-
摘要:
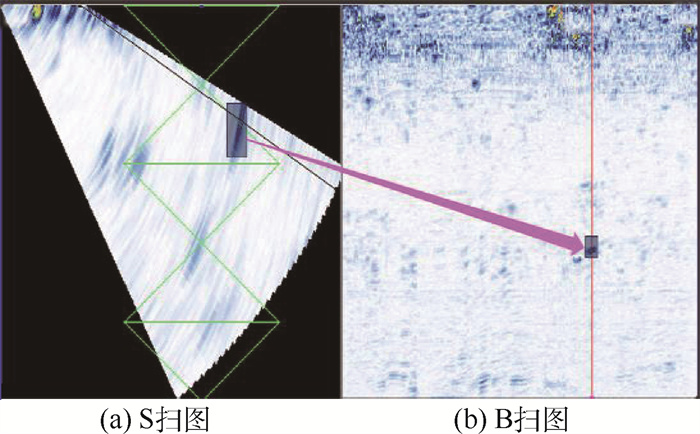
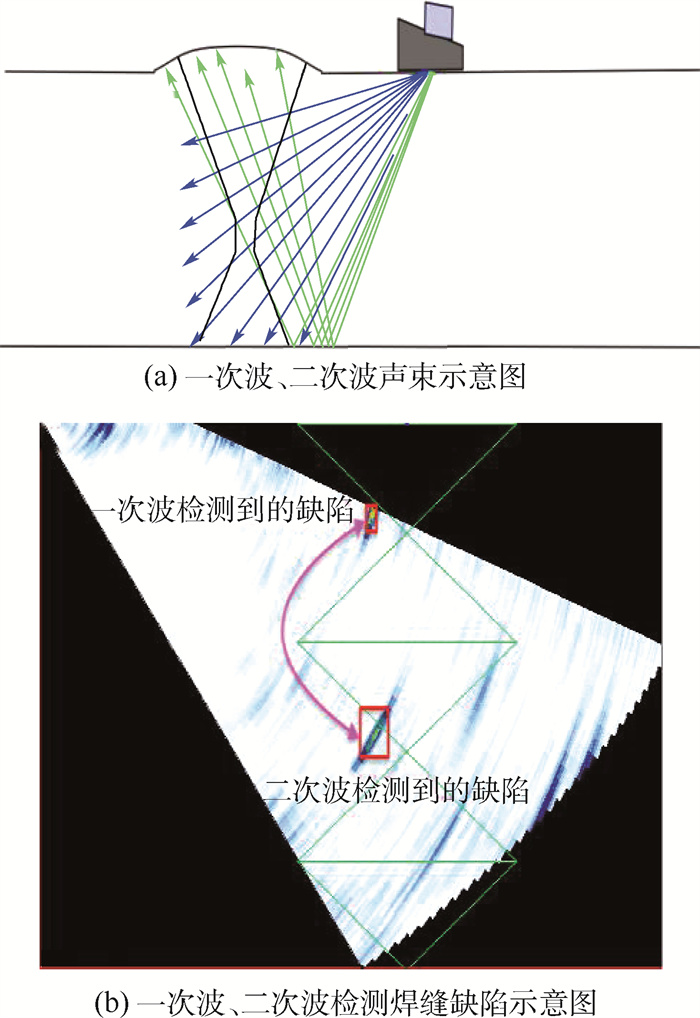
超声相控阵检测技术(PAUT)凭借其突出的技术优势被广泛应用在船舶、铁路、石油石化和航空航天等诸多领域。在焊缝超声相控阵检测(PAUT)中,对检测数据缺陷的识别定位目前多采用传统的人工判读方式,判读效率较低,对检测人员的判读经验有较高要求,难以满足自动化超声检测的要求。基于深度学习中的目标检测和跟踪算法构建智能识别模型,通过对焊缝超声相控阵检测的S、B扫图特征进行融合,并结合焊缝的三维结构信息,识别并定位出缺陷在焊缝中的三维空间位置。实验结果显示: 缺陷框的平均三维IOU(预测三维缺陷框和实际三维缺陷框的平均交并比)达到0.644 9,较为接近缺陷的真实空间位置,可以实现焊缝超声相控阵检测成像结果智能识别和定位。
Abstract:In the welding seam phased array ultrasonic testing (PAUT), the traditional manual judgment method is used to identify and locate the defects in the inspection data. However, this method has lower interpretation efficiency and higher requirements for the experience of the inspectors, and it has difficulty for meeting the requirements of automated ultrasound inspection. In this paper, combined with the features of S and B scan images of welding seam PAUT and 3D structure of weld, an intelligent recognition model based on target detection and tracking algorithm in deep learning is proposed to identify and locate the weld defect automatically. The experimental results show that the average value of 3D IOU of the defects (the average intersection ratio of the predicted and the actual 3D defect frame) reaches 0.644 9, which is close to the real defects' location. This method can realize the intelligent recognition and positioning from PAUT imaging data in welding seam.
-
表 1 焊缝样本缺陷信息
Table 1. Defect information of weld seam sample
参数 数值 缺陷总个数 56 未熔合缺陷个数 15 焊趾裂纹个数 15 根部裂纹个数 8 体积型缺陷个数 18 表 2 Faster R-CNN在验证集上的验证结果
Table 2. Faster R-CNN verification results on verification set
显示形式 验证集样本数 平均召回率 平均准确率 AP值 S扫图 496 0.517 8 0.999 2 0.909 1 B扫图 168 0.500 4 0.998 3 0.908 1 表 3 Faster R-CNN在测试集上的测试结果
Table 3. Faster R-CNN test results on test set
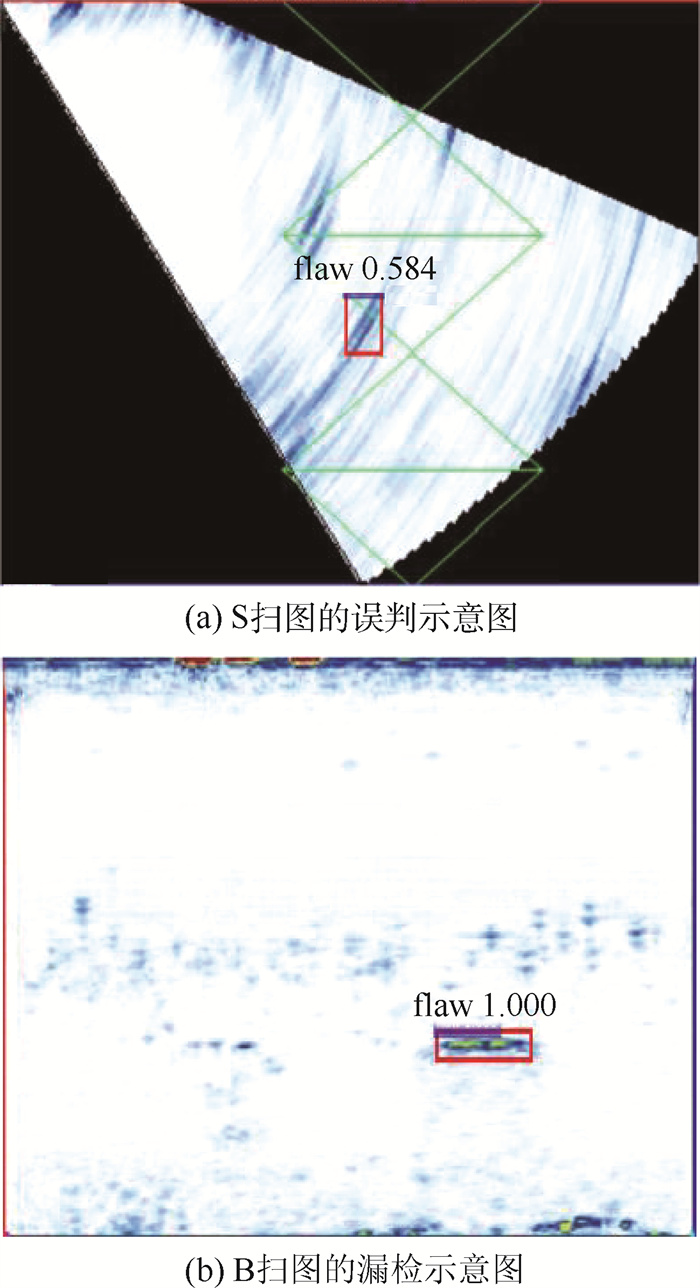
显示形式 测试集样本数 漏检样本数 误判样本数 准确率 S扫图 600 0 5 0.991 7 B扫图 62 4 0 0.935 5 表 4 预测的三维缺陷框的位置信息
Table 4. Location information of predicted 3D defect box
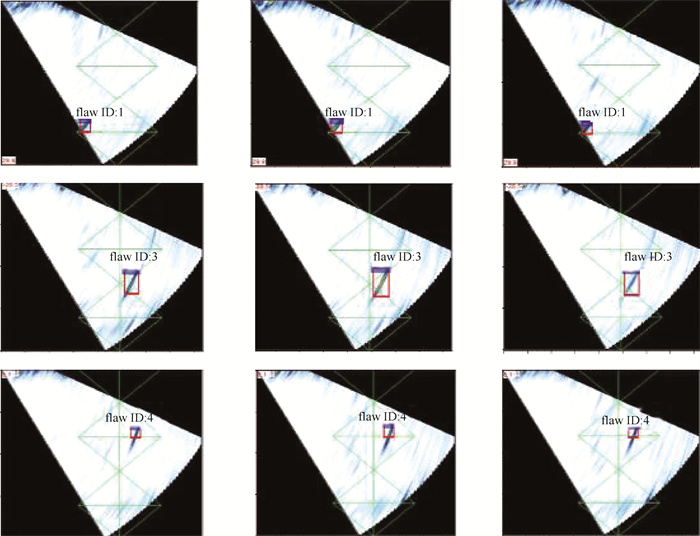
焊缝 缺陷ID 缺陷框中心与焊缝中心距离/mm 缺陷框中心埋深/mm 缺陷框中心切片位置/mm 缺陷框长度/ mm 缺陷框宽度/ mm 缺陷框高度/ mm 1 1 -7.71 1.34 2.95 3.90 2.56 2.62 3 2.60 6.42 96.95 11.90 4.02 5.19 4 3.72 10.81 130.65 5.90 2.69 2.54 2 1 -3.54 7.47 208.80 35.60 3.45 4.29 2 6.77 1.62 245.45 27.70 3.90 3.53 3 6.63 1.10 270.15 3.90 2.51 2.24 4 8.46 2.14 284.55 8.90 3.64 4.22 表 5 实际的三维缺陷框的位置信息
Table 5. Location information of actual 3D defect box
焊缝 缺陷ID 缺陷框中心与焊缝中心距离/mm 缺陷框中心埋深/mm 缺陷框中心切片位置/mm 缺陷框长度/ mm 缺陷框宽度/ mm 缺陷框高度/ mm 焊缝1 1 7.90 1.25 3.45 4.90 2.20 2.30 3 2.52 6.20 95.50 8.00 3.40 4.70 4 3.95 10.6 130.15 6.90 2.30 2.80 焊缝2 1 3.60 7.70 207.80 31.60 3.60 3.80 2 7.00 2.05 248.90 18.80 4.20 4.10 3 6.40 1.30 270.15 3.90 2.20 2.60 4 8.70 1.90 284.55 8.90 3.00 3.80 表 6 三维IOU计算结果
Table 6. Calculated results of 3D IOU
焊缝 缺陷ID IOUV IOUV 焊缝1 1 0.627 5 0.644 9 3 0.514 9 4 0.643 3 焊缝2 1 0.760 3 2 0.527 4 3 0.709 2 4 0.732 0 -
[1] 李京安. 超声相控阵扇形扫描检测成像技术研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2009.LI J A. Research on phased array ultrasonic sector-scan inspection imaging technology[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2009(in Chinese). [2] 陈彦华, 李明轩. 人工神经网络在超声无损检测中的应用[J]. 应用声学, 1996, 15(3): 40-44.CHEN Y H, LI M X. Application of artificial neural network to ultrasonic nondestructive testing[J]. Applied Acoustics, 1996, 15(3): 40-44(in Chinese). [3] 刘镇清. 人工神经网络BP算法的改进及其在无损检测中的应用[J]. 测控技术, 2001, 20(3): 56-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8829.2001.03.020LIU Z Q. Improvement of BP training algorithm for artificial neural network and its application in NDT[J]. Measurement & Control Technology, 2001, 20(3): 56-58(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8829.2001.03.020 [4] 陈国华, 张新梅, 谢常欢, 等. 超声检测中裂纹型缺陷深度的智能识别[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 33(8): 1-5. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-565X.2005.08.001CHEN G H, ZHANG X M, XIE C H, et al. Intelligent recognition of crack depth in ultrasonic testing[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science), 2005, 33(8): 1-5(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-565X.2005.08.001 [5] 黄民, 李功. 焊缝超声无损检测中的缺陷智能识别方法[J]. 北京信息科技大学学报, 2009, 24(2): 33-36.HUANG M, LI G. Intelligent defect recognition methods in the ultrasonic non-destructive test of welds[J]. Journal of Beijing Information Science and Technology University, 2009, 24(2): 33-36(in Chinese). [6] 施成龙, 师芳芳, 张碧星. 利用深度神经网络和小波包变换进行缺陷类型分析[J]. 声学学报, 2016, 41(4): 499-506.SHI C L, SHI F F, ZHANG B X. Analysis on defect classification by deep neural networks and wavelet packet transform[J]. Acta Acustica, 2016, 41(4): 499-506(in Chinese). [7] MENG M, CHUA Y J, WOUTERSON E, et al. Ultrasonic signal classification and imaging system for composite materials via deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Neurocomputing, 2017, 257: 128-135. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2016.11.066 [8] 黄焕东, 胡利晨, 李斌彬, 等. 基于区域的快速卷积神经网络的焊缝TOFD检测缺陷识别[J]. 无损检测, 2019, 41(7): 12-18.HUANG H D, HU L C, LI B B, et al. Recognition of defect in TOFD image based on faster region convolutional neural networks[J]. Nondestructive Testing Technologying, 2019, 41(7): 12-18(in Chinese). [9] 刘志浩. 对接焊缝的超声相控阵检测及三维成像分析[D]. 南昌: 南昌航空大学, 2016.LIU Z H. Butt welding inspection and defects three-dimensional imaging using ultrasonic phased array technology[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang Hangkong University, 2016(in Chinese). [10] REN S Q, HE K M, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 39(6): 1137-1149. [11] GIRSHICK R. Fast R-CNN[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 1440-1448. [12] BEWLEY A, GE Z Y, OTT L, et al. Simple online and realtime tracking[C]//2016 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 3464-3468. [13] 包俊, 董亚超, 刘宏哲. 基于Deep-Sort的目标跟踪算法综述[C]//中国计算机用户协会网络应用分会2019年第二十三届网络新技术与应用年会, 2019: 13-17.BAO J, DONG Y C, LIU H Z. Survey of object tracking algorithms based on Deep-Sort[C]//China Computer Users Association, Proceedings of the 23rd Annual Conference on New Network Technologies and Applications, 2019: 13-17(in Chinese). [14] 闫庆森, 李临生, 徐晓峰, 等. 视频跟踪算法研究综述[J]. 计算机科学, 2013, 40(S1): 204-209.YAN Q S, LI L S, XU X F, et al. Survey of visual tracking algorithm[J]. Computer Science, 2013, 40(S1): 204-209(in Chinese). [15] 尹宏鹏, 陈波, 柴毅, 等. 基于视觉的目标检测与跟踪综述[J]. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(10): 1466-1489.YIN H P, CHEN B, CHAI Y, et al. Vision-based object detection and tracking: A review[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(10): 1466-1489(in Chinese). [16] 彭丁聪. 卡尔曼滤波的基本原理及应用[J]. 软件导刊, 2009, 8(11): 32-34.PENG D C. Basic principle and application of Kalman filter[J]. Software Guide, 2009, 8(11): 32-34(in Chinese). [17] 王学斌, 徐建宏, 张章. 卡尔曼滤波器参数分析与应用方法研究[J]. 计算机应用与软件, 2012, 29(6): 212-215.WANG X B, XU J H, ZHANG Z. On analysis and application approach for Kalman filter parameters[J]. Computer Applications and Software, 2012, 29(6): 212-215(in Chinese). [18] 叶斌, 徐毓. 强跟踪滤波器与卡尔曼滤波器对目标跟踪的比较[J]. 空军雷达学院学报, 2002, 16(2): 17-19.YE B, XU Y. Comparison between a strong tracking filter and Kalman filter for target tracking[J]. Journal of Air Force Radar Academy, 2002, 16(2): 17-19(in Chinese). [19] 周鑫, 何晓新, 郑昌文. 基于图像深度学习的无线电信号识别[J]. 通信学报, 2019, 40(7): 114-125.ZHOU X, HE X X, ZHENG C W. Radio signal recognition based on image deep learning[J]. Journal on Communications, 2019, 40(7): 114-125(in Chinese). -








 下载:
下载: