-
摘要:
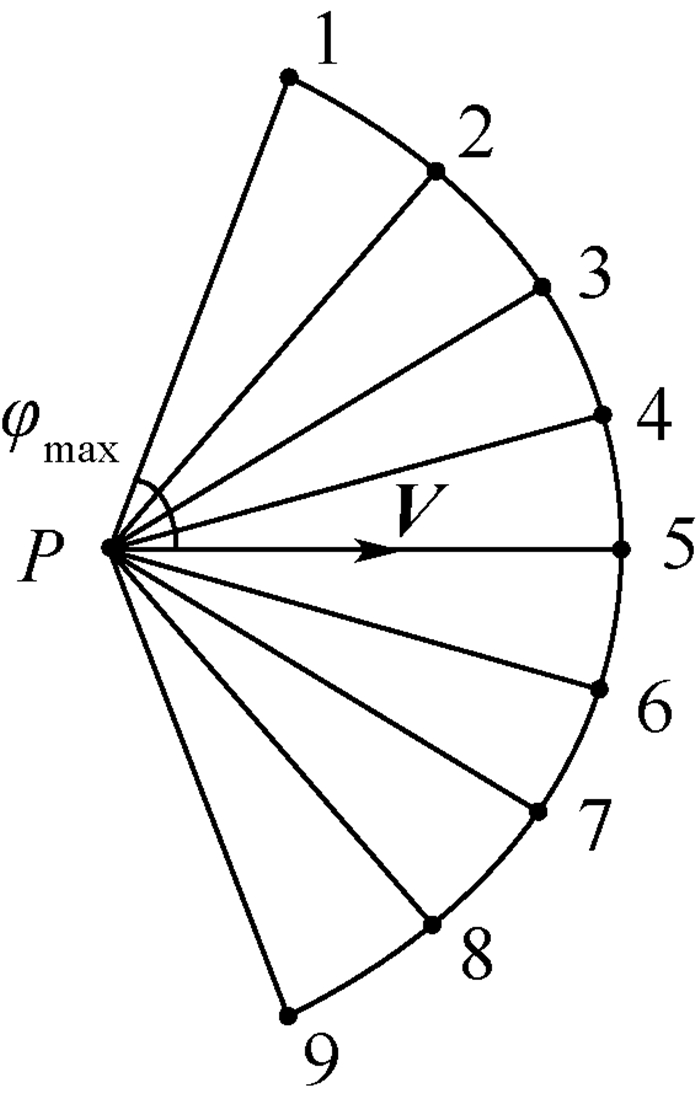
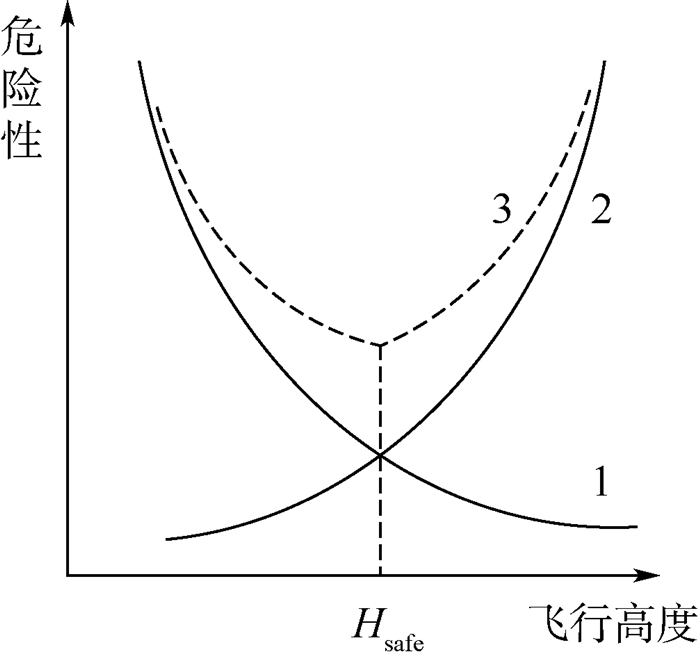
针对直接在三维空间进行无人机(UAV)航迹规划难度较大的问题,将三维规划分解为二维平面规划和高度规划,最后再合成得到三维航迹,使规划空间得以简化,降低问题的复杂度;为实现在威胁区域对航迹的精细搜索,降低危险性,提出了一种根据与威胁的距离而动态调整搜索步长的策略;当无人机遇到突发威胁时,通过设置子目标点,帮助无人机快速修正航迹,实现航迹重规划。仿真试验结果验证了所提方法的有效性,无人机可以安全绕开突发威胁,实现三维规划,采用动态步长,航迹的受威胁程度降低。
Abstract:Because planning unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) path directly in 3D space is difficult, we divide 3D path planning into 2D plane path planning and height planning, and then combine them to get the 3D path so that planning space is simplified and complexity is reduced. To search the path subtly in the region near threat, we propose a dynamic searching step strategy according to the distance between UAV and threat. Setting sub-goal helps UAV to quickly modify the path and realize path re-planning when UAV meets the unexpected threat. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed method is effective. UAV can bypass the unexpected threat and plan 3D path successfully. The threat probability of path decreases through taking dynamic step.
-
Key words:
- unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) /
- path planning /
- sub-goal /
- dynamic step /
- 2D plane path planning /
- height planning
-
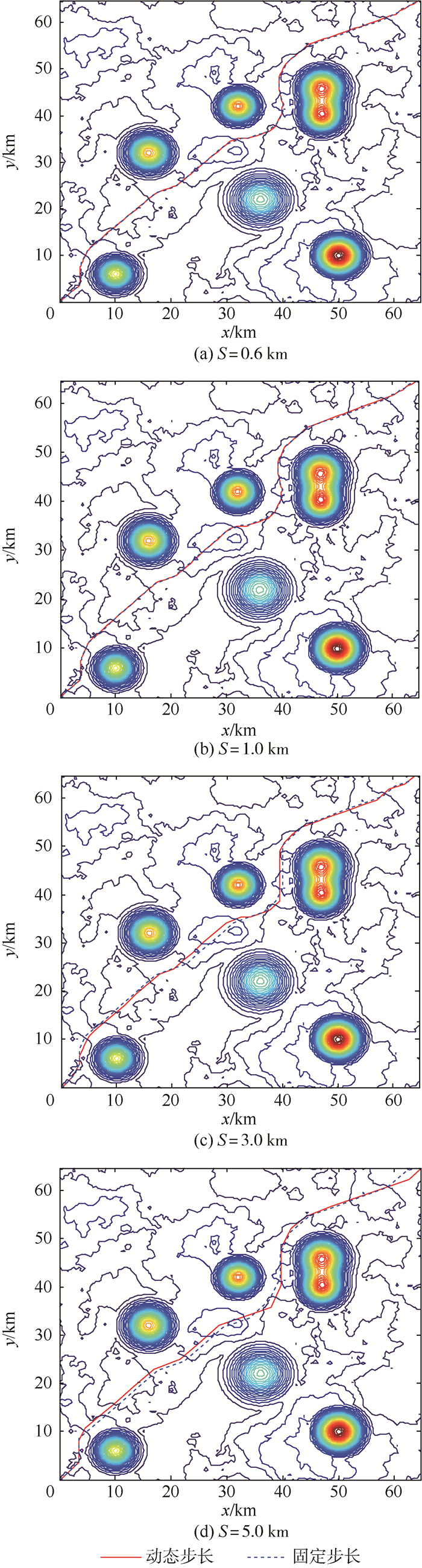
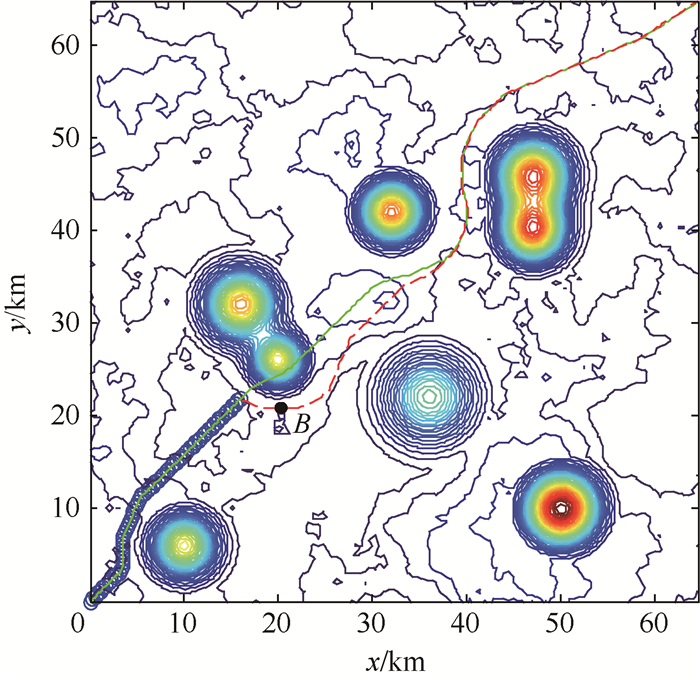
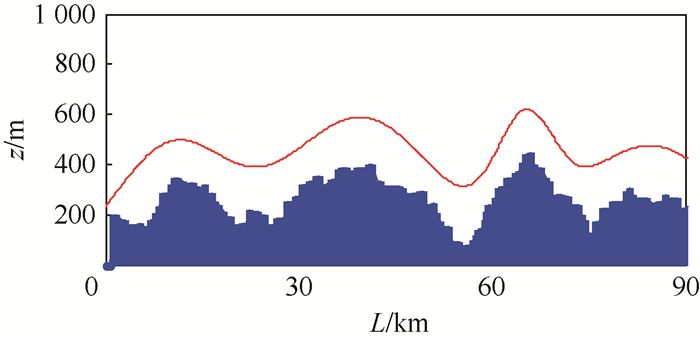
表 1 威胁具体参数
Table 1. Specific parameters of threats
威胁类型 中心坐标/km 中心点高度/km λ 山峰1 (10,6) 25 0.10 山峰2 (16,32) 28 0.08 山峰3 (36,22) 18 0.05 山峰4 (32,42) 30 0.10 雷达1 (47,40) 32 0.10 雷达2 (47,46) 32 0.08 雷达3 (50,10) 40 0.08 表 2 固定步长与动态步长仿真结果对比
Table 2. Comparison of simulation results between fixed step and dynamic step
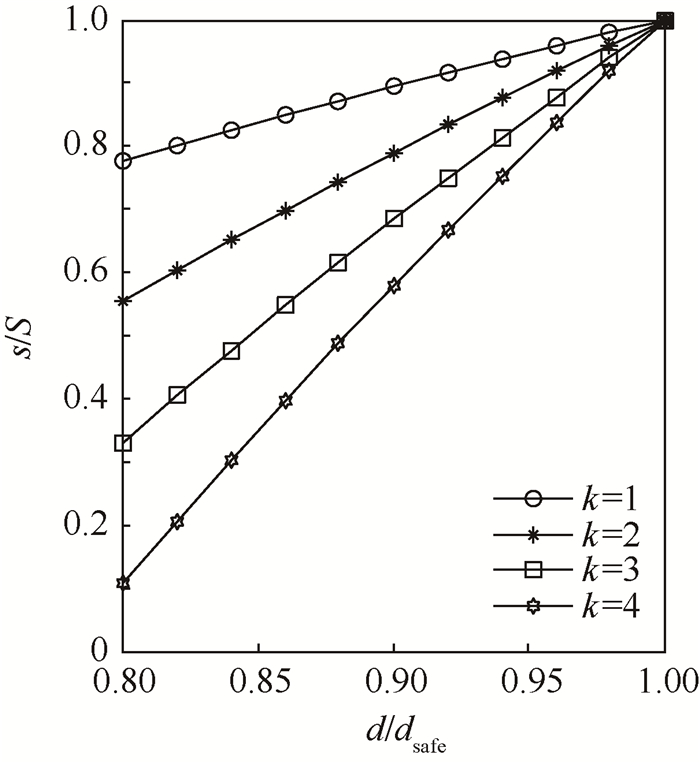
S/km 步长策略 节点数 时间/s 航程/km 平均威胁概率 0.6 动态步长 217 2.177 99.459 0.034 固定步长 166 2.156 99.351 0.028 1.0 动态步长 129 2.076 99.472 0.038 固定步长 100 2.066 99.400 0.040 3.0 动态步长 42 1.988 98.943 0.099 固定步长 33 1.979 99.449 0.195 5.0 动态步长 25 1.971 98.263 0.269 固定步长 20 1.965 99.078 0.580 -
[1] 沈林成, 陈璟, 王楠.飞行器任务规划技术综述[J].航空学报, 2014, 35(3):593-606. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKXB201403001.htmSHEN L C, CHEN J, WANG N.Overview of air vehicle mission planning techniques[J].Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2014, 35(3):593-606(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKXB201403001.htm [2] BAE K Y, KIMB Y D, HAN J H.Finding a risk-constrained shortest path for an unmanned combat vehicle[J].Computer and Industrial Engineering, 2015, 80:245-253. doi: 10.1016/j.cie.2014.12.016 [3] 姚远, 周兴社, 张凯龙, 等.基于稀疏A*搜索和改进人工势场的无人机动态航迹规划[J].控制理论与应用, 2010, 27(7):953-959.YAO Y, ZHOU X S, ZHANG K L, et al.Dynamic trajectory planning for unmanned aerial vehicle based on sparse A* search and improved artificial potential field[J].Control Theory & Applications, 2010, 27(7):953-959(in Chinese). [4] OSCAR M, ULISES O R, ROBERTO S.Path planning for mobile robots using bacterial potential field for avoiding static and dynamic obstacles[J].Expert System with Application, 2015, 42(12):5177-5191. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2015.02.033 [5] MENG G L, GUO J L, SUN F Q, et al.UAV real-time path planning using dynamic RCS based on velocity vector field[C]//26th Chinese Control and Decision Conference, CCDC 2014.Piscataway, NJ:IEEE Press, 2014:1376-1380. [6] 严平, 丁明跃, 周成平, 等.飞行器多任务在线实时航迹规划[J].航空学报, 2004, 25(5):485-489. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKXB200405013.htmYAN P, DING M Y, ZHOU C P, et al.On-line real-time multiple-mission route planning for air vehicle[J].Acta Aeronautic et Astronautica Sinica, 2004, 25(5):485-489(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKXB200405013.htm [7] PENG Z H, LI B, CHEN X T, et al.Online route planning for UAV based on model predictive control and particle swarm optimization algorithm[C]//10th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation.Piscataway, NJ:IEEE Press, 2012:397-401. [8] SHEKHAR R C, KEARNEY M, SHAMES I.Robust model predictive control of unmanned aerial vehicle using waysets[J].Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2015, 38(10):1898-1907. doi: 10.2514/1.G000787 [9] WU J, ZHANG D H, PEI D H.Autonomous route planning for UAV when threats are uncertain[C]//6th IEEE Chinese Guidance, Navigation and Control Conference, CGNCC 2014.Piscataway, NJ:IEEE Press, 2014:19-22. [10] REDDING J, AMIN J N, BOŠKOVIC J D.A real-time obstacle detection and reactive path planning system for autonomous small-scale helicopters[C]//AIAA Guidance, Navigation and Control Conference and Exhibit 2007.Reston:AIAA, 2007, 1:989-1010. [11] 何平川, 戴树岭.一种改进UAV三维航迹实时规划算法[J].北京航空航天大学学报, 2010, 36(10):1248-1251.HE P C, DAI S L.Improved 3-D real-time trajectory algorithm for UAV[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2010, 36(10):1248-1251(in Chinese). [12] 张帅, 李学仁, 张鹏, 等.基于改进A*算法的无人机航迹规划[J].飞行力学, 2016, 34(3):39-43.ZHANG S, LI X R, ZHANG P, et al.UAV path planning based on improved A* algorithm[J].Flight Dynamics, 2016, 34(3):39-43(in Chinese). [13] 常波, 王瑞.基于几何法的无人机航迹规划[J].计算机系统应用, 2015, 24(1):109-113. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTYY201501019.htmCHANG B, WANG R.Path planning based on geometric method for unmanned aerial vehicles[J].Computer System Applications, 2015, 24(1):109-113(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTYY201501019.htm [14] 占伟伟, 王伟, 陈能成, 等.一种利用改进A*算法的无人机航迹规划[J].武汉大学学报·信息科学版, 2015, 40(3):315-320.ZHAN W W, WANG W, CHEN N C, et al.Path planning strategies for UAV based on improved A* algorithm[J].Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2015, 40(3):315-320(in Chinese). [15] 温乃峰, 苏小红, 马培军, 等.低空复杂环境下基于采样空间约减的无人机在线航迹规划算法[J].自动化学报, 2014, 40(7):1376-1390. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MOTO201407013.htmWEN N F, SU X H, MA P J, et al.Sampling space reduction-based UAV online path planning algorithm in complex low altitude environments[J].Acta Automatic Sinica, 2014, 40(7):1376-1390(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MOTO201407013.htm [16] ZHAN B C, MAO Z L, LIU W Q, et al.Geometric reinforcement learning for path planning of UAVs[J].Journal of Robotic System, 2015, 77(2):391-409. doi: 10.1007/s10846-013-9901-z [17] 关震宇, 杨东晓, 李杰, 等.基于Dubins路径的无人机避障规划算法[J].北京理工大学学报, 2014, 34(6):570-575. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJLG201406005.htmGUAN Z Y, YANG D X, LI J, et al.Obstacle avoidance planning algorithm for UAV based on Dubins path[J].Transaction of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2014, 34(6):570-575. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJLG201406005.htm [18] 郑昌文.飞行器航迹规划方法研究[D].武汉:华中科技大学, 2003:22-25.ZHENG C W.Research on route planning for air vehicles[D].Wuhan:Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2003:22-25(in Chinese). [19] 蔡满意.飞行控制系统[M].北京:国防工业出版社, 2007:144-145.CAI M Y.Flight control system[M].Beijing:National Defence Industry Press, 2007:144-145(in Chinese). -








 下载:
下载: