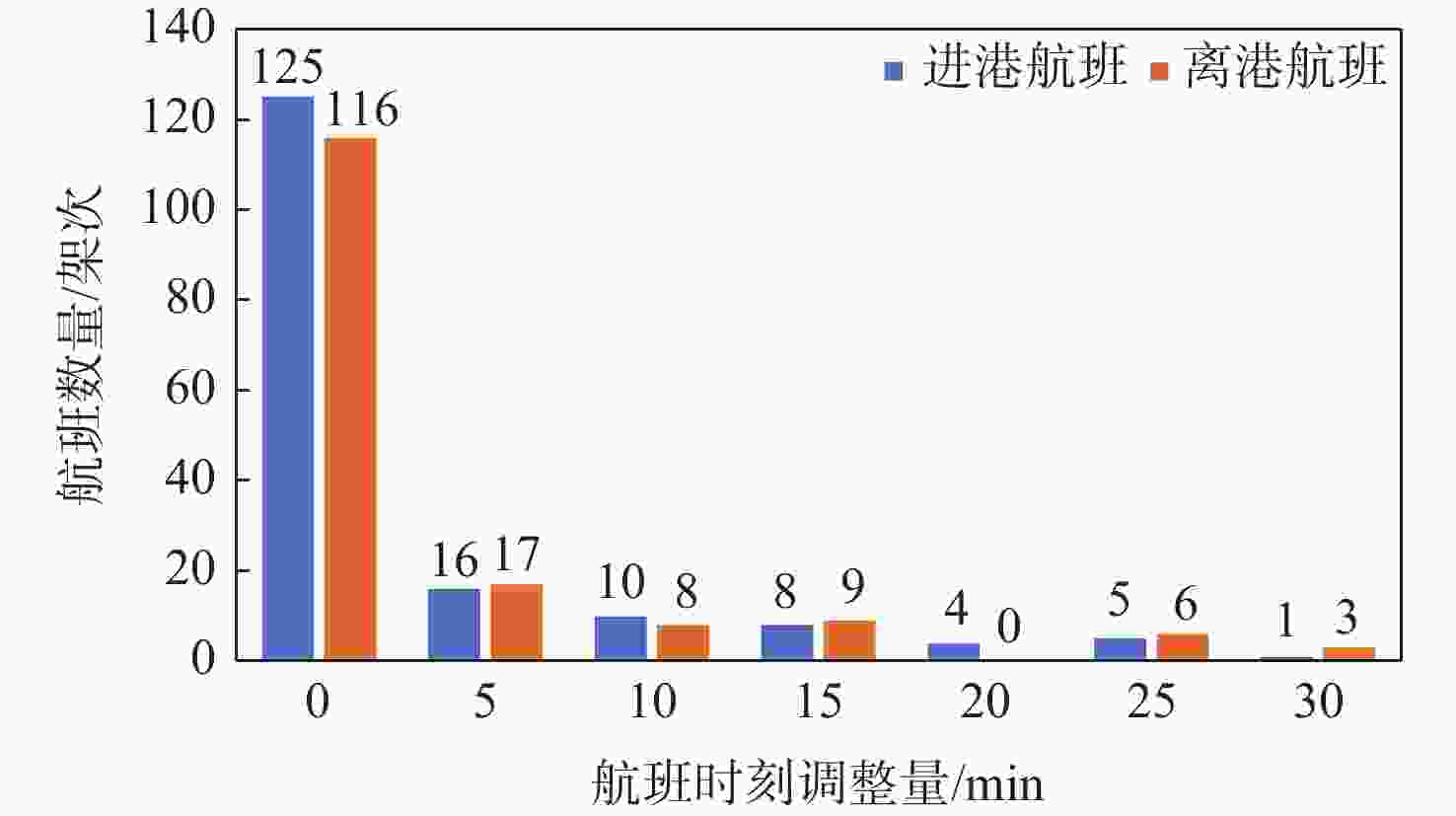
针对当前时刻优化未充分考虑旅客选择偏好导致航班中转吸引力和机场中转衔接效率较低问题,对旅客中转时长和中转服务选择偏好影响下的航班时刻优化问题进行研究。从中转旅客的实际选择偏好出发,采用选择行为实验收集数据,构建条件Logit模型分析影响旅客中转航班选择行为的航班特性。基于选择偏好分析结果,定义中转航班旅客吸引力参数,以中转航班吸引力最大、可衔接航班配对数最大和总航班时刻调整量最小为目标,建立航班时刻优化模型。通过对比粒子群算法、第2代非支配排序遗传算法(NSGA-Ⅱ)和NSGA-Ⅲ的求解效果,提出考虑中转旅客选择偏好的航班时刻优化方案。结果表明:票价、中转时长和中转便利化服务是影响旅客选择的主要因素;所提方案优化后的航班时刻表中转航班旅客吸引力提升391.22%,可中转衔接航班配对数增加了31.28%,机场中转能力得到有效提升;同时,时刻调整航班占比26.52%,所有调整航班的平均调整量为12.35 min,符合航空公司接受范围。所提方案为航班时刻优化提供了新的视角和方法,有助于提升中国枢纽中转能力,便利旅客中转出行。
Abstract:Addressing the issue of low attractiveness and inefficient airport transit connections due to current schedule optimizations that do not fully consider passengers’ selection preferences, an investigation into flight schedule optimization influenced by passengers’ transit duration and transit service selection preferences was conducted. Starting from the actual selection preferences of transfer passengers, a selection behavior experiment was conducted to collect data, and a conditional Logit model was constructed to analyze the flight characteristics that influence passengers’ choices for transit flights. Based on the findings of the selection preference analysis, a passenger attractiveness parameter for transit flights was defined. Subsequently, a flight schedule optimization model was developed with the objectives of maximizing the attractiveness of transit flights, maximizing the number of connectable flight pairs, and minimizing the total flight schedule adjustment. By comparing the solution effectiveness of particle swarm, non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm Ⅱ(NSGA-Ⅱ), and NSGA-Ⅲ, a flight schedule optimization scheme that considers the selection preferences of transfer passengers was proposed. The results indicate that fares, transit duration, and transit facilitation services are the primary factors affecting passengers’ selection behavior. The results demonstrate that the proposed optimized flight schedule is significantly more attractive to transfer passengers, with the attractiveness of transit flights increasing by 391.22%, the number of connectable flight pairs increasing by 31.28%, and the airport’s transit capacity being effectively enhanced. Additionally, 26.52% of flights were adjusted, with an average adjustment of 12.35 minutes, which falls within the airlines’ acceptable range. This study offers new perspectives and methods for flight schedule optimization, contributing to the enhancement of Chinese hub airports’ transit capacity and facilitating passengers’ travel experiences.
-
表 1 条件Logit模型拟合结果
Table 1. Conditional Logit model fitting results
变量 回归系数 Z值 p值 OR值 CI(OR值95%) $ {X_1} $ −0.307*** 0.047 0 0.735 0.671~0.806 $ {X_2} $ −0.377*** 0.053 0 0.686 0.618~0.762 $ {X_3} $ 0.236*** 0.050 0 1.266 1.149~1.396 $ {X_0} $ −0.271*** 0.068 0 0.763 0.668~0.871 注:***表示系数在1%的水平上显著,即p<0.01。 表 2 兰州中川机场原始进港航班计划(部分)
Table 2. Lanzhou Zhongchuan airport original arrival flight plan (partial)
航班号 出发机场 计划起飞时刻 到达机场 计划降落时刻 TV6061 XIY 06:25 LHW 08:00 TV6046 INC 07:10 LHW 08:15 G54653 CKG 06:55 LHW 08:40 GJ8295 CGO 06:30 LHW 08:45 DR5323 DNH 07:00 LHW 08:55 GS7877 TSN 06:35 LHW 08:55 3U8361 CTU 07:40 LHW 09:05 MU2471 TFU 07:40 LHW 09:05 TV9913 LXA 07:00 LHW 09:10 CA2581 TFU 07:35 LHW 09:15 表 3 兰州中川机场原始离港航班计划(部分)
Table 3. Lanzhou Zhongchuan airport original departure flight plan (partial)
航班号 出发机场 计划起飞时刻 到达机场 计划降落时刻 9C6737 LHW 07:00 AKA 08:25 CZ5370 LHW 06:00 SHE 08:50 MU2195 LHW 07:00 CGO 08:50 MU2249 LHW 07:15 KMG 09:20 9C6533 LHW 08:30 IQN 09:25 MU2373 LHW 07:55 TYN 09:30 9C6305 LHW 07:25 TSN 09:40 9C7087 LHW 07:00 HGH 09:50 MU6810 LHW 07:10 PVG 09:50 9C6187 LHW 07:20 NKG 09:50 表 4 不同算法收敛后的IGD
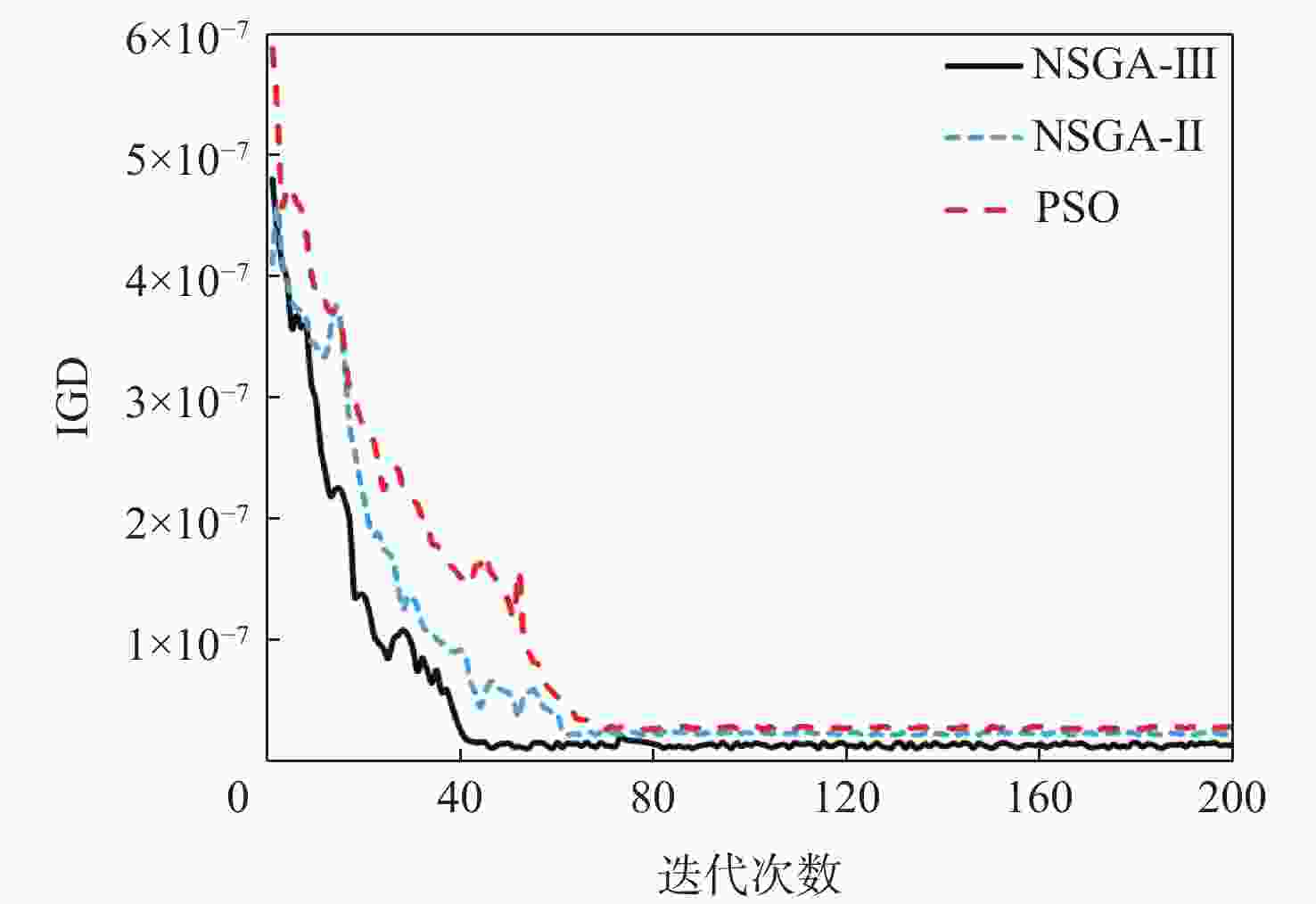
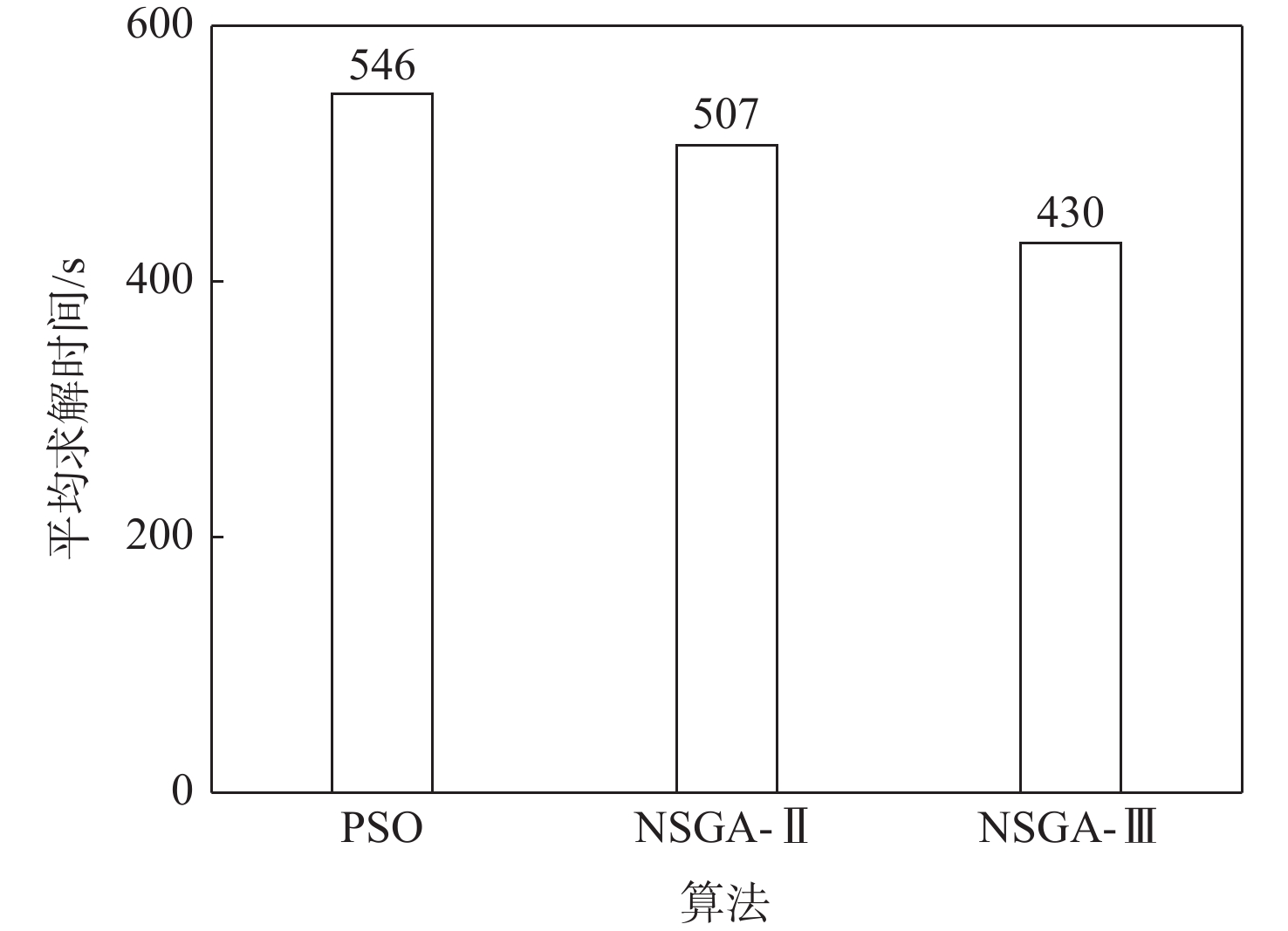
Table 4. IGD values after convergence of different algorithms
算法 IGD PSO 0.265 5×10−7 NSGA-Ⅱ 0.204 0×10−7 NSGA-Ⅲ 0.149 9×10−7 表 5 优化后进港航班时刻调整结果(部分)
Table 5. Results of arrive flight schedule adjustments (partial)
航班号 起飞机场 降落机场 优化前时刻 优化后时刻 调整量/min TV6046 INC LHW 8:15 8:05 +10 UQ3562 HTN LHW 12:10 12:15 +5 CZ6491 SHE LHW 12:15 12:25 +10 CA1207 PEK LHW 12:25 12:50 +25 9C6134 HFE LHW 13:05 13:10 +5 ZH9237 SZX LHW 13:20 13:15 −5 9C6188 NKG LHW 13:40 13:15 −25 MU2412 PKX LHW 13:50 13:20 −30 MU6499 TNA LHW 13:55 13:30 −25 表 6 优化后离港航班时刻调整结果(部分)
Table 6. Results of departure flight schedule adjustments (partial)
航班号 起飞机场 降落机场 优化前时刻 优化后时刻 调整量/min HU7537 LHW DSN 8:40 8:50 +10 HU7553 LHW SJW 8:40 8:50 +10 MU9873 LHW JGN 9:30 9:55 +25 3U3675 LHW CZX 9:40 9:55 +15 3U8362 LHW CTU 9:55 10:20 +25 TV9914 LHW LXA 9:55 10:25 +30 CA2582 LHW TFU 10:20 10:35 +15 NS3310 LHW SJW 10:25 10:40 +15 CA8598 LHW WNZ 10:50 10:55 +5 表 7 优化前后各目标函数值
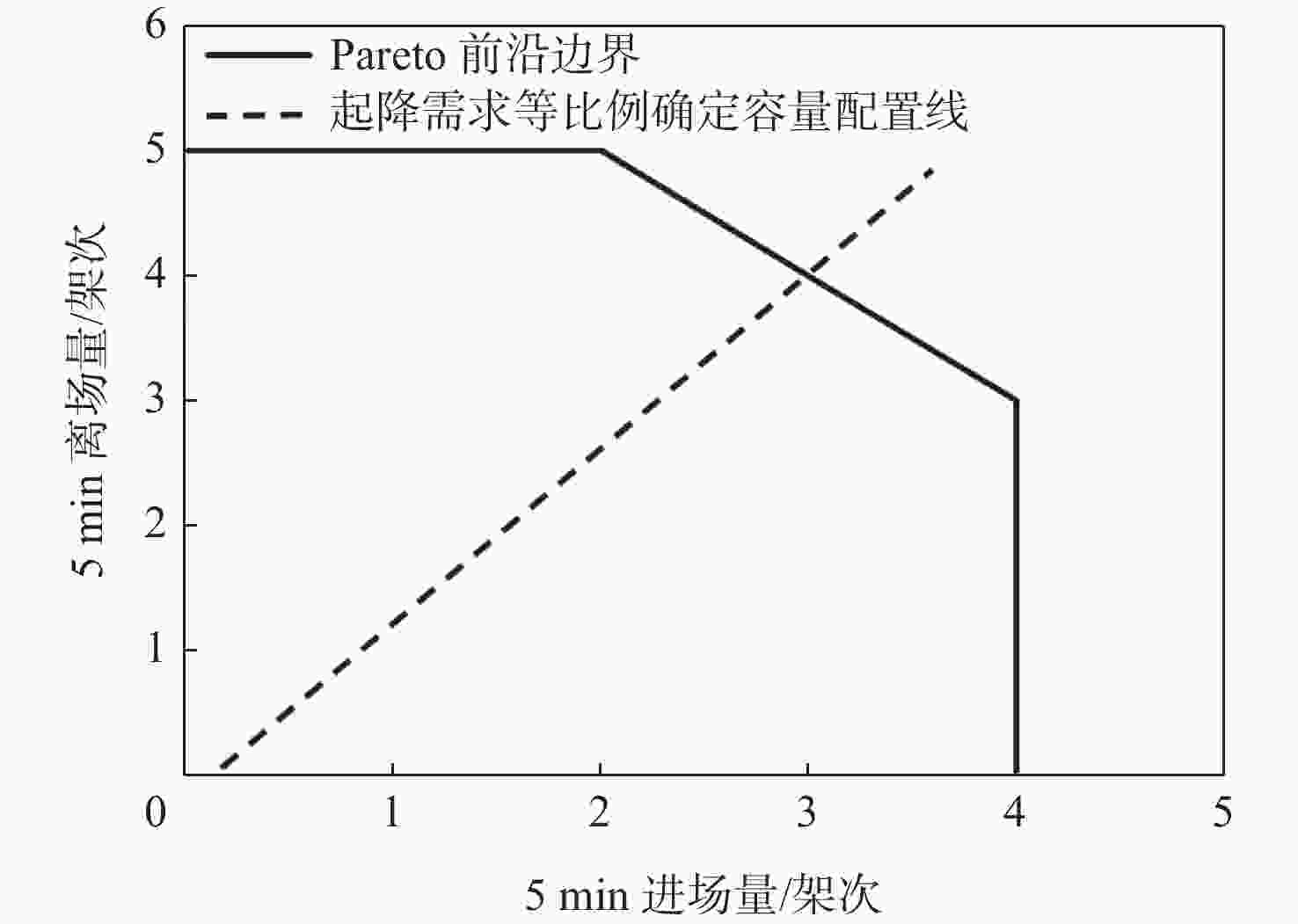
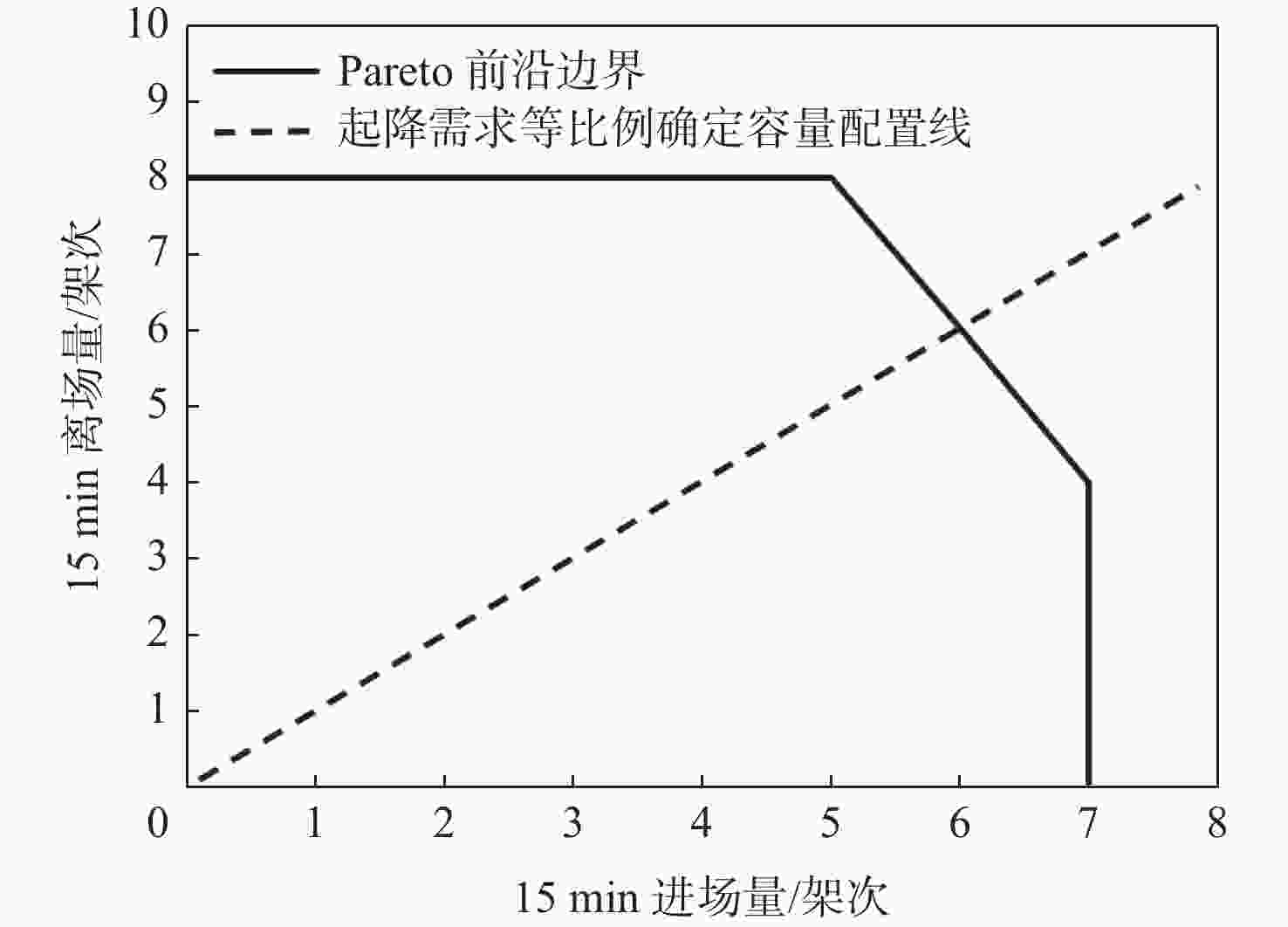
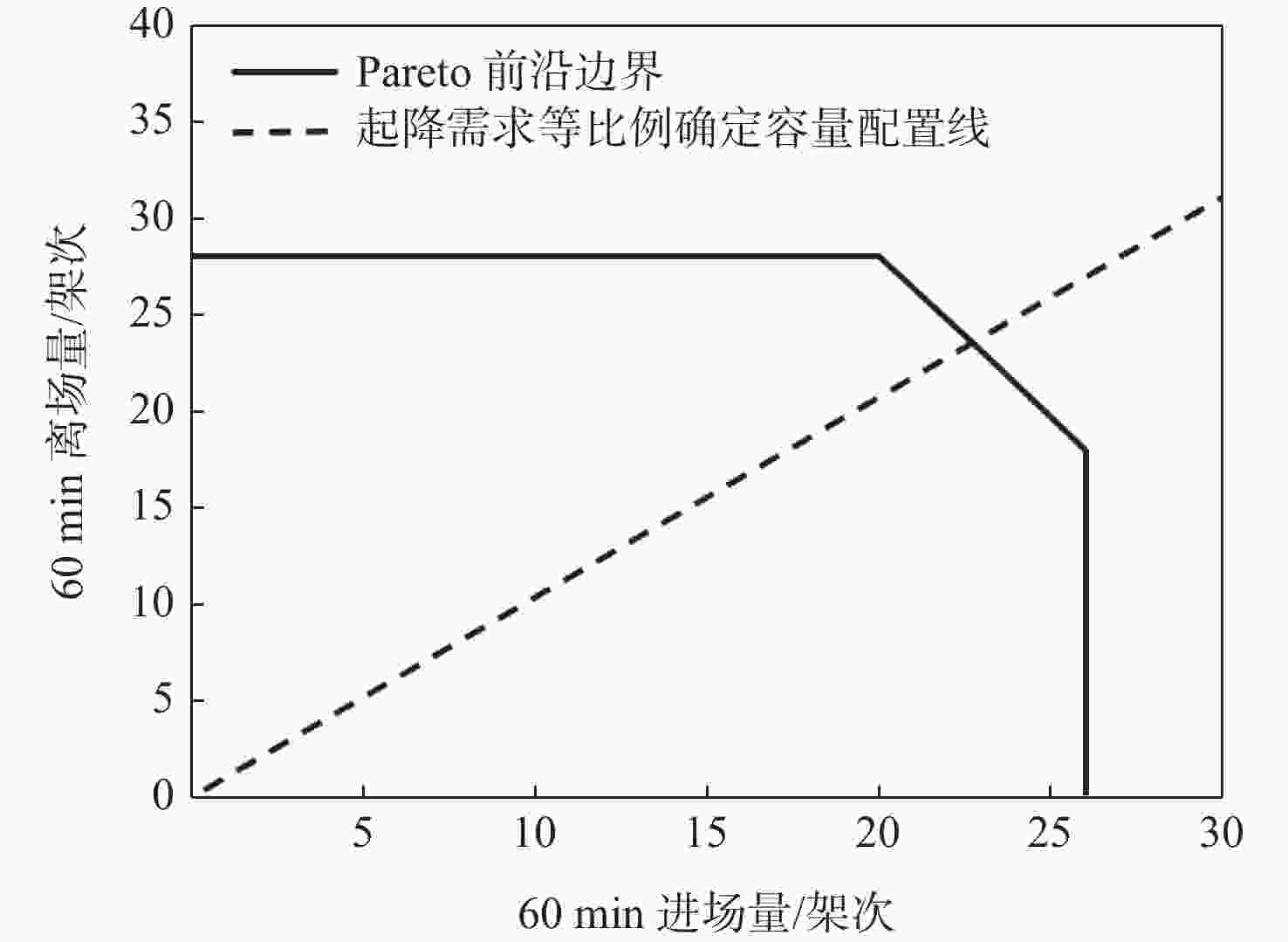
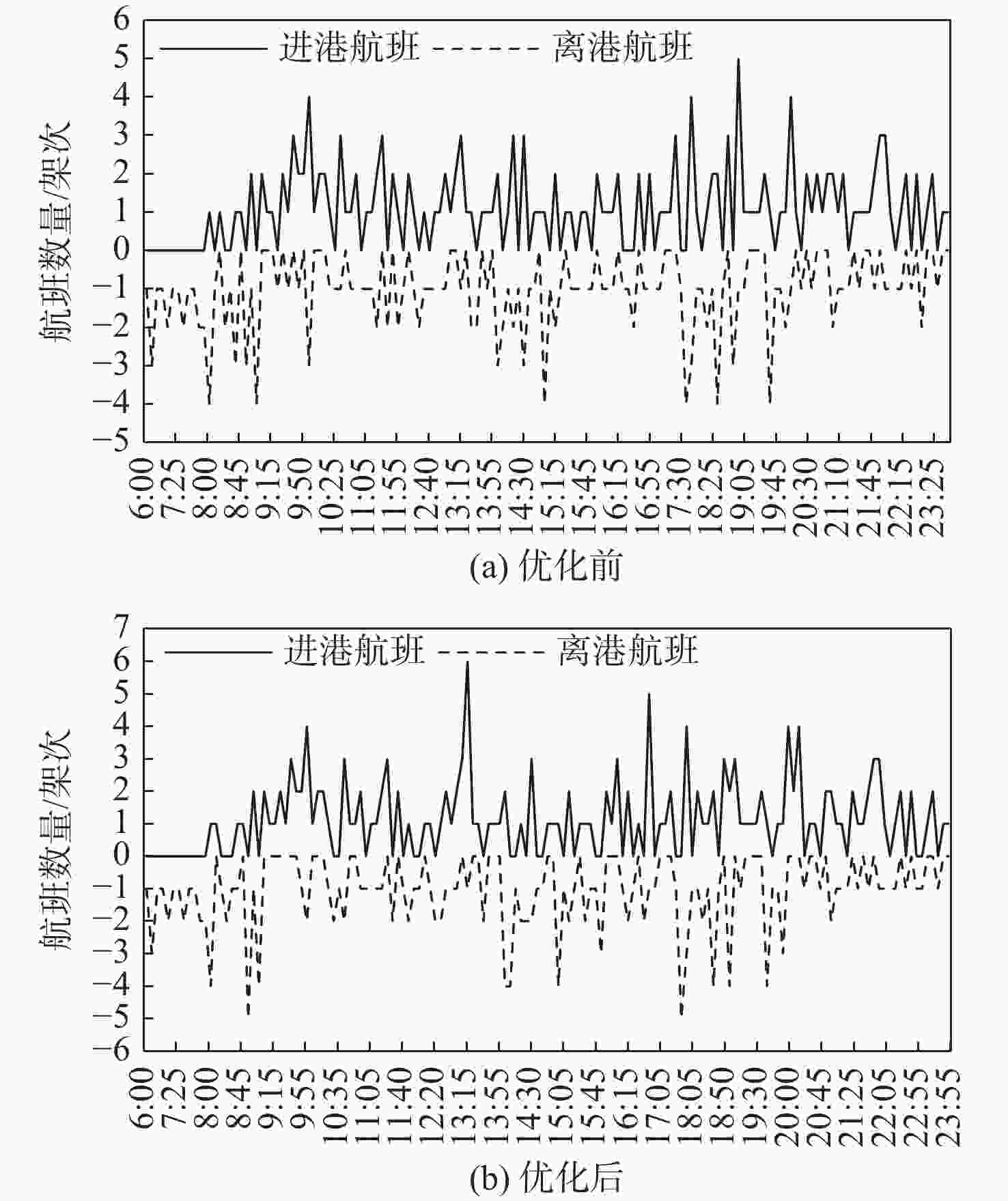
Table 7. Value of each objective function before and after optimization
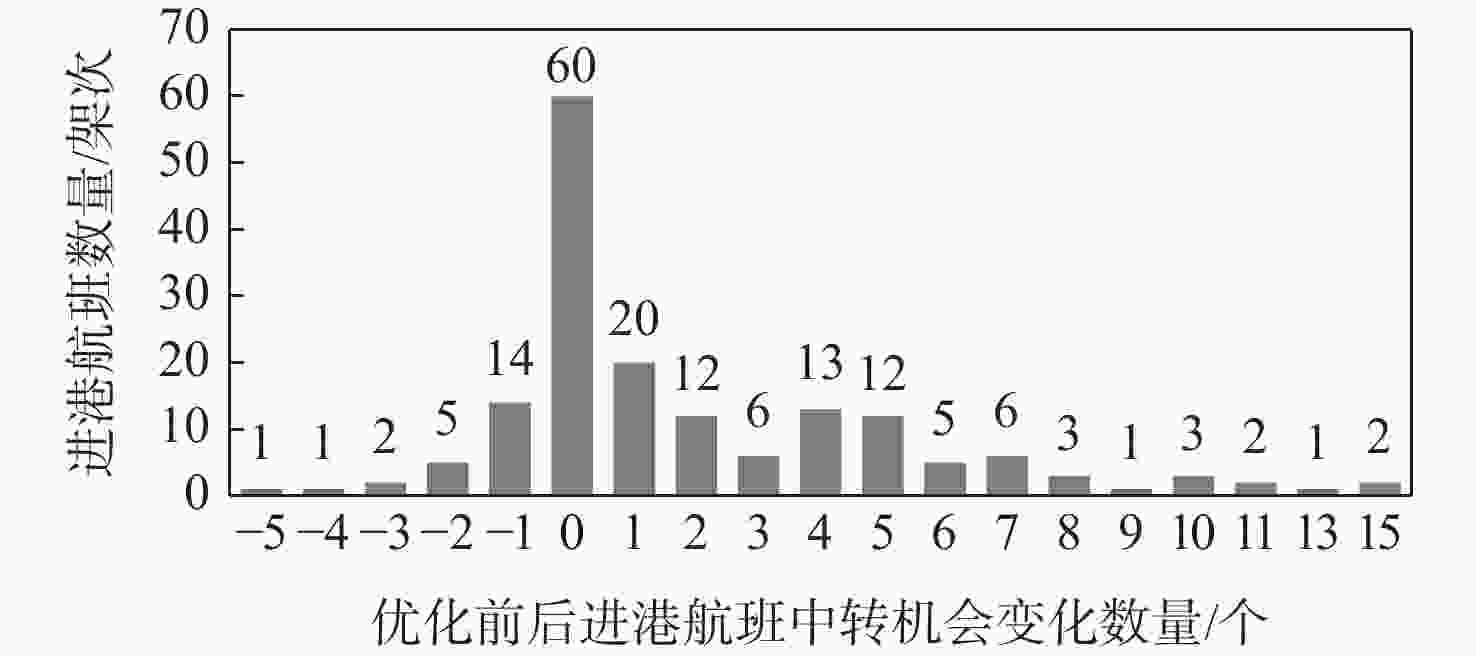
优化 Z1 Z2/对 Z3/min 优化前 27.57 1071 优化后 135.43 1406 1075 表 8 优化后中转机会增量较大的进港航班
Table 8. Arrival flights with large incremental transit opportunities after optimization
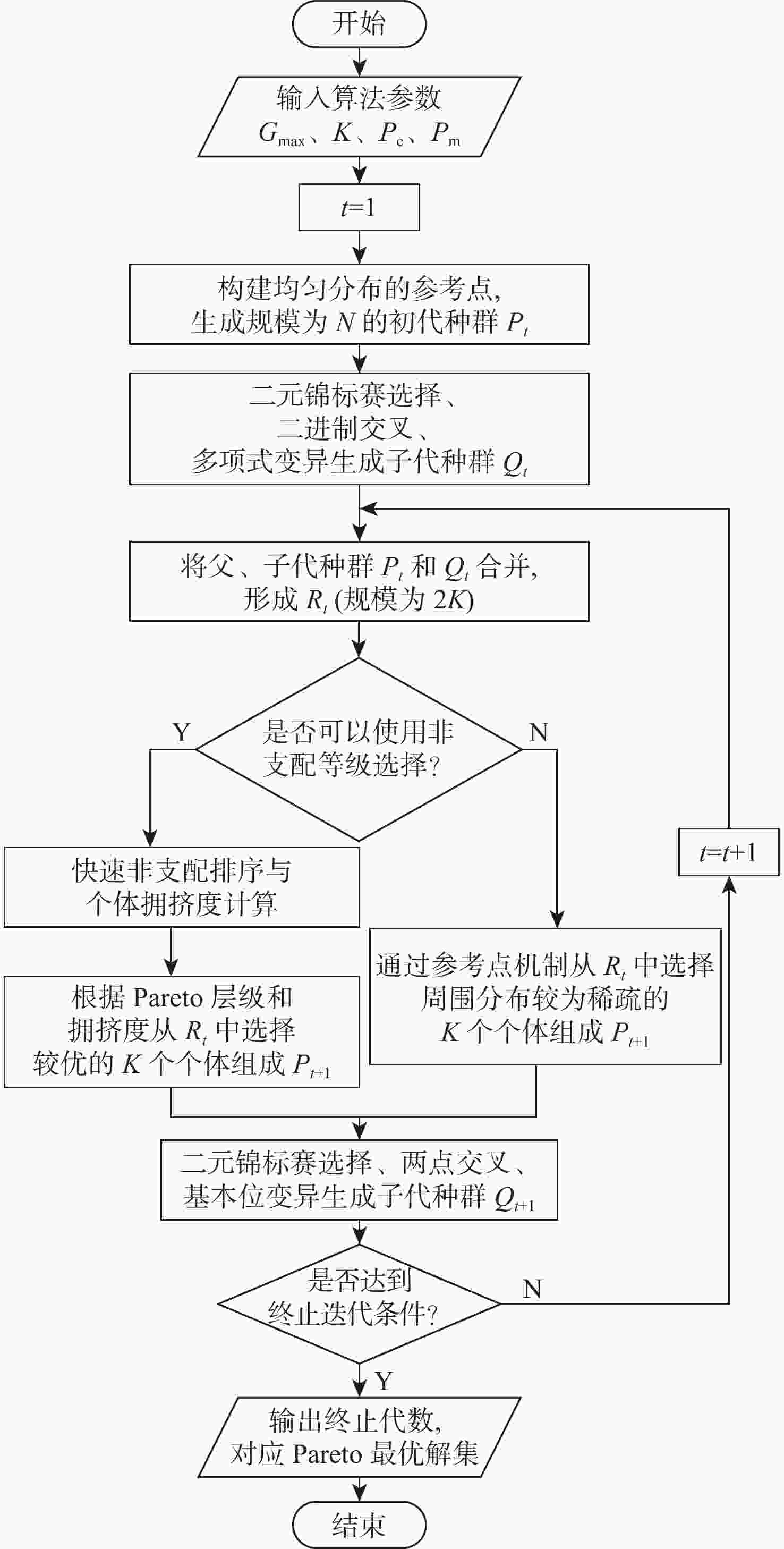
进港航班 始发机场 优化前
中转机会数/个优化后
中转机会数/个MU2415 敦煌机场 17 32 MU2417 嘉峪关机场 15 30 HO1102 金昌机场 23 33 TV6062 林芝机场 15 25 3U3590 甘孜机场 13 24 MU9677 嘉峪关机场 4 14 HU7420 新疆库尔勒机场 4 14 9C6186 敦煌机场 1 14 -
[1] PELLEGRINI P, CASTELLI L, PESENTI R. Secondary trading of airport slots as a combinatorial exchange[J]. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 2012, 48(5): 1009-1022. doi: 10.1016/j.tre.2012.03.004 [2] JIANG Y, ZOGRAFOS K G. A decision making framework for incorporating fairness in allocating slots at capacity-constrained airports[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2021, 126: 103039. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2021.103039 [3] RIBEIRO N A, JACQUILLAT A, ANTUNES A P, et al. An optimization approach for airport slot allocation under IATA guidelines[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2018, 112: 132-156. doi: 10.1016/j.trb.2018.04.005 [4] International Air Transport Association (IATA). Worldwide slot guidelines (WSG)[M]. Montreal-Geneva: IATA Publications, 2011: 156-178. [5] JORGE D, RIBEIRO N A, ANTUNES A P. Towards a decision-support tool for airport slot allocation: application to Guarulhos (Sao Paulo, Brazil)[J]. Journal of Air Transport Management, 2021, 93: 102048. doi: 10.1016/j.jairtraman.2021.102048 [6] FAIRBROTHER J, ZOGRAFOS K G. Optimal scheduling of slots with season segmentation[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2021, 291(3): 961-982. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2020.10.003 [7] 曾维理, 刘丹丹, 杨磊, 等. 考虑延误传播的枢纽机场航班时刻优化方法[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2023, 23(1): 242-255.ZENG W L, LIU D D, YANG L, et al. Flight schedule optimization method for hub airport considering delay propagation[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2023, 23(1): 242-255(in Chinese). [8] 卢婷婷, 刘计民, 史一鸣, 等. 考虑目的地机场繁忙程度的航班时刻优化[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2023, 23(11): 4894-4900. doi: 10.12404/j.issn.1671-1815.2023.23.11.04894LU T T, LIU J M, SHI Y M, et al. Flight schedule optimization considering the busy degree of destination airport[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2023, 23(11): 4894-4900(in Chinese). doi: 10.12404/j.issn.1671-1815.2023.23.11.04894 [9] 王莉莉, 潘越. 基于航班收益最大化的机场航班时刻分配[J]. 飞行力学, 2024, 42(2): 89-94.WANG L L, PAN Y. Airport schedule allocation based on flight revenue maximization[J]. Flight Dynamics, 2024, 42(2): 89-94(in Chinese). [10] 胡明华, 于婧怡, 赵征, 等. 基于改进鲸鱼优化算法的离场航班时刻优化[J]. 重庆交通大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 43(10): 54-60.HU M H, YU J Y, ZHAO Z, et al. Optimization of departure flight schedule based on improved whale optimization algorithm[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University (Natural Science), 2024, 43(10): 54-60(in Chinese). [11] DENNIS N. Airline hub operations in Europe[J]. Journal of Transport Geography, 1994, 2(4): 219-233. doi: 10.1016/0966-6923(94)90047-7 [12] ÇIFTÇI M E, ÖIKIR V. Optimising flight connection times in airline bank structure through Simulated Annealing and Tabu Search algorithms[J]. Journal of Air Transport Management, 2020, 87: 101858. doi: 10.1016/j.jairtraman.2020.101858 [13] BIROLINI S, JACQUILLAT S, SCHMEDEMAN P, et al. Passenger-centric slot allocation at schedule-coordinated airports[J]. Transportation Science, 2023, 57(1): 4-26. doi: 10.1287/trsc.2022.1165 [14] 宋溢露, 贺翀, 袁娜. 基于旅客中转满意度的天津机场航班波优化[J]. 综合运输, 2019, 41(6): 112-116.SONG Y L, HE C, YUAN N. Flight time schedule optimization of Tianjin Binhai Airport based on the satisfaction of passenger transfer[J]. China Transportation Review, 2019, 41(6): 112-116(in Chinese). [15] 马辰婷, 吴薇薇, 李名杰, 等. 考虑航班波结构特征的机场中转水平研究[J]. 交通运输工程与信息学报, 2023, 21(4): 129-137.MA C T, WU W W, LI M J, et al. Airport transfer level investigation considering flight wave structure characteristics[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering and Information, 2023, 21(4): 129-137(in Chinese). [16] 叶志坚, 胡罗丹, 高伟. 枢纽机场中转衔接性的评估与优化[J]. 重庆交通大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 42(11): 108-117.YE Z J, HU L D, GAO W. Evaluation and optimization of hub-airport transit connectivity[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University (Natural Science), 2023, 42(11): 108-117(in Chinese). [17] 马辰婷, 吴薇薇, 关柏川, 等. 考虑中转旅客的枢纽机场航班时刻优化[J]. 南京航空航天大学学报, 2024, 56(6): 1013-1023.MA C T, WU W W, GUAN B C, et al. Optimization of flight schedules at hub airports considering transit passengers[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics, 2024, 56(6): 1013-1023(in Chinese). [18] ZHANG G Q, LU J, MONTERO J, et al. Model, solution concept, and Kth-best algorithm for linear trilevel programming[J]. Information Sciences, 2010, 180(4): 481-492. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2009.10.013 [19] 黄世豪, 叶志坚. 基于命中的机场中转连接质量研究[J]. 综合运输, 2020, 42(12): 44-53.HUANG S H, YE Z J. Airport transit connection quality study based on hit[J]. China Transportation Review, 2020, 42(12): 44-53(in Chinese). [20] 中国民用航空局. 民航航班时刻管理办法[EB/OL]. (2018-01-05)[2024-11-28]. http://www.caac.gov.cn/XXGK/XXGK/ZFGW/201802/t20180224_49532.html.Civial Aviation Administration of China. Measures for the administration of civil aviation flight timing[EB/OL]. (2018-01-05)[2024-11-28]. http://www.caac.gov.cn/XXGK/XXGK/ZFGW/201802/t20180224_49532.html(in Chinese). [21] 中国民用航空局. 机场时刻容量评估技术规范[EB/OL]. (2017-05-09) [2025-02-24]. http://www.caac.gov.cn/XXGK/XXGK/GFXWJ/201705/t20170510_44023.html.Cival Aviation Administration of China. Technical specification for airport moment capacity assessment[EB/OL]. (2017-05-09)[2025-02-24]. http://www.caac.gov.cn/XXGK/XXGK/GFXWJ/201705/t20170510_44023.html(in Chinese). [22] SRINIVAS N, DEB K. Muiltiobjective optimization using nondominated sorting in genetic algorithms[J]. Evolutionary Computation, 1994, 2(3): 221-248. doi: 10.1162/evco.1994.2.3.221 [23] DEB K, PRATAP A, AGARWAL S, et al. A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-Ⅱ[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2002, 6(2): 182-197. doi: 10.1109/4235.996017 [24] DEB K, JAIN H. An evolutionary many-objective optimization algorithm using reference-point-based nondominated sorting approach, part I: solving problems with box constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2014, 18(4): 577-601. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2013.2281535 [25] DEHGHANI M, VAHDAT V, AMIRI M, et al. A multi-objective optimization model for a reliable generalized flow network design[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2019, 138: 106074. [26] 戴理朝, 康哲, 陈瑞, 等. 基于NSGA-Ⅲ的桥梁网络多目标维修决策优化研究[J]. 土木工程学报, 2024, 57(5): 41-52.DAI L Z, KANG Z, CHEN R, et al. Study on multi-objective maintenance decision optimization for bridge networks based on NSGA-Ⅲ[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2024, 57(5): 41-52(in Chinese). [27] DIANA T. Discrete choice modelling and air travel demand: theory and applications[J]. Journal of Airport Management, 2010, 5(1): 88. doi: 10.69554/IRHR1842 [28] 王莉莉, 侯鉴虓. 时刻调整范围不确定的机场群航班时刻优化[J]. 计算机仿真, 2023, 40(10): 61-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2023.10.012WANG L L, HOU J X. Research on flight slot optimization of airport groups with uncertain slot adjustment range[J]. Computer Simulation, 2023, 40(10): 61-65(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2023.10.012 [29] ZITZLER E, THIELE L, LAUMANNS M, et al. Performance assessment of multiobjective optimizers: an analysis and review[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2003, 7(2): 117-132. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2003.810758 [30] MOHAMMADI A, OMIDVAR M N, LI X D. A new performance metric for user-preference based multi-objective evolutionary algorithms[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2013: 2825-2832. -







 下载:
下载: