-
摘要:
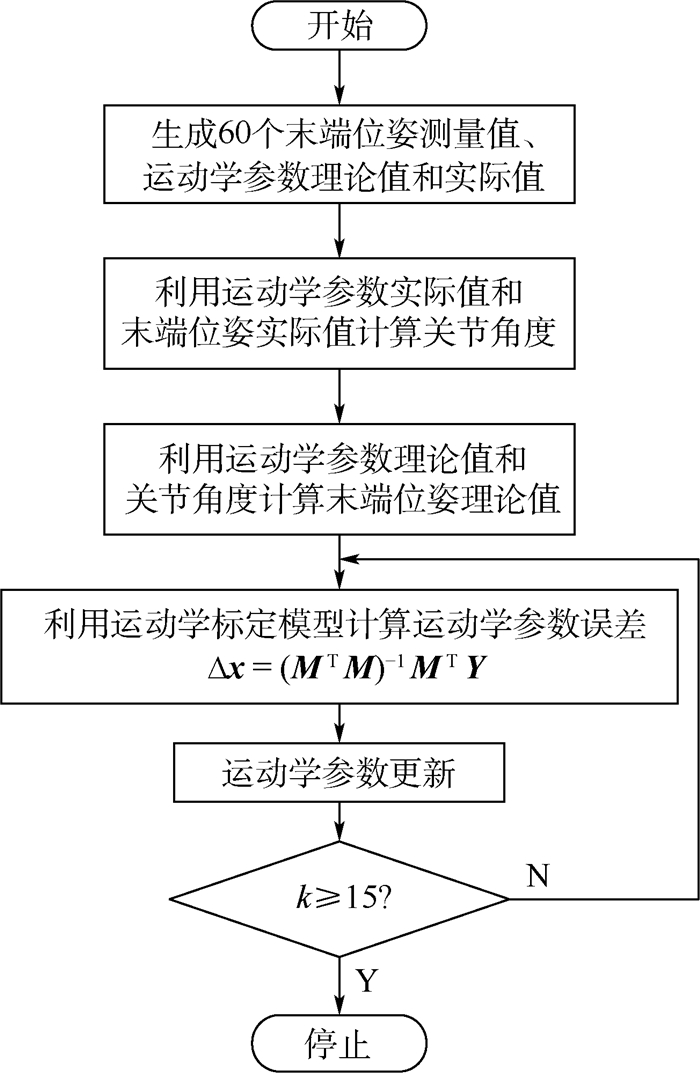
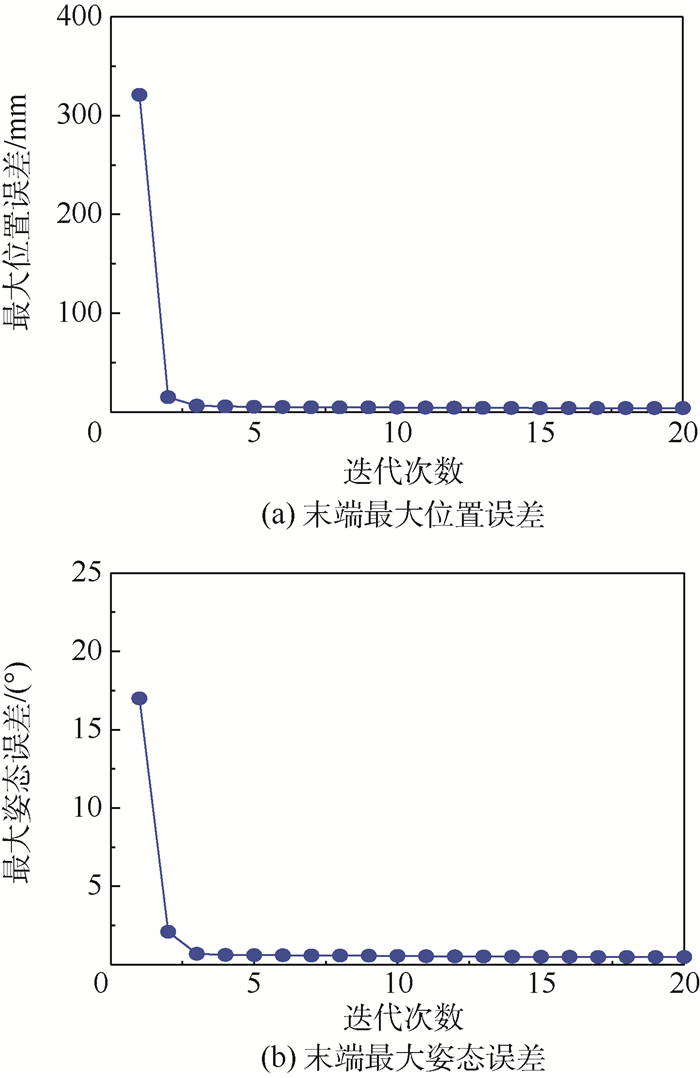
为了克服发射过程和在轨极端温度环境对空间机械臂末端位姿精度的影响,提出了一种基于指数积(POE)公式的空间机械臂运动学在轨自标定方法。该方法使用空间机械臂末端双目空间相机和棋盘式标定板测量空间机械臂末端位姿实际值。根据关节旋量理论值和实际值之间的伴随变换关系建立了空间机械臂实际运动学模型,对运动学模型取微分建立了线性化的运动学误差模型,给出了基于最小二乘法的运动学标定模型。进行了7自由度空间机械臂运动学自标定仿真,仿真结果表明运动学标定过程能快速收敛到稳定值,标定后空间机械臂末端位姿精度有明显提高。
Abstract:To overcome the influence of launching process and on-orbit extreme temperature environment on the tool pose accuracy of a space manipulator, a space manipulator kinematics on-orbit self-calibration method based on product of exponentials (POE) formula was presented. Using the binocular space camera fixed on the end-effector and a checkerboard calibration plate, the actual tool pose of the space manipulator was measured. According to the adjoint transformation between the theoretical value and actual value of joint twists, the actual kinematics model of the space manipulator was established. The linearized kinematics error model of the space manipulator was obtained by differentiating the kinematics model. A least-squares kinematics calibration model for the space manipulator was given. Kinematics self-calibration simulation of a seven-degree-of-freedom space manipulator was carried out. The simulation results show that the kinematics calibration process can converge to a stable value quickly and there is a significant improvement on the tool pose accuracy of the space manipulator after kinematics calibration.
-
表 1 空间机械臂运动学参数理论值和实际值
Table 1. Theoretical values and actual values of kinematics parameters of the space manipulator
参数 理论值 实际值(预设值) ξ1 [0 0 1 0 0 0]T [0.005 3 -0.005 2 1.000 0 0.100 5 -0.099 5 -0.001 0]T ξ2 [1 0 0 0 1 500 0]T [1.000 0 0.007 0 -0.006 9 -10.401 3 1 500.128 8 10.237 0]T ξ3 [0 0 1 0 -1 000 0]T [0.008 8 -0.008 7 0.999 9 8.851 8 -1 000.122 7 -8.729 7]T ξ4 [0 0 1 0 -5 000 0]T [0.010 6 -0.010 4 0.999 9 52.616 0 -5 000.248 9 -52.372 8]T ξ5 [0 0 1 0 -9 000 0]T [0.012 4 -0.012 1 0.999 9 110.220 7 -9 000.253 1 -109.983 9]T ξ6 [1 0 0 0 4 500 0]T [0.999 8 0.015 7 -0.015 7 -69.617 5 4 500.653 5 69.001 3]T ξ7 [0 0 1 0 -10 000 0]T [0.017 8 -0.017 1 0.099 7 173.282 4 -9 998.774 8 -174.560 3]T ξst [0 0 0 10 000 0 6 000]T [0.114 4 0.129 3 0.114 4 9 603.673 9 -199.070 3 6 652.637 1]T -
[1] BAI Y, WANG D L. Improve the robot calibration accuracy using a dynamic online fuzzy error mapping system[J]. IEEE Transactionson Systems, Man and Cybernetics, 2004, 34(2):1155-1160. doi: 10.1109/TSMCB.2003.821453 [2] CHEN G, LI T, CHU M, et al. Review on kinematics calibration technology of serial robots[J].International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, 2014, 15(8):1759-1774. doi: 10.1007/s12541-014-0528-1 [3] ROTH Z S, MOORING B W, RAVANI B.An overview of robot calibration[J].IEEE Journal of Robotics and Automation, 1987, 3(5):377-385. doi: 10.1109/JRA.1987.1087124 [4] SCHROER K, ALBRIGHT S L, GRETHLEIN M.Complete, minimal and model-continuous kinematic models for robot calibration[J].Robotics and Computer-integrated Manufacturing, 1997, 13(1):73-85. doi: 10.1016/S0736-5845(96)00025-7 [5] HAYATI S.Robot arm geometric link parameter estimation[C]//22nd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 1983, 22: 1477-1483. [6] STONE H W.Kinematic modeling, identification, and control of robotic manipulators[M].New York:Kluwer Academic Publisher, 1987. [7] ZHUANG H Q, ROTH Z S, HAMANO F.A complete and parametrically continuous kinematic model for robot manipulators[J].IEEE Transactions on Robotics & Automation, 1992, 8(4):451-463. [8] ZHUANG H Q, WANG L K, ROTH Z S.Error-model-based robot calibration using a modified CPC model[J].Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 1993, 10(4):287-299. doi: 10.1016/0736-5845(93)90042-I [9] CHEN I M, YANG G L.Kinematic calibration of modular reconfigurable robots using product-of-exponentials formula[J].Journal of Robotic Systems, 1997, 14(11):807-821. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1097-4563 [10] HE R B, ZHAO Y J, YANG S N, et al.Kinematic-parameter identification for serial-robot calibration based on POE formula[J].IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2010, 26(3):411-423. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2010.2047529 [11] HE R B, LI X W, SHI T L, et al.A kinematic calibration method based on the product of exponentials formula for serial robot using position measurements[J].Robotica, 2015, 33(6):1295-1313. doi: 10.1017/S026357471400071X [12] CHEN G L, WANG H, LIN Z Q.Determination of the identifiable parameters in robot calibration based on the POE formula[J].IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2014, 30(5):1066-1077. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2014.2319560 [13] ANGULO V R D, TORRAS C.Self-calibration of a space robot[J].IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 1997, 8(4):951-963. doi: 10.1109/72.595895 [14] LIANG P, CHANG Y L, HACKWOOD S.Adaptive self-calibration of vision-based robot systems[J].IEEE Transactions on Systems Man & Cybernetics, 1989, 19(4):811-824. [15] GONG C, YUAN J, NI J.Nongeometric error identification and compensation for robotic system by inverse calibration[J].International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture, 2000, 40(14):2119-2137. [16] LIU Y, LIU H, NI F L, et al.New self-calibration approach to space robots based on hand-eye vision[J].Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2011, 18(4):1087-1096. doi: 10.1007/s11771-011-0808-1 [17] DU G L, ZHANG P.Online robot calibration based on vision measurement[J].Robotics and Computer-integrated Manufacturing, 2013, 29(6):484-492. doi: 10.1016/j.rcim.2013.05.003 [18] ZHANG X C, SONG Y T, YANG Y, et al.Stereo vision based autonomous robot calibration[J].Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2017, 93:43-51. doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2017.04.001 [19] 高文斌, 王洪光, 姜勇.一种基于指数积的串联机器人标定方法[J].机器人, 2013, 35(2):156-161.GAO W B, WANG H G, JIANG Y.A calibration method for serial robots based on POE formula[J].Robot, 2013, 35(2):156-161(in Chinese). [20] LOU Y J, CHEN T N, WU Y Q, et al.Improved and modified geometric formulation of POE based kinematic calibration of serial robots[C]//IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2009: 5261-5266. [21] PARK F C, OKAMURA K.Kinematic calibration and the product of exponentials formula[M].Cambridge:MIT Press, 1994:119-128. -







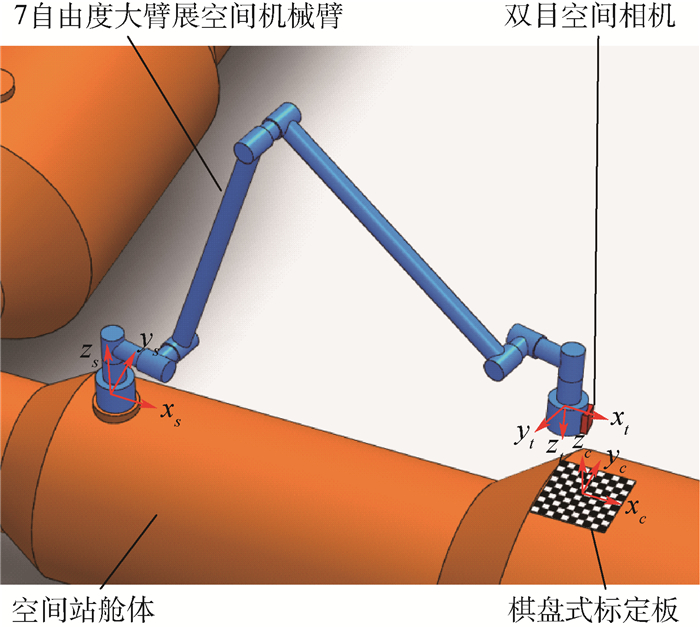
 下载:
下载: